First case of superficial infection due to Naganishia albida (formerly Cryptococcus albidus) in Iran: A review of the literature
|
|
|
- Coleen Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Current Medical Mycology 2017, 3(2): First case of superficial infection due to Naganishia albida (formerly Cryptococcus albidus) in Iran: A review of the literature Aghaei Gharehbolagh S 1, Nasimi M 2, Agha Kuchak Afshari S 1, Ghasemi Z 3, Rezaie S 1* 1 Department of Medical Mycology and Parasitology, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 2 Department of Dermatology, Razi Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 3 Department of Medical Mycology, Razi Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran Article Info Article type: Case report Article History: Received: 27 September 2017 Revised: 13 November 2017 Accepted: 29 November 2017 * Corresponding author: Sassan Rezaie Division of Molecular Biology, Department of Medical Mycology and Parasitology, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. srezaie@tums.ac.ir A B S T R A C T Background and Purpose: Naganishia albida (formerly Cryptococcus albidus) is a non-neoformans cryptococcal species rarely isolated as a human pathogen. Case report: Herein, we present the case of a 26-year-old Iranian man with a superficial cutaneous lesion in the axilla. The initial treatment for pityriasis versicolor by clotrimazole was unsuccessful. We performed skin sampling based on the standard protocol and conducted further investigations by the conventional laboratory tests and molecular analysis of the skin samples. All the mentioned analyses revealed N. albida as the causative agent of infection. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) analysis was carried out for the isolated agent, and the patient was treated using 100 mg daily of oral itraconazole. Conclusion: N. albida can be the causative agent of some superficial infections. This is the first report on the successful detection and treatment of a superficial skin infection due to N. albida by oral itraconazole. Keywords: Cutaneous, Cryptococcus albidus, Infection, Itraconazole, Naganishia albida, Superficial How to cite this paper Aghaei Gharehbolagh S, Nasimi M, Agha Kuchak Afshari S, Ghasemi Z, Rezaie S. First case of superficial infection due to Naganishia albida (formerly Cryptococcus albidus) in Iran: A review of the literature. Curr Med Mycol. 2017; 3(2): DOI: /cmm Introduction C ryptococcus spp. are basidiomycetous yeasts considered as the responsible agents for a wide range of diseases, among which C. neoformans and C. gattii are mentioned as the most common pathogenic species [1-3]. However, the incidence of infection due to non-neoformans cryptococcal species such as Papiliotrema laurentii (formerly C. laurentii) and Naganishia albida has increased recently [4, 5]. N. albida is an encapsulated yeast occasionally detected on human skin, air, and soil [6, 7]. Some cases of infection caused by N. albida such as keratitis, pneumonia, encephalitis, and cutaneous and disseminated cryptococcosis have been reported [8-10]. The treatment regimen for systemic cryptococcosis is amphotericin B in combination with flucytosine followed by fluconazole as consolidation therapy [8, 11, 12]. To date, there is no defined treatment for superficial cryptococcal infection. In the current study, we presented the first case of superficial cutaneous infection caused by N. albida, as well as its successful treatment with 100 mg daily of oral itraconazole. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on superficial cutaneous infection due to N. albida. Case report A 26-year-old Iranian man without any underlying diseases was referred to Razi Hospital, a referral center for skin diseases in Iran that is affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences, with a hyperpigmented patch in the axilla. Based on clinical examination, the diagnosis was made as pityriasis versicolor. However, treatment with clotrimazole cream was not successful and he returned to the hospital after one month. Direct microscopic examination of the scales after mixing with 10% potassium hydroxide revealed the Copyright 2017, Published by Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences on behalf of Iranian Society of Medical Mycology and Invasive Fungi Research Center. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY) License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
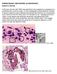
2 Figure 1. Macroscopic (A) and microscopic (B) demonstration of N. albida, which was as the causative agent of superficial infection in the present case presence of yeast cells. Furthermore, the scales cultured on Dixon Agar (Quelab, Canada) plates for five days at 32 C produced white and creamy colonies with smooth surfaces. By Lactophenol Cotton Blue Staining of the smears, yeast cells similar to Cryptococcus were observed under microscope (Figure 1). Genomic DNA was extracted from culture using glass beads method [13], and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed using universal primers [14] of ITS1 (5'-TCC GTA GGT GAA CCT GCG G- 3') and ITS4 (5'-TCC TCC GCT TAT TGA TAT GC- 3') (Sinaclon, Iran). The PCR product with the approximate size of 600 bp was applied for sequencing (Macrogen, South Korea). Alignment of the obtained sequence in BLAST revealed high homology (99%) with N. albida, which is with GenBank ID: MG In the following step, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values for itraconazole, voriconazole, and amphotericin B were determined using the microbroth dilution method according to the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) standard protocols [15]. Briefly, the test was performed in 96-well round-bottom microtiter plates. Drug concentration ranges were 0.03 to 16 µg/ml for itraconazole, voriconazole, and amphotericin B. Yeast suspensions were prepared in RPMI-1640 medium and adjusted to provide a final inoculum concentration of about to cells/ml. The culture plates were then incubated at 35 C followed by reading after 48 h according to the M27-S3 supplement of the CLSI guideline [15]. The MIC results were then compared with a drug-free control culture plate. The MIC values for itraconazole, voriconazole, and amphotericin B were µg/ml, µg/ml, and µg/ml, respectively, revealing the sensitivity of the mentioned causative agent. The patient was finally treated successfully using 100 mg daily of oral itraconazole. The Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences approved this report with the code No. IR.TUMS.SPH.REC Discussion N. albida is a non-neoformans species of the genus Cryptococcus with a similar morphology to C. neoformans. However, they can be differentiated by their reaction to biochemical tests such as phenol oxidase and color changes in Bird Seed Agar medium [9, 16-19]. In addition, N. albida is an opportunistic and encapsulated yeast found on human skin [6, 7]. Although N. albida rarely causes any diseases, there have been some case reports, including cases of meningitis, peritonitis, fungaemia, pulmonary and cutaneous infections, and keratitis (Table 1). Moreover, cases of encephalitis, disseminated cryptococcosis, and pneumonia have been reported [4, 8, 20-29]. However, N. albida has never been reported as the causative agent of a superficial skin infection (Table 1). As can be observed in this table, the majority of reported cases were from the USA, whereas there was only one record from other countries such as Turkey. Besides, the most reported cases were isolated from blood (fungemia) and the most effective treatment protocol was with amphotericin B. To the best of our knowledge, the case described here is the first report of a pityriasis versicolor-like superficial infection due to N. albida. In addition, treatment choices are limited for cryptococcal infections. The first choice of treatment for these infections is the combination of amphotericin B and flucytosine [11, 12]. Nonetheless, the treatment for infections due to N. albida is not well-defined, and amphotericin B has been mentioned to have limited efficacy in the treatment of N. albida [9]. N. albida shows various responses to different antifungal treatments. Therefore, there is no common treatment protocol for infections caused by this fungus. 34 Curr Med Mycol, 2017, 3(2): 33-37
