Effects of clozapine on cerebral catecholaminergic neurone systems
|
|
|
- Duane Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 46, Effects of clozapine on cerebral catecholaminergic neurone systems G. BARTHOLINI, W. HAEFELY, M. JALFRE, H. H. KELLER AND A. PLETSCHER Medical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co., Ltd., Basle, Switzerland Summary 1. Clozapine, a dibenzodiazepine derivative claimed to possess antipsychotic properties in man without producing extrapyramidal disorders, greatly increased the turnover of cerebral dopamine in the rat. 2. The drug itself was virtually devoid of cataleptigenic activity in rats; however, it antagonized prochlorperazine-induced catalepsy. 3. It is proposed that clozapine causes a blockade of striatal dopamine receptors which is of the surmountable type in contrast to that produced by cataleptigenic neuroleptics. In addition, clozapine may also increase the turnover of cerebral noradrenaline. Introduction The classic neuroleptic drugs, e.g. chlorpromazine and haloperidol, are thought to block dopamine receptors in the brain, thereby causing catalepsy in the rat and extrapyramidal disorders in man. Furthermore, these drugs enhance the turnover of cerebral dopamine which is generally assumed to be a direct consequence of the blockade of dopamine receptors (Carlsson & Lindqvist, 1963; Anden, Roos & Werdinius, 1964; Pletscher, Gey & Burkard, 1967; O'Keefe, Sharman & Vogt, 1970). Whether the altered activity of the extrapyramidal brain centres resulting from this blockade (Stille, 1971) is essential for the antipsychotic effect of neuroleptics in schizophrenia has not yet been clarified. Recently, the tricyclic drug, 8-chloro-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo(b,e) (1,4) diazepine (clozapine) (Stille, Lauener & Eichenberger, 1971), has been reported to possess an antipsychotic action in schizophrenia without producing catalepsy in rats or major extrapyramidal disorders in man (Angst, Jaenicke, Padrutt & Scharfetter, 197 1a; Angst, Bente, Berner, Heiman, Helmchen & Hippus, 197 1b; Stille & Hippius, 1971). It was therefore of interest to investigate whether clozapine differs from classic neuroleptic drugs in its action on cerebral catecholaminergic neurone systems. So far, only the effect of the drug on homovanillic acid (HVA) in the rat brain has been studied but not definitely established (Stille & Lauener, 1971; Stille, et al., Methods Male albino rats of Wistar origin (Fiillinsdorf) weighing g, kept at room temperature, were injected with various doses of clozapine i.p. Two hours later, HVA (Murphy, Robinson & Sharman, 1969) and dopamine (Laverty & Taylor,
2 Clozapine and cerebral catecholamines 1968) were determined in the brain (without cerebellum). Another group of animals was kept at an environmental temperature of 320 C which prevented hypothermia. Rectal temperature was measured every hour. These rats received an intraperitoneal injection of 300 mg/kg a-methyl-p-tyrosine-methylester hydrochloride (a-mt) alone or 1 h after 50 mg/kg clozapine i.p. Dopamine and noradrenaline (Laverty & Taylor, 1968) were assayed 2 h after the administration of a-mt. Rats injected with 0-9% w/v NaCl solution (saline) and kept at room temperature, served as controls. Catalepsy was measured as follows: The homolateral limbs of the rats were crossed by the experimenter; animals which maintained this imposed abnormal position for more than 10 s were considered to be cataleptic. After i.p. injection of either clozapine or 3-chloro-10-[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-propyl] phenothiazine (prochlorperazine) followed by clozapine (see Results and Fig. 2), the number of animals which showed catalepsy was counted every 30 min during 6 hours. Results Clozapine in a dose range of mg/kg i.p. caused a significant (P>0 01) dose-dependent increase in the cerebral concentration of HVA in rats kept at room temperature (Fig. 1). The maximal effect was attained 1-2 h following i.p. injection of 30 mg/kg clozapine and after 4 h the HVA concentrations had returned to normal. Similar results were obtained when the HVA measurements were carried out in the striatum. Clozapine (50 mg/kg) did not significantly affect the cerebral dopamine concentrations (P>0 05) (Fig. 1). Rats kept at 320 C in order to prevent the hypothermia produced by clozapine showed a somewhat higher rise of HVA than those at room temperature, whereas the dopamine content did not change. /g/g HVA DA o I 0 _ O*5 _ 0 0 S mg/kg Clozapine FIG. 1. Content of homovanillic acid (HVA) and dopamine (DA) in rat brain 2 h after i.p. administration of clozapine. In the dopamine experiments the dose of clozapine was 50 mg/kg. The values are expressed in,ug/g wet tissue and represent means with S.E.M. of 3-10 and 3 experiments for HVA and dopamine, respectively. The point 0 on the abscissae indicates the concentration of HVA in control rats. Open column-control rats. Cross-hatched column-clozapine-treated rats.
3 738 G. Bartholini, W. Haefely, M. Jailfre, H. H. Keller and A. Pletscher Three hours after i.p. administration of 50 mg/kg of clozapine, the cerebral content of noradrenaline in normothermic animals (kept at 32 C) was decreased to P8% of controls (P<0001) (Table 1). Doses of clozapine as low as 5 mg/kg already had a significant effect (reduction of cerebral noradrenaline to 93-1+P15% after 1 h) (P<0 01). The concentration of cerebral 5-hydroxytryptamine in normothermic rats was not changed and that of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid was slightly increased ( % of control values) 1 h after administration of clozapine (50 mg/kg). In normothermic animals the a-mt-induced decrease in cerebral dopamine and noradrenaline was significantly accelerated by clozapine (P<0 001) (Table 1). Following intraperitoneal injection of 50 and 100 mg/kg clozapine, only 7 and 11%, respectively, of the rats were cataleptic. However, clozapine, in a dosedependent manner, was able to antagonize the catalepsy induced by a dose of prochlorperazine (22 5 mg/kg i.p.) which produced a cataleptic effect in all animals (Fig. 2). TABLE 1. Effect of clozapine on the disappearance of cerebral catecholamines induced by a-methylp-tyrosine (amt) in normothermic rats Treatment Dopamine Noradrenaline ( /0) (M%) Saline V Clozapine 107 4±P * amt 53-2±V14 66A4±2-4 amt+clozapine 40-5±:12t 26-9+± 1-3 t Clozapine (50 ng/kg) and amt (300 mg/kg) were injected intraperitoneally 3 and 2 h respectively, before the rats were killed. The concentration of dopamine and noradrenaline in control rats were ±0012 and ,g/g wet weight, respectively. Averages with S.E.M. of 3 experiments, each performed with 4-6 rats per group. * Comparison with control value; P<0 001 (Student's t test). t Comparison with concentration in animals treated with amt alone; P<0 001 (Student's t test). Prochlorperazine Saline or Clozapine ,P 10 mg/kg Clozapine E ~ c g-0 \ /tt.8 a \ / 30 mg/kg Clozapine U6- o0\ / 100 mg/kg Clozapine 42- z Time (h) FIG. 2. Antagonism of the prochlorperazine-induced catalepsy by clozapine. Groups of 12 rats were given a dose of prochlorperazine i.p. (225 mg/kg) which produced catalepsy in all animals. Three hours later, 0 9% w/v NaCl solution (saline) or clozapine was injected i.p.
