STEREOTYPED AND AGGRESSIVE BEHAVIOR INDUCED BY SUSTAINED HIGH DOSE OF THEOPHYLLINE IN RATS<SUP> </SUP>
|
|
|
- Lily Jones
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 STEREOTYPED AND AGGRESSIVE BEHAVIOR INDUCED BY SUSTAINED HIGH DOSE OF THEOPHYLLINE IN RATS<SUP> </SUP> Toshiie SAKATA and Hideaki FUCHIMOTO The First Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan Accepted April 9, 1973 AbstractRepeated administrations of high doses of theophylline to rats resulted in a series of stages which progressed as treatments were continued, <I>i.e.</I> hypoactivity, stereotypy, killing attack and automutilation, etc. Stereotyped behavior was con tinuous sniffing with backward locomotion, biting of the cage floor. standing on hind legs with forelimbs-flapping and turning somersaults in the cage. The aggressive behavior associated with theophylline treatment was that seen in affective aggression. The theophyllinized killers vigorously attacked animate as well as inanimate objects including rat-pups but never consumed their prey. Possible mechanisms of the ef fect of theophylline on aggressive behavior are discussed. There has not been any demonstration assigning a definite role to methylxanthines in the central nervous system, although Quadbeck and Sachsse (I) have suggested that it may induce an increase in the permeability of the blood brain barrier. Several studies have shown that, of all mammalian tissues, the brain has the highest activity of adenyl cyclase as well as cyclic 3', 5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase, that is responsible for the destruction of cyclic AMP, and that is inhibited by methylxanthines (2, 3). In addition to these findings, cyclic AMP has a possible involvement as a mediator of behavioral change (4). This experimental evidence led to the proposal that theophylline may affect fear-moti vated behavior in shuttle avoidance responding in rats (in preparation). During the course of these studies, it was observed that some rats chronically injected with theophylline (i.p.) became aggressive and strenuously resisted handling. The purpose of the present study was to observe whether or not theophylline, when administered chronically has effects on aggressiveness, particularly from the point of gross behavior. MATERIALS AND METHODS Male albino rats of the Wisiar strain, days of age at the beginning of the ex periment were used. Subjects were housed in groups. Prior to the start of injections, each subject was handled five min a day for two successive days and was housed in an in dividual cage. On the day following the handling procedure, 28 subjects were randomly divided into 18 as the theophylline group and 10 as the saline control. The dose of theo * Supported in part by the Pharmacopsychiatry Research Foundation, and Scientific Research tyrant No from the Ministry of Education, Japan.
2 phylline used was five mg in one nil saline per 100 g body wt. with the same volume of saline being used for the controls. Each subject was given i.p. injections three times daily for four weeks with a one hr interval between injections, i.e. the daily dose of theophylline amounted to 15 mg per 100 g body wt. The animals were carefully observed for signs of stereotyped behavior, depilation and scarring before and after every injection. The stereotyped behavior was defined as a single activity which was performed continuously and dominated the subject's behavior, e.g. continuous sniffing or biting. The subjects were also presented with a series of stand ardized tests in which their killing responses were measured. The objects used as victims were rat-pups, mice and frogs as animate objects, and stuffed rats, recently deceased rats and immobile and mobile dolls as inanimate objects. The observation was done 60 min after the last injection of each of the first five days and every four days after day six. A victim was introduced into the home cage of the rat, then if a kill did not occur within three min after the confrontation, the victim was removed. Each subject was given a three min trial with each of the objects on each experimental day. A pilot study showed that a kill rarely occurred after three min in the case of the theophyllinized rats. RESULTS Ten subjects out of 18 in the theophyllinized group died from the toxic effects of the drag, while none of the controls died. As shown in Table 1, the effects of theophyllinc seemed to develop in a series of stages which progressed as treatments continued. In the hypoactive stage, theophyllinized rats sat still in a crouched posture with piloerection in a corner of a cage and seldom responded to such external stimuli as tapping on the back, pushing the side of the body or blowing air over the body, etc. The animals looked quiet and weak, but they did not lose norm,ii activities, such as eating, grooming, rearing, preen in(! and forward locomotion. The stereotyped behavior stihich developed next included continuous sniffing with TABLE I. Latency and frequency to the distinguished gross signs and behaviors, plus the mortality observed in theophyllinized rats. I "Days at onset" refers to the range of days at which the different rats first ex hibited different behavior. 2 Each point of numerator represents number of rats exhibiting the behavior and each point of the denominator the number of survivals. 3 Significance of difference (Fisher exact probability test) in respect to the control group :: p.05, _* p.01. k:. p _.001.
3 backward locomotion, biting of the cage floor, standing on hind legs with forelimbs-flapp ing, sometimes pressing of the body against the cage wall and turning somersaults, how ever normal activities were also present. Various killing behaviors, whether the victim was animate or inanimate, developed almost at the same stage. A kill did occur in about 60"') of the theophyllinized rats, in which case all these killing responses were provoked within several sec after a victim was introduced into a home cage of the theophyllinized rat. established, it continued for the remainder of the experiment. Once the killing behavior was The extreme and persistent attack was directed not only against live victims, but also against inanimate objects in cluding stuffed rats. The killing behavior produced in the theophyllinized rats never re sulted in the consumption of the prey. Theophylline-treated rats killed by biting their victims through the spinal cord in the cervical region. The killer was very likely to hold the victim with his teeth and struggle vigorously, when the victim was removed from a cage. These killing patterns did not change until the end of the experiment, whether the victim was animate or inanimate, including rat-pups. Ficn. I. Automutilation around the root of the tail in a rat treated with sustained high dose of theophylline. Rats on theophyllin also mutilated themselves by biting and tearing their paws and the tail and the skin around the root of the tail, shown in Fig. 1, in the same manner as described by Seegmiller (5). There were no apparent differences between the sexes con cerning elicitation. The hair over the abdomen or the legs fell oj' gradually and scars were sometimes evident on the limbs and the tail. The theophyllinized rats responded much more quickly to noises than did the controls, and consumed their food more rapidly. None of the control animals revealed any of the behavior observed in the theophylline treated animals.
