Iraqi JMS. Conventional Methods for the Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Immunocompromised Iraqi Patients
|
|
|
- Jonathan Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN Conventional Methods for the Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Immunocompromised Iraqi Patients Isa S. Touhali 1 MSc, Azhar A.F. Ibrahim 1 PhD, Haider N. Dawood 2 FIBM FABM 1 Dept. of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Al-Nahrain University, 2 Dept. of Medicine, Al-Imammian Al-Kadhmain Medical City, Baghdad, Iraq Abstract Background Objectives Methods Results Conclusion Keywords Pneumocystis jirovecii is the causative agent of pneumocystis pneumonia, one of the most frequent and severe opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients. To determine the possible implication of pneumocystis jirovecii in immunocompromised Iraqi patients with pulmonary infections, and investigate the efficiency of indirect qualitative immunofluorescence diagnosis in compared with conventional stains for the detection of this agent. A total of 200 clinical samples from 100 immunocompromised patients (70 bronchoalveolar lavage, 21 sputum samples and 9 pleural fluids). One hundred samples from immunocompetent individuals (50 bronchoalveolar lavage, 30 sputum samples and 20 pleural fluids). Detection of pneumocystosis was done by conventional satins and indirect qualitative immunofluorescence technique. Fourteen samples gave positive results by indirect immunofluorescence monoclonal antibody test. Twelve out of 100 samples were positive by each Gomori methenamine silver, modified toluidine blue O stains and Diff-Quik stain (modified Giemsa). Pneumocystis jirovecii is the fundamental opportunistic infection among immunocompromised patients. The indirect qualitative immunofluorescence method gives a promise for use as a primary method for diagnosis of pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia or as rapid screen to exclude the presence of pneumocystis jirovecii in sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage samples. Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii), pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, immunocompromised, Iraqi patients. List of abbreviation: p. jirovecii = pneumocystis jirovecii, PCP = Pneumocystis pneumonia, BAL = bronchoalveolar lavage, GMS = Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver stain, DQS = differential Quik stain, TOB = Toluidine blue, PE = pleural effusion, IS = induced sputum, IFA = indirect Immunofluorescence antibody. Introduction P neumocystis jirovecii (p. jirovecii), previously known as Pneumocystis carinii) is an unusual opportunistic organism. P. jirovecii most commonly causes Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome and patients receiving intensive or prolonged immune suppressive treatment for malignancy, (1-3) transplantation and immune disorders which causes a severe and often fatal pneumonia in immunocompromised individuals (4). The organism has a unique tropism for the lungs, where it exists primarily as an alveolar pathogen. Individuals with intact immunity control this primary infection, there are no apparent clinical manifestations of primary infection in immunocompetent individuals, and the organism likely remains latent in the lungs for long periods of time, clinically apparent pneumonia occurs when cellular or humoral immunity becomes severely deficient, the organisms proliferate, evoking a mononuclear cell response, alveoli become filled with 80
2 Iraqi JMS 2016; Vol. 14(1) proteinaceous material and intact and degenerating organisms (5,6). P. jirovecii inability to culture suggests that it has evolved to require a very specific environment that is not easy to reproduce outside its host (7). The diagnosis of P. jirovecii disease requires the demonstration of cysts or trophozoites within tissue or body fluids via colorimetric or immunofluorescent stains since the human organism cannot be cultured in vitro and vivo (8). The aims of this study was to determine the possible implication of P. jirovecii in a sample of immunocompromised Iraqi patients, and investigate the efficiency of indirect qualitative immunofluorescence diagnosis in comparing with conventional stains for the detection of this agent. Methods Patient's selection This study included a total of 200 clinical samples from 100 immunocompromised patients (43 men, 57 women; average age years) as 70 bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), 21 sputum samples and 9 pleural fluids, with different underlying immunocompromised diseases including 22 (22%) leukemia, 17(17%) solid tumor, 15(15%) lymphomas, 12(12%) chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, 10(10%) asthma (steroid therapy), 10(10%) rheumatoid arthritis (cytotoxic therapy), 8(8%) solid-organ transplantation and 6(6%) Multiple myeloma with suspected of pneumocystosis. Control group included 100 samples (50 BAL, 30 sputum samples and 20 pleural fluids) from immunocompetent individuals were collected from in-and out patients who attended of Al- Imammian Al-Kadhmain Medical City, Baghdad teaching Hospital, Baghdad, and Al-Zahra Teaching Hospital, Wasit province and other private laboratories, during the period from May 2014 to March The ethical aspects of this study have been approved by the Institute Review Board of the College of Medicine, Al-Nahrain University. Samples collection Bronchialveolar lavage (BAL) was performed by a bronchofibroscope (STORZ, Germany) wedged in segmental orifice of sedated spontaneous breathing patients or intubated patients, in most cases, ml warmed saline was infused into targeted segment followed by gentle suction by specialist physician. BAL fluids were directly collected by sterile syringe. About ml were dispensed into sterile test tube and immediately placed on ice then transmitted to the laboratory for processing. Induced sputum samples (IS) were obtained by induction in patients involved in the study. Sputum induction was done using an ultrasonic nebulizer (serial No. 2000, England). This was done in an open space using a 3ml saline as an inducing fluid, from each induced patient by nurse practitioner; this sputum sample (10-15ml) was directly collected by sterile screw cup bottles and immediately placed on ice then transmitted to the laboratory for processing. Induced sputum were divided into two portions and treated with either 0.1% Dithiothreitol or with 0.9% NaCl alone. Pleural effusion samples (PE) was done by aspirating pleural fluid with 25G needle after marking, cleaning the suspected area with antiseptic and then local anesthetic (5-10 ml of 2% lidocaine) was injected locally; this method was done by specialist physician. Ten-15ml pleural fluid was aspirated into sterile test tube and immediately placed on ice then transmitted to the laboratory for further processing. Samples processing BAL, sputum and pleural fluid containing mucous martial were added to a 2-fold volume of 0.9% NaCl and were mixed vigorously vortexes for 5 minutes. Samples centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes, supernatants were discarded and the precipitated pellets were placed into a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes according to Alexander et al (9) several slides 81