3 Table 1. Overview of 24 reported cases of Naganishia albida ( ) No Age/sex/year Location Host status Clinical presentation Examination Treatment Outcome Reference 1 68/ M/ 1972 USA Pulmonary AmB Cured [20] 2 45/ M/ 1973 USA Meningitis India ink, AmB Cured [21] 3 29/M / 1980 USA Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, Alcoholic liver disease, receiving corticosteroids Meningitis AmB Expired [22] 4 65/ F/ 1987 USA 5 NA/NA/1989 NA 6 NA/NA/1993 USA Acute myelogenous leukemia Pemphigus foliaceus, steroid therapy Receiving long-term hemodialysis Fungemia India ink AmB, 5FC Expired [23] Fungemia KET Cured [24] Renal disease NA NA [25] 7 38/M / 1996 France AIDS Septicaemia FLU, ITC Expired [26] 8 4/F / 1998 Tennessee 9 70/ M/ 2000 U.K. Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia Sézary syndrome, Noninsulin-dependent diabetes Fungemia AmB Cured [27] Cutaneous, biopsy FLU Expired [16] 10 73/ F/ 2004 USA Rheumatoid arthritis Pulmonary, biopsy FLU 11 16/ F/ 2004 USA AIDS 12 23/M /2004 Korea 13 51/ M/ 2004 USA Renal transplant recipient Ddiabetes mellitus, lymphoma, Autologous progenitor cell transplant Scleral ulceration Disseminated [1] AmB, ITC Cured [30] Biopsy, FLU Cured [17] AmB, ITC Cured [33] 14 69/F/2005 USA Corneal transplantation keratitis Cured [2] 15 44/ M/2007 Turkey Acute respiratory failure Pneumonia Histopathology, AmB Cured [4] 16 14/M/2007 USA Etanercept therapy Cutaneous FLU Cured [10] 17 NA/NA/2011 USA Immunosuppressed, palmopustular psoriasis NA NA NA NA [18] 18 0/ M/2011 Greece Premature neonate Fungemia NA AmB, 5FC NA [29] 19 55/M/2013 USA liver transplant recipient Fungemia POS Cured [19] 20 28/M/2014 China AIDS Encephalitis India ink FLU Expired [9] 21 57/M/2015 USA Peritoneal Dialysis, hepatitis C, type 2 diabetes Peritonitis AmB 22 45/M/2015 Taiwan Hit by a plant Keratitis PCR FLU, AmB Cured [8] 23 83/M/2017 Hungary Receiving methylprednisolone Cutaneous Histopathology FLU 24 26/M/2017 Iran Immunocompetent Superficial, PCR ITC Cured M, male; F, female; AmB, amphotericin B; FLU, fluconazole; ITC, itraconazole; KET, ketoconazole; 5FC, 5 flucytosine; POS, posaconazole. NA = not available (Original publication could not be accessed, information gathered from related abstracts) [28] [31] Present case Recently, it has been that N. albida is only sensitive to amphotericin B and itraconazole [4, 30, 31]. Other reports revealed side effects due to the conventional amphotericin B (1 mg/kg/day) therapy against N. albida, which led the therapy to change to itraconazole [32]. Besides, successful treatment with fluconazole has been reported in patients with cutaneous infections caused by N. albida using a mean treatment period of 56 days [16]. In the present case, after MIC approval, we chose 100 mg daily of itraconazole in a 10-day treatment period, which resulted in successful treatment. The three-month follow up of the patient revealed no relapse of the infection and no evidence of any clinical manifestations at the involved site. Furthermore, several factors such as the anatomical location of involvement, the power of immune system in host, and tissue damages can determine the proper medication and the required treatment duration for cryptococcal infections due to non-neoformans species [4, 5, 17, 33]. Conclusion In conclusion, N. albida was found to have the ability to cause superficial infections. The case presented here is the first report of successful detection and treatment of infection by this yeast. N. albida was Curr Med Mycol, 2017, 3(2):
4 detected by sequencing of ITS1-4 rdna in this report and treated using oral itraconazole. Acknowledgments This investigation was supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences grant No Author s contribution S. R. designed and managed the project. M. N. was the clinical consultant. S. A.G. performed the tests. S. A.G. and S. A.K.A. wrote the first draft of the manuscript. S. R. edited the final manuscript. S. A.K.A. and Z. G. were project partners. Conflicts of interest None declared. Financial disclosure No financial interests related to the materials of this manuscript have been declared. References 1. Faress JA, Hejal R. Pulmonary crytpococcosis due to C. albidus in a patient on Infliximab. Chest. 2004; 126(4):987S de Castro LE, Sarraf OA, Lally JM, Sandoval HP, Solomon KD, Vroman DT. Cryptococcus albidus keratitis after corneal transplantation. Cornea. 2005; 24(7): Hagen F, Lumbsch HT, Arsic Arsenijevic V, Badali H, Bertout S, Billmyre RB, et al. Importance of resolving fungal nomenclature: the case of multiple pathogenic species in the Cryptococcus genus. Msphere. 2017; 2(4):e Burnik C, Altintaş N, Özkaya G, Serter T, Selcuk Z, Firat P, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome due to Cryptococcus albidus pneumonia: case report and review of the literature. Med Mycol. 2007; 45(5): Khawcharoenporn T, Apisarnthanarak A, Mundy LM. Non-neoformans cryptococcal infections: a systematic review. Infection. 2007; 35(2): Kano R, Kitagawa M, Oota S, Oosumi T, Murakami Y, Tokuriki M, et al. First case of feline systemic Cryptococcus albidus infection. Med Mycol. 2008; 46(1): Labrecque O, Sylvestre D, Messier S. Systemic Cryptococcus albidus infection in a Doberman Pinscher. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2005; 17(6): Huang YH, Lin IH, Chang TC, Tseng SH. Early diagnosis and successful treatment of Cryptococcus albidus keratitis: a case report and literature review. Medicine. 2015; 94(19):e Liu Y, Ma S, Wang X, Xu W, Tang J. Cryptococcus albidus encephalitis in newly diagnosed HIV-patient and literature review. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2014; 3: Hoang JK, Burruss J. Localized cutaneous Cryptococcus albidus infection in a 14-year-old boy on etanercept therapy. Pediatr Dermatol. 2007; 24(3): Huang W, Liao G, Baker GM, Wang Y, Lau R, Paderu P, et al. Lipid flippase subunit Cdc50 mediates drug resistance and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. MBio. 2016; 7(3):e Smith KD, Achan B, Hullsiek KH, McDonald TR, Okagaki LH, Alhadab AA, et al. Increased antifungal drug resistance in clinical isolates of Cryptococcus neoformans in Uganda. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015; 59(12): Yamada Y, Makimura K, Merhendi H, Ueda K, Nishiyama Y, Yamaguchi H, et al. Comparison of different methods for extraction of mitochondrial DNA from human pathogenic yeasts. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2002; 55(4): Zarrinfar H, Kaboli S, Dolatabadi S, Mohammadi R. Rapid detection of Candida species in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with pulmonary symptoms. Braz J Microbiol. 2016; 47(1): Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Reference method for broth dilution anti-fungal susceptibility testing of yeasts; approved standard-third edition, M27 A3. Wayne: CLSI; Narayan S, Batta K, Colloby P, Tan C. Cutaneous cryptococcus infection due to C. albidus associated with Sezary syndrome. Br J Dermatol. 2000; 143(3): Lee YA, Kim HJ, Lee TW, Kim MJ, Lee MH, Lee JH, et al. First report of Cryptococcus albidus-induced disseminated cryptococcosis in a renal transplant recipient. Korean J Intern Med. 2004; 19(1): Endo JO, Klein SZ, Pirozzi M, Pirozzi C, Hull CM. Generalized Cryptococcus albidus in an immunosuppressed patient with palmopustular psoriasis. Cutis. 2011; 88(3): Cleveland KO, Gelfand MS, Rao V. Posaconazole as successful treatment for fungemia due to Cryptococcus albidus in a liver transplant recipient. QJM. 2013; 106(4): Krumholz RA. Pulmonary cryptococcosis. A case due to Cryptococcus albidus. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972; 105(3): da Cunha T, Lusins J. Cryptococcus albidus meningitis. South Med J. 1973; 66(11): Melo JC, Srinivasan S, Scott ML, Raff MJ. Cryptococcus albidus meningitis. J Infect. 