4 Recent studies have shown that caffeine and theophylline at mild or strong doses produce apparent sedation, lack of movement (6, 7) and anxiety-reducing activity (8), though re versal of effects is observed only after acute drug administration. The behavioral hypo active effects observed herein during acute administration of theophylline support this finding. The present study was primarily concerned with behavioral changes which de veloped during the course of chronic administration of theophylline. Emphasis is, there fore, placed on the fact that the effects of theophylline under conditions of chronic admin istration developed not only in the hypoactive stage as the initial effect of the drug, but were also observed in such a series of stages as stereotypy, killing attack and automutila tion, etc. The types of stereotyped behavior in these theophyllinized rats are somewhat similar to those seen with several stimulant drugs represented by amphetamine. Many findings indicate that the development of stereotypy induced by classical stimulants is associated with dopaminergic mechanisms in the corpus striatum, in which the dopamine of the brain is highly concentrated (6). Although additional research is necessary to elucidate the biochemical mechanisms involved in eliciting stereotypy, Waldeck (9) has indicated that methylxanthines increase the turnover of noradrenaline and dopamine in the mouse brain when given in sufficiently large doses, and inferred that the effect of methylxanthines on catecholamines could be due to inhibition of the catabolism of intraneuronal cyclic AMP. The aggressive behavior associated with theophylline treatment is consistent with that seen in affective aggression. Moyer (10) classifies the various types of aggression into seven categories in which the affective aggressions are characterized by the following responses: attack is not followed by the consumption of prey, a wide variety of inanimate as well as animate objects is attacked, and the range of stimuli which will elicit affective aggression is extremely broad. These characteristic traits are consistent with the behavioral responses seen in theophyllinized rats, which responded vigorously to noises, while intense noise is normally ineffective in producing fighting behavior in rats (11). In addition, once theophylline treatment induced the rats to kill, these rats attacked inanimate as well as animate objects without consuming them, though attackers, developed in other procedures, interrupt the attacking response toward dolls as well as stuffed mice and rats (11, 12). Myer (13) shows that olfactory cues control inhibition of killing rat-pups in mouse killing rats and Karl] el al. (12) suggest that the production of the killing response results from the suppression of an active inhibition mediated through the olfactory pathways which inhibit the facilitating influence of the killing response exerted by the central nucleus of the amygdala. On the other hand, the fact that serotonin has a depressant action on the activity of amygdaloid neurons led them to observe an important reduction of the sero tonin content in the amygdala in consequence of the removal of the olfactory bulbs (12). These studies suggest that the behavioral mechanism observed in the development of the killing of rat-pups may depend on the biochemical breakdown of the inhibitory mechanism through the olfactory pathways, which theophylline may have as an effect on the CNS of rats.
5 Acknowledgments: Thanks are due to Dr. 1. Arthur Mirsky and Dr. Robert E. Miller of Laboratory of Clinical Science, University of Pittsburgh, U.S.A. for suggestions and a critical reading of the manuscript, Dr. Akio Kudo of Department of Mathematics, Kyushu University for the data analysis, and Dr. Toshiyuki Yanase of the First Depart ment of Internal Medicine, Kyushu University for his interest and advice concerning the subject. REFERENCES1 ) QUADBECK, G. AND SACHSSE, W.: Nervenarzt 32, 32 (1961) 2) SUTHERLAND, E.W., RALL, T.W. AND MENON, T.: J. biol. Chem. 237, 1220 (1962) 3) BUTCHER, R.W. AND SUTHERLAND, E.W.: J. Biol. Chem. 237, 1244 (1962) 4) GESSA, G.L., KRISHNA, G., FORN, J., TAGLIAMONTE, A. AND BRODIE, B.B.: Role of cyclic AMP in cell function, Edited by COSTA, E. AND GREENGARD, P., p. 371, Raven, New York (1970) 5) SEEGMILLER, J.E.: Fedn. Proc. 27, 1042 (1968) 6) RANDRUP, A. AND MUNKVAD, International I.: symposium on amphetamines and related compounds, Edited by COSTA, E. AND GARATTINI, S., p. 695, Raven, New York (1970) 7) BERKOWITZ, B.A., SPECTOR, S. AND POOL, W.: Europ. J. Pharmacol. 16, 315 (1971) 8) BEER, B., CHASIN, M., CLODY, D.E., VOGEL, J.R. AND HOROVITZ, Z.P.: Science 176, 428 (1972) 9) WALDECK, B.: J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 23, 824 (1971) 10) MOYER, K.E.: Commun. Behav. Biol. 2, 65 (1968) 11) ULRICH, R.E. AND AZRIN, N.H.: J. Expl. Anal. Behav. 5, 511 (1962) 12) KARLI, P., VERGNES, M. AND DIDIERGEORGES, F.: Aggressive behavior, Edited by GARATTINI, S. AND SIGG, E.B., p. 47, Excepta Medica Foundation, Amsterdam (1969) 13) MYER, J.S.: J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 58, 112 (1964)
ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE
 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE V. P. GADA. V. V. JOSHI. J. J. BALSARA AND A. G. CHANDORKAR Department
SHORT COMMUNICATION ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE V. P. GADA. V. V. JOSHI. J. J. BALSARA AND A. G. CHANDORKAR Department
Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6
 Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6 I. WHAT IS AN EMOTION? A. Three components (Oately & Jenkins, 1996) 1. caused by conscious or unconscious evaluation of an event as relevant to a goal that is important
Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6 I. WHAT IS AN EMOTION? A. Three components (Oately & Jenkins, 1996) 1. caused by conscious or unconscious evaluation of an event as relevant to a goal that is important
Effects of amphetamine on the turnover rate of brain catecholamines and motor activity
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 44, 742-751. Effects of amphetamine on the turnover rate of brain catecholamines and motor activity E. COSTA, A. GROPPETTI* AND M. K. NAIMZADA* Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 44, 742-751. Effects of amphetamine on the turnover rate of brain catecholamines and motor activity E. COSTA, A. GROPPETTI* AND M. K. NAIMZADA* Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology,
STIMULATION1. of clear plastic. The floor consisted of steel. rods, %2 in. in diameter and spaced 0.5 in.
 JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR VOLUME 5, NUMBER 4 OCTOBER, 1962 REFLEXIVE FIGHTING IN RESPONSE TO A VERSIVE STIMULATION1 R. E. ULRICH AND N. H. AZRIN ILLINOIS WESLEYAN UNIVERSITY, ANNA
JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR VOLUME 5, NUMBER 4 OCTOBER, 1962 REFLEXIVE FIGHTING IN RESPONSE TO A VERSIVE STIMULATION1 R. E. ULRICH AND N. H. AZRIN ILLINOIS WESLEYAN UNIVERSITY, ANNA
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury
 Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses Toxins prevent the release of acetylcholine ex. Clostridium botulinum (botulism: muscle paralysis)/ Clostridium tetani (tetanus: a disease characterized
Biology 3201 Nervous System #6: Effects of Drugs at Synapses Toxins prevent the release of acetylcholine ex. Clostridium botulinum (botulism: muscle paralysis)/ Clostridium tetani (tetanus: a disease characterized
CNS Tour (Lecture 12)
 A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
EFFECT OF ETHOSUXIMIDE ON DOPAMINERGICALLY MEDIATED BEHAVIOURS. Department of Phermecoloqv, v.m. Medical College, So/apur
 EFFECT OF ETHOSUXIMIDE ON DOPAMINERGICALLY MEDIATED BEHAVIOURS J. H. JADHAV. J. J. BALSA RA A. J. JEURKAR AND A. G. CHANDORKAR Department of Phermecoloqv, v.m. Medical College, So/apur - 413003 (Received
EFFECT OF ETHOSUXIMIDE ON DOPAMINERGICALLY MEDIATED BEHAVIOURS J. H. JADHAV. J. J. BALSA RA A. J. JEURKAR AND A. G. CHANDORKAR Department of Phermecoloqv, v.m. Medical College, So/apur - 413003 (Received
A QUANTITATIVE METHOD FOR CONTINUOUS RECORDING OF SPONTANEOUS ACTIVITY IN SMALL ANIMALS
 A QUANTITATIVE METHOD FOR CONTINUOUS RECORDING OF SPONTANEOUS ACTIVITY IN SMALL ANIMALS SHOWA UEKI AND HISANOBU SUGANO Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, and Department of
A QUANTITATIVE METHOD FOR CONTINUOUS RECORDING OF SPONTANEOUS ACTIVITY IN SMALL ANIMALS SHOWA UEKI AND HISANOBU SUGANO Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, and Department of
Ch. 18. Brain Mechanisms of Emotion. Bear et al., Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3 rd ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006, pp
 Ch. 18. Brain Mechanisms of Emotion Bear et al., Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3 rd ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006, pp 564-583. WHAT IS EMOTION? Love, hate, disgust, joy, shame, envy, guilt,
Ch. 18. Brain Mechanisms of Emotion Bear et al., Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3 rd ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006, pp 564-583. WHAT IS EMOTION? Love, hate, disgust, joy, shame, envy, guilt,
Evidence for separate receptors for melanophore stimulating hormone and catecholamine regulation of cyclic AMP in the control of melanophore responses
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 160-166. Evidence for separate receptors for melanophore stimulating hormone and catecholamine regulation of cyclic AMP in the control of melanophore responses J. M. GOLDMAN
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 160-166. Evidence for separate receptors for melanophore stimulating hormone and catecholamine regulation of cyclic AMP in the control of melanophore responses J. M. GOLDMAN
The Effect of Dietary Wheat Protein. on Rat Behavior
 The Effect of Dietary Wheat Protein on Rat Behavior E.W. Williams ¹ Summary After oral administration of wheat proteins to rats maintained on "normal" cereal containing diet and "wheat-free" rats, the
The Effect of Dietary Wheat Protein on Rat Behavior E.W. Williams ¹ Summary After oral administration of wheat proteins to rats maintained on "normal" cereal containing diet and "wheat-free" rats, the
Safe Pig Handling: Pig Behavior and You
 Safe Pig Handling: Pig Behavior and You National Pork Board Pigs interact with Other pigs Their environment You Why do pigs act like pigs? Behavior is a result of thousands of years of adaptations Pig
Safe Pig Handling: Pig Behavior and You National Pork Board Pigs interact with Other pigs Their environment You Why do pigs act like pigs? Behavior is a result of thousands of years of adaptations Pig
Effects of Maternal Mobility, Partner, and Endocrine State on Social Responsiveness of Adolescent Rhesus Monkeys
 Effects of Maternal Mobility, Partner, and Endocrine State on Social Responsiveness of Adolescent Rhesus Monkeys CLARK O. ANDERSON Department of Psychology University of California Santa Barbara, California
Effects of Maternal Mobility, Partner, and Endocrine State on Social Responsiveness of Adolescent Rhesus Monkeys CLARK O. ANDERSON Department of Psychology University of California Santa Barbara, California
processes in the central nervous system (CNS), affecting many of the during the course of ethanol treatment. Ethanol stimulates the release of
 INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Neuroscience research is essential for understanding the biological basis of ethanol-related brain alterations and for identifying the molecular targets for therapeutic compounds
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Neuroscience research is essential for understanding the biological basis of ethanol-related brain alterations and for identifying the molecular targets for therapeutic compounds
Pharmacological study
 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY Pharmacology is one of the cornerstones of the drug discovery process. The medicinal chemist may create the candidate compound, but the pharmacologist is the one who tests it for
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY Pharmacology is one of the cornerstones of the drug discovery process. The medicinal chemist may create the candidate compound, but the pharmacologist is the one who tests it for
Hypothermia produced in mice by histamine
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 42, 205-214. Hypothermia produced in mice by histamine acting on the central nervous system GRAHAM G. SHAW Pharmacology Laboratories, Department of Pharmacy, University of Nottingham,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 42, 205-214. Hypothermia produced in mice by histamine acting on the central nervous system GRAHAM G. SHAW Pharmacology Laboratories, Department of Pharmacy, University of Nottingham,