3 Touhali et al, Pneumocystis jirovecii in Immuno were prepared simultaneously, depending on the number of stains to be employed, with a few spare slides prepared for any repeat stains which might be needed. A portion of precipitate pellets (100µl) was used to prepare smears for each Diff-Quik stain (SYRBIO, Syria), Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver stain (abcam, UK), Toluidine blue stain (BHD, England) and for fluorescent monoclonal antibody test (IF: Detect IF PC, Axis-Shield Diagnostics, Dundee, UK). Results Descriptive data on study subjects Among those 100 immunocompromised patients, 43 were males and 57 were females whereas in the control group each group comprised of 50 subjects. The age of the patients ranges from years (Mean± S.D = 54.56±16.46 years) as compared to years (Mean± S.D = 37.33±13.24 years) of the control group (p < 0.001). Laboratory Diagnosis of P. jirovecii Gomori s Methenamine Silver stain (GMS) Under light microscope, cysts of P. jirovecii, the diagnostic form, had a characteristic appearance as a spherical, cup-shaped, or crescent-shape object stained by GMS which usually crowded in foamy alveolar casts in BAL. GMS used for staining carbohydrates producing gray to black and green background counterstained with light green, this stain is useful for identifying cyst form 12(12%) out 100 samples were positive (Fig. 1). Fig. 1. Gomori's methenamine silver (GMS) stained smear of BAL from leukemia gray to black color of the fungus is seen against a light green background, the cysts of P. jirovecii were crowed in foamy alveolar casts in BAL. The cyst appears as a spherical, cup-shaped, or crescent-shaped object. Some cysts are empty and collapsed; others contain dark bodies or dots, which acquire different positions in relation to the cyst depending on the angle of visualization (X1000). Modified toluidine blue O Stain (MTolB) Cyst forms of P. jirovecii are cup-shaped appear as violet to purple. The cyst outline is distinct, and the internal region stains uniformly. The cysts were frequently observed in clusters, while trophic form cannot be stained 12(12%) out 100 samples were positive (Fig. 2). 82
4 Iraqi JMS 2016; Vol. 14(1) Fig. 2. Toludine blue (TOB) stained smear from BAL of solid tumor, the cyst of P. jirovecii forms appear as violet to purple.(x1000). Differential Quik Stain Kit (Modified Giemsa) Specimens were collected and stained with Diff-Quik stain (modified Giemsa). By this technique, it was possible to demonstrate cystic and trophic forms of P. jirovecii and confirm the diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in this patient. Stained slides were examined using a light microscope 12(12%) out 100 samples were positive (Fig. 3). Fig. 3. Diff-Quik stain (modified Giemsa). Stained sputum smear from leukemia, the cysts of P. jirovecii appear as spherical dark blue (A). Stained BAL smear from asthma, the cysts of P. jirovecii appear as aggregated spherical dark blue forms (B). Stained BAL smear from solid tumor (intracystic bodies were arrowed) (C). Stained sputum smear lymphoma, (intracystic bodies were arrowed) (D) X1000). Indirect qualitative immunofluorescence The pellets from (BAL, IS or PE) specimens were placed on slides and fixed for the detection of P. jirovecii by a monoclonal antibodies technique. This technique was performed according to manufacturer s instructions. 83
5 Touhali et al, Pneumocystis jirovecii in Immuno Stained slides were examined by a fluorescence microscope, oocysts show as medium bright to bright apple green color they may be evenly or unevenly labeled 14(14%) out 100 samples were positive (Fig. 4). Fig. 4. Immunofluorescent staining using monoclonal antibodies against P jirovecii. (A) stained smear from BAL of lymphoma disease, the cyst of P. jirovecii appears bright to bright apple green (X1000). (B) stained smear from BAL of leukemia disease showing bright to bright apple green cysts with different size (X400). (C) stained smear from sputum of kidney transplantation, many aggregated cysts of P jirovecii which appear bright to bright apple green (X1000). (D) Negative control (X1000). Overall results of conventional methods The organism was detected in BAL, and/or sputum of immunocompromised patients only. Fourteen samples gave positive results by indirect immunofluorescence monoclonal antibody test within this number only 12 (12%) were positive by Gomori methenamine silver (GMS), 12 (12%) were positive by modified toluidine blue O stains (TOB), and 12 (12%) were positive by Diff-Quik stain (DQS) modified Giemsa (Fig. 5). These samples were obtained from 14 immunocompromised patients including, four with leukemia, three with solid tumor, two with lymphoma, and only one for each chronic pulmonary obstructive disease, asthma (steroid therapy), rheumatoid arthritis (cytotoxic therapy), solid-organ transplantation and multiple myeloma disease. Eighty six immunocompromised patients were initially negative by both indirect immunofluorescence and staining methods (GMS, TOB and DQS), while only 12 samples were positive by both methods. Discussion P. jirovecii is the causative agent of Pneumocystis pneumonia, one of the most frequent and severe opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients. As P. jirovecii cannot be grown in culture from clinical specimens (10,11). The current laboratory diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia has relied mainly upon microscopic techniques, for 84
6 Iraqi JMS 2016; Vol. 14(1) detection of cysts and trophozoites of the organism by cytological staining or by immunefluorescent assay (IFA) with monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies (12,13). In this study the positive results of 12 samples by three staining methods (GMS, TOB and DQS), is in consistent with Ng et al. (14) who proved, that the specimens were considered to contain P. jirovecii (i.e., a truly positive specimen) if this organism was detected by two or more of the staining methods. Conversely, specimens were considered to not contain the organism (i.e., a truly negative specimen) if all stains were negative or if only one stain was positive that could not be corroborated. Fig. 5. Pneumocystis jirovecii detection methods using Gomori's methenamine silver, Diff-Quik stain (modified Giemsa), Toludine blue and Immunofluorescent staining in bronchoalveolar lavage and sputum samples. LaRocque et al (15) found that the choice of the optimal staining method for the detection of Pneumocystis was also important for patients with other immune-compromising conditions who were at risk for infection. In fact, the choice of the optimal staining method may be more important for the detection of Pneumocystis in the non-hiv-infected, immunocomp-romised patients, since it has been shown that respiratory specimens from these patients have a lower burden of organisms than those from HIV-infected, immune-compromised patients. Results of the current study is in consistent with Yehia et al (16) who diagnosed P. jirovecii infection by conventional methods only from lower respiratory tract of both immunecompetent and immunocomp-romised Iraq patients. The organism was detected in alveolar lavage and/or sputum of immunecompromised patients only. P. jirovecii was diagnosed by direct microscopical examination with different stains included calcofluor stain, Giemsa and TOB was identified in 8 cases out 150 samples with immune-compromised patients with malignant diseases under radiation and/or cytotoxic therapy In this study the results of the detection of P. jirovecii in respiratory samples BAL and sputum (17) agree with this by Turner et al who diagnosed the diseases by using three different staining techniques, included silver stain, Diff- Quik (a modified Giemsa stain) modified toluidine blue, and found that Induced sputum (IS) has been shown to be a reliable tool in terms of sensitivity and specificity comparable to BAL sample in diagnosing PCP. 85
