Cholangitis/ Cholangiohepatitis Syndrome (Inflammation of the Bile Duct System and Liver) Basics
|
|
|
- Warren O’Connor’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Glendale Animal Hospital Cholangitis/ Cholangiohepatitis Syndrome (Inflammation of the Bile Duct System and Liver) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid substance involved in digestion of fats); bile ducts begin within the liver itself as tiny channels to transport bile the ducts join together to form larger bile ducts and finally enter the extrahepatic or common bile duct, which empties into the upper small intestine; the system of bile ducts is known as the biliary tree The gallbladder is the storage unit for bile; bile is stored until it is needed for fat digestion Cholangitis is inflammation of the bile duct or the biliary tree Cholangiohepatitis is inflammation of biliary structures and surrounding liver tissue Cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome occurs more commonly in cats; it is classified as suppurative or nonsuppurative (lymphoplasmacytic, lymphocytic), granulomatous, or lymphoproliferative (transition to lymphoma) based on microscopic examination of biopsy samples Suppurative refers to the presence of pus in the affected tissue; nonsuppurative refers to an inflammatory process that is not characterized by the presence of pus in cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome, the inflammatory process is characterized by the presence of lymphocytes and plasma cells (so-called lymphoplasmacytic disease) or lymphocytes (so-called lymphocytic disease); lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that are formed in lymphatic tissues throughout the body lymphocytes are involved in the immune process; plasma cells are specialized white blood cells; plasma cells are lymphocytes that have been altered to produce immunoglobulin, an immune protein or antibody necessary for fighting disease
2 Granulomatous refers to nodular, inflammatory lesions; lymphoproliferative refers to conditions in which an excessive number of lymphocytes are produced; lymphoma is a type of cancer that develops from lymphoid tissue, including lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell formed in lymphatic tissues throughout the body SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET Species Cats (common) Dogs (uncommon) Breed Predilections Cats possibly Himalayan, Persian, and Siamese Mean Age and Range Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome range, years of age; mostly young to middle-aged cats Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome range, 2 17 years of age; mostly middle-aged cats Predominant Sex Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome male cats more likely to be affected than female cats Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome none SIGNS/OBSERVED CHANGES IN THE PET Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome most severe clinical illness characterized by acute abdomen (sudden onset of severe abdominal pain), fever, often less than 5 days in duration; associated with blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (known as extrahepatic bile duct obstruction ) Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome sudden (acute) illness; fever; lack of appetite (known as anorexia ); vomiting; painful abdomen; may have yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (known as jaundice or icterus ); dehydration; collapse; generalized bacterial infection (known as sepsis ); shock Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome illness of greater than 3 weeks in duration (may have signs of illness for months to years); cyclic illness; long-term (chronic) vague signs: sluggishness (lethargy), vomiting, lack of appetite (anorexia), and weight loss; few physical abnormalities other than enlarged liver (known as hepatomegaly ); thickened intestines with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); variable yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (jaundice or icterus); rare fluid buildup in the abdomen (known as abdominal effusion or ascites ) Decreased number of bile ducts (known as ductopenia ) associated with nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome in cats increased appetite (known as polyphagia ) due to reduced bile flow with poor digestion of fats and presence of large amounts of fat in the stool, due to the inability to digest the fat (known as steatorrhea ) leading to decreased levels of fat-soluble substances (such as vitamin K1, essential fatty acids, vitamin E); unkempt coat, variable hair loss on the sides of the chest; variable pale or grayish coloration to the stools (known as acholic feces ), due to the lack of bile pigments that cause the normal brown color of bowel movements CAUSES Suppurative Cholangitis/Cholangiohepatitis Syndrome Bacterial infection most common in cats: E. coli, Enterobacter, Enterococcus, β-hemolytic Streptococcus, Klebsiella, Actinomyces, Clostridia, and Bacteroides; also rarely associated with toxoplasmosis; dogs: intestinal bacterial opportunists (bacteria that usually do not cause disease, but are able to cause disease because the pet's body and/or immune system has been weakened by some other disease process); rare cases with Campylobacter, Salmonella, and Leptospira Condition may be seen following blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) and diseases in which flow of bile is decreased or stopped (known as cholestasis ) Nonsuppurative Cholangitis/Cholangiohepatitis Syndrome Co-existent disorders inflammation of the gallbladder (known as cholecystitis ); presence of hard, solid material in the bile duct or gallbladder (known as cholelithiasis ); inflammation of the pancreas (known as pancreatitis ); blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction);
