Biochemistry Liver Function Tests (LFTs)
|
|
|
- Cora Phillips
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HbA NH 2 H 2 O 2 KClO3 Cl 2 O 7 PO 4 CH2O NAOH KMnO 4 M E D I C I N E KING SAUD UNIVERSITY Co 2 COOH MgCl 2 H 2 O Important Extra Information Doctors slides Doctors notes SO 2 HCN CCl 4 CuCl 2 SiCl 4 Biochemistry Liver Function Tests (LFTs) Work hard in silence, let your success be your noise Editing file
2 O B J E C T I V E S Upon completion of this lecture, the students should be able to: Understand the major metabolic functions of the liver and causes of liver dysfunction. Discuss markers of liver function tests such as liver enzymes, bilirubin, albumin and prothrombin time that can diagnose hepatic injury and assess hepatic function. you don't have to memorize any number. Just the numbers that we tell you to memorize This video is recommended by Dr. sumbul
3 Information that Dr. Sumbul recalled at the beginning of the lecture: -The liver is an important organ, everything we take in the body has to go through the liver. whether we re eating food (no need) -Functions of the liver: 1-detoxification, which clears the ammonia from the blood and converts it into urea (less toxic). Also bilirubin + cholesterol + drugs are all cleared out through the liver. 2-Synthesis of the majority of plasma proteins, some enzymes, bile (which helps in digestion),and cholesterol (which is a parent molecule for all the steroids in the body). 3-Storage of fat soluble vitamins such as vitamin A,K,D and E -so anything that causes damage to the liver by any disease that associated with it assess that we do the liver function test,so the major metabolic functions of the liver for ex plasma protein albumin + cholesterol + triglycerides. -which lipoprotein synthesized in the liver? VLDL, so the triglycerides is carried to the liver and then the liver transport it to the rest of the tissues as VLDL
4 Lecture Overview
5 Major Metabolic Functions of the Liver Major Metabolic Functions of the Liver Synthetic Function Detoxification and excretion Storage Function Production of bile salts Plasma proteins (albumin, globulins), cholesterol, triglycerides and lipoproteins (VLDL) Ammonia to urea (urea cycle), bilirubin, cholesterol, drug metabolites Vitamins A, D, E, K and B 12 Helps in digestion
6 Some example of liver dysfunction Hepatocellular disease Cholestasis (obstruction of bile flow) Cirrhosis Steatosis (fatty liver) quite common in a lot of people Hepatitis Jaundice Liver cancer
7 Some example of liver dysfunction: Genetic Disorders : Hemochromatosis (iron storage disease) To differentiate between hemochromatosis and hemosiderosis Disease Hemochromatosis Hemosiderosis Etiology: Genetic Repeated blood transfusion Cause: Mechanism: Complications: Storage: Due to iron overload disorders Iron gets stored in the organ and it s toxic to the organ majority stored in the liver Causes damage to the liver and other thing Hemochromatosis storage or the accumulation of the iron is happening in the liver. Iron ( hemosiderin) is stored in macrophages.
8 Liver Function Tests (LFTs) We have to check a list of tests to detect a liver disease and we will discuss the major ones. Noninvasive methods for screening of liver dysfunction Help in identifying general types of disorder Assess severity and allow prediction of outcome Disease and treatment follow up Broadly classified as : 1. Tests to detect hepatic injury: (affecting structure) Mild or severe; acute or chronic Nature of liver injury (hepatocellular or cholestasis) 2. Tests to assess hepatic function (affecting function) The good thing is that there are non invasive and invasive so, baiscally it s not a liver function test it s liver dysfunction test (don t think this is necessary) We are basically testing and screening for liver dysfunction. what are the indications for doing a liver function test? 1-When there are symptoms like (Jaundice or abdominal pain or anorexia or nausea and vomiting) 2-If a person is on drugs which cause liver toxicity or if you want to start a treatment and you want to make sure that the patient's liver is healthy or not ( so by knowing that you can change the treatment or modify the dose). 3- Alcoholism
9 Classification Classification of LFTs: Group I: Markers of liver dysfunction Group II: Markers of hepatocellular injury Group III: Markers of cholestasis
10 Classification Group I: Markers of liver dysfunction Serum bilirubin: total and conjugated Urine: bile salts and urobilinogen Total protein, serum albumin and albumin/globulin ratio Prothrombin Time Group II: Markers of hepatocellular injury (at the level of the cells) conditions that cause damage to hepatocytes. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) Group III: Markers of cholestasis markers of obstruction Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) g-glutamyltransferase (GGT)
11 Limitations of LFTs Limitations of LFTs There are some limitations because non of the markers are perfect and can tell you exactly what is wrong with the liver. That s why we have more the one marker Normal LFT values do not always indicate absence of liver disease Liver a has very large reserve capacity * Asymptomatic people may have abnormal LFT results Diagnosis should be based on clinical examination Liver is a big organ so a lot of times if the cell injury wasn t severe (even if we choose more than one marker) we may not see a difference in the levels of the markers. Unless the injury has gone for a long time or the injury is really severe. (because the liver is a large organ that compensates ). * There could be something wrong in the liver but it may not reflect on the values.