1980; 2(1): Gluck JL, Myers JP, Pass LM. Cryptococcemia due to cryptococcus albidus. South Med J. 1987; 80(4): Lin SR, Peng CF, Yang SA, Yu HS. Isolation of Cryptococcus albidus var. albidus in patient with pemphigus foliaceus. Gaoxiong Yi Xue Ke Xue Za Zhi. 1989; 5(2): Horowitz ID, Blumberg EA, Krevolin L. Cryptococcus albidus and mucormycosis empyema in a patient receiving hemodialysis. South Med J. 1993; 86(9): Loison J, Bouchara JP, Gueho E, de Gentile L, Cimon B, Chennebault JM, et al. First report of Cryptococcus albidus septicaemia in an HIV patient. J Infect. 1996; 33(2): Wells GM, Gajjar A, Pearson TA, Hale KL, Shenep JL. Pulmonary cryptosporidiosis and cryptococcus albidus fungemia in a child with acute lymphocytic leukemia. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1998; 31(6): Ragupathi L, Reyna M. Case report of Cryptococcus albidus peritonitis in a peritoneal dialysis patient and a review of the literature. Perit Dial Int. 2015; 35(4): Papadopoulou M, Kimouli M, Spanou S, Isidorou M, Rekliti N, Antonogeorgos G, et al. Cryptococcus albidus fungemia in premature neonate. Acta Paediatr. 2011; 100: Garelick JM, Khodabakhsh AJ, Lopez Y, Bamji M, Lister M. Scleral ulceration caused by Cryptococcus albidus in a patient with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Cornea. 2004; 23(7): Gyimesi A, Bator A, Gorog P, Telegdy E, Szepes E, Kappeter A, et al. Cutaneous Cryptococcus albidus 36 Curr Med Mycol, 2017, 3(2): 33-37
5 infection. Int J Dermatol. 2017; 56(4): Custis LP, Haller JA, de Juan E Jr. An unusual case of cryptococcal endophthalmitis. Retina. 1995; 15(4): Ramchandren R, Gladstone DE. Cryptococcus albidus infection in a patient undergoing autologous progenitor cell transplant. Transplantation. 2004; 77(6):956. Curr Med Mycol, 2017, 3(2):
ACCEPTED. Title: False Positive Culture Results from Patient Tissue Specimens Due to. Contamination of RPMI Medium with Cryptococcus albidus
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 February 2007 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02447-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 February 2007 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02447-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data
 2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit
 ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
Antifungal Resistance in Asia: Mechanisms, Epidemiology, and Consequences
 5th MMTN Conference 5-6 November 2016 Bangkok, Thailand 10:20-10:45, 6 Nov, 2016 Antifungal Resistance in Asia: Mechanisms, Epidemiology, and Consequences Yee-Chun Chen, M.D., PhD. Department of Medicine,
5th MMTN Conference 5-6 November 2016 Bangkok, Thailand 10:20-10:45, 6 Nov, 2016 Antifungal Resistance in Asia: Mechanisms, Epidemiology, and Consequences Yee-Chun Chen, M.D., PhD. Department of Medicine,
Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens
 Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens Cryptococcus neoformans Candida albicans Aspergillus species Pneumocystis carinii 1 Dermatophytes Named for derma skin Cause
Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens Cryptococcus neoformans Candida albicans Aspergillus species Pneumocystis carinii 1 Dermatophytes Named for derma skin Cause
Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient. Dr Kirsty Dodgson
 Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient Dr Kirsty Dodgson Aims Discuss different types of fungi Overview of types of clinical infections Clinical Manifestations Fungus Includes Moulds Aspergillus
Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient Dr Kirsty Dodgson Aims Discuss different types of fungi Overview of types of clinical infections Clinical Manifestations Fungus Includes Moulds Aspergillus
VIRULENCE FACTORS AND SUSCEPTIBILITY OF CANDIDA SPP. CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF NEONATAL INFECTIONS
 VIRULENCE FACTORS AND SUSCEPTIBILITY OF CANDIDA SPP. CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF NEONATAL INFECTIONS Nikola Stojanović, Predrag Stojanović, Suzana Otašević, Valentina Arsić-Arsenijević What do we know? - Third
VIRULENCE FACTORS AND SUSCEPTIBILITY OF CANDIDA SPP. CAUSATIVE AGENTS OF NEONATAL INFECTIONS Nikola Stojanović, Predrag Stojanović, Suzana Otašević, Valentina Arsić-Arsenijević What do we know? - Third
In Vitro Interactions of Antifungal agents and Tacrolimus against Aspergillus Biofilms
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 24 August 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01510-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 In Vitro Interactions
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 24 August 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01510-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 In Vitro Interactions
Introduction. Study of fungi called mycology.
 Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Scedosporium apiospermum
 223 Scedosporium apiospermum 1 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 16 7 14 16 10 12 Candida Aspergillus 82 2000 10 2001 1 12 MRI 2 1 Scedosporium apiospermum Key words: Scedosporium apiospermum, Aspergillus,
223 Scedosporium apiospermum 1 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 16 7 14 16 10 12 Candida Aspergillus 82 2000 10 2001 1 12 MRI 2 1 Scedosporium apiospermum Key words: Scedosporium apiospermum, Aspergillus,
Table 1. Antifungal Breakpoints for Candida. 2,3. Agent S SDD or I R. Fluconazole < 8.0 mg/ml mg/ml. > 64 mg/ml.
 AUSTRALIAN ANTIFUNGAL SUSCEPTIBILITY DATA 2008-2011 Part 1: The Yeasts In this article, an update of recent changes to the CLSI antifungal standards for susceptibility testing of yeasts is presented. We
AUSTRALIAN ANTIFUNGAL SUSCEPTIBILITY DATA 2008-2011 Part 1: The Yeasts In this article, an update of recent changes to the CLSI antifungal standards for susceptibility testing of yeasts is presented. We
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/s1678-9946201759049 Cryptococcus neoformans and C. gattii isolates from both HIV-infected and uninfected patients: antifungal susceptibility and outcome of cryptococcal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/s1678-9946201759049 Cryptococcus neoformans and C. gattii isolates from both HIV-infected and uninfected patients: antifungal susceptibility and outcome of cryptococcal
Antifungal susceptibilities of Cryptococcus species complex isolates from AIDS and non-aids patients in Southeast China
 BRAZ J INFECT DIS. 2012;16(2):175-179 The Brazilian Journal of INFECTIOUS DISEASES www.elsevier.com/locate/bjid Brief Communication Antifungal susceptibilities of Cryptococcus species complex isolates
BRAZ J INFECT DIS. 2012;16(2):175-179 The Brazilian Journal of INFECTIOUS DISEASES www.elsevier.com/locate/bjid Brief Communication Antifungal susceptibilities of Cryptococcus species complex isolates
Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD
 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Candida albicans 426 (64.0 ) C. albicans non-albicans
 74 2006 1) 2) 1) 3) 4) 5) 6) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 17 9 26 18 3 8 2003 10 2004 3 6 9,083 666 (7.3 ) Candida albicans 426 (64.0 ) C. albicans non-albicans 233 (35.0 ) Non-albicans Candida glabrata Candida tropicalis
74 2006 1) 2) 1) 3) 4) 5) 6) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 17 9 26 18 3 8 2003 10 2004 3 6 9,083 666 (7.3 ) Candida albicans 426 (64.0 ) C. albicans non-albicans 233 (35.0 ) Non-albicans Candida glabrata Candida tropicalis
Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease
 Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease Assist Prof. Somnuek Sungkanuparph Division of Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol
Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease Assist Prof. Somnuek Sungkanuparph Division of Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol
7/13/09. Definition. Infections Due to Malassezia. Case Report 1. Case Report 1 (cont.) Case Report 1 (cont.)
