Early Intervention for Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
|
|
|
- Amice Armstrong
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) Early Intervention for Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Blair Paley, PhD David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, USA February 2011 Introduction First identified in the United States over 35 years ago, 1,2 Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a major birth defect resulting from prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) and is characterized by a distinct pattern of facial abnormalities, growth retardation and central nervous system dysfunction. The term fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) 3 is used to reflect the full range of effects associated with PAE, and in addition to FAS, includes partial FAS, alcohol related neurodevelopmental disorder (ARND), and alcohol related birth defects (ARBD). 4 FASD places a significant burden on both affected families and society. The lifetime cost for a person with FAS is estimated to be approximately $2 million, most of which reflects special education and medical and mental health treatment. 5 Subject This paper reviews recent progress in developing early interventions for children with FASD, current challenges in providing services for this high-risk population, and possible directions for future research. Problems The deleterious effects of PAE are evident from infancy among both animals 6,7 and humans, 8-10 with many studies highlighting impairments in self-regulation. In infants and toddlers, PAE is associated with poorer orientation 9,11 and habituation, 12 problems with state 12 and autonomic 11 regulation, sleep abnormalities, 13 and increased level of activity. 14 Studies have also documented greater reactivity to stress, 15,16 alterations in the pain regulatory systems, 17 and increased negative affect and higher rates of insecure attachment behaviour in these children. Such problems do not appear to be transient. Significant behavioural, cognitive and emotional difficulties have CEECD / SKC-ECD FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) 1
2 been reported among individuals with FASD throughout life, including intellectual and learning disabilities, executive dysfunction, memory problems, speech and language delays, and internalizing and externalizing behaviour problems Moreover, such individuals are at increased risk for many secondary disabilities, including comorbid psychiatric conditions, school failure, alcohol and substance abuse problems, and delinquency Despite these findings, many children may not be referred for screening until relatively late (if ever), thus missing out on the potential benefit of early intervention. 34 FASD appears to be under-recognized and under-treated, particularly in certain high-risk settings, including psychiatric populations, the child welfare system, and juvenile detention and correctional facilities. 29,35,36 The importance of early identification is highlighted by findings that an early diagnosis is one of the strongest predictors of more positive outcomes for these individuals. 33 Research Context In the last few years, some initial progress has been made in the development of treatments for individuals with FASD, but those focusing on young children have been extremely limited. Early intervention studies present significant methodological challenges with this population. Recruitment of study participants can be challenging when children with FASD are often not identified until school-age. 34 Additionally, as many children with FASD are involved in the child welfare system, obtaining proper consent to enroll them in early intervention programs can be difficult. Selecting an appropriate control group can also be challenging. Given the dearth of services for this population, utilizing no-treatment control groups raises ethical issues, whereas utilizing standard of care control groups may work against finding any significant effects for programs in their early stages of development. Key Research Questions Several key lines of inquiry are currently being addressed in research on early intervention for FASD. Such questions include: 1. How can animal models inform our development of interventions for young children with PAE? 2. To what extent can early intervention programs ameliorate some of the primary deficits seen in infants and young children affected by PAE? 3. What functional domains are appropriate targets of intervention? Recent Research Results 1. Animal studies Several lines of animal research suggest the promise of various prenatal and neonatal interventions. For example, recent studies suggest that lithium may offer some protection against ethanol-induced neuroapoptosis. 37 The benefits of prenatal and postnatal treatment with neuroprotective peptides in mitigating the effects of PAE on brain development have also been reported Studies have also documented the protective effects of various nutrients, including folate, selenium, vitamin C, zinc and choline Other research has demonstrated some positive effects of neonatal handling, postnatal environment enrichment and rehabilitative training on rats and mice with perinatal alcohol exposure. 46 For example, voluntary exercise has been found to improve spatial CEECD / SKC-ECD FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) 2
3 memory among alcohol-exposed rats, 47 whereas introducing complex motor training during the postnatal period effectively remediated the motor deficits of alcohol-exposed rats Programs for mothers with substance abuse problems Treatment programs for mothers with substance abuse problems have been one route to early intervention for young children with FASD, either by providing direct services for children or by connecting mothers to services in their community. The program New Choices provides services for mothers with substance abuse problems and their children aged 0 to 5 years, including addiction counseling, parent education and counseling, peer support and enrichment programs for children. 49 A preliminary evaluation found that mothers demonstrated improvements in depressive symptoms and empathy for their children, and children exhibited improvements in social development. 50 In Seattle s Birth to Three Program, 51 paraprofessionals work with mothers with alcohol and substance use problems to connect them with appropriate services and to facilitate their ability to provide a safe caregiving environment for their children, but do not provide direct intervention services for the children. While positive effects have been found for mothers, at a three-year follow-up, no significant differences were found between the treatment and control group children on a measure of developmental functioning. 52 Such findings suggest there may be limited effects of this type of intervention on child outcomes, particularly if direct early intervention is not provided to the child. 3. Parent-focused intervention While not focusing exclusively on very young children with FASD, some studies have nonetheless included younger children in their samples. 53 One promising approach, Families Moving Forward (FMF), 54 provides supportive behavioural consultation to promote parental self-efficacy and reduce child behaviour problems in families raising children aged 4 to 11 years with FASD. Caregivers who participated in the FMF group reported greater improvements in parenting efficacy and greater reductions in child behaviour problems, compared to caregivers in the community standard of care group Cognitive and educational interventions A small number of cognitive and educational interventions for FASD have also included young children in their samples. Children aged 3 to 10 years with FASD who participated in a socio-cognitive habilitation program in mathematics in addition to receiving educational support showed greater gains on mathematics outcome measures compared to those who received educational support only, 55 and these gains were maintained six months later. 56 To address impairments in working memory, Loomes and colleagues developed an intervention to promote the use of rehearsal strategies among children aged 4 to 11 years with FASD. 57 Children in the experimental condition demonstrated significant improvement in their scores on a digit span task across three sessions whereas the control group showed no such improvement. 5. Adaptive skills training Individuals with FASD show deficits across multiple domains of adaptive functioning, including communication, socialization, and personal and community skills. 58 To address the lack of safety awareness often seen in children with FASD, a computer-based intervention was designed to increase fire and street safety skills in CEECD / SKC-ECD FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) 3
4 children aged 4 to 10 years old with FASD. Children receiving the intervention demonstrated significantly greater gains in safety-related knowledge and appropriate behavioural responses in comparison to the control group. 59 Targeting impairments in social functioning, an evidence-based, manualized, parent-assisted social skills intervention, Children s Friendship Training (CFT), 60 was adapted for use with 6- to 12-year-old children with FASD. Compared to children in the control group, those who received CFT showed significantly greater improvement in their knowledge of appropriate social behaviour and were rated by their parents as having better social skills and fewer behaviour problems following treatment, and these gains were maintained at a three month follow-up Pharmacological interventions Young children are increasingly likely to receive pharmacological interventions to address behaviour problems, 62 and given their increased risk for behaviour problems, children with FASD are likely to receive such interventions. Community and clinic-based surveys indicate that stimulants are commonly used in children with FASD. 63 Despite their common use, research on the efficacy of these medications for FASD has been limited by small samples or has entailed retrospective chart reviews rather than large-scale, double-blind, randomized controlled trials. Studies including children with FASD as young as 3 years old reveal a mixed pattern of findings, with some suggestion that symptoms of inattention may be less responsive to stimulants than hyperactive symptoms. 64,65 Additionally, children with FASD may be especially vulnerable to negative side effects, 66 or may experience atypical reactions to medications. 63 Until more systematic studies have been done examining both the benefits and potential adverse effects of pharmacological regimens with this population, it is important to use caution in prescribing medications for children with FASD, particularly young children whose still-developing brains have already been impacted by PAE. Research Gaps Several lines of inquiry are ripe for further investigation. What are the most effective strategies for identifying young children impacted by PAE so that they may be directed towards appropriate interventions as early as possible? There also remains a need for long-term follow-up studies to examine whether early intervention programs are robust enough to reduce the emergence of secondary disabilities later in life. Future studies might also investigate whether children with FASD can benefit from adaptations of existing early intervention programs, 67 including those that aim to promote more positive parent-child relationships, such as Right From the Start 68 or Attachment Biobehavioral Catch-Up, 69 as well as those designed to better equip parents to care for high risk children in foster care, such as Multidimensional Treatment Foster Care Program for Preschoolers. 70 Identifying moderators of treatment outcomes may allow programs to be tailored for certain subgroups. For example, early interventions may need to be adapted in different ways depending on the family context (i.e., birth families vs. adoptive/foster families). Conclusions Previous research has demonstrated that PAE can significantly compromise an infant s early development, particularly their capacity for self-regulation, which in turn may place them well on course for negative developmental trajectories. Deficits in self-regulation may confer further vulnerability by compromising early parent-child relationships (and potentially jeopardizing stable placements), impairing a child s ability to manage CEECD / SKC-ECD FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) 4
