What is Graft Vs Host Disease?
|
|
|
- Patience Haynes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acute Graft Versus Host Disease Objectives Review pathophysiology of Acute Graft vs. Host Disease (agvhd) Identify Risk factors for agvhd Alison Thomsen RN, CPON Clinical Educator Inpatient Cancer Care Unit Seattle Children s Hospital Seattle, Washington Describe physical manifestations and grading of agvhd Review nursing interventions for skin, gut and liver agvhd Review disease prophylaxis and standard therapy Discuss alternate therapies for agvhd GVHD Definitions What is Graft Vs Host Disease? Acute Graft vs Host Disease (agvhd): An immunologic reaction of the transplanted immune system (graft) against the recipient patient (host) classically occurring in the first 100 days post BMT involving the skin, liver, and gut. Chronic Graft vs Host Disease (cgvhd): An immunologic reaction resembling an auto-immune disorder (scleroderma, Sjogren s syndrome) potentially involving many of the organs and structures of the body without features of agvhd. GVHD Classification Acute Graft Versus Host Disease 1
2 Significance of GVHD GVHD is one of the most frequent complications after HSCT Incidence 30-70% in matched transplants Major cause of morbidity and mortality after HSCT Mortality (direct or indirect) can reach 50% Pathophysiology Three Step Process 1. Tissue 2. Donor T-cell activation and cytokine secretion 3. Cellular and inflammatory effectors 1 Tissue Immunology Review 2 Priming/ activation Donor T cells are central 3 Target tissue 9 Hematopoiesis T Cells Generals and Assassins Stem Cell CLP Committed Cell CMP Adaptive T Lymphocytes B Innate Eosinophil Neutrophil Granulocytes Basophil Monocyte and Macrophage Platelet Type of Lymphocyte T-Cells are produced in marrow and mature in the Thymus (T) Many sub-types Helper T Cells Generals Cytotoxic T Cells Assassins Memory Regulatory And others Erythrocyte 2
3 T Cell Subtypes Helper T Cells (CD4) Mature B cells into plasma cells Activate cytotoxic T cells and macrophages Cytotoxic T Cells (CD8, Killer) Destroy virally infected and tumor cells Recognize self from not self T Cell Subtypes Regulatory T Cells Shut down T cell function towards the end of a response Memory T Cells Can differentiate into other types of T cells Subtypes found in lymph nodes and circulation, others reside in tissues T Cell Subtypes Effector Cells; Superset of T cell types that can respond immediately to a stimulus causing an effect Helper Killer Regulatory Effector cells may be pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) Cells that internalize pathogens (phagocitosis) and display a small piece of protein from that pathogen on it s surface T Cells have receptors that receive this protein and the ability to recognize or not Examples of APCs are; Macrophages Neutrophils B Cells Cytokines Chemical/hormonal messengers that allow immune cells to communicate to each other Back to GVHD Immune cells need to; Produce them Release them Receive messages (receptors) React to them Examples of Cytokines; Interferon Interleukin Tumor necrosis factor 3
4 1 Tissue Step 1: Tissue Damage 2 Priming/ activation Donor T cells are central 3 Target tissue Prior to transplant, patient's tissues are d by: Underlying disease and its treatment Infection Drugs and radiation used in conditioning regimen 19 Effects of Conditioning 1 Tissue Chemotherapy and radiation therapy leads to tissue This s causes; Activation of host antigen presenting cells (APCs) Cells that display a foreign antigen with HLA on its surface (recognized by T cells) Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) to leak through the intestinal mucosa into the circulation LPS stimulates the release of the inflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor (TNFα), IL-1, and others 2 Priming/ activation Donor T cells are central 3 Target tissue 22 Step 2: Donor T-cell Activation and Cytokine Secretion 1 Tissue Inflammatory cytokines and LPS help to activate donor T-cells Activated T-cells proliferate and secrete cytokines, including IL-2 and Interferon Secretion of cytokines activates phagocytes 2 Priming/ activation Donor T cells are central 3 Target tissue 24 4
5 Step 3: Cellular and Inflammatory Effectors Activated phagocytes, along with T cells, secrete inflammatory cytokines that cause target cell death (apoptosis) and tissue Who is at greater risk for GVHD? Damage to the GI tract, caused principally by inflammatory cytokines, amplifies LPS release and leads to "cytokine storm" and further tissue Acute GVHD: Well Established Risk Factors GVHD Onset Increased Risk: HLA-mismatch Older recipients Older donors High-dose TBI Sex mismatch (esp female to male) Unrelated donors Reduced Risk: T cell depletion Cord blood GVHD will become evident in patients soon after engraftment Median onset: Day +19 Exceptions Hyperacute GVHD: Early GVHD that occurs Day +7 to +14 before ANC returns which includes fever, generalized erythroderma and desquamation GVHD in nonmyeloablative HSCT: Late GVHD that can occur 6-12 months after transplant Manifestations of Acute GVHD GVHD is a massive inflammatory response to a foreign agent the patient! Skin GI Tract Liver Diagnosis and Staging 5
6 Diagnosis of GVHD May be clinical Liver enzymes Biopsy Skin Endoscopy (upper or lower) Biopsy result may be needed for some study enrollment, even if clinical findings are clear Acute GVHD: Clinical Stage (Modified Glucksberg) Stage Skin Rash %BSA Liver Bilirubin mg/dl Upper GI Symptoms 1 <25% Persistent nausea, vomiting or anorexia Gut Diarrhea (10 ml/kg - peds) 2 25%-50% (20 ml/kg - peds) 3 >50% generalized erythroderma 4 Plus bullae and desquamation >1500 (30 ml/kg - peds) >15 - Severe abdominal pain ileus, frank blood/melena The Grade of agvhd influences response to therapy and survival Grade Response rate (%) Survival at D100 (%) I NA II III IV GVHD Signs and Symptoms: Skin Organ most commonly affected by GVHD Initial presentation often involves the skin and may seem like a flush of the face, ears, palms, soles, and upper trunk Maculopapular rash may become generalized When severe, rash may progress to bulla formation and widespread desquamation How to we care for patients with skin agvhd? 6
7 Nursing Interventions Assess skin frequently Especially groin, axilla, skin folds Skin should be kept clean Daily baths/showers with gentle cleansers Infection prophylaxis Use non-perfumed, heavy emollients frequently Avoid tape and other irritants Nursing Interventions Pain control Treat as burn in severe cases Refer to Standard Practice or institutional guidelines or care Patient and family education GI Tract GI manifestations highly variable and non-specific Diarrhea is most common symptom Anorexia, nausea, food intolerance, cramping, abdominal pain, bloody stools, mucosal sloughing, and ileus may also be present How do we care for patients with GI agvhd? Nursing Intervention Monitor intake, nausea and anti-emetic use/patterns Monitor, describe and test all emesis and stool R/O pathogens Strict I/Os Weight monitoring Nursing Intervention Peri-rectal care Gut rest for severe cases Alternate diets Low fat, low fiber, low lactose TPN/Fluid and electrolyte management Patient and family education Volume replacement as needed 7
