Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) quantitative PCR to differentiate Pj pneumonia from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients
|
|
|
- Tyrone Ryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI /s ARTICLE Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) quantitative PCR to differentiate Pj pneumonia from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients M. Maillet & D. Maubon & J. P. Brion & P. François & L. Molina & J. P. Stahl & O. Epaulard & A. Bosseray & P. Pavese Received: 3 July 2013 /Accepted: 12 August 2013 # Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2013 Abstract Conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in respiratory samples does not differentiate between Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) and Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) colonization. We used Pj real-time quantitative PCR (qpcr) with the objective to discriminate PCP from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients. All positive Pj qpcr [targeting the major surface glycoprotein (MSG) gene] obtained in respiratory samples from immunocompromised patients presenting pneumonia at the Grenoble University Hospital, France, were collected between August 2009 and April Diagnoses were retrospectively determined by a multidisciplinary group of experts blinded to the Pj qpcr results. Thirty-one bronchoalveolar lavages and four broncho aspirations positive for the Pj qpcr were obtained from 35 immunocompromised patients. Diagnoses of definite, probable, and possible PCP, and pneumonia from another etiology were retrospectively made for 7, 4, 5, and 19 patients, respectively. Copy numbers were significantly higher in the definite group (median 465,000 copies/ml) than in the probable group (median 38,600 copies/ml), the possible group (median 1,032 copies/ml), and the other diagnosis group (median 390 copies/ml). With the value of 3,160 copies/ml, the sensitivity and specificity of qpcr for the diagnosis of PCP were 100 % and 70 %, respectively. With the value of 31,600 copies/ml, the sensitivity and specificity were 80 % and 100 %, respectively. The positive predictive value was 100 % for results with more than 31,600 copies/ml and the negative predictive value was 100 % for results with fewer than 3,160 copies/ml. qpcr targeting the MSG gene can be helpful to discriminate PCP from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients, using two cut-off values, with a gray zone between them. M. Maillet (*): J. P. Brion : J. P. Stahl : O. Epaulard : P. Pavese (*) Infectious Diseases Department, CHU de Grenoble, BP 218, Grenoble cedex 9, France mmaillet@chu-grenoble.fr ppavese@chu-grenoble.fr D. Maubon Infectious Agents Department, Parasitology-Mycology Laboratory, CHU Grenoble, Grenoble, France P. François Public Health Department, CHU Grenoble, Grenoble, France L. Molina Hematology Department, CHU Grenoble, Grenoble, France A. Bosseray Internal Medicine Department, CHU Grenoble, Grenoble, France Introduction The incidence of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients has decreased since the introduction of chemoprophylaxis and antiretroviral therapy [1]; meanwhile, the incidence of PCP in non-hiv immunocompromised patients is increasing [2]. The standard laboratory method to diagnose PCP remains the microscopic identification of Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) by staining methods in respiratory samples. However, studies highlighted the low burden of Pj in non-hiv immunocompromised patients [3] and the lack of sensitivity of microscopic methods [4]. This justifies the increasing use of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods for diagnosis [5, 6]. The detection of Pj in individuals presenting without pneumonia or with pneumonia from another etiology has been defined as colonization or carriage [7]. Conventional Pj PCR is qualitative and very
2 sensitive, but does not differentiate between active PCP and Pj colonization. The aim of this study was to use Pj real-time quantitative PCR (qpcr) in order to differentiate PCP and Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients. Patients and methods Patients and clinical samples All positive Pj qpcr obtained in respiratory samples from immunosuppressed patients presenting with pneumonia at the Grenoble University Hospital, France, were collected between August 2009 and April We retrospectively studied the clinical histories of the concerned patients. Clinical data The collected clinical data included: age, sex, underlying diseases, immunosuppression therapy during the previous months, PCP prophylaxis, clinical symptoms, routine laboratory data, anti-pneumocystis treatment, stay in a critical care unit, mechanical ventilation, hypoxemia (PaO 2 <70 mmhg in room air or requirement for supplemental oxygen), use of other anti-infectious agents, and outcome. Staining methods The bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and broncho aspirations samples were stained and examined by a qualified microscopist at the Laboratory of Parasitology-Mycology, with 400 μl of fluid analyzed by Fast Giemsa and 800 μl observedafter Gomori Grocott staining. Real-time qpcr A DNA extract solution from each sample was tested with a Pj qpcr targeting the major surface glycoprotein (MSG) gene of Pj as previously described [4, 8]. The results were expressed as the number of MSG copies/ml of BAL fluid. Diagnosis of Pj pneumonia and Pj colonization A group of six experts, including three infectious diseases specialists, one internist, one hematologist, and one mycologist, classified the clinical histories of these patients in one of the following categories: definite, probable, and possible PCP, or other diagnosis (case definitions in Table 1). The experts were blinded to the Pj PCR results. Statistical analysis Statistical analyses were performed with the StatView software (for Windows, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Categorical variables were compared using the Fisher s exact test. Continuous variables were compared using the Kruskal Wallis test. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for copy numbers was constructed and used to define cut-off values in order to discriminate the definite and probable PCP groups from the colonized group (possible PCP group and other diagnosis). A p-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant. The Youden s index(se+sp 1) was calculated for each cut-off value, as well as the number of correctly classified patients, in order to determine an optimal cut-off value. Results Thirty-one BAL samples and four broncho aspirations with positive Pj qpcr were obtained from 35 immunocompromised patients. Broncho aspirations were used when BAL could not be performed. All of these patients had clinical presentations such as fever, cough, sputum, or dyspnea, and suspected pneumonia. Seven patients met all the criteria for definite PCP, four patients for probable PCP, and five for possible PCP; another diagnosis was finally made for 19 patients. Prophylaxis therapy was used in one of the 35 patients (2 %). All definite, Table 1 Diagnosis definitions used by the experts Definite PCP - clinical signs of progressive pneumonia - ground glass opacities in chest computed tomography - microscopical identification of Pj with Musto or RAL staining methods Probable PCP - clinical signs of progressive pneumonia - ground glass opacities in chest computed tomography - complete resolution of symptoms after a full course of anti-pcp treatment - absence of microscopical identification of Pj with staining methods Possible PCP - clinical signs of progressive pneumonia and: - either compatible radiological signs - or complete resolution of symptoms after anti-pcp treatment - absence of microscopical identification of Pj with staining methods Other diagnosis none of the above criteria The definite PCP and probable PCP groups were then re-assigned to the final diagnosis of PCP group, and the possible PCP and other diagnosis groups were re-assigned to the non-pcp group in order to construct a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve
3 possible, and probable patients had received anti-pcp treatment. Microscopic examination was positive in 8 of 32 samples of BAL fluid samples (one patient s retained diagnosis was allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis). Clinical features The clinical features for each group are described in Table 2. There was no statistical difference between the four groups. Real-time qpcr qpcr copy numbers were significantly higher in the definite group (median 465,000 copies/ml, range 99, ,290,000) than in the probable group (median 38,600 copies/ml, range 7, ,982) and the possible group (median 1,032 copies/ml, range ,000) or the other diagnosis group (median 390 copies/ml, range 145 2,833) (Fig. 1). The difference was significant between the four groups (p <0.0001). ROC curve analysis gave an area under the curve of 0.97 (Fig. 2), confirming the ability of qpcr to discriminate PCP from colonization. The sensitivity and specificity of qpcr on BAL fluids for discrimination between PCP and colonization were estimated with different qpcr cut-off values. Two cutoff values were determined to give 100 % positive and negative predictive values, with a gray zone between them. The estimated cut-off values were 31,600 and 3,160 copies/ml, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of qpcr for the diagnosis of PCP are specified in Fig. 2 for each cut-off value. The Youden s index and the rate of correctly classified patients for each cut-off value provided an optimal cut-off value of 36,100 copies/ml for the diagnosis of PCP (Fig. 3). Table 2 Clinical features Characteristics Definite PCP a (n =7) Probable PCP (n =4) Possible PCP (n =5) Other diagnosis d (n =19) p-value Age, years 66 (47 69) 66 (52 75) 65 (60 67) 49 (42 66) 0.34 Male sex 3 (43 %) 1 (25 %) 2 (40 %) 9 (47 %) Underlying disease Hematological malignancy 4 (57 %) 4 (100 %) 4 (80 %) 13 (68 %) 0.46 Solid malignancy 1 (14 %) 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 1 (5 %) 0.68 Organ transplantation 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 4 (21 %) 0.28 HIV b infection 2 (29 %) 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 1 (5 %) 0.2 Inflammatory disease 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 1 (20 %) 0 (0 %) 0.1 Corticosteroids 2 (29 %) 1 (25 %) 2 (40 %) 4 (21 %) 0.85 Anti-tumor chemotherapy 2 (29 %) 2 (50 %) 2 (40 %) 11 (58 %) 0.59 Immunosuppressive agents other than 1 (14 %) 1 (25 %) 2 (40 %) 3 (16 %) 0.64 corticosteroids or chemotherapy PCP prophylaxis 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 1 (5 %) 0.83 Hypoxia 7 (100 %) 3 (75 %) 5 (100 %) 11 (58 %) 0.19 Stay in ICU c 2 (29 %) 2 (50 %) 0 (0 %) 5 (26 %) 0.39 Anti-PCP treatment 7 (100 %) 4 (100 %) 5 (100 %) 12 (63 %) 0.06 Mechanical ventilation 2 (29 %) 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 5 (26 %) 0.38 Laboratory findings Leucocytes, /mm 3 2,100 (1,700 9,825) 7,150 (6, ) 9,100 ( ) 3,700 (2,325 5,900) 0.4 Neutrophils, /mm 3 1,400 (1,125 5,650) 5,850 (5,200 7,250) 4,650 (1,800 8,150) 2,600 (2,200 5,525) 0.28 Lymphocytes, /mm ( ) 950 (450 1,300) 400 (350 2,150) 500 ( ) 0.77 C-reactive protein, mg/dl 11.8 ( ) 10.5 ( ) 10.7 (4.5 20) 9.3 ( ) 0.99 Creatinine, mg/dl 0.8 (0.61 1) 0.84 ( ) 0.71 ( ) 0.97 ( ) 0.91 Death 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 0 (0 %) 3 (16 %) 0.43 Data are presented as n (%) or median (interquartile range) a Pneumocystis pneumonia b Human immunodeficiency virus c Intensive care unit d The other diagnoses group included bacterial pneumonia (n =2), atypical pneumonia (n =2), influenza virus pneumonia (n =1), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) due to sepsis (n =1), candidemia (n =1), bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (n =1), drug-induced pneumonia (n =1), bronchial hamartoma (n =1), multifactorial pulmonary fibrosis (n =1), allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (n =1), pulmonary lymphoma (n =2), and undetermined (n =5)
4 Discussion The diagnostic performance of the microscopic visualization of Pj is dependent on the quality and type of sample, the number of organisms, and the experience of the microscopist [9]. The higher sensitivity of PCR for Pj detection has been demonstrated previously [4]. The main risk of using conventional PCR for the diagnosis of PCP is a positive result for colonized patients having pneumonia from another etiology [7, 10 17]. In this study, we observed that the qpcr results in the probable PCP group were significantly higher than those in the possible PCP group and in the group with another etiology, and were significantly lower than those in the definite PCP group. These results suggest that qpcr can help discriminate PCP from colonization and are in concordance with the hypothesis that the burden of Pj is lower in colonized people than in patients with PCP [18]. This is particularly interesting for non-hiv-infected immunocompromised patients, who often present with PCP with a low burden of Pj organisms and may not be diagnosed using microscopic examination [3]. qpcr values between 3,160 and 31,600 copies/ml fall within a gray zone, in which curative or prophylactic treatment should be discussed individually. It included nine out of the 35 (25 %) patients. Nevertheless, the Youden s index and the rate of correctly classified patients allowed determining the optimal cut-off value of 31,600 copies/ml, maximizing the accuracy for the diagnosis of PCP. A recent study concluded that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the survival of PCP patients without HIV infection [19], suggesting that a rapid and accurate PCP diagnosis method such as qpcr should be used in these patients Fig. 2 Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve of P. jirovecii copy numbers for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP). The arrows indicate cut-off values of 3,160 copies/ml, and 31,600 copies/ml with a low burden of Pj. In our study, the cut-off value of 3,160 copies/ml would have avoided 13 of 17 (76 %) treatments prescribed to patients whose final diagnosis was not PCP. This cut-off would allow physicians to stop probabilistic treatment, and, therefore, limit adverse effects, cost of treatment, and development of resistances [7, 20]. A meta-analysis showed that PCR has good diagnosis accuracy and may be a useful tool for the diagnosis of PCP in immunocompromised patients [21]. Previous studies determined various cut-offs of qpcr targeting different genes to discriminate PCP from colonization: for MSG gene, Larsen et al. proved that a cut-off value of 50 copies/tube for qpcr in % log copies/ml index Fig. 1 Box and whisker plots of Pneumocystis jirovecii copy numbers according to patient group. The boxes contain 50 % of the sample data, with the median value indicated by a horizontal bar rate of correctly classified patients Youden's index Fig. 3 Rate of correctly classified patients and Youden s index for each cut-off value