5 stressful situations, and interfering with their mastery of developmentally-appropriate tasks. Encouragingly, a small but growing number of studies have demonstrated with both animals and humans that early intervention can at least partially remediate some of the primary deficits associated with PAE. Such approaches are promising as they may also have the potential to mitigate some of the serious adverse outcomes often seen in individuals with FASD later in life. However, there remains much work to be done in order to identify affected children as early as possible and to develop a comprehensive continuum of services for these children and their families. Implications for Parents, Services and Policy 1. Continued efforts must be made to improve training of professionals who work with young children, such as pediatricians, pediatric nurses, child welfare workers, daycare providers, preschool teachers and early childhood mental health consultants. Such training should include a better understanding of the full range of effects that may be associated with PAE, the importance of asking about and documenting a history of prenatal exposure to not only illicit substances but to alcohol as well, and the importance of early intervention for this population. 2. Better collaboration across different systems of care (e.g., hospitals, child welfare, regional centers, Early Start and Head Start programs) is critical to track and coordinate services for children with FASD. Improved collaboration can help ensure that these children do not slip through the cracks and are directed towards effective interventions. 3. It is critical that intervention for children with FASD involves the entire family system in order to enhance the daily functioning and quality of life for these children and to better prepare and support their parents and caregivers. However, many mental health agencies are precluded from providing integrated services for children and parents by funding requirements. 71 Amending such policies would likely facilitate better parent-child relationships, and promote more stable and nurturing caregiving environments for these vulnerable children. References 1. Jones KL, Smith DW. Recognition of the fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy. Lancet 1973;302(7836): Jones KL, Smith DW, Ulleland CN, Streissguth AP. Pattern of malformations in offspring of alcoholic mothers. Lancet 1973;301(7815): Warren K, Floyd L, Calhoun F, Stone D, Bertrand J, Streissguth A, eds. Consensus statement on FASD. Washington, DC: National Organization on Fetal Alcohol Syndrome; Stratton KR, HOWE CJ, Battaglia, FC, Committee to study Fetal Alcohol Syndrome, Institute of Medicine, eds. Fetal alcohol syndrome: Diagnosis, epidemiology, prevention, and treatment. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; Lupton C, Burd L, Harwood R. Cost of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. American Journal of Medical Genetics 2004;127C(1): Lee S, Choi I, Kang S, Rivier C. Role of various neurotransmitters in mediating the long-term endocrine consequences of prenatal alcohol exposure. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2008;1144: Zhang X, Sliwowska JH, Weinberg J. Prenatal alcohol exposure and fetal programming: effects on neuroendocrine and immune function. Experimental Biology and Medicine 2005;230(6): Carter RC, Jacobson SW, Molteno CD, Chiodo LM, Viljoen D, Jacobson JL. Effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on infant visual acuity. Journal of Pediatrics 2005;147: Kable JA, Coles CD. The impact of prenatal alcohol exposure on neurophysiological encoding of environmental events at six months. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2004;28: CEECD / SKC-ECD FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) 5
6 10. Zeskind PS, Coles CD, Platzman KA, Schuetze P. Cry analysis detects subclinical effects of prenatal alcohol exposure in newborn infants. Infant Behavior and Development 1996;19: Smith I, Coles C, Lancaster J, Fernhoff P, Falek A. The effect of volume and duration of exposure on neonatal physical and behavioral development. Neurobehavioral Toxicology and Teratology 1986;8: Streissguth AP, Barr HM, Martin DC. Maternal alcohol use and neonatal habituation assessed with the Brazelton scale. Child Development 1983;54: Chen ML, Carmichael Olson H. Caregiver report of sleep problems in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2008;177:A Coles CD, Smith I, Fernhoff PM, Falek A. Neonatal neurobehavioral characteristics as correlates of maternal alcohol use during gestation. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1985;9: Haley DW, Handmaker NS, Lowe J. Infant stress reactivity and prenatal alcohol exposure. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2006;30: Jacobson SW, Bihun JT, Chiodo LM. Effects of prenatal alcohol and cocaine exposure on infant cortisol levels. Developmental Psychopathology 1999;11: Oberlander TF, Jacobson SW, Weinberg J, Grunau RE, Molteno CD, Jacobson JL. Prenatal alcohol exposure alters biobehavioral reactivity to pain in newborns. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2010;(34)4: Lemola S, Stadlmayr W, Crob A. Infant irritability: The impact of fetal alcohol exposure, maternal depressive symptoms, and low emotional support from the husband. Infant Mental Health Journal 2009;30: O Connor MJ. Prenatal alcohol exposure and infant negative affect as precursors of depressive features in children. Infant Mental Health Journal 2001;22: O Connor MJ, Sigman M, Kasari C. Interactional model for the association among maternal alcohol consumption, mother-infant characteristics and infant cognitive development. Infant Behavior and Development 1993;16: Burd L, Klug, MG, Martsolf, JT, Kerbeshian J. Fetal alcohol syndrome: neuropsychiatric phenomics. Neurotoxicology and Teratology 2003;25: Guerri C, Bazinet A, Riley EP. Foetal alcohol spectrum disorders and alterations in brain and behavior. Alcohol and Alcohol Research 2009;44: Kodituwakku PW. Defining the behavioral phenotype in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: A review. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 2007;31: Kvigne VL, Leonardson GR, Neff-Smith M, Brock E, Borzelleca J, Welty TK. Characteristics of children who have full or incomplete Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. Journal of Pediatrics 2004;145: Rasmussen C. Executive functioning and working memory in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2005;29: Streissguth AP. Offspring effects of prenatal alcohol exposure from birth to 25 years: The Seattle Prospective Longitudinal study. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings 2007;14: Alati R, Clavarino A, Najman JM, O Callaghan M, Bor W, Mamun AA, Williams GM. The developmental origin of adolescent alcohol use: Findings from the Mater University Study of Pregnancy and its outcomes. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2008;93: Baer JS, Sampson PD, Barr HM, Connor PD, Streissguth AP. A 21-year longitudinal analysis of the effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on young adult drinking. Archives of General Psychiatry 2003;60: Burd L, Selfridge R, Klug M, Bakko S. Fetal alcohol syndrome in the United States corrections system. Addiction Biology 2004;9: Fast DK, Conry J. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders and the criminal justice system. Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews 2009;(15)3: Huggins J, Grant T, O Malley K, Streissguth AP. Suicide attempts among adults with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Clinical implications. Mental Health Aspects of Developmental Disabilities 2008;11: O Connor MJ, Paley, B. Psychiatric conditions associated with prenatal alcohol exposure. Developmental Disabilities Research Review 2009;15(3): Streissguth AP, Bookstein FL, Barr HM, Sampson PD, O Malley K, Young JK. Risk factors for adverse life outcomes in Fetal Alcohol Syndrome and Fetal Alcohol Effects. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 2004;25: Olson HC, Jirikowic T, Kartin D, Astley S. Responding to the challenge of early intervention for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Infants and Young Children 2007;20: CEECD / SKC-ECD FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) 6