8 Liver Jaundice and/or an increase in alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin are early signs of GVHD Obstructive hyperbilirubinemia is the primary hepatic manifestation Measurement of severity of liver involvement is based on total bilirubin level Liver biopsy helpful in discerning underlying etiology Nursing Interventions Strict I/Os Management of symptoms Pruritis and skin care Nausea and vomiting Monitor for confusion/lethargy Fall precautions Maintain safe environment Patient/family education Autologous Pseudo Graft vs. Host Disease Stem cells collected from patient after mobilization may develop capacity to produce selfreactivity after autologous HSCT when the patient lacks immune regulation due to conditioning. Manifestations: Maculopapular skin rash (can be histologically identical to agvhd) Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea Incidence: <8% Onset: Day +7 to +21 Treatment: Steroids Prevention of Acute GVHD Prophylaxis; Pre Day 0 Conditioning Regimen Reduced Intensity Regimens T-cell Depletion Reduced Intensity Regimens Reduced intensity conditioning regimens result in less severe agvhd, as a result of diminished cellular injury from reduced endotoxin exposure due to less mucosal injury Delayed onset of GVHD seen with reduced intensity conditioning regimens 8
9 Probability of Acute GVHD 2-4 Acute GVHD is delayed and is less frequent after Non-Ablative compared to Ablative transplants Related Donor Non-Ablative Ablative 77% 62% T-Cell Depletion The number of T cells in donor stem cells is directly associated with severity of agvhd T-cell depletion is one of the most effective forms of GVHD prophylaxis However, overall survival rates equivalent 0% Days since Transplant What are the Pros and Cons of taking T-Cells out? Advantages and Disadvantages of T-Cell Depletion Advantages Low incidence of acute and chronic GVHD Reduced or no requirement for post-transplantation immune suppression Decreased pulmonary and hepatic toxicity early after HSCT Decreased early transplantrelated mortality Disadvantages Higher incidence of graft failure Loss of GVL activity (higher incidence of disease relapse) Delayed immune reconstitution Increased risk for posttransplantation EBV-LPDs Higher incidence of CMV reactivation Overall survival not improved compared to non-tcd HSCT Graft vs Leukemia or Tumor Effect (GVL or GVT) GVL and Type of Malignancy The beneficial effect that agvhd and cgvhd have on reducing relapse. There is an increased incidence of disease relapse in T-cell depleted, autologous and syngeneic transplants where there is less GVHD and decreased incidence of disease relapse in patients with GVHD Immunologic mechanisms mediated by the donor immune cells contained in or derived from the stem cell graft assist in the eradication of malignant cells after allogeneic HSCT All malignancies were not created equally when it comes to GVL GVL has been most effective in liquid tumors, especially CML, ALL, AML, MDS, CLL and MM 9
10 Manipulating GVL: Current Methods Pre-emptive; Goals for GVL designed into GVHD prophylaxis Questions about GVL? Discontinuation of immunosuppressive therapy if relapse post-bmt occurs Donor Lymphocyte Infusions (post-bmt) Interleukin-2 administration (post-bmt) Non-myeloablative BMT Prophylaxis; Post-Day 0 Drugs Commonly Used in GVHD Prophylaxis Calcineurin Inhibitors Cyclosporine or Tacrolimus Calcineurin inhibitors; decrease production of IL-2 and affect the receptor for IL-2 on T cells; result is decreased ability of resting T cells to be stimulated to become active Prophylaxis - Gold Standard Tacrolimus increasingly being used in place of CSP Continuous infusions preferred over bolus dosing for decrease in toxicities and constancy in serum levels Usually starts hours pretransplant 10
11 Calcineurin Inhibitors Dose Adjust according to blood levels Taper varies depending on protocol CSP; Oral Neoral dose = 2.5X the IV dose Tac; Oral Prograf dose = 4X the IV dose Usually given as 23.5hr continuous infusion May be given Q12 IV/PO Calcineurin Inhibitors; Considerations Do not give with beverages containing bergamottin (grapefruit juice, Sunny Delight, Fresca and Squirt) If patient vomits within one hour of oral dose, repeat dose Patients should receive 3 bolus doses or 24 hours of continuous infusion before receiving stem cells Serum levels drawn from opposite lumen Based on target level range Steady levels not achieved for hours after dose adjustment Calcineurin Inhibitors; Side Effects What are some side effects from Cyclosporine and Tacrolimus? Hypertension Tremor Headache Hirsutism (CSP) N/V Diarrhea Infection Hyperlipidemia Hyperkalemia Hypomagnesemia Elevated BUN/Cr Infusion related effects: flushing, erythema, hand & foot paresthesias (CSP) Hemolysis Abdominal discomfort Hyperbilirubinemia Elevated transaminases Hyperglycemia Acne Delirium Prophylaxis - Gold Standard Methotrexate Usually given day +1, 3, 6, 11 Allogeneic fully myeloablative transplants Folate inhibitor that blocks production of reduced folates which are necessary for DNA synthesis; this effect is not specific to T cells Methotrexate Side Effects Anorexia Rash Diarrhea N/V Increased mucositis Myelosuppression Increased LFTs NOTE; dose is ordered on day of administration and may be held if SOS or third spacing present 11
12 4 Sandmaier, et al. Blood : 506 Sandmaier, et al. Blood : 506 Mycophenolate Mofetil (MMF) New Triple Prophylaxis for NMT Minis and cords Decreases lymphocyte proliferation Given Q8 or Q12 IV/PO IV dose equal to PO dose Side Effects Constipation Diarrhea N/V Confusion Tremor Gastrointestinal bleeding Hypertension Peripheral edema Cough Myelosuppression Infection Comparing CSP + MMF vs CSP + MMF + Sirolimus Survival (n=158) p= % at 1 year 72% at 1 year Acute Grades II-IV GVHD (n=158) p= % 25% Sirolimus (Rapamycin) Blocks ability of IL-2 to stimulate progression of a T cell through it s cell cycle, reducing T cell proliferation Only oral Usually given for cgvhd cyclosporine sirolimus levels and sirolimus may cyclosporine levels Do not give within 4 hours of CSP Check levels Immunosuppressive Medications used to Prevent GVHD Based on Transplant Type (Seattle Cancer Care Alliance) GVHD Prophylaxis Allogeneic Transplants Tacrolimus & Methotrexate Cord Blood Transplants Cyclosprine & Mycophenylate Non-myeloablative Transplants Tacrolimus or Cyclosprine & Mycophenolate Side Effects; BP, headache, BUN/Cr, rash Alternate Prophylaxis Post Day 0 Ursodial (Ursodeoxycholic acid) A bile acid that comprises, in part of bear bile Stabilizes hepatocyte cell membranes Reduces the release and expression of inflammatory cytokines Used for Sinusoidal Obstructive Syndrome (SOS) prophylaxis also affecting liver, skin and gut GVHD! Alternate Prophylaxis Post HSCT Cytoxan 2 doses given between day +2/4 Studies show decrease in GVHD and mucusitis Shows decrease in CD8 and increase in CD4 12
