muscle biopsy How to do it
|
|
|
- Dinah Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How to do it muscle biopsy Gillian Hall Department of Clinical Neurosciences, Western General Hospital, Edinburgh EH4 2XU. INTRODUCTION Good clinical evaluation remains the most effective tool in the assessment of disorders of muscle. Muscle biopsy, like expensive genetic analysis, when used appropriately is a valuable diagnostic aid. When undertaken inappropriately, at best it wastes the time and resources of the surgeon and histopathology department, and at worst has subjected the patient to an unnecessary invasive test. The usefulness of a muscle biopsy depends on consideration of all the following four criteria: appropriateness of the test; choice of muscle; biopsy technique; array of histopathology performed. APPROPRIATENESS OF THE TEST Biopsy is most useful for the diagnosis of: Inflammatory myopathies (diagnosis and to monitor treatment). Certain muscular dystrophies for which the structural abnormality is known but genetic testing is not readily available (where there are many different mutations within the abnormal gene, e.g. the sarcoglycanopathies). DECEMBER
2 114 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY Good clinical evaluation remains the most effective tool in the assessment of disorders of muscle It is good practice to use the same muscle for every biopsy as far as is possible Mitochondrial cytopathies, both to look for the presence of ragged red and cytochrome c oxidase-negative fibres and as a source of mitochondrial DNA (mtdna). If the clinical picture is such that a defined mitochondrial cytopathy is suspected, known mutations may be detected in mtdna extracted from peripheral leucocytes. Remember that abnormal mtdna can be seen in certain mitochondrial cytopathies that appear to be Mendelian traits, e.g. multiple mtdna deletions in autosomal dominant progressive external ophthalmoplegia. Metabolic myopathies. Again there are some provisos. For patients with clinically probable McArdle s disease (see pp ), especially if there is an affected sibling, it may be more appropriate to perform genetic analysis from peripheral blood, hence sparing the patient an invasive procedure. Three mutations make up approximately 90% of those found in McArdle s disease, but analysis for only the most common is widely available. Biopsy is not appropriate for first line diagnosis of: Neuromuscular disorders that can be confirmed by electrophysiology, e.g. myasthenia gravis and related syndromes, motor neurone disease. Genetic disorders for which diagnostic genetic analysis is available, e.g. certain muscular dystrophies (such as Becker s and Duchenne muscular dystrophies, facioscapulohumeral dystrophy and myotonic dystrophy) and spinal muscular atrophy (homozygous deletions of SMN1 gene found in approximately 96% of all cases). Biopsy is of least use in the following situation: Non specific history with normal examination, creatinine kinase and electomyography. Remember, if the clinician cannot find something wrong it is highly unlikely that the tests will! CHOICE OF MUSCLE It is good practice to use the same muscle for every biopsy as far as is possible. This is because there are variations in normal between different muscles, subtle changes that might be accepted as normal in one muscle might be considered abnormal in another. For example, muscles with a heavy work load such as gastrocnemius may appear myopathic and tibialis anterior has an abundance of type 1 over type 2 fibres. By looking at the same muscle as often as possible, the pathologist will recognize variations from normal more readily. Biceps brachialis in the upper limb and vastus lateralis in the lower limb are most frequently chosen but the following must also be considered: The chosen muscle must be involved in the process (weak) but not severely so. Using the British Medical Research Council Scale, a power of 4/5 is desirable. Worse than that and one risks only obtaining end stage muscle in which muscle fibres have been replaced with fat and fibrous tissue and the original pathology is obscured. The muscle site must be free from trauma, iatrogenic or otherwise. This includes previous biopsy and recent intra muscular injection or insertion of EMG needles. An example of good clinical practice within a department is that, for patients with symmetrical muscle disease in whom a biopsy is being considered, EMG is always performed on the right and biopsy on the left (given the majority of patients are right handed). If the disease is focal or distal, extensor carpi radialis or tibialis anterior may be used, accepting the pitfalls mentioned above. In the UK, CT and MRI are not routinely employed to image the distribution of muscle involvement, but may be useful in certain cases. Consider cosmetic issues. A biopsy scar is more discrete on the thigh than upper limb. Likewise biopsy of facial muscle should be avoided. Consider functional issues. Biopsy should be of large muscles in a limb, small muscles in the hand with important function should be avoided. Beware of muscle affected by a second pathological process, such as a radiculopathy, which may confuse interpretation of the biopsy. BIOPSY TECHNIQUE Preparing the patient Muscle biopsy requires written, informed consent. The procedure should be explained to the patient, the precise muscle having been predetermined using the criteria above and named on the consent form. The muscle and site of biopsy can be marked at this stage. This should be over
3 the belly of the muscle muscle taken from close to normal tendinous insertion can have findings mistaken for pathology. If the biopsy is to be performed by anyone other than the clinician involved, it is doubly important to name and mark the chosen muscle. Preparing the pathologist No matter how technically good the biopsy, the pathologist requires detailed clinical information so that the specimen is processed and interpreted in a way that maximizes diagnostic information. The pathologist (a fellow doctor and not merely the neurologists technician) will need to know the clinical picture; whether there is a family history, and if so, both the pedigree and whether any family members have had previous biopsies; drug history if relevant; examination findings and the results of investigations such as creatinine kinase, inflammatory markers and EMG. Technique There is a debate as to the pros and cons of open vs. needle biopsy. The latter is a less invasive and quicker technique that can be performed in a clean ward treatment room. However, the biopsies are smaller and even in the most experienced hands the regularity with which reliable specimens are obtained must be less. Furthermore, there is a higher chance of missing patchy/focal pathology such as inflammation. The technique of open biopsy will be described. The biopsy is best performed in an operating theatre, by direct visualization and under sterile conditions. The skin over the biopsy site is cleaned and prepared. The surrounding area is infiltrated with local anaesthetic containing adrenalin. A skin incision of approximately one inch in adults is made over the previously marked site. The fatty subcutaneous tissue is gently teased apart to reveal the fascia overlying the muscle. This in turn is then incised to expose the muscle. The biopsy is taken with the muscle fibre fascicles running longitudinally. The size and number of biopsies should be depend on the age of the patient and what tests are required and must be decided in advance. Ideally the laboratory has been alerted and the fresh specimens are transported immediately for freezing (histochemical and biochemical analysis) and fixing (electron microscopy) as required. Haemostasis is then achieved and the fascia sutured before closing the skin wound. If uncomplicated, the patient can be discharged later the same day, with advice regarding wound care and removal of sutures. ARRAY OF HISTOPATHOLOGY PERFORMED If an urgent therapeutic decision is to be made depending on the biopsy findings, e.g. acute inflammatory or necrotic myopathies, a preliminary examination can be made using only haematoxilin and eosin stain. It is important to look at different levels of the biopsy for an inflammatory infiltrate that may be patchy. This is sufficient to give information regarding fibre size and the presence of necrosis and regeneration and abnormalities of the interstitium including an inflammatory infiltrate. Routinely, however, a battery of histology, histochemical stains and specific enzyme analysis as shown in Table 1 is employed. More focused histochemistry and immunocytochemistry and electron microscopy can then be used as indicated (Table Table 1 Routine stains Haematoxilin and eosin cellular infiltrate interstitial fibrosis cytoarchitectural abnormalities necrosis and regeneration Myosin ATPase ph 4.3,4.6 and 9.4 Gomori s trichrome nemaline rods Oil Red O/sudan black Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) Oxidative enzymes NADH-TR acid phosphatase cytochrome c oxidase (COX) succinic dehydrogenase (SDH) fibre size fibre type distribution ragged red fibres lipid glycogen DECEMBER myofibrillar architecture, mitochondria, target fibres lysosomes, macrophages, rimmed vacuoles mitochondrial myopathy (complex IV) nuclear encoded complex II
4 116 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY Myophosphorylase Phosphofructokinase Immunocytochemistry Dystrophies Dys1,2 and 3 (antibodies to the N and C terminals and to the rod portion of dystrophin) Sarcoglycans (limb girdle picture with autosomal recessive family history) (adhalin) Dysferlin Calveolin 3 (limb girdle picture with autosomal dominant family history) Laminin- 1 Laminin- 2 Emerin Other immunocytochemistry CD4,CD8 and CD 20 MHC class I Tau, ubiquitin, -amyloid and others Developmental myosin heavy chain mainly Neonatal myosin heavy chain Table 2 Examples of more specialized histochemistry McArdle s disease (type V glycogenosis) type VII glycogenosis Duchenne and Becker dystrophy and female carriers protein usually absent in Duchenne and reduced in Becker dystrophy and carriers LGMD2D LGMD2E LGMD2C LGMD2F LGMD2B distal muscular dystrophy/miyoshi myopathy LGMD1C not specific but found as a secondary phenomenon in a number of conditions, usually autosomal dominant, including autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy and some patients with Bethlem myopathy. congenital muscular dystrophy/myopathy Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy T cell subsets and B cell markers expressed on mature fibres in inflammatory myopathies inclusion body myositis (sporadic, autosomal dominant or both) regenerating fibres expressed in injury, denervation 2). If required, muscle can be stored at 70 C for further examination, such as DNA analysis, at a later date. BIOPSY FINDINGS To maximize the diagnostic power of a muscle biopsy, suspicion of a condition may be required and that suspicion must be conveyed to the histopathologist. For example, a muscle biopsy in McArdle s disease may be normal unless myophosphorylase staining has been performed, in which case absence of this enzyme is demonstrated. By the same logic, a normal muscle biopsy does not exclude a more obscure metabolic myopathy. Fibre size and distribution Muscle contains slow-twitch type I fibres and fast-twitch type II fibres, which are identified by enzyme histochemistry. Type I fibres contain greater numbers of mitochondria and therefore stain darkly with the oxidative stains NADH-TR, COX and SDH. The use of myosin ATPase with preincubation at varying phs allows subdivision of type II fibres into type IIA, IIB and IIC.
5 DECEMBER Small groups of atrophied fibres point to denervation. Type specific grouping is characteristic of reinervation. Specific type I fibre atrophy may be a congenital finding or is seen in myotonic dystrophy. Type II fibre atrophy is a more nonspecific finding and indicates an unhealthy muscle. Common causes are steroid use, systemic illness and simple disuse. Predominance of type I fibres is seen in congenital myopathies but may also be non specific. Variation in fibre size, including hypertrophied fibres, is characteristic of a dystrophic process. Perifascicular atrophy is found in dermatomyositis. Abnormalities of the cytoarchitecture The NADH-TR and Gomori s trichrome stains can demonstrate a wide range of inclusions and other cytoarchitectural abnormalities. Most are nonspecific as a scattered isolated finding but, if numerous, suggest certain disease processes. PAS and Oil Red O stain glycogen and lipid stores, respectively, and the oxidative enzymes are useful when looking for cores. Ragged red fibres [Figure 1(a)] are seen with ageing but are found more frequently than expected in mitochondrial myopathies and certain drug induced myopathies. However, not all mtdna mutations cause mitochondrial proliferation (ragged red fibres), e.g. NARP (neurogenic weakness, ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa). (COX)-negative fibres also suggest mitochondrial dysfunction. Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies and rimmed vacuoles are seen in both sporadic and hereditary inclusion body myositis. Inflammation is only found in sporadic cases. Nemaline rods are found in congenital nemaline myopathy. Tubular aggregates are found in many conditions. Although classically associated with the periodic paralyses, in particular hypokalaemic periodic paralyses, and related myotonias, they are an inconsistent and minor finding in a wide range of conditions. More recently, three clinical presentations in which tubular aggregates are the major pathological finding have been described: familial limb girdle myasthenia, progressive limb girdle weakness and exercise related muscle pain and cramps. Target cells. Seen with denervation Cores. Seen in some congenital myopathies, e.g. central core disease [Figure 1(b)], minicore disease and myotubular myopathy Lobulated fibres. Found in some muscular dystrophies, including facioscapulohumeral dystrophy [Figure 1(c)]. Evidence of abnormalities of lipid or glycogen storage. Necrosis and regeneration This is found in addition to an inflammatory infiltrate in the context of inflammatory myopathies, or without inflammation as seen with toxic and metabolic myopathies. Inflammation An inflammatory infiltrate is predominantly perimysial in dermatomyositis but found within the fascicle and invading the individual muscle fibres in polymyositis [Figure 1(d)]. Inflammation is seen in sporadic but not hereditary inclusion body myositis. If the biopsy is to be performed by anyone other than the clinician involved, it is doubly important to name and mark the chosen muscle
6 118 PRACTICAL NEUROLOGY (a) (c) Figure 1 (a) Ragged red fibres (Gomori-Trichrome); (b) Central cores in central core disease (NADH); (c) Lobulated fibres in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy; (d) Inflammatory infiltrate in polymyositis (H + E). (b) (d) More information on the nature of the infiltrate can be gained from lymphocyte markers. In dermatomyositis, the perimysial infiltrate is predominantly B and CD4+ve T cells, whereas in polymyositis and sporadic inclusion body myosititis, the endomysial T cells are mainly CD8+ ve. Interstitium Perivascular infiltrate seen in the vasculitides and dermatomyositis. Fibrosis is a feature of many conditions. LIMITATIONS OF MUSCLE BIOPSY Adhering to the above recommendations will maximize the diagnostic yield, but in not all cases is the histology pathognomonic. It may elucidate the disease process, for example dystrophic, my- opathic, inflammatory, neurogenic, etc., without specifying the cause. Limitations may reflect inappropriate indication for biopsy. However, as the primary protein deficits of more and more genetic disorders of muscle are identified, the possibility of immunochemical diagnostic specificity increases. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Many thanks to Professor James Ironside for kindly providing the histology slides. FURTHER READING Janice R Anderson (1997) Recommendations for the biopsy procedure and assessment of skeletal muscle biopsies. Virchows Arch, 431, (More detail with regard to handling the biopsy, transport to laboratory, different types of fixation and freezing of specimens.)
III./10.4. Diagnosis. Introduction. A.) Laboratory tests. Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques
 III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
III./10.4. Diagnosis Laboratory tests, electrophysiology, muscle biopsy, genetic testing, imaging techniques After studying this chapter, you will become familiar with the most commonly used diagnostic
Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light.
 Cơ vân Cơ vân Cơ vân (cắt dọc) Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light. (A, Congo Red). Amyloid neuropathy:
Cơ vân Cơ vân Cơ vân (cắt dọc) Amyloid neuropathy: (A) scattered Congo Red positive material in endoneurium displays apple green birefringence under polarized light. (A, Congo Red). Amyloid neuropathy:
Case 1: History of J.H. Outside Evaluation. Outside Labs. Question #1
 Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Case 1: History of J.H. 64 yo man seen at UCSF 6-256 25-07. 9 months ago onset progressive weakness of arms and legs, with muscle atrophy in arms. 4 months ago red scaly rash on face, back of hands and
Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease
 Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Muscle Normal Muscle The Sarcomere The names
Electron microscopy in the investigation and diagnosis of muscle disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Muscle Normal Muscle The Sarcomere The names
Muscle biopsies. There are two different types of muscle biopsy. 1. Needle biopsy
 Muscle biopsies What is a muscle biopsy? A muscle biopsy is a procedure in which a small sample of muscle usually about the size of an orange pip is taken and examined under a microscope. It is considered
Muscle biopsies What is a muscle biopsy? A muscle biopsy is a procedure in which a small sample of muscle usually about the size of an orange pip is taken and examined under a microscope. It is considered
Please Silence Your Cell Phones. Thank You
 Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You From Morphology to Molecular Genetics: Role of the Pathologist in Diagnosis of Muscle Disorders Karen M. Weidenheim, M.D. Department of Pathology (Neuropathology),
Please Silence Your Cell Phones Thank You From Morphology to Molecular Genetics: Role of the Pathologist in Diagnosis of Muscle Disorders Karen M. Weidenheim, M.D. Department of Pathology (Neuropathology),
Publications List. 1. General factsheets. 2. Medical conditions factsheets
 Publications List We produce a wide range of publications, from factsheets about specific medical conditions to comprehensive guides on adapting your home. To order a free publication: Call the Information
Publications List We produce a wide range of publications, from factsheets about specific medical conditions to comprehensive guides on adapting your home. To order a free publication: Call the Information
Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle
 Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle Zarife Sahenk, MD. PhD. Research Institute at Nationwide Children s Hospital Center for gene therapy, Neuromuscular Program Experimental & Clinical Neuromuscular
Pathology of Neuromuscular Disease Part 1: muscle Zarife Sahenk, MD. PhD. Research Institute at Nationwide Children s Hospital Center for gene therapy, Neuromuscular Program Experimental & Clinical Neuromuscular
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report
 Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Genetic diagnosis of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, A Case Report Roshanak Jazayeri, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medical Genetics Faculty of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference. November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D.
 Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
Muscle Pathology Surgical Pathology Unknown Conference November, 2008 Philip Boyer, M.D., Ph.D. Etiologic Approach to Differential Diagnosis Symptoms / Signs / Imaging / Biopsy / CSF Analysis Normal Abnormal
CNEMG. Myopathy, Stålberg. At rest denervation and spec spontaneous activity (myotonia, CRD, neuromyotonia) MUP number of fibres in recorded area
 clincial heredity biochem MYOPATHY biopsy Erik Stålberg Uppsala, Sweden imaging genetics Electrodes A B C MU D E Conc EMG signals from 2-15 muscle fibres CNEMG At rest denervation and spec spontaneous
clincial heredity biochem MYOPATHY biopsy Erik Stålberg Uppsala, Sweden imaging genetics Electrodes A B C MU D E Conc EMG signals from 2-15 muscle fibres CNEMG At rest denervation and spec spontaneous
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of One Hundred Pediatric Muscle Biopsies During A 2-Year Period in Mofid Children And Toos Hospitals
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of One Hundred Pediatric Muscle Biopsies During A 2-Year Period in Mofid Children And Toos Hospitals How to Cite This Article: : Nilipor Y, Shariatmadari F, Abdollah gorji F,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of One Hundred Pediatric Muscle Biopsies During A 2-Year Period in Mofid Children And Toos Hospitals How to Cite This Article: : Nilipor Y, Shariatmadari F, Abdollah gorji F,
Proceedings des 36èmes Journées Annuelles de l Association Vétérinaire Equine Française
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings des 36èmes Journées Annuelles de l Association Vétérinaire Equine Française 9-11 Octobre 2008 - Reims, France Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings des 36èmes Journées Annuelles de l Association Vétérinaire Equine Française 9-11 Octobre 2008 - Reims, France Reprinted in IVIS with the Permission
Disorders of Muscle. Disorders of Muscle. Muscle Groups Involved in Myopathy. Needle Examination of EMG. History. Muscle Biopsy
 Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Disorders of Muscle Disorders of Muscle Zakia Bell, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Virginia Commonwealth University Cardinal symptom of diseases of the muscle
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction
 Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Diseases of Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Neuromuscular Junction Muscle Myastenia Gravis Eaton-Lambert Syndrome Toxic Infllammatory Denervation Atrophy
CONTENT ANATOMIC LOCI OF NM DISEASE ASSOCIATED FEATURES FUNCTIONAL DIFFICULTIES. CLINICAL HISTORY IN NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASES Weakness 06/11/60
 CONTENT HOW TO APPROACH LIMB GIRDLE AND NON-LIMB GIRDLE WEAKNESS Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn, M.D. Professor Thammasat University Clinical approach in NM disease and phenotype Common and uncommon LGMDs Common
CONTENT HOW TO APPROACH LIMB GIRDLE AND NON-LIMB GIRDLE WEAKNESS Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn, M.D. Professor Thammasat University Clinical approach in NM disease and phenotype Common and uncommon LGMDs Common
Neonatal Hypotonia. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy. Neurology Chapter of IAP
 The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
The floppy infant assumes a frog legged position. On ventral suspension, the baby can not maintain limb posture against gravity and assumes the position of a rag doll. Encephalopathy acute No encephalopathy
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral
 Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral Matthew Harmelink, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurology Medical College of Wisconsin Objectives: 1. Understand common presentations
Neuromuscular in the Pediatric Clinic: Recognition and Referral Matthew Harmelink, MD Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurology Medical College of Wisconsin Objectives: 1. Understand common presentations
CLASSIFICATION OF PERIPHERAL NERVE DISEASES
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory loss + 0 Loss of reflexes early late CSF protein elevated normal Electromyography neurogenic
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory loss + 0 Loss of reflexes early late CSF protein elevated normal Electromyography neurogenic
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease. Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine
 Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Muscular Dystrophies. Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018
 Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
Muscular Dystrophies Pinki Munot Consultant Paediatric Neurologist Great Ormond Street Hospital Practical Neurology Study days April 2018 Definition and classification Clinical guide to recognize muscular
Immunohistochemical Study of Dystrophin Associated Glycoproteins in Limb-girdle Muscular Dystrophies
 Dystrophin Immunohistochemical Study of Dystrophin Associated Glycoproteins in Limb-girdle Muscular Dystrophies NSC 89-2314-B-002-111 88 8 1 89 7 31 ( Peroxidase -AntiPeroxidase Immnofluorescence) Abstract
Dystrophin Immunohistochemical Study of Dystrophin Associated Glycoproteins in Limb-girdle Muscular Dystrophies NSC 89-2314-B-002-111 88 8 1 89 7 31 ( Peroxidase -AntiPeroxidase Immnofluorescence) Abstract
Index. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 445 453 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid maltase deficiencies, electrodiagnosis of, 420, 422 Acquired peripheral neuropathy,
Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 14 (2003) 445 453 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid maltase deficiencies, electrodiagnosis of, 420, 422 Acquired peripheral neuropathy,
EDX in Myopathies Limitations. EDX in Myopathies Utility Causes of Myopathy. Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies
 J.A.L.Bulcke A.L.Baert Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies CT Scanning EMG Radioisotopes With 151 Figures and 30 Tables Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH Dr. JAN A. L BULCKE K. U. Leuven,
J.A.L.Bulcke A.L.Baert Clinical and Radiological Aspects of Myopathies CT Scanning EMG Radioisotopes With 151 Figures and 30 Tables Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH Dr. JAN A. L BULCKE K. U. Leuven,
Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during treatment in hypothyroid myopathy
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 229-233 Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during in hypothyroid myopathy R. 0. McKERAN",4, P. WARD2, G. SLAVIN2 3, AND E. A. PAUL5 From the Divisions
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 229-233 Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during in hypothyroid myopathy R. 0. McKERAN",4, P. WARD2, G. SLAVIN2 3, AND E. A. PAUL5 From the Divisions
A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies.
 1 A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies. Available on-line at: Bill Tillier Calgary Alberta September, 2008. Terminology.
1 A very simplified introduction to neuromuscular illnesses (NMIs) with a particular focus on the muscular dystrophies. Available on-line at: Bill Tillier Calgary Alberta September, 2008. Terminology.