PROBABILITY OF SHOCK IN THE PRESENCE AND ABSENCE OF CS IN FEAR CONDITIONING 1
 Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 1968, Vol. 66, No. I, 1-5 PROBABILITY OF SHOCK IN THE PRESENCE AND ABSENCE OF CS IN FEAR CONDITIONING 1 ROBERT A. RESCORLA Yale University 2 experiments
Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 1968, Vol. 66, No. I, 1-5 PROBABILITY OF SHOCK IN THE PRESENCE AND ABSENCE OF CS IN FEAR CONDITIONING 1 ROBERT A. RESCORLA Yale University 2 experiments
The effect of thyroid hormones on the action of some centrally acting drugs
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 40, 747-758. The effect of thyroid hormones on the action of some centrally acting drugs P. F. COVLLE* AND J. M. TELFORD* Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, College
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 40, 747-758. The effect of thyroid hormones on the action of some centrally acting drugs P. F. COVLLE* AND J. M. TELFORD* Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, College
INFLUENCE OF TEMPERATURE ON YEAST GROWTH AND FERMENTATION. By J. White, B.Sc., F.RJ.C, and D. J. Munns, B.Sc., A.R.I.C. Received 1st February, 1951
 280 WHITE AND MUNNSI YEAST GROWTH AND FERMENTATION [Juty-Aug., 1951 formed, the assimilation of the fructose is initially rapid, presumably because it is in the furanose form, but becomes slow as the preferential
280 WHITE AND MUNNSI YEAST GROWTH AND FERMENTATION [Juty-Aug., 1951 formed, the assimilation of the fructose is initially rapid, presumably because it is in the furanose form, but becomes slow as the preferential
The Effects of MÛGÛKA (Catha edulis vahl) on the Behaviour of Rats
 The Effects of MÛGÛKA (Catha edulis vahl) on the Behaviour of Rats N.G Obonyo, K.S Cheroigin, M.M Kariuki, K.M Sumuni, O Lang at, B.K Njogu, M.M Masika, N.B Patel ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Mûgûka (Catha edulis
The Effects of MÛGÛKA (Catha edulis vahl) on the Behaviour of Rats N.G Obonyo, K.S Cheroigin, M.M Kariuki, K.M Sumuni, O Lang at, B.K Njogu, M.M Masika, N.B Patel ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION: Mûgûka (Catha edulis
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Fluctuations of adenylate cyclase activity during anterior regeneration in Owenia fusiformis (Polychaete Annelid)
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 48, pp. 73-78, 1978 73 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1978 Fluctuations of adenylate cyclase activity during anterior regeneration in Owenia fusiformis
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 48, pp. 73-78, 1978 73 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1978 Fluctuations of adenylate cyclase activity during anterior regeneration in Owenia fusiformis
Reflexes. Dr. Baizer
 Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
ANNA STATE HOSPITAL. peated measurement of the attack. A mechanical
 JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR VOLUME 8, NUMBER 3 MAY, 1965 THE OPPORTUNITY FOR AGGRESSION AS AN OPERANT REINFORCER DURING AVERSIVE STIMULATION' N. H. AZRIN, R. R. HUTCHINSON, AND R.
JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR VOLUME 8, NUMBER 3 MAY, 1965 THE OPPORTUNITY FOR AGGRESSION AS AN OPERANT REINFORCER DURING AVERSIVE STIMULATION' N. H. AZRIN, R. R. HUTCHINSON, AND R.
INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 366-370. INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE BY B. G. BENFEY AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 366-370. INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE BY B. G. BENFEY AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
Variables and Methods for Studying Primates (Overview)
 Variables and Methods for Studying Primates (Overview) History of Field Primatology Variables: the traits you measure when you do research Examples of variables from primatology Ethograms and methods for
Variables and Methods for Studying Primates (Overview) History of Field Primatology Variables: the traits you measure when you do research Examples of variables from primatology Ethograms and methods for
Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1
 Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1 1. Suppose you observe that song sparrows sing more at dawn than at other times of the day. Hmm, maybe singing early in the morning communicates to female
Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1 1. Suppose you observe that song sparrows sing more at dawn than at other times of the day. Hmm, maybe singing early in the morning communicates to female
ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN
 Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 131-138, 26. ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN NOREEN SAMAD, TAHIRA PARVEEN, SAIDA HAIDER AND DARAKHSHAN JABEEN HALEEM
Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 131-138, 26. ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN NOREEN SAMAD, TAHIRA PARVEEN, SAIDA HAIDER AND DARAKHSHAN JABEEN HALEEM
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
AVOIDANCE LEARNING IN SHUTTLING AND NONSHUTTLING SITUATIONS, WITH AND WITHOUT A BARRIER. Kobe Juvenile Detention and Classification Home
 Japanese Psychological Research 1964, Vol.6, No.3, 129-135 AVOIDANCE LEARNING IN SHUTTLING AND NONSHUTTLING SITUATIONS, WITH AND WITHOUT A BARRIER EIJI KUNITOMI, Kobe Juvenile Detention and Classification
Japanese Psychological Research 1964, Vol.6, No.3, 129-135 AVOIDANCE LEARNING IN SHUTTLING AND NONSHUTTLING SITUATIONS, WITH AND WITHOUT A BARRIER EIJI KUNITOMI, Kobe Juvenile Detention and Classification
Animals4Balance STRETCHING. for the Horse Owner STRETCHING FOR THE HORSE OWNER
 STRETCHING FOR THE HORSE OWNER STRETCHING for the Horse Owner Peggy Sofley MAM, MMAA The Old Vicarage Cottage Metfield Nr Harleston Norfolk IP20 0PG Phone; 07796133825 E mail; animals4balance@btinternet.com
STRETCHING FOR THE HORSE OWNER STRETCHING for the Horse Owner Peggy Sofley MAM, MMAA The Old Vicarage Cottage Metfield Nr Harleston Norfolk IP20 0PG Phone; 07796133825 E mail; animals4balance@btinternet.com
Pharmacological evaluation of the central nervous system activity of Aframomum melegueta seed extract in mice