5 oral-wash samples increased the specificity for diagnosis of PCP to 100 % [18]. Flori et al. s study established that a cutoffof10 3 copies of DNA per capillary of BAL (PCR targeting the MSG gene) increased the specificity from 84.9 to 98.6 % with 100 % sensitivity [4]. Other studies highlighted the usefulness of qpcr in discriminating colonization from PCP: Alanio et al. proposed two cut-off values (120 and 1,900 trophic forms equivalents/ml) with a qpcr targeting the mitochondrial large subunit ribosomal RNA gene [22]; for Matsumura et al., the value of 1,300 copies/ml distinguished PCP from colonization with a sensitivity of 100 % and a specificity of 80 %, using qpcr targeting the DHPS (dihydropteroate synthase) gene [23]. We need to consider limitations when interpreting our results: this is a single-center study, the number of patients is relatively small, and we combined the data from the BAL and the broncho aspiration samples to evaluate the qpcr. Without a test capable of confirming or excluding the diagnosis of PCP, the classification of patients is uncertain. However, one quality of our study is that patients were classified by a multidisciplinary group of experts, ruling by consensus in view of all the clinical and complementary data. The fact that the experts did not know the qpcr results avoids classification bias. In spite of the small number of patients, the observed differences between the groups are statistically significant, which suggests that these differences are important. In our study, we used qpcr targeting the MSG gene, which is appropriate in discuss PCP diagnosis: the sensitivity is excellent, and it has been proved that qpcr analysis and the MSG target have the highest specificity compared with other PCR assays [24]. We can note that the rate of anti-pneumocystis prophylaxis was very low in our population. There is no current recommendation for anti-pcp prophylaxis or empirical therapy for non-hiv immunocompromised patients. It is known that colonization can sometimes lead to the development of PCP [7]. We propose to treat patients with a high probability of PCP and Pj burdens in the gray zone, and to monitor patients with low burdens and low probability of PCP with biological markers such as β-d-glucan, while prescribing a prophylactic treatment [23, 25, 26]. The proportion of patients having a hematological malignancy was very high in our population. We hypothesize that cut-off values may differ with the underlying diseases and may vary from one center to another. In conclusion, our study shows that our qpcr targeting the MSG gene in respiratory samples can help discriminate PCP from pneumonia with Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients, using two cut-off values of 3,160 and 31,600 copies/ml, with a gray zone between them. Cut-off values should be determined for each laboratory and each population of patients. Conflict of interest interest. The authors declare they have no conflict of References 1. Kelley CF, Checkley W, Mannino DM, Franco-Paredes C, Del Rio C, Holguin F (2009) Trends in hospitalizations for AIDS-associated Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in the United States (1986 to 2005). Chest 136: Mansharamani NG, Garland R, Delaney D, Koziel H (2000) Management and outcome patterns for adult Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, 1985 to 1995: comparison of HIV-associated cases to other immunocompromised states. Chest 118: Thomas CF Jr, Limper AH (2004) Pneumocystis pneumonia. N Engl J Med 350: Flori P, Bellete B, Durand F et al (2004) Comparison between realtime PCR, conventional PCR and different staining techniques for diagnosing Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia from bronchoalveolar lavage specimens. J Med Microbiol 53: Botterel F, Cabaret O, Foulet F, Cordonnier C, Costa JM, Bretagne S (2012) Clinical significance of quantifying Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA by using real-time PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from immunocompromised patients. J Clin Microbiol 50(2): Durand-Joly I, Chabé M, Soula F, Delhaes L, Camus D, Dei-Cas E (2005) Molecular diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia. FEMS ImmunolMedMicrobiol45: Morris A, Norris KA (2012) Colonization by Pneumocystis jirovecii and its role in disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 25(2): Chumpitazi BFF, Flori P, Kern JB et al (2011) Characteristics and clinical relevance of the quantitative touch-down major surface glycoprotein polymerase chain reaction in the diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia. Med Mycol Oct 49: Carmona EM, Limper AH (2011) Update on the diagnosis and treatment of Pneumocystis pneumonia. Ther Adv Respir Dis 5: Morris A, Wei K, Afshar K, Huang L (2008) Epidemiology and clinical significance of Pneumocystis colonization. J Infect Dis 197: Ponce CA, Gallo M, Bustamante R, Vargas SL (2010) Pneumocystis colonization is highly prevalent in the autopsied lungs of the general population. Clin Infect Dis 50: Spencer L, Ukwu M, Alexander T et al (2008) Epidemiology of Pneumocystis colonization in families. Clin Infect Dis 46: Dei-Cas E (2000) Pneumocystis infections: the iceberg? Med Mycol 38(Suppl 1): Calderon EJ, Dei-Cas E (2010) Pneumocystis infection: unraveling the colonization-to-disease shift. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 8(3): Mekinian A, Durand-Joly I, Hatron PY et al (2011) Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases: prevalence, risk factors of colonization and outcome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50: Medrano FJ, Montes-Cano M, Conde M et al (2005) Pneumocystis jirovecii in general population. Emerg Infect Dis Feb 11(2): Maskell NA, Waine DJ, Lindley A et al (2003) Asymptomatic carriage of Pneumocystis jiroveci in subjects undergoing bronchoscopy: a prospective study. Thorax 58: Larsen HH, Masur H, Kovacs JA et al (2002) Development and evaluation of a quantitative, touch-down, real-time PCR assay for diagnosing Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Clin Microbiol 40(2): Asai N, Motojima S, Ohkuni Y et al (2012) Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the survival of Pneumocystis pneumonia patients without human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Chemother 18(6): Thomas CF Jr, Limper AH (2007) Current insights into the biology and pathogenesis of Pneumocystis pneumonia. Nature 5(4): Summah H, Zhu YG, Falagas ME, Vouloumanou EK, Qu JM (2013) Use of real-time polymerase chain reaction for the diagnosis of
6 Pneumocystis pneumonia in immunocompromised patients: a metaanalysis. Chin Med J (Engl) 126(10): Alanio A, Desoubeaux G, Sarfati C et al (2011) Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised patients. Clin Microbiol Infect 17: Matsumura Y, Ito Y, Iinuma Y et al (2012) Quantitative real-time PCR and the (1 3)-β-D-glucan assay for differentiation between Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization. Clin Microbiol Infect 18(6): Lu Y, Ling G, Qiang C et al (2011) PCR diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia: a bivariate meta-analysis. J Clin Microbiol 49(12): Persat F, Ranque S, Derouin F, Michel-Nguyen A, Picot S, Sulahian A (2008) Contribution of the (1 3)-β-D-glucan assay for diagnosis of invasive fungal infections. J Clin Microbiol 46: Onishi A, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y et al (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of serum 1,3-β-D-glucan for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, invasive candidiasis, and invasive aspergillosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Microbiol 50(1):7 15
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
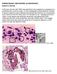 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Outcomes of Moderate-to-Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia Treated with Adjunctive Steroid in Non-HIV-Infected Patients