Clinical and pathologic aspects of congenital myopathies
 Neurol J Southeast Asia 2001; 6 : 99 106 88 Clinical and pathologic aspects of congenital myopathies Ikuya NONAKA MD National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Kodaira, Tokyo, Japan Abstract The term
Neurol J Southeast Asia 2001; 6 : 99 106 88 Clinical and pathologic aspects of congenital myopathies Ikuya NONAKA MD National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Kodaira, Tokyo, Japan Abstract The term
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES
 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory dysfunction + 0 Loss of reflexes early late Serum enzymes +/- +++ CSF protein may be elevated
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF NEUROGENIC DISORDERS & MYOPATHIES NEUROPATHY MYOPATHY Weakness distal proximal Sensory dysfunction + 0 Loss of reflexes early late Serum enzymes +/- +++ CSF protein may be elevated
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress MYOPATHIES OF DOGS AND CATS Richard A. LeCouteur, BVSc, PhD, Dip ACVIM (Neurology), Dip ECVN University of California,
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress MYOPATHIES OF DOGS AND CATS Richard A. LeCouteur, BVSc, PhD, Dip ACVIM (Neurology), Dip ECVN University of California,
A rare case of muscular dystrophy with POMT2 and FKRP gene mutation. Present by : Ghasem Khazaei Supervisor :Dr Mina Mohammadi Sarband
 A rare case of muscular dystrophy with POMT2 and FKRP gene mutation Present by : Ghasem Khazaei Supervisor :Dr Mina Mohammadi Sarband Index : Congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) Dystroglycanopathies Walker-Warburg
A rare case of muscular dystrophy with POMT2 and FKRP gene mutation Present by : Ghasem Khazaei Supervisor :Dr Mina Mohammadi Sarband Index : Congenital muscular dystrophy (CMD) Dystroglycanopathies Walker-Warburg
Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1966, 29, 23 Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle Part III Neurogenic muscular atrophies VICTOR DUBOWITZ From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1966, 29, 23 Enzyme histochemistry of skeletal muscle Part III Neurogenic muscular atrophies VICTOR DUBOWITZ From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 myopathies and muscle diseases handbook of clinical neurology myopathies and muscle diseases
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MYOPATHIES AND MUSCLE DISEASES HANDBOOK OF CLINICAL NEUROLOGY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 myopathies and muscle diseases handbook of clinical neurology myopathies and muscle diseases
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease.
 Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Dysferlinopathies. LGMD2B, Miyoshi & Others. 2B Empowered Conference
 Dysferlinopathies LGMD2B, Miyoshi & Others 2B Empowered Conference Matthew P. Wicklund, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics Penn State Health May 24, 2015 Outline A. Empower you with knowledge
Dysferlinopathies LGMD2B, Miyoshi & Others 2B Empowered Conference Matthew P. Wicklund, MD, FAAN Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics Penn State Health May 24, 2015 Outline A. Empower you with knowledge
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils
 Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers Characteristic IIb IIx IIa Type I V max (speed of shortening) Highest Intermediate Low Resistance to fatigue
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers Characteristic IIb IIx IIa Type I V max (speed of shortening) Highest Intermediate Low Resistance to fatigue
LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN?
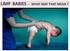 LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN? ARE WE LOOKING WHERE WE SHOULD? FLOPPY = LIMP = FLACCID = WEAK Poor head control when pulled C-posture sitting, or in ventral susp. Frog-leg lying Dropping arms Casey
LIMP BABIES - WHAT MAY THAT MEAN? ARE WE LOOKING WHERE WE SHOULD? FLOPPY = LIMP = FLACCID = WEAK Poor head control when pulled C-posture sitting, or in ventral susp. Frog-leg lying Dropping arms Casey
Limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B masquerading as inflammatory myopathy: case report
 Jethwa et al. Pediatric Rheumatology 2013, 11:19 CASE REPORT Limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B masquerading as inflammatory myopathy: case report Hannah Jethwa 1, Thomas S Jacques 2, Roxanna Gunny
Jethwa et al. Pediatric Rheumatology 2013, 11:19 CASE REPORT Limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2B masquerading as inflammatory myopathy: case report Hannah Jethwa 1, Thomas S Jacques 2, Roxanna Gunny
Lipid changes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 658-663 B. P. HUGHES From the Muscular Dystrophy Research Laboratory, Institute of Neurology, The National Hospital, London SUMMARY Thin layer
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 658-663 B. P. HUGHES From the Muscular Dystrophy Research Laboratory, Institute of Neurology, The National Hospital, London SUMMARY Thin layer
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer
 AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
Johns Hopkins Medicine - eform A
 Johns Hopkins Medicine - eform A Use the section headings to write the eform A, inserting the appropriate material in each. If a section is not applicable, leave heading in and insert N/A. When submitting
Johns Hopkins Medicine - eform A Use the section headings to write the eform A, inserting the appropriate material in each. If a section is not applicable, leave heading in and insert N/A. When submitting
New method for the estimation of the number of
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 1195-121 New method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle 2 Duchenne, limb-girdle and facioscapulohumeral, and myotonic
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 1195-121 New method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle 2 Duchenne, limb-girdle and facioscapulohumeral, and myotonic
An Introduction to mitochondrial disease.
 9 th September 2017 An Introduction to mitochondrial disease. Dr Andy Schaefer Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Lead NHS Highly Specialised Rare Mitochondrial Disease Service and Wellcome Trust Centre
9 th September 2017 An Introduction to mitochondrial disease. Dr Andy Schaefer Consultant Neurologist and Clinical Lead NHS Highly Specialised Rare Mitochondrial Disease Service and Wellcome Trust Centre
Muscle Metabolism. Dr. Nabil Bashir
 Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy
 Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Reza Shervin Badv MD, Pediatric Neurologist Children s Medical Center Pediatrics Center of Excellence Tehran University of Medical Sciences Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies(lgmd)
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Reza Shervin Badv MD, Pediatric Neurologist Children s Medical Center Pediatrics Center of Excellence Tehran University of Medical Sciences Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies(lgmd)
The limb girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMDs)
 The limb gird muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) This factsheet is for all peop for whom a diagnosis of limb gird muscular dystrophy (LGMD) has been suggested. This is a complicated subject since there are many
The limb gird muscular dystrophies (LGMDs) This factsheet is for all peop for whom a diagnosis of limb gird muscular dystrophy (LGMD) has been suggested. This is a complicated subject since there are many
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Case 3. Your Diagnosis?
 Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
NCG Diagnostic and Management Service for McArdle Disease and Related Disorders Lead clinician: Dr Ros Quinlivan
 Queen Square Centre for Neuromuscular Diseases NCG Diagnostic and Management Service for McArdle Disease and Related Disorders Lead clinician: Dr Ros Quinlivan Described 1951 Autosomal recessive McArdle
Queen Square Centre for Neuromuscular Diseases NCG Diagnostic and Management Service for McArdle Disease and Related Disorders Lead clinician: Dr Ros Quinlivan Described 1951 Autosomal recessive McArdle
Investigation of muscle disease
 256 26ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1996;60:256-274 NEUROLOGICAL INVESTIGATIONS Investigation of muscle disease F L Mastaglia, N G Laing Various pathological processes, some genetically
256 26ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1996;60:256-274 NEUROLOGICAL INVESTIGATIONS Investigation of muscle disease F L Mastaglia, N G Laing Various pathological processes, some genetically
Diagnosis of McArdle's disease in an elderly patient: Case report and review of literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurology Volume 9 Number 1 Diagnosis of McArdle's disease in an elderly patient: Case report and review of literature R Makary, A Berger, N Talpur, S Shuja Citation R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurology Volume 9 Number 1 Diagnosis of McArdle's disease in an elderly patient: Case report and review of literature R Makary, A Berger, N Talpur, S Shuja Citation R
9/16/2009. Fast and slow twitch fibres. Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers
 Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Fast and slow twitch fibres Rat hindlimb muscle ATPase staining at different ph and NADH Muscle fibre shortening velocity lengths/second Properties of Muscle Fiber
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Fast and slow twitch fibres Rat hindlimb muscle ATPase staining at different ph and NADH Muscle fibre shortening velocity lengths/second Properties of Muscle Fiber
Bcl-2, Bcl-x, and Bax Expression by Immunohistochemistry in Inclusion Body Myositis A Study of 27 Cases
 Bcl-2, Bcl-x, and Bax Expression by Immunohistochemistry in Inclusion Body Myositis A Study of 27 Cases Richard A. Prayson, MD; Albert C. Yu, MD Context. Bcl-2, Bcl-x, and Bax are among the variety of
Bcl-2, Bcl-x, and Bax Expression by Immunohistochemistry in Inclusion Body Myositis A Study of 27 Cases Richard A. Prayson, MD; Albert C. Yu, MD Context. Bcl-2, Bcl-x, and Bax are among the variety of
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
An autoimmune perspective on neuromuscular diseases
 An autoimmune perspective on neuromuscular diseases Colin Chalk MD,CM FRCPC Montreal General Hospital McGill University Schlomchik 2001 The proportion of neuromuscular patients who have an autoimmune cause
An autoimmune perspective on neuromuscular diseases Colin Chalk MD,CM FRCPC Montreal General Hospital McGill University Schlomchik 2001 The proportion of neuromuscular patients who have an autoimmune cause
Steps in EMG analysis
 Steps in EMG analysis at rest - spontaneous activity fibs, psw, myotonia, complex rep discharges fasciculations, myokymia at slight voluntary contraction - MUP shape parameters, stability (jiggle), behaviour
Steps in EMG analysis at rest - spontaneous activity fibs, psw, myotonia, complex rep discharges fasciculations, myokymia at slight voluntary contraction - MUP shape parameters, stability (jiggle), behaviour
Lumbosacral plexus lesion Lumbosacral plexus disorders G54.1 Neuralgic amyotrophy Neuralgic amyotrophy G
 ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(1):111 115 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Value of immunohistochemical investigation in the diagnosis of neuromuscular
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, 52(1):111 115 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Value of immunohistochemical investigation in the diagnosis of neuromuscular
Early-Onset LMNA-Associated Muscular Dystrophy with Later Involvement of Contracture
 JCN Open Access pissn 1738-6586 / eissn 2005-5013 / J Clin Neurol 2017;13(4):405-410 / https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2017.13.4.405 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early-Onset LMNA-Associated Muscular Dystrophy with Later
JCN Open Access pissn 1738-6586 / eissn 2005-5013 / J Clin Neurol 2017;13(4):405-410 / https://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2017.13.4.405 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early-Onset LMNA-Associated Muscular Dystrophy with Later
Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease. Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013
 Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013 Disclosures I have no financial relationships to disclose that are relative to the content of my presentation. Basic Tenets of
Abnormal EMG Patterns in Disease Amanda C. Peltier, MD MS October 12, 2013 Disclosures I have no financial relationships to disclose that are relative to the content of my presentation. Basic Tenets of
Objectives. Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies. Abnormal Muscle Signal Intensity. Inflammatory Myositis. Polymyostis / Dermatomyositis.
 Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies Ali Naraghi Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Objectives Define the range of non-traumatic pathologies affecting
Non-Traumatic Muscle Pathologies Ali Naraghi Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging University of Toronto Objectives Define the range of non-traumatic pathologies affecting
MRI and proteomic studies in normal and
 MRI and proteomic studies in normal and pathological muscles. Isabel ILLA. Catedrática Medicina de la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. Chief Neuromuscular Diseases Unit. Hospital Santa Creu i Sant Pau.
MRI and proteomic studies in normal and pathological muscles. Isabel ILLA. Catedrática Medicina de la Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. Chief Neuromuscular Diseases Unit. Hospital Santa Creu i Sant Pau.
What can neuromuscular ultrasound do for you? 2017 Gloor Lecture
 What can neuromuscular ultrasound do for you? 2017 Gloor Lecture Dr. Nens van Alfen, neurologist/clinical neurophysiologist Radboud university medical center Nijmegen, The Netherlands Learning objectives
What can neuromuscular ultrasound do for you? 2017 Gloor Lecture Dr. Nens van Alfen, neurologist/clinical neurophysiologist Radboud university medical center Nijmegen, The Netherlands Learning objectives
BTS Guideline for Respiratory Management of Children with Neuromuscular Weakness
 BTS Guideline for Respiratory Management of Children with Neuromuscular Weakness Online Appendix 2 Search strategy: Run March 2010 and May 2011 Databases searched: MEDLINE (Ovid) MEDLINE In-Process & Other
BTS Guideline for Respiratory Management of Children with Neuromuscular Weakness Online Appendix 2 Search strategy: Run March 2010 and May 2011 Databases searched: MEDLINE (Ovid) MEDLINE In-Process & Other
Biopsy Pathology of Museie
 Biopsy Pathology of Museie BIOPSY PA THOLOGY SERIES General Editors Professor Leonard S. Gottlieb, MD, MPH Mallory Institute of Pathology, Boston, USA Professor A. Munro Neville, PhD, DSc, MD, FRC Path.
Biopsy Pathology of Museie BIOPSY PA THOLOGY SERIES General Editors Professor Leonard S. Gottlieb, MD, MPH Mallory Institute of Pathology, Boston, USA Professor A. Munro Neville, PhD, DSc, MD, FRC Path.
