Distinct Encoding of Spatial and Nonspatial Visual Information in Parietal Cortex
|
|
|
- Rosaline Stokes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 29, (17): Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Distinct Encoding of Spatial and Nonspatial Visual Information in Parietal Cortex David J. Freedman and John A. Assad Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts It is well established that the primate parietal cortex plays an important role in visuospatial processing. Parietal cortex damage in both humans and monkeys can lead to behavioral deficits in spatial processing, and many parietal neurons, such as in the macaque lateral intraparietal area (LIP), are strongly influenced by visual spatial factors. Several recent studies have shown that LIP neurons can also convey robust signals related to nonspatial factors, such as color, shape, and the behavioral context or rule that is relevant for solving the task at hand. But what is the relationship between the encoding of spatial factors and more abstract, nonspatial, influences in LIP? To examine this, we trained monkeys to group visual motion patterns into two arbitrary categories, and recorded the activity of LIP neurons while monkeys performed a categorization task in which stimuli were presented either inside each neuron s receptive field (RF) or at a location in the opposite visual field. While the activity of nearly all LIP neurons showed strong spatial dependence (i.e., greater responses when stimuli were presented within neurons RFs), we also found that many LIP neurons also showed reliable encoding of the category membership of stimuli even when the stimuli were presented away from neurons RFs. This suggests that both spatial and nonspatial information can be encoded by individual LIP neurons, and that parietal cortex may be a nexus for the integration of visuospatial signals and more abstract task-dependent information during complex visually based behaviors. Introduction Neuropsychological and neurophysiological studies have established that the cortical areas in and around the intraparietal sulcus (IPS) are important for spatial perception and spatial behaviors such as reaching and saccadic eye movements. Damage or inactivation of these areas often results in deficits in visuospatial processing or visually guided actions (Critchley, 1953; Wardak et al., 2002). Neurophysiological studies in nonhuman primates have also given considerable support for parietal cortex s role in spatial processing. The macaque lateral intraparietal area (LIP) has been studied with particular intensity. While its precise role in visuospatial and visuomotor processing is debated, it is widely agreed that neuronal responses in LIP seem well suited for a role in spatial processing, and are neither purely sensory nor purely motor in nature. For example, most LIP neurons show short latency responses to visual stimuli presented within their receptive field (RF), but many LIP neurons also fire persistently when the animals covertly attend to or plan saccades to the location of the RF, even in the absence of an explicit visual target (Mountcastle et al., 1975; Gnadt and Andersen, 1988; Bisley et al., 2004). Received June 23, 2008; revised Jan. 17, 2009; accepted Feb. 18, This work was supported by National Eye Institute (NEI) Grant EY02106, NEI Vision Core Grant EY12196, a Kirschstein postdoctoral National Research Service Award from NEI (D.J.F.), and a postdoctoral fellowship from the Charles H. Hood Foundation (D.J.F.). For their valuable comments, help, and discussions, we thank Jamie Fitzgerald, Constance Freedman, Todd Herrington, Camillo Padoa-Schioppa, Douglas Ruff, Sruthi Swaminathan, and Daniel Zaksas. We also thank Kimberly Irwin, Tim Lafratta, and John LeBlanc for providing excellent technical assistance. Correspondence should be addressed to David J. Freedman at his present address: Department of Neurobiology, The University of Chicago, 947 East 58th Street, Abbott 310, Chicago, IL dfreedman@uchicago.edu. DOI: /JNEUROSCI Copyright 2009 Society for Neuroscience /09/ $15.00/0 Other studies have found neuronal encoding in the intraparietal sulcus that is difficult to explain based on a purely spatial processing framework. For example, in our laboratory we trained monkeys to perform a categorization task in which they grouped 360 of visual motion directions into two arbitrary groups, or categories, that were separated by a learned category boundary. Neurophysiological recordings from LIP neurons revealed encoding of the category membership of visual stimuli: neurons showed stronger and more uniform responses to all the directions in one category, and weaker responses to stimuli in the other category, with a sharp difference in activity between directions on different sides of the category boundary (Freedman and Assad, 2006). This suggested a plasticity of direction selectivity that depended on the behavioral relevance of those motion directions. Thus category selectivity in LIP could not be easily explained by differences in spatial attention or planned eye movements between the two categories, because stimuli from both categories were always presented at the same location within the RF, and because the categories were not paired with unique, spatially distinct behavioral responses (Freedman and Assad, 2006). Other studies have also shown that LIP neurons can reflect a variety of factors, such as value- and decision-related variables (Platt and Glimcher, 1999; Shadlen and Newsome, 2001; Gold and Shadlen, 2007). However, these previous studies generally required the animals to signal their behavioral report in a manner that was inherently spatial, such as an eye movement toward or away from the RF, making it difficult to dissociate the influences of spatial and nonspatial factors (Maunsell, 2004). More generally, the relationship between spatial factors and nonspatial influences in parietal cortex is unclear. Is nonspatial encoding independent of spatial encoding, or are the two related in some way?
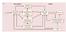
2 5672 J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP This question is central to understanding how parietal cortex integrates or associates information from different parts of the brain. For example, nonspatial information could be forwarded to LIP from neurons with discrete RFs that overlap the RFs of LIP neurons, so that spatial and nonspatial encoding would be closely intertwined. Alternatively, nonspatial information could be fed to LIP from neurons with nonoverlapping or less precise RFs, perhaps by feedback from frontal brain areas. In this study, we have addressed these issues by examining the spatial dependence of the nonspatial motion-category effects in LIP that we had observed in our previous studies (Freedman and Assad, 2006). We trained monkeys to perform a task in which they again had to identify and match the category of motion stimuli. Previously, the stimuli were always presented within each neuron s RF. Here, we examined the relationship between spatial effects and nonspatial category effects in LIP by placing the stimuli either inside the RF or outside the RF. Materials and Methods Physiological techniques. Two male rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta, 14.5 kg) were implanted with a head post, scleral search coil, and recording chamber. Recording chambers were centered at coordinates posterior 3.0 mm, lateral 10.0 mm relative to the intra-aural line and allowed access to the intraparietal sulcus via a dorsal approach. All surgical and experimental procedures followed Harvard Medical School and National Institutes of Health guidelines. Electrophysiological recordings were made from single neurons using tungsten microelectrodes (FHC, 75 m shaft diameter) and a guide-tube/grid system. Spike times were recorded with 1 ms resolution, and waveforms were sorted online using a dual amplitude time window discriminator (BAK Electronics). Horizontal and vertical eye positions were measured using the sclera search coil technique (Robinson, 1963; Judge et al., 1980) (Riverbend Instruments) and sampled at 200 Hz. During LIP recordings, electrode penetrations sequentially encountered both the medial and lateral banks of the IPS. IPS neurons were tested with a delayed memory-saccade task, and most were also tested with a spot of light flashed over a grid of locations while the animal passively fixated (grid width: 25.0, grid spacing: 5.0 ) to generate a detailed spatial map of each neuron s RF. Neurons were considered to be in LIP if they showed spatially selective delay activity during the memorysaccade task or were located between such neurons in that electrode penetration. LIP neurons were not prescreened for direction selectivity. Delayed match-to-category task. Over the course of several weeks of training, monkeys learned to group 360 of motion directions into two categories that were separated into two arbitrary groups by a learned category boundary (Fig. 1a). During training, stimuli were chosen in 1.0 increments, but for neurophysiological recordings, monkeys were tested with six evenly spaced motion directions that were either 30 or 90 from the category boundary. Two monkeys were trained to perform a delayed match-to-category (DMC) task in which they had to indicate (by releasing a lever) whether a sample and a test stimulus (separated by a 1 s delay) were in the same category (Fig. 1b). If the test stimulus was not a category match to the sample, a second test stimulus that was always a match to the sample was presented after a brief delay. The motor response (the lever Figure 1. DMC task. a, Monkeys were trained to group six evenly spaced directions of random-dot motion into two categories (corresponding to the red and blue arrows) separated by a learned category boundary. b, Monkeys performed a DMC task. A sample stimulus was followed by a delay and test stimulus. If the sample and test were in the same category (a match), the monkeywasrequiredtoreleasealeverbeforethetestdisappeared. Ifthetestwasanonmatch, therewasaseconddelayfollowed by a match (that required a lever release). Note that two directions could be visually dissimilar but belong on the same category, while visually similar directions could belong to different categories. Match and nonmatch trials were randomly interleaved. release) indicated match and was thus not rigidly associated with either category. On each trial, the directions of both sample and test stimuli were selected randomly, and the monkeys could not predict (during the sample or delay periods) whether a trial would require a lever release to the first test stimulus. Because of this task design, any neuronal selectivity observed during the sample and delay epochs could not be attributed to differences in motor planning and is due to selectivity among the sample stimuli themselves. The monkeys were initially trained to perform the DMC task with stimuli in the visual hemifield that was contralateral to their LIP recording chamber, and on a given trial, sample and test stimuli were always presented in the same location on the display monitor. After this initial training and subsequent neurophysiological recordings (these were the same two monkeys used in our previous study with the DMC task), the monkeys were given considerable practice ( 1 month of daily training sessions) on the DMC task with sample and test stimuli presented at different locations from one another within a trial, and at any location on the display monitor (the previously untrained visual hemifield was emphasized during these training sessions). During LIP recordings, we used a memory delayed saccade task and a passive RF-mapping task (see above) to identify two locations on the display monitor (one inside and one outside the RF) for further testing. Monkeys performed the DMC task in four blocks of 54 trials (on average, nine trials for each of the six sample-stimulus directions in each block), which tested each of the four possible combination of sample and test stimuli presented inside and outside of that neuron s RF (Fig. 2a). Because separate blocks were used for the four spatial conditions, the animals could come to expect the stimuli to fall either inside or outside the RF on a given trial. During recording sessions, monkeys performed at least two cycles (and often