13 Prednisone (mg/kg/day) Treatment of GVHD 1 st Line Standard Treatment - Corticosteroids Steroids, steroids, steroids! Steroids (prednisone) at 0.5 mg/kg up to 2 mg/kg depending on initial grade and extent of skin, liver and/or gut involvement and severity B&B (beclomethasone + budesonide) often added to coat GI tract and spare higher dose prednisone Many effects Decrease proliferation of T cells by decreasing production of IL-1 and IL-2 Usually highly effective Randomized phase III studies that compared prednisone alone with prednisone plus something else have so far not shown benefit Goal is to control acute manifestations and then to taper as soon as possible Topical Steroids 2 orbec stops at D50 Taken orally to coat the gut, and decrease inflammatory response locally 1.6 Standard prednisone taper B&B Beclomethasone Dipropionate (orbec ) Immediate release used for upper GI tract GVHD Budesonide Extended release form of Beclomethasone used for lower GI tract GVHD Little absorption systemically (more in peds) Prednisone taper with OrBec Given in combination with systemic steroids Can enable more rapid weaning Studies open, using B&B as GVHD prophylaxis Days Steroid Side Effects Immunosuppressive Medications used to Treat GVHD Based on Transplant Type (Seattle Cancer Care Alliance) Euphoria Depression Abdominal discomfort Hypertension Sodium and fluid retention Impaired skin healing Infection Osteoporosis Avascular necrosis Skin atrophy Cataracts Glaucoma Muscle weakness Hyperglycemia Cushing s syndrome Attention deficit Insomnia GVHD Treatment Allogeneic Transplants Steroids (± budesonide /beclomethasone) Mycophenolate Sirolimus Iinfliximab Autologous Transplants Steroids (for pseudo- GVHD) Cord Blood Transplants Steroids (± budesonide /beclomethasone) Tacrolimus Sirolimus Infliximab Non-myeloablative Transplants Steroids (± budesonide /beclomethasone) Tacrolimus Sirolimus Infliximab 13
14 SCCA Treatment; Mild vs More than Mild Overall Grade Skin Stage GI 1 (mild) I to II (moderate) I to III I I Liver 3 (severe) II to III II to III II to IV 4 (life threatening) II to IV II to IV II to IV Steroid-Refractory GVHD Definition: Experience return of symptoms when weaning attempted Have progressive or unstable disease on maximum steroid therapy 82% of patients with severe (grade III-IV) agvhd will be steroid refractory Steroid refractory GVHD is associated with 20% survival past day 200 Steroid-Refractory GVHD - Options Alternate immunosuppressive medications MMF Rapomycin Pentostatin Topical steroids ATG Monoclonal antibodies For example; Visilizumab Dacluzimab Alemtuzumab Infliximab Ultraviolet light therapy Extra-corporeal photopheresis (ECP) Psoralen Ultra Violet A therapy (PUVA) Future Directions Mesenchymal Stem Cells Fusion Proteins Monoclonal Antibodies Monoclonal Antibodies (MABs) Development of very specific antibodies through hybridoma technology Several MABs in use/being studied for GVHD Monoclonal Antibodies (MABs) MAB action in GVHD therapy Targets and tags a specific antigen which will then be destroyed May be a certain type of T cell or cytokine Blocks receptors (usually IL-2) on the surface of T cells, therefore blocking their ability to be activated 14
15 Monoclonal Antibodies (MABs) Alemtuxumab (Campath ) Targets CD52 Expressed on many cells involved in GVHD Mature T and B lymphocytes Natural killer cells Most monocytes Macrophages Some dendritic cells Linked to increased risk of opportunistic infections Especially Cytomegaly Virus (CMV) Monoclonal Antibodies (MABs) Infliximab Blocks TNF-α A cytokine that stimulates recruitment of neutrophils and monocytes Especially helpful for Gut GVHD Side Effects; heart rate/bp, headache, dizziness, fever, fatigue, pain, dyspnea Monitor VS during infusion Ultra-Violet Light Therapy Ultra-Violet Light Therapy 8-Methoxypsoralen (Psoralen ) is a plant-derived photo-sensitizer given prior to UV light exposure Exposure to Psoralen and long wavelength ultra violet light causes DNA strand breaks, leading to poor repair and cell death Depletion of cell surface markers Ultra-Violet Light Therapy ECP Extra-corporeal photopheresis (ECP) is a process of Collecting T cells by apheresis Adding Psoralen to cells Exposing T cells to UVA Returning cells to the patient Future Directions Hope to affect more organs Usually given on 2 consecutive days every week or other week Takes time to work; treatment can last weeks to months 15
16 Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are undifferentiated, pluripotent cells that give rise to mesodermal tissue, including Bone Cartilage Muscle Tendon Fat MSCs constitute the supportive stroma within the bone marrow that provides the microenvironment for HSCs Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells The immune-regulatory properties of MSCs may be useful in preventing and treating GVHD Modify the response of inflammatory immune cells Assist with tissue repair, especially in the gut and liver Suppress lymphocyte proliferation and inflammation Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells MSCs might enhance engraftment After conditioning, marrow stroma is d and slow to reconstitute MSC infusion in animals have been shown to help reconstitution of stroma and enhance engraftment MSCs produce important cytokines that promote expansion and differentiation of HSCs Ruxolitinib JAK 1/2 Inhibitor Blocks signals from inflammatory cytokines Increases regulatory T cells T Cell Selected Transplants Selective Depletion of CD45RA+ T Cells From Allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Grafts From HLA-Matched Related and Unrelated Donors in Preventing GVHD CD45RA+ cells are memory T cells that can turn into CD8 (cytotoxic T Cells) Idea is that engraftment and potentially GVL effect will remain the same and that GVHD will be reduced Early impact is promising mostly for cgvhd Fusion Proteins Proteins created by fusing genes Ontak (Denilleukin Diftitox) Fusion protein combining IL-2 and Diptheria toxin Binds to cells with IL-2 receptors and introduces the diptheria toxin into the cell, killing it Ontak works best on cells with high affinity IL-2 receptors; Some leukemia and lymphoma cells and cytotoxic T cells This not only kills the cell, but stops the growth, differentiation and survival of activated T cells 16