 Definition Infections Due to Malassezia Various species of Malassezia cause both opportunistic, superficial infections and occasionally systemic infections Common superficial infections include: Pityriasis
Definition Infections Due to Malassezia Various species of Malassezia cause both opportunistic, superficial infections and occasionally systemic infections Common superficial infections include: Pityriasis
Cutaneous Cryptococcosis in an Immunocompetent Host
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 3 (2015) pp. 593-597 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Cutaneous Cryptococcosis in an Immunocompetent Host Rahul Kamble* Department of Microbiology, T.N.M.C.
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 3 (2015) pp. 593-597 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Cutaneous Cryptococcosis in an Immunocompetent Host Rahul Kamble* Department of Microbiology, T.N.M.C.
Antifungal Activity of Voriconazole on Local Isolates: an In-vitro Study
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Antifungal Activity of Voriconazole on Local Isolates: an In-vitro Study Karina Q. De Sagun-Bella, MD, 1 Archimedes Lee D. Agahan, MD, 1 Leo DP. Cubillan,
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Antifungal Activity of Voriconazole on Local Isolates: an In-vitro Study Karina Q. De Sagun-Bella, MD, 1 Archimedes Lee D. Agahan, MD, 1 Leo DP. Cubillan,
Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases
 Medical Mycology (BIOL 4849) Summer 2007 Dr. Cooper Epidemiology of Mycoses Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases Mycosis (pl., mycoses) - an infection caused by a fungus Two broad categories
Medical Mycology (BIOL 4849) Summer 2007 Dr. Cooper Epidemiology of Mycoses Epidemiology and Laboratory Diagnosis of Fungal Diseases Mycosis (pl., mycoses) - an infection caused by a fungus Two broad categories
14-ID-07. Standardized Surveillance Case Definition for Cryptococcus gattii infection
 14-ID-07 Committee: Infectious Disease Title: tandardized urveillance Case Definition for Cryptococcus gattii infection I. tatement of the Problem Cryptococcal infections are caused by the environmentally
14-ID-07 Committee: Infectious Disease Title: tandardized urveillance Case Definition for Cryptococcus gattii infection I. tatement of the Problem Cryptococcal infections are caused by the environmentally
Common Fungi. Catherine Diamond MD MPH
 Common Fungi Catherine Diamond MD MPH Birth Month and Day & Last Four Digits of Your Cell Phone # BEFORE: http://tinyurl.com/kvfy3ts AFTER: http://tinyurl.com/lc4dzwr Clinically Common Fungi Yeast Mold
Common Fungi Catherine Diamond MD MPH Birth Month and Day & Last Four Digits of Your Cell Phone # BEFORE: http://tinyurl.com/kvfy3ts AFTER: http://tinyurl.com/lc4dzwr Clinically Common Fungi Yeast Mold
1* 1. Vijaya S. Rajmane, Shivaji T. Mohite
 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the VITEK 2 Yeast Antifungal Susceptibility ing with CLSI Broth Microdilution Reference for ing Four Antifungal Drugs against Candida species Isolated from
ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the VITEK 2 Yeast Antifungal Susceptibility ing with CLSI Broth Microdilution Reference for ing Four Antifungal Drugs against Candida species Isolated from
Optimizing antifungal dosing regimens. Joseph Meletiadis, PhD, FECMM Assistant Professor of Microbiology
 ATHENA 2017 International Conference November 28 30, 2017 Optimizing antifungal dosing regimens Joseph Meletiadis, PhD, FECMM Assistant Professor of Microbiology Clinical Microbiology Laboratory, «Attikon»
ATHENA 2017 International Conference November 28 30, 2017 Optimizing antifungal dosing regimens Joseph Meletiadis, PhD, FECMM Assistant Professor of Microbiology Clinical Microbiology Laboratory, «Attikon»
Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I
 BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
Tween 40-based precipitate production observed on modified chromogenic agar and development of biological identification kit for Malassezia species
 Medical Mycology May 2006, 44, 227231 Tween 40-based precipitate production observed on modified chromogenic agar and development of biological identification kit for Malassezia species TAKAMASA KANEKO*$,
Medical Mycology May 2006, 44, 227231 Tween 40-based precipitate production observed on modified chromogenic agar and development of biological identification kit for Malassezia species TAKAMASA KANEKO*$,
An Update in the Management of Candidiasis
 An Update in the Management of Candidiasis Daniel B. Chastain, Pharm.D., AAHIVP Infectious Diseases Pharmacy Specialist Phoebe Putney Memorial Hospital Adjunct Clinical Assistant Professor UGA College
An Update in the Management of Candidiasis Daniel B. Chastain, Pharm.D., AAHIVP Infectious Diseases Pharmacy Specialist Phoebe Putney Memorial Hospital Adjunct Clinical Assistant Professor UGA College
Antifungal drugs Dr. Raz Muhammed
 Antifungal drugs 13. 12. 2018 Dr. Raz Muhammed 2. Flucytosine (5-FC) Is fungistatic Is a synthetic pyrimidine antimetabolite Is often used in combination with amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic
Antifungal drugs 13. 12. 2018 Dr. Raz Muhammed 2. Flucytosine (5-FC) Is fungistatic Is a synthetic pyrimidine antimetabolite Is often used in combination with amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic
Invasive Fungal Infections in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients
 Outlines Epidemiology Candidiasis Aspergillosis Invasive Fungal Infections in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients Hsin-Yun Sun, M.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Department of Internal Medicine National
Outlines Epidemiology Candidiasis Aspergillosis Invasive Fungal Infections in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients Hsin-Yun Sun, M.D. Division of Infectious Diseases Department of Internal Medicine National
Nationwide survey of treatment for pediatric patients with invasive fungal infections in Japan
 J Infect Chemother (2013) 19:946 950 DOI 10.1007/s10156-013-0624-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nationwide survey of treatment for pediatric patients with invasive fungal infections in Japan Masaaki Mori Received:
J Infect Chemother (2013) 19:946 950 DOI 10.1007/s10156-013-0624-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nationwide survey of treatment for pediatric patients with invasive fungal infections in Japan Masaaki Mori Received:
Mycology Reference Centre, Leeds Information for Service Users 2017
 The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Mycology Reference Centre, Leeds Information for Service Users 2017 Contents Contents...1 The Mycology Reference Centre...1 Request Forms... 1 Specimen Transportation...
The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust NHS Mycology Reference Centre, Leeds Information for Service Users 2017 Contents Contents...1 The Mycology Reference Centre...1 Request Forms... 1 Specimen Transportation...
Study of systemic fungal infections in renal transplant recipients
 Original Research Article Study of systemic fungal infections in renal transplant recipients N.D. Srinivasaprasad 1*, G. Chandramohan 1, M. Edwin Fernando 2 1 DM (Nephrology), Assistant Professor, 2 DM
Original Research Article Study of systemic fungal infections in renal transplant recipients N.D. Srinivasaprasad 1*, G. Chandramohan 1, M. Edwin Fernando 2 1 DM (Nephrology), Assistant Professor, 2 DM
Cryptococcus gattii Meningitis Developed after Pneumonectomy in A Case of Necrotizing Pneumonia
 2014 25 1-6 Cryptococcus gattii Meningitis Developed after Pneumonectomy in A Case of Necrotizing Pneumonia Chih-Chen Lin 1 *, Hsiang-Kuang Tseng 1,2,3 *, Wei-Sheng Wang 1,2,3, Yee-Chun Chen 4, Tseng-Yu
2014 25 1-6 Cryptococcus gattii Meningitis Developed after Pneumonectomy in A Case of Necrotizing Pneumonia Chih-Chen Lin 1 *, Hsiang-Kuang Tseng 1,2,3 *, Wei-Sheng Wang 1,2,3, Yee-Chun Chen 4, Tseng-Yu
HISTOPLASMOSIS - LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS IN VIETNAM
 HISTOPLASMOSIS - LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS IN VIETNAM National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology, Hanoi, Vietnam, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan, Bach Mai hospital, Vietnam, Military
HISTOPLASMOSIS - LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS IN VIETNAM National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology, Hanoi, Vietnam, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan, Bach Mai hospital, Vietnam, Military
Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy
 Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy Subject Voriconazole Effective Date... 3/15/2018 Next Review Date... 3/15/2019 Coverage Policy Number... 4004 Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 General Background...