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Oct. 2011, p. 4613 4618 Vol. 55, No. 10 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.00669-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Outcomes
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Oct. 2011, p. 4613 4618 Vol. 55, No. 10 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.00669-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Outcomes
Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised A. Alanio 1, G. Desoubeaux 1, C. Sarfati
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised A. Alanio 1, G. Desoubeaux 1, C. Sarfati
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:478-485 Clinical significance of positive Pneumocystis jirovecii polymerase chain reaction in non-human immunodeficiency virus immunocompromised patients in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:478-485 Clinical significance of positive Pneumocystis jirovecii polymerase chain reaction in non-human immunodeficiency virus immunocompromised patients in
Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al.
 Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) processing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods The BAL procedure was performed following a standardized protocol by an experienced
Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) processing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods The BAL procedure was performed following a standardized protocol by an experienced
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit
 ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
Pneumocystis colonisation is common among hospitalised HIV infected patients with non- Pneumocystis pneumonia
 1 Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, San Francisco General Hospital, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA; 2 HIV/AIDS Division, San Francisco General Hospital,
1 Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, San Francisco General Hospital, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA; 2 HIV/AIDS Division, San Francisco General Hospital,
Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside. Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London
 Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London Presented at ECCMID Berlin April 30 th 2013 Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file
Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London Presented at ECCMID Berlin April 30 th 2013 Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file
Pierre Flori, 1 Bahrie Bellete, 1 Fabrice Durand, 1 Hélène Raberin, 1 Céline Cazorla, 2 Jamal Hafid, 1 Frédéric Lucht 2 and Roger Tran Manh Sung 1
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 603 607 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45528-0 Comparison between real-time PCR, conventional PCR and different staining techniques for diagnosing Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 603 607 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45528-0 Comparison between real-time PCR, conventional PCR and different staining techniques for diagnosing Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii
 141 Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients with Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Blinded Comparison to Standard Methods Juan Torres, 1,a Mitchell Goldman,
141 Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients with Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Blinded Comparison to Standard Methods Juan Torres, 1,a Mitchell Goldman,
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5,
 Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
5/15/2017. What Does HIV/AIDS Look Like in DC in Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections
 Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University Washington, DC FORMATTED: 4/28/217 Learning Objectives After attending
Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University Washington, DC FORMATTED: 4/28/217 Learning Objectives After attending
TOP PAPERS in MEDICAL MYCOLOGY Laboratory Diagnosis Manuel Cuenca-Estrella Abril 2018
 TOP PAPERS in MEDICAL MYCOLOGY Laboratory Diagnosis Manuel Cuenca-Estrella Abril 2018 MCE01 Conflict of interest disclosure In the past 5 years, M.C.E. has received grant support from Astellas Pharma,
TOP PAPERS in MEDICAL MYCOLOGY Laboratory Diagnosis Manuel Cuenca-Estrella Abril 2018 MCE01 Conflict of interest disclosure In the past 5 years, M.C.E. has received grant support from Astellas Pharma,
High prevalence of Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization among HIV-positive patients in southern Brazil
 Medical Mycology, 2014, 52, 804 809 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myu059 Advance Access Publication Date: 6 October 2014 Original Article Original Article High prevalence of Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization among
Medical Mycology, 2014, 52, 804 809 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myu059 Advance Access Publication Date: 6 October 2014 Original Article Original Article High prevalence of Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization among
Controversies in management: prophylaxis or diagnostics
 5 th Advances Against Aspergillosis Controversies in management: prophylaxis or diagnostics Caveats in the use of biological markers for early diagnosis Drosos E. Karageorgopoulos, MD Researcher, Alfa
5 th Advances Against Aspergillosis Controversies in management: prophylaxis or diagnostics Caveats in the use of biological markers for early diagnosis Drosos E. Karageorgopoulos, MD Researcher, Alfa
Outline NEW DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS WHY? WHICH TESTS? WHEN TO USE THEM? Documented IFI
 New Developments and Challenges in Diagnostics of Invasive Fungal Infections O. Marchetti, MD Infectious Diseases Service, Department of Medicine, CHUV and University of Lausanne, Switzerland Workshop
New Developments and Challenges in Diagnostics of Invasive Fungal Infections O. Marchetti, MD Infectious Diseases Service, Department of Medicine, CHUV and University of Lausanne, Switzerland Workshop
Clinical significance of quantifying Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA using real-time. PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from immunocompromised patients
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 December 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06036-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 December 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06036-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in immunocompromised patients by real-time PCR:
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 9 July 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01480-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Diagnosis of Pneumocystis
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 9 July 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01480-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Diagnosis of Pneumocystis
Pneumocystis PCR: It Is Time to Make PCR the Test of Choice
 Open Forum Infectious Diseases MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis PCR: It Is Time to Make PCR the Test of Choice Laura Doyle, Sherilynn Vogel, and Gary W. Procop Section of Clinical Microbiology, Department of
Open Forum Infectious Diseases MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis PCR: It Is Time to Make PCR the Test of Choice Laura Doyle, Sherilynn Vogel, and Gary W. Procop Section of Clinical Microbiology, Department of
WHICH ANTIFUNGAL AGENT IS THE CHOICE FOR SUSPECTED FUNGAL INFECTIONS?