3 inflammatory bowel disease; long-term (chronic) inflammation of the tissue spaces in the kidneys (known as chronic interstitial nephritis ) in cats RISK FACTORS Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction); diseases in which flow of bile is decreased or stopped (cholestasis); infections elsewhere in the body Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome in cats inflammatory bowel disease; inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis); blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction); possibly long-term (chronic) inflammation of the tissue spaces in the kidneys (chronic interstitial nephritis) Treatment HEALTH CARE Inpatient Management Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome with sudden (acute) illness characterized by fever, painful abdomen, abnormal white blood cell count hydration support; antibiotics; if the pet has blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) or inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis): administer antibiotics before surgery; continue antibiotics for at least 4 8 weeks; treat with medications (such as ursodeoxycholic acid, SAMe) to improve the secretion of bile until liver enzyme values normalize on bloodwork (serum biochemistry profile) Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome in cats with clinical signs of disease fluid therapy, as necessary; diagnostic evaluations; liver biopsy (administer vitamin K1 before liver biopsy) Both forms of cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome in cats may need blood transfusion following surgery or biopsy Supplement fluids with B vitamins, potassium chloride, and potassium phosphate, as needed; avoid dextrose supplements Outpatient Management Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome after sudden (acute) crisis has been managed Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome after resolution of sudden (acute) crisis, provide lifelong treatment to alter the immune system (known as immune-system modulation ) as well as antioxidant and liver-protective therapy ACTIVITY Restricted while the pet has clinical signs of disease DIET Nutritional support to avoid hepatic lipidosis, feed a balanced high-protein, high-calorie feline diet; supplement water-soluble vitamins (such as vitamin B); hepatic lipidosis is a disease in which fats and lipids (compounds that contain fats or oils) accumulate in the liver as a possible complication of lack of appetite (anorexia) Antigen-restricted diet with co-existent inflammatory bowel disease Fat-restricted diet, if the pet has severe decrease in bile ducts (ductopenia), abnormal absorption of fat (known as fat malabsorption ), or long-term (chronic) inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis) causing abnormal digestion of food (known as maldigestion ) May require feeding tubes; rarely requires feeding through intravenous fluids (known as parenteral nutrition ) SURGERY Surgical removal of the gallbladder (known as cholecystectomy ) if the pet has inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) Surgical procedure to produce a new connection between the biliary tree and the small intestines (known as cholecystoenterostomy ) may be needed in pets with blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction)
4 Surgical removal of stones in the gallbladder (stones known as choleliths ) Medications Medications presented in this section are intended to provide general information about possible treatment. The treatment for a particular condition may evolve as medical advances are made; therefore, the medications should not be considered as all inclusive ANTIBIOTICS FOR SUPPURATIVE CHOLANGITIS/CHOLANGIOHEPATITIS SYNDROME Antibiotics that kill bacteria (known as bactericidal antibiotics ) against intestinal bacterial opportunists (bacteria that usually do not cause disease, but are able to cause disease because the pet's body and/or immune system has been weakened by some other disease process); amoxicillin-clavulanic acid (Clavamox) or enrofloxacin combined with metronidazole Resistant enterococci vancomycin; enterococci are bacteria normally found in bowel movement of animals and people that occasionally cause disease Modify antibiotics, based on bacterial culture and sensitivity reports MEDICATIONS TO ALTER THE IMMUNE RESPONSE (IMMUNOMODULATION) FOR NONSUPPURATIVE CHOLANGITIS/CHOLANGIOHEPATITIS SYNDROME Steroids prednisolone; long-term (chronic) therapy usually needed Metronidazole in combination with prednisolone, especially if the pet has co-existent inflammatory bowel disease Cats with confirmed decreased number of bile ducts (ductopenia) require more aggressive treatment; clinical experience suggests combination of prednisolone, metronidazole with pulsed methotrexate (a chemotherapeutic drug); provide folate (folinic acid); may use chlorambucil instead of methotrexate Some cats require chemotherapy protocols developed for intestinal lymphoma ( lymphoma is a type of cancer that develops from lymphoid tissue, including lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell formed in lymphatic tissues throughout the body) ANTIOXIDANTS Vitamin E (tocopherol) higher dose if the pet has long-term (chronic) blockage of the extrahepatic or common bile duct (extrahepatic bile duct obstruction) or decrease in the number of bile ducts (ductopenia) because of abnormal absorption of fat (fat malabsorption) S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe, Denosyl SD4) OTHER Ursodeoxycholic acid has numerous potentially beneficial effects, including altering the immune response (immunomodulation), protecting the liver, causing secretion of bile, and providing antioxidant effects B-vitamin supplementation with thiamine (B1) and B12 Follow-Up Care PATIENT MONITORING Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome initially, monitor bloodwork (liver enzyme and bilirubin levels) every 7 14 days; with remission, assess bloodwork quarterly PREVENTIONS AND AVOIDANCE Control inflammatory bowel disease POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome may transform into nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome or sclerosing cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome (characterized by thickening or hardening of the biliary and/or liver tissues) Diabetes mellitus in 30% of cats with sclerosing cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome treated with