Cigna Drug and Biologic Coverage Policy Subject Voriconazole Effective Date... 3/15/2018 Next Review Date... 3/15/2019 Coverage Policy Number... 4004 Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 General Background...
Antifungal Agents. Polyenes Azoles Allyl and Benzyl Amines Other antifungals
 OPTO 6434 General Pharmacology Antifungal Agents Dr. Alison McDermott Room 254 HBSB, Phone 713-743 1974 Email amcdermott@optometry.uh.edu Fall 2015 Reading: Chapter 50 Brody s Human Pharmacology by Wecker
OPTO 6434 General Pharmacology Antifungal Agents Dr. Alison McDermott Room 254 HBSB, Phone 713-743 1974 Email amcdermott@optometry.uh.edu Fall 2015 Reading: Chapter 50 Brody s Human Pharmacology by Wecker
Antifungal Treatment in Neonates
 Antifungal Treatment in Neonates Irja Lutsar University of Tartu, Estonia Lisbon, 12. October 2015 Prevalence of invasive fungal infections in NeoINN database 2005-2014 UK; 2012-2014 Estonia & Greece 1
Antifungal Treatment in Neonates Irja Lutsar University of Tartu, Estonia Lisbon, 12. October 2015 Prevalence of invasive fungal infections in NeoINN database 2005-2014 UK; 2012-2014 Estonia & Greece 1
Condition First line Alternative Comments Candidemia Nonneutropenic adults
 Recommendations for the treatment of candidiasis. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Candidiasis: 2009 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Condition First line Alternative
Recommendations for the treatment of candidiasis. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Candidiasis: 2009 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Condition First line Alternative
Deep Dermatophytosis
 Deep Dermatophytosis 2016-11-06 MMTN/Bangkok Department of Dermatology Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou Branch Taoyuan, Taiwan Superficial dermatophytosis Wikimedia Stratum corneum Tinea faciei Tinea
Deep Dermatophytosis 2016-11-06 MMTN/Bangkok Department of Dermatology Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou Branch Taoyuan, Taiwan Superficial dermatophytosis Wikimedia Stratum corneum Tinea faciei Tinea
Therapy of Hematologic Malignancies Period at high risk of IFI
 Therapy of Hematologic Malignancies Period at high risk of IFI Neutrophils (/mm 3 ) 5 Chemotherapy Conditioning Regimen HSCT Engraftment GVHD + Immunosuppressive Treatment Cutaneous and mucositis : - Direct
Therapy of Hematologic Malignancies Period at high risk of IFI Neutrophils (/mm 3 ) 5 Chemotherapy Conditioning Regimen HSCT Engraftment GVHD + Immunosuppressive Treatment Cutaneous and mucositis : - Direct
Epidemiology and ecology of fungal diseases
 Epidemiology and ecology of fungal diseases Healthcare Focus on: - individual - diagnosis - treatment Public Health Focus on: - population - prevention The nature of fungi Kingdom Fungi (lat. fungus, -i)
Epidemiology and ecology of fungal diseases Healthcare Focus on: - individual - diagnosis - treatment Public Health Focus on: - population - prevention The nature of fungi Kingdom Fungi (lat. fungus, -i)
Antifungal resistance mechanisms in pathogenic fungi
 Antifungal resistance mechanisms in pathogenic fungi Shivaprakash M Rudramurthy Additional Professor, Mycology Division Center of Advanced Research in Medical Mycology, National Culture Collection of Pathogenic
Antifungal resistance mechanisms in pathogenic fungi Shivaprakash M Rudramurthy Additional Professor, Mycology Division Center of Advanced Research in Medical Mycology, National Culture Collection of Pathogenic
Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis
 QJM Advance Access published February 6, 2014 Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis Yu-Hsiang Juan MD 1,2, Sachin S Saboo, MD FRCR 1, Yu-Ching Lin MD 2, James R. Conner MD, Ph.D 3, Francine L. Jacobson
QJM Advance Access published February 6, 2014 Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis Yu-Hsiang Juan MD 1,2, Sachin S Saboo, MD FRCR 1, Yu-Ching Lin MD 2, James R. Conner MD, Ph.D 3, Francine L. Jacobson
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
mycoses Antifungal susceptibilities of Cryptococcus neoformans cerebrospinal fluid isolates from AIDS patients in Kenya Summary Introduction
 mycoses Diagnosis,Therapy and Prophylaxis of Fungal Diseases Original article Antifungal susceptibilities of Cryptococcus neoformans cerebrospinal fluid isolates from AIDS patients in Kenya Rennatus Mdodo,
mycoses Diagnosis,Therapy and Prophylaxis of Fungal Diseases Original article Antifungal susceptibilities of Cryptococcus neoformans cerebrospinal fluid isolates from AIDS patients in Kenya Rennatus Mdodo,
SYNERGISTIC ACTIVITIES OF TWO PROPOLIS WITH AMPHOTERICIN B AGAINST SOME AZOLE-RESISTANT CANDIDA STRAINS. PART II
 SYNERGISTIC ACTIVITIES OF TWO PROPOLIS WITH AMPHOTERICIN B AGAINST SOME AZOLE-RESISTANT CANDIDA STRAINS. PART II DURAN NIZAMI 1, MUZ MUSTAFA 2, DURAN GULAY GULBOL 3, OZER BURCIN 1, ONLEN YUSUF 4 1 Mustafa
SYNERGISTIC ACTIVITIES OF TWO PROPOLIS WITH AMPHOTERICIN B AGAINST SOME AZOLE-RESISTANT CANDIDA STRAINS. PART II DURAN NIZAMI 1, MUZ MUSTAFA 2, DURAN GULAY GULBOL 3, OZER BURCIN 1, ONLEN YUSUF 4 1 Mustafa
Antifungal Pharmacodynamics A Strategy to Optimize Efficacy
 Antifungal Pharmacodynamics A Strategy to Optimize Efficacy David Andes, MD Associate Professor, Department of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Microbiology and Immunology University of
Antifungal Pharmacodynamics A Strategy to Optimize Efficacy David Andes, MD Associate Professor, Department of Medicine Division of Infectious Diseases Medical Microbiology and Immunology University of
North American Endemic Fungi
 North American Endemic Fungi Boni Elizabeth Elewski, MD Chair Department of Dermatology University of Alabama at Birmingham James Elder Professor of Graduate Medical Education DISCLOSURE OF FINANCIAL RELATIONSHIPS
North American Endemic Fungi Boni Elizabeth Elewski, MD Chair Department of Dermatology University of Alabama at Birmingham James Elder Professor of Graduate Medical Education DISCLOSURE OF FINANCIAL RELATIONSHIPS
Cryptococcosis*,** *usually considered to be an opportunistic mycosis that often becomes systemic.