7 Touhali et al, Pneumocystis jirovecii in Immuno In another study, John et al (18) who used direct immunofluorescence monoclonal antibody (DFA) method for identification of P. jirovecii in induced sputum and BAL specimens was compared in a blinded study with an established Giemsa stain method, for the 67 patients (64%) infected with the human immunodeficiency virus 49 were initially negative by both the DFA and Giemsa methods, none were negative by DFA and positive by Giemsa, 6 were positive by DFA and negative by Giemsa, and 12 were positive by both methods, were indicates that the DFA method represents an advance as a sensitive, simple, and rapid way to identify P. jirovecii in induced sputum and BAL specimens from HIVinfected patients and suggests greater sensitivity of the DFA than the Giemsa method in this patient population. This result in line with the present study concerning immunofluorescence mono-clonal method compared with staining methods. Procop et al (19) who used four staining methods on replicate smears of respiratory specimens submitted for Pneumocystis jirovecii examination, he found that the indirect immunofluorescent antibody stain is the more sensitive than silver stain (GMS), Diff-Quik stain and Merifluor Pneumocystis stain. Baughman et (20) al who described the sensitivity of an indirect immunofluorescent antibody stain it was the superior in comparison with a modified Wright stain and GMS stain. In another studies when compare the feasibility of different stain methods were applied in respiratory secretions to stain the P. jirovecii (Methenamine Silver stain, TOB, Acridine Orange, Diff-Quik, Gram- Weigert, etc.) they found the low sensitivity although these stains are cheap and easily applicable (21-24). However, commercial immunofluorescence (IF) kit which contains monoclonal antibodies has, subsequently, increased the specificity and sensitivity for diagnosis (25-27). It is concluded from this study that the P. jirovecii, is the fundamental opportunistic infection among immunocompromised 86 patients. GMS staining may have the best overall predictive values for routine clinical use when monoclonal antibody staining is not available, Diff-Quik is a good diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of, P. jirovecii because of its costeffectiveness and because of its rapid diagnosis of severe pneumocystosis. In the present study showed the indirect qualitative immunefluorescence method give a promise for use as a primary method for diagnosis of P. jirovecii pneumonia or as rapid screen to exclude the presence of P. jirovecii in sputum and BAL samples. Acknowledgment We are thankful to all medical staff of Al- Imammian Al-Kadhmain Medical City, Baghdad, Baghdad Teaching Hospital, Baghdad and Al- Zahra Teaching Hospital, Wasit, especially those working in the Bronchoscopy Unit for their kind help in providing the clinical specimens. Author contributions Touhali conducted the sampling, isolation, and staining, the molecular work and writing the manuscript. Dr. Ibrahim and Dawood supervised the work, edit and finalize the writing of the study. Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. Funding This work was not granted by any agency. References 1. Gianella S, Haeberli L, Joos B, et al. Molecular evidence of inter human transmission in an outbreak of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia among renal transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 2010; 12: Louie GH, Wang Z, Ward MM. Trends in hospitalizations for Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia among patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the US: Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62: Wakefield AE. Pneumocystis carinii. Br Med Bull. 2002; 61: Botterel F, Cabaret O, Foulet F, et al. Clinical significance of quantifying Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA by using real-time PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
8 Iraqi JMS 2016; Vol. 14(1) from immunocompromised patients. J. Clin Microbiol. 2011; 50: Ryan KJ, Ray CG. Sherris medical microbiology, an introduction to infectious diseases 4 th.ed. New York 2004; Pp William E, Dismukes MD, Peter G, et al. Clinical Mycology. Oxford University press, Inc. New York 2003; Pp Morris A, Norris KA. Colonization by Pneumocystis jirovecii and its role in disease. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2012; 25: Brenda MM, Catherine MS, Marco Z, et al. Pneumocystis pneumonia in South African children diagnosed by molecular methods. BMC Res Notes. 2014; 7: Mu XD, Wang GF, Su L. A clinical comparative study of polymerase chain reaction assay for diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in non-aids patients. Chin Med J (Engl) 2011; 124: Alvarez-Martinez MJ, Miro JM, Valls ME, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of nested and real-time PCR for the detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii in clinical specimens. Diag Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006; 56: Sing A, Trebesius K, Roggenkamp A, et al. Evaluation of diagnostic value and epidemiological implications of PCR for Pneumocystis jirovecii in different immunosuppressed and immune-competent patient groups. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38: Caldero n EJ, Gutie rrez-rivero S, Durand-Joly I, et al. Pneumocystis infection in humans: diagnosis and treatment. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010; 8: Elvin K. Laboratory diagnosis and occurrence of Pneumocystis carinii. Scand J Infect Dis. 1994; 94: Ng VL, Yajko DM, McPhaul LW, et al. Evaluation of an indirect fluorescent-antibody stain for detection of Pneumocystis carinii in respiratory specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990; 28: LaRocque RC, Katz JT, Perruzzi P, et al. The utility of sputum induction for diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia in immunocompromised patients without human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2003; 37: Yehia MM, Al-Habbo DJ, Abdulla ZA. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jirovecii) from Iraqi Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections. Iraqi J Med Sci. 2014; 12: Turner D, Schwarz Y, Yust I. Induced sputum for diagnosing Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in HIV patients: new data, new issues. Eur Respir J. 2003; 21: John S, Wolfson M, Ann W, et al. Blinded comparison of a direct immunofluorescent monoclonal antibody staining method and a giemsa staining method for identification of Pneumocystis carinii in induced sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage specimens of patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990; 28: Procop GW, Haddad S, Quinn J, et al. Detection of Pneumocystis jiroveci in respiratory specimens by four staining methods. J Clin Microbiol. 2004; 42: Baughman RP, Strohofer SS, Clinton BA, et al. The use of an indirect fluorescent antibody test for detecting Pneumocystis carinii. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989; 113: Schumann GB, Swensen JJ. Comparison of Papanicolaou s stain with the Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS) stains for the cytodiagnosis of P.carinii in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. Am J Clin Pathol. 1991; 95: Arast'eh KN, Simon V, Musch R, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of indirect immunofluorescence and Grocott-technique in comparison with immunocytology (alkaline phosphatase anti-alkaline phosphatase =PAAP) for the diagnosis of P. carinii in BAL. Eur J Med Res. 1998; 3: Lorca M, Tasarsa R, Denegri M. P. carinii infection various aspects on its clinical and laboratory diagnosis. Rev Med Clin. 1992; 120: Tiley SM, Marriot DJ, Harkness JL. An evaluation of four methods for the detection of P. carinii in clinical specimens. Pathology. 1994; 26: Durand-Joly I, Chabé M, Soula F, et al. Molecular diagnosis of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PcP). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005; 45: Rigole P, Basset D, Dedet JP. Biological diagnosis of Pneumocyctis infection. Evaluation and value of a new direct immunofluorescence technique. Pathol Biol. 1997; 45: Flori P, Bellete B, Durand F, et al. Comparison between real-time PCR, conventional PCR and different staining techniques for diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia from bronchoalveolar lavage specimens. J Med Microbiol. 2004; 53: Correspondence to Isa S. Touhali isaswadi@yahoo.com Received 13 th Sep. 2015: Accepted 10 th Feb
Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
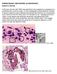 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data
 2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia M. Olsson 1, K. Strålin 2 and H. Holmberg 2 1 Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia M. Olsson 1, K. Strålin 2 and H. Holmberg 2 1 Department
Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine
 Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY PULMONARY SPECIMENS (Sputum, Post-Bronchoscopy Sputum, Bronchial Brushings, Bronchial Washings, Bronchoalveolar Lavage)
 NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY PULMONARY SPECIMENS (Sputum, Post-Bronchoscopy Sputum, Bronchial Brushings, Bronchial Washings, Bronchoalveolar Lavage) I. Purpose The adequacy of a sputum specimen is determined
NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY PULMONARY SPECIMENS (Sputum, Post-Bronchoscopy Sputum, Bronchial Brushings, Bronchial Washings, Bronchoalveolar Lavage) I. Purpose The adequacy of a sputum specimen is determined
Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) quantitative PCR to differentiate Pj pneumonia from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients
 DOI 10.1007/s10096-013-1960-3 ARTICLE Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) quantitative PCR to differentiate Pj pneumonia from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients M. Maillet & D. Maubon & J. P. Brion
DOI 10.1007/s10096-013-1960-3 ARTICLE Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) quantitative PCR to differentiate Pj pneumonia from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients M. Maillet & D. Maubon & J. P. Brion
Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al.
 Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) processing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods The BAL procedure was performed following a standardized protocol by an experienced
Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) processing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods The BAL procedure was performed following a standardized protocol by an experienced
Pneumocystis PCR: It Is Time to Make PCR the Test of Choice
 Open Forum Infectious Diseases MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis PCR: It Is Time to Make PCR the Test of Choice Laura Doyle, Sherilynn Vogel, and Gary W. Procop Section of Clinical Microbiology, Department of
Open Forum Infectious Diseases MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis PCR: It Is Time to Make PCR the Test of Choice Laura Doyle, Sherilynn Vogel, and Gary W. Procop Section of Clinical Microbiology, Department of
Outcomes of Moderate-to-Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia Treated with Adjunctive Steroid in Non-HIV-Infected Patients
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Oct. 2011, p. 4613 4618 Vol. 55, No. 10 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.00669-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Outcomes
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Oct. 2011, p. 4613 4618 Vol. 55, No. 10 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.00669-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Outcomes
Product # Kit Components
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Pneumocystis jirovecii PCR Kit Product # 42820 Product Insert Background Information
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit
 ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING IN PICU
 MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING IN PICU This is a guideline for the taking of microbiological samples in PICU to diagnose or exclude infection. The diagnosis of infection requires: Ruling out non-infectious causes
MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING IN PICU This is a guideline for the taking of microbiological samples in PICU to diagnose or exclude infection. The diagnosis of infection requires: Ruling out non-infectious causes
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection. Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA
 Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Value of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Cytology in the Diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia: A Review of 30 Cases
 http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2011.71.5.322 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2011;71:322-327 CopyrightC2011. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights
http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2011.71.5.322 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2011;71:322-327 CopyrightC2011. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights
Pneumocystis Carinii Real Time PCR Kit. For In Vitro Diagnostic Use Only User Manual
 Revision No.: ZJ0003 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 Pneumocystis Carinii Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: QD-0082-02 For use with ABI Prism 7000/7300/7500/7900; Smart CyclerII; icycler iq 4/iQ 5; Rotor Gene 2000/3000;
Revision No.: ZJ0003 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 Pneumocystis Carinii Real Time PCR Kit Cat. No.: QD-0082-02 For use with ABI Prism 7000/7300/7500/7900; Smart CyclerII; icycler iq 4/iQ 5; Rotor Gene 2000/3000;
Laboratory investigation of Pneumocystis carinii
 336 Department of Microbiology, Raigmore Hospital, Inverness 1V2 3UJ, UK J M W Chatterton Genitourin Med 1992;68:336-341 Laboratory investigation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia JMW Chatterton, D O Ho
336 Department of Microbiology, Raigmore Hospital, Inverness 1V2 3UJ, UK J M W Chatterton Genitourin Med 1992;68:336-341 Laboratory investigation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia JMW Chatterton, D O Ho
Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii
 141 Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients with Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Blinded Comparison to Standard Methods Juan Torres, 1,a Mitchell Goldman,
141 Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients with Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Blinded Comparison to Standard Methods Juan Torres, 1,a Mitchell Goldman,
Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia by Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology: Experience at a Tertiary Care Centre in India
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia by Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology: Experience at a Tertiary Care Centre in India Sonika Dahiya, Sandeep R. Mathur, Venkateswaran K. Iyer, Kusum Kapila
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia by Bronchoalveolar Lavage Cytology: Experience at a Tertiary Care Centre in India Sonika Dahiya, Sandeep R. Mathur, Venkateswaran K. Iyer, Kusum Kapila
Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis
 PARA 317331 Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Microspora A group of organisms: small single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites belonging to Phylum Microspora Early-
PARA 317331 Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Microspora A group of organisms: small single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites belonging to Phylum Microspora Early-
5/15/2017. What Does HIV/AIDS Look Like in DC in Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections
 Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University Washington, DC FORMATTED: 4/28/217 Learning Objectives After attending
Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University Washington, DC FORMATTED: 4/28/217 Learning Objectives After attending
Cytology Specimen Collection Procedures
 BERKSHIRE HEALTH SYSTEM LABORATORIES Berkshire Medical Center Cytology Specimen Collection Procedures Conventional Pap Smears SurePath Pap Smears Sputum Specimens Urine Specimens Breast Discharge Direct
BERKSHIRE HEALTH SYSTEM LABORATORIES Berkshire Medical Center Cytology Specimen Collection Procedures Conventional Pap Smears SurePath Pap Smears Sputum Specimens Urine Specimens Breast Discharge Direct
Pierre Flori, 1 Bahrie Bellete, 1 Fabrice Durand, 1 Hélène Raberin, 1 Céline Cazorla, 2 Jamal Hafid, 1 Frédéric Lucht 2 and Roger Tran Manh Sung 1
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 603 607 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45528-0 Comparison between real-time PCR, conventional PCR and different staining techniques for diagnosing Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 603 607 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45528-0 Comparison between real-time PCR, conventional PCR and different staining techniques for diagnosing Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
IMMUNOGLOBULIN LEVELS IN SERUM AND CERVICOVAGINAL SECRETIONS OF PATIENTS INFECTED WITH TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS
 Journal of Al-Nahrain University Vol13 (2), June, 2010, pp147-151 Science IMMUNOGLOBULIN LEVELS IN SERUM AND CERVICOVAGINAL SECRETIONS OF PATIENTS INFECTED WITH TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS Ekhlas Mushrif *,
Journal of Al-Nahrain University Vol13 (2), June, 2010, pp147-151 Science IMMUNOGLOBULIN LEVELS IN SERUM AND CERVICOVAGINAL SECRETIONS OF PATIENTS INFECTED WITH TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS Ekhlas Mushrif *,
Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System
 Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System Histoplasmosis(cave disease) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasma capsulatum, is usually
Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System Histoplasmosis(cave disease) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasma capsulatum, is usually
Inflammation class 2. Inflammation part 2. Rheumatic fever RF. Rheumatic fever - pathogenesis. Hypersensitivity reactions. Rheumatic fever RF
 Inflammation class 2 Inflammation part 2 Rheumatic endocarditis Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Cytomegalic pneumonia Aspergillosis Actinomycosis Rheumatic fever RF An acute, immunologically mediated multisystem
Inflammation class 2 Inflammation part 2 Rheumatic endocarditis Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia Cytomegalic pneumonia Aspergillosis Actinomycosis Rheumatic fever RF An acute, immunologically mediated multisystem
Cytology Specimen Collection Procedures Outpatient. Direct Skin Scraping/Tzanck Prep. Bronchial Washings/Brushings/BAL
 Cytology Specimen Collection Procedures Outpatient Conventional Pap Smears Sure Path Pap Smears Sputum Specimens Urine Specimens Breast Discharge Direct Skin Scraping/Tzanck Prep Bronchial Washings/Brushings/BAL
Cytology Specimen Collection Procedures Outpatient Conventional Pap Smears Sure Path Pap Smears Sputum Specimens Urine Specimens Breast Discharge Direct Skin Scraping/Tzanck Prep Bronchial Washings/Brushings/BAL
Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised A. Alanio 1, G. Desoubeaux 1, C. Sarfati
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY Real-time PCR assay-based strategy for differentiation between active Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia and colonization in immunocompromised A. Alanio 1, G. Desoubeaux 1, C. Sarfati
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
The goal of teaching:
 The goal of teaching: 1. Principles of LDG of SFI: Hair Nail Skin Mucosal Eye Ear 3. Methods for fungal identification Test methods for fungal susceptibility testing Diffusion Dilution Etest 2. Principles
The goal of teaching: 1. Principles of LDG of SFI: Hair Nail Skin Mucosal Eye Ear 3. Methods for fungal identification Test methods for fungal susceptibility testing Diffusion Dilution Etest 2. Principles
Int J Pharm Bio Sci. V Ramadevi*et al Available Online through IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH
 Page32 EVALUATION OF C-RP LEVELS AS PROGNOSTIC INDICATORS OF OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS IN AIDS PATIENTS & CORRELATION WITH CD4 COUNTS A STUDY V Ramadevi*, K Kamal chand**, Mera bai***, E. Sravya **** *
Page32 EVALUATION OF C-RP LEVELS AS PROGNOSTIC INDICATORS OF OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS IN AIDS PATIENTS & CORRELATION WITH CD4 COUNTS A STUDY V Ramadevi*, K Kamal chand**, Mera bai***, E. Sravya **** *
Fellowship in Cytopathology Department of Pathology. All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India
 Fellowship in Cytopathology Department of Pathology All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Syllabus for Fellowship in Cytopathology: FNAC Direct, Guided, EUS Exfoliative
Fellowship in Cytopathology Department of Pathology All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India Syllabus for Fellowship in Cytopathology: FNAC Direct, Guided, EUS Exfoliative
Usefulness of Induced Sputum and Fibreoptic Bronchoscopy Specimens in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2005; 33: 260 265 Usefulness of Induced Sputum and Fibreoptic Bronchoscopy Specimens in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis L SAGLAM 1, M AKGUN 1 AND E
The Journal of International Medical Research 2005; 33: 260 265 Usefulness of Induced Sputum and Fibreoptic Bronchoscopy Specimens in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis L SAGLAM 1, M AKGUN 1 AND E
Respiratory Interactive Session. Elaine Borg
 Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011
 Diagnosis of TB Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011 Alfred Lardizabal, MD NJMS Global Tuberculosis Institute Diagnosis of TB, 2011 Diagnosis follows Suspicion When should we Think TB? Who is
Diagnosis of TB Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011 Alfred Lardizabal, MD NJMS Global Tuberculosis Institute Diagnosis of TB, 2011 Diagnosis follows Suspicion When should we Think TB? Who is
Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD
 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Atlas of Stains. Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro
 Atlas of Stains Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro Intended use Routinely processed samples (paraffin-embedded) may be used. The preferred fixative is neutral buffered formalin. The clinical interpretation
Atlas of Stains Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro Intended use Routinely processed samples (paraffin-embedded) may be used. The preferred fixative is neutral buffered formalin. The clinical interpretation
Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside. Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London
 Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London Presented at ECCMID Berlin April 30 th 2013 Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file
Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London Presented at ECCMID Berlin April 30 th 2013 Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file
EXOTESTTM. ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids
 DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
Information for staff on Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PcP)
 Information for staff on Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PcP) Outbreak Prevention and Management The purpose of this information is to provide an aide-memoire for clinical staff and Infection Prevention and Control