7 35. Astley SJ, Stachowiak J, Clarren SK, Clausen, C. Application of the fetal alcohol syndrome facial photographic screening tool in a foster care population. Journal of Pediatrics 2002;141: O Connor MJ, Mccracken J, Best A. Under recognition of prenatal alcohol exposure in a child inpatient psychiatric setting. Mental Health Aspects of Developmental Disabilities 2006;9: Luo J. Lithium-mediated protection against ethanol neurotoxicity. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2010;4; Incerti M, Vink J, Roberson R, Wood L, Abebe D, Spong CY. Reversal of alcohol-induced learning deficits in the young adult in a model of fetal alcohol syndrome. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2010;115: Incerti M, Vink, J, Roberson R, Benassou I, Abebe D, Spong CY. Prevention of the alcohol-induced changes in brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression using neuroprotective peptides in a model of fetal alcohol syndrome. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2010;202(5);457e Zhou FC, Fang C, Goodlett C. Peptidergic agonists of activity-dependent neurotrophic factor protect against prenatal alcohol-induced neural tube defects and serotonin neuron loss. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;32: Naseer MI, Lee HY, Kim MO. Neuroprotective effect of Vitamin C against the ethanol and nicotine modulation of GABA(B) receptor and PKAalpha expression in prenatal rat brain. Synapse 2010;64(6): Ojeda ML, Nogales F, Jotty K, Barrero Mj, Murillo ML, Carreras O. Dietary selenium plus folic acid as an antioxidant therapy for ethanolexposed pups. Birth Defects Research 2009;86(6): Serrano M, Han MD, Brinez P, & Linask KK. Fetal alcohol syndrome: Cardiac birth defects in mice and prevention with folate. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2010;203(1);75e Summers BL, Rofe AM, Coyle P. Dietary zinc supplementation throughout pregnancy protects against fetal dysmorphology and improves postnatal survival after prenatal ethanol exposure in mice. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2009;33(4): Thomas JD, Abou EJ, Dominguez HD. Prenatal choline supplementation mitigates the adverse effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on development in rats. Neurotoxicology and Teratology 2009;31(5): Hannigan JH, O Leary-Moore SK, Berman RF. Postnatal environmental or experiential amelioration of neurobehavioral effects of perinatal alcohol exposure in rats. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Review 2007;31: Thomas JD, Sather TM, Whinery LA. Voluntary exercise influences behavioral development in rats exposed to alcohol during the neonatal brain growth spurt. Behavioral Neuroscience 2008;122: Guerri C, Pascual M, Garcia-Minguillán, Charness ME, Wilkemeyer MF, Klinstova AY, Goodlett CR, Greenough WT, Sakata-Haga H, Dominguez HD, Thomas JD. Fetal alcohol effects: Potential treatments from basic science. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2005;29: Sword W, Niccols A, Fan AM. New Choices for women with addictions: perceptions of program participants. BMC Public Health 2004;4: Niccols A, Sword W. New Choices for substance using mothers and their young children: Preliminary evaluation. Journal of Substance Use 2005;10: Grant TM, Ernst CC, Streissguth AP. Intervention with high-risk alcohol and drug-abusing mothers: Administrative strategies of the Seattle model of paraprofessional advocacy. Journal of Community Psychology 1999;27(1): Kartin D, Grant TM, Streissguth, AP, Sampson PD, Ernst CC. Three-year developmental outcomes in children with prenatal alcohol and drug exposure. Pediatric Physical Therapy 2002;14(3): Bertrand J, Interventions for Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Research Consortium. Interventions for children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Overview of findings for five innovative research projects. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2009;30: Olson HC, Brooks A, Quamma J, Lehman K, Ranna M, Davis C, Kerns K, Astley S. Efficacy of a new model of behavioral consultation for families raising school-aged children with FASDs and behavior problems. In preparation. 55. Kable JA, Coles, CD, Taddeo E. Socio-cognitive habilitation using the math interactive learning experience program for alcohol affected children. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2007;31: Coles CD, Kable JA, Taddeo E. Math performance and behavior problems in children affected by prenatal alcohol exposure: Intervention and follow-up. Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics 2009;30: Loomes C, Rasmussen C, Pei J, Manji S, Andrew G. The effects of rehearsal training on working memory span of children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2008;29: Jirikowic T, Kartin D, Olson HC. Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: A descriptive profile of adaptive function. Canadian Journal of Occupational Therapy 2008;75: CEECD / SKC-ECD FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) 7
8 59. Coles CD, Strickland DC, Padgett L, Bellmoff L. Games that work : Using computer games to teach alcohol-affected children about fire and street safety. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2007;28: Frankel F, Myatt R. Children s friendship training. New York, NY: Brunner-Routledge Publishers; O Connor MJ, Frankel F, Paley B, Schonfeld AM, Carpenter E, Laugeson E, Marquardt R. A controlled social skills training for children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2006;74: Fanton J, Gleason MM. Psychopharmacology and preschoolers: a critical review of current conditions. Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinics of North America 2009;18(3): O Malley KD, Nanson J. Clinical implications of a link between Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 2002;47: Doig J, McLennan JD, Gibbard WB. Medication effects on symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in child with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology 2008;18: Oesterheld JR, Kofoed L, Tervo R, Fogas B, Wilson A, Fiechtner H. Effectiveness of methylphenidate in Native American children with fetal alcohol syndrome and/or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A controlled pilot study. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology 1998;8: Coe J, Sidders J, Riley K, Waltermire J, Hagerman R. A survey of medication responses in children and adolescents with fetal alcohol syndrome. Mental Health Aspects of Developmental Disabilities 2001;4: Olson HC, Montague R. An innovative look at early intervention for children affected by prenatal alcohol exposure. In: Adubato S, Cohen D, eds. Prenatal alcohol use and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Diagnosis, assessment and new directions in research and multimodal treatment. In press. 68. Niccols A. Right From the Start : Randomized trial comparing an attachment group intervention to supportive home visiting. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 2008;49: Dozier, M, Lindhiem, O, Lewis, E, Bick, J, Bernard, K, Peloso, E. Effects of a foster parent training program on children s attachment behaviors: Preliminary evidence from a randomized clinical trial. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal 2009;26: Fisher PA, Kim HK. Intervention effects on foster preschoolers attachment-related behaviors from a randomized trial. Prevention Science 2007;8: Children s Law Center of Los Angeles. Making reform real: Addressing the mental health needs of children in the dependency system. Monterey Park, CA: Children's Law Center of Los Angeles; CEECD / SKC-ECD FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) 8
FAS/FAE: Their Impact on Psychosocial Child Development with a View to Diagnosis
 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) FAS/FAE: Their Impact on Psychosocial Child Development with a View to Diagnosis Susan Astley, PhD University of Washington, USA February 2003 Introduction Fetal
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) FAS/FAE: Their Impact on Psychosocial Child Development with a View to Diagnosis Susan Astley, PhD University of Washington, USA February 2003 Introduction Fetal
FAE/FAS: Prevention, Intervention and Support Services Commentary on Burd and Juelson, Coles, and O Malley and Streissguth
 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) FAE/FAS: Prevention, Intervention and Support Services Commentary on Burd and Juelson, Coles, and O Malley and Streissguth Edward P. Riley, PhD Center for Behavioral
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) FAE/FAS: Prevention, Intervention and Support Services Commentary on Burd and Juelson, Coles, and O Malley and Streissguth Edward P. Riley, PhD Center for Behavioral
Just Do It! Improving Cognition in FASD. Although FAS and associated disorders were first described in 1973 (Jones &
 Just Do It! Improving Cognition in FASD Although FAS and associated disorders were first described in 1973 (Jones & Smith), only recently has attention been paid to finding effective methods for intervention
Just Do It! Improving Cognition in FASD Although FAS and associated disorders were first described in 1973 (Jones & Smith), only recently has attention been paid to finding effective methods for intervention
Fetal Alcohol Exposure
 Fetal Alcohol Exposure Fetal alcohol exposure occurs when a woman drinks while pregnant. Alcohol can disrupt fetal development at any stage during a pregnancy including at the earliest stages before a
Fetal Alcohol Exposure Fetal alcohol exposure occurs when a woman drinks while pregnant. Alcohol can disrupt fetal development at any stage during a pregnancy including at the earliest stages before a
FAS/FAE and Its Impact on Psychosocial Child Development
 Topic Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder FAS/FAE and Its Impact on Psychosocial Child Development SANDRA JACOBSON, PhD JOSEPH JACOBSON, PhD Wayne State University School of Medicine, USA (Published online
Topic Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder FAS/FAE and Its Impact on Psychosocial Child Development SANDRA JACOBSON, PhD JOSEPH JACOBSON, PhD Wayne State University School of Medicine, USA (Published online
Exposure to alcohol in utero is considered to be the
 DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES RESEARCH REVIEWS 15: 258 267 (2009) INTERVENTION FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS: TREATMENT APPROACHES AND CASE MANAGEMENT Blair Paley* and Mary J. O Connor
DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES RESEARCH REVIEWS 15: 258 267 (2009) INTERVENTION FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS: TREATMENT APPROACHES AND CASE MANAGEMENT Blair Paley* and Mary J. O Connor
Nutritional Supplementation and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 Nutritional Supplementation and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder 1,2 Anna Patten, PhD; 1,2 Brian Christie, PhD; 3 Courtney Green, PhD and 3 Jocelynn Cook, PhD MBA. 1 Division of Medical Sciences, University
Nutritional Supplementation and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder 1,2 Anna Patten, PhD; 1,2 Brian Christie, PhD; 3 Courtney Green, PhD and 3 Jocelynn Cook, PhD MBA. 1 Division of Medical Sciences, University
Recommended Assessment Tools for Children and Adults with confirmed or suspected FASD
 Recommended Assessment Tools for Children and Adults with confirmed or suspected FASD 2001 Teresa Kellerman, revised October 2005 Thousands of children are born with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD),
Recommended Assessment Tools for Children and Adults with confirmed or suspected FASD 2001 Teresa Kellerman, revised October 2005 Thousands of children are born with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD),
The Essential Role of Growth Deficiency in the Diagnosis of FASD
 The Essential Role of Growth Deficiency in the Diagnosis of FASD Susan Astley PhD Julia Bledsoe MD Julian Davies MD Members of the FAS DPN FASD Diagnostic Team University of Washington Seattle WA Published
The Essential Role of Growth Deficiency in the Diagnosis of FASD Susan Astley PhD Julia Bledsoe MD Julian Davies MD Members of the FAS DPN FASD Diagnostic Team University of Washington Seattle WA Published
A court team model for young children in foster care: The role of prenatal alcohol exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
 Journal of Psychiatry & Law 39/Spring 2011 179 A court team model for young children in foster care: The role of prenatal alcohol exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders BY LARRY BURD, PH.D., HON.