 Cryptococcosis*,** Definition - a chronic, subacute or rarely acute pulmonary, systemic or meningitic infection caused by Cryptococcus neoformans - the encapsulated Blastomycetes anamorph of Filobasidiella
Cryptococcosis*,** Definition - a chronic, subacute or rarely acute pulmonary, systemic or meningitic infection caused by Cryptococcus neoformans - the encapsulated Blastomycetes anamorph of Filobasidiella
Management of fungal infection
 Management of fungal infection HKDU symposium 17 th May 2015 Speaker: Dr. Thomas Chan MBBS (Hons), MRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Synopsis Infection caused by fungus mycoses Skin infection by fungus is common in general
Management of fungal infection HKDU symposium 17 th May 2015 Speaker: Dr. Thomas Chan MBBS (Hons), MRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Synopsis Infection caused by fungus mycoses Skin infection by fungus is common in general
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author. CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel
 CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
Micafungin and Candida spp. Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints. Version February 2013
 Micafungin and Candida spp. Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints. Version 1.0 5 February 2013 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised
Micafungin and Candida spp. Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints. Version 1.0 5 February 2013 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised
Fungi. Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy:
 MYCOLOGY Mycology I Fungi Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy: Morphology Spore formation FFungi Yeast Mold Yeastlike
MYCOLOGY Mycology I Fungi Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy: Morphology Spore formation FFungi Yeast Mold Yeastlike
PROGRESSI NELLA TERAPIA ANTIFUNGINA. A tribute to Piero Martino
 PROGRESSI NELLA TERAPIA ANTIFUNGINA A tribute to Piero Martino 1946-2007 ITALIAN ICONS IERI, OGGI, E DOMANI IERI, OGGI, E DOMANI IERI, OGGI, E DOMANI 1961 CAUSES OF DEATH IN PATIENTS WITH MALIGNANCIES
PROGRESSI NELLA TERAPIA ANTIFUNGINA A tribute to Piero Martino 1946-2007 ITALIAN ICONS IERI, OGGI, E DOMANI IERI, OGGI, E DOMANI IERI, OGGI, E DOMANI 1961 CAUSES OF DEATH IN PATIENTS WITH MALIGNANCIES
Voriconazole. Voriconazole VRCZ ITCZ
 7 7 8 7 8 fluconazole itraconazole in vitro in vivo Candida spp. C. glabrata C. krusei Cryptococcus neoformans in vitro Aspergillus spp. in vitro in vivo Aspergillus fumigatus Candida albicans C. krusei
7 7 8 7 8 fluconazole itraconazole in vitro in vivo Candida spp. C. glabrata C. krusei Cryptococcus neoformans in vitro Aspergillus spp. in vitro in vivo Aspergillus fumigatus Candida albicans C. krusei
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS
 GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS Full title of guideline Guideline for the management of cryptococcal meningitis Author Dr P Venkatesan (ID consultant) Division and specialty Medicine,
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS Full title of guideline Guideline for the management of cryptococcal meningitis Author Dr P Venkatesan (ID consultant) Division and specialty Medicine,
Current and Emerging Azole Antifungal Agents
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Jan. 1999, p. 40 79 Vol. 12, No. 1 0893-8512/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Current and Emerging Azole Antifungal Agents
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Jan. 1999, p. 40 79 Vol. 12, No. 1 0893-8512/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Current and Emerging Azole Antifungal Agents
In vitro antifungal susceptibility of Scopulariopsis brevicaulis isolates
 Medical Mycology, 2014, 52, 723 727 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myu039 Advance Access Publication Date: 21 July 2014 Original Article Original Article In vitro antifungal susceptibility of Scopulariopsis brevicaulis
Medical Mycology, 2014, 52, 723 727 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myu039 Advance Access Publication Date: 21 July 2014 Original Article Original Article In vitro antifungal susceptibility of Scopulariopsis brevicaulis
Update from the Laboratory: Clinical Identification and Susceptibility Testing of Fungi and Trends in Antifungal Resistance 13
 Fungal Infections Preface: Fungal Infections Luis Ostrosky-Zeichner and Jack D. Sobel xiii The Global Burden of Fungal Diseases 1 Snigdha Vallabhaneni, Rajal K. Mody, Tiffany Walker, and Tom Chiller Fungal
Fungal Infections Preface: Fungal Infections Luis Ostrosky-Zeichner and Jack D. Sobel xiii The Global Burden of Fungal Diseases 1 Snigdha Vallabhaneni, Rajal K. Mody, Tiffany Walker, and Tom Chiller Fungal
No Evidence As Yet. Georg Maschmeyer. Dept. of Hematology, Oncology & Palliative Care Klinikum Ernst von Bergmann Potsdam, Germany
 Is Combined Antifungal Therapy More Efficient than Single Agent Therapy? No Evidence As Yet www.ichs.org Georg Maschmeyer Dept. of Hematology, Oncology & Palliative Care Klinikum Ernst von Bergmann Potsdam,
Is Combined Antifungal Therapy More Efficient than Single Agent Therapy? No Evidence As Yet www.ichs.org Georg Maschmeyer Dept. of Hematology, Oncology & Palliative Care Klinikum Ernst von Bergmann Potsdam,
Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Cryptococcal Disease: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America
 IDSA GUIDELINES Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Cryptococcal Disease: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America John R. Perfect, 1 William E. Dismukes, 2 Francoise Dromer,
IDSA GUIDELINES Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Cryptococcal Disease: 2010 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America John R. Perfect, 1 William E. Dismukes, 2 Francoise Dromer,
Case. Fungal infections for the community provider. Case. Case. April 25, 2014 Peter V. Chin-Hong M.D. Infectious Diseases UCSF UCSF
 Case Fungal infections for the community provider April 25, 2014 Peter V. Chin-Hong M.D. Infectious Diseases UCSF peter.chin-hong@ucsf.edu UCSF A 38-year-old African-American female financial analyst is
Case Fungal infections for the community provider April 25, 2014 Peter V. Chin-Hong M.D. Infectious Diseases UCSF peter.chin-hong@ucsf.edu UCSF A 38-year-old African-American female financial analyst is
Title. individual. Author(s) Medical Mycology, 46(4), pp Issue Date Right
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Reversible visual disturbance due t individual. Nakamura, Shigeki; Izumikawa, Koich Kyoko; Mishima, Kazuaki; Kakeya, Hi Yanagihara, Katsunori;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Reversible visual disturbance due t individual. Nakamura, Shigeki; Izumikawa, Koich Kyoko; Mishima, Kazuaki; Kakeya, Hi Yanagihara, Katsunori;
WHICH ANTIFUNGAL AGENT IS THE CHOICE FOR SUSPECTED FUNGAL INFECTIONS?