 WHICH ANTIFUNGAL AGENT IS THE CHOICE FOR SUSPECTED FUNGAL INFECTIONS? Assoc. Prof. Dr. Serkan SENER Acibadem University Medical School Department of Emergency Medicine, Istanbul Acibadem Ankara Hospital,
WHICH ANTIFUNGAL AGENT IS THE CHOICE FOR SUSPECTED FUNGAL INFECTIONS? Assoc. Prof. Dr. Serkan SENER Acibadem University Medical School Department of Emergency Medicine, Istanbul Acibadem Ankara Hospital,
PCR Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia: A Bivariate Meta-analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 October 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06066-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 October 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06066-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Eosinophilic lung diseases
 Eosinophilic lung diseases Chai Gin Tsen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital The eyes do not see what the mind does not know Not very common A high index of suspicion
Eosinophilic lung diseases Chai Gin Tsen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital The eyes do not see what the mind does not know Not very common A high index of suspicion
A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients T. Tia 1, C. Putaporntip 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients T. Tia 1, C. Putaporntip 1,
ARDS during Neutropenia. D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010
 ARDS during Neutropenia D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010 Definitions Neutropenia is a decrease in circulating neutrophil white cells in the peripheral blood. neutrophil count of 1,000 1,500 cells/ml = mild
ARDS during Neutropenia D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010 Definitions Neutropenia is a decrease in circulating neutrophil white cells in the peripheral blood. neutrophil count of 1,000 1,500 cells/ml = mild
Open Forum Infectious Diseases Advance Access published February 11, 2016
 Open Forum Infectious Diseases Advance Access published February 11, 2016 1 A Critical Reappraisal of Prolonged Neutropenia as a Risk Factor for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Michael S. Abers 1,2, Musie
Open Forum Infectious Diseases Advance Access published February 11, 2016 1 A Critical Reappraisal of Prolonged Neutropenia as a Risk Factor for Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Michael S. Abers 1,2, Musie
Diffusion of Pneumocystis jirovecii in the surrounding air of patients with Pneumocystis colonization: frequency and putative risk factors
 Medical Mycology, 2017, 55, 568 572 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myw113 Advance Access Publication Date: 2 November 2016 Brief Report Brief Report Diffusion of Pneumocystis jirovecii in the surrounding air of patients
Medical Mycology, 2017, 55, 568 572 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myw113 Advance Access Publication Date: 2 November 2016 Brief Report Brief Report Diffusion of Pneumocystis jirovecii in the surrounding air of patients
DAILY SCREENING FORM
 DAILY SCREENING FORM Patient s initials: Date of admission: Time of admission: Gender: M F Year of Birth: Type of admission: Medical/Surgical/Postoperative (elective) Days Date Mechanical ventilation Lung
DAILY SCREENING FORM Patient s initials: Date of admission: Time of admission: Gender: M F Year of Birth: Type of admission: Medical/Surgical/Postoperative (elective) Days Date Mechanical ventilation Lung
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data
 2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia: High-Resolution CT Findings in Patients With and Without HIV Infection
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kanne et al. CT of Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey P. Kanne 1 Donald R. Yandow Cristopher. Meyer Kanne JP, Yandow
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kanne et al. CT of Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey P. Kanne 1 Donald R. Yandow Cristopher. Meyer Kanne JP, Yandow
Top 5 papers in clinical mycology
 Top 5 papers in clinical mycology Dirk Vogelaers Department of General Internal Medicine University Hospital Ghent Joint symposium BVIKM/BSIMC and SBMHA/BVMDM Influenza-associated aspergillosis in critically
Top 5 papers in clinical mycology Dirk Vogelaers Department of General Internal Medicine University Hospital Ghent Joint symposium BVIKM/BSIMC and SBMHA/BVMDM Influenza-associated aspergillosis in critically
Adjunctive steroid in HIV-negative patients with severe Pneumocystis pneumonia
 Lemiale et al. Respiratory Research 2013, 14:87 RESEARCH Open Access Adjunctive steroid in HIV-negative patients with severe Pneumocystis pneumonia Virginie Lemiale 1*, Alexandre Debrumetz 1, Alexandra
Lemiale et al. Respiratory Research 2013, 14:87 RESEARCH Open Access Adjunctive steroid in HIV-negative patients with severe Pneumocystis pneumonia Virginie Lemiale 1*, Alexandre Debrumetz 1, Alexandra
Prognostic Value of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Patients with Non-HIV Pneumocystis Pneumonia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Value of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Patients with Non-HIV Pneumocystis Pneumonia Koji Tamai, Ryo Tachikawa, Keisuke Tomii, Kazuma Nagata, Kojiro Otsuka, Atsushi Nakagawa, Kyoko
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Value of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Patients with Non-HIV Pneumocystis Pneumonia Koji Tamai, Ryo Tachikawa, Keisuke Tomii, Kazuma Nagata, Kojiro Otsuka, Atsushi Nakagawa, Kyoko
Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia M. Olsson 1, K. Strålin 2 and H. Holmberg 2 1 Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia M. Olsson 1, K. Strålin 2 and H. Holmberg 2 1 Department
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Jain S, Kamimoto L, Bramley AM, et al. Hospitalized patients
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Jain S, Kamimoto L, Bramley AM, et al. Hospitalized patients
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement
 CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients
clinical investigations in critical care The Role of Open-Lung Biopsy in ARDS*
 clinical investigations in critical care The Role of Open-Lung Biopsy in ARDS* Sanjay R. Patel, MD; Dimitri Karmpaliotis, MD; Najib T. Ayas, MD; Eugene J. Mark, MD; John Wain, MD, FCCP; B. Taylor Thompson,
clinical investigations in critical care The Role of Open-Lung Biopsy in ARDS* Sanjay R. Patel, MD; Dimitri Karmpaliotis, MD; Najib T. Ayas, MD; Eugene J. Mark, MD; John Wain, MD, FCCP; B. Taylor Thompson,
Iraqi JMS. Conventional Methods for the Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Immunocompromised Iraqi Patients
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq Conventional Methods for the Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq Conventional Methods for the Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP. Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital
 Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital Is this topic still relevant? Is this topic still relevant?
Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital Is this topic still relevant? Is this topic still relevant?
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids
 Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study
 MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study J. R. Zahar, 1,a M. Robin, 1 E. Azoulay, 2 F. Fieux, 2 G. Nitenberg, 1 and B. Schlemmer 2 1
MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study J. R. Zahar, 1,a M. Robin, 1 E. Azoulay, 2 F. Fieux, 2 G. Nitenberg, 1 and B. Schlemmer 2 1
UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE
 UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE FLORIDA CHAPTER ACP MEETING 2016 Himangi Kaushal, M.D., F.A.C.P. Program Director Memorial Healthcare System Internal Medicine Residency DISCLOSURES None OBJECTIVES Review some
UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE FLORIDA CHAPTER ACP MEETING 2016 Himangi Kaushal, M.D., F.A.C.P. Program Director Memorial Healthcare System Internal Medicine Residency DISCLOSURES None OBJECTIVES Review some
Research priorities in medical mycology
 Research priorities in medical mycology David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Agenda How many patients are there with serious
Research priorities in medical mycology David W. Denning National Aspergillosis Centre University Hospital of South Manchester The University of Manchester Agenda How many patients are there with serious
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
PNEUMONIA IN A PRESUMED IMMUNOCOMPETENT PATIENT
 Dr Marie Bruyneel and Deborah Konopnicki BVIKM/SBMIC November 8th, 2012 PNEUMONIA IN A PRESUMED IMMUNOCOMPETENT PATIENT Men, 54 years Emergency room on end october 2009 Sent by his family doctor for Influenza
Dr Marie Bruyneel and Deborah Konopnicki BVIKM/SBMIC November 8th, 2012 PNEUMONIA IN A PRESUMED IMMUNOCOMPETENT PATIENT Men, 54 years Emergency room on end october 2009 Sent by his family doctor for Influenza
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Viral Load in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) and Plasma to Diagnose Lung Transplant Associated CMV Pneumonia
 Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Viral Load in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) and Plasma to Diagnose Lung Transplant Associated CMV Pneumonia I.P. Lodding 1,2, H.H. Schultz 3, J.U. Jensen 1,5, C. Andersen 4,
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Viral Load in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) and Plasma to Diagnose Lung Transplant Associated CMV Pneumonia I.P. Lodding 1,2, H.H. Schultz 3, J.U. Jensen 1,5, C. Andersen 4,
Dr Marie Bruyneel and Deborah Konopnicki. BVIKM/SBMIC November 8th, 2012
 Dr Marie Bruyneel and Deborah Konopnicki BVIKM/SBMIC November 8th, 2012 Men, 54 years Emergency room on end october 2009 Sent by his family doctor for Influenza A H1N1? Viral syndrom, cough, fever 39 (7j)
Dr Marie Bruyneel and Deborah Konopnicki BVIKM/SBMIC November 8th, 2012 Men, 54 years Emergency room on end october 2009 Sent by his family doctor for Influenza A H1N1? Viral syndrom, cough, fever 39 (7j)
Original Article Clinical Microbiology
 Original Article Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 219;39:176-182 https://doi.org/1.3343/alm.219.39.2.176 ISSN 2234-386 eissn 2234-3814 Comparative Evaluation Between the RealStar Pneumocystis jirovecii
Original Article Clinical Microbiology Ann Lab Med 219;39:176-182 https://doi.org/1.3343/alm.219.39.2.176 ISSN 2234-386 eissn 2234-3814 Comparative Evaluation Between the RealStar Pneumocystis jirovecii
Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine
 Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory
NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY PULMONARY SPECIMENS (Sputum, Post-Bronchoscopy Sputum, Bronchial Brushings, Bronchial Washings, Bronchoalveolar Lavage)
 NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY PULMONARY SPECIMENS (Sputum, Post-Bronchoscopy Sputum, Bronchial Brushings, Bronchial Washings, Bronchoalveolar Lavage) I. Purpose The adequacy of a sputum specimen is determined
NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY PULMONARY SPECIMENS (Sputum, Post-Bronchoscopy Sputum, Bronchial Brushings, Bronchial Washings, Bronchoalveolar Lavage) I. Purpose The adequacy of a sputum specimen is determined
TOWARDS PRE-EMPTIVE? TRADITIONAL DIAGNOSIS. GALACTOMANNAN Sensitivity 61% Specificity 93% Neg Predict Value >95% β-d-glucan Neg Predict Value 100% PCR
 TOWARDS PRE-EMPTIVE? GALACTOMANNAN Sensitivity 61% Specificity 93% Neg Predict Value >95% TRADITIONAL DIAGNOSIS β-d-glucan Neg Predict Value 100% PCR diagnostics FUNGAL BURDEN FIRST TEST POSITIVE FOR ASPERGILLOSIS
TOWARDS PRE-EMPTIVE? GALACTOMANNAN Sensitivity 61% Specificity 93% Neg Predict Value >95% TRADITIONAL DIAGNOSIS β-d-glucan Neg Predict Value 100% PCR diagnostics FUNGAL BURDEN FIRST TEST POSITIVE FOR ASPERGILLOSIS
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than
 TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of. Pulmonary Mycetoma. Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu***
 Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of Pulmonary Mycetoma Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu*** Departments of *Respiratory Medicine, **Physiology, and ***Radiodiagnosis,
Pneumothorax: A Rare Presentation of Pulmonary Mycetoma Prem Parkash Gupta* Sanjay Fotedar* Dipti Agarwal** Kuldeep Saini* Sarita Magu*** Departments of *Respiratory Medicine, **Physiology, and ***Radiodiagnosis,
J F Huggett, 1 M S Taylor, 2 G Kocjan, 3 H E Evans, 4 S Morris-Jones, 5 V Gant, 5 T Novak, 1 A M Costello, 6 A Zumla, 1 R F Miller 4,7
 1 Centre for Infectious Diseases and International Health, Windeyer Institute for Medical Sciences, University College London, London, UK; 2 Welcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford,
1 Centre for Infectious Diseases and International Health, Windeyer Institute for Medical Sciences, University College London, London, UK; 2 Welcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford,
Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form
 Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No. 0920-0004 Exp. Date 6/30/2013 Reporter Information State: Date reported to state/local health department: / / (MM/DD/YYYY)
Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No. 0920-0004 Exp. Date 6/30/2013 Reporter Information State: Date reported to state/local health department: / / (MM/DD/YYYY)
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY FOR HEART AND LUNG TRANSPLANTATION a Society that includes Basic Science, the Failing Heart, and Advanced Lung Disease
 International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Advisory Statement on the Implications of Pandemic Influenza for Thoracic Organ Transplantation This advisory statement has been produced by the
International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation Advisory Statement on the Implications of Pandemic Influenza for Thoracic Organ Transplantation This advisory statement has been produced by the
Diagnosis of Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia: Where are we now?
