TB Infection Control in Healthcare Settings
|
|
|
- Hugh Rogers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TB Infection Control in Healthcare Settings Wendi K. Drummond DO, MPH Medical Director, Infection Prevention Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health April 6, 2018
2
3 Objectives Understand the epidemiology of TB in health care settings and risk factors for transmission Review the elements of a TB infection control program Understand the implementation of different aspects of environmental and respiratory controls
4 How contagious is tuberculosis? Factors in influencing TB transmission Source case (*AFB smear status, treatment status, frequency of cough) The environment Among household contacts of smear-positive cases, the rates of tuberculin positivity are 30-50% above those among age-matched community controls Duration and intensity of exposure The contact The tubercle bacillus Sepkowitz, KA, 1996
5 How contagious is tuberculosis? Smear positive cases expectorate bacilli daily (or about AFB/ml sputum) Smear negative sputum contains < 10 3 bacilli/ml of sputum Treatment decreases contagiousness, regardless of smear and culture status by decreasing the number of bacilli expectorated + introduces antibiotic into the infectious droplet nuclei
6 TB Transmission Person-to-person transmission of TB occurs via inhalation of droplet nuclei (airborne particles 1-2 microns in diameter approximately 1/100 th the width of a human hair) Droplet nuclei can remain airborne in room air for a long period of time (until removed by natural or mechanical ventilation) Persons with active pulmonary or laryngeal TB are contagious (especially if a cavity is present or when the sputum is acidfast-bacilli (AFB) smear positive) Coughing, sneezing, singing, shouting, talking or breathing
7 TB Transmission Patients with sputum that is smear negative but culture positive pulmonary TB are still contagious Procedures associated with the dissemination of droplet nuclei have been associated with an increased risk of TB (ET, bronchoscopy, sputum induction, aerosol treatments, irrigation of abscess, autopsy) Most exposed persons do not become infected
8 Environmental Factors That Increase Risk for Transmission Exposure in small, enclosed spaces Inadequate ventilation Recirculating air containing infectious droplets Inadequate cleaning and disinfection of equipment Improper specimen-handling procedures
9 TB Transmission Source patient Infectious TB of lungs or larynx Smear positivity Suceptible host Inhales droplet nucleii containing TB TB Exposure Disease Infection
10
11 TB Infection versus TB Disease Latent TB infection (LTBI) is identified with a tuberculin skin test (TST) or interferon gamma release assay (IGRA) blood test LTBI does not cause a person to be sick and there are no symptoms Persons with LTBI are not infectious
12 Latent Tuberculosis Infection LTBI progresses to TB disease in Small number of persons soon after infection 5% 10% of persons with untreated LTBI sometime during lifetime About 10% of persons with HIV and untreated LTBI per year
13 TB Infection versus TB Disease High risk persons for progression from LTBI TB disease HIV infected persons, diabetes, renal conditions (dialysis), immune compromised persons Infection with M. tuberculosis within the last 2 years Infants and children < 4 years old Immune compromising situations (cancer therapy, prolonged steroid use) History of untreated or inadequately treated TB
14 TB in Healthcare workers: risk Varies by healthcare setting Occupational group Prevalence of TB in the community Patient population Effectiveness of TB infection control measures Procedures
15 A Case 62 year old Vietnamese male with a long history of smoking presents to pulmonary clinic in December (12/2) for an outpatient evaluation of a L hilar mass and LUL consolidative area (5.8x5.3 cm) with a cavitary lesion. Daughter present as translator. Presenting symptoms included dyspnea on exertion, dry cough, poor appetite x 4 months, weight loss. No history of hemoptysis. No night sweats endorsed on initial visit. Spirometry obtained. Labs. Multiple tests ordered and scheduled after initial visit. Patient returns January 4 for ABG, walk oximetry, PFTs, PET CT. Returns in February to discuss test results. Induced sputums ordered at February 9 visit.