 WHICH ANTIFUNGAL AGENT IS THE CHOICE FOR SUSPECTED FUNGAL INFECTIONS? Assoc. Prof. Dr. Serkan SENER Acibadem University Medical School Department of Emergency Medicine, Istanbul Acibadem Ankara Hospital,
WHICH ANTIFUNGAL AGENT IS THE CHOICE FOR SUSPECTED FUNGAL INFECTIONS? Assoc. Prof. Dr. Serkan SENER Acibadem University Medical School Department of Emergency Medicine, Istanbul Acibadem Ankara Hospital,
Case Presentation. Intern Tutor VS 2007/01/26
 Case Presentation Intern 8931150 Tutor VS 2007/01/26 About The Patient 38 years old worker ID: M120794700 Admission date: 2006/12/28 C.C.: Fever with headache for 2 days Present Illness Smoker, alcoholism
Case Presentation Intern 8931150 Tutor VS 2007/01/26 About The Patient 38 years old worker ID: M120794700 Admission date: 2006/12/28 C.C.: Fever with headache for 2 days Present Illness Smoker, alcoholism
Ali Alabbadi. Sarah Jaar ... Nader
 24 Ali Alabbadi Sarah Jaar... Nader Intro to Mycology *underlined text was explained in the lecture but is not found in the slides -mycology: the study of the mycoses of man (fungal infections) -less than
24 Ali Alabbadi Sarah Jaar... Nader Intro to Mycology *underlined text was explained in the lecture but is not found in the slides -mycology: the study of the mycoses of man (fungal infections) -less than
Challenges in Management of Cryptococcal Meningitis. Yunus Moosa Department of ID NRMSM Durban
 Challenges in Management of Cryptococcal Meningitis Yunus Moosa Department of ID NRMSM Durban Overview Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Prognostic factors Antifungal Treatment
Challenges in Management of Cryptococcal Meningitis Yunus Moosa Department of ID NRMSM Durban Overview Epidemiology Pathogenesis Clinical presentation Diagnosis Prognostic factors Antifungal Treatment
Trichophyton Microsporum Epidermophyton. dermatomycosis. Dematiaceous(pigmented fungi ) Dimorphic fungi Yeast and yeast like saprophyte
 Cutaneous candidiasis dermatophytosis Trichophyton Microsporum Epidermophyton dermatomycosis Dematiaceous(pigmented fungi ) Dimorphic fungi Yeast and yeast like saprophyte dermatomycosis Yeast & yeast
Cutaneous candidiasis dermatophytosis Trichophyton Microsporum Epidermophyton dermatomycosis Dematiaceous(pigmented fungi ) Dimorphic fungi Yeast and yeast like saprophyte dermatomycosis Yeast & yeast
Efficacy of a Novel Echinocandin, CD101, in a Mouse Model of Azole-Resistant Disseminated Candidiasis
 Efficacy of a Novel Echinocandin, CD0, in a Mouse Model of Azole-Resistant Disseminated Candidiasis L. Miesel, K-Y Lin, J. C. Chien, M. L. Hsieh, V. Ong, and K. Bartizal Eurofins Panlabs, Taipei, Taiwan
Efficacy of a Novel Echinocandin, CD0, in a Mouse Model of Azole-Resistant Disseminated Candidiasis L. Miesel, K-Y Lin, J. C. Chien, M. L. Hsieh, V. Ong, and K. Bartizal Eurofins Panlabs, Taipei, Taiwan
Use of Antifungals in the Year 2008
 Use of Antifungals in the Year 2008 Jose G. Montoya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Associate Chief for Clinical Affairs Division of Infectious Diseases Stanford University School of Medicine Diagnosis
Use of Antifungals in the Year 2008 Jose G. Montoya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Associate Chief for Clinical Affairs Division of Infectious Diseases Stanford University School of Medicine Diagnosis
Management Strategies For Invasive Mycoses: An MD Anderson Perspective
 Management Strategies For Invasive Mycoses: An MD Anderson Perspective Dimitrios P. Kontoyiannis, MD, ScD, FACP, FIDSA Professor of Medicine Director of Mycology Research Program M. D. Anderson Cancer
Management Strategies For Invasive Mycoses: An MD Anderson Perspective Dimitrios P. Kontoyiannis, MD, ScD, FACP, FIDSA Professor of Medicine Director of Mycology Research Program M. D. Anderson Cancer
Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data
 Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Registry Use Only Sequence Number: Date Received: CIBMTR Center Number: Event date: / / CIBMTR Form 2046 revision 5 (page 1 of 5). Last Updated May, 2018. Infection Episode
Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Registry Use Only Sequence Number: Date Received: CIBMTR Center Number: Event date: / / CIBMTR Form 2046 revision 5 (page 1 of 5). Last Updated May, 2018. Infection Episode
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 The antibacterial experience: indications for clinical use of antimicrobial combinations To prevent the emergence of resistant organisms (tuberculosis) To treat polymicrobial infections (abdominal complicated
The antibacterial experience: indications for clinical use of antimicrobial combinations To prevent the emergence of resistant organisms (tuberculosis) To treat polymicrobial infections (abdominal complicated
MANAGEMENT OF HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED FUNGAL INFECTIONS
 MANAGEMENT OF HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED FUNGAL INFECTIONS Paul D. Holtom, MD Associate Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine Numbers of Cases of Sepsis in the United States, According
MANAGEMENT OF HOSPITAL-ACQUIRED FUNGAL INFECTIONS Paul D. Holtom, MD Associate Professor of Medicine and Orthopaedics USC Keck School of Medicine Numbers of Cases of Sepsis in the United States, According
Cryptococcal Meningitis: Looking beyond HIV
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 3, March 2013 1 Cryptococcal Meningitis: Looking beyond HIV Deepak Nayak M *. Sushma V. Belurkar **, Chethan Manohar ***,
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 3, March 2013 1 Cryptococcal Meningitis: Looking beyond HIV Deepak Nayak M *. Sushma V. Belurkar **, Chethan Manohar ***,
Research priorities in medical mycology
 Research priorities in medical mycology David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Agenda How many patients are there with serious
Research priorities in medical mycology David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Agenda How many patients are there with serious
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Fungal infections in ICU. Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
 Fungal infections in ICU Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Epidemiology of invasive fungal infections - US +300% Martin GS, et al. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1546-1554
Fungal infections in ICU Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Epidemiology of invasive fungal infections - US +300% Martin GS, et al. N Engl J Med 2003;348:1546-1554
Medical Mycology 2002, 40, 21±26 Accepted 25 April 2001
 ã Medical Mycology 2002, 40, 21±26 Accepted 25 April 2001 Effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on polymorphonuclear neutrophils, monocytes
ã Medical Mycology 2002, 40, 21±26 Accepted 25 April 2001 Effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on polymorphonuclear neutrophils, monocytes
Updated Guidelines for Management of Candidiasis. Vidya Sankar, DMD, MHS April 6, 2017
 Updated Guidelines for Management of Candidiasis Vidya Sankar, DMD, MHS April 6, 2017 Statement of Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this presentation Outline
Updated Guidelines for Management of Candidiasis Vidya Sankar, DMD, MHS April 6, 2017 Statement of Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this presentation Outline
number Done by Corrected by Doctor د.حامد الزعبي
 number Fungi#1 Done by نرجس الس ماك Corrected by مهدي الشعراوي Doctor د.حامد الزعبي Introduction to Mycology -Terms: -Medical Mycology: The study of mycosis and their etiological agents -Mycosis: Disease
number Fungi#1 Done by نرجس الس ماك Corrected by مهدي الشعراوي Doctor د.حامد الزعبي Introduction to Mycology -Terms: -Medical Mycology: The study of mycosis and their etiological agents -Mycosis: Disease
Mycology. BioV 400. Subcutaneous Mycoses. Ecological associations. Geographic distribution World-wide
 BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
Update zu EUCAST 2012 Cornelia Lass-Flörl