 Diagnosis of Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia: Where are we now? Gary French Guy s & St. Thomas Hospital & King s College, London BSAC Guideline 2008 Masterton R, Galloway A, French G, Street M, Armstrong
Diagnosis of Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia: Where are we now? Gary French Guy s & St. Thomas Hospital & King s College, London BSAC Guideline 2008 Masterton R, Galloway A, French G, Street M, Armstrong
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Case Studies in Fungal Infections and Antifungal Therapy
 Case Studies in Fungal Infections and Antifungal Therapy Wayne L. Gold MD, FRCPC Annual Meeting of the Canadian Society of Internal Medicine November 4, 2017 Disclosures No financial disclosures or industry
Case Studies in Fungal Infections and Antifungal Therapy Wayne L. Gold MD, FRCPC Annual Meeting of the Canadian Society of Internal Medicine November 4, 2017 Disclosures No financial disclosures or industry
patients with HIV infection or hematological malignancy
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 October 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01756-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 October 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01756-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Rayos Prior Authorization Program Summary
 Rayos Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE FDA-Approved Indications: 1 Agent Indication Dosage Rayos (prednisone delayedrelease tablet) as an anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive
Rayos Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE FDA-Approved Indications: 1 Agent Indication Dosage Rayos (prednisone delayedrelease tablet) as an anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive
Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients
 Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Quantitative and qualitative comparison of DNA
 1404 JClin Pathol 1993;46: 140-144 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Westminster Hospital, Horseferry Road, London SWIP 2AP T R Leigh J V Collins Department of HIV Medicine B G Gazzard Protein Reference
1404 JClin Pathol 1993;46: 140-144 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Westminster Hospital, Horseferry Road, London SWIP 2AP T R Leigh J V Collins Department of HIV Medicine B G Gazzard Protein Reference
Outline. Cryptococcosis Pneumocystosis Diarrhea. Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015
 AU Edited: 05/06/15 Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015 Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University School of Medicine Bethesda, Maryland Washington,
AU Edited: 05/06/15 Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015 Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University School of Medicine Bethesda, Maryland Washington,
A comparison of capillary electrophoresis and direct sequencing in upstream conserved sequence region analysis of Pneumocystis jirovecii strains
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2013), 62, 560 564 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.045336-0 A comparison of capillary electrophoresis and direct sequencing in upstream conserved sequence region analysis of Pneumocystis
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2013), 62, 560 564 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.045336-0 A comparison of capillary electrophoresis and direct sequencing in upstream conserved sequence region analysis of Pneumocystis
To interrupt or not to interrupt Are we SMART enough?
 SMART To interrupt or not to interrupt Are we SMART enough? highly active antiretroviral therapy 5 1996 1997 10 25 43 45 35 metabolism 50 copies/ml lipodystrophy [fat redistribution syndrome] lactic acidosis
SMART To interrupt or not to interrupt Are we SMART enough? highly active antiretroviral therapy 5 1996 1997 10 25 43 45 35 metabolism 50 copies/ml lipodystrophy [fat redistribution syndrome] lactic acidosis
The goal of teaching:
 The goal of teaching: 1. Principles of LDG of SFI: Hair Nail Skin Mucosal Eye Ear 3. Methods for fungal identification Test methods for fungal susceptibility testing Diffusion Dilution Etest 2. Principles
The goal of teaching: 1. Principles of LDG of SFI: Hair Nail Skin Mucosal Eye Ear 3. Methods for fungal identification Test methods for fungal susceptibility testing Diffusion Dilution Etest 2. Principles
NCCID RAPID REVIEW. 1. What are the case definitions and guidelines for surveillance and reporting purposes?
 NCCID RAPID REVIEW 1. What are the case definitions and guidelines for surveillance and reporting purposes? Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus: Ten Questions and Answers for Canadian Public Health
NCCID RAPID REVIEW 1. What are the case definitions and guidelines for surveillance and reporting purposes? Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus: Ten Questions and Answers for Canadian Public Health
ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST
 ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Dr J Garbino University Hospital Geneva ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST INTRODUCTION SWISS ASPERGILLOSIS SURVEY IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Introduction
ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Dr J Garbino University Hospital Geneva ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST INTRODUCTION SWISS ASPERGILLOSIS SURVEY IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Introduction
Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum
 Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Successful treatment of larynxtracheobronchial-pulmonary
 Case Report Successful treatment of larynxtracheobronchial-pulmonary aspergillosis in an immunocompetent host W.X. Qu, X.W. Feng and L. Zhao The First Respiratory Department of Shengjing Hospital, China
Case Report Successful treatment of larynxtracheobronchial-pulmonary aspergillosis in an immunocompetent host W.X. Qu, X.W. Feng and L. Zhao The First Respiratory Department of Shengjing Hospital, China
EMERGING FUNGAL INFECTIONS IN IMMUNOCOMPROMISED PATIENTS
 EMERGING FUNGAL INFECTIONS IN IMMUNOCOMPROMISED PATIENTS DR LOW CHIAN YONG MBBS, MRCP(UK), MMed(Int Med), FAMS Consultant, Dept of Infectious Diseases, SGH Introduction The incidence of invasive fungal
EMERGING FUNGAL INFECTIONS IN IMMUNOCOMPROMISED PATIENTS DR LOW CHIAN YONG MBBS, MRCP(UK), MMed(Int Med), FAMS Consultant, Dept of Infectious Diseases, SGH Introduction The incidence of invasive fungal
Complications after HSCT. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Complications after HSCT ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Type of HSCT HSCT Improved outcome due to better HLA matching, conditioning regimens, post transplant supportive care Over one-third have pulmonary
Complications after HSCT ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Type of HSCT HSCT Improved outcome due to better HLA matching, conditioning regimens, post transplant supportive care Over one-third have pulmonary
Methods ROLE OF OPEN LUNG BIOPSY IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE LUNG INFILTRATES AND ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
 ROLE OF OPEN LUNG BIOPSY IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE LUNG INFILTRATES AND ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Li-Hui Soh, Chih-Feng Chian, Wen-Lin Su, Horng-Chin Yan, Wann-Cherng Perng, and Chin-Pyng Wu Background
ROLE OF OPEN LUNG BIOPSY IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE LUNG INFILTRATES AND ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Li-Hui Soh, Chih-Feng Chian, Wen-Lin Su, Horng-Chin Yan, Wann-Cherng Perng, and Chin-Pyng Wu Background
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection. Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA
 Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Swine Influenza Update #3. Triage, Assessment, and Care of Patients Presenting with Respiratory Symptoms
 Updated 12:00 p.m. April 30, 2009 Swine Influenza Update #3 Introduction: This document revises our last update which was sent April 28 th, 2009. The most important revisions include the following: 1.