12 Common serum liver chemistry tests
13 Bilirubin Bilirubin A byproduct of red blood cell (hemoglobin) breakdown It is the yellowish pigment observed in jaundice in sclera, skin and mucous High bilirubin levels are observed in: Gallstones, acute and chronic hepatitis
14 Bilirubin cycle -The life span of RBC S is 120 days. The RBC S keeps on dying in the system and are cleared up by the macrophages (of RES) in the spleen and the liver,so these macrophages produce bilirubin as byproduct. -The bilirubin is not soluble it requires a lot of water or fluids to be soluble so it has to go to the liver to become soluble. From the macrophages it goes to the liver as a complex with albumin - Albumin carries the bilirubin to the liver and once it goes to the liver, the hepatocytes take it in with the help of ligandin..( it facilitate the transport of bilirubin inside the hepatocyte). Once inside the hepatocyte they are conjugated with a carbohydrate called glucuronic acid. 2 molecules of glucuronic acid are bound to 1 molecule of bilirubin and that is done by the enzyme glucuronyl transferase ( it s microsomal enzyme present in the endoplasmic reticulum). - After that it is actively secreted into bile and enters the bile duct to reach the intestine. Once in the intestine, it s acted upon by the intestinal bacteria which removes the glucuronic acid from the bilirubin and convert it into a molecule called urobilinogen. -Majority of urobilinogen gets oxidized ( by intestinal bacteria) to stercobilin which is excreted with the feces (gives the feces it s brown color). -The remaining urobilinogen are reabsorbed into the blood and goes back to the liver through the portal circulation ( known as enterohepatic circulation). Some of it goes to the kidney where it is converted to urobilin ( that gives urine it s yellow color) and get excreted in urine. Side note: Bilirubin makes a complex with Albumin and is conjugated with glucuronic acid
15 Bilirubin cycle Summary: Urobilinogen has 3 fates: 1- Oxidized by intestinal bacteria into stercobilin and excreted into feces (majority) 2_ Reabsorbed from the gut and enters the portal blood to go back to the liver ( enterohepatic circulation) (Some) 3- Reabsorbed from the gut and enters the blood to reach the kidney where they are converted into urobillin and excreted in urine.
16 Bilirubin metabolism The role of the liver is basically conjugation which turns the non soluble bilirubin into a soluble form that can be easily excreted out of the body.
17 Serum bilirubin levels Normal Unconjugated (indirect) Conjugated (direct) Latent jaundice Jaundice mg/dl mg/dl mg/dl Above 1 mg/dl Above 2 mg/dl Bilirubin levels and jaundice Class of Jaundice Pre-hepatic or hemolytic (mainly unconjugated bilirubin in the serum) Hepatic or Hepatocellular (both conjugated and unconjugated) Post-hepatic (Conjugated) Causes Abnormal red cells; antibodies; drugs and toxins; thalassemia Hemoglobinopathies, Gilbert s, Crigler- Najjar syndrome Viral hepatitis, toxic hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis Extrahepatic cholestasis; gallstones; tumors of the bile duct, carcinoma of pancreas
18 Urobilinogen (UBG), bile salts and serum albumin Urobilinogen (UBG) and bile salts Serum Albumin Most UBG is metabolized in the large intestine but a fraction is excreted in urine (less than 4 mg/day) If there is too much bilirubin present then this fraction gets increased Normally bile salts are NOT present in urine Normally 95% of bile salts are reabsorbed and only 5% gets excreted. Obstruction in the biliary passages causes: 1. Leakage of bile salts into circulation 2. Excretion in urine Obstruction leads to regurgitation of bile salts into the blood and there for excreted in urine The most abundant protein synthesized by the liver One of the most important and abundant protein synthesis in the liver the half life of it is 20 days. Normal serum levels: g/dl Synthesis depends on the extent of functioning liver cell mass Since the liver is a large organ and the 1/2 life of albumin is long. The disease should be either chronic or acute (but really severe) in order to see change in the level of albumin. Its levels decrease in all chronic liver diseases
19 Serum Globulin Globulin Albumin to globulin (A/G) ratio Normal serum levels: g/dL a and b-globulins mainly synthesized by the liver They constitute immunoglobulins (antibodies) High serum g-globulins are observed in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis : 1. IgG in autoimmune hepatitis 2. IgA in alcoholic liver disease Normal A/G ratio: 1.2/1 1.5/1 Globulin levels increase in hypoalbuminemia as a compensation When the synthetic function of the liver is affected, the albumin levels falls. So in order to maintain the osmosis of the system and compensate for the loss of albumin, there is a compensatory increase in the globulin synthesis. you start making lots of globulin that leads to a change in the ratio of albumin/globulin. The ratio will be decreased.
20 Prothrombin Time (PT) Prothrombin time is the time needed for blood clot to form. Prothrombin is clotting factor number 2 Prothrombin: synthesized by the liver, a marker of liver function.. We should say dysfunction not function Half-life: 6 hours. (indicates the present function of the liver) PT is prolonged only when liver loses more than 80% of its reserve capacity Vitamin K deficiency also causes prolonged PT Intake of vitamin K does not affect PT in liver disease You have to give an injection of vitamin K to make sure if it's due to Vit k or liver injury PT is affected by vitamin K or liver injury
21 AST and ALT Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) These numbers are important Normal range: 8 20 U/L A marker of hepatocellular damage High serum levels are observed in: Chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and liver cancer AST and ALT are both produced by the liver but AST is less specific More liver-specific than AST Normal range (U/L): Male: Female: High serum levels in acute hepatitis ( U/L) Moderate elevation in alcoholic hepatitis ( U/L) Minor elevation in cirrhosis, hepatitis C and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) (50-100U/L) Appears in plasma many days before clinical signs appear (good thing about it) A normal value doesn t always indicate absence of liver damage Obese but otherwise normal individuals may have elevated ALT levels (minor elevation will appear in obese people)
22 Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) A non-specific marker of liver disease Produced by bone osteoblasts (for bone calcification) Present on hepatocyte membrane Normal range: U/L Moderate elevation observed in: Infective hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma Not specific because : 1- it is present in bone 2- synthesized in the placenta therefore pregnant females have elevated ALP levels. 3- hepatocyte membrane High levels are observed in: Extrahepatic obstruction (obstructive jaundice) and intrahepatic cholestasis Very high levels are observed in: Bone diseases
23 gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) GGT It s a marker for alcohol abuse Used for glutathione synthesis Normal range: 10 30U/L Moderate elevation observed in: Infective hepatitis and prostate cancers GGT is increased in alcoholics despite normal liver function tests Highly sensitive to detecting alcohol abuse