3 Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): Figure 2. Spatial location of stimuli relative to LIP RFs and behavioral performance. a, Sample and test stimuli were presented either inside or outside LIP RFs in four blocks of 54 trials, and monkeys typically worked for two or more cycles through the four blocks. Sample stimuli were presented inside the RF in blocks 1 and 2, while test stimuli were presented inside the field in blocks 1 and 3. b, The monkeys average DMC-task performance across all recording sessions was greater than chance (50%) both for samplestimulithatwerecloseto(30 )andfartherfrom(90 )thecategoryboundary.behavioralperformancewas 85%correct when sample and test stimuli were presented either inside or outside LIP RFs, although performance was slightly worse when stimuli were presented in the ipsilateral hemifield (where the monkeys had less experience and training on the task). Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean. deg, Degress. three) through each of the four blocks. Monkeys typically completed a block of 54 trials in 5 6 min, resulting in min per block cycle. The relatively rapid progression through the four blocks and repeated cycles allowed us to minimize and evaluate differences in behavioral and neurophysiological parameters between the four blocks. These factors could include changes in the animal s motivation and quality of neuronal recording. For each neuron in our population, we took care to only include neurons with high recording quality and stable isolation. In addition, we examined peristimulus time histograms for each neuron separately in each block cycle to verify stable neuronal responses and selectivity across cycles. Stimuli were circular patches (9.0 diameter) of 300 high contrast 0.1 square dots that moved in one of six directions (evenly spaced at 60 apart) with 100% motion coherence and at a speed of 12.0 /s. For the majority of recordings (n 22 neurons from monkey S and 47 neurons from monkey H), directions between 45 and 225 were in one category while the remaining directions were in another. For the remaining sessions (n 15 neurons from monkey H), directions between 45 and 135 were in one category while the remaining directions were in another. Trials began with the onset of a 0.25 spot that monkeys were required to fixate within a 1.5 square window for the duration of the trial. Trials were followed by a 1.5 s intertrial interval, and monkeys typically performed 1500 correct trials each day. Data analysis. All analyses were conducted across correct trials. The pattern of behavioral and neuronal results was similar, and all main effects were observed in both monkeys. Thus we have combined the two datasets for all population analyses. For population analyses, firing rates were computed for each neuron in three time windows corresponding to the three phases of the task sample, delay, and test. The sample epoch was a 650 ms window that began 75 ms after sample onset (to account for neuronal response latencies). The delay epoch was the final 650 ms of the delay period, and the test epoch was 300 ms in duration beginning at test onset. The test epoch was necessarily shorter since the match trials ended with the monkey s reaction. To assess whether and how the firing of individual neurons reflected the learned direction categories, we computed two parameters for each neuron: a between-category difference (BCD) in firing rate between pairs of stimuli in different categories and a within-category difference (WCD) in activity for stimuli in the same category. For both BCD and WCD, we computed the difference in firing rate between all possible pairs of motion directions that were either 60 or 120 apart, and these two intervals (60 and 120 ) were equally weighted in the BCD and WCD calculation. From these values, we constructed a selectivity index by calculating the difference between BCD and WCD divided by their sum, which gave values between 1 and 1. Positive values of the index indicate larger differences in activity between categories and more similar activity within each category, while values near zero indicate that there was no difference in average firing between and within categories. The time courses of category and spatial selectivity were evaluated and compared using a receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis (Green and Swets, 1966; Tolhurst et al., 1983) with a sliding analysis window. The area under the ROC curve was computed and returned a value between 0.5 and 1.0, indicating the performance of an ideal observer in discriminating between firing rates of the two groups (i.e., the two spatial locations or the two categories). In both cases, we used a 50 ms analysis window that was stepped in 5 ms intervals over the course of the trial. Qualitatively similar results were observed with ROC windows of a variety of widths. The time course of category selectivity was determined by computing ROC values using the firing rates on trials in which the sample stimulus was in category 1 versus trials in which the sample was in category 2. The time course of spatial selectivity was determined by comparing firing rates between trials in block 1 (sample and test stimuli in the RF) and those in block 4 (sample and test stimuli outside the RF). Across
4 5674 J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP the LIP population, the latency of selectivity was defined as the time at which the mean ROC value during the fixation period was exceeded by 5 SDs for three consecutive time epochs. Results Across all behavioral sessions during which we successfully recorded from an LIP neuron (n 84), the monkeys performed the DMC task with a high level of accuracy (mean 90.0% correct, excluding fixation breaks) on all four spatial blocks (see Materials and Methods), although performance was slightly higher when sample stimuli were presented in the contralateral visual hemifield (91.7% correct on average during blocks 1 and 2) than when they were presented in the ipsilateral hemifield (88.3% correct on average during blocks 3 and 4) (Fig. 2b) according to a paired t test comparing average performance with sample stimuli presented in the contralateral versus ipsilateral visual hemifields ( p ). This difference in behavioral performance is likely due to the animals training history, as both monkeys were subjects in our previous study using the DMC task in which stimuli were typically presented in the hemifield contralateral to the recording chamber. The two monkeys average reaction time during the DMC task were ms and ms, respectively. We recorded from 84 LIP neurons from two monkeys (monkey H, n 62; monkey S, n 22) during performance of the DMC task, in four blocks of trials with sample and test stimuli presented both inside and outside each neuron s RF, as described above. Stability of neuronal isolation was monitored in real time during recordings, as we recorded from only one neuron at a time with a single electrode (see Materials and Methods). We also conducted a one-way ANOVA (with the block cycle number as the factor) to evaluate whether neurons showed statistically similar baseline firing rates across repeated block cycles. Indeed, we found that a majority of LIP neurons (60% or n 50/84) showed consistent baseline firing rates across repetitions of the same block type (i.e., did not show a main effect of block cycle; p 0.01). We also verified that all analyses yielded qualitatively similar results when applied only to this subset of the neuronal population. Before running the DMC task, we estimated the RF location and size using a delayed-saccade task and a simple RFmapping protocol using a flashed stimulus while the animals passively fixated. The size of LIP RFs was approximately proportional to their eccentricity, although their shapes were often irregular (noncircular). Not surprisingly, LIP activity during the DMC task depended greatly on whether stimuli were presented inside or outside the neurons RFs. This is clearly evident in the population peristimulus time histograms averaged across the entire population of LIP neurons (Fig. 3). When sample stimuli were presented within LIP neurons RFs (during blocks 1 and 2), the population showed a strong visual response during the sample period and persistent elevated firing rates during the delay period (Fig. 3a, Table 1). In contrast, the LIP population did not show elevated firing rates during the sample or delay periods when stimuli were presented away from each neuron s RF (Fig. 3b, Table 1). Similar effects were also observed during the test period: average neuronal responses were strong when test stimuli were presented inside the RF and much weaker when test stimuli were presented away from the RF (Fig. 3a,b). As in our previous study using the DMC task, many LIP neurons showed activity during the sample or delay periods that reflected the category membership of the sample stimuli when those stimuli were presented within the neurons RFs. This effect is evident in the single-neuron examples in Figure 4, a and b. Figure 3. LIP population activity depended on stimulus location relative to neurons RFs. Population histograms (averaged across correct trials and all motion directions) across the entire LIP population from both monkeys (n 84 neurons) show the strength and time course of neuronal activity when sample stimuli were presented inside (a) and outside (b) LIP RFs. In both plots, the darker and lighter traces correspond to test stimuli presented inside and outside neurons RFs, respectively. Neuronal activity for these plots was smoothed by convolving the raw firing rates with a Gaussian with a width of 10 ms. The three vertical dotted lines on each panel indicate (from left to right) the times of sample onset, sample offset, and test onset. Table 1. Incidence of visual responsiveness above baseline in LIP In in (block 1) In out (block 2) Out in (block 3) Out out (block 4) Sample Delay Test Numbers indicate number of neurons with significant effects (paired t test, p 0.01). n 84 neurons. When sample stimuli were presented inside the RF (during blocks 1 and 2), each neuron showed a relatively uniform level of responses to stimuli within each category and a sharp difference in activity between categories during the sample and/or delay periods. When sample stimuli were presented outside the RF (during blocks 3 and 4), each of these neurons responded more weakly on average; however, they still showed clear selectivity between the two categories, and that selectivity reflected the same category preference as when the stimuli were presented inside the RF. The third single-neuron example (Fig. 4c) also showed clear category selectivity for the remotely presented sample stimuli, even though its activity was suppressed during the sample period when sample stimuli were presented inside the RF (as for all of our LIP recordings, the RF location for this neuron was defined as the location that selectively elicited delay-period activity during the memory-saccade task). The tendency for LIP neurons to show category selectivity for stimuli presented either inside or outside their RFs was also evi-
5 Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): Figure 4. Many LIP single neurons reflected stimulus category membership when stimuli were presented both inside and outside their RFs. The activity of three LIP neurons (a c) is shown for all four blocks of trials (with sample and test stimuli presented inside and outside the field). The red and blue traces indicate the three directions in category 1 and category 2, respectively. Each of these neurons showed stronger responses during the sample and/or delay epochs when stimuli were presented inside the RF, but maintained significant category selectivity (and the same category preference) when stimuli were presented outside the field. The three vertical dotted lines on each panel indicate (from left to right) the times of sample onset, sampleoffset,andtestonset.categoryindex(ci)valuesforthesample,delay,andtestepochsareshownforeachneuronforeach of the four blocks. ep, Epoch. dent across the neuronal population. To analyze these effects across the population, we computed neuronal firing rates in three nonoverlapping time epochs (see Materials and Methods), which corresponded to the sample, delay, and test phases of the task. We evaluated the selectivity for sample-stimulus category and location (i.e., inside or outside the field) by computing a three-way ANOVA (factor 1: stimulus category; factor 2: sample location; factor 3: test location) for each LIP neuron. As shown in Table 2, a substantial fraction of LIP neurons showed a main effect (at p 0.01) of sample category during the sample (39/84 or 46%), delay (39/84 or 46%), and test (40/84 or 48%), indicating category-selective activity that was consistent across all blocks, regardless of whether the stimuli were inside or outside the RF (23/84 or 27% of LIP neurons had a main effect of category during the sample and delay; 16/84 or 19% were category selective in all three time periods). In addition, a majority of LIP neurons had activity that varied with stimulus location (inside vs outside the RF) during the sample (79/84 or 94%) and delay (59/84 or 70%). During the sample and delay epochs, there was a greater tendency for a main effect of location than for a main effect of category. Interestingly, this pattern reversed during the test epoch, in that fewer neurons showed a main effect of sample location (34/84) than sample category (40/84). In fact, the incidence of main effects of sample location was significantly lower during the test period than sample period ( 2 test, p 0.001). This suggests a trend toward spatially independent category encoding during the later phases of the task. To quantify the strength of neuronal category selectivity, we computed a category-tuning index that measured, for each neuron, the average difference in firing rate between pairs of stimuli in the same category and between those in different categories (see Materials and Methods). Values of the category index could vary from 1.0 to 1.0. Positive values indicate a greater difference between directions in different categories and more similar activity with each category, while negative values indicate the opposite. Index values near zero indicate that neuronal responses between sample directions show a similar degree of discrimination for within- and between-category pairs. For each of the four blocks, we focused our analysis on a population of 66/84 neurons (monkey H: n 52, monkey S: n 14) that were selective with respect to the six