16 Fundamental Control Measures Designating responsibility for TB infection control It should be part of a comprehensive infection control plan (ICP) Having a written infection control plan Infection control efforts coordinated with local health departments All healthcare workers need to be educated regarding TB epidemiology, symptoms, transmission, and prevention
17 Appropriate signage should be posted providing instructions for appropriate respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette
18 Fundamentals of TB infection control Administrative controls Reduce the risk of exposure to persons who might have TB disease Environmental controls Prevent the spread and reduce the concentration of infectious droplet nuclei in ambient air Respiratory-infection controls Use of respiratory protective equipment in situations that pose a high risk for exposure
19 What did we learn from prior nosocomial or health care associated outbreaks? Outbreaks in the 1980 s 1990 s paralleled the increase in the prevalence of HIV and TB co-infection Lapses in infection control practices Delays in diagnosis and treatment of persons with infectious TB The appearance and transmission of MDR TB strains Mirrored the overall increase in TB
20 Outbreak: MDR-TB-AIDS (NYC) Edlin. NEJM N=18, Attack rate = 6%, Incubation d ( )
21 Transmission in healthcare facilities Contributing factors for nosocomial transmission Deterioration of public health infrastructure Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV epidemic) Inadequate infection control measures
22 Outbreak: Failures Failure to isolate Failure to separate AIDS and TB patients No negative pressure rooms No respirators Edlin. NEJM 1992; Stroud. ICHE 1995.
23 Risk Factors for Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis History of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Prior positive tuberculin skin test (TST) or interferongamma assay Emigration from a country with an increased prevalence of TB Homelessness Prior incarceration Immune suppression (including HIV) with cough>2 weeks, hemoptysis, fevers, night sweats, weight loss
24
25 Outpatient and Emergency Room Management Patients with active TB may frequently present in an outpatient setting or Emergency Department Ask about signs of symptoms of TB and know the risk factors It is imperative that these patients be promptly identified and evaluated to minimize exposure to others Patients with known or suspected TB should be placed in an airborne infection isolation (AII) room (previously referred to as negative pressure isolation rooms) If an isolation room is not available, the patient should be placed in an enclosed area with a surgical mask in place
26 Ambulatory Care Settings Contact with immune compromised patients should be avoided The patient should be instructed to cover the mouth and nose with tissues when sneezing or coughing If an area other than an airborne infection isolation room is used, it should not be used again for one hour after the patient has left Contact the infection preventionist or the designee who is knowledgeable in managing these issues Avoid unnecessary aerosol-inducing procedures on these individuals
27 Back to our case. Sputum results come back.. 1+ AFB smear positive Friday afternoon
28 Administrative Controls Infection control program and plan Administrative commitment, infrastructure Annual TB risk assessment: low, medium or potential for ongoing transmission Monitoring and re-evaluation
29 TB Risk Classifications All healthcare settings should perform risk classification as part of risk assessment to determine need for and frequency of an HCW testing program, regardless of likelihood of encountering persons with TB disease
30 TB Risk Classifications Low risk Persons with TB disease not expected to be encountered; exposure unlikely Medium risk HCWs will or might be exposed to persons with TB disease Potential ongoing transmission Temporary classification for any settings with evidence of person-to-person transmission of M. tuberculosis
31 TB Risk Classifications Inpatient Settings <200 beds 200 beds Low <3 TB patients/yr Medium >3 TB patients/yr <6 TB patients/yr >6 TB patients/yr Potential Ongoing Transmission Evidence of ongoing transmission, regardless of setting
32 TB Risk Classifications Outpatient Settings TB treatment facilities, medical offices, ambulatory care settings Low <3 TB patients/yr Medium >3 TB patients/yr Potential Ongoing Transmission Evidence of ongoing transmission, regardless of setting
33 CDC 2005 TB Risk Classifications Nontraditional Facility-based Settings Emergency medical service (EMS), medical settings in correctional facilities, outreach care, long-term care facilities Low Only patients with LTBI treated No coughinducing procedures are performed in setting System to detect/triage persons with TB symptoms Medium Settings where TB patients are expected to be encountered Potential Ongoing Transmission Evidence of ongoing transmission regardless of setting