24 Take Home Messages LFTs help detect liver injury and function. LFTs do have some limitations.
25 Summary Marker Normal levels Abnormal levels Causes Bilirubin Urobilinogen and bile salts mg/dl Unconjugated: mg/dl Conjugated: mg/dl UG: less than 4 mg/day in urine Bile salts: never in urine Latent jaundice: above 1 mg/dl Jaundice: above 2 mg/dl Pre-hepatic: abnormal RBC, Thalassemia, hemoglobinapothies Hepatic: viral hepatitis, toxic hepatitis, and intrahepatic cholestasis Post-hepatic: extra hepatic cholestasis, tumors of bile duct, and pancreatic carcinoma -- Obstruction of biliary passage Albumin g/dl decreased All chronic liver diseases Serum Globulin g/dl elevated Albumin/Globulin ratio /1 Globulin increases in hypoalbuminemia Prothrombin Time (PT) Chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis IgG: autoimmune IgA: alcoholic liver disease -- When liver loses 80% of capacity Vitamin K deficiency prolongs PT
26 Summary Marker Normal values Abnormal value Causes AST 8-20 U/L High levels ALT Male: U/L Female: U/L (high): acute hepatits (mod): alcoholic hepatitis (minor) in cirrhosis, hepatitis C, non alcoholic steatohepatitis ALP U/L -- GGT U/L -- Chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer Signifies hepatocellular damage -- Mod. Elevation: infective hepatitis, alcoholic hepatitis, hepatocellular carcinoma High levels: extra-hepatic obstruction, intrahepatic cholestasis Very high levels: bone disease Mod. In infective hepatitis Increased naturally in alcoholics
27 QUIZ Q1 : Which ONE of the following enzymes is more liver specific? A. ALT B. AST C. LD D. None of them Q2 : Which of these enzymes are highly sensitive in detecting alcohol abuse? A. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) B. gamma glutamyl-transferase (GGT) C. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) D. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) Q3 : Increased conjugated bilirubin is due to? A. Pre hepatic B. Post hepatic C. Hepatic D. Both (B&C) Q4 : Jaundice has no clinical manifestation when the bilirubin serum levels are? A. Less than 1 mg /dl B. Between 2 and 3 mg /dl C. More than 3 mg/dl D. Both (B&C) Q5 : ALT & AST are markers of? A. Markers of cholestasis B. Markers hepatocellular damage C. Markers for biliary obstruction D. All of the above Q6 : Which ONE of the following has a (very high absorbed) level in bone diseases? A. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) B. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) C. Gamma glutamyl-transferase (GGT) D. Both (A&C)
28 QUIZ Q7 : Explain why Prothrombin Time (PT) is good as a prognostic tool? It has a short half life of 6 hours. Q8 : What does Prothrombin Time (PT) means? And how is that relevant to liver dysfunction? PT means how much time it takes for the blood to clot, PT is synthesized by the liver Q9 : Explain why albumin is not a good indicator of an acute hepatic dysfunction? Q10 : A 26 year old male comes to the clinic with a yellowish tinge to the eyes and skin and complains of abdominal pain, fatigue and weakness, liver function tests only shows mildly elevated bilirubin (mostly unconjugated) and the rest of the parameters were all normal. Which ONE of the following is the most likely diagnosis? Gilbert's Syndrome It has a long half life of 20 days. It s good in detecting chronic liver diseases. Suggestions and recommendations 1) A 2) B 3) D 4) D 5) B 6) A
29 T E A M M E M B E R S TEAM LEADERS Mohammad Almutlaq Rania Alessa Najd altheeb Haifa bin taleb Rana almanea
30 THANK YOU FOR CHECKING OUR WORK PLEASE CONTACT US IF YOU HAVE ANY ISSUE Lippincott's Illusrated Reviews Biochemistry 6 th E Review the Biochemistryteam436@gmail.com
-Liver function tests -
 -Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
-Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
6. Production or formation of plasma protein and clotting factors and heparin.
 Liver function test Clinical pathology dr. Ali H. Liver function test The liver has many vital physiologic functions involving synthesis, excretion, and storage. When a disease process damages cells within
Liver function test Clinical pathology dr. Ali H. Liver function test The liver has many vital physiologic functions involving synthesis, excretion, and storage. When a disease process damages cells within
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease
 Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease. Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya
 Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Interpreting Liver Function Tests
 PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
Definition of bilirubin Bilirubin metabolism
 Definition of bilirubin Bilirubin metabolism obilirubin formation otransport of bilirubin in plasma ohepatic bilirubin transport oexcretion through intestine Other substances conjugated by glucuronyl transferase.
Definition of bilirubin Bilirubin metabolism obilirubin formation otransport of bilirubin in plasma ohepatic bilirubin transport oexcretion through intestine Other substances conjugated by glucuronyl transferase.