6 5676 J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP sample stimulus directions during any of the four blocks or in any time epoch (oneway ANOVA; p 0.01, uncorrected) (Table 3). While category selectivity was weaker for sample stimuli presented outside the RF, we found significantly positive values of the category index in all four blocks across the LIP population during the sample period (mean index values, block 1: 0.16, block 2: 0.12, block 3: 0.10, Table 2. Category and spatial selectivity in LIP block 4: 0.12; greatest p value 0.005), delay period (block 1: 0.25, block 2: 0.27, block 3: 0.10, block 4: 0.09; greatest p value 0.004), and test period (block 1: 0.23, block 2: 0.27, block 3: 0.14, block 4: 0.20; greatest p value ) according to two-tailed paired t tests comparing the distribution of indices to a mean of zero. The distributions of category-tuning index values for each of the four blocks in the sample, delay, and test epochs are shown in Figure 5. On average, category-index values were reduced by 21% (sample), 64% (delay), and 32% (test) during blocks in which stimuli were presented outside versus inside the RF. We characterized the time course of category selectivity in more detail by computing the category index using a sliding analysis window (window width 150 ms, step size 50 ms) across the same population of 66 direction-selective LIP neurons. As shown in Figure 6, category selectivity in all four blocks emerged with a relatively short latency ( 200 ms) after sample onset. When sample stimuli were presented in the RF during blocks 1 and 2 (Fig. 6a,b), index values remained high throughout the delay and reached peak values toward the end of the delay and early test epoch. When sample stimuli were presented outside the RF during blocks 3 and 4 (Fig. 6c,d), the strength of category selectivity waned during the early delay, but showed a sharp increase during the late delay and early test epochs. As seen in the single-neuron examples in Figure 4, the latency of category selectivity following sample onset appeared to be somewhat longer than the visual-response latency. Many LIP neurons, such as those in Figure 4, a and b, showed a strong, short-latency visual response that was initially nonselective for the sample directions, followed by strong category selectivity. To evaluate this trend across the population, we computed the time course and latency of both category selectivity and spatial selectivity using an ROC analysis (see Materials and Methods). To do so, we computed two sliding ROC analyses. For category selectivity, we compared firing rates between the two categories during block 1 (sample and test inside the RF). For spatial selectivity, we compared firing rates between block 1 (sample and test stimuli inside the RF) and block 4 (sample and test outside the RF), pooling all trials within each block. A 50-ms-wide analysis window was stepped every 5 ms. The analysis was applied to the population of 53 LIP neurons that were direction selective during block 1. The latency of selectivity for both category and spatial position was defined as the point at which the ROC value exceeded that observed during the fixation period by 5 SDs for at least three consecutive time bins. As shown in Figure 7, spatial selectivity in LIP appeared with a shorter latency (40 ms) than motion-category selectivity (80 ms). In addition to showing category selectivity for stimuli presented both inside and outside LIP neurons RFs, we also found that neurons tended to maintain consistent category preferences for sample stimuli across blocks 1 4. For this analysis, we focused on neurons in each time epoch (sample: n 39; delay: n 39; test: n 40) that showed a main effect of sample category according to a three-way ANOVA (described above and in Table 2). We Main effects Interactions Categ Samp Loc Test Loc Cat S Loc Cat T Loc S Loc T Loc Three-way Sample Delay Test Numbersindicatenumberofneuronswithsignificanteffects(three-wayANOVA,p 0.01;factor1:category;factor2:samplelocation;factor3:testlocation). n 84 neurons. Categ, Category; Samp, sample; Loc, location; S, sample; T, test. Table 3. Incidence of sample-direction selectivity in LIP In in (block 1) In out (block 2) Out in (block 3) Out out (block 4) Sample Delay Test Numbers indicate number of neurons with significant effects (one-way ANOVA, six directions, p 0.01). n 84 neurons. found that a greater percentage of neurons than expected by chance (chance 12.5%) showed the same category preference in each of the blocks 1 4, during the sample (16/39 or 41%), delay (24/39 or 62%), and test (28/40 or 70%) epochs. To evaluate whether neurons tended to show the same category preferences across multiple time epochs, we first determined that 23/84 neurons showed a main effect of sample category during both the sample and delay epochs (according to the three-way ANOVA; see above and Table 2). Of these neurons, the numbers of neurons that showed the same category preferences during both epochs (computed separately in each of the four blocks) were as follows: block 1: 19/23, block 2: 20/23, block 3: 13/23, and block 4: 11/23. Since 50% of neurons would be expected to show the same category preference in the two epochs by chance, this indicates a greater tendency for LIP neurons to maintain consistent category selectivity across multiple time epochs when sample stimuli were presented inside the RF (blocks 1 and 2). We also found that neurons that showed strong category selectivity when sample stimuli were presented within their RFs also tended to show strong effects when stimuli were presented outside the field. This was particularly evident during the test epoch (Fig. 8), although a weaker but significant trend was also evident during the sample and delay epochs. For each neuron (n 84), we measured the strength and reliability of samplecategory selectivity using an ROC analysis that captured the degree of overlap between the distributions of firing rates obtained when the sample stimulus was in category A versus category B. The results of this analysis indicated the probability (ranging from 0.5 to 1.0) with which an ideal observer could correctly report the sample category on each trial given the firing rates from an individual LIP neuron (Green and Swets, 1966; Tolhurst et al., 1983). When we applied this analysis to the test epoch, we only compared test-epoch selectivity between blocks in which test stimuli were presented in the same location. We did so to eliminate response variability related to the presence or absence of a visual response to the test stimulus, because neurons responded more strongly when the test stimulus was presented in the RF. When the test stimulus was presented inside the RF (Fig. 8a), we found a clear positive relationship between the strength of sample-category selectivity when the sample stimulus had been presented inside (block 2) and outside (block 4) the neurons RFs (linear regression: slope 0.77, r , p ). A similar relationship was observed when test stimuli were presented outside the RFs, as shown in Figure 8b (linear regression: slope 0.57, r , p ). This analysis was also
7 Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): applied to the LIP population during the sample (linear regression: slope 0.41, r , p 0.015) and delay (linear regression: slope 0.45, r , p 0.011). The consistency of category selectivity for sample stimuli that were presented inside versus outside LIP RFs (particularly during the test) suggests a spatially independent encoding of the sample stimulus (category membership) that was relevant for solving the task. These results also serve as a rigorous control for the unlikely possibility that these category effects were due to differences in spatial attention or planned eye movements (although the monkey s reported their category judgments with a lever release, not an eye movement) between the two categories, since placing stimuli in the opposite quadrant of the display monitor should result in a reversal of such spatial relationships in the DMC task. Discussion We compared the relationship between the neuronal encoding of spatial and task-related, nonspatial information in the lateral intraparietal area. Monkeys were trained to perform a categorymatching task in which they grouped motion directions into two categories that were defined by a learned category boundary. As in a previous study, we found that the activity of many individual LIP neurons reflected the learned category membership of the motion directions when those stimuli were presented in the neurons RFs (Freedman and Assad, 2006). Here, we asked whether this abstract and learning-dependent category encoding was also present when stimuli were presented outside the neurons RFs. We found that, while firing rates were substantially reduced when stimuli were presented outside the RFs, many neurons still maintained clear category selectivity for the remotely presented stimuli, although that selectivity was weaker than for stimuli presented in the RF. Across the neuronal population, LIP exhibited significant category selectivity with a relatively short latency following stimulus onset, both for stimuli presented inside and outside the RFs. In addition, category selectivity persisted following sample offset, and many LIP neurons showed category selectivity that increased in strength toward the end of the delay (perhaps in anticipation of the upcoming test stimulus) and early test period. This suggests a role for LIP in both rapid visual processing and short-term-memory-related encoding of nonspatial variables (e.g., category membership) that are relevant for solving the task at hand. This idea is also supported by our observation that the prevalence of spatial encoding was greatest during the sample period, but became less prevalent later in the trial, while categorical encoding became more prevalent. Overall our results suggest that nonspatial factors can exert a modulatory influence on LIP activity without a stimulus present in the RF, or if attention or planned action are directed away from the RF. As in our previous study in LIP using the motion DMC task, neuronal encoding that reflects the learned categories cannot be explained by differences in motor planning among the sample directions during the sample or delay epochs. This is because the monkeys could not make their decision about whether or not to release the lever (which signaled that the test was a category match to the sample) until the presentation of the test stimulus. 4 Figure 5. Distributions of category-tuning index values across LIP population. A categorytuning index was computed that measured the strength of category selectivity of individual neurons (see Materials and Methods). Positive values of the index indicate larger activity differences between categories and/or more similar activity within categories. The light gray bars show index values across the entire population of LIP neurons, whereas the dark gray bars show those for neurons that were direction selective (in any block and any time epoch). The sample is shown in a d, delay in e h, and test in i l. In each time epoch, the distribution of indices is shown for each of the four spatial blocks (block 1: sample in RF, test in RF; block 2: sample in, test out; block 3: test out, sample in; block 4: sample out, test out).