4 Clozapine and cerebral catecholamines 739 Discussion The inciease in the concentration of cerebral HVA observed after the administration of clozapine is probably not due to a reserpine-like release of dopamine from its tissue stores since the drug does not change the concentration of the endogenous cerebral amine. An amphetamine-like liberation of dopamine also seems improbable, as the rise in HVA is too pronounced. Furthermore, clozapine probably does not raise the HVA concentrations by an unspecific inhibition of the outflow of phenolcarboxylic acids from the brain since the drug caused only a slight increase in cerebral 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. Therefore, the clozapine-induced elevation of HVA concentrations is likely to be the result of an accelerated dopamine turnover. The enhancement of the a-mt-induced decrease in cerebral dopamine by clozapine supports this view. The present resots demonstrate that clozapine, in contrast to the classic neuroleptics, has little c*leptigenic action even in doses which greatly enhance the turnover of cerebral dopamine, for with doses as high as 50 and 100 mg/kg only slight cataleptic symptoms were observed. The virtual absence of catalepsy in rats treated with clozapine does not seem to be due to a central anticholinergic action of the drug which might antagonize its possible cataleptic effect. In fact, the sinistrotorsion of guinea-pigs elicited by an injection of physostigmine into the right carotid artery (De Jonge & Funcke, 1962) was poorly antagonized by clozapine in contrast to anticholinergic drugs and chlorpromazine (Jalfre, unpublished results). The surprising observation that clozapine affects the dopaminergic system of the basal ganglia without producing catalepsy, requires further investigation. As a working hypothesis we propose that clozapine, like the classic neuroleptics, causes a blockade of dopamine receptors in the striatum which is assumed to enhance the dopamine turnover by a neuronal feed-back mechanism. However, the blockade of dopamine receptors by clozapine, in contrast to that of classic neuroleptics, is possibly of the surmountable type. On this assumption, the clozapine-induced receptor blockade may be partially overcome by the increased liberation of dopamine at the receptor site resulting from the feed-back activation of dopaminergic neurones, thus preventing catalepsy. This hypothesis is supported by the findings that clozapine antagonizes the cataleptigenic action of high doses of prochlorperazine and, as we have observed in preliminary experiments, has an additive effect with low doses of this potent neuroleptic drug. This suggests that both clozapine and prochlorperazine occupy the same binding sites at the dopamine receptors. Clozapine greatly accelerated the decrease in noradrenaline induced by a-mt. Since clozapine caused a diminution of endogenous cerebral noradrenaline, a direct amine-releasing action of clozapine cannot be excluded. However, it has been reported that clozapine is a potent peripheral a-adrenoceptor blocking agent (Stille & Hippius, 1971). Therefore, the enhancement of the a-mt-induced noradrenaline decrease by clozapine might also be the result of a blockade of central noradrenaline receptors leading to an increased impulse flow in noradrenergic neurones as a consequence of a feed-back mechanism. It has to be assumed that the enhanced release of noradrenaline due to the increased neuronal activity is not fully compensated for by the synthesis of the amine. This insufficient noradrenaline synthesis may result from an inadequate activity of dopamine-,l-hydroxylase rather than of tyrosine-hydroxylase, since the latter is able to maintain the dopamine concentration at a normal level. An inhibition of dopamine-,f-hydroxylase by clozapine was not observed in preliminary experiments (Kettler, unpublished results).
5 740 G. Bartholini, W. Haefely, M. Jalfre, H. H. Keller and A. Pletscher Whether the effect on dopamine and/or noradrenaline receptors is related to the reported antipsychotic action of clozapine in schizophrenia (Angst et al., 1971a, b; Stille & Hippius, 1971) remains to be investigated. Clozapine was kindly provided by Dr. A. Wander, Ltd., Berne, Switzerland. REFERENCES ANDAN, N. E., Roos, B. E. & WERDNUS, B. (1964). Effect of chlorpromazine, haloperidol-andreserpine on the levels of phenolic acids in rabbit corpus striatum. Life Sci., 3, ANGST, J., JAENICKE, U., PADRUTr, A. & SCHARFETTER, CH. (1971a). Ergebnisse eines Doppelblindversuchs von Clozapin (8-Chlor-11-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-5-H-dibenzo(b,e)(1,4)diazepin im Vergleich zu Levomepromazin. Pharmakopsychiat., 4, ANGST, J., BENTE, D., BERNER, P., HEIMANN, H., HELMCHEN, H. & HIPPIUs, H. (1971b). Das klinische Wirkungsbild von Clozapin. Pharmakopsychiat., 4, CARLMSSON, A. & LINDQVIST, M. (1963). Effect of chlorpromazine and haloperidol on formation of 3-methoxy-tyramine and normetanephrine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmac. et Toxicol., 20, DE JONGE, M. C. & FuNcKE, A. B. H. (1962). Sinistrotorsion in guinea pigs as a method of screening central anticholinergic activity. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn., 137, LAVERTY, R. & TAYLOR, K. M. (1968). The fluorometric assay of catecholamines and related compounds: improvements and extensions to the hydroxyindole technique. Analyt. Biochem., 22, MuRPHSy, G. F., ROBINSON, D. & SHARMAN, D. F. (1969). Effect of tropolone on the formation of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylacetic acid in the brain of the mouse. Br. J. Pharmac., 36, O'KEEFE, R., SHARMAN, D. F. & VOGT, M. (1970). Effect of drugs used in psychoses on cerebral dopamine metabolism. Br. J. Pharmac., 38, PLETSCHER, A., GEY, K. F. & BURKARD, W. P. (1967). Effect of neuroleptics on the cerebral metabolism of catecholamines. In: Toxicity and side effects of psychotropic drugs, p Excerpta Medica int. Congr., Series 145. ST1LLE, G. (1971). Zur Pharmakologie katatonigener Stoffe. V. Die Wirkung von Neuroleptika. Arzneimittel-Forsch., 21, STILLE, G. & HrPpius, A. (1971). Kritische Stellungsnahme zum Begriff der Neuroleptika (anhand von pharmakologischen und klinischen Befunden mit Clozapin). Pharmakopsychiat., 4, STILLE, G. & LAUENER, H. (1971). Zur Pharmakologie katatonigener Stoffe. I. Korrelation zwischen neuroleptischer Katalepsie und Homovanillinsauregehalt im C. striatum bei Ratten. Arzneimittel-Forsch., 21, STILLE, G., LAUENER, H. & EICHENBERGER, E. (1971). The pharmacology of 8-chloro-1 1-(4-methyl-1- piperazinyl)-5h-dibenzo [b,e] [1,4] diazepine (clozapine). II Farmaco, 26, (Received April 24, 1972)
ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF CLOZAPINE ON THE ADRENERGIC NEURONE
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1976), 56, 279-283 ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF CLOZAPINE ON THE ADRENERGIC NEURONE R.L. DORRIS & P.A. SHORE Department of Pharmacology, University of Texas Health Science Center, Dallas,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1976), 56, 279-283 ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF CLOZAPINE ON THE ADRENERGIC NEURONE R.L. DORRIS & P.A. SHORE Department of Pharmacology, University of Texas Health Science Center, Dallas,
INTERACTION WITH MORPHINE AND HALOPERIDOL
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1978), 62, 213-218 EFFECT OF MECAMYLAMNE ON THE FATE OF DOPAMNE N STRATAL AND MESOLMBC AREAS OF RAT BRAN; NTERACTON WTH MORPHNE AND HALOPERDOL LSA AHTEE' & SEPPO KAAKKOLA Department of
Br. J. Pharmac. (1978), 62, 213-218 EFFECT OF MECAMYLAMNE ON THE FATE OF DOPAMNE N STRATAL AND MESOLMBC AREAS OF RAT BRAN; NTERACTON WTH MORPHNE AND HALOPERDOL LSA AHTEE' & SEPPO KAAKKOLA Department of
EVIDENCE THAT TRANQUILIZING ACTION OF RESERPINE IS ASSOCIATED WITH CHANGE IN BRAIN SEROTONIN AND NOT IN BRAIN NOREPINEPHRINE
 835 EVIDENCE THAT TRANQUILIZING ACTION OF RESERPINE IS ASSOCIATED WITH CHANGE IN BRAIN SEROTONIN AND NOT IN BRAIN NOREPINEPHRINE EFFECTS OF RESERPINE, RAUNESCI NE, BENZOQUI NOLIZI NES, DIMETHYL- AMINOBENZOYL
835 EVIDENCE THAT TRANQUILIZING ACTION OF RESERPINE IS ASSOCIATED WITH CHANGE IN BRAIN SEROTONIN AND NOT IN BRAIN NOREPINEPHRINE EFFECTS OF RESERPINE, RAUNESCI NE, BENZOQUI NOLIZI NES, DIMETHYL- AMINOBENZOYL
Passage into the rat brain of dopa and dopamine injected into the lateral ventricle