Liver Function Tests
 Liver Function Tests The liver is of vital importance in intermediary metabolism and in the detoxification and elimination of toxic substances. Damage to the organ may not obviously affects its activity
Liver Function Tests The liver is of vital importance in intermediary metabolism and in the detoxification and elimination of toxic substances. Damage to the organ may not obviously affects its activity
Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University
 Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
JAUNDICE. Zdeněk Fryšák 3rd Clinic of Internal Medicine Nephrology-Rheumatology-Endocrinology Faculty Hospital Olomouc
 JAUNDICE Zdeněk Fryšák 3rd Clinic of Internal Medicine Nephrology-Rheumatology-Endocrinology Faculty Hospital Olomouc Definition of Jaundice Icterus A yellowish staining of the skin, sclerae and deeper
JAUNDICE Zdeněk Fryšák 3rd Clinic of Internal Medicine Nephrology-Rheumatology-Endocrinology Faculty Hospital Olomouc Definition of Jaundice Icterus A yellowish staining of the skin, sclerae and deeper
WEEK. MPharm Programme. Liver Biochemistry. Slide 1 of 49 MPHM14 Liver Biochemistry
 MPharm Programme Liver Biochemistry Slide 1 of 49 MPHM Liver Biochemistry Learning Outcomes Assess and evaluate the signs and symptoms of illness Assess and critically appraise a patients medication regimen,
MPharm Programme Liver Biochemistry Slide 1 of 49 MPHM Liver Biochemistry Learning Outcomes Assess and evaluate the signs and symptoms of illness Assess and critically appraise a patients medication regimen,
Liver Function Tests. Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy
 Liver Function Tests Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Metabolic function Excretory function Synthetic fuction Detoxification function Storage function
Liver Function Tests Dr. Abdulhussien Aljebory Babylon university College of Pharmacy FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Metabolic function Excretory function Synthetic fuction Detoxification function Storage function
HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM
 EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon
 What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
Liver function and clinical chemistry of liver
 INTRODUCTION Liver function and clinical chemistry of liver The liver plays a major role in carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism with the processes of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle,,homeostasis synthesis
INTRODUCTION Liver function and clinical chemistry of liver The liver plays a major role in carbohydrate, lipid and protein metabolism with the processes of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle,,homeostasis synthesis
Hepatocytes produce. Proteins Clotting factors Hormones. Bile Flow
 R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD
 Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD The assessment of patients with abnormal liver tests is common in both primary care and gastroenterology clinics. However, among patients
Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD The assessment of patients with abnormal liver tests is common in both primary care and gastroenterology clinics. However, among patients
Mr Ricky Gellissen Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK
 Mr Ricky Gellissen Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK Ms Sally Bufton University Hospital Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham Mrs Janet Catt Royal Free
Mr Ricky Gellissen Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK Ms Sally Bufton University Hospital Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham Mrs Janet Catt Royal Free
HEMOLYSIS AND JAUNDICE:
 1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR HEMOLYSIS AND JAUNDICE: An overview
1 University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR HEMOLYSIS AND JAUNDICE: An overview
Bilirubin Metabolism. Prof. Dr. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin. 1 Prof. Dr. El-Yassin
 Bilirubin Metabolism Prof. Dr. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin 1 Prof. Dr. El-Yassin Objectives: 1. To outline the basic metabolic pathway of bilirubin breakdown and conjugation 2. To state the basic metabolic
Bilirubin Metabolism Prof. Dr. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin 1 Prof. Dr. El-Yassin Objectives: 1. To outline the basic metabolic pathway of bilirubin breakdown and conjugation 2. To state the basic metabolic
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
HEMOLYSIS & JAUNDICE: An Overview
 HEMOLYSIS & JAUNDICE: An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL MBBS III
HEMOLYSIS & JAUNDICE: An Overview University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine and Health Sciences Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL MBBS III
ROUTINE LAB STUDIES. Routine Clinic Lab Studies
 ROUTINE LAB STUDIES Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a tacrolimus or cyclosporine level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not
ROUTINE LAB STUDIES Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a tacrolimus or cyclosporine level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not
Around million aged erythrocytes/hour are broken down.