8 5678 J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP In addition, since the animal s performance was equally good for both categories, the two learned categories did not substantially differ from one another in their probability of leading to a reward. In our previous study, there was somewhat lower performance for directions very close to (15 ) the category boundary that could, in principle, have led to lower reward expectation for those sample directions. However, we did not observe neuronal activity in LIP that tracked such a putative reward-expectation signal (Freedman and Assad, 2006). These results are complementary to several recent studies that have demonstrated that LIP neurons can encode nonspatial factors, such as visual shape and color (Sereno and Maunsell, 1998; Toth and Assad, 2002; Sereno and Amador, 2006; Janssen et al., 2008), numerical quantity (Nieder and Miller, 2004; Nieder et al., 2006), and the rule that is relevant for solving the currently relevant task (Stoet and Snyder, 2004). However, several of these previous studies did not measure RF location and/or placed stimuli in random locations on the display, while others measured RF properties but then only tested conditions in which stimuli were presented within the RF of each neuron. Thus it was unclear whether LIP neurons conveyed information only about stimuli that were in close proximity to their RFs, or whether they might show a more spatially independent encoding, particularly for more abstract or task-dependent information. It is notable that, while spatial selectivity in LIP neurons is generally present throughout the entire duration of the trial, nonspatial selectivity in both our study and previous studies in dorsal-stream areas (Stoet and Snyder, 2004; Zaksas and Pasternak, 2006) is often present in somewhat shorter time periods that do not always span the entire trial or even an entire task period (e.g., sample or delay). Our findings may be related to results from Oristaglio et al. (2006), who found that the activity of some LIP neurons is modulated by whether the animal used its right or left hand to report the orientation of a visual target, even when that target was placed outside the RF. In addition, our results are compatible with those from Zaksas and Pasternak (2005), who found that neuronal activity in the middle temporal (MT) area was informative about the direction of motion for stimuli presented outside neurons RFs during a direction-matching task. However, in contrast with our LIP results presented here, MT direction selectivity in that study was observed almost exclusively during the visual response period. More broadly, our results may also be related to featurebased attention, particularly if the two categories in our study are considered as more abstract features than the concrete visual features typically used in neurophysiological studies of featurebased attention (Treue and Martínez Trujillo, 1999; Maunsell and Treue, 2006). A better understanding of the origin of nonspatial selectivity in LIP will be essential for determining whether or not parietal cortex plays a direct functional role in nonspatial processing. One possibility is that the nonspatial signals (e.g., category selectivity) that we have observed in LIP are due to top-down inputs from brain areas, such as the prefrontal cortex (PFC), that are known Figure 6. Time course of category selectivity across LIP population. The time course of category selectivity was determined for each of blocks 1 4 (a d) by computing a sliding version of the category-tuning index (window width 150 ms, step size 50 ms) averaged across the 66/84 neurons that were direction selective during any of the three time epochs (sample, delay, and test) and in any of the four blocks. The gray area around the solid black trace (the mean index value) indicates the SEM. The three vertical dotted lines on each panel indicate (from left to right) the times of sample onset, sample offset, and test onset. Figure 7. Time course of spatial selectivity and category selectivity across LIP population. The time courses of spatial selectivity (black trace) and category selectivity (gray trace) are shown for the population of 53 LIP neurons that were determined to be direction selective during block 1. In both cases, selectivity was measured using an ROC analysis. To measure category selectivity, firing rates to the two categories were compared during block 1 (both sample and test stimuli presented in the RF). For spatial selectivity, firing rates were compared between all trials in block 1 (stimuli presented in the RF) and block 4 (stimuli presented outside the RF). The three vertical dotted lines on each panel indicate (from left to right) the times of sample onset, sample offset, and test onset. to encode abstract nonspatial factors (Freedman et al., 2001, 2002, 2003; Wallis et al., 2001) and are interconnected with parietal cortex (Petrides and Pandya, 1984; Cavada and Goldman- Rakic, 1989; Felleman and Van Essen, 1991). In that case, nonspatial selectivity in LIP may be a passive reflection of selectivity in PFC, and may not play a direct role in nonspatial perception and behavior. On the other hand, LIP may be more directly involved in the generation of nonspatial selectivity. This is supported by the observation that LIP category selectivity arises with a relatively short latency, and is encoded strongly by LIP neurons when stimuli are presented within their RFs. Additional work is needed to understand the origin of outside-the-rf selectivity and how spatial and nonspatial signals are combined by LIP neurons. LIP s encoding of remotely pre-
9 Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): sented stimuli could arise by top-down inputs from PFC, or via interhemispheric connections with LIP neurons with RFs in the location at which stimuli were presented. While our study suggests that LIP neurons can combine spatial and nonspatial information that likely arise from separate inputs, the underlying mechanisms of this process (e.g., additive vs multiplicative combination of spatial and nonspatial signals) remain to be determined, and need to be studied in more detail (perhaps by parametrically varying both spatial and nonspatial factors). It also remains to be determined whether the outsidethe-rf effects that we have observed play a functional role in perception and behavior. The observation that LIP firing rates were much weaker for stimuli presented outside the RF is consistent with the possibility that these weaker firing may have little impact on the perception or actions of the monkey. Even so, an interesting hypothesis is that modulations of LIP activity due to nonspatial factors could, in principle, interfere with LIP spatial or saccadic encoding. In addition, since we also found nonspatial modulation for stimuli outside as well as inside the RFs (although it was weaker outside the RF), it follows that this information would have been encoded in a very large population of neurons, i.e., not limited to neurons with RFs in a particular location. This contrasts with spatial encoding in LIP, where stimulus-related information is assumed to be represented by a smaller fraction of neurons whose RFs overlap the spatial location of the stimulus. Thus, the possibility remains that these outside-the-rf effects in LIP may play a functional role in perception and behavior. Figure 8. Individual neurons maintained consistent category selectivity across spatial conditions. The strength and reliability of category selectivity was computed with an ROC analysis. During the test epoch (when category selectivity for the previously presented sample stimulus was strongest across the population), ROC values for all neurons (n 84) were compared between blocks 1 and 3 (when the test stimulus was in the field) (a) and blocks 2 and 4 (when there was no test stimulus in the field) (b). Dashed lines have a slope of 1. References Bisley JW, Krishna BS, Goldberg ME (2004) A rapid and precise onresponse in posterior parietal cortex. J Neurosci 24: Cavada C, Goldman-Rakic PS (1989) Posterior parietal cortex in rhesus monkey: II. Evidence for segregated corticocortical networks linking sensory and limbic areas with the frontal lobe. J Comp Neurol 287: Critchley M (1953) The parietal lobes. New York: Hafner. Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC (1991) Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 1:1 47. Freedman DJ, Assad JA (2006) Experience-dependent representation of visual categories in parietal cortex. Nature 443: Freedman DJ, Riesenhuber M, Poggio T, Miller EK (2001) Categorical representation of visual stimuli in the primate prefrontal cortex. Science 291: Freedman DJ, Riesenhuber M, Poggio T, Miller EK (2002) Visual categorization and the primate prefrontal cortex: neurophysiology and behavior. J Neurophysiol 88: Freedman DJ, Riesenhuber M, Poggio T, Miller EK (2003) A comparison of primate prefrontal and inferior temporal cortices during visual categorization. J Neurosci 23: Gnadt JW, Andersen RA (1988) Memory related motor planning activity in posterior parietal cortex of macaque. Exp Brain Res 70: Gold JI, Shadlen MN (2007) The neural basis of decision making. Annu Rev Neurosci 30: Green DM, Swets JA (1966) Signal detection theory and psychophysics. New York: Wiley. Janssen P, Srivastava S, Ombelet S, Orban GA (2008) Coding of shape and position in macaque lateral intraparietal area. J Neurosci 28: Judge SJ, Richmond BJ, Chu FC (1980) Implantation of magnetic search coils for measurement of eye position: an improved method. Vision Res 20: Maunsell JHR (2004) Neuronal representations of cognitive state: reward or attention? Trends Cogn Sci 8: Maunsell JHR, Treue S (2006) Feature-based attention in visual cortex. Trends Neurosci 29: Mountcastle VB, Lynch JC, Georgopoulos A, Sakata H, Acuna C (1975) Posterior parietal association cortex of the monkey: command functions for operations within extrapersonal space. J Neurophysiol 38: Nieder A, Miller EK (2004) A parieto-frontal network for visual numerical information in the monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101: Nieder A, Diester I, Tudusciuc O (2006) Temporal and spatial enumeration processes in the primate parietal cortex. Science 313: Oristaglio J, Schneider DM, Balan PF, Gottlieb J (2006) Integration of visuospatial and effector information during symbolically cued limb movements in monkey lateral intraparietal area. J Neurosci 26: Petrides M, Pandya DN (1984) Projections to the frontal cortex from the
10 5680 J. Neurosci., April 29, (17): Freedman and Assad Spatial and Nonspatial Encoding in Area LIP posterior parietal region in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 228: Platt ML, Glimcher PW (1999) Neural correlates of decision variables in parietal cortex. Nature 400: Robinson DA (1963) A method of measuring eye movements using a scleral search coil in a magnetic field. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 10: Sereno AB, Amador SC (2006) Attention and memory related responses of neurons in the lateral intraparietal area during shape and spatial delayed match-to-sample tasks. J Neurophysiol 95: Sereno AB, Maunsell JH (1998) Shape selectivity in primate lateral intraparietal cortex. Nature 395: Shadlen MN, Newsome WT (2001) Neural basis of a perceptual decision in the parietal cortex (area LIP) of the rhesus monkey. J Neurophysiol 86: Stoet G, Snyder LH (2004) Single neurons in posterior parietal cortex (PPC) of monkeys encode cognitive set. Neuron 42: Tolhurst DJ, Movshon JA, Dean AF (1983) The statistical reliability of signals in single neurons in cat and monkey visual cortex. Vision Res 23: Toth LJ, Assad JA (2002) Dynamic coding of behaviorally relevant stimuli in parietal cortex. Nature 415: Treue S, Martínez Trujillo JC (1999) Feature-based attention influences motion processing gain in macaque visual cortex. Nature 399: Wallis JD, Anderson KC, Miller EK (2001) Single neurons in prefrontal cortex encode abstract rules. Nature 411: Wardak C, Olivier E, Duhamel JR (2002) Saccadic target selection deficits after lateral intraparietal area inactivation in monkeys. J Neurosci 22: Zaksas D, Pasternak T (2005) Area MT neurons respond to visual motion distant from their receptive fields. J Neurophysiol 94: Zaksas D, Pasternak T (2006) Directional signals in the prefrontal cortex and in area MT during a working memory for visual motion task. J Neurosci 26:
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Area MT Neurons Respond to Visual Motion Distant From Their Receptive Fields
 J Neurophysiol 94: 4156 4167, 2005. First published August 24, 2005; doi:10.1152/jn.00505.2005. Area MT Neurons Respond to Visual Motion Distant From Their Receptive Fields Daniel Zaksas and Tatiana Pasternak
J Neurophysiol 94: 4156 4167, 2005. First published August 24, 2005; doi:10.1152/jn.00505.2005. Area MT Neurons Respond to Visual Motion Distant From Their Receptive Fields Daniel Zaksas and Tatiana Pasternak
U.S. copyright law (title 17 of U.S. code) governs the reproduction and redistribution of copyrighted material.