17 Current agvhd Studies Open at SCCA; Sirolimus, Cyclosporine, and Mycophenolate Mofetil in Preventing Graft-versus-Host Disease in Treating Patients With Blood Cancer Undergoing Donor Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplant Adults Selective Depletion of CD45RA+ T Cells From Allogeneic Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Grafts From HLA-Matched Related and Unrelated Donors in Preventing GVHD Age 14+ UVADEX and ECP for the Treatment of Pediatric Patients With Steroid Refractory Acute Graft Versus Host Disease All patients will receive UVADEX (methoxsalen) Sterile Solution in Conjunction with the THERAKOS CELLEX Photopheresis System, as part of the same interventional treatment for 12 weeks. Treatments will be given 3 times a week for Weeks 1-4 and 2 times a week for Weeks Ruxolitinib in Combination With Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease Ages 12+ Conclusions GVHD, especially severe and steroidrefractory GVHD is a major, life threatening complication of BMT Advances in HLA typing, reduced intensity conditioning regimens, and T cell selection have the potential to decrease the incidence and severity of GVHD Continued development of targeted and alternative therapies will improve treatment of GVHD and steroid-refractory GVHD, morbidity, and mortality Thank You! 17
What is Graft Vs Host Disease?
 Graft Failure Graft Versus Host Disease Graft Versus Leukemia Objectives Define graft failure Describe Graft vs. Leukemia effect Review pathophysiology and risk factors for Graft vs. Host Disease (GVHD)
Graft Failure Graft Versus Host Disease Graft Versus Leukemia Objectives Define graft failure Describe Graft vs. Leukemia effect Review pathophysiology and risk factors for Graft vs. Host Disease (GVHD)
Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University
 Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD) Background GVHD is an immunologic reaction of the donor immune cells (Graft) against
Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD) Background GVHD is an immunologic reaction of the donor immune cells (Graft) against
5/9/2018. Bone marrow failure diseases (aplastic anemia) can be cured by providing a source of new marrow
 5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014
 Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Treatments for Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD) following Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Treatments for Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD) following Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Reference: NHS England F01X08/01 1 Information Reader Box (IRB)
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Treatments for Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD) following Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Reference: NHS England F01X08/01 1 Information Reader Box (IRB)
Acknowledgements. Department of Hematological Malignancy and Cellular Therapy, University of Kansas Medical Center
 The Addition of Extracorporeal Photopheresis (ECP) to Tacrolimus and Methotrexate to Prevent Acute and Chronic Graft- Versus Host Disease in Myeloablative Hematopoietic Cell Transplant (HCT) Anthony Accurso,
The Addition of Extracorporeal Photopheresis (ECP) to Tacrolimus and Methotrexate to Prevent Acute and Chronic Graft- Versus Host Disease in Myeloablative Hematopoietic Cell Transplant (HCT) Anthony Accurso,
Kavita Raj Consultant Haematologist KHP
 Kavita Raj Consultant Haematologist KHP 1950s Billingham and Brent injection of spleen cells from adult mice into newborn mice Thickening and loss elasticity of skin, red soles, exfoliation, diarrhoea
Kavita Raj Consultant Haematologist KHP 1950s Billingham and Brent injection of spleen cells from adult mice into newborn mice Thickening and loss elasticity of skin, red soles, exfoliation, diarrhoea
What s a Transplant? What s not?
 What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
The future of HSCT. John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD
 The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
Immunosuppressants. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Immunosuppressants Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Immunosuppressive Agents Very useful in minimizing the occurrence of exaggerated or inappropriate
Immunosuppressants Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Immunosuppressive Agents Very useful in minimizing the occurrence of exaggerated or inappropriate
An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation
 An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation October 24, 2009 Stephen Couban Department of Medicine Dalhousie University Objectives What are the types of blood and marrow transplantation? Who may benefit
An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation October 24, 2009 Stephen Couban Department of Medicine Dalhousie University Objectives What are the types of blood and marrow transplantation? Who may benefit
Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology. Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases
 One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
ASH 2011 aktualijos: MSC TPŠL gydyme. Mindaugas Stoškus VULSK HOTC MRMS
 ASH 2011 aktualijos: MSC TPŠL gydyme Mindaugas Stoškus VULSK HOTC MRMS #3042. Yukiyasu Ozawa et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells As a Treatment for Steroid-Resistant Acute Graft Versus Host Disease (agvhd);
ASH 2011 aktualijos: MSC TPŠL gydyme Mindaugas Stoškus VULSK HOTC MRMS #3042. Yukiyasu Ozawa et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells As a Treatment for Steroid-Resistant Acute Graft Versus Host Disease (agvhd);
Transplantation Immunology
 Transplantation Immunology Mitchell S. Cairo, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Medicine and Pathology Chief, Division, Pediatric Hematology & Blood & Marrow Transplantation Children s Hospital New York Presbyterian
Transplantation Immunology Mitchell S. Cairo, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Medicine and Pathology Chief, Division, Pediatric Hematology & Blood & Marrow Transplantation Children s Hospital New York Presbyterian
Transplantation Immunology
 Transplantation Immunology MHC Restricted Allograft Rejection Mitchell S. Cairo, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Medicine and Pathology Chief, Division, Pediatric Hematology & Blood & Marrow Transplantation
Transplantation Immunology MHC Restricted Allograft Rejection Mitchell S. Cairo, MD Professor of Pediatrics, Medicine and Pathology Chief, Division, Pediatric Hematology & Blood & Marrow Transplantation