34 Administrative Controls Triage Isolate Diagnose Treat
35 Sensitivity of AFB Smear Al Zahrani. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2001.
36 Sensitivity of AFB Smear Leonard. AJIC 2005.
37 Infectiousness of AFB smear-negative disease Estimated 17% of transmission events due to smear negative case Compared to smear positive cases, 22% as likely to transmit TB Source-Case Variables Tuberculin Reactors (%) Bacteriologic status Smear, culture 14.3 Smear, culture Smear +, culture Loudon RG. ARRD 1969;99:109; presentation of data shown in this slide courtesy of Charles Daley and Robert Belknap Behr MA et al, Lancet 1999; 353:
38 Discontinuation of Airborne Precautions-Suspected TB TB disease is considered unlikely, and Alternative diagnosis explaining the clinical syndrome has been established 3 consecutive, negative AFB sputum smears Demonstration of 2 negative sputum Xpert MTB/RIF results (serial sputum collection for mycobacterial culture is still necessary because Xpert doesn t detect all patients with pulmonary TB and recovery of organism is needed for drug susceptibility testing) Continue if suspicion for TB remains CDC 2005.
39 Discontinuation of Airborne Precautions-Confirmed TB Response to therapy Clinical improvement (4-7 days) 3 consecutive, negative AFB smears or one negative Xpert and two negative sputum smears Patients with < 7 days of treatment Some favor at least 2 weeks of TB treatment for patients with positive AFB smears prior to discontinuation of isolation Continue until discharge or negative culture for MDR-TB CDC 2005.
40 Discharge to Home: Smear Positive Public health follow-up and DOT Household members previously exposed No household members <4 years old or immunocompromised Patient will remain home Must wear a surgical mask with visitors or when leaving home CDC 2005.
41 Screening for TB in HCWs Baseline 2-step TST or IGRA Annual symptom screen and testing (medium risk facility) CXR and treatment if positive test Investigate conversions CDC 2005.
42 Elements of Infection Control 1 st Priority 2 nd Priority 3 rd Priority Administrative Controls Environmental Controls Respiratory Protection CDC 2005; WHO 1999; WHO 2009.
43 Environmental Controls Isolation room (patients with risk factors for active pulmonary TB should be placed in airborne infection isolation (AII) rooms) Airborne Infection Isolation (AII) rooms employ negative pressure to prevent escape of droplet nuclei Doors must remain closed to maintain negative pressure (should be verified daily)
44 Environmental Controls 6 air exchanges per hour are acceptable in pre-existing rooms 12 are required for new construction or renovation Air should be exhausted to the exterior removed from intake vents If recirculation is not avoidable, High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters must be installed in exhaust ducts
45 Environmental Controls Anterooms are often employed for maintaining negative pressure The door to the anteroom and the door to the AII should not be open at the same time If the patient must leave the room, he or she must wear a surgical mask All individuals entering the room must wear appropriate respiratory protection
46 General Ventilation CDC 2005.
47 Negative Pressure CDC 2005.
48 HEPA Filters CDC 2005.
49 Elements of Infection Control 1 st Priority 2 nd Priority 3 rd Priority Administrative Controls Environmental Controls Respiratory Protection CDC 2005; WHO 1999; WHO 2009.