 U.S. copyright law (title 17 of U.S. code) governs the reproduction and redistribution of copyrighted material. The Journal of Neuroscience, June 15, 2003 23(12):5235 5246 5235 A Comparison of Primate
U.S. copyright law (title 17 of U.S. code) governs the reproduction and redistribution of copyrighted material. The Journal of Neuroscience, June 15, 2003 23(12):5235 5246 5235 A Comparison of Primate
Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load
 Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load Intro Examine attention response functions Compare an attention-demanding
Attention Response Functions: Characterizing Brain Areas Using fmri Activation during Parametric Variations of Attentional Load Intro Examine attention response functions Compare an attention-demanding
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Recording technique Multi-unit activity (MUA) was recorded from electrodes that were chronically implanted (Teflon-coated platinum-iridium wires) in the primary visual cortex representing
Supplemental Material Recording technique Multi-unit activity (MUA) was recorded from electrodes that were chronically implanted (Teflon-coated platinum-iridium wires) in the primary visual cortex representing
Flexibility of Sensory Representations in Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cell Type
 Article Flexibility of Sensory Representations in Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cell Type Cory R. Hussar 1,2 and Tatiana Pasternak 1,2, * 1 Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy 2 Center for Visual Science
Article Flexibility of Sensory Representations in Prefrontal Cortex Depends on Cell Type Cory R. Hussar 1,2 and Tatiana Pasternak 1,2, * 1 Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy 2 Center for Visual Science
Experience-Dependent Sharpening of Visual Shape Selectivity in Inferior Temporal Cortex
 Cerebral Cortex Advance Access published December 28, 2005 Cerebral Cortex doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj100 Experience-Dependent Sharpening of Visual Shape Selectivity in Inferior Temporal Cortex David J. Freedman
Cerebral Cortex Advance Access published December 28, 2005 Cerebral Cortex doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj100 Experience-Dependent Sharpening of Visual Shape Selectivity in Inferior Temporal Cortex David J. Freedman
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature14066 Supplementary discussion Gradual accumulation of evidence for or against different choices has been implicated in many types of decision-making, including value-based decisions
doi:10.1038/nature14066 Supplementary discussion Gradual accumulation of evidence for or against different choices has been implicated in many types of decision-making, including value-based decisions
A Neurally-Inspired Model for Detecting and Localizing Simple Motion Patterns in Image Sequences
 A Neurally-Inspired Model for Detecting and Localizing Simple Motion Patterns in Image Sequences Marc Pomplun 1, Yueju Liu 2, Julio Martinez-Trujillo 2, Evgueni Simine 2, and John K. Tsotsos 2 1 Department
A Neurally-Inspired Model for Detecting and Localizing Simple Motion Patterns in Image Sequences Marc Pomplun 1, Yueju Liu 2, Julio Martinez-Trujillo 2, Evgueni Simine 2, and John K. Tsotsos 2 1 Department
PFC Neurons Reflect Categorical Decisions about Ambiguous Stimuli
 PFC Neurons Reflect Categorical Decisions about Ambiguous Stimuli Jefferson E. Roy, Timothy J. Buschman, and Earl K. Miller Abstract We examined whether PFC neuron activity reflects categorical decisions
PFC Neurons Reflect Categorical Decisions about Ambiguous Stimuli Jefferson E. Roy, Timothy J. Buschman, and Earl K. Miller Abstract We examined whether PFC neuron activity reflects categorical decisions
Effects of Attention on MT and MST Neuronal Activity During Pursuit Initiation
 Effects of Attention on MT and MST Neuronal Activity During Pursuit Initiation GREGG H. RECANZONE 1 AND ROBERT H. WURTZ 2 1 Center for Neuroscience and Section of Neurobiology, Physiology and Behavior,
Effects of Attention on MT and MST Neuronal Activity During Pursuit Initiation GREGG H. RECANZONE 1 AND ROBERT H. WURTZ 2 1 Center for Neuroscience and Section of Neurobiology, Physiology and Behavior,
Directional Signals in the Prefrontal Cortex and in Area MT during a Working Memory for Visual Motion Task
 11726 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 8, 2006 26(45):11726 11742 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Directional Signals in the Prefrontal Cortex and in Area MT during a Working Memory for Visual Motion
11726 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 8, 2006 26(45):11726 11742 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Directional Signals in the Prefrontal Cortex and in Area MT during a Working Memory for Visual Motion
Selective bias in temporal bisection task by number exposition
 Selective bias in temporal bisection task by number exposition Carmelo M. Vicario¹ ¹ Dipartimento di Psicologia, Università Roma la Sapienza, via dei Marsi 78, Roma, Italy Key words: number- time- spatial
Selective bias in temporal bisection task by number exposition Carmelo M. Vicario¹ ¹ Dipartimento di Psicologia, Università Roma la Sapienza, via dei Marsi 78, Roma, Italy Key words: number- time- spatial
Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
Decoding a Perceptual Decision Process across Cortex
 Article Decoding a Perceptual Decision Process across Cortex Adrián Hernández, 1 Verónica Nácher, 1 Rogelio Luna, 1 Antonio Zainos, 1 Luis Lemus, 1 Manuel Alvarez, 1 Yuriria Vázquez, 1 Liliana Camarillo,
Article Decoding a Perceptual Decision Process across Cortex Adrián Hernández, 1 Verónica Nácher, 1 Rogelio Luna, 1 Antonio Zainos, 1 Luis Lemus, 1 Manuel Alvarez, 1 Yuriria Vázquez, 1 Liliana Camarillo,
Retinotopy & Phase Mapping
 Retinotopy & Phase Mapping Fani Deligianni B. A. Wandell, et al. Visual Field Maps in Human Cortex, Neuron, 56(2):366-383, 2007 Retinotopy Visual Cortex organised in visual field maps: Nearby neurons have
Retinotopy & Phase Mapping Fani Deligianni B. A. Wandell, et al. Visual Field Maps in Human Cortex, Neuron, 56(2):366-383, 2007 Retinotopy Visual Cortex organised in visual field maps: Nearby neurons have
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab
 TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab This report details my summer research project for the REU Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience program as
TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab This report details my summer research project for the REU Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience program as
Memory-Guided Sensory Comparisons in the Prefrontal Cortex: Contribution of Putative Pyramidal Cells and Interneurons
 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 22, 2012 32(8):2747 2761 2747 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Memory-Guided Sensory Comparisons in the Prefrontal Cortex: Contribution of Putative Pyramidal Cells and
The Journal of Neuroscience, February 22, 2012 32(8):2747 2761 2747 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Memory-Guided Sensory Comparisons in the Prefrontal Cortex: Contribution of Putative Pyramidal Cells and
Limb-Specific Representation for Reaching in the Posterior Parietal Cortex
 6128 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 11, 2008 28(24):6128 6140 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Limb-Specific Representation for Reaching in the Posterior Parietal Cortex Steve W. C. Chang, Anthony R. Dickinson,
6128 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 11, 2008 28(24):6128 6140 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Limb-Specific Representation for Reaching in the Posterior Parietal Cortex Steve W. C. Chang, Anthony R. Dickinson,
Visual Categorization: How the Monkey Brain Does It
 Visual Categorization: How the Monkey Brain Does It Ulf Knoblich 1, Maximilian Riesenhuber 1, David J. Freedman 2, Earl K. Miller 2, and Tomaso Poggio 1 1 Center for Biological and Computational Learning,
Visual Categorization: How the Monkey Brain Does It Ulf Knoblich 1, Maximilian Riesenhuber 1, David J. Freedman 2, Earl K. Miller 2, and Tomaso Poggio 1 1 Center for Biological and Computational Learning,
Competitive Mechanisms Subserve Attention in Macaque Areas V2 and V4
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1, 1999, 19(5):1736 1753 Competitive Mechanisms Subserve Attention in Macaque Areas V2 and V4 John H. Reynolds, 1 Leonardo Chelazzi, 2 and Robert Desimone 1 1 Laboratory
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1, 1999, 19(5):1736 1753 Competitive Mechanisms Subserve Attention in Macaque Areas V2 and V4 John H. Reynolds, 1 Leonardo Chelazzi, 2 and Robert Desimone 1 1 Laboratory
Dissociation of Response Variability from Firing Rate Effects in Frontal Eye Field Neurons during Visual Stimulation, Working Memory, and Attention
 2204 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 8, 2012 32(6):2204 2216 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Dissociation of Response Variability from Firing Rate Effects in Frontal Eye Field Neurons during Visual
2204 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 8, 2012 32(6):2204 2216 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Dissociation of Response Variability from Firing Rate Effects in Frontal Eye Field Neurons during Visual
Correlation between Speed Perception and Neural Activity in the Middle Temporal Visual Area
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 19, 2005 25(3):711 722 711 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Correlation between Speed Perception and Neural Activity in the Middle Temporal Visual Area Jing Liu and William
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 19, 2005 25(3):711 722 711 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Correlation between Speed Perception and Neural Activity in the Middle Temporal Visual Area Jing Liu and William
Vision Research 49 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Vision Research. journal homepage:
 Vision Research 49 (29) 29 43 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Vision Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/visres A framework for describing the effects of attention on visual responses
Vision Research 49 (29) 29 43 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Vision Research journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/visres A framework for describing the effects of attention on visual responses
Models of Attention. Models of Attention
 Models of Models of predictive: can we predict eye movements (bottom up attention)? [L. Itti and coll] pop out and saliency? [Z. Li] Readings: Maunsell & Cook, the role of attention in visual processing,
Models of Models of predictive: can we predict eye movements (bottom up attention)? [L. Itti and coll] pop out and saliency? [Z. Li] Readings: Maunsell & Cook, the role of attention in visual processing,
Visual Categorization and the Primate Prefrontal Cortex: Neurophysiology and Behavior
 J Neurophysiol 88: 929 941, 2002; 10.1152/jn.00040.2002. Visual Categorization and the Primate Prefrontal Cortex: Neurophysiology and Behavior DAVID J. FREEDMAN, 1,2,5 MAXIMILIAN RIESENHUBER, 3 5 TOMASO
J Neurophysiol 88: 929 941, 2002; 10.1152/jn.00040.2002. Visual Categorization and the Primate Prefrontal Cortex: Neurophysiology and Behavior DAVID J. FREEDMAN, 1,2,5 MAXIMILIAN RIESENHUBER, 3 5 TOMASO
Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4.
 Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4. Jude F. Mitchell, Kristy A. Sundberg, and John H. Reynolds Systems Neurobiology Lab, The Salk Institute,
Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4. Jude F. Mitchell, Kristy A. Sundberg, and John H. Reynolds Systems Neurobiology Lab, The Salk Institute,
Neuronal representations of cognitive state: reward or attention?
 Opinion TRENDS in Cognitive Sciences Vol.8 No.6 June 2004 representations of cognitive state: reward or attention? John H.R. Maunsell Howard Hughes Medical Institute & Baylor College of Medicine, Division
Opinion TRENDS in Cognitive Sciences Vol.8 No.6 June 2004 representations of cognitive state: reward or attention? John H.R. Maunsell Howard Hughes Medical Institute & Baylor College of Medicine, Division
Beyond bumps: Spiking networks that store sets of functions
 Neurocomputing 38}40 (2001) 581}586 Beyond bumps: Spiking networks that store sets of functions Chris Eliasmith*, Charles H. Anderson Department of Philosophy, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ont, N2L
Neurocomputing 38}40 (2001) 581}586 Beyond bumps: Spiking networks that store sets of functions Chris Eliasmith*, Charles H. Anderson Department of Philosophy, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ont, N2L
Direction Selectivity of Neurons in the Macaque Lateral Intraparietal Area
 J Neurophysiol 1: 289 35, 9. First published November 5, 8; doi:.1152/jn.4.7. Direction Selectivity of Neurons in the Macaque Lateral Intraparietal rea lessandra Fanini and John. ssad Department of Neurobiology,
J Neurophysiol 1: 289 35, 9. First published November 5, 8; doi:.1152/jn.4.7. Direction Selectivity of Neurons in the Macaque Lateral Intraparietal rea lessandra Fanini and John. ssad Department of Neurobiology,
Comparison of Associative Learning- Related Signals in the Macaque Perirhinal Cortex and Hippocampus
 Cerebral Cortex May 2009;19:1064--1078 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn156 Advance Access publication October 20, 2008 Comparison of Associative Learning- Related Signals in the Macaque Perirhinal Cortex and Hippocampus
Cerebral Cortex May 2009;19:1064--1078 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn156 Advance Access publication October 20, 2008 Comparison of Associative Learning- Related Signals in the Macaque Perirhinal Cortex and Hippocampus
The primate amygdala combines information about space and value
 The primate amygdala combines information about space and Christopher J Peck 1,8, Brian Lau 1,7,8 & C Daniel Salzman 1 6 npg 213 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. A stimulus predicting reinforcement
The primate amygdala combines information about space and Christopher J Peck 1,8, Brian Lau 1,7,8 & C Daniel Salzman 1 6 npg 213 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. A stimulus predicting reinforcement
Tadashi Ogawa and Hidehiko Komatsu J Neurophysiol 101: , First published Dec 10, 2008; doi: /jn
 Tadashi Ogawa and Hidehiko Komatsu J Neurophysiol 101:721-736, 2009. First published Dec 10, 2008; doi:10.1152/jn.90817.2008 You might find this additional information useful... This article cites 58 articles,
Tadashi Ogawa and Hidehiko Komatsu J Neurophysiol 101:721-736, 2009. First published Dec 10, 2008; doi:10.1152/jn.90817.2008 You might find this additional information useful... This article cites 58 articles,
 Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Peripheral facial paralysis (right side). The patient is asked to close her eyes and to retract their mouth (From Heimer) Hemiplegia of the left side. Note the characteristic position of the arm with
Prefrontal Cortex Activity during Flexible Categorization
 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 23, 1 3(2):19 2 19 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Prefrontal Cortex Activity during Flexible Categorization Jefferson E. Roy, 1, Maximilian Riesenhuber, Tomaso Poggio, 2,3,
The Journal of Neuroscience, June 23, 1 3(2):19 2 19 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Prefrontal Cortex Activity during Flexible Categorization Jefferson E. Roy, 1, Maximilian Riesenhuber, Tomaso Poggio, 2,3,
From Rule to Response: Neuronal Processes in the Premotor and Prefrontal Cortex
 J Neurophysiol 90: 1790 1806, 2003. First published May 7, 2003; 10.1152/jn.00086.2003. From Rule to Response: Neuronal Processes in the Premotor and Prefrontal Cortex Jonathan D. Wallis and Earl K. Miller
J Neurophysiol 90: 1790 1806, 2003. First published May 7, 2003; 10.1152/jn.00086.2003. From Rule to Response: Neuronal Processes in the Premotor and Prefrontal Cortex Jonathan D. Wallis and Earl K. Miller
Key questions about attention
 Key questions about attention How does attention affect behavioral performance? Can attention affect the appearance of things? How does spatial and feature-based attention affect neuronal responses in
Key questions about attention How does attention affect behavioral performance? Can attention affect the appearance of things? How does spatial and feature-based attention affect neuronal responses in
Neuroscience Tutorial
 Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Neuroscience Tutorial Brain Organization : cortex, basal ganglia, limbic lobe : thalamus, hypothal., pituitary gland : medulla oblongata, midbrain, pons, cerebellum Cortical Organization Cortical Organization
Contributions of Orbitofrontal and Lateral Prefrontal Cortices to Economic Choice and the Good-to-Action Transformation
 Article Contributions of Orbitofrontal and Lateral Prefrontal Cortices to Economic Choice and the Good-to-Action Transformation Xinying Cai 1 and Camillo Padoa-Schioppa 1,2,3, * 1 Department of Anatomy
Article Contributions of Orbitofrontal and Lateral Prefrontal Cortices to Economic Choice and the Good-to-Action Transformation Xinying Cai 1 and Camillo Padoa-Schioppa 1,2,3, * 1 Department of Anatomy
Complementary Roles for Primate Frontal and Parietal Cortex in Guarding Working Memory from Distractor Stimuli
 Neuron Article Complementary Roles for Primate Frontal and Parietal Cortex in Guarding Working Memory from Distractor Stimuli Simon Nikolas Jacob,2, * and Andreas Nieder Animal Physiology, Institute of
Neuron Article Complementary Roles for Primate Frontal and Parietal Cortex in Guarding Working Memory from Distractor Stimuli Simon Nikolas Jacob,2, * and Andreas Nieder Animal Physiology, Institute of
Prefrontal Neurons of Opposite Spatial Preference Display Distinct Target Selection Dynamics
 9520 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 29, 2013 33(22):9520 9529 Behavioral/Cognitive Prefrontal Neurons of Opposite Spatial Preference Display Distinct Target Selection Dynamics Therese Lennert 1 and Julio
9520 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 29, 2013 33(22):9520 9529 Behavioral/Cognitive Prefrontal Neurons of Opposite Spatial Preference Display Distinct Target Selection Dynamics Therese Lennert 1 and Julio
Reward-Dependent Modulation of Working Memory in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 11, 29 29(1):3259 327 3259 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Reward-Dependent Modulation of Working Memory in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex Steven W. Kennerley and Jonathan D.
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 11, 29 29(1):3259 327 3259 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Reward-Dependent Modulation of Working Memory in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex Steven W. Kennerley and Jonathan D.
Neural Activity in Primate Parietal Area 7a Related to Spatial Analysis of Visual Mazes
 Neural Activity in Primate Parietal Area 7a Related to Spatial Analysis of Visual Mazes David A. Crowe 1,2, Matthew V. Chafee 1,3, Bruno B. Averbeck 1,2 and Apostolos P. Georgopoulos 1 5 1 Brain Sciences
Neural Activity in Primate Parietal Area 7a Related to Spatial Analysis of Visual Mazes David A. Crowe 1,2, Matthew V. Chafee 1,3, Bruno B. Averbeck 1,2 and Apostolos P. Georgopoulos 1 5 1 Brain Sciences
Time Course of Attention Reveals Different Mechanisms for Spatial and Feature-Based Attention in Area V4
 Neuron, Vol. 47, 637 643, September 1, 2005, Copyright 2005 by Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.07.020 Time Course of Attention Reveals Different Mechanisms for Spatial and Feature-Based Attention
Neuron, Vol. 47, 637 643, September 1, 2005, Copyright 2005 by Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.07.020 Time Course of Attention Reveals Different Mechanisms for Spatial and Feature-Based Attention
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 11: Attention & Decision making Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 11: Attention & Decision making Lesson Title 1 Introduction 2 Structure and Function of the NS 3 Windows to the Brain 4 Data analysis 5 Data analysis
Expansion of MT Neurons Excitatory Receptive Fields during Covert Attentive Tracking
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 26, 2011 31(43):15499 15510 15499 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Expansion of MT Neurons Excitatory Receptive Fields during Covert Attentive Tracking Robert Niebergall,
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 26, 2011 31(43):15499 15510 15499 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Expansion of MT Neurons Excitatory Receptive Fields during Covert Attentive Tracking Robert Niebergall,
Attentional Changes in Either Criterion or Sensitivity Are Associated with Robust Modulations in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex
 Article Attentional Changes in Either Criterion or Sensitivity Are Associated with Robust Modulations in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex Highlights d Two behavioral components of visuospatial attention were
Article Attentional Changes in Either Criterion or Sensitivity Are Associated with Robust Modulations in Lateral Prefrontal Cortex Highlights d Two behavioral components of visuospatial attention were
Single cell tuning curves vs population response. Encoding: Summary. Overview of the visual cortex. Overview of the visual cortex
 Encoding: Summary Spikes are the important signals in the brain. What is still debated is the code: number of spikes, exact spike timing, temporal relationship between neurons activities? Single cell tuning
Encoding: Summary Spikes are the important signals in the brain. What is still debated is the code: number of spikes, exact spike timing, temporal relationship between neurons activities? Single cell tuning
The Integration of Features in Visual Awareness : The Binding Problem. By Andrew Laguna, S.J.
 The Integration of Features in Visual Awareness : The Binding Problem By Andrew Laguna, S.J. Outline I. Introduction II. The Visual System III. What is the Binding Problem? IV. Possible Theoretical Solutions
The Integration of Features in Visual Awareness : The Binding Problem By Andrew Laguna, S.J. Outline I. Introduction II. The Visual System III. What is the Binding Problem? IV. Possible Theoretical Solutions
Responses to Auditory Stimuli in Macaque Lateral Intraparietal Area I. Effects of Training
 Responses to Auditory Stimuli in Macaque Lateral Intraparietal Area I. Effects of Training ALEXANDER GRUNEWALD, 1 JENNIFER F. LINDEN, 2 AND RICHARD A. ANDERSEN 1,2 1 Division of Biology and 2 Computation
Responses to Auditory Stimuli in Macaque Lateral Intraparietal Area I. Effects of Training ALEXANDER GRUNEWALD, 1 JENNIFER F. LINDEN, 2 AND RICHARD A. ANDERSEN 1,2 1 Division of Biology and 2 Computation
Representation of Multiple, Independent Categories in the Primate Prefrontal Cortex
 Article Representation of Multiple, Independent Categories in the Primate Prefrontal Cortex Jason A. Cromer, Jefferson E. Roy, and Earl K. Miller, * The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and Department
Article Representation of Multiple, Independent Categories in the Primate Prefrontal Cortex Jason A. Cromer, Jefferson E. Roy, and Earl K. Miller, * The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and Department
Double dissociation of value computations in orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate neurons
 Supplementary Information for: Double dissociation of value computations in orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate neurons Steven W. Kennerley, Timothy E. J. Behrens & Jonathan D. Wallis Content list: Supplementary
Supplementary Information for: Double dissociation of value computations in orbitofrontal and anterior cingulate neurons Steven W. Kennerley, Timothy E. J. Behrens & Jonathan D. Wallis Content list: Supplementary
Attention improves performance primarily by reducing interneuronal correlations
 Attention improves performance primarily by reducing interneuronal correlations Marlene R Cohen & John H R Maunsell 29 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. Visual attention can improve behavioral
Attention improves performance primarily by reducing interneuronal correlations Marlene R Cohen & John H R Maunsell 29 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. Visual attention can improve behavioral
Visual and Visual-Motor Functions of the Posterior Parietal Cortex
 Neurobiology of Neocortex eds. P. Rakic and W. Singer. pp. 285-295 John Wiley & Sons Limited S. Bernhard. Dahlem Konferenzen, 1988. Visual and Visual-Motor Functions of the Posterior Parietal Cortex RA
Neurobiology of Neocortex eds. P. Rakic and W. Singer. pp. 285-295 John Wiley & Sons Limited S. Bernhard. Dahlem Konferenzen, 1988. Visual and Visual-Motor Functions of the Posterior Parietal Cortex RA
Ventrolateral Prefrontal Neuronal Activity Related to Active Controlled Memory Retrieval in Nonhuman Primates
 Cerebral Cortex 2007;17:i27-i40 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm086 Ventrolateral Prefrontal Neuronal Activity Related to Active Controlled Memory Retrieval in Nonhuman Primates Genevie` ve Cadoret and Michael Petrides
Cerebral Cortex 2007;17:i27-i40 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm086 Ventrolateral Prefrontal Neuronal Activity Related to Active Controlled Memory Retrieval in Nonhuman Primates Genevie` ve Cadoret and Michael Petrides
Quantitative Comparison Between Neural Response in Macaque Inferotemporal Cortex and Behavioral Discrimination of Photographic Images
 J Neurophysiol 98: 263 277, 27. First published June 27, 27; doi:.52/jn.6.27. Quantitative Comparison etween Neural Response in Macaque Inferotemporal Cortex and ehavioral Discrimination of Photographic
J Neurophysiol 98: 263 277, 27. First published June 27, 27; doi:.52/jn.6.27. Quantitative Comparison etween Neural Response in Macaque Inferotemporal Cortex and ehavioral Discrimination of Photographic
From feedforward vision to natural vision: The impact of free viewing and clutter on monkey inferior temporal object representations
 From feedforward vision to natural vision: The impact of free viewing and clutter on monkey inferior temporal object representations James DiCarlo The McGovern Institute for Brain Research Department of
From feedforward vision to natural vision: The impact of free viewing and clutter on monkey inferior temporal object representations James DiCarlo The McGovern Institute for Brain Research Department of
Time [ms]
![Time [ms] Time [ms]](/thumbs/95/126316840.jpg) Magazine R1051 Brief motion stimuli preferentially activate surroundsuppressed neurons in macaque visual area MT Jan Churan, Farhan A. Khawaja, James M.G. Tsui and Christopher C. Pack Intuitively one might
Magazine R1051 Brief motion stimuli preferentially activate surroundsuppressed neurons in macaque visual area MT Jan Churan, Farhan A. Khawaja, James M.G. Tsui and Christopher C. Pack Intuitively one might
A Comparison of Abstract Rules in the Prefrontal Cortex, Premotor Cortex, Inferior Temporal Cortex, and Striatum
 A Comparison of Abstract Rules in the Prefrontal Cortex, Premotor Cortex, Inferior Temporal Cortex, and Striatum Rahmat Muhammad 1, Jonathan D. Wallis 1,2, and Earl K. Miller 1 Abstract & The ability to
A Comparison of Abstract Rules in the Prefrontal Cortex, Premotor Cortex, Inferior Temporal Cortex, and Striatum Rahmat Muhammad 1, Jonathan D. Wallis 1,2, and Earl K. Miller 1 Abstract & The ability to
A Role for Neural Integrators in Perceptual Decision Making
 A Role for Neural Integrators in Perceptual Decision Making Mark E. Mazurek, Jamie D. Roitman, Jochen Ditterich and Michael N. Shadlen Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Physiology and Biophysics,
A Role for Neural Integrators in Perceptual Decision Making Mark E. Mazurek, Jamie D. Roitman, Jochen Ditterich and Michael N. Shadlen Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Physiology and Biophysics,
Attention March 4, 2009
 Attention March 4, 29 John Maunsell Mitchell, JF, Sundberg, KA, Reynolds, JH (27) Differential attention-dependent response modulation across cell classes in macaque visual area V4. Neuron, 55:131 141.
Attention March 4, 29 John Maunsell Mitchell, JF, Sundberg, KA, Reynolds, JH (27) Differential attention-dependent response modulation across cell classes in macaque visual area V4. Neuron, 55:131 141.
A normalization model suggests that attention changes the weighting of inputs between visual areas
 A normalization model suggests that attention changes the weighting of inputs between visual areas Douglas A. Ruff a,1 and Marlene R. Cohen a a Department of Neuroscience and Center for the Neural Basis
A normalization model suggests that attention changes the weighting of inputs between visual areas Douglas A. Ruff a,1 and Marlene R. Cohen a a Department of Neuroscience and Center for the Neural Basis
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Neural correlates of multisensory cue integration in macaque MSTd
 Neural correlates of multisensory cue integration in macaque MSTd Yong Gu, Dora E Angelaki,3 & Gregory C DeAngelis 3 Human observers combine multiple sensory cues synergistically to achieve greater perceptual
Neural correlates of multisensory cue integration in macaque MSTd Yong Gu, Dora E Angelaki,3 & Gregory C DeAngelis 3 Human observers combine multiple sensory cues synergistically to achieve greater perceptual
Supplemental Information. Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking. Activity in Early Visual Cortex. Supplemental Information Inventory:
 Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Extrastriate Visual Areas February 27, 2003 A. Roe
 Extrastriate Visual Areas February 27, 2003 A. Roe How many extrastriate areas are there? LOTS!!! Macaque monkey flattened cortex Why? How do we know this? Topography Functional properties Connections
Extrastriate Visual Areas February 27, 2003 A. Roe How many extrastriate areas are there? LOTS!!! Macaque monkey flattened cortex Why? How do we know this? Topography Functional properties Connections
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nature. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 August 17.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2008 May 15; 453(7193): 406 409. doi:10.1038/nature06849. Free choice activates a decision circuit between frontal and parietal
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2008 May 15; 453(7193): 406 409. doi:10.1038/nature06849. Free choice activates a decision circuit between frontal and parietal
Representation of Multiple, Independent Categories in the Primate Prefrontal Cortex
 Representation of Multiple, Independent Categories in the Primate Prefrontal Cortex Jason A. Cromer, Jefferson E. Roy, and Earl K. Miller* The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and Department of
Representation of Multiple, Independent Categories in the Primate Prefrontal Cortex Jason A. Cromer, Jefferson E. Roy, and Earl K. Miller* The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and Department of
Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition
 Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition Charles F. Cadieu, Ha Hong, Daniel L. K. Yamins, Nicolas Pinto, Diego Ardila, Ethan A. Solomon, Najib
Deep Neural Networks Rival the Representation of Primate IT Cortex for Core Visual Object Recognition Charles F. Cadieu, Ha Hong, Daniel L. K. Yamins, Nicolas Pinto, Diego Ardila, Ethan A. Solomon, Najib
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Neural Netw. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2007 November 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neural Netw. 2006 November ; 19(9): 1447 1449. Models of human visual attention should consider trial-by-trial variability in preparatory
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neural Netw. 2006 November ; 19(9): 1447 1449. Models of human visual attention should consider trial-by-trial variability in preparatory
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in. primate lateral prefrontal cortex
 Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Motor Systems I Cortex. Reading: BCP Chapter 14
 Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Motor Systems I Cortex Reading: BCP Chapter 14 Principles of Sensorimotor Function Hierarchical Organization association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest signals flow between levels over
Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation. Tom Hartley
 Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation Tom Hartley t.hartley@psychology.york.ac.uk Typical Model Neuron x i w ij x j =f(σw ij x j ) w jk x k McCulloch & Pitts (1943), Rosenblatt (1957) Net input:
Cognitive Modelling Themes in Neural Computation Tom Hartley t.hartley@psychology.york.ac.uk Typical Model Neuron x i w ij x j =f(σw ij x j ) w jk x k McCulloch & Pitts (1943), Rosenblatt (1957) Net input:
Adaptation to Speed in Macaque Middle Temporal and Medial Superior Temporal Areas
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 6, 2013 33(10):4359 4368 4359 Systems/Circuits Adaptation to Speed in Macaque Middle Temporal and Medial Superior Temporal Areas Nicholas S. C. Price 1 and Richard T.
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 6, 2013 33(10):4359 4368 4359 Systems/Circuits Adaptation to Speed in Macaque Middle Temporal and Medial Superior Temporal Areas Nicholas S. C. Price 1 and Richard T.
Short Term and Working Memory
 Short Term and Working Memory 793 Short Term and Working Memory B R Postle, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI, USA T Pasternak, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA ã 29 Elsevier Ltd.
Short Term and Working Memory 793 Short Term and Working Memory B R Postle, University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI, USA T Pasternak, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY, USA ã 29 Elsevier Ltd.
Limits to the Use of Iconic Memory
 Limits to Iconic Memory 0 Limits to the Use of Iconic Memory Ronald A. Rensink Departments of Psychology and Computer Science University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4 Canada Running Head: Limits
Limits to Iconic Memory 0 Limits to the Use of Iconic Memory Ronald A. Rensink Departments of Psychology and Computer Science University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4 Canada Running Head: Limits
Perceptual Read-Out of Conjoined Direction and Disparity Maps in Extrastriate Area MT
 Perceptual Read-Out of Conjoined Direction and Disparity Maps in Extrastriate Area MT Gregory C. DeAngelis 1*, William T. Newsome 2 PLoS BIOLOGY 1 Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, Washington University
Perceptual Read-Out of Conjoined Direction and Disparity Maps in Extrastriate Area MT Gregory C. DeAngelis 1*, William T. Newsome 2 PLoS BIOLOGY 1 Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology, Washington University
Persistent Spatial Information in the Frontal Eye Field during Object-Based Short-Term Memory
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 8, 2012 32(32):10907 10914 10907 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Persistent Spatial Information in the Frontal Eye Field during Object-Based Short-Term Memory Kelsey L.
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 8, 2012 32(32):10907 10914 10907 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Persistent Spatial Information in the Frontal Eye Field during Object-Based Short-Term Memory Kelsey L.
Selectivity of Inferior Temporal Neurons for Realistic Pictures Predicted by Algorithms for Image Database Navigation
 J Neurophysiol 94: 4068 4081, 2005. First published August 24, 2005; doi:10.1152/jn.00130.2005. Selectivity of Inferior Temporal Neurons for Realistic Pictures Predicted by Algorithms for Image Database
J Neurophysiol 94: 4068 4081, 2005. First published August 24, 2005; doi:10.1152/jn.00130.2005. Selectivity of Inferior Temporal Neurons for Realistic Pictures Predicted by Algorithms for Image Database
Perceptual Decisions between Multiple Directions of Visual Motion
 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 3, 8 8(7):4435 4445 4435 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Perceptual Decisions between Multiple Directions of Visual Motion Mamiko Niwa and Jochen Ditterich, Center for Neuroscience
The Journal of Neuroscience, April 3, 8 8(7):4435 4445 4435 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Perceptual Decisions between Multiple Directions of Visual Motion Mamiko Niwa and Jochen Ditterich, Center for Neuroscience
Chapter 7: First steps into inferior temporal cortex
 BEWARE: These are preliminary notes. In the future, they will become part of a textbook on Visual Object Recognition. Chapter 7: First steps into inferior temporal cortex Inferior temporal cortex (ITC)
BEWARE: These are preliminary notes. In the future, they will become part of a textbook on Visual Object Recognition. Chapter 7: First steps into inferior temporal cortex Inferior temporal cortex (ITC)
Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey
 3.6.QH Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey Versnel, Huib; Zwiers, Marcel; Van Opstal, John Department of Biophysics University of Nijmegen Geert Grooteplein 655
3.6.QH Spectro-temporal response fields in the inferior colliculus of awake monkey Versnel, Huib; Zwiers, Marcel; Van Opstal, John Department of Biophysics University of Nijmegen Geert Grooteplein 655
The detection of visual signals by macaque frontal eye field during masking
 articles The detection of visual signals by macaque frontal eye field during masking Kirk G. Thompson and Jeffrey D. Schall Vanderbilt Vision Research Center, Department of Psychology, Wilson Hall, Vanderbilt
articles The detection of visual signals by macaque frontal eye field during masking Kirk G. Thompson and Jeffrey D. Schall Vanderbilt Vision Research Center, Department of Psychology, Wilson Hall, Vanderbilt
Report. Attention Narrows Position Tuning of Population Responses in V1
 Current Biology 19, 1356 1361, August 25, 2009 ª2009 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.059 Attention Narrows Position Tuning of Population Responses in V1 Report Jason Fischer
Current Biology 19, 1356 1361, August 25, 2009 ª2009 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.059 Attention Narrows Position Tuning of Population Responses in V1 Report Jason Fischer
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch!
 Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention
 Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
Cognitive Neuroscience Attention There are many aspects to attention. It can be controlled. It can be focused on a particular sensory modality or item. It can be divided. It can set a perceptual system.
Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings
 Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings J. Besle, P. Lakatos, C.A. Schevon, R.R. Goodman, G.M. McKhann, A. Mehta, R.G. Emerson, C.E.
Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings J. Besle, P. Lakatos, C.A. Schevon, R.R. Goodman, G.M. McKhann, A. Mehta, R.G. Emerson, C.E.
Representation of 3-D surface orientation by velocity and disparity gradient cues in area MT
 J Neurophysiol 107: 2109 2122, 2012. First published January 4, 2012; doi:10.1152/jn.00578.2011. Representation of 3-D surface orientation by velocity and disparity gradient cues in area MT Takahisa M.
J Neurophysiol 107: 2109 2122, 2012. First published January 4, 2012; doi:10.1152/jn.00578.2011. Representation of 3-D surface orientation by velocity and disparity gradient cues in area MT Takahisa M.
Adventures into terra incognita
 BEWARE: These are preliminary notes. In the future, they will become part of a textbook on Visual Object Recognition. Chapter VI. Adventures into terra incognita In primary visual cortex there are neurons
BEWARE: These are preliminary notes. In the future, they will become part of a textbook on Visual Object Recognition. Chapter VI. Adventures into terra incognita In primary visual cortex there are neurons
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Neural Correlates of Structure-from-Motion Perception in Macaque V1 and MT
 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 15, 2002, 22(14):6195 6207 Neural Correlates of Structure-from-Motion Perception in Macaque V1 and MT Alexander Grunewald, David C. Bradley, and Richard A. Andersen Division
The Journal of Neuroscience, July 15, 2002, 22(14):6195 6207 Neural Correlates of Structure-from-Motion Perception in Macaque V1 and MT Alexander Grunewald, David C. Bradley, and Richard A. Andersen Division
Priming in Macaque Frontal Cortex during Popout Visual Search: Feature-Based Facilitation and Location-Based Inhibition of Return
 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2002, 22(11):4675 4685 Priming in Macaque Frontal Cortex during Popout Visual Search: Feature-Based Facilitation and Location-Based Inhibition of Return Narcisse P.
The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2002, 22(11):4675 4685 Priming in Macaque Frontal Cortex during Popout Visual Search: Feature-Based Facilitation and Location-Based Inhibition of Return Narcisse P.
Spatial Distribution of Contextual Interactions in Primary Visual Cortex and in Visual Perception
 Spatial Distribution of Contextual Interactions in Primary Visual Cortex and in Visual Perception MITESH K. KAPADIA, 1,2 GERALD WESTHEIMER, 1 AND CHARLES D. GILBERT 1 1 The Rockefeller University, New
Spatial Distribution of Contextual Interactions in Primary Visual Cortex and in Visual Perception MITESH K. KAPADIA, 1,2 GERALD WESTHEIMER, 1 AND CHARLES D. GILBERT 1 1 The Rockefeller University, New
Neural Basis of Executive Control in Prefrontal Cortical Networks
 Neural Basis of Executive Control in Prefrontal Cortical Networks A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Shikha Jain Goodwin IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Neural Basis of Executive Control in Prefrontal Cortical Networks A DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Shikha Jain Goodwin IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT
Neurons in Dorsal Visual Area V5/MT Signal Relative
 17892 The Journal of Neuroscience, December 7, 211 31(49):17892 1794 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Neurons in Dorsal Visual Area V5/MT Signal Relative Disparity Kristine Krug and Andrew J. Parker Oxford
17892 The Journal of Neuroscience, December 7, 211 31(49):17892 1794 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Neurons in Dorsal Visual Area V5/MT Signal Relative Disparity Kristine Krug and Andrew J. Parker Oxford
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Table 1 Patient characteristics Preoperative. language testing
 Categorical Speech Representation in the Human Superior Temporal Gyrus Edward F. Chang, Jochem W. Rieger, Keith D. Johnson, Mitchel S. Berger, Nicholas M. Barbaro, Robert T. Knight SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Categorical Speech Representation in the Human Superior Temporal Gyrus Edward F. Chang, Jochem W. Rieger, Keith D. Johnson, Mitchel S. Berger, Nicholas M. Barbaro, Robert T. Knight SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
Neural intrinsic timescales in the macaque dorsal premotor cortex predict the strength of spatial response coding
 Accepted Manuscript Neural intrinsic timescales in the macaque dorsal premotor cortex predict the strength of spatial response coding Rossella Cirillo, Valeria Fascianelli, Lorenzo Ferrucci, Aldo Genovesio
Accepted Manuscript Neural intrinsic timescales in the macaque dorsal premotor cortex predict the strength of spatial response coding Rossella Cirillo, Valeria Fascianelli, Lorenzo Ferrucci, Aldo Genovesio
Encoding of Reward and Space During a Working Memory Task in the Orbitofrontal Cortex and Anterior Cingulate Sulcus
 J Neurophysiol 12: 3352 3364, 29. First published September 23, 29; doi:1.1152/jn.273.29. Encoding of Reward and Space During a Working Memory Task in the Orbitofrontal Cortex and Anterior Cingulate Sulcus
J Neurophysiol 12: 3352 3364, 29. First published September 23, 29; doi:1.1152/jn.273.29. Encoding of Reward and Space During a Working Memory Task in the Orbitofrontal Cortex and Anterior Cingulate Sulcus