 Anemia Degradation ofheme Around 100 200 million aged erythrocytes/hour are broken down. The degradation process starts in reticuloendothelial cells in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow. [1] The tetrapyrrole
Anemia Degradation ofheme Around 100 200 million aged erythrocytes/hour are broken down. The degradation process starts in reticuloendothelial cells in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow. [1] The tetrapyrrole
CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice
 CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice Episode overview: 1) Describe heme metabolism 2) List common pre-hepatic/hepatic/post-hepatic causes of jaundice Wisecracks: 1) What are clinical signs of liver disease? 2)
CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice Episode overview: 1) Describe heme metabolism 2) List common pre-hepatic/hepatic/post-hepatic causes of jaundice Wisecracks: 1) What are clinical signs of liver disease? 2)
A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Jane D. Ricaforte-Campos, MD FPCP, FPSG, FPSDE 2013 HSP Post-graduate Course Radisson Blu Hotel, Cebu City misnomer Liver Function Tests Does
A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Jane D. Ricaforte-Campos, MD FPCP, FPSG, FPSDE 2013 HSP Post-graduate Course Radisson Blu Hotel, Cebu City misnomer Liver Function Tests Does
BCM 317 LECTURE OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 317 LECTURE BY OJEMEKELE O. JAUNDICE Jaundice is yellowish discoloration of the skin, sclera and mucous membrane, resulting from an increased bilirubin concentration in the body fluid. It is usually
BCM 317 LECTURE BY OJEMEKELE O. JAUNDICE Jaundice is yellowish discoloration of the skin, sclera and mucous membrane, resulting from an increased bilirubin concentration in the body fluid. It is usually
Biochemistry Vitamins B6 and B12
 HbA NH 2 H 2 O 2 KClO3 Cl 2 O 7 PO 4 CH2O NAOH KMnO 4 M E D I C I N E KING SAUD UNIVERSITY Co 2 COOH MgCl 2 H 2 O Important Extra Information Doctors slides Doctors notes SO 2 HCN CCl 4 CuCl 2 SiCl 4 Biochemistry
HbA NH 2 H 2 O 2 KClO3 Cl 2 O 7 PO 4 CH2O NAOH KMnO 4 M E D I C I N E KING SAUD UNIVERSITY Co 2 COOH MgCl 2 H 2 O Important Extra Information Doctors slides Doctors notes SO 2 HCN CCl 4 CuCl 2 SiCl 4 Biochemistry
CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS
 CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS Interpreting abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) and trying to diagnose any underlying liver disease is a common scenario in Primary
CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS Interpreting abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) and trying to diagnose any underlying liver disease is a common scenario in Primary
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust
 ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic
 Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic substances. Describe the formation of bile,its constitents
Physiological functions of the liver. Describe the major functions of the liver with respect to metabolism,detoxification & excretion of hydrophobic substances. Describe the formation of bile,its constitents
Mrs Janet Catt. Pre-Conference Nurse s Course. Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust. Janet Catt MSc RN Lead Nurse Specialist Practic 12/12/2014
 Pre-Conference Nurse s Course in partnership with Mrs Janet Catt Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust Janet Catt MSc RN Lead Nurse Specialist Practic 1 Liver blood tests monitoring cirrhosis HIV/HCV
Pre-Conference Nurse s Course in partnership with Mrs Janet Catt Royal Free London NHS Foundation Trust Janet Catt MSc RN Lead Nurse Specialist Practic 1 Liver blood tests monitoring cirrhosis HIV/HCV
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS A- Metabolic Functions of the Liver: 1. The liver plays a major role in carbohydrate, lipid and protein homeostasis, with the processes of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, gluconeogenesis,
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS A- Metabolic Functions of the Liver: 1. The liver plays a major role in carbohydrate, lipid and protein homeostasis, with the processes of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, gluconeogenesis,
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Prof. Dr. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin. Prof. Dr. El-Yassin
 Prof. Dr. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin 1 1. To define jaundice 2. To describe the types of jaundice 3. To tabulate and evaluate Laboratory results in all types of jaundice 2 } This is a condition where there
Prof. Dr. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin 1 1. To define jaundice 2. To describe the types of jaundice 3. To tabulate and evaluate Laboratory results in all types of jaundice 2 } This is a condition where there
Clinical enzymology. University of Babylon College of pharmacy Second semester - biochemistry 3 rd class By Dr. Abdulhussien M. K.
 Clinical enzymology University of Babylon College of pharmacy Second semester - biochemistry 3 rd class 2014 2015 By Dr. Abdulhussien M. K. Aljebory Enzyme activity Enzyme assays usually depend on the
Clinical enzymology University of Babylon College of pharmacy Second semester - biochemistry 3 rd class 2014 2015 By Dr. Abdulhussien M. K. Aljebory Enzyme activity Enzyme assays usually depend on the
Efficient detoxification depends on the Kupffer cell function.
 Liver Functions of liver: 1- Metabolic functions and blood glucose regulation: When the glucose concentration is high in the portal veinit is converted to glycogen (glycogenesis) During fasting the systemic
Liver Functions of liver: 1- Metabolic functions and blood glucose regulation: When the glucose concentration is high in the portal veinit is converted to glycogen (glycogenesis) During fasting the systemic
Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder
 Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder 解剖學科徐淑媛 本堂重點 1. Liver : functions & histology 2. Gallbladder Physiology Liver Produce circulating plasma proteins Vitamin Iron Degradation Metabolism Bile manufacture (exocrine)
Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder 解剖學科徐淑媛 本堂重點 1. Liver : functions & histology 2. Gallbladder Physiology Liver Produce circulating plasma proteins Vitamin Iron Degradation Metabolism Bile manufacture (exocrine)
Hepatology Case reports
 Hepatology Case reports Prof.. MUDr. Libor VítekV tek,, PhD, MBA IV. Dept. Int Med and Institute of Clinical Biochemistry and laboratory diagnostics VFN and 1. LF UK in Praze Biochemical methods in hepatology
Hepatology Case reports Prof.. MUDr. Libor VítekV tek,, PhD, MBA IV. Dept. Int Med and Institute of Clinical Biochemistry and laboratory diagnostics VFN and 1. LF UK in Praze Biochemical methods in hepatology
An Approach to Jaundice Block 10. Dr AJ Terblanche Department of Paediatrics and Child Health
 An Approach to Jaundice Block 10 Dr AJ Terblanche Department of Paediatrics and Child Health JAUNDICE (ICTERUS) Yellow discoloration skin, sclerae, mucous membranes Observed 60% term, 80% preterm infants
An Approach to Jaundice Block 10 Dr AJ Terblanche Department of Paediatrics and Child Health JAUNDICE (ICTERUS) Yellow discoloration skin, sclerae, mucous membranes Observed 60% term, 80% preterm infants
What Is Cirrhosis? CIRRHOSIS. Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is. by chronic conditions and diseases. permanently scarred or injured