50
51 Respiratory Protection All healthcare workers who work in situations that pose a high risk for exposure should be trained in the use of respiratory protection Individuals entering the rooms of a patient with suspected or known TB must wear appropriate respiratory protection This may include an N95 mask or a PAPR
52 Respiratory Protection Protection must also be worn by persons present during procedures for patients with known or suspected TB that induce coughing or aerosolization Bronchoscopy Induced sputum collection Administration of aerosolized medications and by individuals in closed spaces with patients with known or suspected TB (transport vehicles)
53 Respiratory Protection N95 PAPR
54 N95 Masks These masks filter particles > 1 micron in diameter with at least 95% efficiency with flow rates up to 50 liters/minute The mask must fit to a person s face with less than 10% seal leakage Masks should be available outside all rooms in several sizes to ensure optimal fit and usage
55 N95 Masks All healthcare workers should be fit tested prior to usage in order to determine appropriate fit and mask size Healthcare workers unable to use an N95 mask due to poor fit (facial structure or beards which may prevent a tight seal) should use a PAPR
56 Respiratory Protection: Patients Patients with known or suspected TB should not wear N95 masks (designed to filter air before it is inhaled) Patients should wear a surgical mask as these are designed to prevent respiratory secretions of the persons wearing the mask from entering the environment
57 Our case Exposure investigation conducted by employee health and infection prevention HCWs potentially exposed identified and screened No conversions Re-examined lines of communication and staff education
58 TB Surveillance Periodic risk assessment is important and should include a review of TB incidence and affected groups Cases over the last 5 years should be assessed Lapses in infection control should be identified and rectified Annual screening requirements are based on a facilities risk assessment
59 References Sepkowitz KA. How Contagious is Tuberculosis? Clinical Infectious Diseases. 1996; 23; The Curry Center. Tuberculosis Infection Control. A Practical Manual for Preventing TB, Moran. Ann Emerg Med Cobo, J et al. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis Eur J Clin Nov;20(11): Edlin BR, Tokars JI, Grieco MH, et al. An outbreak of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among hospitalized patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med 1992; 326: Taylor Z, Nolan C et al. Controlling Tuberculosis in the United States Recommendations from the American Thoracic Society, CDC, and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. MMWR November 4, 2005 / 54(RR12);1-81
TB CONTROL IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES: A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PREVENTION
 TB CONTROL IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES: A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PREVENTION HOW TB IS SPREAD GENERATION OF TB DROPLET NUCLEI One cough produces 500 droplets Average TB patient generates 75,000 droplets/day (before
TB CONTROL IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES: A PRACTICAL GUIDE FOR PREVENTION HOW TB IS SPREAD GENERATION OF TB DROPLET NUCLEI One cough produces 500 droplets Average TB patient generates 75,000 droplets/day (before
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis Infection Control
 Chapter 7 Tuberculosis Infection Control Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 187 Introduction.... 189 Infectiousness.... 190 TB Infection Control Measures... 194 TB Infection Control Program................................................
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis Infection Control Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 187 Introduction.... 189 Infectiousness.... 190 TB Infection Control Measures... 194 TB Infection Control Program................................................
TB Program Management San Antonio, Texas November 5-7, 2008
 TB Program Management San Antonio, Texas November 5-7, 2008 Infection Control Lynelle Phillips, RN, MPH November 7, 2008 Infection Control Lynelle Phillips, RN MPH Nurse Consultant Heartland National TB
TB Program Management San Antonio, Texas November 5-7, 2008 Infection Control Lynelle Phillips, RN, MPH November 7, 2008 Infection Control Lynelle Phillips, RN MPH Nurse Consultant Heartland National TB
Rebecca O. Sanchez, BSN., RN., MPH. has the following disclosures to make:
 INFECTION CONTROL PRACTICES Rebecca O. Sanchez, RN, BSN, MPH Texas Department of State Health Services Texas Center for Infectious Disease Rebecca O. Sanchez, BSN., RN., MPH. has the following disclosures
INFECTION CONTROL PRACTICES Rebecca O. Sanchez, RN, BSN, MPH Texas Department of State Health Services Texas Center for Infectious Disease Rebecca O. Sanchez, BSN., RN., MPH. has the following disclosures
TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control
 TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control Bradley Allen, MD, PhD, FACP, FIDSA. 2014 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures Medical Consultant, TB Control Program Indiana State Department of Health Past clinical
TB Transmission, Pathogenesis & Infection Control Bradley Allen, MD, PhD, FACP, FIDSA. 2014 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures Medical Consultant, TB Control Program Indiana State Department of Health Past clinical
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, TB Infection Control Robert Petrossian March 8, 2012
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, 2012 TB Infection Control Robert Petrossian March 8, 2012 Robert Petrossian has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas March 7 9, 2012 TB Infection Control Robert Petrossian March 8, 2012 Robert Petrossian has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
At the end of this session, participants will be able to:
 Advanced Concepts in Pediatric Tuberculosis: Infection Control, Source Case and Contact Investigation Ana M. Alvarez, M.D. Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology University
Advanced Concepts in Pediatric Tuberculosis: Infection Control, Source Case and Contact Investigation Ana M. Alvarez, M.D. Associate Professor Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology University
The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control
 The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control Session Four of a Four-Part Webinar Series Presented in Partnership with the BC Lung Association January 10, 2014 Facilitators: Nash Dhalla,
The Air We Share: Principles and Practices of TB Infection Control Session Four of a Four-Part Webinar Series Presented in Partnership with the BC Lung Association January 10, 2014 Facilitators: Nash Dhalla,
Tuberculosis What you need to know. James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director
 Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
Tuberculosis What you need to know James Zoretic M.D., M.P.H. Regions 2 and 3 Director What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacillus
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS IN INSTITUTIONAL FACILITIES" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow"
What s New in TB Infection Control?