Journal of Psychiatry & Law 39/Spring 2011 179 A court team model for young children in foster care: The role of prenatal alcohol exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders BY LARRY BURD, PH.D., HON.
Mental Health Problems in Individuals with Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 Mental Health Problems in Individuals with Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Presenter: Date: Jacqueline Pei, R. Psych., PhD Carmen Rasmussen, PhD May 5, 2009 The FASD Learning
Mental Health Problems in Individuals with Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Presenter: Date: Jacqueline Pei, R. Psych., PhD Carmen Rasmussen, PhD May 5, 2009 The FASD Learning
Children and Youth With Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Summary of Intervention Recommendations After Clinical Diagnosis
 INTELLECTUAL AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES VOLUME 48, NUMBER 5: 330 344 OCTOBER 2010 Children and Youth With Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Summary of Intervention Recommendations After Clinical Diagnosis
INTELLECTUAL AND DEVELOPMENTAL DISABILITIES VOLUME 48, NUMBER 5: 330 344 OCTOBER 2010 Children and Youth With Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Summary of Intervention Recommendations After Clinical Diagnosis
Taking the Next Step: Innovative Interventions for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs) A Description of Conference Proceedings
 Taking the Next Step: Innovative Interventions for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs) A Description of Conference Proceedings The second Marcus Autism Center Leadership Conference, entitled Taking
Taking the Next Step: Innovative Interventions for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs) A Description of Conference Proceedings The second Marcus Autism Center Leadership Conference, entitled Taking
FASD Diagnosis, Intervention, & Prevention
 FASD Diagnosis, Intervention, & Prevention Susan Astley PhD Professor Director Washington State FAS Diagnostic & Prevention Network University of Washington Seattle WA, U.S.A fasdpn.org 07 WA State FAS
FASD Diagnosis, Intervention, & Prevention Susan Astley PhD Professor Director Washington State FAS Diagnostic & Prevention Network University of Washington Seattle WA, U.S.A fasdpn.org 07 WA State FAS
Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) is a permanent birth defect syndrome caused by
 Children With Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Problem Behaviors and Sensory Processing Laureen Franklin, Jean Deitz, Tracy Jirikowic, Susan Astley KEY WORDS fetal alcohol spectrum disorders pediatrics
Children With Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Problem Behaviors and Sensory Processing Laureen Franklin, Jean Deitz, Tracy Jirikowic, Susan Astley KEY WORDS fetal alcohol spectrum disorders pediatrics
Safe Babies Foster Parent Training Program
 Safe Babies Foster Parent Training Program Module 1: Introduction to the Safe Babies Program 1 Begin the process of group participation Learning outcomes Understand the purpose and origins of the Safe
Safe Babies Foster Parent Training Program Module 1: Introduction to the Safe Babies Program 1 Begin the process of group participation Learning outcomes Understand the purpose and origins of the Safe
FAS Behavioral Survey of Traits: Screening for Effects of Prenatal Exposure to Alcohol
 Digital Commons @ George Fox University Faculty Publications - Grad School of Clinical Psychology Graduate School of Clinical Psychology 2010 FAS Behavioral Survey of Traits: Screening for Effects of Prenatal
Digital Commons @ George Fox University Faculty Publications - Grad School of Clinical Psychology Graduate School of Clinical Psychology 2010 FAS Behavioral Survey of Traits: Screening for Effects of Prenatal
FASD Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 FAS pfas ARND Fetal Alcohol Syndrome partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Alcohol Related Neurodevelopment Disorder FASD Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder ARBD Alcohol Related Birth Defects #1 cause of birth defects
FAS pfas ARND Fetal Alcohol Syndrome partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Alcohol Related Neurodevelopment Disorder FASD Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder ARBD Alcohol Related Birth Defects #1 cause of birth defects
Comorbidity Associated with FASD: A Behavioral Phenotype?
 Comorbidity Associated with FASD: A Behavioral Phenotype? P.W. Kodituwakku, Ph.D. Departments of Pediatrics and Neurosciences School of Medicine University of New Mexico Significance of the study of comorbid
Comorbidity Associated with FASD: A Behavioral Phenotype? P.W. Kodituwakku, Ph.D. Departments of Pediatrics and Neurosciences School of Medicine University of New Mexico Significance of the study of comorbid
PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE. Special Section
 Special Section THE LONG-TERM NEUROCOGNITIVE CONSEQUENCES OF PRENATAL ALCOHOL EXPOSURE: A 14-Year Study Ann P. Streissguth, 1 Helen M. Barr, 1 Fred L. Bookstein, 2 Paul D. Sampson, 3 and Heather Carmichael
Special Section THE LONG-TERM NEUROCOGNITIVE CONSEQUENCES OF PRENATAL ALCOHOL EXPOSURE: A 14-Year Study Ann P. Streissguth, 1 Helen M. Barr, 1 Fred L. Bookstein, 2 Paul D. Sampson, 3 and Heather Carmichael
The Undiscovered Country: Why and How to Carry Out FASD Research Across the Life Span
 7th National Biennial Conference on Adolescents and Adults with FASD Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada April 7, 2016 The Undiscovered Country: Why and How to Carry Out FASD Research Across the Life Span
7th National Biennial Conference on Adolescents and Adults with FASD Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada April 7, 2016 The Undiscovered Country: Why and How to Carry Out FASD Research Across the Life Span
Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years?
 Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years? Kenneth Lyons Jones, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics University of California, San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, CA Generalizations About Phenotype
Alcohol and Pregnancy: What Have We Learned in 37 Years? Kenneth Lyons Jones, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics University of California, San Diego School of Medicine La Jolla, CA Generalizations About Phenotype
Prevention of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) Prevention of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders R. Louise Floyd, RN, DSN, Clark Denny, PhD, Mary Kate Weber, MPH Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) Prevention of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders R. Louise Floyd, RN, DSN, Clark Denny, PhD, Mary Kate Weber, MPH Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD): How Judges Can Improve Outcomes for Affected Children and Parents
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD): How Judges Can Improve Outcomes for Affected Children and Parents Larry Burd, PhD, Professor, Department of Pediatrics, University of North Dakota School of Medicine
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD): How Judges Can Improve Outcomes for Affected Children and Parents Larry Burd, PhD, Professor, Department of Pediatrics, University of North Dakota School of Medicine
COSTS OF HEALTH SERVICES UTILIZATION OF PEOPLE WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER BY SEX AND AGE GROUP IN ALBERTA, CANADA
 COSTS OF HEALTH SERVICES UTILIZATION OF PEOPLE WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER BY SEX AND AGE GROUP IN ALBERTA, CANADA Nguyen Xuan Thanh 1,2, Egon Jonsson 1,2,3 1 Institute of Health Economics, Edmonton,
COSTS OF HEALTH SERVICES UTILIZATION OF PEOPLE WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER BY SEX AND AGE GROUP IN ALBERTA, CANADA Nguyen Xuan Thanh 1,2, Egon Jonsson 1,2,3 1 Institute of Health Economics, Edmonton,
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENTS AND AGE-RELATED DIFFERENCES IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS
 NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENTS AND AGE-RELATED DIFFERENCES IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Sukhpreet Tamana 1, Jacqueline Pei 1, Donald Massey 1, Valerie Massey 1, Carmen
NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENTS AND AGE-RELATED DIFFERENCES IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Sukhpreet Tamana 1, Jacqueline Pei 1, Donald Massey 1, Valerie Massey 1, Carmen
Unique Characteristics Protective Factors. Risks
 Unique Characteristics Protective Factors Risks Desire to please Funny, great laugh Determined Stable, nurturing home Appropriate services Prenatal alcohol exposure Childhood trauma 2 Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Unique Characteristics Protective Factors Risks Desire to please Funny, great laugh Determined Stable, nurturing home Appropriate services Prenatal alcohol exposure Childhood trauma 2 Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
FASD 101: Diagnosis and Support of FASD
 FASD 101: Diagnosis and Support of FASD Presenter: Date: Gail Andrew MDCM, FRCP(C) November 6, 2009 The FASD Learning Series is part of the Alberta government s commitment to programs and services for
FASD 101: Diagnosis and Support of FASD Presenter: Date: Gail Andrew MDCM, FRCP(C) November 6, 2009 The FASD Learning Series is part of the Alberta government s commitment to programs and services for
Consumption of Tobacco During Pregnancy and Its Impact on Child Development
 TOBACCO AND PREGNANCY Consumption of Tobacco During Pregnancy and Its Impact on Child Development Peter A. Fried, PhD Carleton University, Canada June 2002 Introduction Although the prevalence of smoking
TOBACCO AND PREGNANCY Consumption of Tobacco During Pregnancy and Its Impact on Child Development Peter A. Fried, PhD Carleton University, Canada June 2002 Introduction Although the prevalence of smoking
SAMHSA FASD Center for Excellence
 FASD FACTS: How You Can Help Prevent Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS The Basics Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Umbrella term describing the range of effects that
FASD FACTS: How You Can Help Prevent Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS The Basics Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Umbrella term describing the range of effects that
Clinical Intervention and Support for Children Aged Zero to Five Years with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Their Parents/Caregivers
 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) Clinical Intervention and Support for Children Aged Zero to Five Years with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Their Parents/Caregivers Kieran O Malley, MB, D.A.B.P.N.
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASD) Clinical Intervention and Support for Children Aged Zero to Five Years with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Their Parents/Caregivers Kieran O Malley, MB, D.A.B.P.N.
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON
 UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON THE FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME DIAGNOSTIC AND PREVENTION NETWORK (FAS DPN) Center for Human Development and Disability Dear Sir or Madam, Thank you very much for your request for an
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON THE FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME DIAGNOSTIC AND PREVENTION NETWORK (FAS DPN) Center for Human Development and Disability Dear Sir or Madam, Thank you very much for your request for an
Birth mother Foster carer Other
 PATIENT DETAILS NAME Sex Female Male Other Date of birth (DD/MM/YYYY) / / Age at assessment: Racial/ ethnic background Preferred language Hospital number (if applicable) Referral source, date, provider
PATIENT DETAILS NAME Sex Female Male Other Date of birth (DD/MM/YYYY) / / Age at assessment: Racial/ ethnic background Preferred language Hospital number (if applicable) Referral source, date, provider
American Academy of Pediatrics 2014 Educational Webinar Series Monday, July 28, 3:00 3:30 pm ET
 American Academy of Pediatrics 2014 Educational Webinar Series Monday, July 28, 3:00 3:30 pm ET FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASDS): DETECTION, DISCOVERY, AND DIAGNOSIS PRESENTED BY YASMIN SENTURIAS,
American Academy of Pediatrics 2014 Educational Webinar Series Monday, July 28, 3:00 3:30 pm ET FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS (FASDS): DETECTION, DISCOVERY, AND DIAGNOSIS PRESENTED BY YASMIN SENTURIAS,
THE IMPACT OF FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS ON DRUG & ALCOHOL ADDICTION AND TREATMENT
 THE IMPACT OF FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS ON DRUG & ALCOHOL ADDICTION AND TREATMENT FASd Estimated Incidence Rate: 9.1/1,000 live births (Sampson et al, Teratology 56:317-326, 1997) Incidence rates
THE IMPACT OF FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS ON DRUG & ALCOHOL ADDICTION AND TREATMENT FASd Estimated Incidence Rate: 9.1/1,000 live births (Sampson et al, Teratology 56:317-326, 1997) Incidence rates
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS
 FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Christi Masters, M.S., CCC-SLP Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing Sciences DISCLOSURE STATEMENT The presenter has no relevant financial
FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDERS Christi Masters, M.S., CCC-SLP Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing Sciences DISCLOSURE STATEMENT The presenter has no relevant financial
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs)
 TOPICAL ISSUE BRIEF Intervention IDEAs for Infants, Toddlers, Children, and Youth Impacted by Overview Prevalence are sometimes referred to as hidden disabilities because the diagnosis often does not occur
TOPICAL ISSUE BRIEF Intervention IDEAs for Infants, Toddlers, Children, and Youth Impacted by Overview Prevalence are sometimes referred to as hidden disabilities because the diagnosis often does not occur
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is a preventable birth defect that is caused by a woman consuming alcohol during her pregnancy.
 1 This presentation will cover the following topics: Terminology Many different terms have been used to describe individuals who are affected by prenatal exposure to alcohol. In this presentation, we will
1 This presentation will cover the following topics: Terminology Many different terms have been used to describe individuals who are affected by prenatal exposure to alcohol. In this presentation, we will
Alcohol and Pregnancy prevention and legal issues of FASD FASD
 Alcohol and Pregnancy prevention and legal issues of FASD By Egon Jonsson, University of Alberta, and University of Calgary, Head of the Institute of Health Economics, Edmonton, Canada www.fasdedmonton2013.ca
Alcohol and Pregnancy prevention and legal issues of FASD By Egon Jonsson, University of Alberta, and University of Calgary, Head of the Institute of Health Economics, Edmonton, Canada www.fasdedmonton2013.ca
CHANGING PUBLIC POLICY WITH THE JUVENILE COURTS: WHAT WORKS WITH KIDS WITH FAS?
 CHANGING PUBLIC POLICY WITH THE JUVENILE COURTS: WHAT WORKS WITH KIDS WITH FAS? William J. Edwards Deputy Public Defender County of Los Angeles 1. ASSESSMENT A. Early Diagnosis- Many families that enter
CHANGING PUBLIC POLICY WITH THE JUVENILE COURTS: WHAT WORKS WITH KIDS WITH FAS? William J. Edwards Deputy Public Defender County of Los Angeles 1. ASSESSMENT A. Early Diagnosis- Many families that enter
1/30/2018. Risk factors: substance exposure. MY LAB S RESEARCH: Risk factors: Toxicants (BPA)
 Risk factors: substance exposure Cocaine Exposure Cannabis Exposure Tobacco Exposure Roussotte F, Soderberg L, et al. 2012. J Neurodev Disorders. 4:22. Marround HE, Tiemeier H, et al. 2016. Biological
Risk factors: substance exposure Cocaine Exposure Cannabis Exposure Tobacco Exposure Roussotte F, Soderberg L, et al. 2012. J Neurodev Disorders. 4:22. Marround HE, Tiemeier H, et al. 2016. Biological
FASD in Waterloo Region
 An Integrated Approach to Address FASD in Waterloo Region Why is this important? Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) is the term used to describe the range of permanent disabilities caused by alcohol
An Integrated Approach to Address FASD in Waterloo Region Why is this important? Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) is the term used to describe the range of permanent disabilities caused by alcohol
Clinical Intervention and Support for Children Aged Zero to Five Years with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Their Parents/Caregivers
 Centre of Excellence for Early Childhood Development FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME Clinical Intervention and Support for Children Aged Zero to Five Years with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Their Parents/Caregivers
Centre of Excellence for Early Childhood Development FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME Clinical Intervention and Support for Children Aged Zero to Five Years with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and Their Parents/Caregivers
Across the Lifespan Questions Developmental Psychologists Ask
 Across the Lifespan Developmental psychology: The study of how people change physically, mentally, and socially throughout the lifespan. Questions Developmental Psychologists Ask What is the age range
Across the Lifespan Developmental psychology: The study of how people change physically, mentally, and socially throughout the lifespan. Questions Developmental Psychologists Ask What is the age range
Probable Link Evaluation of Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Children
 1 July 30, 2012 Probable Link Evaluation of Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Children Conclusion: On the basis of epidemiologic and other data available to the C8 Science Panel, we conclude that there is
1 July 30, 2012 Probable Link Evaluation of Neurodevelopmental Disorders in Children Conclusion: On the basis of epidemiologic and other data available to the C8 Science Panel, we conclude that there is
Washington, DC Washington, DC Services, Education, and Related Agencies Services, Education, and Related Agencies
 June 12, 2018 The Honorable Roy Blunt The Honorable Tom Cole Chair Chair Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies Services,
June 12, 2018 The Honorable Roy Blunt The Honorable Tom Cole Chair Chair Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies Services,
STATEMENT OF THE PUBLIC AFFAIRS COMMITTEE OF THE TERATOLOGY SOCIETY ON THE FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME
 STATEMENT OF THE PUBLIC AFFAIRS COMMITTEE OF THE TERATOLOGY SOCIETY ON THE FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME The following statement has been prepared by the Public Affairs Committee and approved by the Council.