Information for staff on Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PcP) Outbreak Prevention and Management The purpose of this information is to provide an aide-memoire for clinical staff and Infection Prevention and Control
Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis
 QJM Advance Access published February 6, 2014 Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis Yu-Hsiang Juan MD 1,2, Sachin S Saboo, MD FRCR 1, Yu-Ching Lin MD 2, James R. Conner MD, Ph.D 3, Francine L. Jacobson
QJM Advance Access published February 6, 2014 Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis Yu-Hsiang Juan MD 1,2, Sachin S Saboo, MD FRCR 1, Yu-Ching Lin MD 2, James R. Conner MD, Ph.D 3, Francine L. Jacobson
PCR Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia: A Bivariate Meta-analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 October 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06066-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 October 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06066-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Pneumocystis jirovecii Colonization in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Based on Nested-PCR Detection in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Samples
 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 42, No.3, Mar 2013, pp.298-305 Original Article Pneumocystis jirovecii Colonization in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Based on Nested-PCR Detection in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Samples
Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 42, No.3, Mar 2013, pp.298-305 Original Article Pneumocystis jirovecii Colonization in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Based on Nested-PCR Detection in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Samples
TISSUE COLLECTION. SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research
 TISSUE COLLECTION SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research Somphong Narkpinit, MD. Department of Pathobiology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Learning
TISSUE COLLECTION SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research Somphong Narkpinit, MD. Department of Pathobiology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Learning
Standard Operating Procedure
 Standard Operating Procedure 1. Definitions Section: Laboratory Version No. 1.2 Initials: AD Title: 2.0 Testing Algorithm Revision Date: 01 Sep 2011 1.1 SOP: Standard Operating Procedure 1.2 CRF: Case
Standard Operating Procedure 1. Definitions Section: Laboratory Version No. 1.2 Initials: AD Title: 2.0 Testing Algorithm Revision Date: 01 Sep 2011 1.1 SOP: Standard Operating Procedure 1.2 CRF: Case
TB in Children. Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012
 TB in Children Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012 Contents Epidemiology Transmission and pathogenesis Diagnosis of TB TB and HIV Management Epidemiology The year 2000 8.3 million new TB cases diagnosed
TB in Children Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012 Contents Epidemiology Transmission and pathogenesis Diagnosis of TB TB and HIV Management Epidemiology The year 2000 8.3 million new TB cases diagnosed
Outline. Cryptococcosis Pneumocystosis Diarrhea. Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015
 AU Edited: 05/06/15 Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015 Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University School of Medicine Bethesda, Maryland Washington,
AU Edited: 05/06/15 Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015 Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University School of Medicine Bethesda, Maryland Washington,
Chapter 8. Other Important Tests and Procedures. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Efficacy of caspofungin, a 1,3-β-D-glucan synthase inhibitor, on Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in rats
 Medical Mycology, 2014, 52, 798 803 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myu060 Advance Access Publication Date: 6 October 2014 Original Article Original Article Efficacy of caspofungin, a 1,3-β-D-glucan synthase inhibitor,
Medical Mycology, 2014, 52, 798 803 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myu060 Advance Access Publication Date: 6 October 2014 Original Article Original Article Efficacy of caspofungin, a 1,3-β-D-glucan synthase inhibitor,
Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii) Real-TM
 IVD For in Vitro Diagnostic Use Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii) Real-TM Handbook Real Time PCR Kit for the detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii) in biological materials REF P2-50FRT REF TP2-50FRT
IVD For in Vitro Diagnostic Use Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii) Real-TM Handbook Real Time PCR Kit for the detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii (carinii) in biological materials REF P2-50FRT REF TP2-50FRT
Detection of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis and Viruses in Presumably Immunocompetent Infants Who Died in the Hospital or in the Community
 BRIEF REPORT Detection of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis and Viruses in Presumably Immunocompetent Infants Who Died in the Hospital or in the Community Sergio L. Vargas, 1 Carolina A. Ponce, 1 Vivian
BRIEF REPORT Detection of Pneumocystis carinii f. sp. hominis and Viruses in Presumably Immunocompetent Infants Who Died in the Hospital or in the Community Sergio L. Vargas, 1 Carolina A. Ponce, 1 Vivian
Microscopic Morphology in Smears Prepared from MGIT Broth Medium for Rapid Presumptive Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 33, no. 2, 2003 179 Microscopic Morphology in Smears Prepared from MGIT Broth Medium for Rapid Presumptive Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex,
Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 33, no. 2, 2003 179 Microscopic Morphology in Smears Prepared from MGIT Broth Medium for Rapid Presumptive Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex,
CHART ELEVEN (11) KENYAN FIGURES (KENYA DEMOGRAPHIC HEALTH SURVEY REVISED 2004)
 CHART ELEVEN (11) KENYAN FIGURES (KENYA DEMOGRAPHIC HEALTH SURVEY REVISED 2004) Adults living with HIV/AIDS - 1.1 million Children - 150,000 Number using ART - 24,000 Number needing ARVs - 200,000 National
CHART ELEVEN (11) KENYAN FIGURES (KENYA DEMOGRAPHIC HEALTH SURVEY REVISED 2004) Adults living with HIV/AIDS - 1.1 million Children - 150,000 Number using ART - 24,000 Number needing ARVs - 200,000 National
Quantitative and qualitative comparison of DNA
 1404 JClin Pathol 1993;46: 140-144 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Westminster Hospital, Horseferry Road, London SWIP 2AP T R Leigh J V Collins Department of HIV Medicine B G Gazzard Protein Reference
1404 JClin Pathol 1993;46: 140-144 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Westminster Hospital, Horseferry Road, London SWIP 2AP T R Leigh J V Collins Department of HIV Medicine B G Gazzard Protein Reference
Endoscopy. Pulmonary Endoscopy
 Pulmonary 1 Direct visualization of TB tree Developed in 1890 s to remove foreign bodies - rigid metal tube Advances added light system, Sx Flexible fiberoptic scopes introduced in early 1960 s 2 Used
Pulmonary 1 Direct visualization of TB tree Developed in 1890 s to remove foreign bodies - rigid metal tube Advances added light system, Sx Flexible fiberoptic scopes introduced in early 1960 s 2 Used
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS
 Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiencies Due to impaired function of one or more components of the immune or inflammatory responses. Problem may be with: B cells T cells phagocytes or complement
Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiencies Due to impaired function of one or more components of the immune or inflammatory responses. Problem may be with: B cells T cells phagocytes or complement
Cryptosporidium Veterinary
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August Pneumococcal Disease, Invasive (IPD)
 August 2011 Pneumococcal Disease, Invasive (IPD) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August
August 2011 Pneumococcal Disease, Invasive (IPD) Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August
IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STAINING FOR RESPIRATORY VIRUS DETECTION: INFLUENZA A, INFLUENZA B AND RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS
 IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STAINING FOR RESPIRATORY VIRUS DETECTION: INFLUENZA A, INFLUENZA B AND RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS A. Introduction Influenza A, Influenza B and RSV are responsible for serious respiratory
IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STAINING FOR RESPIRATORY VIRUS DETECTION: INFLUENZA A, INFLUENZA B AND RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS A. Introduction Influenza A, Influenza B and RSV are responsible for serious respiratory
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Deaths Case Report Form
 STATE USE ONLY DO NOT SEND INFORMATION IN THIS SECTION TO CDC Form approved OMB No. 0920-0007 Last Name: First Name: County: Address: City: State, Zip: Patient Demographics 1. State: 2. County: 3. State
STATE USE ONLY DO NOT SEND INFORMATION IN THIS SECTION TO CDC Form approved OMB No. 0920-0007 Last Name: First Name: County: Address: City: State, Zip: Patient Demographics 1. State: 2. County: 3. State
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No
 Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No. 0920-0004 STATE USE ONLY DO NOT SEND INFORMATION IN THIS SECTION TO CDC Last Name: First Name: County: Address: City: State,
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No. 0920-0004 STATE USE ONLY DO NOT SEND INFORMATION IN THIS SECTION TO CDC Last Name: First Name: County: Address: City: State,
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
CLINICAL GUIDELINES. Summary of Literature and Recommendations Concerning Immunization and Steroid Injections Thomas J. Gilbert M.D., M.P.P.
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES Summary of Literature and Recommendations Concerning Immunization and Steroid Injections Thomas J. Gilbert M.D., M.P.P. 11/2/15 Several practices routinely delay steroid injections
CLINICAL GUIDELINES Summary of Literature and Recommendations Concerning Immunization and Steroid Injections Thomas J. Gilbert M.D., M.P.P. 11/2/15 Several practices routinely delay steroid injections
Opportunistic infections
 Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections Decrease in number of CD4 lymphocytes is condition for development of opportunistic infections Risk is started, when number of CD4 lymphocytes drops to
Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections Decrease in number of CD4 lymphocytes is condition for development of opportunistic infections Risk is started, when number of CD4 lymphocytes drops to
SHASTA PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATES CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN COLLECTION
 SHASTA PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATES CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN COLLECTION I. PRINCIPLE: Proper collection and handling of all cytology specimens helps ensure the most accurate results possible from the specimen. Cytology
SHASTA PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATES CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN COLLECTION I. PRINCIPLE: Proper collection and handling of all cytology specimens helps ensure the most accurate results possible from the specimen. Cytology
Alveolar proteinosis in a patient recovering from Pneumocystis carinii infection: A
 Alveolar proteinosis in a patient recovering from Pneumocystis carinii infection: A case report with a review of literature. Abstract Background Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is a rare lung disorder,
Alveolar proteinosis in a patient recovering from Pneumocystis carinii infection: A case report with a review of literature. Abstract Background Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is a rare lung disorder,
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement
 CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
CHEST VOLUME 117 / NUMBER 4 / APRIL, 2000 Supplement Evidence-Based Assessment of Diagnostic Tests for Ventilator- Associated Pneumonia* Executive Summary Ronald F. Grossman, MD, FCCP; and Alan Fein, MD,
Diagnosing Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia by
 J Clin Pathol 1986;39:945-949 Diagnosing Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia by cytological examination of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: report of 15 cases JENNIFER A YOUNG,* J W STONE,t R J S MCGONIGLE,4 D
J Clin Pathol 1986;39:945-949 Diagnosing Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia by cytological examination of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: report of 15 cases JENNIFER A YOUNG,* J W STONE,t R J S MCGONIGLE,4 D
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Viral Load in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) and Plasma to Diagnose Lung Transplant Associated CMV Pneumonia
 Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Viral Load in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) and Plasma to Diagnose Lung Transplant Associated CMV Pneumonia I.P. Lodding 1,2, H.H. Schultz 3, J.U. Jensen 1,5, C. Andersen 4,
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Viral Load in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) and Plasma to Diagnose Lung Transplant Associated CMV Pneumonia I.P. Lodding 1,2, H.H. Schultz 3, J.U. Jensen 1,5, C. Andersen 4,
Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal transplant
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10683-10689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0050944 Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10683-10689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0050944 Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal
DIAGNOSTIC YIELD OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE IN BRONCHOALVEOLAR LAVAGE
 DIAGNOSTIC YIELD OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE IN BRONCHOALVEOLAR LAVAGE Wipa Reechaipichitkul 1, Viraphong Lulitanond 2, Boonsong Patjanasoontorn 1, Watchara Boonsawat 1 and Anakapong Phunmanee 1 1 Division
DIAGNOSTIC YIELD OF ADENOSINE DEAMINASE IN BRONCHOALVEOLAR LAVAGE Wipa Reechaipichitkul 1, Viraphong Lulitanond 2, Boonsong Patjanasoontorn 1, Watchara Boonsawat 1 and Anakapong Phunmanee 1 1 Division
Collection (Specimen Source Required on all tests) Sputum: >5 ml required. First morning specimen preferred.
 Type Acid Fast (Mycobacteria) Sputum: >5 ml required. First morning specimen preferred. For blood, sodium heparin tube preferred. Lithium heparin acceptable. Do not centrifuge.. delay. Swabs are not appropriate
Type Acid Fast (Mycobacteria) Sputum: >5 ml required. First morning specimen preferred. For blood, sodium heparin tube preferred. Lithium heparin acceptable. Do not centrifuge.. delay. Swabs are not appropriate
Seasonal Influenza. Provider Information Sheet. Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program
 August 2007 te: This sheet contains information on seasonal influenza. For information on avian or pandemic influenza, contact the (800-423-1271 or 304-558-5358). What is influenza-like illness (ILI)?