Updated 12:00 p.m. April 30, 2009 Swine Influenza Update #3 Introduction: This document revises our last update which was sent April 28 th, 2009. The most important revisions include the following: 1.
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association
 Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association Els Vandecasteele, Jan De Waele, Dominique Vandijck, Stijn Blot, Dirk
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association Els Vandecasteele, Jan De Waele, Dominique Vandijck, Stijn Blot, Dirk
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update
 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update Prof. A.S.M. Areef Ahsan FCPS(Medicine) MD(Critical Care Medicine) MD ( Chest) Head, Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital INTRODUCTION
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) An Update Prof. A.S.M. Areef Ahsan FCPS(Medicine) MD(Critical Care Medicine) MD ( Chest) Head, Dept. of Critical Care Medicine BIRDEM General Hospital INTRODUCTION
PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DEFINITIONS AND BACKGROUND Uncomplicated influenza illness is characterized by the abrupt onset of constitutional and respiratory signs and symptoms. Signs
PEDIATRIC INFLUENZA CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES DEFINITIONS AND BACKGROUND Uncomplicated influenza illness is characterized by the abrupt onset of constitutional and respiratory signs and symptoms. Signs
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
ANWICU knowledge
 ANWICU knowledge www.anwicu.org.uk This presenta=on is provided by ANWICU We are a collabora=ve associa=on of ICUs in the North West of England. Permission to provide this presenta=on has been granted
ANWICU knowledge www.anwicu.org.uk This presenta=on is provided by ANWICU We are a collabora=ve associa=on of ICUs in the North West of England. Permission to provide this presenta=on has been granted
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Deaths Case Report Form
 STATE USE ONLY DO NOT SEND INFORMATION IN THIS SECTION TO CDC Form approved OMB No. 0920-0007 Last Name: First Name: County: Address: City: State, Zip: Patient Demographics 1. State: 2. County: 3. State
STATE USE ONLY DO NOT SEND INFORMATION IN THIS SECTION TO CDC Form approved OMB No. 0920-0007 Last Name: First Name: County: Address: City: State, Zip: Patient Demographics 1. State: 2. County: 3. State
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author. CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel
 CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
High Lymphocyte Percentage in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Patients with H1N1-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
 DOI 10.6314/JIMT.201802_29(1).06 2018 29 46-53 High Lymphocyte Percentage in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Patients with H1N1-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Cheng-Kai Hsu 1, Chien-Ming
DOI 10.6314/JIMT.201802_29(1).06 2018 29 46-53 High Lymphocyte Percentage in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Patients with H1N1-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Cheng-Kai Hsu 1, Chien-Ming
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Torres A, Sibila O, Ferrer M, et al. Effect of corticosteroids on treatment failure among hospitalized patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory
Supplementary Online Content Torres A, Sibila O, Ferrer M, et al. Effect of corticosteroids on treatment failure among hospitalized patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and high inflammatory
Development and validation of a Pneumocystis jirovecii real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia
 Original Article Development and validation of a Pneumocystis jirovecii real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia Deirdre L Church MD PhD 1,2,3, Anshula Ambasta
Original Article Development and validation of a Pneumocystis jirovecii real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia Deirdre L Church MD PhD 1,2,3, Anshula Ambasta
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Interstitial syndrome
 Interstitial syndrome Ground-glass attenuation Miliary and nodular images linear images Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
Interstitial syndrome Ground-glass attenuation Miliary and nodular images linear images Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
HIV/AIDS MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: HIV/AIDS MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN HIV/AIDS MEASURES GROUP: #159. HIV/AIDS: CD4+ Cell Count or CD4+ Percentage Performed #160. HIV/AIDS: Pneumocystis
2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: HIV/AIDS MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN HIV/AIDS MEASURES GROUP: #159. HIV/AIDS: CD4+ Cell Count or CD4+ Percentage Performed #160. HIV/AIDS: Pneumocystis
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 03 Page March 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i3.50 Original Article A Study on the Incidence of Pneumocystis
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i3.50 Original Article A Study on the Incidence of Pneumocystis
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen An outbreak of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia with 1 predominant genotype among renal transplant recipients de Boer, Mark G J; Bruijnesteijn van Coppenraet, Lesla E S; Gaasbeek,
University of Groningen An outbreak of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia with 1 predominant genotype among renal transplant recipients de Boer, Mark G J; Bruijnesteijn van Coppenraet, Lesla E S; Gaasbeek,
Microbiology Laboratory Directors, Infection Preventionists, Primary Care Providers, Emergency Department Directors, Infectious Disease Physicians
 MEMORANDUM DATE: October 1, 2009 TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Microbiology Laboratory Directors, Infection Preventionists, Primary Care Providers, Emergency Department Directors, Infectious Disease Physicians Michael
MEMORANDUM DATE: October 1, 2009 TO: FROM: SUBJECT: Microbiology Laboratory Directors, Infection Preventionists, Primary Care Providers, Emergency Department Directors, Infectious Disease Physicians Michael
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Immunocompromised Patients
 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Immunocompromised Patients Laveena Munshi, MD, MSc Critical Care Canada Forum November 2018 Interdepartmental Division of Critical Care Medicine Mount Sinai Hospital/University
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Immunocompromised Patients Laveena Munshi, MD, MSc Critical Care Canada Forum November 2018 Interdepartmental Division of Critical Care Medicine Mount Sinai Hospital/University