5 prednisolone Hepatic lipidosis may develop with inadequate nutritional intake and in some cats, with steroid therapy; hepatic lipidosis is a disease in which fats and lipids (compounds that contain fats or oils) accumulate in the liver of cats EXPECTED COURSE AND PROGNOSIS Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome may be cured Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome long-term (chronic) disease; long-term remission possible (remission greater than 8 years has been documented) Key Points Cholangitis is inflammation of the bile duct or the biliary tree Cholangiohepatitis is inflammation of biliary structures and surrounding liver tissue Cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome occurs primarily in cats; it is classified as suppurative or nonsuppurative (lymphoplasmacytic, lymphocytic), granulomatous, or lymphoproliferative based on microscopic examination of biopsy samples Suppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome sudden (acute) illness; fever; lack of appetite (anorexia); vomiting; painful abdomen; may have yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (jaundice or icterus); dehydration; collapse; shock Nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome illness of greater than 3 weeks in duration (may have signs of illness for months to years); cyclic illness; long-term (chronic) vague signs: sluggishness (lethargy), vomiting, lack of appetite (anorexia), and weight loss; few physical abnormalities other than enlarged liver (hepatomegaly); thickened intestines with inflammatory bowel disease; variable yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (jaundice or icterus); rare fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites) Long-term (chronic) nature of nonsuppurative cholangitis/cholangiohepatitis syndrome requires lifelong therapy
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics
 Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid
Yellowish Discoloration to the Tissues of the Body
 Yellowish Discoloration to the Tissues of the Body (Jaundice or Icterus) Basics OVERVIEW Yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (known as jaundice or icterus ) Serum total bilirubin
Yellowish Discoloration to the Tissues of the Body (Jaundice or Icterus) Basics OVERVIEW Yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (known as jaundice or icterus ) Serum total bilirubin
Yellowish Discoloration to the Tissues of the Body
 Yellowish Discoloration to the Tissues of the Body (Jaundice or Icterus) Basics OVERVIEW Yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (known as jaundice or icterus ) Serum total bilirubin
Yellowish Discoloration to the Tissues of the Body (Jaundice or Icterus) Basics OVERVIEW Yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (known as jaundice or icterus ) Serum total bilirubin
Fibrosis and Cirrhosis of the Liver
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Fibrosis and Cirrhosis of the Liver Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Fibrosis and Cirrhosis of the Liver Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland
Chylothorax Basics OVERVIEW GENETICS SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET
 Chylothorax Basics OVERVIEW Chylo- refers to chyle; thorax refers to the chest Chyle is a milky to slightly yellow fluid composed of lymph and fats (rich in triglycerides) taken up from the intestines
Chylothorax Basics OVERVIEW Chylo- refers to chyle; thorax refers to the chest Chyle is a milky to slightly yellow fluid composed of lymph and fats (rich in triglycerides) taken up from the intestines
Chronic Active Hepatitis (Long-Term, Ongoing Inflammation of the Liver) Basics
 Chronic Active Hepatitis (Long-Term, Ongoing Inflammation of the Liver) Basics OVERVIEW Long-term (known as chronic ), ongoing (known as active ) inflammation of the liver (known as hepatitis ) associated
Chronic Active Hepatitis (Long-Term, Ongoing Inflammation of the Liver) Basics OVERVIEW Long-term (known as chronic ), ongoing (known as active ) inflammation of the liver (known as hepatitis ) associated
Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs
 Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW A change in the frequency, consistency, and volume of bowel movement (feces) for more than 3 weeks Can be either small bowel (small intestine) diarrhea, large bowel
Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW A change in the frequency, consistency, and volume of bowel movement (feces) for more than 3 weeks Can be either small bowel (small intestine) diarrhea, large bowel
Lymphoplasmacytic-Plasmacytic Gastroenteritis
 Lymphoplasmacytic-Plasmacytic Gastroenteritis (Inflammation of the Stomach and Intestines, Characterized by the Presence of Lymphocytes and Plasmacytes [Types of White Blood Cell]) Basics OVERVIEW An inflammatory
Lymphoplasmacytic-Plasmacytic Gastroenteritis (Inflammation of the Stomach and Intestines, Characterized by the Presence of Lymphocytes and Plasmacytes [Types of White Blood Cell]) Basics OVERVIEW An inflammatory
Hypoadrenocorticism or Addison's Disease (Inadequate Production of Hormones by the Adrenal Glands) Basics
 Hypoadrenocorticism or Addison's Disease (Inadequate Production of Hormones by the Adrenal Glands) Basics OVERVIEW A hormonal disorder resulting from decreased production of hormones (glucocorticoids and/or
Hypoadrenocorticism or Addison's Disease (Inadequate Production of Hormones by the Adrenal Glands) Basics OVERVIEW A hormonal disorder resulting from decreased production of hormones (glucocorticoids and/or
Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics
![Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics](/thumbs/75/72552398.jpg) Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics OVERVIEW A group of conditions of differing cause in which insoluble proteins (amyloid) are deposited outside
Amyloidosis (Disorder Caused by Deposition of Proteins [Amyloid] in Various Organs) Basics OVERVIEW A group of conditions of differing cause in which insoluble proteins (amyloid) are deposited outside
Sudden (Acute) Liver Failure
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Sudden (Acute) Liver Failure Basics OVERVIEW Sudden (acute) damage to the liver
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Sudden (Acute) Liver Failure Basics OVERVIEW Sudden (acute) damage to the liver
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) Basics
 Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) Basics OVERVIEW Abnormally low blood glucose (sugar) concentration SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET Species Dogs Cats SIGNS/OBSERVED CHANGES IN THE PET Seizures Partial paralysis
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar) Basics OVERVIEW Abnormally low blood glucose (sugar) concentration SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET Species Dogs Cats SIGNS/OBSERVED CHANGES IN THE PET Seizures Partial paralysis