 What s New in TB Infection Control? Mark Lobato, MD Division of TB Elimination CDC / USPHS March 24, 2010 Providence, RI Keeping the scourge at bay Early disease prevention Modern cough etiquette When
What s New in TB Infection Control? Mark Lobato, MD Division of TB Elimination CDC / USPHS March 24, 2010 Providence, RI Keeping the scourge at bay Early disease prevention Modern cough etiquette When
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
 TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB in the United States Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB) From 1953 to 1984, reported cases decreased by approximately 5.6% each year From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% 25,313 cases reported
TB Infection Control. Carol Staton, RN, BSN March 17, TB Nurse Case Management March 17 19, 2015 San Antonio, Texas
 TB Infection Control Carol Staton, RN, BSN March 17, 2015 TB Nurse Case Management March 17 19, 2015 San Antonio, Texas EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Carol Staton, RN, BSN has the following disclosures
TB Infection Control Carol Staton, RN, BSN March 17, 2015 TB Nurse Case Management March 17 19, 2015 San Antonio, Texas EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Carol Staton, RN, BSN has the following disclosures
2018 Tuberculosis Clinical Intensive: Infection Prevention & Control. > No disclosures
 2018 Tuberculosis Clinical Intensive: Infection Prevention & Control > No disclosures 1 Objectives By the end of today s session, hopefully you will be able to: > Recognize potential TB exposures in healthcare
2018 Tuberculosis Clinical Intensive: Infection Prevention & Control > No disclosures 1 Objectives By the end of today s session, hopefully you will be able to: > Recognize potential TB exposures in healthcare
Issues in TB Infection Control. Stopping transmission of TB. The Issue: Transmission of TB. TB Infection Control
 Curry International TB Center Issues in TB Infection Control Lisa Chen, MD CITC TB Intensive, Oct. 2017 Stopping transmission of TB TB Infection Control A combination of measures aimed at minimizing the
Curry International TB Center Issues in TB Infection Control Lisa Chen, MD CITC TB Intensive, Oct. 2017 Stopping transmission of TB TB Infection Control A combination of measures aimed at minimizing the
TUBERCULOSIS. Pathogenesis and Transmission
 TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission TUBERCULOSIS Pathogenesis and Transmission Infection to Disease Diagnostic & Isolation Updates Treatment Updates Pathogenesis Droplet nuclei of 5µm or less are
Preventing Tuberculosis (TB) Transmission in Ambulatory Surgery Centers. Heidi Behm, RN, MPH TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program
 Preventing Tuberculosis (TB) Transmission in Ambulatory Surgery Centers Heidi Behm, RN, MPH TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program Topics of Discussion TB Overview Epidemiology of TB in Oregon Annual Facility
Preventing Tuberculosis (TB) Transmission in Ambulatory Surgery Centers Heidi Behm, RN, MPH TB Controller HIV/STD/TB Program Topics of Discussion TB Overview Epidemiology of TB in Oregon Annual Facility
"GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "GUARDING AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS AS A FIRST RESPONDER" Training For THE CDC "TUBERCULOSIS PREVENTION GUIDELINES" "Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today...and Tomorrow" Outline
Guidelines for Preventing the Transmission of M. tuberculosis in Health-Care Settings, Division of Tuberculosis Elimination
 Guidelines for Preventing the Transmission of M. tuberculosis in Health-Care Settings, 2005 Division of Tuberculosis Elimination September 2006 Purpose of 2005 Guidelines Update and replace 1994 Mycobacterium
Guidelines for Preventing the Transmission of M. tuberculosis in Health-Care Settings, 2005 Division of Tuberculosis Elimination September 2006 Purpose of 2005 Guidelines Update and replace 1994 Mycobacterium
TB and Respiratory Protection
 Slide 1 TB and Respiratory Protection Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease present throughout the United States. Lehigh Valley Health Network is concerned about your health and needs your help to prevent the
Slide 1 TB and Respiratory Protection Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease present throughout the United States. Lehigh Valley Health Network is concerned about your health and needs your help to prevent the
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist
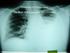 Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
Tuberculosis Elimination: The Role of the Infection Preventionist Preface: What Happens when Health Care Professionals are not familiar with TB? A 15 year old student was diagnosed with highly infectious
TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks
 1 TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks 2 Page 1 4 NHS Lothian Infection Prevention and Control Study Day On
1 TB facts & figures Microbiology of TB Transmission of TB Infection control in health care settings Special cases Resistant TB Masks 2 Page 1 4 NHS Lothian Infection Prevention and Control Study Day On
TB Clinical Guidelines: Revision Highlights March 2014
 TB Clinical Guidelines: Revision Highlights March 2014 AIR TRAVEL & TB CONTROL With respect to non-ambulance air travel of patients diagnosed with or suspected as having active Mycobacterium tuberculosis,
TB Clinical Guidelines: Revision Highlights March 2014 AIR TRAVEL & TB CONTROL With respect to non-ambulance air travel of patients diagnosed with or suspected as having active Mycobacterium tuberculosis,
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL. Emergency Department and Receiving Areas CHAPTER 24: Author P. Suri, MD R. Gopaul, MD
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 24: Emergency Department and Receiving Areas Author P. Suri, MD R. Gopaul, MD Chapter Editor Gonzalo Bearman MD, MPH, FACP, FSHEA, FIDSA Topic Outline
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 24: Emergency Department and Receiving Areas Author P. Suri, MD R. Gopaul, MD Chapter Editor Gonzalo Bearman MD, MPH, FACP, FSHEA, FIDSA Topic Outline
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Etiological Agent: Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT. Definition
 Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Definition Tuberculosis is a contagious bacterial infection of the lungs caused by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (TB) Etiological Agent: Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
Protecting Healthcare Workers from TB in Iowa Douglas Hornick, MD September 27, 2011
 TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Protecting Healthcare Workers from TB in Iowa Douglas Hornick, MD September 27, 2011 Douglas Hornick, MD has the following disclosures to
TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Protecting Healthcare Workers from TB in Iowa Douglas Hornick, MD September 27, 2011 Douglas Hornick, MD has the following disclosures to
Standard Precautions & Isolation Precautions. If you have questions about this module, contact the Infection Prevention department at your facility.