August 2007 te: This sheet contains information on seasonal influenza. For information on avian or pandemic influenza, contact the (800-423-1271 or 304-558-5358). What is influenza-like illness (ILI)?
Test Requested Specimen Ordering Recommendations
 Microbiology Essentials Culture and Sensitivity (C&S) Urine C&S Catheter Surgical (excluding kidney aspirates) Voided Requisition requirements o Specific method of collection MUST be indicated o Indicate
Microbiology Essentials Culture and Sensitivity (C&S) Urine C&S Catheter Surgical (excluding kidney aspirates) Voided Requisition requirements o Specific method of collection MUST be indicated o Indicate
Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12
 Diagnostic Microbiology Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12 Electron Microscopy 106 virus particles per ml required for visualization, 50,000-60,000 magnification normally used. Viruses may be detected
Diagnostic Microbiology Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12 Electron Microscopy 106 virus particles per ml required for visualization, 50,000-60,000 magnification normally used. Viruses may be detected
Acceptability of Sputum Specimens
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1982, p. 627-631 0095-1137/82/100627-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1982, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 4 Comparison of Six Different Criteria for Judging
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1982, p. 627-631 0095-1137/82/100627-05$02.00/0 Copyright C 1982, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 4 Comparison of Six Different Criteria for Judging
Investigation of CD4+ T cell numbers in HIV-infected patients among smokers and non-smokers in Thailand
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(5):867-871 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Investigation of CD4+ T cell numbers in HIV-infected
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(5):867-871 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Investigation of CD4+ T cell numbers in HIV-infected
A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients T. Tia 1, C. Putaporntip 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients T. Tia 1, C. Putaporntip 1,
Immune System and Disease. Chapter 31
 Immune System and Disease Chapter 31 31.1 PATHOGENS AND HUMAN ILLNESS Key Concept Germs cause many diseases in humans Microogranisms (microscopic particles) cause certain diseases proposed by Louis Pasteur
Immune System and Disease Chapter 31 31.1 PATHOGENS AND HUMAN ILLNESS Key Concept Germs cause many diseases in humans Microogranisms (microscopic particles) cause certain diseases proposed by Louis Pasteur
Pneumocystis colonisation is common among hospitalised HIV infected patients with non- Pneumocystis pneumonia
 1 Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, San Francisco General Hospital, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA; 2 HIV/AIDS Division, San Francisco General Hospital,
1 Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, San Francisco General Hospital, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA; 2 HIV/AIDS Division, San Francisco General Hospital,
Norgen s HIV proviral DNA PCR Kit was developed and validated to be used with the following PCR instruments: Qiagen Rotor-Gene Q BioRad icycler
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product # 33840 Product Insert Background Information
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com HIV Proviral DNA PCR Kit Product # 33840 Product Insert Background Information
Cytological evaluation of effusion fluid with cell block technique and cytology smears among Sudanese patients
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 3/ June 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Cytological evaluation of effusion fluid with cell block technique
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 3/ June 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Cytological evaluation of effusion fluid with cell block technique
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
OTKA azonosító: Típus: K Vezető kutató: Gergely Lajos
 Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), mostly variant B reactivation in renal transplant patients has been published previously, but the pathogenetic role of HHV-6 variant A has not been clarified. During the project
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), mostly variant B reactivation in renal transplant patients has been published previously, but the pathogenetic role of HHV-6 variant A has not been clarified. During the project
Transplantation. Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University
 Transplantation Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University Objectives To understand the diversity among human leukocyte antigens (HLA) or major histocompatibility complex (MHC) To know the
Transplantation Immunology Unit College of Medicine King Saud University Objectives To understand the diversity among human leukocyte antigens (HLA) or major histocompatibility complex (MHC) To know the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:478-485 Clinical significance of positive Pneumocystis jirovecii polymerase chain reaction in non-human immunodeficiency virus immunocompromised patients in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:478-485 Clinical significance of positive Pneumocystis jirovecii polymerase chain reaction in non-human immunodeficiency virus immunocompromised patients in
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017.
 This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017. 0 There is good evidence to suggest that patients eventually diagnosed with HIV infection have had contact with medical services, with symptoms
This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017. 0 There is good evidence to suggest that patients eventually diagnosed with HIV infection have had contact with medical services, with symptoms
Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel
 Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel 2017 A leading cause of death and increased morbidity for hospitalized ptns Hospitals, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, home care settings Higher rate
Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel 2017 A leading cause of death and increased morbidity for hospitalized ptns Hospitals, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, home care settings Higher rate
Appendix E1. Epidemiology
 Appendix E1 Epidemiology Viruses are the most frequent cause of human infectious diseases and are responsible for a spectrum of illnesses ranging from trivial colds to fatal immunoimpairment caused by
Appendix E1 Epidemiology Viruses are the most frequent cause of human infectious diseases and are responsible for a spectrum of illnesses ranging from trivial colds to fatal immunoimpairment caused by
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
Chapter 12 Preventing Infection
 Chapter 12 Preventing Infection Infection is a major safety and health hazard. Minor infections cause acute illnesses and some infections are serious and can cause death. Microbe/microorganism is a small
Chapter 12 Preventing Infection Infection is a major safety and health hazard. Minor infections cause acute illnesses and some infections are serious and can cause death. Microbe/microorganism is a small
David Helfinstine Clinical Microbiology II July 31, Parvovirus B19
 David Helfinstine Clinical Microbiology II July 31, 2007 Parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Family: Parvoviridae Latin parvus means small ~20 nm in diameter (0.02 µm) Single-stranded DNA virus Icosahedral capsid
David Helfinstine Clinical Microbiology II July 31, 2007 Parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Family: Parvoviridae Latin parvus means small ~20 nm in diameter (0.02 µm) Single-stranded DNA virus Icosahedral capsid
High prevalence of Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization among HIV-positive patients in southern Brazil
 Medical Mycology, 2014, 52, 804 809 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myu059 Advance Access Publication Date: 6 October 2014 Original Article Original Article High prevalence of Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization among
Medical Mycology, 2014, 52, 804 809 doi: 10.1093/mmy/myu059 Advance Access Publication Date: 6 October 2014 Original Article Original Article High prevalence of Pneumocystis jirovecii colonization among