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Inflammation of the Prostate (Prostatitis) and Prostatic Abscess
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Inflammation of the Prostate (Prostatitis) and Prostatic Abscess Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Inflammation of the Prostate (Prostatitis) and Prostatic Abscess Basics OVERVIEW
10/13 Tuesday 2:30-3:20 PM UPDATE ON FELINE LIVER DISEASE David C. Twedt, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 10/13 Tuesday 2:30-3:20 PM UPDATE ON FELINE LIVER DISEASE David C. Twedt, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO There are a number of specific liver diseases unique to the cat
10/13 Tuesday 2:30-3:20 PM UPDATE ON FELINE LIVER DISEASE David C. Twedt, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO There are a number of specific liver diseases unique to the cat
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Increased Number of Red Blood Cells (Polycythemia) Basics
 Increased Number of Red Blood Cells (Polycythemia) Basics OVERVIEW Blood consists of red blood cells (the most numerous cells normally), white blood cells, platelets, and plasma (the liquid portion of
Increased Number of Red Blood Cells (Polycythemia) Basics OVERVIEW Blood consists of red blood cells (the most numerous cells normally), white blood cells, platelets, and plasma (the liquid portion of
Immune-Mediated Anemia
 Immune-Mediated Anemia (Destruction of Red Blood Cells Caused by an Immune Response) Basics OVERVIEW Accelerated destruction or removal of red blood cells related to an immune response, in which the body
Immune-Mediated Anemia (Destruction of Red Blood Cells Caused by an Immune Response) Basics OVERVIEW Accelerated destruction or removal of red blood cells related to an immune response, in which the body
Hyperadrenocorticism or Cushing's Syndrome in Dogs
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Hyperadrenocorticism or Cushing's Syndrome in Dogs (Excessive Levels of Steroids
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Hyperadrenocorticism or Cushing's Syndrome in Dogs (Excessive Levels of Steroids
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Bacterial Pneumonia Basics
 Bacterial Pneumonia Basics OVERVIEW Inflammation in the lung as a response to disease-causing bacteria, characterized by accumulation of inflammatory cells and fluid in the lung, conducting airways (bronchi
Bacterial Pneumonia Basics OVERVIEW Inflammation in the lung as a response to disease-causing bacteria, characterized by accumulation of inflammatory cells and fluid in the lung, conducting airways (bronchi
Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis (Calcium Oxalate Stones in the Urinary Tract) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis (Calcium Oxalate Stones in the Urinary Tract) Basics
Gastrointestinal Obstruction
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Gastrointestinal Obstruction (Blockage of the Gastrointestinal Tract) Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Gastrointestinal Obstruction (Blockage of the Gastrointestinal Tract) Basics OVERVIEW
BILIARY ATRESIA. What is biliary atresia?
 The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. BILIARY ATRESIA What is
The Childhood Liver Disease Research Network strives to provide information and support to individuals and families affected by liver disease through its many research programs. BILIARY ATRESIA What is
My dog or cat has pancreas problems what do I do now?
 TROVET Digestion Support, dietary supplement for the targeted tackling of pancreas problems in dogs and cats My dog or cat has pancreas problems what do I do now? reliable and affordable dietary pet food
TROVET Digestion Support, dietary supplement for the targeted tackling of pancreas problems in dogs and cats My dog or cat has pancreas problems what do I do now? reliable and affordable dietary pet food
Hepatic Encephalopathy
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Hepatic Encephalopathy (Brain Disorder Secondary to Liver Disease) Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Hepatic Encephalopathy (Brain Disorder Secondary to Liver Disease) Basics OVERVIEW
Etiology Bacteria Sand particles Particles of ingesta / intestinal contents Desquamated epithelium
 10 CONCRETIONS Concretions Calculi o Urinary Calculi o Biliary Calculi o Salivary Calculi o Pancreatic Calculi o Enteric Calculi Piliconcretions Phytoconcretions Polyconcretions Model Questions CONCRETIONS
10 CONCRETIONS Concretions Calculi o Urinary Calculi o Biliary Calculi o Salivary Calculi o Pancreatic Calculi o Enteric Calculi Piliconcretions Phytoconcretions Polyconcretions Model Questions CONCRETIONS
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
X-Plain Pancreatic Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Pancreatic cancer is the 4th leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. About 37,000 new cases of pancreatic cancer are diagnosed each year in the
Liver Toxins (Hepatotoxins) Basics
 Liver Toxins (Hepatotoxins) Basics OVERVIEW A toxin is a poisonous substance; hepato- refers to the liver Liver toxins are substances (such as drugs or toxins) that cause liver injury or damage Direct
Liver Toxins (Hepatotoxins) Basics OVERVIEW A toxin is a poisonous substance; hepato- refers to the liver Liver toxins are substances (such as drugs or toxins) that cause liver injury or damage Direct
Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics
 Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW Increased levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood (known as hyperglycemia ) when the dog has
Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW Increased levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood (known as hyperglycemia ) when the dog has
C International Veterinary Branding
 C International Veterinary Branding The pancreas is a gland that is located in the front part of the abdomen. It lies just below the stomach and directly beside the upper part of the small intestine. The
C International Veterinary Branding The pancreas is a gland that is located in the front part of the abdomen. It lies just below the stomach and directly beside the upper part of the small intestine. The
Case Study BMIs in the range of are considered overweight. Therefore, F.V. s usual BMI indicates that she was overweight.
 Morgan McFarlane February 26 th, 2013 HHP 439 Professor White Case Study 7.10 1. What is your interpretation of F.V. s clinical data? F.V. s clinical data includes chronic abdominal pain, loose stools,
Morgan McFarlane February 26 th, 2013 HHP 439 Professor White Case Study 7.10 1. What is your interpretation of F.V. s clinical data? F.V. s clinical data includes chronic abdominal pain, loose stools,
Aortic Thromboembolism
 Aortic Thromboembolism (Blood Clots in the Aorta) Basics OVERVIEW Aortic refers to the aorta, the main artery of the body; thromboembolism is blockage of blood flow secondary to the presence of a blood
Aortic Thromboembolism (Blood Clots in the Aorta) Basics OVERVIEW Aortic refers to the aorta, the main artery of the body; thromboembolism is blockage of blood flow secondary to the presence of a blood
In The Name of God. Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics
 Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
My dog or cat has problems with the stomach, intestines or liver... what do I do now?
 Dietary food for the targeted tackling of gastrointestinal and/or liver problems in dogs and cats My dog or cat has problems with the stomach, intestines or liver... what do I do now? reliable and and
Dietary food for the targeted tackling of gastrointestinal and/or liver problems in dogs and cats My dog or cat has problems with the stomach, intestines or liver... what do I do now? reliable and and
Pyothorax (Pus in the Pleural Space, the Space between the Chest Wall and the Lungs) Basics
 Pyothorax (Pus in the Pleural Space, the Space between the Chest Wall and the Lungs) Basics OVERVIEW Accumulation of pus within the pleural space (the space between the chest wall and lungs, which is lined
Pyothorax (Pus in the Pleural Space, the Space between the Chest Wall and the Lungs) Basics OVERVIEW Accumulation of pus within the pleural space (the space between the chest wall and lungs, which is lined
Saliva & Feces analysis
 Saliva & Feces analysis Saliva analysis What is Saliva? Watery substance present in humans and animals and secreted by salivary glands and aids in digestion It is a filtrate of plasma Contains electrolytes,
Saliva & Feces analysis Saliva analysis What is Saliva? Watery substance present in humans and animals and secreted by salivary glands and aids in digestion It is a filtrate of plasma Contains electrolytes,
Crohn's Disease. What causes Crohn s disease? What are the symptoms?
 Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Crohn's Disease Crohn s disease is an ongoing disorder that causes inflammation of the digestive tract, also referred to as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Crohn s disease can affect any area of the GI
Kidney Failure Sudden (Acute) Uremia
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Kidney Failure Sudden (Acute) Uremia Basics OVERVIEW Uremia is the medical term
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Kidney Failure Sudden (Acute) Uremia Basics OVERVIEW Uremia is the medical term
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM-PART 3
 Welcome back to InterpreterPrep.com THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM-PART 3 This is the third part of a series of 4 presentations on the DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. We will be continuing our journey down the digestive tract
Welcome back to InterpreterPrep.com THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM-PART 3 This is the third part of a series of 4 presentations on the DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. We will be continuing our journey down the digestive tract
Lymphoma. What is cancer? What are signs that my cat has lymphoma. How is Lymphoma diagnosed?
 What is cancer? Lymphoma Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of a small population of abnormal cells. These abnormal cells form by a mutation during the normal division cycle and are able to escape detection
What is cancer? Lymphoma Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of a small population of abnormal cells. These abnormal cells form by a mutation during the normal division cycle and are able to escape detection
Biliary Atresia. Who is at risk for biliary atresia?
 Biliary Atresia Biliary atresia is a life-threatening condition in infants in which the bile ducts inside or outside the liver do not have normal openings. Bile ducts in the liver, also called hepatic
Biliary Atresia Biliary atresia is a life-threatening condition in infants in which the bile ducts inside or outside the liver do not have normal openings. Bile ducts in the liver, also called hepatic
Gallstones Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Gutscharity.org.uk
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about gallstones Gall is an old-fashioned word for bile, a liquid made in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics
 Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Proteinuria is the medical term for protein in the urine Urinary protein is detected by urine dipstick analysis, urinary protein: creatinine ratio (UP:C
Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Proteinuria is the medical term for protein in the urine Urinary protein is detected by urine dipstick analysis, urinary protein: creatinine ratio (UP:C
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Gastroduodenal Ulcer Disease
 Gastroduodenal Ulcer Disease (Ulcers in the Stomach and Upper Small Intestine [Duodenum]) Basics OVERVIEW Gastro- refers to the stomach; duodenal refers to the upper small intestine or duodenum Ulcers
Gastroduodenal Ulcer Disease (Ulcers in the Stomach and Upper Small Intestine [Duodenum]) Basics OVERVIEW Gastro- refers to the stomach; duodenal refers to the upper small intestine or duodenum Ulcers
Crohn's disease CAUSES COURSE OF CROHN'S DISEASE TREATMENT. Sulfasalazine
 Crohn's disease Crohn's disease is an inflammatory condition of the digestive tract that affects children and adults. Common features of Crohn's disease include mouth sores, diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight
Crohn's disease Crohn's disease is an inflammatory condition of the digestive tract that affects children and adults. Common features of Crohn's disease include mouth sores, diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer
 Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
Quick Facts about Bile Duct Cancer What is the bile duct? The bile duct is a thin tube, about 10 centimetres to 15 centimetres long, that carries a fluid called bile from the liver and gallbladder to the
INFORMATION ON PANCREATIC HEAD AND PERIAMPULLARY CANCER
 INFORMATION ON PANCREATIC HEAD AND PERIAMPULLARY CANCER What is Pancreas? The pancreas is a gland located in the back of your abdomen behind the stomach. pancreas is divided into four parts: the head,
INFORMATION ON PANCREATIC HEAD AND PERIAMPULLARY CANCER What is Pancreas? The pancreas is a gland located in the back of your abdomen behind the stomach. pancreas is divided into four parts: the head,
Conjunctivitis in Dogs
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Dogs (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Dogs (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Jaundice , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. syf80102 Last reviewed: 05/05/2017 1
 Jaundice Introduction Jaundice causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to turn yellow. Too much bilirubin causes jaundice. Bilirubin is a yellow chemical in hemoglobin, the substance that carries
Jaundice Introduction Jaundice causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to turn yellow. Too much bilirubin causes jaundice. Bilirubin is a yellow chemical in hemoglobin, the substance that carries
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer
 Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Quick facts about gallbladder cancer What is the gallbladder? Princess Margaret The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located under right side of the liver. The gallbladder concentrates and stores
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
What Is Cirrhosis? CIRRHOSIS. Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is. by chronic conditions and diseases. permanently scarred or injured
 What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
UNDERSTANDING CYSTIC FIBROSIS INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis is a chronic disease that affects the respiratory and gastrointestinal systems. People with cystic fibrosis have a genetic defect of the lungs
TREATMENT FOR SEVERE FELINE HEPATIC LIPIDOSIS. Disorders Associated with Secondary Feline Hepatic Lipidosis Syndrome
 H Hepatology TREATMENT FOR SEVERE FELINE HEPATIC LIPIDOSIS Sharon A. Center, DVM, Dipl ACVIM College of Veterinary Medicine Cornell University Ithaca New York USA 14853 Sac6@cornell.edu The feline hepatic
H Hepatology TREATMENT FOR SEVERE FELINE HEPATIC LIPIDOSIS Sharon A. Center, DVM, Dipl ACVIM College of Veterinary Medicine Cornell University Ithaca New York USA 14853 Sac6@cornell.edu The feline hepatic
Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i
 Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Customer Care Team on 0800 374 208 email: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk.
Chronic Pancreatitis (1 of 4) i If you need this information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact the Customer Care Team on 0800 374 208 email: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk.
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions
 2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
2.08 Understand the functions and disorders of the digestive system Essential questions What are the functions of the digestive system? How do the functions of chemical and physical digestion interrelate?
Pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis
 Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Pancreatitis Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large gland behind the stomach and close to the duodenum. The duodenum is the upper part of the small intestine. The pancreas
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Chronic Kidney Disease and Kidney Failure (CRF)(CKD) Basics
 Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Chronic Kidney Disease and Kidney Failure (CRF)(CKD) Basics OVERVIEW Long-term kidney disease is known as chronic kidney disease or CKD; it is defined
Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Chronic Kidney Disease and Kidney Failure (CRF)(CKD) Basics OVERVIEW Long-term kidney disease is known as chronic kidney disease or CKD; it is defined
Inflammation of the Esophagus (Esophagitis) Basics
 Inflammation of the Esophagus (Esophagitis) Basics OVERVIEW Inflammation of the esophagus typically involves the tubular area of the esophagus itself (known as the esophageal body ) and the muscular area
Inflammation of the Esophagus (Esophagitis) Basics OVERVIEW Inflammation of the esophagus typically involves the tubular area of the esophagus itself (known as the esophageal body ) and the muscular area
Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis
 1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
Glomerulonephritis (Kidney Inflammation Involving the Glomerulus, the Blood Filter ) Basics
 Glomerulonephritis (Kidney Inflammation Involving the Glomerulus, the Blood Filter ) Basics OVERVIEW The kidney filters the blood and removes various waste products from the body as it produces urine;
Glomerulonephritis (Kidney Inflammation Involving the Glomerulus, the Blood Filter ) Basics OVERVIEW The kidney filters the blood and removes various waste products from the body as it produces urine;
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
6. Production or formation of plasma protein and clotting factors and heparin.
 Liver function test Clinical pathology dr. Ali H. Liver function test The liver has many vital physiologic functions involving synthesis, excretion, and storage. When a disease process damages cells within
Liver function test Clinical pathology dr. Ali H. Liver function test The liver has many vital physiologic functions involving synthesis, excretion, and storage. When a disease process damages cells within
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT. Lecture 5. Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT Lecture 5 Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract Enrique Aburto Winter 2015 IX. Diseases of uncertain origin Equine serum hepatitis Idiopathic
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER & BILIARY TRACT Lecture 5 Idiopathic & proliferative conditions; diseases of the biliary tract Enrique Aburto Winter 2015 IX. Diseases of uncertain origin Equine serum hepatitis Idiopathic
Biomarkers of GI tract diseases. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a complex system performing multiple biological functions which are anatomically distributed Site for food processing and absorption
By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Introduction The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a complex system performing multiple biological functions which are anatomically distributed Site for food processing and absorption
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
What Is Pancreatitis?
 What Is Pancreatitis? Pancreatitis is inflammation (swelling) of the pancreas that is most often caused by gallstones or alcohol abuse. There are other causes that your gastroenterologist will look for,
What Is Pancreatitis? Pancreatitis is inflammation (swelling) of the pancreas that is most often caused by gallstones or alcohol abuse. There are other causes that your gastroenterologist will look for,
Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders
 Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders Mary DeLetter, PhD, RN Associate Professor Dept. of Baccalaureate and Graduate Nursing Eastern Kentucky University Disorders of Accessory Organs Portal
Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders Mary DeLetter, PhD, RN Associate Professor Dept. of Baccalaureate and Graduate Nursing Eastern Kentucky University Disorders of Accessory Organs Portal
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics
 Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two
Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics
 Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics OVERVIEW Clinical condition that results from inadequate production and release of thyroid
Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics OVERVIEW Clinical condition that results from inadequate production and release of thyroid
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
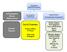 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Cholelithiasis (Gallstones)
 GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
GALL BLADDER Cholelithiasis (Gallstones) Gallstones afflict 10-20% of adult populations in northern hemisphere Western countries. Adult prevalence rates are higher in Latin American countries (20-40%)
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal pain, enteral therapy in acute pancreatitis and, 812 Abscess(es), pancreatic, nutritional support for, 814 815 Acute Physiology and
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal pain, enteral therapy in acute pancreatitis and, 812 Abscess(es), pancreatic, nutritional support for, 814 815 Acute Physiology and
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems
 Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Chapter 20 Diet and Gastrointestinal Problems Objectives Explain uses of diet therapy in gastrointestinal disturbances Identify foods allowed and disallowed in therapeutic diets discussed Adapt normal
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg
 Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Laparoscopic cholecystectomyy
 Laparoscopic cholecystectomyy What is the gall bladder? The gallbladder is a small pear sized organ that stores bile. Bile is necessary for the digestion of fatty food. The bile duct is a tube that carries
Laparoscopic cholecystectomyy What is the gall bladder? The gallbladder is a small pear sized organ that stores bile. Bile is necessary for the digestion of fatty food. The bile duct is a tube that carries
Brachycephalic Airway Syndrome (Upper Airway Problems Seen in Short-Nosed Breeds) Basics
 Brachycephalic Airway Syndrome (Upper Airway Problems Seen in Short-Nosed Breeds) Basics OVERVIEW Partial upper airway obstruction in short-nosed, flat-faced (brachycephalic) breeds of dogs and cats caused
Brachycephalic Airway Syndrome (Upper Airway Problems Seen in Short-Nosed Breeds) Basics OVERVIEW Partial upper airway obstruction in short-nosed, flat-faced (brachycephalic) breeds of dogs and cats caused
Osteomyelitis (Inflammation of the Bone and Bone Marrow) Basics
 Osteomyelitis (Inflammation of the Bone and Bone Marrow) Basics OVERVIEW Sudden (acute) or long-term (chronic) inflammation of bone and its associated soft-tissue elements of bone marrow, endosteum (lining
Osteomyelitis (Inflammation of the Bone and Bone Marrow) Basics OVERVIEW Sudden (acute) or long-term (chronic) inflammation of bone and its associated soft-tissue elements of bone marrow, endosteum (lining
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis What is Primary Biliary Cirrhosis? Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic liver disease resulting from progressive destruction of the bile ducts in the liver called the
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis What is Primary Biliary Cirrhosis? Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic liver disease resulting from progressive destruction of the bile ducts in the liver called the
Chronic GI PROBLEMS in Cats & dogs
 Chronic GI PROBLEMS in Cats & dogs Chronic vomiting, diarrhea or both are fairly common problems in dogs and cats. They may be related to relatively minor causes, such as chronic swallowing of hair, or
Chronic GI PROBLEMS in Cats & dogs Chronic vomiting, diarrhea or both are fairly common problems in dogs and cats. They may be related to relatively minor causes, such as chronic swallowing of hair, or
Otitis Externa and Media
 Otitis Externa and Media (Inflammation of the Outer and Middle Ear) Basics OVERVIEW Otitis externa inflammation of the outer ear or external ear canal Otitis media inflammation of the middle ear The terms
Otitis Externa and Media (Inflammation of the Outer and Middle Ear) Basics OVERVIEW Otitis externa inflammation of the outer ear or external ear canal Otitis media inflammation of the middle ear The terms
CATS AND KIDNEY DISEASE
 CATS AND KIDNEY DISEASE Kidney structure and function Like all mammals, cats have 2 kidneys located in the abdomen just below the lumbar spinal region. Each is normally similar in size and shape to a small
CATS AND KIDNEY DISEASE Kidney structure and function Like all mammals, cats have 2 kidneys located in the abdomen just below the lumbar spinal region. Each is normally similar in size and shape to a small
Autoimmune Liver Disease
 Autoimmune Liver Disease A Guide An explanation of what autoimmune liver diseases are including autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune sclerosis cholangitis What are autoimmune diseases?... 4 What is autoimmune
Autoimmune Liver Disease A Guide An explanation of what autoimmune liver diseases are including autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune sclerosis cholangitis What are autoimmune diseases?... 4 What is autoimmune
Laryngeal Diseases. (Diseases of the Voice Box or Larynx) Basics
 Laryngeal Diseases (Diseases of the Voice Box or Larynx) Basics OVERVIEW The respiratory tract consists of the upper respiratory tract (the nose, nasal passages, throat, and windpipe [trachea]) and the
Laryngeal Diseases (Diseases of the Voice Box or Larynx) Basics OVERVIEW The respiratory tract consists of the upper respiratory tract (the nose, nasal passages, throat, and windpipe [trachea]) and the
Bacteriology. Mycology. Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: Rare. Rare. Positive. Brown. Negative *NG. Negative
 Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: 3.2 0.9-26.8 U/g 1.2 0.2-3.3 mg/g 2.2 1.3-8.6 micromol/g 1.1 1.3-23.7 mg/g 1.1 0.2-3.5 mg/g Rare 1.0 0.2-8.8 mg/g Rare 4.4 2.6-32.4 mg/g 64.6 >= 13.6 micromol/g Bacteriology
Patient: SAMPLE PATIENT DOB: Sex: MRN: 3.2 0.9-26.8 U/g 1.2 0.2-3.3 mg/g 2.2 1.3-8.6 micromol/g 1.1 1.3-23.7 mg/g 1.1 0.2-3.5 mg/g Rare 1.0 0.2-8.8 mg/g Rare 4.4 2.6-32.4 mg/g 64.6 >= 13.6 micromol/g Bacteriology
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Pediatric PSC A children s tale
 Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Conjunctivitis in Cats
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Cats (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Cats (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Acute Pancreatitis. What is the Pancreas? What does it do? What is acute pancreatitis? What causes acute pancreatitis? What symptoms do you get?
 In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Acute Pancreatitis www.corecharity.org.uk What is the Pancreas? What does it do? What is acute pancreatitis? What causes
In association with: Primary Care Society for Gastroenterology INFORMATION ABOUT Acute Pancreatitis www.corecharity.org.uk What is the Pancreas? What does it do? What is acute pancreatitis? What causes
LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY Treating Gallbladder Problems with Laparoscopy A Common Problem If you ve had an attack of painful gallbladder symptoms, you re not alone. Gallbladder disease is very common.
LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY Treating Gallbladder Problems with Laparoscopy A Common Problem If you ve had an attack of painful gallbladder symptoms, you re not alone. Gallbladder disease is very common.
Disorders of the Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas
 Disorders of the Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas Objectives: Disorders of the liver Disorders of the gall bladder Disorders of the pancreas Part 1: Disorders of the Liver 1 Jaundice: is a manifestation
Disorders of the Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas Objectives: Disorders of the liver Disorders of the gall bladder Disorders of the pancreas Part 1: Disorders of the Liver 1 Jaundice: is a manifestation
Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Patient Information
 Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Patient Information Author ID: MP Leaflet Number: Surg 060 Name of Leaflet: Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Version: 1 Date Produced: October 2017
Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Patient Information Author ID: MP Leaflet Number: Surg 060 Name of Leaflet: Cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder) Version: 1 Date Produced: October 2017
Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