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
Project Initiation Document Including Criteria for a Regional Approach
 Meeting: IPG Date: 6 th March 2013 Item: 20/13 (ii) NORTH OF SCOTLAND PLANNING GROUP Project Initiation Document Including Criteria for a Regional Approach Clinical Facilitator - Neuromuscular Author:
Meeting: IPG Date: 6 th March 2013 Item: 20/13 (ii) NORTH OF SCOTLAND PLANNING GROUP Project Initiation Document Including Criteria for a Regional Approach Clinical Facilitator - Neuromuscular Author:
Muscular Dystrophy Ireland Information Day Rochestown Park Hotel, Cork Saturday 10 th October 2009
 Muscular Dystrophy Ireland Information Day Rochestown Park Hotel, Cork Saturday 10 th October 2009 In conjunction with Dr. Aisling Ryan, Consultant Neurologist in Cork University Hospital, Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular Dystrophy Ireland Information Day Rochestown Park Hotel, Cork Saturday 10 th October 2009 In conjunction with Dr. Aisling Ryan, Consultant Neurologist in Cork University Hospital, Muscular Dystrophy
Glossary of terms used in the Neuromuscular Disorders Service
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Glossary of terms used in the Neuromuscular Disorders Service This glossary has been put together to help you during
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Glossary of terms used in the Neuromuscular Disorders Service This glossary has been put together to help you during
Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Place and role of the pathology in the medicine. Structure of pathology and methods of investigation
 Place and role of the pathology in the medicine. Structure of pathology and methods of investigation Dr. Attila Zalatnai (Just for educational purposes) Without pathology there is no modern diagnostics!
Place and role of the pathology in the medicine. Structure of pathology and methods of investigation Dr. Attila Zalatnai (Just for educational purposes) Without pathology there is no modern diagnostics!
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM. Andrzej Sladkowski
 Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies
 Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies This leaflet provides a brief summary of the genetics of the muscular dystrophies. An understanding of their inheritance patterns makes it possible for families
Inheritance and the muscular dystrophies This leaflet provides a brief summary of the genetics of the muscular dystrophies. An understanding of their inheritance patterns makes it possible for families
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
PATHOLOGY OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN FIBROMYALGIA: A HISTO-IMMUNOCHEMICAL AND ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1993;32:479^83 PATHOLOGY OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN FIBROMYALGIA: A HISTO-IMMUNOCHEMICAL AND ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY A. M. DREWES*, A. ANDREASEN*, H. D. SCHR0DERt, B. HOGSAA* and
British Journal of Rheumatology 1993;32:479^83 PATHOLOGY OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN FIBROMYALGIA: A HISTO-IMMUNOCHEMICAL AND ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDY A. M. DREWES*, A. ANDREASEN*, H. D. SCHR0DERt, B. HOGSAA* and
Facts About Limb-Girdle. Muscular Dystrophies
 Facts About Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies Updated December 2009 Mandy Van Benthuysen Dear Friends: When I was 4 years old, my parents took me to a specialist to find out why I walked with an unusual
Facts About Limb-Girdle Muscular Dystrophies Updated December 2009 Mandy Van Benthuysen Dear Friends: When I was 4 years old, my parents took me to a specialist to find out why I walked with an unusual
Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis
 Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis Thomas Lloyd, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Neurology and Neuroscience Co-director, Johns Hopkins Myositis Center Sporadic IBM (IBM) Age at onset usually > 50 Prevalence
Genetics of Inclusion Body Myositis Thomas Lloyd, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Neurology and Neuroscience Co-director, Johns Hopkins Myositis Center Sporadic IBM (IBM) Age at onset usually > 50 Prevalence
Biochemistry #02. The biochemical basis of skeletal muscle and bone disorders Dr. Nabil Bashir Bara Sami. 0 P a g e
 ]Type text[ ]Type text[ ]Type text[ Biochemistry #02 The biochemical basis of skeletal muscle and bone disorders Dr. Nabil Bashir Bara Sami 0 P a g e Greetings everyone, ladies and gentlemen The biochemical
]Type text[ ]Type text[ ]Type text[ Biochemistry #02 The biochemical basis of skeletal muscle and bone disorders Dr. Nabil Bashir Bara Sami 0 P a g e Greetings everyone, ladies and gentlemen The biochemical
External and Internal Influences on Muscle Pathology
 External and Internal Influences on Muscle Pathology Paul E. McKeever, MD, PhD; Sandra Camelo-Piragua, MD; James Dowling, MD, PhD Three cases of different types of neuromuscular diseases demonstrate different
External and Internal Influences on Muscle Pathology Paul E. McKeever, MD, PhD; Sandra Camelo-Piragua, MD; James Dowling, MD, PhD Three cases of different types of neuromuscular diseases demonstrate different
The Muscular System III: Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training PSK 4U NGDHS MR. S. KELLY
 The Muscular System III: Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training PSK 4U NGDHS MR. S. KELLY Muscle Hypertrophy Defined: growth of component cells of skeletal muscle which leads to an overall increase in skeletal
The Muscular System III: Neuromuscular Adaptations to Training PSK 4U NGDHS MR. S. KELLY Muscle Hypertrophy Defined: growth of component cells of skeletal muscle which leads to an overall increase in skeletal
REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST BE FILLED OUT COMPLETELY FOR SAMPLE TO BE PROCESSED. Last First Last First
 #: DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY COLUMBIA COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS Room 4-420 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032 Telephone #: 212-305-3947 Fax#: 212-305-3986 REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST
#: DEPARTMENT OF NEUROLOGY COLUMBIA COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS & SURGEONS Room 4-420 630 West 168th Street, New York, NY 10032 Telephone #: 212-305-3947 Fax#: 212-305-3986 REQUISITION FORM NOTE: ALL FORMS MUST
Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository
 Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository Steven A. Moore, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Iowa Department of Pathology and Iowa Wellstone Muscular Dystrophy Cooperative Research Center
Iowa Wellstone Center Muscle Tissue and Cell Culture Repository Steven A. Moore, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Iowa Department of Pathology and Iowa Wellstone Muscular Dystrophy Cooperative Research Center
Case Studies in Peripheral Neurophysiology. Elliot L. Dimberg Mayo Clinic Florida 2015 American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Annual Meeting
 Case Studies in Peripheral Neurophysiology Elliot L. Dimberg Mayo Clinic Florida 2015 American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Annual Meeting Disclosures None Goals and Objectives To provide a concise,
Case Studies in Peripheral Neurophysiology Elliot L. Dimberg Mayo Clinic Florida 2015 American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Annual Meeting Disclosures None Goals and Objectives To provide a concise,
Myopathy in Post-Radiation Cervico-Scapular Syndrome
 http://escholarship.umassmed.edu/neurol_bull Myopathy in Post-Radiation Cervico-Scapular Syndrome Anna Kogan, Galyna Pushchinska, and Roberta Seidman Department of Neurology Stony Brook University Hospital
http://escholarship.umassmed.edu/neurol_bull Myopathy in Post-Radiation Cervico-Scapular Syndrome Anna Kogan, Galyna Pushchinska, and Roberta Seidman Department of Neurology Stony Brook University Hospital
Correlation of Electromyogram and Muscle Biopsy in Myopathy of Young Age
 780 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation of and Muscle Biopsy in of Young Age Jihoon Chang, MD, Yoon Ghil Park, MD, PhD, Young-chul Choi, MD, PhD, Jung Hwa Choi, MD, Jae Ho Moon, MD ABSTRACT. Chang JH, Park YG,
780 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation of and Muscle Biopsy in of Young Age Jihoon Chang, MD, Yoon Ghil Park, MD, PhD, Young-chul Choi, MD, PhD, Jung Hwa Choi, MD, Jae Ho Moon, MD ABSTRACT. Chang JH, Park YG,
Myopathies. Team Members: Aroob Alhuthail, Moayed Ahmad, Rema Albarrak, Ghadah Almazrou, Noura AlShabib
 Myopathies Objectives: Understanding normal muscle histology and physiology. Understanding Myopathy definition. Understanding Approach to myopathy. Knowing the most common hereditary myopathies. Knowing
Myopathies Objectives: Understanding normal muscle histology and physiology. Understanding Myopathy definition. Understanding Approach to myopathy. Knowing the most common hereditary myopathies. Knowing
Granulomatous Myositis Clinicopathologic Study of 12 Cases
 Anatomic Pathology / GRANULOMATOUS MYOSITIS Granulomatous Myositis Clinicopathologic Study of 12 Cases Richard A. Pray son, MD Key Words: Granulomas; Granulomatous myositis; Myositis; Granulomatous inflammation
Anatomic Pathology / GRANULOMATOUS MYOSITIS Granulomatous Myositis Clinicopathologic Study of 12 Cases Richard A. Pray son, MD Key Words: Granulomas; Granulomatous myositis; Myositis; Granulomatous inflammation
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function
 Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
The Floppy Baby. Clare Betteridge
 The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
The Floppy Baby Clare Betteridge The floppy baby Identification Evaluation Investigation Diagnosis Examples What is a floppy baby? Elbows and knees loosely extended. Head control is usually poor or absent.
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis
 Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis Marianne de Visser, Dept. of Neurology, Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs),
Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies excluding inclusion body myositis Marianne de Visser, Dept. of Neurology, Academic Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIMs),
The relative frequency of common neuromuscular diagnoses in a reference center
 https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x20170151 ARTICLE The relative frequency of common neuromuscular diagnoses in a reference center Frequência relativa de diagnósticos neuromusculares comuns em um serviço
https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-282x20170151 ARTICLE The relative frequency of common neuromuscular diagnoses in a reference center Frequência relativa de diagnósticos neuromusculares comuns em um serviço
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA AGING, July 2014, Vol. 6 No. 7
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure S1. Muscle mass changes in different anatomical regions with age. (A) The TA and gastrocnemius muscle showed a significant loss of weight in aged mice (24 month old) compared to
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Figure S1. Muscle mass changes in different anatomical regions with age. (A) The TA and gastrocnemius muscle showed a significant loss of weight in aged mice (24 month old) compared to
TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart
 TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart Below you find a list of the information that is asked in the CTSR of all registered neuromuscular disease sites. For more information please visit
TREAT-NMD Care and Trial Sites Registry Information Chart Below you find a list of the information that is asked in the CTSR of all registered neuromuscular disease sites. For more information please visit
Histopathology of Wooden Breast
 Histopathology of Wooden Breast Canadian Poultry and Egg Processors Council Aviagen Frederic J. Hoerr, DVM, PhD June 10, 2016 Halifax, Nova Scotia FJ Hoerr 1 Normal Veterinary Diagnostic Pathology, LLC
Histopathology of Wooden Breast Canadian Poultry and Egg Processors Council Aviagen Frederic J. Hoerr, DVM, PhD June 10, 2016 Halifax, Nova Scotia FJ Hoerr 1 Normal Veterinary Diagnostic Pathology, LLC
Original Article Pathological findings in sporadic inclusion body myositis and GNE myopathy
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(5):2907-2911 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0064777 Original Article Pathological findings in sporadic inclusion body myositis and GNE myopathy Yutong Zhang 1, Chuanqiang
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(5):2907-2911 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0064777 Original Article Pathological findings in sporadic inclusion body myositis and GNE myopathy Yutong Zhang 1, Chuanqiang
MUSCLE DISEASE ANTIBODIES NOVOCASTRA ADVANCING MUSCLE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND RESEARCH RESULTS YOU CAN RELY ON
 MUSCLE DISEASE ANTIBODIES ADVANCING MUSCLE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND RESEARCH NOVOCASTRA RESULTS YOU CAN RELY ON Novocastra Muscle Disease Antibodies The Novocastra muscle disease portfolio comprises
MUSCLE DISEASE ANTIBODIES ADVANCING MUSCLE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND RESEARCH NOVOCASTRA RESULTS YOU CAN RELY ON Novocastra Muscle Disease Antibodies The Novocastra muscle disease portfolio comprises