 Update zu EUCAST 2012 Cornelia Lass-Flörl Frühjahrstagung 2012 Paul-Ehrlich-Gesellschaft Sektion Antimykotische Chemotherapie Bonn, 4./5. Mai 2012 Agenda 1. Breakpoints 2. Rationale documents and technical
Update zu EUCAST 2012 Cornelia Lass-Flörl Frühjahrstagung 2012 Paul-Ehrlich-Gesellschaft Sektion Antimykotische Chemotherapie Bonn, 4./5. Mai 2012 Agenda 1. Breakpoints 2. Rationale documents and technical
HAEMATOLOGY ANTIFUNGAL POLICY
 HAEMATOLOGY ANTIFUNGAL POLICY PROPHYLAXIS Primary Prophylaxis Patient Group Patients receiving intensive remissioninduction chemotherapy for Acute Leukaemia (excluding patients receiving vinca alkaloids)
HAEMATOLOGY ANTIFUNGAL POLICY PROPHYLAXIS Primary Prophylaxis Patient Group Patients receiving intensive remissioninduction chemotherapy for Acute Leukaemia (excluding patients receiving vinca alkaloids)
Te-Yu Lin, Kuo-Ming Yeh, Jung-Chung Lin, Ning-Chi Wang, Ming-Yieh Peng, Feng-Yee Chang
 J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 9;:-6 Cryptococcal disease in patients with or without human immunodeficiency virus: clinical presentation and monitoring of serum cryptococcal antigen titers Te-Yu Lin, Kuo-Ming
J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 9;:-6 Cryptococcal disease in patients with or without human immunodeficiency virus: clinical presentation and monitoring of serum cryptococcal antigen titers Te-Yu Lin, Kuo-Ming
Fungal Infections in Solid Organ Recipients
 Fungal Infections in Solid Organ Recipients Parisa Badiee, 1 Parivash Kordbacheh, 1 Abdolvahab Alborzi, 2 Farideh Zeini, 1 Hossein Mirhendy, 1 Mahmood Mahmoody 1 1 Department of Medical Parasitology and
Fungal Infections in Solid Organ Recipients Parisa Badiee, 1 Parivash Kordbacheh, 1 Abdolvahab Alborzi, 2 Farideh Zeini, 1 Hossein Mirhendy, 1 Mahmood Mahmoody 1 1 Department of Medical Parasitology and
Fungal Meningitis. Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse Bern
 Fungal Meningitis Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse 51 3010 Bern Death due to infectious diseases in sub-saharan Africa Park BJ. Et al AIDS 2009;23:525
Fungal Meningitis Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse 51 3010 Bern Death due to infectious diseases in sub-saharan Africa Park BJ. Et al AIDS 2009;23:525
Molecular phylogeny of Australian isolates of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato. David New Microbiology Registrar, PathWest
 Molecular phylogeny of Australian isolates of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato David New Microbiology Registrar, PathWest Background Sporothrix schenckii causes a cutaneous mycosis Sporotrichosis (aka rose
Molecular phylogeny of Australian isolates of Sporothrix schenckii sensu lato David New Microbiology Registrar, PathWest Background Sporothrix schenckii causes a cutaneous mycosis Sporotrichosis (aka rose
CURRENT AND NEWER ANTI-FUNGAL THERAPIES- MECHANISMS, INDICATIONS, LIMITATIONS AND PROBLEMS. Dr AMIT RAODEO DM SEMINAR
 CURRENT AND NEWER ANTI-FUNGAL THERAPIES- MECHANISMS, INDICATIONS, LIMITATIONS AND PROBLEMS Dr AMIT RAODEO DM SEMINAR Introduction The incidence of invasive fungal infections in critically ill intensive
CURRENT AND NEWER ANTI-FUNGAL THERAPIES- MECHANISMS, INDICATIONS, LIMITATIONS AND PROBLEMS Dr AMIT RAODEO DM SEMINAR Introduction The incidence of invasive fungal infections in critically ill intensive
Antifungal Pharmacotherapy
 Interpreting Antifungal Susceptibility Testing: Science or Smoke and Mirrors A. W. F O T H E R G I L L, M A, M B A U N I V E R S I T Y O F T E X A S H E A L T H S C I E N C E C E N T E R S A N A N T O
Interpreting Antifungal Susceptibility Testing: Science or Smoke and Mirrors A. W. F O T H E R G I L L, M A, M B A U N I V E R S I T Y O F T E X A S H E A L T H S C I E N C E C E N T E R S A N A N T O
AUSTRALIAN ANTIFUNGAL SUSCEPTIBILITY DATA : PART 2 THE MOULDS ASPERGILLUS, SCEDOSPORIUM AND FUSARIUM.
 AUSTRALIAN ANTIFUNGAL SUSCEPTIBILITY DATA 00-0: PART THE MOULDS ASPERGILLUS, SCEDOSPORIUM AND FUSARIUM. AUSTRALIAN Sarah Kidd, Rose Handke and ANTIFUNGAL David Ellis SUSCEPTIBILITY DATA 00-00 David SA
AUSTRALIAN ANTIFUNGAL SUSCEPTIBILITY DATA 00-0: PART THE MOULDS ASPERGILLUS, SCEDOSPORIUM AND FUSARIUM. AUSTRALIAN Sarah Kidd, Rose Handke and ANTIFUNGAL David Ellis SUSCEPTIBILITY DATA 00-00 David SA
Pattern of Antifungal Susceptibility in Pathogenic Molds by Microdilution Method at a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Original Article Pattern of Antifungal Susceptibility in Pathogenic Molds by Microdilution Method at a Tertiary Care Hospital Maria Khan*, Aamer Ikram, Gohar Zaman, Adeel Gardezi and Farida Khurram Lalani
Original Article Pattern of Antifungal Susceptibility in Pathogenic Molds by Microdilution Method at a Tertiary Care Hospital Maria Khan*, Aamer Ikram, Gohar Zaman, Adeel Gardezi and Farida Khurram Lalani
Japan Antifungal Surveillance Program (1):
 183 Japan Antifungal Surveillance Program (1): 2001 2002 1) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 1) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 16 9 14 16 10 12 2001 6 2002 3 2 11 576 fluconazole (FLCZ),
183 Japan Antifungal Surveillance Program (1): 2001 2002 1) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 1) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 16 9 14 16 10 12 2001 6 2002 3 2 11 576 fluconazole (FLCZ),
Combination Treatment of Invasive Fungal Infections
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Jan. 2005, p. 163 194 Vol. 18, No. 1 0893-8512/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.18.1.163 194.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Combination
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Jan. 2005, p. 163 194 Vol. 18, No. 1 0893-8512/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.18.1.163 194.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Combination
In vitro susceptibility to antifungal agents of environmental Cryptococcus spp. isolated in the city of Ribeirão Preto, São Paulo, Brazil
 Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 101(3): 239-243, May 2006 239 In vitro susceptibility to antifungal agents of environmental Cryptococcus spp. isolated in the city of Ribeirão Preto, São Paulo,
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 101(3): 239-243, May 2006 239 In vitro susceptibility to antifungal agents of environmental Cryptococcus spp. isolated in the city of Ribeirão Preto, São Paulo,
Fungal Infection in the ICU: Current Controversies
 Fungal Infection in the ICU: Current Controversies Andrew F. Shorr, MD, MPH, FCCP, FACP Washington Hospital Center Georgetown University, Washington, DC Disclosures I have served as a consultant to, researcher/investigator
Fungal Infection in the ICU: Current Controversies Andrew F. Shorr, MD, MPH, FCCP, FACP Washington Hospital Center Georgetown University, Washington, DC Disclosures I have served as a consultant to, researcher/investigator
Use of Antifungal Drugs in the Year 2006"
 Use of Antifungal Drugs in the Year 2006" Jose G. Montoya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Associate Chief for Clinical Affairs Division of Infectious Diseases Stanford University School of Medicine
Use of Antifungal Drugs in the Year 2006" Jose G. Montoya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Associate Chief for Clinical Affairs Division of Infectious Diseases Stanford University School of Medicine
Multi-clonal origin of macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae isolates. determined by multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 30 May 2012 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00678-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Multi-clonal origin
Itraconazole DIGICON. Composition: MOLECULAR INTRODUCTION
 Itraconazole DIGICON Composition: Itraconazole 100 mg MOLECULAR INTRODUCTION Itraconazole is a triazole medicine used to treat fungal infections. It is effective against a broad spectrum of fungi including:
Itraconazole DIGICON Composition: Itraconazole 100 mg MOLECULAR INTRODUCTION Itraconazole is a triazole medicine used to treat fungal infections. It is effective against a broad spectrum of fungi including:
