Endocrine Control. Chapter 35
|
|
|
- Silvester Warner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endocrine Control Chapter 35
2 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects
3 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate Endocrine System Animal cells communicate with one another by way of a variety of short-range and long-range chemical signals Animal cells communicate with adjacent cells through gap junctions and by releasing molecules that bind to receptors in or on other cells
4 Shot-Distance Signaling Neurotransmitters secreted by neurons diffuse across the synaptic cleft to the target cell Local signaling molecules, such as prostaglandins released by injured cells, affect only neighboring cells
5 Long-Distance Signaling Animal hormones secreted into interstitial fluid enter capillaries, are distributed throughout the body, and have wide-reaching effects Pheromones diffuse through water or air and bind to target cells in other individuals (help integrate social behavior)
6 Overview of the Endocrine System Hormones Internal secretions carried by the blood that influence the activities of specific body organs Endocrine system Glands and other hormone-secreting sources
7 Nervous-Endocrine Interactions Nervous and endocrine systems interact Both respond to the hypothalamus, a command center in the forebrain Most organs receive and respond to both nervous signals and hormones
8 The Human Endocrine System
9 Hypothalamus Makes and secretes releasers and inhibitors, hormones that act in the anterior lobe of the pituitary. Pituitary gland Anterior lobe makes and secretes ACTH, TSH, LH, FSH (stimulate secre- tion by other endocrine glands), pro- lactin (acts on mammary glands) and growth hormone (affects overall growth). Adrenal glands (one pair) Adrenal cortex makes and secretes cortisol (affects metabolism, immune response), aldosterone (acts in kid- neys), small amount of sex hormones. Ovaries (one pair of female gonads) Make and secrete progesterone and estrogens (affect primary sex organs and influence secondary sexual traits). Testes (one pair of male gonads) Make and secrete testosterone and other androgens (affect primary sex organs and influence secondary sexual traits). closer view of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland hypothalamus pituitary gland Pineal gland Makes and secretes melatonin (affects sleep/wake cycles, onset of puberty). Thyroid gland Makes and secretes thyroid hormone (metabolic and developmental effects) and calcitonin (lowers blood calcium). Parathyroid glands (four) Make and secrete parathyroid hormone (raises blood calcium level). Thymus gland Makes and secretes thymosins (act in maturation of T cells, a type of white blood cell). Pancreas Makes and secretes insulin (lowers blood glucose level) and glucagon (raises blood glucose level). Fig. 35-2, p. 599
10 Fig , p. 615
11 35.2 The Nature of Hormone Action Cell communication involves three steps For a hormone to have an effect, it must bind to protein receptors on or inside a target cell
12 Animation: Major human endocrine glands
13 Categories and Examples of Hormones
14 Intracellular Receptors Steroid hormones are made from cholesterol and can diffuse across the plasma membrane Most steroid hormones form a hormone-receptor complex that binds to a promoter inside the nucleus and alters the expression of specific genes
15 Receptors at the Plasma Membrane Large amine, peptide and protein hormones bind to a receptor at the plasma membrane Binding triggers formation of a second messenger (molecule that relays signal into cell) Enzyme converts ATP to camp camp activates a cascading series of reactions
16 Hormone Actions
17 Fig. 35-3a, p. 601
18 Step 2 Being lipid soluble, the hormone easily diffuses across the cell s plasma membrane. Step 1 A steroid hormone molecule is moved from blood into interstitial fluid bathing a target cell. Step 3 The hormone diffuses through the cytoplasm and nuclear envelope. It binds with its receptor in the nucleus. gene product Step 5 The resulting mrna moves into the cytoplasm and is transcribed into a protein. hormone receptor complex receptor Step 4 The hormone receptor complex triggers transcription of a specific gene. Fig. 35-3a, p. 601
19 Fig. 35-3b, p. 601
20 Step 1 A peptide hormone molecule, glucagon, diffuses from blood into interstitial fluid bathing the plasma membrane of a liver cell. unoccupied glucagon receptor at target cell s plasma membrane ATP Step 2 Glucagon binds with a receptor. Binding activates an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cyclic AMP from ATP inside the cell. cyclic AMP + P i Step 3 Cyclic AMP activates another enzyme in the cell. Step 4 The enzyme activated by cyclic AMP activates another enzyme, which in Step 5 The turn activates another kind that enzyme activated catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen to its also inhibits by cyclic AMP glucose monomers. glycoge synthesis Fig. 35-3b, p. 601
21 Step 1 A steroid hormone molecule is moved from blood into interstitial fluid bathing a target cell. Step 1 A peptide hormone molecule, glucagon, diffuses from blood into interstitial fluid bathing the plasma membrane of a liver cell. Step 2 Being lipid soluble, the hormone easily diffuses across the cell s plasma membrane. Step 3 The hormone diffuses through the cytoplasm and nuclear envelope. It binds with its receptor in the nucleus. ATP unoccupied glucagon receptor at target cell s plasma membrane cyclic AMP + P i Step 5 The resulting mrna moves into the cytoplasm and is transcribed into a protein. gene product hormone receptor complex receptor Step 4 The hormone receptor complex triggers transcription of a specific gene. Step 2 Glucagon binds with a receptor. Binding activates an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cyclic AMP from ATP inside the cell. Step 4 The enzyme activated by cyclic AMP activates another enzyme, which in turn activates another kind that catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen to its glucose monomers. Step 3 Cyclic AMP activates another enzyme in the cell. Step 5 The enzyme activated by cyclic AMP also inhibits glycoge synthesis Stepped Art Fig. 35-3, p. 601
22 Animation: Mechanism of a steroid hormone
23 Animation: Mechanism of a peptide hormone
24 Hypothalamus GnRH Anterior Pituitary FSH, LH Gonads Sex hormones Stepped Art Fig , p. 612
25 Receptor Function and Diversity Only cells with appropriate and functional receptor proteins can respond to a hormone Gene mutations that alter receptor structure can prevent or change cell response to a hormone Examples: Androgen insensitivity syndrome, variations in ADH receptors
26 Key Concepts Signaling Mechanisms Hormones and other signaling molecules function in communication among body cells A hormone travels through the blood and acts on any cell that has receptors for it The receptor may be at a target cell s surface or inside the cell
27 35.3 The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and pituitary gland deep inside the brain interact as a central command center
28 hypothalamus anterior lobe of pituitary posterior lobe of pituitary Fig. 35-4, p. 602
29 Hypothalamus Hypothalamus Main center for control of internal environment Lies deep inside the forebrain and interacts, structurally and functionally, with the pituitary gland
30 Pituitary Gland Pituitary gland Posterior lobe secretes hormones made in the hypothalamus Anterior lobe synthesizes its own hormones The hypothalamus signals the pituitary by way of secretory neurons that make hormones
31 Posterior Pituitary Function Some secretory neurons of the hypothalamus make hormones that move through axons into the posterior pituitary, which releases them Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Oxytocin (OT)
32 Interactions of Hypothalamus and Posterior Pituitary
33 A Cell bodies of secretory neurons in hypothalamus synthesize ADH or oxytocin. B The ADH or oxytocin moves downward inside the axons of the secretory neurons and accumulates in the axon terminals. C Action potentials trigger the release of these hormones, which enter blood capillaries in the posterior lobe of the pituitary. D Blood vessels carry hormones to the general circulation. Fig. 35-5, p. 603
34 A Cell bodies of secretory neurons in hypothalamus synthesize ADH or oxytocin. B The ADH or oxytocin moves downward inside the axons of the secretory neurons and accumulates in the axon terminals. C Action potentials trigger the release of these hormones, which enter blood capillaries in the posterior lobe of the pituitary. D Blood vessels carry hormones to the general circulation. Stepped Art Fig. 35-5, p. 603
35 Animation: Posterior pituitary function
36 Anterior Pituitary Function Other hypothalamus neurons produce releasers and inhibitors carried by blood that regulate secretion of anterior pituitary hormones Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Prolactin (PRL) Growth hormone (GH)
37 Interactions of Hypothalamus and Anterior Pituitary
38 A Cell bodies of secretory neurons in hypothalamus synthesize inhibitors or releasers that are secreted into the stalk that connects to the pituitary. D When encouraged by a releaser, anterior pituitary cells secrete hormone that enters blood vessels that lead into the general circulation. B The inhibitors or releasers picked up by capillaries in the stalk get carried in blood to the anterior pituitary. C The inhibitors or releasers diffuse out of capillaries in the anterior pituitary and bind to their target cells. Fig. 35-6, p. 603
39 A Cell bodies of secretory neurons in hypothalamus synthesize inhibitors or releasers that are secreted into the stalk that connects to the pituitary. D When encouraged by a releaser, anterior pituitary cells secrete hormone that enters blood vessels that lead into the general circulation. B The inhibitors or releasers picked up by capillaries in the stalk get carried in blood to the anterior pituitary. C The inhibitors or releasers diffuse out of capillaries in the anterior pituitary and bind to their target cells. Stepped Art Fig. 35-6, p. 603
40 Animation: Anterior pituitary function
41 Primary Actions of Pituitary Hormones
42 Feedback Controls of Hormone Secretion Positive feedback mechanisms Response increases the intensity of the stimulus Example: Oxytocin and childbirth contractions Negative feedback mechanisms Response decreases the stimulus
43 35.4 Growth Hormone Function and Disorders Excessive growth hormone (GH) causes faster than normal bone growth Occurrence in childhood results in gigantism Occurrence in adulthood results in acromegaly A deficiency of GH during childhood can cause dwarfism
44 Examples of Disrupted GH Function
45 Key Concepts A Master Integrating Center In vertebrates, the hypothalamus and pituitary gland are connected structurally and functionally Together, they coordinate activities of many other glands Pituitary hormones affect growth, reproductive functions, and composition of extracellular fluid
46 35.5 Sources and Effects of Other Vertebrate Hormones In addition to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland, endocrine glands and endocrine cells secrete hormones The gut, kidneys, and heart are among the organs that are not glands, but include hormonesecreting cells
47 Sources and Actions of Vertebrate Hormones
48 Multiple Hormone Receptors Most cells have receptors for multiple hormones, and the effect of one hormone can be enhanced or opposed by another one Example: Skeletal muscle hormone receptors Glucagon, insulin, cortisol, epinephrine, estrogen testosterone, growth hormone, somatostatin, thyroid hormone and others
49 35.6 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands The thyroid regulates metabolic rate, and the adjacent parathyroids regulate calcium levels
50 thyroid cartilage (Adam s apple) Thyroid Gland trachea (windpipe) anterior Fig. 35-8a, p. 606
51 epiglottis pharynx Thyroid Gland Parathyroid Glands posterior Fig. 35-8b, p. 606
52 The Thyroid Gland Thyroid gland Located at the base of the neck; secretes iodinecontaining thyroid hormones and calcitonin Regulated by a negative feedback loop Hypothyroidism Low levels of thyroid hormone, caused by iodine deficiency or Graves disease, causes goiter
53 Negative Feedback Control of Thyroid
54 Blood level of STIMULUS + Hypothalamus thyroid hormone falls below a set point. RESPONSE TRH Anterior Pituitary TSH Thyroid Gland Rise of thyroid hormone level in blood inhibits the secretion of TRH and TSH. Thyroid hormone is secreted. Fig. 35-9, p. 606
55 Blood level of STIMULUS + Hypothalamus thyroid hormone falls below a set point. RESPONSE TRH Anterior Pituitary TSH Thyroid Gland Rise of thyroid hormone level in blood inhibits the secretion of TRH and TSH. Thyroid hormone is secreted. Stepped Art Fig. 35-9, p. 606
56 The Parathyroid Glands Parathyroid glands Release parathyroid hormone (PTH) in response to low blood calcium levels Targets bone cells and kidney cells Stimulates conversion of vitamin D to calcitriol
57 Thyroid and Parathyroid Diseases
58 35.7 Twisted Tadpoles Impaired thyroid function in frogs: An example of hormone-disruptor pollution in the environment Includes pesticides, perchlorates
59 35.8 Pancreatic Hormones Pancreas Exocrine cells secrete digestive enzymes Endocrine cells clustered in pancreatic islets
60 stomach pancreas small intestine Fig (top), p. 608
61 Insulin and Glucagon Two pancreatic hormones with opposing effects work together to regulate blood sugar levels Insulin Increases cell uptake and storage of glucose Secreted in response to high blood glucose Glucagon Increases breakdown of glycogen to glucose Secreted in response to low blood glucose
62 Responses to Changes in Blood Glucose
63 A Stimulus Increase in blood glucose F Stimulus Decrease in blood glucose PANCREAS PANCREAS B alpha cells C beta cells G alpha cells H beta cells glucagon insulin glucagon insulin LIVER MUSCLE FAT CELLS LIVER D Body cells, especially those muscle and adipose tissue, take up and use more glucose. Cells in skeletal muscle and liver store glucose in the form of glycogen. E Response Decrease in blood glucose I Cells in liver break down glycogen faster. The released glucose monomers enter blood. J Response Increase in blood glucose Fig (right), p. 608
64 Animation: Hormones and glucose metabolism
65 35.9 Blood Sugar Disorders Glucose is the main energy source for brain cells and the only energy source for red blood cells Having too much or too little glucose in blood causes problems throughout the body
66 Diabetes Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder in which cells do not take up glucose properly Results in complications throughout the body Type 1 diabetes (juvenile-onset diabetes) Autoimmune disease that destroys insulinproducing cells; requires insulin injections Type 2 diabetes (adult onset diabetes) Target cells do not respond to insulin
67 Some Complications of Diabetes
68 Controlling Diabetes
69 Hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia Blood glucose levels low enough to disrupt normal body functions Caused by excess insulin production or overdose of injected insulin in diabetics Can cause dizziness, confusion, and shock
70 35.10 The Adrenal Glands Adrenal glands Sit atop kidneys Have two parts (adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla) that are controlled by different mechanisms and release different hormones
71 Hormonal Control of Adrenal Cortex The adrenal cortex secretes steroid hormones Small amounts of sex hormones Aldosterone controls sodium and water reabsorption in the kidneys Cortisol affects metabolism and the stress response; controlled by negative feedback
72 Cortisol: Negative Feedback Control
73 STIMULUS + A Blood level of cortisol falls below a set point. Hypothalamus B CRH RESPONSE adrenal cortex adrenal medulla Anterior Pituitary ACTH Adrenal Cortex D Hypothalamus and pituitary detect rise in blood level of cortisol and slow its secretion. kidney C Cortisol is secreted and has the following effects: Cellular uptake of glucose from blood slows in many tissues, especially muscles (but not in the brain). Protein breakdown accelerates, especially in muscles. Some of the amino acids freed by this process get converted to glucose. Fats in adipose tissue are degraded to fatty acids and enter blood as an alternative energy source, indirectly conserving glucose for the brain. Fig , p. 610
74 STIMULUS + A Blood level of cortisol falls below a set point. Hypothalamus B CRH RESPONSE adrenal cortex adrenal medulla Anterior Pituitary ACTH Adrenal Cortex D Hypothalamus and pituitary detect rise in blood level of cortisol and slow its secretion. C Cortisol is secreted and has the following effects: Cellular uptake of glucose from blood slows in many tissues, especially muscles (but not in the brain). kidney Protein breakdown accelerates, especially in muscles. Some of the amino acids freed by this process get converted to glucose. Fats in adipose tissue are degraded to fatty acids and enter blood as an alternative energy source, indirectly conserving glucose for the brain. Stepped Art Fig , p. 610
75 Animation: Control of cortisol secretion
76 Nervous Control of the Adrenal Medulla The adrenal medulla contains specialized nerves of the sympathetic division that release epinephrine and norepinephrine, which stimulate the fight-flight response
77 35.11 Too Much or Too Little Cortisol Cortisol has many functions Induces liver cells to break down glycogen Suppresses uptake of glucose by other cells Causes adipose cells to degrade fats, and skeletal muscles to degrade proteins Suppresses immune responses Suppresses inflammatory response
78 Chronic Stress and Elevated Cortisol Chronic stress can produce high cortisol levels Impairs growth, healing, sexual function, memory High blood pressure and blood sugar
79 Low Cortisol Level Hypocortisolism (Addison s disease) results from adrenal gland damage Blood pressure and blood sugar fall Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, depression, weight loss, darkening of skin
80 35.12 Other Endocrine Glands Outputs from gonads, pineal gland, and thymus all change as an individual enters puberty (a stage of development when reproductive organs and structures mature)
81 The Gonads Gonads are the primary reproductive organs that produce gametes (eggs and sperm) Testes produce testosterone Ovaries produce estrogens and progesterone
82 testis (where sperm originate) ovary (where eggs develop) Fig , p. 612
83 Control of Sex Hormone Secretion The hypothalamus and anterior pituitary control secretion of sex hormones by gonads
84 Hypothalamus GnRH Anterior Pituitary FSH, LH Gonads Sex hormones Fig , p. 612
85 Pineal Gland and Thymus Pineal gland secretes melatonin Part of an internal biological clock Secretion declines when the retina detects light Thymus secretes thymosins Helps infection-fighting T cells mature
86 Key Concepts Other Hormone Sources Negative feedback loops to the hypothalamus and pituitary control secretions from many glands Signals from the nervous system and internal solute concentrations also influence hormone secretion
87 35.13 A Comparative Look at a Few Invertebrates Genes for hormone receptors and enzymes involved in hormone synthesis evolved over time We can trace the evolutionary roots of the vertebrate endocrine system in invertebrates
88 Evolution of Hormone Diversity Cnidarians (e.g. sea anemones) and mollusks (e.g. sea slugs) have receptors that resemble those that bind vertebrate hormones
89 Hormones and Molting Some hormones are unique to invertebrates Example: ecdysone, a steroid hormone that controls molting in arthropods Hormone-secreting neurons in the brain respond to signals such as light and temperature Mechanisms differ in crustaceans and insects
90 Molting: Hormonal Control in Crustaceans
91 Absence of suitable stimuli Presence of suitable stimuli X organ releases molt-inhibiting hormone (MIH) Signals from brain inhibit release of MIH MIH prevents Y organ from making ecdysone Y organ makes and releases ecdysone No molting Molting Fig , p. 613
92 35.13 Key Concepts Invertebrate Hormones Hormones control molting and other events in invertebrate life cycles Vertebrate hormones and receptors for them first evolved in ancestral lineages of invertebrates