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 32-38. Passage into the rat brain of dopa and dopamine injected into the lateral ventricle J. CONSTANTINIDIS, J. M. GAILLARD, F. GEISSBUHLER AND R. TISSOT The University Psychiatric
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 32-38. Passage into the rat brain of dopa and dopamine injected into the lateral ventricle J. CONSTANTINIDIS, J. M. GAILLARD, F. GEISSBUHLER AND R. TISSOT The University Psychiatric
INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 366-370. INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE BY B. G. BENFEY AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 366-370. INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE BY B. G. BENFEY AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
On the role of central nervous system catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the nialamide-induced behavioural syndrome
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 46, 3245. On the role of central nervous system catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the nialamide-induced behavioural syndrome K. MODIGH AND T. H. SVENSSON Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 46, 3245. On the role of central nervous system catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the nialamide-induced behavioural syndrome K. MODIGH AND T. H. SVENSSON Department of Pharmacology,
Effect of phenmetrazine, aminorex and (+) p-chloramphetamine on the motor activity and turnover rate of brain catecholamines
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 570-579. Effect of phenmetrazine, aminorex and (+) p-chloramphetamine on the motor activity and turnover rate of brain catecholamines E. COSTA, K. M. NAIMZADA* AND A. REVUELTA
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 570-579. Effect of phenmetrazine, aminorex and (+) p-chloramphetamine on the motor activity and turnover rate of brain catecholamines E. COSTA, K. M. NAIMZADA* AND A. REVUELTA
THE INVOLVEMENT OF CATECHOLAMINE IN SCOPOLAMINE-INDUCED LOCOMOTOR ACTIVATION AND ROTATIONAL BEHAVIOUR IN MICE
 THE INVOLVEMENT OF CATECHOLAMINE IN SCOPOLAMINE-INDUCED LOCOMOTOR ACTIVATION AND ROTATIONAL BEHAVIOUR IN MICE Hiroshi WATANABE, Kazuo WATANABE and Koji HAGINO Department of Pharmacometrics, Research Institute
THE INVOLVEMENT OF CATECHOLAMINE IN SCOPOLAMINE-INDUCED LOCOMOTOR ACTIVATION AND ROTATIONAL BEHAVIOUR IN MICE Hiroshi WATANABE, Kazuo WATANABE and Koji HAGINO Department of Pharmacometrics, Research Institute
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 Neuropharmacology, 1976, 15, 755-762 Self-inhibition By Dopaminergic Neurones: Disruption By (+/-)-alpha-methylp-tyrosine Pretreatment Or Anterior Diencephalic Lesions* P. M. Groves, S. J. Young and C.
Neuropharmacology, 1976, 15, 755-762 Self-inhibition By Dopaminergic Neurones: Disruption By (+/-)-alpha-methylp-tyrosine Pretreatment Or Anterior Diencephalic Lesions* P. M. Groves, S. J. Young and C.
ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE
![ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE](/thumbs/74/71109260.jpg) Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1962), 18, 161-166. ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE BY G. HERTTING,* J. AXELROD AND R. W. PATRICK From the Laboratory of Clinical
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1962), 18, 161-166. ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE BY G. HERTTING,* J. AXELROD AND R. W. PATRICK From the Laboratory of Clinical
1. The relationship between tremor and change in brain acetylcholine concentration. by injection of tremorine or oxotremorine in the rat
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1969), 35, 295-303. The relationship between tremor and change in brain acetylcholine concentration produced by injection of tremorine or oxotremorine in the rat B. COX AND D. POTKONJAK
Br. J. Pharmac. (1969), 35, 295-303. The relationship between tremor and change in brain acetylcholine concentration produced by injection of tremorine or oxotremorine in the rat B. COX AND D. POTKONJAK
ROLE OF ADRENAL HORMONES IN MAINTAINING TISSUE STORES OF NORADRENALINE DURING INCREASED SYMPATHETIC ACTIVITY
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1966), 27, 532-535. ROLE OF ADRENAL HORMONES IN MAINTAINING TISSUE STORES OF NORADRENALINE DURING INCREASED SYMPATHETIC ACTIVITY BY V. M. AVAKIAN* AND MARTHE VOGT From the Agricultural
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1966), 27, 532-535. ROLE OF ADRENAL HORMONES IN MAINTAINING TISSUE STORES OF NORADRENALINE DURING INCREASED SYMPATHETIC ACTIVITY BY V. M. AVAKIAN* AND MARTHE VOGT From the Agricultural
A STUDY OF THE ROLE OF BRAIN CATECHOLAMINES IN DRUG INDUCED TREMOR
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1967), 3, 349-353. A STUDY OF THE ROLE OF BRAIN CATECHOLAMINES IN DRUG INDUCED TREMOR BY S. L. AGARWAL AND D. BOSE From the Department of Pharmacology, M.G.M. Medical College,
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1967), 3, 349-353. A STUDY OF THE ROLE OF BRAIN CATECHOLAMINES IN DRUG INDUCED TREMOR BY S. L. AGARWAL AND D. BOSE From the Department of Pharmacology, M.G.M. Medical College,
INDUCED BY PERUVOSIDE AND OUABAIN IN CATS
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1975), 54, 157-12 ROLE OF CATECHOLAMINES IN THE CENTRAL MECHANISM OF EMETIC RESPONSE INDUCED BY PERUVOSIDE AND OUABAIN IN CATS B.B. GAITONDE & S.N. JOGLEKAR Haffkine Institute, Parel,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1975), 54, 157-12 ROLE OF CATECHOLAMINES IN THE CENTRAL MECHANISM OF EMETIC RESPONSE INDUCED BY PERUVOSIDE AND OUABAIN IN CATS B.B. GAITONDE & S.N. JOGLEKAR Haffkine Institute, Parel,
concentration in patients with Parkinsonism treated with L-dopa
 J. NeuroL Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 1-6 The cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid concentration in patients with Parkinsonism treated with L-dopa G. CURZON, R. B. GODWIN-AUSTEN, E. B. TOMLINSON,
J. NeuroL Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 1-6 The cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid concentration in patients with Parkinsonism treated with L-dopa G. CURZON, R. B. GODWIN-AUSTEN, E. B. TOMLINSON,
Amine metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid in Huntington's chorea
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 514-519 Amine metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid in Huntington's chorea G. CURZON, JOHN GUMPERT, AND DAVID SHARPE From the Institute of
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 514-519 Amine metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid in Huntington's chorea G. CURZON, JOHN GUMPERT, AND DAVID SHARPE From the Institute of
Hypothermia produced in mice by histamine
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 42, 205-214. Hypothermia produced in mice by histamine acting on the central nervous system GRAHAM G. SHAW Pharmacology Laboratories, Department of Pharmacy, University of Nottingham,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 42, 205-214. Hypothermia produced in mice by histamine acting on the central nervous system GRAHAM G. SHAW Pharmacology Laboratories, Department of Pharmacy, University of Nottingham,
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/300/97-FINAL November 1997 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS AZAPERONE SUMMARY REPORT
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/300/97-FINAL November 1997 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS AZAPERONE SUMMARY REPORT
Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 139-143. Effect of cocaine on the affinity of a-adrenoceptors for noradrenaline I. R. INNES AND R. MAILHOT* Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Faculty of Medicine,
EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL ON DOPAMINE DEPENDENT BEHAVIOURS IN RATS
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1999; 43 (1) : 44-52 EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL ON DOPAMINE DEPENDENT BEHAVIOURS IN RATS A. R. MALEKAR, J. J. BALSARA* AND R. K. GAONKAR Department of Pharmacology, Krishna Institute
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1999; 43 (1) : 44-52 EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL ON DOPAMINE DEPENDENT BEHAVIOURS IN RATS A. R. MALEKAR, J. J. BALSARA* AND R. K. GAONKAR Department of Pharmacology, Krishna Institute
LEVODOPA IN PATIENTS WITH PARKINSONISM
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1974), 1, 417424 THE ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF A STANDARD ORAL DOSE OF LEVODOPA IN PATIENTS WITH PARKINSONISM S. BERGMANN' National Hospital, Queen Square, London WC1 G. CURZON
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1974), 1, 417424 THE ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF A STANDARD ORAL DOSE OF LEVODOPA IN PATIENTS WITH PARKINSONISM S. BERGMANN' National Hospital, Queen Square, London WC1 G. CURZON
Pharmacological significance of biogenic amines in the lungs: noradrenaline and dopanine
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 38, 374-385. Pharmacological significance of biogenic amines in the lungs: noradrenaline and dopanine DOMINGO M. AVIADO AND CHIRAVAT SADAVONGVIVAD* Department of Pharmacology, School
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 38, 374-385. Pharmacological significance of biogenic amines in the lungs: noradrenaline and dopanine DOMINGO M. AVIADO AND CHIRAVAT SADAVONGVIVAD* Department of Pharmacology, School
Effects of amphetamine on the turnover rate of brain catecholamines and motor activity
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 44, 742-751. Effects of amphetamine on the turnover rate of brain catecholamines and motor activity E. COSTA, A. GROPPETTI* AND M. K. NAIMZADA* Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 44, 742-751. Effects of amphetamine on the turnover rate of brain catecholamines and motor activity E. COSTA, A. GROPPETTI* AND M. K. NAIMZADA* Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology,
DEPLETION AND REPLACEMENT OF THE ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE CONTENTS OF THE RAT ADRENAL GLAND, FOLLOWING TREATMENT WITH RESERPINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1962), 18, 138-149. DEPLETION AND REPLACEMENT OF THE ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE CONTENTS OF THE RAT ADRENAL GLAND, FOLLOWING TREATMENT WITH RESERPINE BY B. A. CALLINGHAM AND MONICA
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1962), 18, 138-149. DEPLETION AND REPLACEMENT OF THE ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE CONTENTS OF THE RAT ADRENAL GLAND, FOLLOWING TREATMENT WITH RESERPINE BY B. A. CALLINGHAM AND MONICA
suggesting that the release of noradrenaline from sympathetic fibres was dependent on the concentration of Ca2+ outside the fibre.
 214 J. Phy8iol. (1965), 181, pp. 214-223 With 4 text-figurem Printed in Great Britain THE RELEASE OF NORADRENALINE FROM SYMPATHETIC FIBRES IN RELATION TO CALCIUM CONCENTRATION BY J. H. BURN AND W. R. GIBBONS
214 J. Phy8iol. (1965), 181, pp. 214-223 With 4 text-figurem Printed in Great Britain THE RELEASE OF NORADRENALINE FROM SYMPATHETIC FIBRES IN RELATION TO CALCIUM CONCENTRATION BY J. H. BURN AND W. R. GIBBONS
THE LACK OF CROSSED TACHYPHYLAXIS BETWEEN TYRAMINE AND SOME OTHER INDIRECTLY ACTING SYMPATHOMIMETIC AMINES
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chenother. (1967). 30, 631-643. THE LACK OF CROSSED TACHYPHYLAXIS BETWEEN TYRAMINE AND SOME OTHER INDIRECTLY ACTING SYMPATHOMIMETIC AMINES BY M. D. DAY* From the Pharmacology Laboratories,
Br. J. Pharmac. Chenother. (1967). 30, 631-643. THE LACK OF CROSSED TACHYPHYLAXIS BETWEEN TYRAMINE AND SOME OTHER INDIRECTLY ACTING SYMPATHOMIMETIC AMINES BY M. D. DAY* From the Pharmacology Laboratories,
Interrelationship between Angiotensin Catecholamines. Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D.
 Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
INTERACTIONS BETWEEN COCAINE, TYRAMINE AND NORADRENALINE AT THE NORADRENALINE STORE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 2, 54-549. INTERACTIONS BETWEEN COCAINE, TYRAMINE AND NORADRENALINE AT THE NORADRENALINE STORE BY J. FARRANT* From the Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, University
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 2, 54-549. INTERACTIONS BETWEEN COCAINE, TYRAMINE AND NORADRENALINE AT THE NORADRENALINE STORE BY J. FARRANT* From the Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, University
Changes in brain catecholamine levels in human
 Changes in brain catecholamine levels in human cirrhotic hepatic encephalopathy G CUILLERET, G POMIER-LAYRARGUES, F PONS, J CADILHAC, AND H MICHEL Gut, 1980, 21, 565-569 From the Clinique des Maladies
Changes in brain catecholamine levels in human cirrhotic hepatic encephalopathy G CUILLERET, G POMIER-LAYRARGUES, F PONS, J CADILHAC, AND H MICHEL Gut, 1980, 21, 565-569 From the Clinique des Maladies
THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1974), 46, 473 THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO M. R. WASSEF, H. LAL AND BARBARA J. PLEUVRY SUMMARY The cardiovascular effects
Br. J. Anaesth. (1974), 46, 473 THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO M. R. WASSEF, H. LAL AND BARBARA J. PLEUVRY SUMMARY The cardiovascular effects
ANTAGONISM OF THE BLOCKING ACTION OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE PRESSOR EFFECT OF PHYSOSTIGMINE IN THE RAT
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1965), 24, 624-631. ANTAGONISM OF THE BLOCKING ACTION OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE PRESSOR EFFECT OF PHYSOSTIGMINE IN THE RAT BY S. D. GOKHALE, 0. D. GULATI AND N. Y. JOSHI
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1965), 24, 624-631. ANTAGONISM OF THE BLOCKING ACTION OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE PRESSOR EFFECT OF PHYSOSTIGMINE IN THE RAT BY S. D. GOKHALE, 0. D. GULATI AND N. Y. JOSHI
with partial nigrostriatal lesions (dihydroxyphenylacetic acid/homovanillic acid/striatum)
 Proc. Nat!. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 77, No. 7, pp. 4305-4309, July 1980 Medical Sciences Tyrosine administration increases striatal dopamine release in rats with partial nigrostriatal lesions (dihydroxyphenylacetic
Proc. Nat!. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 77, No. 7, pp. 4305-4309, July 1980 Medical Sciences Tyrosine administration increases striatal dopamine release in rats with partial nigrostriatal lesions (dihydroxyphenylacetic
ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE
 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE V. P. GADA. V. V. JOSHI. J. J. BALSARA AND A. G. CHANDORKAR Department
SHORT COMMUNICATION ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE V. P. GADA. V. V. JOSHI. J. J. BALSARA AND A. G. CHANDORKAR Department
Schizophrenic twin. Normal twin
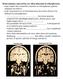 Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF ACTION OF AMANTADINE
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1976), 58, 561-567 STUDIS ON TH MCHANISM OF ACTION OF AMANTADIN F. BROWN & P.H. RDFRN School of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, University of Bath, Claverton Down, Bath BA2 7AY I The effect
Br. J. Pharmac. (1976), 58, 561-567 STUDIS ON TH MCHANISM OF ACTION OF AMANTADIN F. BROWN & P.H. RDFRN School of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, University of Bath, Claverton Down, Bath BA2 7AY I The effect
Effect of frequency of stimulation on the inhibition by noradrenaline of the acetylcholine output from
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 263-272. Effect of frequency of stimulation on the inhibition by noradrenaline of the acetylcholine output from parasympathetic nerve terminals J. KNOLL AND E. S. VIZI Department
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 263-272. Effect of frequency of stimulation on the inhibition by noradrenaline of the acetylcholine output from parasympathetic nerve terminals J. KNOLL AND E. S. VIZI Department
Chlorogenic acid, a polyphenolic compound, ameliorated haloperidol-induced orofacial dyskinesia and catalepsy in rats
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
Growth hormone and prolactin response to bromocriptine in patients with Huntington's chorea
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 135-139 Growth hormone and prolactin response to bromocriptine in patients with Huntington's chorea R. J. CHALMERS, R. H. JOHNSON, H. J. KEOGH,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 135-139 Growth hormone and prolactin response to bromocriptine in patients with Huntington's chorea R. J. CHALMERS, R. H. JOHNSON, H. J. KEOGH,
Final Exam PSYC2022. Fall (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication with cannabis.
 Final Exam PSYC2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Give 2 reasons why it is important for psychological disorders to be accurately diagnosed. (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication
Final Exam PSYC2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Give 2 reasons why it is important for psychological disorders to be accurately diagnosed. (1 point) True or False. The DSM-IV describes the symptoms of acute intoxication
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
Comparative chronotropic activity of 3-adrenoceptive antagonists
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 40, 373-381. Comparative chronotropic activity of 3-adrenoceptive antagonists A. M. BARRETT* AND J. CARTER Department of Pharmacology, Imperial Chemical Industries, Pharmaceutticals
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 40, 373-381. Comparative chronotropic activity of 3-adrenoceptive antagonists A. M. BARRETT* AND J. CARTER Department of Pharmacology, Imperial Chemical Industries, Pharmaceutticals
Blockade of biogenic amine synthesis: its effect on the responses to leptazol and dexamphetamine in rats
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1969), 37, 94-13. Blockade of biogenic amine synthesis: its effect on the responses to leptazol and dexamphetamine in rats P. S. J. SPNCR AND T. A. R. TURNR Departmenit of Pharmacy, Unziversity
Br. J. Pharmac. (1969), 37, 94-13. Blockade of biogenic amine synthesis: its effect on the responses to leptazol and dexamphetamine in rats P. S. J. SPNCR AND T. A. R. TURNR Departmenit of Pharmacy, Unziversity
The occurrence of tolerance to a central depressant effect of nicotine
 Br. J. Pharmac. (I1 Th), 45, 151-156. The occurrence of tolerance to a central depressant effect of nicotine CATHLEEN F. MORRISON AND JANE A. STEPHENSON Tobacco Research Council Laboratories, Otley Road,
Br. J. Pharmac. (I1 Th), 45, 151-156. The occurrence of tolerance to a central depressant effect of nicotine CATHLEEN F. MORRISON AND JANE A. STEPHENSON Tobacco Research Council Laboratories, Otley Road,
A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 748-754. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs A. T. BIRMINGHAM*, G. PATRSON AND J. W6JCICKIt Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 748-754. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs A. T. BIRMINGHAM*, G. PATRSON AND J. W6JCICKIt Department of Pharmacology,
SOME PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIONS OF DIETHYLDITHIOCARBAMATE ON RABBIT AND RAT ILEUM
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 42-49. SOME PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIONS OF DIETHYLDITHIOCARBAMATE ON RABBIT AND RAT ILEUM BY G. G. S. COLLINS* AND G. B. WESTt From the Department of Pharmacology, School
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 42-49. SOME PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIONS OF DIETHYLDITHIOCARBAMATE ON RABBIT AND RAT ILEUM BY G. G. S. COLLINS* AND G. B. WESTt From the Department of Pharmacology, School
following a period of adaptation of 60 min in the supine position. Blood flow in the calf and forefoot was measured
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1980), 10, 115S- 121S ACUTE ACTION OF GUANFACINE ON PERIPHERAL CIRCULATION IN HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS: MEASUREMENTS OF ARTERIAL FLOW OF THE CALF AND OF THE FOREFOOT, OF VENOUS CAPACITY
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1980), 10, 115S- 121S ACUTE ACTION OF GUANFACINE ON PERIPHERAL CIRCULATION IN HYPERTENSIVE PATIENTS: MEASUREMENTS OF ARTERIAL FLOW OF THE CALF AND OF THE FOREFOOT, OF VENOUS CAPACITY
Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003
 Psychological Disorders: General Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 1. What are psychological disorders? 2. What was the main treatment for some psychological disorders prior to the 1950 s? 3. What
Psychological Disorders: General Study Guide Unit 3 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 1. What are psychological disorders? 2. What was the main treatment for some psychological disorders prior to the 1950 s? 3. What
Dopamine-s-Hydroxylase in the Rat Superior Cervical Ganglia
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 68, No. 7, pp. 1598-1602, July 1971 Selective Induction by Nerve Growth Factor of Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Dopamine-s-Hydroxylase in the Rat Superior Cervical Ganglia (dopa
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 68, No. 7, pp. 1598-1602, July 1971 Selective Induction by Nerve Growth Factor of Tyrosine Hydroxylase and Dopamine-s-Hydroxylase in the Rat Superior Cervical Ganglia (dopa
Effect of restraint stress on rat brain serotonin
 Biosci., Vol. 4, Number 3, September 1982, pp. 269-274. Printed in India. Effect of restraint stress on rat brain serotonin S. K. BHATTACHARYA and D. BHATTACHARYA Department of Pharmacology, Institute
Biosci., Vol. 4, Number 3, September 1982, pp. 269-274. Printed in India. Effect of restraint stress on rat brain serotonin S. K. BHATTACHARYA and D. BHATTACHARYA Department of Pharmacology, Institute
EVIDENCE FOR CATECHOLAMINE-DEPLETING ACTION OF FLUOXETlNE
 indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1994; 38(3) : 169-173 EVIDENCE FOR CATECHOLAMINE-DEPLETING ACTION OF FLUOXETlNE MILIND R. PATIL, MILAN C. SATIA, ANITA A. MEHTA AND RAMESH K. GOYAL * Department of Pharmacology,
indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1994; 38(3) : 169-173 EVIDENCE FOR CATECHOLAMINE-DEPLETING ACTION OF FLUOXETlNE MILIND R. PATIL, MILAN C. SATIA, ANITA A. MEHTA AND RAMESH K. GOYAL * Department of Pharmacology,
CSF studies on the relationship between dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in Parkinsonism and other
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 1136-1141 CSF studies on the relationship between dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in Parkinsonism and other movement disorders D. L. W. DAVIDSON'
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 1136-1141 CSF studies on the relationship between dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in Parkinsonism and other movement disorders D. L. W. DAVIDSON'
Brain dopamine and mild hypoxia
 Brain dopamine and mild hypoxia Denoroy L, Orset C, Parrot S, Berod A, Sauvinet V, Cottet-Emard JM, Pequignot JM. Université Claude Bernard, Lyon, France Striatum vulnerable to hypoxia ischemia necrotic
Brain dopamine and mild hypoxia Denoroy L, Orset C, Parrot S, Berod A, Sauvinet V, Cottet-Emard JM, Pequignot JM. Université Claude Bernard, Lyon, France Striatum vulnerable to hypoxia ischemia necrotic
THE MODIFICATION BY PHYSOSTIGMINE OF SOME EFFECTS OF NICOTINE ON BAR-PRESSING BEHAVIOUR OF RATS
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 28-33. THE MODIFICATION BY PHYSOSTIGMINE OF SOME EFFECTS OF NICOTINE ON BAR-PRESSING BEHAVIOUR OF RATS BY CATHLEEN F. MORRISON From the Tobacco Research Council Laboratories,
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 28-33. THE MODIFICATION BY PHYSOSTIGMINE OF SOME EFFECTS OF NICOTINE ON BAR-PRESSING BEHAVIOUR OF RATS BY CATHLEEN F. MORRISON From the Tobacco Research Council Laboratories,
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2000
 The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2000 Press Release NOBELFÖRSAMLINGEN KAROLINSKA INSTITUTET THE NOBEL ASSEMBLY AT THE KAROLINSKA INSTITUTE 9 October 2000 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2000 Press Release NOBELFÖRSAMLINGEN KAROLINSKA INSTITUTET THE NOBEL ASSEMBLY AT THE KAROLINSKA INSTITUTE 9 October 2000 The Nobel Assembly at Karolinska Institutet
A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: INCREASED MAXIMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATIVE NORADREN- ALINE IN THE ISOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 171-176. A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: NCREASED MAXMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATVE NORADREN- ALNE N THE SOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS BY A. BARNETT, D. D. GREENHOUSE AND R..
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 171-176. A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: NCREASED MAXMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATVE NORADREN- ALNE N THE SOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS BY A. BARNETT, D. D. GREENHOUSE AND R..
THE ACTION OF PROMETHAZINE (PHENERGAN) DUE TO HISTAMINE IN PROTECTING MICE AGAINST DEATH
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 510. THE ACTION OF PROMETHAZINE (PHENERGAN) IN PROTECTING MICE AGAINST DEATH DUE TO HISTAMINE BY B. N. HALPERN * AND D. R. WOODt From the Clinique Medicale Propedeutique
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 510. THE ACTION OF PROMETHAZINE (PHENERGAN) IN PROTECTING MICE AGAINST DEATH DUE TO HISTAMINE BY B. N. HALPERN * AND D. R. WOODt From the Clinique Medicale Propedeutique
C'4-tryptophan in rat pineals in organ culture. Other compounds related in
 STIMULATION OF C14-MELATONIN SYNTHESIS FROM C14-TRYPTOPHAN BY NORADRENALINE IN RAT PINEAL IN ORGAN CULTURE* BY JULIUS AXELROD, HARVEY M. SHEIN, AND RICHARD J. WURTMAN LABORATORY OF CLINICAL SCIENCE, NATIONAL
STIMULATION OF C14-MELATONIN SYNTHESIS FROM C14-TRYPTOPHAN BY NORADRENALINE IN RAT PINEAL IN ORGAN CULTURE* BY JULIUS AXELROD, HARVEY M. SHEIN, AND RICHARD J. WURTMAN LABORATORY OF CLINICAL SCIENCE, NATIONAL
PRESYNAPTIC cx-adrenoceptor BLOCKING PROPERTIES AMONG
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1979), 67, 511-517 PRESYNAPTIC cx-adrenoceptor BLOCKING PROPERTIES AMONG TRI- AND TETRA-CYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS BARBARA HARPER & I.E. HUGHES Department of Pharmacology, Medical and
Br. J. Pharmac. (1979), 67, 511-517 PRESYNAPTIC cx-adrenoceptor BLOCKING PROPERTIES AMONG TRI- AND TETRA-CYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS BARBARA HARPER & I.E. HUGHES Department of Pharmacology, Medical and
Role of Clozapine in Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia
 Disease Management and Treatment Strategies Elkis H, Meltzer HY (eds): Therapy-Resistant Schizophrenia. Adv Biol Psychiatry. Basel, Karger, 2010, vol 26, pp 114 128 Role of Clozapine in Treatment-Resistant
Disease Management and Treatment Strategies Elkis H, Meltzer HY (eds): Therapy-Resistant Schizophrenia. Adv Biol Psychiatry. Basel, Karger, 2010, vol 26, pp 114 128 Role of Clozapine in Treatment-Resistant
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE OF
 Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Autonomic Nervous System
 ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
ouabain and their modification by other drugs
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 42, 242-253. Pharmacological properties of centrally administered ouabain and their modification by other drugs N. S. DOGGETT AND P. S. J. SPENCER* Pharmacological Laboratories,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 42, 242-253. Pharmacological properties of centrally administered ouabain and their modification by other drugs N. S. DOGGETT AND P. S. J. SPENCER* Pharmacological Laboratories,
Project Coordinators
 PHARMACOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF AV MEMVITA CAPSULES FOR ANTIPARKINSON ACTIVITY Project Coordinators Dr. Vikram Naharwar Dr. Pratima Tatke Ms. Sonal Kasbe Managing Director Research Guide Junior Research
PHARMACOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF AV MEMVITA CAPSULES FOR ANTIPARKINSON ACTIVITY Project Coordinators Dr. Vikram Naharwar Dr. Pratima Tatke Ms. Sonal Kasbe Managing Director Research Guide Junior Research
MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 539-545. MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE BY K. SHIMAMOTO AND N. TODA From the Department
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 539-545. MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE BY K. SHIMAMOTO AND N. TODA From the Department
THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS
 Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production
 Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production Experiments presented in this chapter were designed to investigate the possible mechanisms
Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production Experiments presented in this chapter were designed to investigate the possible mechanisms
NEUROPSYCHIATRY DSM (PYDI 0416) FALL, 1999 MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY OF ANTIPSYCHOTICS DR. RILEY A. INTRODUCTION
 EUPYCIATY DM (PYDI 0416) ALL, 1999 MEDICIAL CEMITY ATIPYCTIC D. ILEY A. ITDUCTI Antipsychotic (neuroleptic) agents are primarily used in the therapy of schizophrenia, organic psychoses, the manic phase
EUPYCIATY DM (PYDI 0416) ALL, 1999 MEDICIAL CEMITY ATIPYCTIC D. ILEY A. ITDUCTI Antipsychotic (neuroleptic) agents are primarily used in the therapy of schizophrenia, organic psychoses, the manic phase
STUDIES ON THE EXPERIMENTAL GASTROINTESTINAL ULCERS PRODUCED BY RESERPINE AND STRESS II. ULCEROGENIC ACTIVITIES OF RESERPINE AND ITS ANALOGUES
 STUDIES ON THE EXPERIMENTAL GASTROINTESTINAL ULCERS PRODUCED BY RESERPINE AND STRESS II. ULCEROGENIC ACTIVITIES OF RESERPINE AND ITS ANALOGUES MASAMI DOTEUCHI Division of Neuropharmacology, Shionogi Research
STUDIES ON THE EXPERIMENTAL GASTROINTESTINAL ULCERS PRODUCED BY RESERPINE AND STRESS II. ULCEROGENIC ACTIVITIES OF RESERPINE AND ITS ANALOGUES MASAMI DOTEUCHI Division of Neuropharmacology, Shionogi Research
ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (195), 5, 195. THE SITE OF ACTION OF PHENERGAN AND NEOANTERGAN ON BODY TEMPERATURE AND OXYGEN CONSUMPTION IN NORMAL AND ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS BY D. R. WOOD From the Department of Pharmacology,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (195), 5, 195. THE SITE OF ACTION OF PHENERGAN AND NEOANTERGAN ON BODY TEMPERATURE AND OXYGEN CONSUMPTION IN NORMAL AND ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS BY D. R. WOOD From the Department of Pharmacology,
Antipsychotics. BMF 84 - Antipsychotics
 Antipsychotics BMF 84 - Antipsychotics Antipsychotic medications (neuroleptics) are used for the treatment of psychosis, mainly schizophrenia and manic depression (bipolar disorder). They reduce symptoms
Antipsychotics BMF 84 - Antipsychotics Antipsychotic medications (neuroleptics) are used for the treatment of psychosis, mainly schizophrenia and manic depression (bipolar disorder). They reduce symptoms
Schizophrenia, Psychosis, and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Homovanillic Acid Concentrations
 Schizophrenia, Psychosis, and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Homovanillic Acid Concentrations by James W. Maas, Charles L. Bowden, Alexander L. Miller, Martin A. Javors, Linda Q. Funderburg, Nancy Bertram, and
Schizophrenia, Psychosis, and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Homovanillic Acid Concentrations by James W. Maas, Charles L. Bowden, Alexander L. Miller, Martin A. Javors, Linda Q. Funderburg, Nancy Bertram, and
Antipsychotics. Neuroleptics/ Major Tranquilizers. Hiwa K. Saaed, PhD Pharmacology & Toxicology /5/18 1
 Antipsychotics Neuroleptics/ Major Tranquilizers Hiwa K. Saaed, PhD Pharmacology & Toxicology hiwa.saaed@univsul.edu.iq 2018-2019 12/5/18 1 Learning objectives Pharmacy students should: be familiar with
Antipsychotics Neuroleptics/ Major Tranquilizers Hiwa K. Saaed, PhD Pharmacology & Toxicology hiwa.saaed@univsul.edu.iq 2018-2019 12/5/18 1 Learning objectives Pharmacy students should: be familiar with
Dopamine-Sensitive Adenylate Cyclase in Caudate Nucleus of Rat Brain,
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 69, No. 8, pp. 2145-2149, August 1972 Dopamine-Sensitive Adenylate Cyclase in Caudate Nucleus of Rat Brain, and Its Similarity to the "Dopamine Receptor" (extrapyramidal
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 69, No. 8, pp. 2145-2149, August 1972 Dopamine-Sensitive Adenylate Cyclase in Caudate Nucleus of Rat Brain, and Its Similarity to the "Dopamine Receptor" (extrapyramidal
Action of fenfluramine on monoamine stores of rat tissues
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 57-64. Action of fenfluramine on monoamine stores of rat tissues E. STA, A. GROPPETTI AND A. REVUELTA Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology, National Institute of Mental Health,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 57-64. Action of fenfluramine on monoamine stores of rat tissues E. STA, A. GROPPETTI AND A. REVUELTA Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology, National Institute of Mental Health,
Chapter 161 Antipsychotics
 Chapter 161 Antipsychotics Episode Overview Extrapyramidal syndromes are a common complication of antipsychotic medications. First line treatment is benztropine or diphenhydramine. Lorazepam is used in
Chapter 161 Antipsychotics Episode Overview Extrapyramidal syndromes are a common complication of antipsychotic medications. First line treatment is benztropine or diphenhydramine. Lorazepam is used in
The removal of noradrenaline in the pulmonary circulation of rat isolated lungs
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 47, 325-331. The removal of noradrenaline in the pulmonary circulation of rat isolated lungs VALERIE A. ALABASTER AND Y. S. BAKHLE Departtent of Pharmacology, Institute of Basic
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 47, 325-331. The removal of noradrenaline in the pulmonary circulation of rat isolated lungs VALERIE A. ALABASTER AND Y. S. BAKHLE Departtent of Pharmacology, Institute of Basic
Monoamine oxidase in sympathetic nerves: a transmitter specific enzyme type
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 814-818. Monoamine oxidase in sympathetic nerves: a transmitter specific enzyme type C. GORIDIS AND N. H. NEFF Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology, National Institute of
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 814-818. Monoamine oxidase in sympathetic nerves: a transmitter specific enzyme type C. GORIDIS AND N. H. NEFF Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology, National Institute of
Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
A COMPARISON OF TRANSMITTER AND SYNEPHRINE ON LUMINESCENCE INDUCTION IN THE FIREFLY LARVA
 J. Exp. Biol. (197a), 57. 737-743 737 ^Vith 5 text-figures WPrinted in Great Britain A COMPARISON OF TRANSMITTER AND SYNEPHRINE ON LUMINESCENCE INDUCTION IN THE FIREFLY LARVA BY ALBERT D. CARLSON Department
J. Exp. Biol. (197a), 57. 737-743 737 ^Vith 5 text-figures WPrinted in Great Britain A COMPARISON OF TRANSMITTER AND SYNEPHRINE ON LUMINESCENCE INDUCTION IN THE FIREFLY LARVA BY ALBERT D. CARLSON Department
CLOZAPINE. Clozapine, (trade name Clopine and Clozaril in Australia) is a second generation atypical antipsychotic agent.
 CLOZAPINE Introduction Clozapine, (trade name Clopine and Clozaril in Australia) is a second generation atypical antipsychotic agent. Due to its potential for significant toxicity, it is reserved for patients
CLOZAPINE Introduction Clozapine, (trade name Clopine and Clozaril in Australia) is a second generation atypical antipsychotic agent. Due to its potential for significant toxicity, it is reserved for patients
INTRODUCTION. Int J Pharm Bio Sci. Mayur Bhurat* et al
 Page420 Preclinical Evaluation of Remusatia Vivipara Leaves Extracts On Haloperidol Induced Catalepsy In Experimental Animals Mayur Bhurat*, Mohd. Nasir, Swati More, Rupal Sanghavi, Pankaj Salunkhe & Arvind
Page420 Preclinical Evaluation of Remusatia Vivipara Leaves Extracts On Haloperidol Induced Catalepsy In Experimental Animals Mayur Bhurat*, Mohd. Nasir, Swati More, Rupal Sanghavi, Pankaj Salunkhe & Arvind
University of Groningen. Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan
 University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
SAFETY ASPECTS OF MIDAZOLAM
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 37S-41S Biological Pharmaceutical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co Ltd, CH-4002 Basle, Switzerland 1 The LD50 in the rat and the mouse is about 1600 mg/kg
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1983), 16, 37S-41S Biological Pharmaceutical Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche & Co Ltd, CH-4002 Basle, Switzerland 1 The LD50 in the rat and the mouse is about 1600 mg/kg
Relationship between rat brain and cisternal CSF
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 239-243 Relationship between rat brain and cisternal CSF tryptophan concentrations' SIMON N. YOUNG,2 PIERRE ETIENNE,3 AND THEODORE L. SOURKES
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 239-243 Relationship between rat brain and cisternal CSF tryptophan concentrations' SIMON N. YOUNG,2 PIERRE ETIENNE,3 AND THEODORE L. SOURKES
Accepted June 11, 1976
 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDIES ON TRIAZINE DERIVATIVES V. SEDATIVE AND NEUROLEPTIC ACTIONS OF 2-AMINO-4-[4 (2-HYDROXYETHYL)-PIPERAZIN-1-YL]-6-TRIFLUOROMETHYL s-triazine (TR-10) Akihiro TOBE and Toshikatsu KOBAYASHI
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDIES ON TRIAZINE DERIVATIVES V. SEDATIVE AND NEUROLEPTIC ACTIONS OF 2-AMINO-4-[4 (2-HYDROXYETHYL)-PIPERAZIN-1-YL]-6-TRIFLUOROMETHYL s-triazine (TR-10) Akihiro TOBE and Toshikatsu KOBAYASHI
approached by recording the concentration of end-products of dopamine metabolism (Received 24 June 1983)
 J. Phy8i0l. (1984), 348, pp. 457-469 457 With 3 text-ftgures Printed in Great Britain ON THE SIGNIFICANCE OF MONOAMINES AND THEIR METABOLITES IN THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF THE SHEEP BY M. RUCKEBUSCH AND
J. Phy8i0l. (1984), 348, pp. 457-469 457 With 3 text-ftgures Printed in Great Britain ON THE SIGNIFICANCE OF MONOAMINES AND THEIR METABOLITES IN THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID OF THE SHEEP BY M. RUCKEBUSCH AND
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work!
 PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
PHRM20001: Pharmacology - How Drugs Work Drug: a chemical that affects physiological function in a specific way. Endogenous substances: hormones, neurotransmitters, antibodies, genes. Exogenous substances:
Antagonism of Hypotensive and Bradycardic Effects. of Centrally Administered Guanfacine by. Metiamide in Anesthetized Rabbits
 Antagonism of Hypotensive and Bradycardic Effects of Centrally Administered Guanfacine by Metiamide in Anesthetized Rabbits Takeshi OTORII, M.D., Ph.D., Kazuhiro OHKUBO, and Kenichi SUZUKI SUMMA In anesthetized
Antagonism of Hypotensive and Bradycardic Effects of Centrally Administered Guanfacine by Metiamide in Anesthetized Rabbits Takeshi OTORII, M.D., Ph.D., Kazuhiro OHKUBO, and Kenichi SUZUKI SUMMA In anesthetized
Preliminary studies of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 137-142 Preliminary studies of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of prochlorperazine in healthy volunteers WENDY B. TAYLOR & D. N. BATEMAN Wolfson Unit of Clinical
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1987), 23, 137-142 Preliminary studies of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of prochlorperazine in healthy volunteers WENDY B. TAYLOR & D. N. BATEMAN Wolfson Unit of Clinical
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Further evidence for the involvement of kinin in anaphylactic shock in the rat
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1969), 37, 178-184. Further evidence for the involvement of kinin in anaphylactic shock in the rat M. S. STARR* AND G. B. WESTt Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, University
Br. J. Pharmac. (1969), 37, 178-184. Further evidence for the involvement of kinin in anaphylactic shock in the rat M. S. STARR* AND G. B. WESTt Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, University
ISOLATED GUINEA-PIG ATRIA
 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMAOLOGY AND EXPERIMEN ral THERAPEUTIS opyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins o. vol. 168, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. THE NEGATIVE HRONOTROPI EFFET OF TYRAMINE ON ISOLATED GUINEA-PIG ATRIA
THE JOURNAL OF PHARMAOLOGY AND EXPERIMEN ral THERAPEUTIS opyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins o. vol. 168, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A. THE NEGATIVE HRONOTROPI EFFET OF TYRAMINE ON ISOLATED GUINEA-PIG ATRIA
THE INTERACTION OF SOME STIMULANT AND DEPRESSANT DRUGS ON THE FROG HEART
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 21, 78-83. THE INTERACTION OF SOME STIMULANT AND DEPRESSANT DRUGS ON THE FROG HEART BY J. L. BROADBENT From the Smith Kline & French Research Institute, Welwyn Garden City,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 21, 78-83. THE INTERACTION OF SOME STIMULANT AND DEPRESSANT DRUGS ON THE FROG HEART BY J. L. BROADBENT From the Smith Kline & French Research Institute, Welwyn Garden City,
Pharmacological significance of biogenic amines in the lungs: histamine
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 38, 366-373. Pharmacological significance of biogenic amines in the lungs: histamine DOMINGO M. AVIADO AND CHIRAVAT SADAVONGVIVAD* Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 38, 366-373. Pharmacological significance of biogenic amines in the lungs: histamine DOMINGO M. AVIADO AND CHIRAVAT SADAVONGVIVAD* Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine,
Effect of Panax Ginseng on Age-Related Changes in the Spontaneous Motor Activity and Dopaminergic Nervous System in the Rat
 Japan. J. Pharmacol. 55, 51-56 (1991) Effect of Panax Ginseng on Age-Related Changes in the Spontaneous Motor Activity and Dopaminergic Nervous System in the Rat Hiroshi Watanabe, Hiroyuki Ohta, Lisa Imamura,
Japan. J. Pharmacol. 55, 51-56 (1991) Effect of Panax Ginseng on Age-Related Changes in the Spontaneous Motor Activity and Dopaminergic Nervous System in the Rat Hiroshi Watanabe, Hiroyuki Ohta, Lisa Imamura,
Behaviors of Mice Given Forced-Swimming
 Exp. Anim. 50(4), 331 335, 2001 Behaviors of Mice Given Forced-Swimming Yutaka MASUDA 1), Seiki ISHIGOOKA 2), and Yukihisa MATSUDA 2) 1) Psychosomatic Division and 2) Animal Facilities for Experimental
Exp. Anim. 50(4), 331 335, 2001 Behaviors of Mice Given Forced-Swimming Yutaka MASUDA 1), Seiki ISHIGOOKA 2), and Yukihisa MATSUDA 2) 1) Psychosomatic Division and 2) Animal Facilities for Experimental
A method for the estimation of the catecholamines and their metabolites in brain tissue
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 38, 56-71. A method for the estimation of the catecholamines and their metabolites in brain tissue T. B. B. CRAWFORD AND CELIA M. YATES M.R.C. Unit for Research in Brain Metabolism,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 38, 56-71. A method for the estimation of the catecholamines and their metabolites in brain tissue T. B. B. CRAWFORD AND CELIA M. YATES M.R.C. Unit for Research in Brain Metabolism,
INVESTIGATION OF ADRENALINE REVERSAL IN THE RAT UTERUS BY THE INDUCTION OF RESISTANCE TO ISOPRENALINE
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1967), 29, 291-301. INVESTIGATION OF ADRENALINE REVERSAL IN THE RAT UTERUS BY THE INDUCTION OF RESISTANCE TO ISOPRENALINE BY From the Department of Pharmacology, Guy's Hospital
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1967), 29, 291-301. INVESTIGATION OF ADRENALINE REVERSAL IN THE RAT UTERUS BY THE INDUCTION OF RESISTANCE TO ISOPRENALINE BY From the Department of Pharmacology, Guy's Hospital
CHLORPROMAZINE EQUIVALENTS VERSUS DEFINED DAILY DOSES: HOW TO COMPARE ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG DOSES?
 CHLORPROMAZINE EQUIVALENTS VERSUS DEFINED DAILY DOSES: HOW TO COMPARE ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG DOSES? C.A.W. Rijcken 1, T.B.M. Monster 1, J.R.B.J. Brouwers 1, L.T.W. de Jong van den Berg 1 1 Department of Social
CHLORPROMAZINE EQUIVALENTS VERSUS DEFINED DAILY DOSES: HOW TO COMPARE ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG DOSES? C.A.W. Rijcken 1, T.B.M. Monster 1, J.R.B.J. Brouwers 1, L.T.W. de Jong van den Berg 1 1 Department of Social