 What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
Disclosure. Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes
 Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. G M Kellerman. Hunter Area Pathology Service
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS G M Kellerman Hunter Area Pathology Service FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Carbohydrate metabolism storage (glycogen), release, synthesis (gluconeogenesis), interconversion (galactose, fructose),
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS G M Kellerman Hunter Area Pathology Service FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Carbohydrate metabolism storage (glycogen), release, synthesis (gluconeogenesis), interconversion (galactose, fructose),
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Amino acid oxidation and the production of urea
 Seminar 10 Urea cycle Amino acid oxidation and the production of urea Oxidation Waste or Reuse Ammonia has to be eliminated ammonia originates in the catabolism of amino acids that are primarily produced
Seminar 10 Urea cycle Amino acid oxidation and the production of urea Oxidation Waste or Reuse Ammonia has to be eliminated ammonia originates in the catabolism of amino acids that are primarily produced
Digestion and Absorption
 Digestion and Absorption Digestion and Absorption Digestion is a process essential for the conversion of food into a small and simple form. Mechanical digestion by mastication and swallowing Chemical digestion
Digestion and Absorption Digestion and Absorption Digestion is a process essential for the conversion of food into a small and simple form. Mechanical digestion by mastication and swallowing Chemical digestion
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS TtáxÜ `A TuwxÄté Å? c{w Assistant professor of Medical Biochemistry Zagazig University, Egypt University of Bisha, KSA aaserabdelazim@yahoo.com 3/20/2018 of Clinical Medical Biochemistry
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS TtáxÜ `A TuwxÄté Å? c{w Assistant professor of Medical Biochemistry Zagazig University, Egypt University of Bisha, KSA aaserabdelazim@yahoo.com 3/20/2018 of Clinical Medical Biochemistry
Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests
 Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests Note on Referral Guidelines: these revised guidelines are presented as a tool to aid appropriate referral and management of common
Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests Note on Referral Guidelines: these revised guidelines are presented as a tool to aid appropriate referral and management of common
Current Health Sciences Journal Vol. 37, No. 2, Jaundice Obstructive Syndrom TIRZIU CONSTANTIN. University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova
 For Practitioner Jaundice Obstructive Syndrom TIRZIU CONSTANTIN University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova ABSTRACT Jaundice is a yellowish pigmentation of the skin, the conjunctival membranes over
For Practitioner Jaundice Obstructive Syndrom TIRZIU CONSTANTIN University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova ABSTRACT Jaundice is a yellowish pigmentation of the skin, the conjunctival membranes over
EXAM COVER SHEET. Course Code: CLS 432. Course Description: Clinical Biochemistry. Final Exam. Duration: 2 hour. 1st semester 1432/1433.
 EXAM COVER SHEET Course Code: CLS 432 Course Description: Clinical Biochemistry Final Exam Duration: 2 hour 1st semester 1432/1433 Student Name: Student Uni No: Part 1 Multiple choice questions Answer
EXAM COVER SHEET Course Code: CLS 432 Course Description: Clinical Biochemistry Final Exam Duration: 2 hour 1st semester 1432/1433 Student Name: Student Uni No: Part 1 Multiple choice questions Answer
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
EVALUATION & LISTING. Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation. What is the Liver?
 EVALUATION & LISTING Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation The University of Michigan is a national leader in liver transplantation, as well as the surgical and medical management of patients with liver
EVALUATION & LISTING Your Child s Liver Transplant Evaluation The University of Michigan is a national leader in liver transplantation, as well as the surgical and medical management of patients with liver
La b o r at o ry Test s a n d Pr o c e d u r e s
 c h a p t e r La b o r at o ry Test s a n d Pr o c e d u r e s 6 Tina M. St. John, MD Introduction Chronic hepatitis C is a complex disease. The course and symptoms vary from one person to another. The
c h a p t e r La b o r at o ry Test s a n d Pr o c e d u r e s 6 Tina M. St. John, MD Introduction Chronic hepatitis C is a complex disease. The course and symptoms vary from one person to another. The
Routine Clinic Lab Studies
 Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
Routine Lab Studies Routine Clinic Lab Studies With all lab studies, a Tacrolimus level will be obtained. These drug levels are routinely assessed to ensure that there is enough or not too much anti-rejection
ANAESTHESIA AND LIVER DISEASE: UNDERSTANDING BLOOD RESULTS
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk ANAESTHESIA AND LIVER DISEASE: UNDERSTANDING BLOOD RESULTS Author : Marieke De Vries Categories : Vets Date : September 26,
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk ANAESTHESIA AND LIVER DISEASE: UNDERSTANDING BLOOD RESULTS Author : Marieke De Vries Categories : Vets Date : September 26,
Histology. The pathology of the. bile ducts. pancreas. liver. The lecture in summary. Vt-2006
 Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Understanding Blood Tests
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Your heart pumps the blood in your body through a system of blood vessels. Blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body. It also carries away
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Your heart pumps the blood in your body through a system of blood vessels. Blood delivers oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body. It also carries away
The Liver & Gallbladder
 The Liver & Gallbladder The liver has been shown to have more than 500 vital functions We will review only a few of these Main Functions of the Liver PRODUCES BILE Elimination of toxins Fat emulsifier
The Liver & Gallbladder The liver has been shown to have more than 500 vital functions We will review only a few of these Main Functions of the Liver PRODUCES BILE Elimination of toxins Fat emulsifier
Multiphasic Blood Analysis
 Understanding Your Multiphasic Blood Analysis Test Results Mon General thanks you for participating in the multiphasic blood analysis. This test can be an early warning of health problems, including coronary
Understanding Your Multiphasic Blood Analysis Test Results Mon General thanks you for participating in the multiphasic blood analysis. This test can be an early warning of health problems, including coronary
Infective Liver Disease
 The Role oeofdrugs in Non Infective Liver Disease Peter Tenni Senior Lecturer in Therapeutics, School of Pharmacy University of Tasmania Senior Research Fellow Unit for Medication Outcomes Research and
The Role oeofdrugs in Non Infective Liver Disease Peter Tenni Senior Lecturer in Therapeutics, School of Pharmacy University of Tasmania Senior Research Fellow Unit for Medication Outcomes Research and
& CBC Analysis. Getting the Most from the. Session 3. Foundations of Functional Blood Chemistry Analysis Session 3 Dr.
 Functional Blood Chemistry & CBC Analysis Session 3 Li L:iver and Gallbladder Markers SGOT/AST, SGPT/ALT & GGTP Getting the Most from the Liver Panel http://www.fmtown.com 1 Liver Panel Reference Ranges
Functional Blood Chemistry & CBC Analysis Session 3 Li L:iver and Gallbladder Markers SGOT/AST, SGPT/ALT & GGTP Getting the Most from the Liver Panel http://www.fmtown.com 1 Liver Panel Reference Ranges
DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS. Author: Josephine Davis
 DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS Author: Josephine Davis LAB TESTS Think twice before you test. What is the reason for testing? Laboratory tests are generally requested in primary care for one of the following
DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS Author: Josephine Davis LAB TESTS Think twice before you test. What is the reason for testing? Laboratory tests are generally requested in primary care for one of the following
Case Study BMIs in the range of are considered overweight. Therefore, F.V. s usual BMI indicates that she was overweight.
 Morgan McFarlane February 26 th, 2013 HHP 439 Professor White Case Study 7.10 1. What is your interpretation of F.V. s clinical data? F.V. s clinical data includes chronic abdominal pain, loose stools,
Morgan McFarlane February 26 th, 2013 HHP 439 Professor White Case Study 7.10 1. What is your interpretation of F.V. s clinical data? F.V. s clinical data includes chronic abdominal pain, loose stools,
IN THE NAME OF GOD. D r. MANIJE DEZFULI AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST
 IN THE NAME OF GOD AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL D r. MANIJE DEZFULI INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST Acute Viral Hepatitis The Anatomy of the Liver Hepatic Physiology Liver: Largest solid organ
IN THE NAME OF GOD AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL D r. MANIJE DEZFULI INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST Acute Viral Hepatitis The Anatomy of the Liver Hepatic Physiology Liver: Largest solid organ
Med Chem 535 Diagnostic Medicinal Chemistry. Blood Proteins and Serum Enzymes
 Med Chem 535 Diagnostic Medicinal Chemistry Blood Proteins and Serum Enzymes I. Blood Proteins A. Total Protein* B. Albumin* C. The Globulins D. Fibrinogen E. Serum Enzymes II. Liver Function Tests A.
Med Chem 535 Diagnostic Medicinal Chemistry Blood Proteins and Serum Enzymes I. Blood Proteins A. Total Protein* B. Albumin* C. The Globulins D. Fibrinogen E. Serum Enzymes II. Liver Function Tests A.
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland
 Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Biochemistry Lecture #3
 1 P a g e Hello Awn.. This lecture includes the slides.. anything with (!) is important.. and Italic line Any sentence within Double Brackets {{ }} is just for understanding (Not from Slides) Let s start
1 P a g e Hello Awn.. This lecture includes the slides.. anything with (!) is important.. and Italic line Any sentence within Double Brackets {{ }} is just for understanding (Not from Slides) Let s start
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male
 Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
NATIONAL LABORATORY HANDBOOK
 NATIONAL LABORATORY HANDBOOK The Abnormal Liver Chemistry Profile Document reference number Document developed by National Clinical Programme for Pathology Revision number Version 1. Document approved
NATIONAL LABORATORY HANDBOOK The Abnormal Liver Chemistry Profile Document reference number Document developed by National Clinical Programme for Pathology Revision number Version 1. Document approved
BIOCHEMICAL REPORT. Parameters Unit Finding Normal Value. Lipase U/L Amylase U/L
 Lipase U/L 88.9 10-195 Amylase U/L 1181.1 371.3-1192.6 West Delhi :- 7/148, Opp. MCD Office, Major Pankaj Batra Marg, Near Ramesh Nagar, New Delhi-15, Ph. : 011-47562566,9999830187 Liver Function Test
Lipase U/L 88.9 10-195 Amylase U/L 1181.1 371.3-1192.6 West Delhi :- 7/148, Opp. MCD Office, Major Pankaj Batra Marg, Near Ramesh Nagar, New Delhi-15, Ph. : 011-47562566,9999830187 Liver Function Test
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology For The First Class 2 nd Semester Erythrocytes = Red Blood Cells (RBC) Erythrocytes = Red Blood Cells Red blood cells are biconcave discs, they have no nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles.
Anatomy and Physiology For The First Class 2 nd Semester Erythrocytes = Red Blood Cells (RBC) Erythrocytes = Red Blood Cells Red blood cells are biconcave discs, they have no nucleus and cytoplasmic organelles.