 Vol. 5/2 (2005) 141-146 141 JOURNAL OF NATURAL REMEDIES Pharmacological evaluation of the central nervous system activity of Aframomum melegueta seed extract in mice Umukoro S*, Ashorobi R. B. Department
Vol. 5/2 (2005) 141-146 141 JOURNAL OF NATURAL REMEDIES Pharmacological evaluation of the central nervous system activity of Aframomum melegueta seed extract in mice Umukoro S*, Ashorobi R. B. Department
EFFECTS OF PSYCHOTROPIC AGENTS ON SIDMAN AVOIDANCE RESPONSE IN GOOD AND POOR-PERFORMED RATS
 EFFECTS OF PSYCHOTROPIC AGENTS ON SIDMAN AVOIDANCE RESPONSE IN GOOD AND POOR-PERFORMED RATS SHUJI TAKAORI, NORIKO YADA AND GENZABURO MORI Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Kyoto University,
EFFECTS OF PSYCHOTROPIC AGENTS ON SIDMAN AVOIDANCE RESPONSE IN GOOD AND POOR-PERFORMED RATS SHUJI TAKAORI, NORIKO YADA AND GENZABURO MORI Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Kyoto University,
Psychology 020 Chapter 7: Learning Tues. Nov. 6th, 2007
 Psychology 020 Chapter 7: Learning Tues. Nov. 6th, 2007 What is involved in learning? Evolution -The changes in behaviour that accumulate across generations are stored in the genes Combined with natural
Psychology 020 Chapter 7: Learning Tues. Nov. 6th, 2007 What is involved in learning? Evolution -The changes in behaviour that accumulate across generations are stored in the genes Combined with natural
Mental Health Nursing: Suicidal Behavior. By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP
 Mental Health Nursing: Suicidal Behavior By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP Self-Protective Responses Protection and survival are fundamental needs of all living things Life is characterized by risk Individuals
Mental Health Nursing: Suicidal Behavior By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP Self-Protective Responses Protection and survival are fundamental needs of all living things Life is characterized by risk Individuals
Chapter 2. An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology
 Page 1 Chapter 2 An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology One-Dimensional vs. Multidimensional Models One-Dimensional Models Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Could mean an emphasis
Page 1 Chapter 2 An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology One-Dimensional vs. Multidimensional Models One-Dimensional Models Could mean a paradigm, school, or conceptual approach Could mean an emphasis
Dopamine-Sensitive Adenylate Cyclase in Caudate Nucleus of Rat Brain,
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 69, No. 8, pp. 2145-2149, August 1972 Dopamine-Sensitive Adenylate Cyclase in Caudate Nucleus of Rat Brain, and Its Similarity to the "Dopamine Receptor" (extrapyramidal
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 69, No. 8, pp. 2145-2149, August 1972 Dopamine-Sensitive Adenylate Cyclase in Caudate Nucleus of Rat Brain, and Its Similarity to the "Dopamine Receptor" (extrapyramidal
Beta-Adrenergic Stimulation of Pineal N-Acetyltransferase: Adenosine
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 72, No. 6, pp. 2107-2111, June 1975 Beta-Adrenergic Stimulation of Pineal : Adenosine 3':5'-Cyclic Monophosphate Stimulates Both RNA and Protein Synthesis (actinomycin D/circadian
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 72, No. 6, pp. 2107-2111, June 1975 Beta-Adrenergic Stimulation of Pineal : Adenosine 3':5'-Cyclic Monophosphate Stimulates Both RNA and Protein Synthesis (actinomycin D/circadian
Chapter 6. Learning: The Behavioral Perspective
 Chapter 6 Learning: The Behavioral Perspective 1 Can someone have an asthma attack without any particles in the air to trigger it? Can an addict die of a heroin overdose even if they ve taken the same
Chapter 6 Learning: The Behavioral Perspective 1 Can someone have an asthma attack without any particles in the air to trigger it? Can an addict die of a heroin overdose even if they ve taken the same
EVIDENCE THAT TRANQUILIZING ACTION OF RESERPINE IS ASSOCIATED WITH CHANGE IN BRAIN SEROTONIN AND NOT IN BRAIN NOREPINEPHRINE
 835 EVIDENCE THAT TRANQUILIZING ACTION OF RESERPINE IS ASSOCIATED WITH CHANGE IN BRAIN SEROTONIN AND NOT IN BRAIN NOREPINEPHRINE EFFECTS OF RESERPINE, RAUNESCI NE, BENZOQUI NOLIZI NES, DIMETHYL- AMINOBENZOYL
835 EVIDENCE THAT TRANQUILIZING ACTION OF RESERPINE IS ASSOCIATED WITH CHANGE IN BRAIN SEROTONIN AND NOT IN BRAIN NOREPINEPHRINE EFFECTS OF RESERPINE, RAUNESCI NE, BENZOQUI NOLIZI NES, DIMETHYL- AMINOBENZOYL
Stimulation by Dopamine of Adenylate Cyclase in Retinal Homogenates and of Adenosine-3':5'-Cyclic Monophosphate Formation in Intact Retina
 Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 69, No. 3, pp. 539-543, March 1972 Stimulation by Dopamine of Adenylate Cyclase in Retinal Homogenates and of Adenosine-3':5'-Cyclic Monophosphate Formation in Intact Retina
Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 69, No. 3, pp. 539-543, March 1972 Stimulation by Dopamine of Adenylate Cyclase in Retinal Homogenates and of Adenosine-3':5'-Cyclic Monophosphate Formation in Intact Retina
Japan. J. Pharmacol. 50, (1989) 327. Effects of Central Nervous System-Acting Drugs on Urinary Bladder Contraction in Unanesthetized Rats
 Japan. J. Pharmacol. 50, 327-332 (1989) 327 Effects of Central Nervous System-Acting Drugs on Urinary Bladder Contraction in Unanesthetized Rats Hitoshi KONTANI, Mikiko NAKAGAWA and Takeshi SAKAI Department
Japan. J. Pharmacol. 50, 327-332 (1989) 327 Effects of Central Nervous System-Acting Drugs on Urinary Bladder Contraction in Unanesthetized Rats Hitoshi KONTANI, Mikiko NAKAGAWA and Takeshi SAKAI Department
THE PROTEIN REQUIREMENTS OF THE ALBINO MOUSE
 THE PROTEIN REQUIREMENTS OF THE ALBINO MOUSE By FRANKLINC. BING, W. LLOYDADAMSANDRÃœSSEL0. BOWMAN (From the Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Western Reserve University, Cleveland?) Received
THE PROTEIN REQUIREMENTS OF THE ALBINO MOUSE By FRANKLINC. BING, W. LLOYDADAMSANDRÃœSSEL0. BOWMAN (From the Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Western Reserve University, Cleveland?) Received
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models. From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. locomotion.
 STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
Extinction-Induced Aggression in Laboratory Rats
 llinois Wesleyan University Digital Commons @ WU Honors Projects Psychology 1992 Extinction-nduced Aggression in Laboratory Rats Amy K. Rajala '92 llinois Wesleyan University Recommended Citation Rajala
llinois Wesleyan University Digital Commons @ WU Honors Projects Psychology 1992 Extinction-nduced Aggression in Laboratory Rats Amy K. Rajala '92 llinois Wesleyan University Recommended Citation Rajala
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
EVALUATION OF ANTIDEPRESSANT ACTIVITY OF ONDANSETRON IN ALBINO MICE
 EVALUATION OF ANTIDEPRESSANT ACTIVITY OF ONDANSETRON IN ALBINO MICE *Janardhan M. 1, Anil kumar G. 1 and Naveen Kumar T. 2 1 Department of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences and Research,
EVALUATION OF ANTIDEPRESSANT ACTIVITY OF ONDANSETRON IN ALBINO MICE *Janardhan M. 1, Anil kumar G. 1 and Naveen Kumar T. 2 1 Department of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences and Research,
AMOUNT OF RESPONSE-PRODUCED CHANGE IN THE CS AND AVOIDANCE LEARNING 1
 Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 1965, Vol. 59, No. 1, 13-17 AMOUNT OF RESPONSE-PRODUCED CHANGE IN THE CS AND AVOIDANCE LEARNING 1 GORDON BOWER, RONALD STARR, AND LEAH LAZAROVITZ Stanford
Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology 1965, Vol. 59, No. 1, 13-17 AMOUNT OF RESPONSE-PRODUCED CHANGE IN THE CS AND AVOIDANCE LEARNING 1 GORDON BOWER, RONALD STARR, AND LEAH LAZAROVITZ Stanford
Mt. Vesuvius WORKOUT #9. 1 FUNK ROBERTS SPARTAN TRAINING SYSTEM // Workout 9 // Week 10 // week 10
 WORKOUT # week 10 MEDICAL DISCLAIMER This guide is for educational and informative purposes only and is not intended as medical or professional advice. Always consult your doctor before making any changes
WORKOUT # week 10 MEDICAL DISCLAIMER This guide is for educational and informative purposes only and is not intended as medical or professional advice. Always consult your doctor before making any changes
Suicide Rate: Depression vs MS vs TM
 Suicide Rate: Depression vs MS vs TM History and Epidemiology of Cognitive Impairment in MS Charcot (1877) noted that at a certain stage of the disease patients with MS may show marked enfeeblement of
Suicide Rate: Depression vs MS vs TM History and Epidemiology of Cognitive Impairment in MS Charcot (1877) noted that at a certain stage of the disease patients with MS may show marked enfeeblement of
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience lec9_ neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy
 Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Comorbidity of alcoholism and antisocial personality disorder
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Presentations 2005: Alcoholism and Comorbidity 2005 Comorbidity of alcoholism and antisocial personality disorder R. O. Pihl McGill University
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Presentations 2005: Alcoholism and Comorbidity 2005 Comorbidity of alcoholism and antisocial personality disorder R. O. Pihl McGill University
Psychotropic Drugs Critical Thinking - KEY
 Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Lecture 17 (Nov 28 th ): STRESS RESPONSE AND HEALTH Lecture Outline
 Lecture 17 (Nov 28 th ): STRESS RESPONSE AND HEALTH Lecture Outline 1) Three Types of Responses to Stress 1) Direct Behavioral 2) Sympathetic System (Branch of Autonomic System) 3) Hormonal ** there is
Lecture 17 (Nov 28 th ): STRESS RESPONSE AND HEALTH Lecture Outline 1) Three Types of Responses to Stress 1) Direct Behavioral 2) Sympathetic System (Branch of Autonomic System) 3) Hormonal ** there is
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Variety of muscle responses to tactile stimuli
 Variety of muscle responses to tactile stimuli Julita Czarkowska-Bauch Department of Neurophysiology, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, 3 Pasteur St., 02-093 Warsaw, Poland Abstract. Influences
Variety of muscle responses to tactile stimuli Julita Czarkowska-Bauch Department of Neurophysiology, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, 3 Pasteur St., 02-093 Warsaw, Poland Abstract. Influences
samples and assayed for 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) on the rat stomachstrip preparation. Rectal temperature was monitored continuously.
 J. Phy8iol. (1967), 188, pp. 131-140 131 With 3 text-fitgurem Printed in Great Britain MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITION: EFFECT ON 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE OUTPUT FROM PERFUSED THIRD VENTRICLE AND BODY TEMPERATURE
J. Phy8iol. (1967), 188, pp. 131-140 131 With 3 text-fitgurem Printed in Great Britain MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITION: EFFECT ON 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE OUTPUT FROM PERFUSED THIRD VENTRICLE AND BODY TEMPERATURE
A Comparative study of the Anti convulsant effect of Nimodipine and Ketamine combination with standard anticonvulsant drug in Rodents
 Original Article A Comparative study of the Anti convulsant effect of Nimodipine and Ketamine combination with standard anticonvulsant drug in Rodents Prasanand S 1, Pushpalatha C 2, Mohsin MD 3, Sam Pavan
Original Article A Comparative study of the Anti convulsant effect of Nimodipine and Ketamine combination with standard anticonvulsant drug in Rodents Prasanand S 1, Pushpalatha C 2, Mohsin MD 3, Sam Pavan
CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 3.1. THE BASIC STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. The nervous system of all animals is made up of groups of neurons that receive information from sensory systems,
CHAPTER 3 THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 3.1. THE BASIC STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. The nervous system of all animals is made up of groups of neurons that receive information from sensory systems,
Pain-elicited aggression in the squirrel monkey: An implicit avoidance contingency
 Animal Learning & Behavior 1976, Vol. 4(lA), 89-95 Pain-elicited aggression in the squirrel monkey: An implicit avoidance contingency PHILIP J, DUNHAM and ADAM CARR Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova
Animal Learning & Behavior 1976, Vol. 4(lA), 89-95 Pain-elicited aggression in the squirrel monkey: An implicit avoidance contingency PHILIP J, DUNHAM and ADAM CARR Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova
Reinforcers in Infancy: Classical Conditioning Using Stroking or Intra-oral Infbsions
 Reinforcers in Infancy: Classical Conditioning Using Stroking or Intra-oral Infbsions of Milk as UCS REGINA M. SULLIVAN W. G. HALL Department of Psychology Duke University Durham, North Carolina Six-day-old
Reinforcers in Infancy: Classical Conditioning Using Stroking or Intra-oral Infbsions of Milk as UCS REGINA M. SULLIVAN W. G. HALL Department of Psychology Duke University Durham, North Carolina Six-day-old
Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN wawilson@duke.edu There is a lot of epidemiological evidence that addiction begins before brain maturity, and lately some biological
Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN wawilson@duke.edu There is a lot of epidemiological evidence that addiction begins before brain maturity, and lately some biological
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
The function or adaptive value of signals has been broken down into the following classes:
 Communication notes.doc 1 Communication and signals an action on the part of one animal that alters the behavior of another (Wilson 1975). The essence of communication is the relationship between signaler
Communication notes.doc 1 Communication and signals an action on the part of one animal that alters the behavior of another (Wilson 1975). The essence of communication is the relationship between signaler
Biphasic effect of methylxanthines on acetylcholine
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1984),83,069-073 Biphasic effect of methylxanthines on acetylcholine release from electrically-stimulated brain slices Felicita Pedata, G. Pepeu & G. Spignoli Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1984),83,069-073 Biphasic effect of methylxanthines on acetylcholine release from electrically-stimulated brain slices Felicita Pedata, G. Pepeu & G. Spignoli Department of Pharmacology,
Orthostatic Hypotension (Postural Hypotension)
 Orthostatic Hypotension (Postural Hypotension) Authors: SCIRE Community Team Reviewed by: Darryl Caves, PT Last updated: April 9, 2018 Changes to blood pressure control after spinal cord injury (SCI) may
Orthostatic Hypotension (Postural Hypotension) Authors: SCIRE Community Team Reviewed by: Darryl Caves, PT Last updated: April 9, 2018 Changes to blood pressure control after spinal cord injury (SCI) may
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S
 The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
Introduction to seizure and epilepsy
 Introduction to seizure and epilepsy 1 Epilepsy : disorder of brain function characterized by a periodic and unpredictable occurrence of seizures. Seizure : abnormal increased electrical activity in the
Introduction to seizure and epilepsy 1 Epilepsy : disorder of brain function characterized by a periodic and unpredictable occurrence of seizures. Seizure : abnormal increased electrical activity in the
BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES
 Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
J. Physiol. (I942) IOI, I3I-I
 131 J. Physiol. (I942) IOI, I3I-I35 612.392.6 THE EFFECT OF SODIUM AND CALCIUM ON THE TOXICITY OF POTASSIUM IN MICE BY C.. W. EMMENS AND H. P. MARKS National Institute for Medical Research, Hampstead,
131 J. Physiol. (I942) IOI, I3I-I35 612.392.6 THE EFFECT OF SODIUM AND CALCIUM ON THE TOXICITY OF POTASSIUM IN MICE BY C.. W. EMMENS AND H. P. MARKS National Institute for Medical Research, Hampstead,
1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or to the head TA (jcolas).
 Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bi/CNS/NB 150 Problem Set 5 Due: Tuesday, Nov. 24, at 4:30 pm Instructions: 1) Drop off in the Bi 150 box outside Baxter 331 or e-mail to the head TA (jcolas). 2) Submit with this cover page. 3) Use a
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Olfactory cues from an oxytocin-injected male rat can reduce energy loss in its cagemates
 Chemical, Electrical and Magnetic Senses RATS can recognize the odor of a stressed conspecific and react with stress themselves. Stress mobilizes energy, causing increased core temperatures and energy
Chemical, Electrical and Magnetic Senses RATS can recognize the odor of a stressed conspecific and react with stress themselves. Stress mobilizes energy, causing increased core temperatures and energy
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov ( )
 Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (1849-1936) Chapter 7 1 Ivan Petrovich Pavlov 1. Born in Ryazan, Russia on Sep 14, 1849. 2. Studied the digestive system and won the Nobel Prize in 1904 for physiology and medicine.
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov (1849-1936) Chapter 7 1 Ivan Petrovich Pavlov 1. Born in Ryazan, Russia on Sep 14, 1849. 2. Studied the digestive system and won the Nobel Prize in 1904 for physiology and medicine.
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL ON DOPAMINE DEPENDENT BEHAVIOURS IN RATS
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1999; 43 (1) : 44-52 EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL ON DOPAMINE DEPENDENT BEHAVIOURS IN RATS A. R. MALEKAR, J. J. BALSARA* AND R. K. GAONKAR Department of Pharmacology, Krishna Institute
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1999; 43 (1) : 44-52 EFFECTS OF VERAPAMIL ON DOPAMINE DEPENDENT BEHAVIOURS IN RATS A. R. MALEKAR, J. J. BALSARA* AND R. K. GAONKAR Department of Pharmacology, Krishna Institute
PSY402 Theories of Learning. Chapter 9 Biological Influences on Learning
 PSY402 Theories of Learning Chapter 9 Biological Influences on Learning Limits to Learning How general are the laws of learning? Skinner s rules work in both lab and real-world settings, across species.
PSY402 Theories of Learning Chapter 9 Biological Influences on Learning Limits to Learning How general are the laws of learning? Skinner s rules work in both lab and real-world settings, across species.
Reciprocal Hunger-Regulating Circuits Involving Alphaand
 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2, pp. 1063-1070, October 1970 Reciprocal Hunger-Regulating Circuits Involving Alphaand Beta-Adrenergic Receptors Located, Respectively, in
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2, pp. 1063-1070, October 1970 Reciprocal Hunger-Regulating Circuits Involving Alphaand Beta-Adrenergic Receptors Located, Respectively, in
BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1
 BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1 General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. For your own benefit,
BIPN100 F12 (Kristan) MIDTERM #1 Name PID p. 1 General Instructions: READ THIS PAGE BEFORE YOU BEGIN THE EXAM. 1. Write your name on every page. (5 points off for EACH unnamed page.) 2. For your own benefit,
Primate Observation Form (Use the back for continuations or additional observations)
 Primate Observation Form (Use the back for continuations or additional observations) Observer: Zoo: Date of observation: Time observation began: Time observation ended: Common name of primate: Scientific
Primate Observation Form (Use the back for continuations or additional observations) Observer: Zoo: Date of observation: Time observation began: Time observation ended: Common name of primate: Scientific
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Department of Psychology, University of Michigan Dearborn, Michigan 48128
 BEHAVIORAL BIOLOGY, 9, 605-612 (1973) Abstract No. 291 Effects of Intraventricular Norepinephrine and Estradiol Benzoate on Weight Regulatory Behavior in Female Rats JEFFREY J. STERN AND GARY ZWICK Department
BEHAVIORAL BIOLOGY, 9, 605-612 (1973) Abstract No. 291 Effects of Intraventricular Norepinephrine and Estradiol Benzoate on Weight Regulatory Behavior in Female Rats JEFFREY J. STERN AND GARY ZWICK Department
ANTECEDENT REINFORCEMENT CONTINGENCIES IN THE STIMULUS CONTROL OF AN A UDITORY DISCRIMINA TION' ROSEMARY PIERREL AND SCOT BLUE
 JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR ANTECEDENT REINFORCEMENT CONTINGENCIES IN THE STIMULUS CONTROL OF AN A UDITORY DISCRIMINA TION' ROSEMARY PIERREL AND SCOT BLUE BROWN UNIVERSITY 1967, 10,
JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR ANTECEDENT REINFORCEMENT CONTINGENCIES IN THE STIMULUS CONTROL OF AN A UDITORY DISCRIMINA TION' ROSEMARY PIERREL AND SCOT BLUE BROWN UNIVERSITY 1967, 10,
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
Environmental Enrichment for Captive Animals: The Past, Present, and Future
 Environmental Enrichment for Captive Animals: The Past, Present, and Future Ha Lab James C. Ha, PhD Certified Applied Animal Behaviorist and Emeritus Research Professor, Animal Behavior Program, Department
Environmental Enrichment for Captive Animals: The Past, Present, and Future Ha Lab James C. Ha, PhD Certified Applied Animal Behaviorist and Emeritus Research Professor, Animal Behavior Program, Department
The Nervous System. Neuron 01/12/2011. The Synapse: The Processor
 The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
THE ROLE OF ANXIETY IN A RAT MODEL OF SELF-INJURY
 THE ROLE OF ANXIETY IN A RAT MODEL OF SELF-INJURY By XIAOMENG YUAN A MASTER THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
THE ROLE OF ANXIETY IN A RAT MODEL OF SELF-INJURY By XIAOMENG YUAN A MASTER THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
A STUDY OF THE ROLE OF BRAIN CATECHOLAMINES IN DRUG INDUCED TREMOR
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1967), 3, 349-353. A STUDY OF THE ROLE OF BRAIN CATECHOLAMINES IN DRUG INDUCED TREMOR BY S. L. AGARWAL AND D. BOSE From the Department of Pharmacology, M.G.M. Medical College,
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1967), 3, 349-353. A STUDY OF THE ROLE OF BRAIN CATECHOLAMINES IN DRUG INDUCED TREMOR BY S. L. AGARWAL AND D. BOSE From the Department of Pharmacology, M.G.M. Medical College,
Chapter 8. The Nervous System
 Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Lecture 15. Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction
 Lecture 15 Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction So far.. Regulation of mrna synthesis Regulation of rrna synthesis Regulation of trna & 5S rrna synthesis Regulation of gene expression by signals
Lecture 15 Signal Transduction Pathways - Introduction So far.. Regulation of mrna synthesis Regulation of rrna synthesis Regulation of trna & 5S rrna synthesis Regulation of gene expression by signals
The Emotional Nervous System
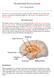 The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
Powerlift Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back. Leader s Guide and Quiz
 ! Powerlift Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back Leader s Guide and Quiz 4894 POWERLIFT: Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back PROGRAM SYNOPSIS: Most workers have been instructed to lift objects safely
! Powerlift Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back Leader s Guide and Quiz 4894 POWERLIFT: Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back PROGRAM SYNOPSIS: Most workers have been instructed to lift objects safely
WHAT S HAPPENING SEPTEMBER - NOVEMBER:
 WHAT S HAPPENING SEPTEMBER - NOVEMBER: In the fall you will see elephant seals that are too young to take part in the winter breeding season hauling out to rest. They gather together in large groups lying
WHAT S HAPPENING SEPTEMBER - NOVEMBER: In the fall you will see elephant seals that are too young to take part in the winter breeding season hauling out to rest. They gather together in large groups lying
Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test.
 Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test. DATE This study was conducted under terms of a Services Agreement between NeuroDetective Inc. and CLIENT, entitled TITLE OF
Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test. DATE This study was conducted under terms of a Services Agreement between NeuroDetective Inc. and CLIENT, entitled TITLE OF
Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011
 Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011 Inside this month's issue Headaches Acute single headaches Recurring Headaches: Migraine What causes Migraine? Treatments for migraine & prevention Headaches
Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011 Inside this month's issue Headaches Acute single headaches Recurring Headaches: Migraine What causes Migraine? Treatments for migraine & prevention Headaches
Development of retinal synaptic arrays in the inner plexiform layer of dark-reared mice
 /. Embryo/, exp. Morph. Vol. 54, pp. 219-227, 1979 219 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1977 Development of retinal synaptic arrays in the inner plexiform layer of dark-reared mice
/. Embryo/, exp. Morph. Vol. 54, pp. 219-227, 1979 219 Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1977 Development of retinal synaptic arrays in the inner plexiform layer of dark-reared mice