93 Animation: Hormones and target cell receptors
94 Animation: Hypothalamus and pituitary
95 Animation: Parathyroid hormone action
96 Video: Hormones in the balance
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45. Intercellular communication. Paracrine and Autocrine Signaling. Signaling by local regulators 11/26/2017
 Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Chapter 26 Hormones and the
 Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Page 1. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
BIOLOGY. CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition. Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor. CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation
 BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Pages
 NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp and Janette Lewis Copyright
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp and Janette Lewis Copyright
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Overview: The Body s Long-Distance Regulators Animal hormones are chemical signals that are secreted into the
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Eighth Edition Overview: The Body s Long-Distance Regulators Animal hormones are chemical signals that are secreted into the
Homeostasis Through Chemistry. The Endocrine System Topic 6.6
 Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
8/26/13. Announcements
 Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
CHAPTER 41: Animal Hormones
 CHAPTER 41: Animal Hormones 1. List a few similarities and differences comparing: a. endocrine system b. nervous system 2. What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands? 3. What is the difference
CHAPTER 41: Animal Hormones 1. List a few similarities and differences comparing: a. endocrine system b. nervous system 2. What is the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands? 3. What is the difference
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN
 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 13 Notes OBJECTIVES HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN 1. Define hormone. 2. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. 3. Explain what makes a cell
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 13 Notes OBJECTIVES HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN 1. Define hormone. 2. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. 3. Explain what makes a cell
The Endocrine System. By Carl Antiado, Marco Habana, Cameron Loewen, and Nikki Ooka
 The Endocrine System By Carl Antiado, Marco Habana, Cameron Loewen, and Nikki Ooka Standards 2.C.2 : Organisms respond to changes in their external environments. 4.A.4: Organisms exhibit complex properties
The Endocrine System By Carl Antiado, Marco Habana, Cameron Loewen, and Nikki Ooka Standards 2.C.2 : Organisms respond to changes in their external environments. 4.A.4: Organisms exhibit complex properties
Homeostasis. Endocrine System Nervous System
 Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING
 HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING TYPES OF CELL JUNCTIONS CHEMICAL SIGNALS AND MODES OF ACTION Endocrine system produces chemical messages = hormones that are transported from endocrine gland to target cell
HORMONES AND CELL SIGNALLING TYPES OF CELL JUNCTIONS CHEMICAL SIGNALS AND MODES OF ACTION Endocrine system produces chemical messages = hormones that are transported from endocrine gland to target cell
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Endocrine system. Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones
 Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system
 Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
Target cells only respond to specific signals Different target cells have different kinds of receptors in their membranes or cytoplasm
 1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Hormones and the Endocrine System
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System
Hormones. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
 Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
The Players. Liver Thyroid Adrenals Pancreas Reproductive System Pituitary Gut Bacteria
 The Players Part I Quick Review Understanding some of the key systems and their relationship to hormones is the best place to start It will help with some of the hormone interconnections Key to understanding
The Players Part I Quick Review Understanding some of the key systems and their relationship to hormones is the best place to start It will help with some of the hormone interconnections Key to understanding
Endocrine System. A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body.
 Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1. Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
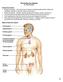 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Lesson 1. Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms
 Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