STATEMENT OF THE PUBLIC AFFAIRS COMMITTEE OF THE TERATOLOGY SOCIETY ON THE FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME The following statement has been prepared by the Public Affairs Committee and approved by the Council.
What is FASD? Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder
 FASD: Normalizing Insanity A Family Story Dennis Riddle, MA, LADAC Memphis, Tennessee 901-496-5762 dennisriddle60@aol.com Sometimes Life Gets This Way. With FASD, It Stays This Way!!!! What is FASD? Fetal
FASD: Normalizing Insanity A Family Story Dennis Riddle, MA, LADAC Memphis, Tennessee 901-496-5762 dennisriddle60@aol.com Sometimes Life Gets This Way. With FASD, It Stays This Way!!!! What is FASD? Fetal
Interventions for Children With Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: A Systematic Review
 St. Catherine University University of St. Thomas Master of Social Work Clinical Research Papers School of Social Work 5-2016 Interventions for Children With Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: A Systematic Review
St. Catherine University University of St. Thomas Master of Social Work Clinical Research Papers School of Social Work 5-2016 Interventions for Children With Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: A Systematic Review
Teresa s Background. Close Family. Sources. The Faces of FASD. Today We Will Learn About
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 1: The Faces of FASD Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division of Developmental
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 1: The Faces of FASD Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division of Developmental
Section F: Discussing the diagnosis and developing a management plan
 Section E: Formulating a diagnosis Information collected during the diagnostic assessment should be reviewed, ideally in a multi-disciplinary team context, to evaluate the strength of evidence to: Support
Section E: Formulating a diagnosis Information collected during the diagnostic assessment should be reviewed, ideally in a multi-disciplinary team context, to evaluate the strength of evidence to: Support
1 Prenatal Alcohol Exposure, FAS, and FASD : An Introduction
 1 1 Prenatal Alcohol Exposure, FAS, and FASD : An Introduction Tanya T. Nguyen, Jennifer Coppens, and Edward P. Riley 1.1 Introduction Prenatal Alcohol Exposure ( PAE ) can result in a wide range of physical,
1 1 Prenatal Alcohol Exposure, FAS, and FASD : An Introduction Tanya T. Nguyen, Jennifer Coppens, and Edward P. Riley 1.1 Introduction Prenatal Alcohol Exposure ( PAE ) can result in a wide range of physical,
Addiction Across the Lifespan
 Addiction Across the Lifespan David Galbis-Reig, M.D., DFASAM Medical Director of Addiction Services Ascension Wisconsin All Saints OBJECTIVES Be able to explain how addiction interacts with psychosocial
Addiction Across the Lifespan David Galbis-Reig, M.D., DFASAM Medical Director of Addiction Services Ascension Wisconsin All Saints OBJECTIVES Be able to explain how addiction interacts with psychosocial
Understanding Prenatal Drug Exposure
 Understanding Prenatal Drug Exposure Prenatal Drug Exposure A mother s drug use hurts her unborn baby. Slide 2 Drug Categories Part 1 Prescription drugs: Prescribed by a doctor and used under a health
Understanding Prenatal Drug Exposure Prenatal Drug Exposure A mother s drug use hurts her unborn baby. Slide 2 Drug Categories Part 1 Prescription drugs: Prescribed by a doctor and used under a health
University of Alberta. Mathematics Intervention for Children with Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
 University of Alberta Mathematics Intervention for Children with Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders by Katrina Violet Kully-Martens A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate
University of Alberta Mathematics Intervention for Children with Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders by Katrina Violet Kully-Martens A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Graduate
Children with FASD. Involved with the Manitoba Child Welfare System
 Children with FASD Involved with the Manitoba Child Welfare System Don Fuchs, University of Manitoba Linda Burnside, Child Protection Branch Shelagh Marchenski, University of Manitoba Andria Mudry, University
Children with FASD Involved with the Manitoba Child Welfare System Don Fuchs, University of Manitoba Linda Burnside, Child Protection Branch Shelagh Marchenski, University of Manitoba Andria Mudry, University
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Updated: May 2015
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Updated: May 2015 Topic Editor : Mary J. O'Connor, PhD, University of California at Los Angeles, USA Table of contents Synthesis 5 Neurobehavioural Profiles of Individuals
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Updated: May 2015 Topic Editor : Mary J. O'Connor, PhD, University of California at Los Angeles, USA Table of contents Synthesis 5 Neurobehavioural Profiles of Individuals
The child-parent relationship is core to a child s development
 M. C O N N I E A L M E I D A, P H D The child-parent relationship is core to a child s development ATTACHMENT The central theme of attachment theory is that mothers / fathers who are available and responsive
M. C O N N I E A L M E I D A, P H D The child-parent relationship is core to a child s development ATTACHMENT The central theme of attachment theory is that mothers / fathers who are available and responsive
The Basics of FASD Awareness and Prevention Cheryl A. Wissick, Ph.D. Trainer, SC FASD Collaborative
 The Basics of FASD Awareness and Prevention Cheryl A. Wissick, Ph.D. Trainer, SC FASD Collaborative Presentation adapted from information from Dan Dubovsky, FASD Specialist, FASD CFE, SAMHSA Roger Zoorob,
The Basics of FASD Awareness and Prevention Cheryl A. Wissick, Ph.D. Trainer, SC FASD Collaborative Presentation adapted from information from Dan Dubovsky, FASD Specialist, FASD CFE, SAMHSA Roger Zoorob,
Fetal Brains Suffer Badly From Effects of Alcohol
 November 4, 2003 Fetal Brains Suffer Badly From Effects of Alcohol By LINDA CARROLL hirty years ago, scientists linked prenatal alcohol exposure with a perplexing pattern of birth defects including neurological
November 4, 2003 Fetal Brains Suffer Badly From Effects of Alcohol By LINDA CARROLL hirty years ago, scientists linked prenatal alcohol exposure with a perplexing pattern of birth defects including neurological
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Common but Under-Recognized in the U.S.
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Common but Under-Recognized in the U.S. Christina Chambers, PhD, MPH Co-Director of the Center for Better Beginnings Professor of Pediatrics Department of Pediatrics Department
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Common but Under-Recognized in the U.S. Christina Chambers, PhD, MPH Co-Director of the Center for Better Beginnings Professor of Pediatrics Department of Pediatrics Department
Common Drugs of Abuse. Tobacco/Nicotine Cannabis Alcohol Opiates Cocaine Methamphetamine. 36 weeks gestation adult
 Long Term Impact of Maternal Substance Abuse on Babies No Disclosures Khalid Awad, MD Methodist Women s Hospital Neonatology Common Drugs of Abuse /Nicotine 22 weeks gestation 32 weeks gestation 36 weeks
Long Term Impact of Maternal Substance Abuse on Babies No Disclosures Khalid Awad, MD Methodist Women s Hospital Neonatology Common Drugs of Abuse /Nicotine 22 weeks gestation 32 weeks gestation 36 weeks
E6 - Prenatal Alcohol Exposure and Social Behavior Function
 The 7th International Conference on FASD Research: Results and Relevance Integrating Research, Policy and Promising Practice Around the World Katrina Kully-Martens, MEd PhD Candidate E6 - Prenatal Alcohol
The 7th International Conference on FASD Research: Results and Relevance Integrating Research, Policy and Promising Practice Around the World Katrina Kully-Martens, MEd PhD Candidate E6 - Prenatal Alcohol
Understanding Prenatal Alcohol Exposure
 Understanding Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Causes Birth Defects Alcohol and pregnancy do not mix. Slide 2 The U.S. Surgeon General s Warning The dangers of consuming alcohol during
Understanding Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Prenatal Alcohol Exposure Causes Birth Defects Alcohol and pregnancy do not mix. Slide 2 The U.S. Surgeon General s Warning The dangers of consuming alcohol during
Closing the gap clearinghouse
 Closing the gap clearinghouse Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: a review of interventions for prevention and management in Indigenous communities Resource sheet no. 36 prepared by the Closing the Gap Clearinghouse
Closing the gap clearinghouse Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: a review of interventions for prevention and management in Indigenous communities Resource sheet no. 36 prepared by the Closing the Gap Clearinghouse
Indian Country Site Visit Executive Summary
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY As part of its outreach efforts in Indian Country, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Center for Excellence
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY As part of its outreach efforts in Indian Country, the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) Center for Excellence
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Cross-ministry results
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Cross-ministry results Download the report at: https://policywise.com/initiatives/cydl/p2 January 27 th, 2017 FASD panel Dr. Christine Werk Research scientist, PolicyWise
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder Cross-ministry results Download the report at: https://policywise.com/initiatives/cydl/p2 January 27 th, 2017 FASD panel Dr. Christine Werk Research scientist, PolicyWise
Contents Definition and History of ADHD Causative Factors
 1 Definition and History of ADHD................... 1 Brain Damage Syndromes........................ 1 Alternative Terms for ADHD...................... 2 Evolution of Present Concept of ADHD................