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for referral 3. Raised ALT +/- GGT p3 4. Non alcoholic fatty liver
1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for referral 3. Raised ALT +/- GGT p3 4. Non alcoholic fatty liver
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
Interpreting Your Tests
 Interpreting Your Tests Lisa M. Forman, MD, MSCE Associate Professor of Medicine Section Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver Outline Bile Duct Anatomy Lab Tests LFTs Tumor
Interpreting Your Tests Lisa M. Forman, MD, MSCE Associate Professor of Medicine Section Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver Outline Bile Duct Anatomy Lab Tests LFTs Tumor
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Postoperative jaundice
 Postoperative jaundice Principles of Surgery Ehren Eksteen 17/3/2010 Abri Bezuidenhout 28/3/2012 Intro Jaundice is defined as yellow discolouration of the skin,sclera and heavily perfused areas in a patient
Postoperative jaundice Principles of Surgery Ehren Eksteen 17/3/2010 Abri Bezuidenhout 28/3/2012 Intro Jaundice is defined as yellow discolouration of the skin,sclera and heavily perfused areas in a patient
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Clinical Chemistry (CHE221) Professor Hicks Lecture 15. Bilirubin and Cholesterol
 linical hemistry (E221) Professor icks Lecture 15 Bilirubin and holesterol opyright 2009 harles icks like dissolves like fats, oils, grease, contain lots of nonpolar bonds water is a polar substance polar
linical hemistry (E221) Professor icks Lecture 15 Bilirubin and holesterol opyright 2009 harles icks like dissolves like fats, oils, grease, contain lots of nonpolar bonds water is a polar substance polar
Alpha-1 Liver Disease
 Alpha-1 Liver Disease Jeffrey Teckman, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics and Biochemistry Associate Chair of Pediatrics for Research Director, Pediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology St. Louis University
Alpha-1 Liver Disease Jeffrey Teckman, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics and Biochemistry Associate Chair of Pediatrics for Research Director, Pediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology St. Louis University
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 8 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Jaundice Chris Wells Regional CMT teaching 6 th June 2017
 Jaundice Chris Wells Regional CMT teaching 6 th June 2017 By the end you will Have a systematic approach to the patient with jaundice Be able to diagnose the cause of jaundice Have a framework for managing
Jaundice Chris Wells Regional CMT teaching 6 th June 2017 By the end you will Have a systematic approach to the patient with jaundice Be able to diagnose the cause of jaundice Have a framework for managing
Basic Blood Chemistry, by Sharlene Peterson CLASS: G610
 Basic Blood Chemistry, by Sharlene Peterson CLASS: G610 This is your test but do not try to fill in the blanks! We created a Test Answer Sheet which is easy to download, fill in the answer, and email.
Basic Blood Chemistry, by Sharlene Peterson CLASS: G610 This is your test but do not try to fill in the blanks! We created a Test Answer Sheet which is easy to download, fill in the answer, and email.
Ms Amanda Clements ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE LIVER. Pre-Conference Nurse s Course. Plymouth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust 12/12/2014
 Pre-Conference Nurse s Course in partnership with Ms Amanda Clements Plymouth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE LIVER Amanda Clements Nurse Consultant Hepatology 1 Anatomy Largest
Pre-Conference Nurse s Course in partnership with Ms Amanda Clements Plymouth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE LIVER Amanda Clements Nurse Consultant Hepatology 1 Anatomy Largest
GI Workshop Case Studies
 GI Workshop Case Studies Cliff Titcomb MD Hannover Re AAIM Annual Meeting San Diego, October, 2012 5 Tests Commonly Known as Liver Function Tests Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) Aspartate Aminotransferase
GI Workshop Case Studies Cliff Titcomb MD Hannover Re AAIM Annual Meeting San Diego, October, 2012 5 Tests Commonly Known as Liver Function Tests Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) Aspartate Aminotransferase
-sheet 3. -Waseem Alhaj. Maha Shomaf
 -sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
-sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
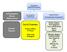 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Liver ISSUES. by Academy EPIC
 Liver ISSUES by Academy EPIC www.academyepic.com Liver Functions produces glycogen from glucose breaks down glycogen into glucose converts non carbohydrates to glucose oxidizes fatty acids synthesizes
Liver ISSUES by Academy EPIC www.academyepic.com Liver Functions produces glycogen from glucose breaks down glycogen into glucose converts non carbohydrates to glucose oxidizes fatty acids synthesizes
Cirrhosis of the Liver
 235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Cirrhosis of the Liver The liver, the largest organ in the body, is
235 60th Street, West New York, NJ 07093 T: (201) 854-4646 F: (201) 854-4647 810 Main Street, Hackensack, NJ 07601 T: (201) 488-0095 Cirrhosis of the Liver The liver, the largest organ in the body, is
The Urinary System. Lab Exercise 38. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
What is Liver Cancer? About the Liver
 Your liver is important and it has many functions. The top three are that it cleans your blood of toxins, gives you energy and produces bile for digestion. What is Liver Cancer? Cancer starts when cells
Your liver is important and it has many functions. The top three are that it cleans your blood of toxins, gives you energy and produces bile for digestion. What is Liver Cancer? Cancer starts when cells
DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION
 DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION ROUTE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND EXTRAHEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM The decline in plasma concentration after drug administration
DRUG ELIMINATION II BILIARY EXCRETION MAMMARY, SALIVARY AND PULMONARY EXCRETION ROUTE OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION AND EXTRAHEPATIC DRUG METABOLISM The decline in plasma concentration after drug administration