Objectives. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Approaches to Transplant. Indications for HSCT. Define HSCT. Provide overview of HSCT process
 Objectives Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Karen Anderson, MN, RN, OCN University of Washington Medical Center Define HSCT Provide overview of HSCT process Discuss acute complications of HSCT Discuss
Objectives Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Karen Anderson, MN, RN, OCN University of Washington Medical Center Define HSCT Provide overview of HSCT process Discuss acute complications of HSCT Discuss
Acute GVHD. ESH-EBMT 2009 Latimer A. Devergie
 Acute GVHD ESH-EBMT 2009 Latimer A. Devergie Acute GVHD Activated Donor T cells damage host epithelial cells after an inflammatory cascade that begins after the preparative regimen GVHD is the major barrier
Acute GVHD ESH-EBMT 2009 Latimer A. Devergie Acute GVHD Activated Donor T cells damage host epithelial cells after an inflammatory cascade that begins after the preparative regimen GVHD is the major barrier
4/28/2016. Disclosure. Management of Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplant Complications. Objectives - Technician. Objectives - Pharmacist
 Disclosure Management of Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplant Complications Jenna Bender has no actual or potential conflicts of interest to report Off-label use of medication will be discussed
Disclosure Management of Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplant Complications Jenna Bender has no actual or potential conflicts of interest to report Off-label use of medication will be discussed
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD
 Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
Mobilization & Pre-Transplant Conditioning Regimens
 Transplant Process & Pre-Transplant Conditioning Regimens (auto patients only) 30 days before BMT (allo donors) 5 days before BMT Conditioning (auto AND allo patients) Transplant A technique used to increase
Transplant Process & Pre-Transplant Conditioning Regimens (auto patients only) 30 days before BMT (allo donors) 5 days before BMT Conditioning (auto AND allo patients) Transplant A technique used to increase
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018
 Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
How I manage patients with complex GI problems. Mark Williams ST5 Haematology Manchester Royal Infirmary
 How I manage patients with complex GI problems Mark Williams ST5 Haematology Manchester Royal Infirmary Contents Causes of transplant (+chemotherapy) associated diarrhoea Conditioning & drug related Graft
How I manage patients with complex GI problems Mark Williams ST5 Haematology Manchester Royal Infirmary Contents Causes of transplant (+chemotherapy) associated diarrhoea Conditioning & drug related Graft
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation
 Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
Transplantation. Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University
 Transplantation Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University Objectives To understand the diversity among human leukocyte antigens (HLA) or major histocompatibility complex (MHC) To know the
Transplantation Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University Objectives To understand the diversity among human leukocyte antigens (HLA) or major histocompatibility complex (MHC) To know the
Dr. Yi-chi M. Kong August 8, 2001 Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs Page 1 of 10 TRANSPLANTATION
 Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs 379-399 Page 1 of 10 TRANSPLANTATION I. KINDS OF GRAFTS II. RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN DONOR AND RECIPIENT Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs 379-399 Page 2 of 10 II.GRAFT REJECTION IS IMMUNOLOGIC
Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs 379-399 Page 1 of 10 TRANSPLANTATION I. KINDS OF GRAFTS II. RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN DONOR AND RECIPIENT Benjamini. Ch. 19, Pgs 379-399 Page 2 of 10 II.GRAFT REJECTION IS IMMUNOLOGIC
Non-infectious hepatic complications in patients with GVHD
 Non-infectious hepatic complications in patients with GVHD Tapani Ruutu Helsinki University Central Hospital Liver dysfunction in allogeneic stem cell transplantation injury secondary to the cytoreductive
Non-infectious hepatic complications in patients with GVHD Tapani Ruutu Helsinki University Central Hospital Liver dysfunction in allogeneic stem cell transplantation injury secondary to the cytoreductive
Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion
 Prevention of graftversus-host disease (GVHD) Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion Information for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and their families 2 This
Prevention of graftversus-host disease (GVHD) Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion Information for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and their families 2 This
Stem cell transplantation. Dr Mohammed Karodia NHLS & UP
 Stem cell transplantation Dr Mohammed Karodia NHLS & UP The use of haemopoeitic stem cells from a donor harvested from peripheral blood or bone marrow, to repopulate recipient bone marrow. Allogeneic From
Stem cell transplantation Dr Mohammed Karodia NHLS & UP The use of haemopoeitic stem cells from a donor harvested from peripheral blood or bone marrow, to repopulate recipient bone marrow. Allogeneic From
An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant
 Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO
 Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Immunosuppressive therapy for graft-versus-host disease. Mohamad Mohty Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Marseille
 Immunosuppressive therapy for graft-versus-host disease Mohamad Mohty Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Marseille Survival according to GVHD grade (Joint SFGM-TC, DFCI and IBMTR data; N=607) Cahn et al., Blood
Immunosuppressive therapy for graft-versus-host disease Mohamad Mohty Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Marseille Survival according to GVHD grade (Joint SFGM-TC, DFCI and IBMTR data; N=607) Cahn et al., Blood
MUD SCT. Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University
 MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016
 BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice
EXTRACORPOREAL PHOTOPHERESIS MAGGIE FOSTER MANAGER ROTHERHAM PHOTOPHERESIS UNIT
 EXTRACORPOREAL PHOTOPHERESIS MAGGIE FOSTER MANAGER ROTHERHAM PHOTOPHERESIS UNIT AIM OF PRESENTATION Explain about Photopheresis. Rotherham service. Conditions treated Advantages /disadvantages of XTS &
EXTRACORPOREAL PHOTOPHERESIS MAGGIE FOSTER MANAGER ROTHERHAM PHOTOPHERESIS UNIT AIM OF PRESENTATION Explain about Photopheresis. Rotherham service. Conditions treated Advantages /disadvantages of XTS &
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017
 Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
2016 BMT Tandem Meetings
 ASBMT CIBMTR 2016 BMT Tandem Meetings for Prevention of Cytomegalovirus after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in CMV-Seropositive Patients A Randomized, Double-Blind, -Controlled, Parallel-Group
ASBMT CIBMTR 2016 BMT Tandem Meetings for Prevention of Cytomegalovirus after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in CMV-Seropositive Patients A Randomized, Double-Blind, -Controlled, Parallel-Group
Neutrophil Recovery: The. Posttransplant Recovery. Bus11_1.ppt
 Neutrophil Recovery: The First Step in Posttransplant Recovery No conflicts of interest to disclose Bus11_1.ppt Blood is Made in the Bone Marrow Blood Stem Cell Pre-B White cells B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte
Neutrophil Recovery: The First Step in Posttransplant Recovery No conflicts of interest to disclose Bus11_1.ppt Blood is Made in the Bone Marrow Blood Stem Cell Pre-B White cells B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte
PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond
 PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond PUO in the immunocompromised host: role of viral infections Nature of host defect T cell defects Underlying disease Treatment Nature of clinical presentation
PUO in the Immunocompromised Host: CMV and beyond PUO in the immunocompromised host: role of viral infections Nature of host defect T cell defects Underlying disease Treatment Nature of clinical presentation
Overview of New Approaches to Immunosuppression in Renal Transplantation
 Overview of New Approaches to Immunosuppression in Renal Transplantation Ron Shapiro, M.D. Professor of Surgery Surgical Director, Kidney/Pancreas Transplant Program Recanati/Miller Transplantation Institute
Overview of New Approaches to Immunosuppression in Renal Transplantation Ron Shapiro, M.D. Professor of Surgery Surgical Director, Kidney/Pancreas Transplant Program Recanati/Miller Transplantation Institute
Transplant Booklet D Page 1
 Booklet D Pretest Correct Answers 4. (A) is correct. Technically, performing a hematopoietic stem cell transplant is one of the simplest transplantation procedures. The hematopoietic stem cells are infused
Booklet D Pretest Correct Answers 4. (A) is correct. Technically, performing a hematopoietic stem cell transplant is one of the simplest transplantation procedures. The hematopoietic stem cells are infused
Immunology. Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Transplant immunology+ Secondary immune deficiency
 Immunology Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Transplant immunology+ Secondary immune deficiency Transplant Immunology Transplantation is the process of moving cells, tissues or organs from one site to another
Immunology Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Transplant immunology+ Secondary immune deficiency Transplant Immunology Transplantation is the process of moving cells, tissues or organs from one site to another
Treatment of Chronic Graft versus Host Disease. Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota
 Treatment of Chronic Graft versus Host Disease Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota October 2013 Infections Transplant Events d-8 0 1mo 3mo 6mo Conditioning Transplant Engraftment Mucositis Organ
Treatment of Chronic Graft versus Host Disease Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota October 2013 Infections Transplant Events d-8 0 1mo 3mo 6mo Conditioning Transplant Engraftment Mucositis Organ
Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT
 Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Assistant Medical Director of Blood, Tissue, and Apheresis Services Children s Healthcare
Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Assistant Medical Director of Blood, Tissue, and Apheresis Services Children s Healthcare
Myeloproliferative Disorders - D Savage - 9 Jan 2002
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
The Immune System. A macrophage. ! Functions of the Immune System. ! Types of Immune Responses. ! Organization of the Immune System
 The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
ERROR CORRECTION FORM
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Registry Use Only Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic, syngeneic unrelated related
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Registry Use Only Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic, syngeneic unrelated related
Post Transplant Immunosuppression: Consideration for Primary Care. Sameh Abul-Ezz, M.D., Dr.P.H.
 Post Transplant Immunosuppression: Consideration for Primary Care Sameh Abul-Ezz, M.D., Dr.P.H. Objectives Discuss the commonly used immunosuppressive medications and what you need to know to care for
Post Transplant Immunosuppression: Consideration for Primary Care Sameh Abul-Ezz, M.D., Dr.P.H. Objectives Discuss the commonly used immunosuppressive medications and what you need to know to care for
Extracorporeal Photopheresis and Crohn s Disease. Jill Adamski MD, PhD Transfusion Medicine Department of Pathology
 Extracorporeal Photopheresis and Crohn s Disease Jill Adamski MD, PhD Transfusion Medicine Department of Pathology Outline 1. Crohn s Disease (CD) 2. Extracoporeal Photopheresis (ECP) 3. Pilot studies
Extracorporeal Photopheresis and Crohn s Disease Jill Adamski MD, PhD Transfusion Medicine Department of Pathology Outline 1. Crohn s Disease (CD) 2. Extracoporeal Photopheresis (ECP) 3. Pilot studies
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK. HCT in Children
 Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
UKALL14. Non-Myeloablative Conditioning Regimen (1/1) Date started (dd/mm/yyyy) (Day 7) Weight (kg) BSA (m 2 )
 Non-Myeloablative Conditioning Regimen (1/1) started (dd/mm/yyyy) (Day 7) BSA (m 2 ) Weight (kg) Please enter the daily dose given in the table below: Day Fludarabine (mg) Melphalan (mg) Alemtuzumab (mg)
Non-Myeloablative Conditioning Regimen (1/1) started (dd/mm/yyyy) (Day 7) BSA (m 2 ) Weight (kg) Please enter the daily dose given in the table below: Day Fludarabine (mg) Melphalan (mg) Alemtuzumab (mg)
Lung Injury after HCT
 Lung Injury after HCT J. Douglas Rizzo, MD, MS Financial Disclosure None SCS06_1.ppt Background HCT an important therapeutic modality for malignant and non-malignant diseases Pulmonary Toxicity common
Lung Injury after HCT J. Douglas Rizzo, MD, MS Financial Disclosure None SCS06_1.ppt Background HCT an important therapeutic modality for malignant and non-malignant diseases Pulmonary Toxicity common
Where in the TED Does HCT Stuff Go?
 Where in the TED Does HCT Stuff Go? Diane J. Knutson TED07_1.ppt Key Concepts What is an HSCT? Why perform one? Who can benefit? Mechanics of transplant Early and Late complications Where on new TED? TED07_2.ppt
Where in the TED Does HCT Stuff Go? Diane J. Knutson TED07_1.ppt Key Concepts What is an HSCT? Why perform one? Who can benefit? Mechanics of transplant Early and Late complications Where on new TED? TED07_2.ppt
3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25)
 3 Results 3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25) Five infusions of monoclonal IL-2 receptor antibody (anti-cd25) were planned according to protocol between day 0 and day
3 Results 3.1 Clinical safety of chimeric or humanized anti-cd25 (ch/anti-cd25) Five infusions of monoclonal IL-2 receptor antibody (anti-cd25) were planned according to protocol between day 0 and day
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B
 Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
 Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
CIBMTR Center Number: CIBMTR Recipient ID: RETIRED. Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed:
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Date Received: Registry Use Only Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic,
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Date Received: Registry Use Only Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic,
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Pre-Engraftment Syndrome after Double-Unit Cord Blood Transplantation: A Distinct Syndrome not Associated with Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease
 Pre-Engraftment Syndrome after Double-Unit Cord Blood Transplantation: A Distinct Syndrome not Associated with Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease Kevin J. Patel, Robert D. Rice, Rebecca Hawke, Michelle Abboud,
Pre-Engraftment Syndrome after Double-Unit Cord Blood Transplantation: A Distinct Syndrome not Associated with Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease Kevin J. Patel, Robert D. Rice, Rebecca Hawke, Michelle Abboud,
Chapter 24 The Immune System
 Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Chapter 24 The Immune System The Immune System Layered defense system The skin and chemical barriers The innate and adaptive immune systems Immunity The body s ability to recognize and destroy specific
Riposta immune versus stato immune
 Riposta immune versus stato immune Russell E. Lewis U.O. Malattie Infettive, Policlinico S. Orsola-Malpighi Dipartimento di Scienze Mediche e Chirurgiche Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna Immunodeficiency
Riposta immune versus stato immune Russell E. Lewis U.O. Malattie Infettive, Policlinico S. Orsola-Malpighi Dipartimento di Scienze Mediche e Chirurgiche Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna Immunodeficiency
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll 2/2001
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll 2/2001
RIC in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
 RIC in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Rainer Storb, MD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle, WA Disclosure Grant Support: NIH grants
RIC in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Rainer Storb, MD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center and the University of Washington School of Medicine Seattle, WA Disclosure Grant Support: NIH grants
General Terms: Appendix B. National Marrow Donor Program and The Medical College of Wisconsin
 Glossary of Terms This appendix is divided into two sections. The first section, General Terms, defines terms used throughout the CIBMTR data collection forms. The second section, FormsNet TM 2 Terms,
Glossary of Terms This appendix is divided into two sections. The first section, General Terms, defines terms used throughout the CIBMTR data collection forms. The second section, FormsNet TM 2 Terms,
Transplantation - Challenges for the future. Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust
 Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Nothing to disclose. Title of the presentation - Author
 Nothing to disclose Title of the presentation - Author 1 www.ebmt.org Complications after HSCT Alicia Rovó MD London 9/04/2013 Introduction Risk factors for transplant complication Type of complications
Nothing to disclose Title of the presentation - Author 1 www.ebmt.org Complications after HSCT Alicia Rovó MD London 9/04/2013 Introduction Risk factors for transplant complication Type of complications
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Transplantation
 Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives
 Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota February, 2013 No matched sib: where to look? URD donor requires close HLA matching and 3-12 weeks
Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota February, 2013 No matched sib: where to look? URD donor requires close HLA matching and 3-12 weeks
Dedicated to Gordon. Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey
 Dedicated to Gordon Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey 1949 Jacobson et al: Radioprotection by lead shielding of the spleen of a lethally irradiated animal 1951 Lorenz et al: Radiation protection
Dedicated to Gordon Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey 1949 Jacobson et al: Radioprotection by lead shielding of the spleen of a lethally irradiated animal 1951 Lorenz et al: Radiation protection
Non-Myeloablative Transplantation
 Non-Myeloablative Transplantation David G. Maloney, Brenda M. Sandmaier, Stephen Mackinnon, and Judith A. Shizuru The concept of utilizing enhanced immunosuppression rather than myeloablative cytotoxic
Non-Myeloablative Transplantation David G. Maloney, Brenda M. Sandmaier, Stephen Mackinnon, and Judith A. Shizuru The concept of utilizing enhanced immunosuppression rather than myeloablative cytotoxic
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation. David Rice, PhD, RN, NP
 BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation March 16, 2017 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice and Education No disclosures Objectives Describe basic concepts
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation March 16, 2017 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice and Education No disclosures Objectives Describe basic concepts
Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia Liat Shragian Alon, MD Rabin Medical Center, ISRAEL #EBMT15 www.ebmt.org Patient: 25-year-old male No prior medical history
Severe Viral Related Complications Following Allo-HCT for Severe Aplastic Anemia Liat Shragian Alon, MD Rabin Medical Center, ISRAEL #EBMT15 www.ebmt.org Patient: 25-year-old male No prior medical history
9/30/ DISCLOSURES. + First: Why immunosuppress? Transplant Immunosuppression and Prophylaxis
 Transplant Immunosuppression and Prophylaxis Sarah Fitz, APN, MSN, ACNP-BC Loyola University Medical Center DISCLOSURES I am not being paid by any entity to endorse a specific product. Any mention of brand
Transplant Immunosuppression and Prophylaxis Sarah Fitz, APN, MSN, ACNP-BC Loyola University Medical Center DISCLOSURES I am not being paid by any entity to endorse a specific product. Any mention of brand
Approach to the Transplant Patient. Amy Musiek, MD AAD Annual Meeting 2018
 Approach to the Transplant Patient Amy Musiek, MD AAD Annual Meeting 2018 Disclosures Actelion: speaker, advisory board, investigator Elorac: investigator Kyowa: investigator, advisory board Seattle genetics:
Approach to the Transplant Patient Amy Musiek, MD AAD Annual Meeting 2018 Disclosures Actelion: speaker, advisory board, investigator Elorac: investigator Kyowa: investigator, advisory board Seattle genetics:
BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE
 BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE Jennifer Shamai MS, RN, AOCNS, BMTCN Professional Practice Leader Department of Clinical Practice And Professional Education Click How to edit the Master Experts
BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE Jennifer Shamai MS, RN, AOCNS, BMTCN Professional Practice Leader Department of Clinical Practice And Professional Education Click How to edit the Master Experts
Revista Cubana de Hematología, Inmunología y Hemoterapia. 2017; 36 (Suplemento).
 Depletion of TCR alpha/beta+ T-lymphocytes from grafts for haplo haematopoietic CELL transplantation (HCT) in children Heilmann C, Ifversen M, Haastrup E, Fischer-Nielsen A. Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Depletion of TCR alpha/beta+ T-lymphocytes from grafts for haplo haematopoietic CELL transplantation (HCT) in children Heilmann C, Ifversen M, Haastrup E, Fischer-Nielsen A. Haematopoietic Cell Transplantation
MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
 MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSP There are no translations available. MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSP There are no translations available. MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
The National Marrow Donor Program. Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Simon Bostic, URD Transplant Recipient
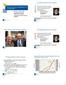 1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
Managing Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicities. Megan L. Menon, Pharm.D., BCOP Roswell Park Cancer Institute
 Managing Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicities Megan L. Menon, Pharm.D., BCOP Roswell Park Cancer Institute Approved Indications Ipilimumab Nivolumab Pembrolizumab* Atezolizumab Avelumab Durvalumab Ipi + Nivol
Managing Checkpoint Inhibitor Toxicities Megan L. Menon, Pharm.D., BCOP Roswell Park Cancer Institute Approved Indications Ipilimumab Nivolumab Pembrolizumab* Atezolizumab Avelumab Durvalumab Ipi + Nivol
T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG
 UCT T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG Nicolas Novitzky PhD, FCP(SA) Engraftment variables in Allo SCT Host HLA identity Integrity of marrow stroma Disease type and status Previous chemotherapy Graft
UCT T-CELL DEPLETION: ALEMTUZUMAB IN THE BAG Nicolas Novitzky PhD, FCP(SA) Engraftment variables in Allo SCT Host HLA identity Integrity of marrow stroma Disease type and status Previous chemotherapy Graft
The Immune System. These are classified as the Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. Innate Immunity
 The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
The Immune System Biological mechanisms that defend an organism must be 1. triggered by a stimulus upon injury or pathogen attack 2. able to counteract the injury or invasion 3. able to recognise foreign
FIT Board Review Corner March 2016
 FIT Board Review Corner March 2016 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Sarah Spriet, DO, and Tammy Peng, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs) to the
FIT Board Review Corner March 2016 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Sarah Spriet, DO, and Tammy Peng, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs) to the
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Complications after HSCT. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Complications after HSCT ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Type of HSCT HSCT Improved outcome due to better HLA matching, conditioning regimens, post transplant supportive care Over one-third have pulmonary
Complications after HSCT ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Type of HSCT HSCT Improved outcome due to better HLA matching, conditioning regimens, post transplant supportive care Over one-third have pulmonary
Objectives. What is Aplastic Anemia. SAA 101: An Introductory Course to Severe Aplastic Anemia
 SAA 101: An Introductory Course to Severe Aplastic Anemia David A. Margolis, MD Professor of Pediatrics/Medical College of Wisconsin Program Director/ Children s Hospital of Wisconsin BMT Program Objectives
SAA 101: An Introductory Course to Severe Aplastic Anemia David A. Margolis, MD Professor of Pediatrics/Medical College of Wisconsin Program Director/ Children s Hospital of Wisconsin BMT Program Objectives
Tolerance Induction in Transplantation
 Tolerance Induction in Transplantation Reza F. Saidi, MD, FACS, FICS Assistant Professor of Surgery Division of Organ Transplantation Department of Surgery University of Massachusetts Medical School Percent
Tolerance Induction in Transplantation Reza F. Saidi, MD, FACS, FICS Assistant Professor of Surgery Division of Organ Transplantation Department of Surgery University of Massachusetts Medical School Percent
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients
 Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients Dr Pamela Lee Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Paediatrics & Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University
Virological Surveillance in Paediatric HSCT Recipients Dr Pamela Lee Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Paediatrics & Adolescent Medicine Queen Mary Hospital LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University
4100: Cellular Therapy Essential Data Follow-Up Form
 4100: Cellular Therapy Essential Data Follow-Up Form Registry Use Only Sequence Number: Date Received: Key Fields CIBMTR Center Number: Event date: Visit: 100 day 6 months 1 year 2 years >2 years, Specify:
4100: Cellular Therapy Essential Data Follow-Up Form Registry Use Only Sequence Number: Date Received: Key Fields CIBMTR Center Number: Event date: Visit: 100 day 6 months 1 year 2 years >2 years, Specify:
Indolent Lymphomas. Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital
 Indolent Lymphomas Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital What does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with
Indolent Lymphomas Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital What does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with
Experience of patients transplanted with naïve T cell depleted stem cell graft in CMUH
 Experience of patients transplanted with naïve T cell depleted stem cell graft in CMUH Tzu-Ting Chen, Wen-Jyi Lo, Chiao-Lin Lin, Ching-Chan Lin, Li-Yuan Bai, Supeng Yeh, Chang-Fang Chiu Hematology and
Experience of patients transplanted with naïve T cell depleted stem cell graft in CMUH Tzu-Ting Chen, Wen-Jyi Lo, Chiao-Lin Lin, Ching-Chan Lin, Li-Yuan Bai, Supeng Yeh, Chang-Fang Chiu Hematology and
Immune system. Aims. Immune system. Lymphatic organs. Inflammation. Natural immune system. Adaptive immune system
 Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and collection. Koen Theunissen Hematologie Jessa Ziekenhuis Hasselt Limburgs Oncologisch Centrum
 Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and collection Koen Theunissen Hematologie Jessa Ziekenhuis Hasselt Limburgs Oncologisch Centrum Transplants Transplant Activity in the U.S. 1980-2010 14,000 12,000
Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and collection Koen Theunissen Hematologie Jessa Ziekenhuis Hasselt Limburgs Oncologisch Centrum Transplants Transplant Activity in the U.S. 1980-2010 14,000 12,000
PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Alexis Rodriguez, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Advocate Children s Hospital Disclosers Abbott Nutrition - Speaker Inflammatory Bowel Disease Chronic inflammatory disease
PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Alexis Rodriguez, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Advocate Children s Hospital Disclosers Abbott Nutrition - Speaker Inflammatory Bowel Disease Chronic inflammatory disease
Stem Cell Transplantation
 Stem Cell Transplantation Evelyne Willems Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, ULg, Liège Post-ASH meeting, January 11, 2012, Brussels Plan 1. Select the patient: validation of HCT-CI 2. Select the donor
Stem Cell Transplantation Evelyne Willems Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, ULg, Liège Post-ASH meeting, January 11, 2012, Brussels Plan 1. Select the patient: validation of HCT-CI 2. Select the donor
Physiology Unit 3. ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response
 Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Physiology Unit 3 ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY The Specific Immune Response In Physiology Today The Adaptive Arm of the Immune System Specific Immune Response Internal defense against a specific pathogen Acquired
Transplantation Immunology Booklet C
 Booklet C Pretest Correct Answers 3. (C) is correct. One of the major barriers to successful hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the antigens coded for by the major histocompatibility gene complex.
Booklet C Pretest Correct Answers 3. (C) is correct. One of the major barriers to successful hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is the antigens coded for by the major histocompatibility gene complex.