1 Definition and History of ADHD................... 1 Brain Damage Syndromes........................ 1 Alternative Terms for ADHD...................... 2 Evolution of Present Concept of ADHD................
Relationships Relationships
 PRENATAL OPIATE EXPOSURE IMPACT ON EARLY CHILDHOOD LEARNING AND BEHAVIOR Ira J. Chasnoff, MD NTI Upstream www.ntiupstream.com Children grow and develop in the context of Attachment: Basic Concept Attachment:
PRENATAL OPIATE EXPOSURE IMPACT ON EARLY CHILDHOOD LEARNING AND BEHAVIOR Ira J. Chasnoff, MD NTI Upstream www.ntiupstream.com Children grow and develop in the context of Attachment: Basic Concept Attachment:
The Mystery of Risk. Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child. Ira J. Chasnoff, MD
 The Mystery of Risk Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child Ira J. Chasnoff, MD irachasnoff@gmail.com Attachment: Basic Concepts n Attachment is the interconnectedness between human beings.
The Mystery of Risk Drugs, Alcohol, Pregnancy and the Vulnerable Child Ira J. Chasnoff, MD irachasnoff@gmail.com Attachment: Basic Concepts n Attachment is the interconnectedness between human beings.
The Effect of Early Intervention on the Social and Emotional Development of Young Children (0-5) with Autism
 AUTISM The Effect of Early Intervention on the Social and Emotional Development of Young Children (0-5) with Autism Yvonne E.M. Bruinsma, MA, Robert L. Koegel, PhD, Lynn Kern Koegel, PhD University of
AUTISM The Effect of Early Intervention on the Social and Emotional Development of Young Children (0-5) with Autism Yvonne E.M. Bruinsma, MA, Robert L. Koegel, PhD, Lynn Kern Koegel, PhD University of
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) and the Criminal Justice System: Causes, Consequences, and Suggested Communication Approaches
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) and the Criminal Justice System: Causes, Consequences, and Suggested Communication Approaches By Anthony P. Wartnik and Jerrod Brown Abstract Afflicting 2% to 5%
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD) and the Criminal Justice System: Causes, Consequences, and Suggested Communication Approaches By Anthony P. Wartnik and Jerrod Brown Abstract Afflicting 2% to 5%
EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONING AND WORKING MEMORY DEFICITS ON THE CANTAB AMONG CHILDREN WITH PRENATAL ALCOHOL EXPOSURE
 EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONING AND WORKING MEMORY DEFICITS ON THE CANTAB AMONG CHILDREN WITH PRENATAL ALCOHOL EXPOSURE Carmen Rasmussen 1, Maryam Soleimani 2, Jacqueline Pei 3 1 Department of Pediatrics, University
EXECUTIVE FUNCTIONING AND WORKING MEMORY DEFICITS ON THE CANTAB AMONG CHILDREN WITH PRENATAL ALCOHOL EXPOSURE Carmen Rasmussen 1, Maryam Soleimani 2, Jacqueline Pei 3 1 Department of Pediatrics, University
WHO International Collaborative Research Project on Child Development and Prenatal Risk Factors with a Focus on FASD. Dr V. Poznyak and Mr Dag Rekve
 WHO International Collaborative Research Project on Child Development and Prenatal Risk Factors with a Focus on FASD Dr V. Poznyak and Mr Dag Rekve 1 Guiding principles of the Global strategy to reduce
WHO International Collaborative Research Project on Child Development and Prenatal Risk Factors with a Focus on FASD Dr V. Poznyak and Mr Dag Rekve 1 Guiding principles of the Global strategy to reduce
University of New Mexico Center for Development & Disability Postdoctoral Psychology Fellowship in Early Childhood Mental Health
 General Description University of New Mexico Center for Development & Disability Postdoctoral Psychology Fellowship in Early Childhood Mental Health The postdoctoral psychology fellowship in Early Childhood
General Description University of New Mexico Center for Development & Disability Postdoctoral Psychology Fellowship in Early Childhood Mental Health The postdoctoral psychology fellowship in Early Childhood
Substance-Exposed Newborns
 Substance-Exposed Newborns State of Oklahoma 2017 Substance-Exposed Newborns State of Oklahoma 2017 Legal Background Oklahoma statute, Title 63, 1-550.3, states, "The Department of Human Services shall
Substance-Exposed Newborns State of Oklahoma 2017 Substance-Exposed Newborns State of Oklahoma 2017 Legal Background Oklahoma statute, Title 63, 1-550.3, states, "The Department of Human Services shall
New Patient Information Form
 New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
New Patient Information Form Patient Identification Prenatal Alcohol & Drug Exposure Clinic FASD CLINIC Patient s OHIP N. Female Male Race Patient s Name Birth Date Age First Middle Last Patient s Address
Part 2 Who Is at Risk? What Does FASD Look Like? FASD Diagnostic Guidelines. Common Challenges Across the Spectrum
 Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 2: Who Is at Risk? Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division of Developmental
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders Understanding Effects Improving Outcomes Part 2: Who Is at Risk? Presentation by Teresa Kellerman Director of the Fetal Alcohol Resource Center Arizona Division of Developmental
FASD in Adopted Children in Israel
 FASD in Adopted Children in Israel Emily Rachel Fisher MD Candidate, 2017 Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Israel Outline Background Objectives Methods Results Implications Outline Background
FASD in Adopted Children in Israel Emily Rachel Fisher MD Candidate, 2017 Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University, Israel Outline Background Objectives Methods Results Implications Outline Background
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME A SOUTH AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE
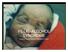 FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME A SOUTH AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE Fetal alcohol syndrome is the most common preventable cause of mental retardation in the world (Sampson PD et al.; Teratology (1997); 56:317-326) RISK
FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME A SOUTH AFRICAN PERSPECTIVE Fetal alcohol syndrome is the most common preventable cause of mental retardation in the world (Sampson PD et al.; Teratology (1997); 56:317-326) RISK
Research-based interventions for children and youth with a Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: revealing the gap
 Blackwell Publishing LtdOxford, UKCCHChild: Care, Health and Development0305-1862; Journal compilation 2006 Blackwell Publishing Ltd? 2006334389397Original ArticleResearch-based interventions for children
Blackwell Publishing LtdOxford, UKCCHChild: Care, Health and Development0305-1862; Journal compilation 2006 Blackwell Publishing Ltd? 2006334389397Original ArticleResearch-based interventions for children
PARENTAL GUIDE TO FASD: A FOCUS ON A MULTIDISCIPLINARY APPROACH AND COMMUNICATING WITH PROFESSIONALS BRYAN BULLOCK
 PARENTAL GUIDE TO FASD: A FOCUS ON A MULTIDISCIPLINARY APPROACH AND COMMUNICATING WITH PROFESSIONALS BRYAN BULLOCK B. A., University of Lethbridge, 2008 A Project Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies
PARENTAL GUIDE TO FASD: A FOCUS ON A MULTIDISCIPLINARY APPROACH AND COMMUNICATING WITH PROFESSIONALS BRYAN BULLOCK B. A., University of Lethbridge, 2008 A Project Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies
Table 1. Research on Prevention and Intervention
 Table 1. Research on Prevention and Intervention Reference Title Sample size (N) Methods and Methodologies Aboriginal Participation/Representation Baydala et al., 2008 A culturally adapted drug and alcohol
Table 1. Research on Prevention and Intervention Reference Title Sample size (N) Methods and Methodologies Aboriginal Participation/Representation Baydala et al., 2008 A culturally adapted drug and alcohol
FASD: A Social Work Perspective. Liam Curran Principal Social Worker Disability Voluntary Services
 FASD: A Social Work Perspective Liam Curran Principal Social Worker Disability Voluntary Services What is Social Work? The definition of Social work is centred on the social context of people s s lives
FASD: A Social Work Perspective Liam Curran Principal Social Worker Disability Voluntary Services What is Social Work? The definition of Social work is centred on the social context of people s s lives
Marijuana Use During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Findings Summary
 The Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE) was assigned the responsibility to appoint a panel of health care professionals with expertise in cannabinoid physiology to monitor the
The Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE) was assigned the responsibility to appoint a panel of health care professionals with expertise in cannabinoid physiology to monitor the
First Peoples Child & Family Review
 volume 8 number 1 First Peoples Child & Family Review 2013 An Interdisciplinary Journal Honoring the Voices, Perspectives and Knowledges of First Peoples through Research, Critical Analyses, Stories, Standpoints
volume 8 number 1 First Peoples Child & Family Review 2013 An Interdisciplinary Journal Honoring the Voices, Perspectives and Knowledges of First Peoples through Research, Critical Analyses, Stories, Standpoints
Sensory Processing and FASD
 Sensory Processing and FASD Tracy Jirikowic, PhD, OTR/L, FAOTA Assistant Professor, University of Washington FASD: Best Practices in the Last Frontier May 23, 2013 1 Objectives Describe how sensory processing
Sensory Processing and FASD Tracy Jirikowic, PhD, OTR/L, FAOTA Assistant Professor, University of Washington FASD: Best Practices in the Last Frontier May 23, 2013 1 Objectives Describe how sensory processing
Outcomes of Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome
 Outcomes of Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Caroline O. Chua, MD, FAAP Medical Director, Division of Neonatology Director, Neonatal Follow Up Clinic Nemours Children s Hospital Orlando, Florida
Outcomes of Infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Caroline O. Chua, MD, FAAP Medical Director, Division of Neonatology Director, Neonatal Follow Up Clinic Nemours Children s Hospital Orlando, Florida
THE FASD PATHWAY. Dr Patricia D. Jackson SACCH MEETING March 2016
 THE FASD PATHWAY Dr Patricia D. Jackson SACCH MEETING March 2016 Why do we need an FASD Pathway? Other countries recognise this as one of the commonest causes of learning disability In Scotland over the
THE FASD PATHWAY Dr Patricia D. Jackson SACCH MEETING March 2016 Why do we need an FASD Pathway? Other countries recognise this as one of the commonest causes of learning disability In Scotland over the
Supplementary Materials: The Effects of Alcohol and Drugs of Abuse on Maternal Nutritional Profile During Pregnancy
 S1 of SX Supplementary Materials: The Effects of Alcohol and Drugs of Abuse on Maternal Nutritional Profile During Pregnancy Giorgia Sebastiani 1, *, Cristina Borrás Novell 1, Miguel Alsina Casanova 1,
S1 of SX Supplementary Materials: The Effects of Alcohol and Drugs of Abuse on Maternal Nutritional Profile During Pregnancy Giorgia Sebastiani 1, *, Cristina Borrás Novell 1, Miguel Alsina Casanova 1,
Running head: COGNITIVE AND PERSONALITY FUNCTIONING COMPARING AND CONTRASTING COGNITIVE AND PERSONALITY FUNCTIONING IN CHILDREN WITH FETAL ALCOHOL
 Running head: COGNITIVE AND PERSONALITY FUNCTIONING COMPARING AND CONTRASTING COGNITIVE AND PERSONALITY FUNCTIONING IN CHILDREN WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER AND CHILDREN WITH ATTENTION-DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY
Running head: COGNITIVE AND PERSONALITY FUNCTIONING COMPARING AND CONTRASTING COGNITIVE AND PERSONALITY FUNCTIONING IN CHILDREN WITH FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER AND CHILDREN WITH ATTENTION-DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY
Lone Star College-Tomball Community Library Tomball Parkway Tomball, TX
 Lone Star College-Tomball Community Library 30555 Tomball Parkway Tomball, TX 77375 http://www.lonestar.edu/library.htm 832-559-4211 PSYCHOLOGY ELECTRONIC JOURNAL LIST Scholarly Electronic Journals The
Lone Star College-Tomball Community Library 30555 Tomball Parkway Tomball, TX 77375 http://www.lonestar.edu/library.htm 832-559-4211 PSYCHOLOGY ELECTRONIC JOURNAL LIST Scholarly Electronic Journals The
The Resilient Revolution takes on
 The Resilient Revolution takes on Attachment, Adverse Childhood Experiences(ACEs) and Neuroscience A Tale of Pathologies? Dr Derek Blincow Blackpool 2018 Grand Theory in Adversity and Child Development
The Resilient Revolution takes on Attachment, Adverse Childhood Experiences(ACEs) and Neuroscience A Tale of Pathologies? Dr Derek Blincow Blackpool 2018 Grand Theory in Adversity and Child Development
ARE MOTHERS WHO DRINK HEAVILY IN PREGNANCY VICTIMS OF FAS? Maud Rouleau,BSc, Zina Levichek, MD, Gideon Koren, MD, FRCPC
 ARE MOTHERS WHO DRINK HEAVILY IN PREGNANCY VICTIMS OF FAS? Maud Rouleau,BSc, Zina Levichek, MD, Gideon Koren, MD, FRCPC ABSTRACT Background Consumption of large amounts of alcohol in pregnancy adversely
ARE MOTHERS WHO DRINK HEAVILY IN PREGNANCY VICTIMS OF FAS? Maud Rouleau,BSc, Zina Levichek, MD, Gideon Koren, MD, FRCPC ABSTRACT Background Consumption of large amounts of alcohol in pregnancy adversely
Behavioral and Early Intervention Reviews/Research
 Behavioral and Early Intervention Reviews/Research INDEPENDENT REVIEWS OF EARLY INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL INTERVENTION Report of the Maine Administrators of Services for Children with Disabilities: Over 30
Behavioral and Early Intervention Reviews/Research INDEPENDENT REVIEWS OF EARLY INTENSIVE BEHAVIORAL INTERVENTION Report of the Maine Administrators of Services for Children with Disabilities: Over 30
Prenatal Cocaine Exposure: Scientific Considerations and Policy Implications
 SUMMARY Prenatal exposure to drugs, including cocaine, is a significant and preventable cause of developmental disability. Almost two decades after the nation first heard stories of crack babies, new research
SUMMARY Prenatal exposure to drugs, including cocaine, is a significant and preventable cause of developmental disability. Almost two decades after the nation first heard stories of crack babies, new research
FASD & Justice: Ontario Survey Key Findings and the Future
 FASD & Justice: Ontario Survey Key Findings and the Future Friday June 20th, 2014 Video Conference Presenters: FASD ONE Justice Action Group Sheila Burns, FASD Specialist, M.S. & Associates Lynda Legge,
FASD & Justice: Ontario Survey Key Findings and the Future Friday June 20th, 2014 Video Conference Presenters: FASD ONE Justice Action Group Sheila Burns, FASD Specialist, M.S. & Associates Lynda Legge,
FAS/FASD (Fetal Alcohol Syndrome/Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder)
 FAS/FASD (Fetal Alcohol Syndrome/Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder) This is a preventable condition The evidence is strong on the link between alcohol intake in pregnancy, and FAS/FASD This is a lifelong
FAS/FASD (Fetal Alcohol Syndrome/Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder) This is a preventable condition The evidence is strong on the link between alcohol intake in pregnancy, and FAS/FASD This is a lifelong
GUIDELINES FOR POST PEDIATRICS PORTAL PROGRAM
 GUIDELINES FOR POST PEDIATRICS PORTAL PROGRAM Psychiatry is a medical specialty that is focused on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of mental, addictive, and emotional disorders throughout the
GUIDELINES FOR POST PEDIATRICS PORTAL PROGRAM Psychiatry is a medical specialty that is focused on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of mental, addictive, and emotional disorders throughout the