 Standard Precautions & If you have questions about this module, contact the Infection Prevention department at your facility. Annual Education 2014 Standard Precautions Standard Precautions should be used
Standard Precautions & If you have questions about this module, contact the Infection Prevention department at your facility. Annual Education 2014 Standard Precautions Standard Precautions should be used
POLICY FOR THE PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF TUBERCULOSIS
 POLICY FOR THE PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF TUBERCULOSIS Policy No: 7.20 Approval Date: Review Date: Lead Director: Under Review Under Review Under Review Page 1 of 7 Polic y_for_the_prevention_and_control_of_tuberculosis
POLICY FOR THE PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF TUBERCULOSIS Policy No: 7.20 Approval Date: Review Date: Lead Director: Under Review Under Review Under Review Page 1 of 7 Polic y_for_the_prevention_and_control_of_tuberculosis
Disclosure. Objectives
 Breaking the Chain of TB Airborne Isolation Regina McDade EdD, MPH, BSN, RN TB Clinical Care Coordinator Jackson Health System Department of Infection Prevention and Control David Ashkin, M.D. FCCP Medical
Breaking the Chain of TB Airborne Isolation Regina McDade EdD, MPH, BSN, RN TB Clinical Care Coordinator Jackson Health System Department of Infection Prevention and Control David Ashkin, M.D. FCCP Medical
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 2-5, 2011 TB Infection Control in Healthcare Settings Robert Petrossian Thursday August 4, 2011 Robert Petrossian has the following disclosures to make: No conflict
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 2-5, 2011 TB Infection Control in Healthcare Settings Robert Petrossian Thursday August 4, 2011 Robert Petrossian has the following disclosures to make: No conflict
Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
 Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Charles Daley, MD National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory Board Horizon, Johnson and Johnson, Otsuka and Spero Investigator Insmed Objectives After attending
Transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Charles Daley, MD National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory Board Horizon, Johnson and Johnson, Otsuka and Spero Investigator Insmed Objectives After attending
TUBERCULOSIS. Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County
 TUBERCULOSIS Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria can attack any
TUBERCULOSIS Presented By: Public Health Madison & Dane County What is Tuberculosis? Tuberculosis, or TB, is a disease caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The bacteria can attack any
Infection Control Standard Precautions and Isolation
 Infection Control Standard Precautions and Isolation Michael Bell, M.D. Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control and Prevention History of Infection Control Precautions in the
Infection Control Standard Precautions and Isolation Michael Bell, M.D. Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Centers for Disease Control and Prevention History of Infection Control Precautions in the
Stop TB Poster (laminated copies are available from TB Control: )
 Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Recommendations For Homeless Shelters in Maine Tool Kit What Your Shelter Can Do to Prevent TB Assessing Your Shelter Guests Risk for TB Cough Alert Policy Think TB
Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Recommendations For Homeless Shelters in Maine Tool Kit What Your Shelter Can Do to Prevent TB Assessing Your Shelter Guests Risk for TB Cough Alert Policy Think TB
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
TB Infection Control
 TB Infection Control Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN K March 7, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management March 7 9, 2017 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN K has the
TB Infection Control Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN K March 7, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management March 7 9, 2017 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN K has the
August 30, 1991 / 40(34);
 August 30, 1991 / 40(34);585-591 Epidemiologic Notes and Reports Nosocomial Transmission of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Among HIV-Infected Persons -- Florida and New York, 1988-1991 During 1990 and
August 30, 1991 / 40(34);585-591 Epidemiologic Notes and Reports Nosocomial Transmission of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Among HIV-Infected Persons -- Florida and New York, 1988-1991 During 1990 and
TB in Corrections Phoenix, Arizona
 TB in Corrections Phoenix, Arizona March 24, 2011 Contact Investigation in the Correctional Setting Jessica Quintero, BAAS March 24, 2011 Jessica Quintero, BAAS has the following disclosures to make: No
TB in Corrections Phoenix, Arizona March 24, 2011 Contact Investigation in the Correctional Setting Jessica Quintero, BAAS March 24, 2011 Jessica Quintero, BAAS has the following disclosures to make: No
TB Infection Control. Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN-K, has the following disclosures to make:
 TB Infection Control Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN-K September 7, 2016 TB Nurse Case Management September 7-9, 2016 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN-K,
TB Infection Control Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN-K September 7, 2016 TB Nurse Case Management September 7-9, 2016 San Antonio, TX EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Delvina Mimi Ford, BSN, RN, CCRN-K,
INSTRUCTOR S GUIDE VERSION
 EHS EXERCISE 1: Risk Assessment: A Case Study of an Investigation of a Tuberculosis (TB) Outbreak in a Health Care Setting Estimated Time to Complete in an Online Course or In-person Course Discussion:
EHS EXERCISE 1: Risk Assessment: A Case Study of an Investigation of a Tuberculosis (TB) Outbreak in a Health Care Setting Estimated Time to Complete in an Online Course or In-person Course Discussion:
TB Skin Test Practicum Houston, Texas Region 6/5 South September 23, 2014
 TB Skin Test Practicum Houston, Texas Region 6/5 South September 23, 2014 Catalina Navarro, BSN, RN has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant financial relationships with
TB Skin Test Practicum Houston, Texas Region 6/5 South September 23, 2014 Catalina Navarro, BSN, RN has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant financial relationships with
Appendix C. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HEALTHCARE SETTING
 Appendix C. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HEALTHCARE SETTING Infection Control Principles for Preventing the Spread of Influenza The following infection control principles apply in any setting
Appendix C. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HEALTHCARE SETTING Infection Control Principles for Preventing the Spread of Influenza The following infection control principles apply in any setting
TB Infection Control: Fears and Facts Lisa V. Adams, MD Elizabeth A. Talbot, MD Dartmouth Medical School June 2011
 TB Infection Control: Fears and Facts Lisa V. Adams, MD Elizabeth A. Talbot, MD Dartmouth Medical School June 2011 Outline Background Warm-up with easy myth busting Challenge round myth busting Your participation
TB Infection Control: Fears and Facts Lisa V. Adams, MD Elizabeth A. Talbot, MD Dartmouth Medical School June 2011 Outline Background Warm-up with easy myth busting Challenge round myth busting Your participation
Investigation of Contacts of Persons with Infectious Tuberculosis, 2005
 1 Investigation of Contacts of Persons with Infectious Tuberculosis, 2005 Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Division of Tuberculosis Elimination Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Philadelphia TB Control
1 Investigation of Contacts of Persons with Infectious Tuberculosis, 2005 Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Division of Tuberculosis Elimination Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Philadelphia TB Control
Vaccine Preventable Respiratory Infections and Tuberculosis
 Vaccine Preventable Respiratory Infections and Tuberculosis Infection Prevention Essentials in Long-Term Care Spring 2019 Teri Hulett, RN, BSN, CIC, FAPIC Leading infection prevention education across
Vaccine Preventable Respiratory Infections and Tuberculosis Infection Prevention Essentials in Long-Term Care Spring 2019 Teri Hulett, RN, BSN, CIC, FAPIC Leading infection prevention education across
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 12 PURPOSE To provide guidelines for the prevention and the treatment of tuberculosis (TB) in the N.C. Department of Correction. POLICY The N. C. Department of Correction will abide by this Tuberculosis
PAGE 1 of 12 PURPOSE To provide guidelines for the prevention and the treatment of tuberculosis (TB) in the N.C. Department of Correction. POLICY The N. C. Department of Correction will abide by this Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis and Diabetes Mellitus. Lana Kay Tyer, RN MSN WA State Department of Health TB Nurse Consultant
 Tuberculosis and Diabetes Mellitus Lana Kay Tyer, RN MSN WA State Department of Health TB Nurse Consultant Learning Objectives Understand the impact of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) on TB infection
Tuberculosis and Diabetes Mellitus Lana Kay Tyer, RN MSN WA State Department of Health TB Nurse Consultant Learning Objectives Understand the impact of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus (DM) on TB infection
The diagnosis of active TB
 The diagnosis of active TB Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Martha Ainslie Relationships with commercial interests: Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: Boehringer Ingelheim Mitigating Potential Bias I have
The diagnosis of active TB Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Martha Ainslie Relationships with commercial interests: Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: Boehringer Ingelheim Mitigating Potential Bias I have
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know
 Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Sixth Edition 2013 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination 1 Chapters
Core Curriculum on Tuberculosis: What the Clinician Should Know Sixth Edition 2013 National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention Division of Tuberculosis Elimination 1 Chapters
TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION
 TB CASE MANAGEMENT AND CONTACT INVESTIGATION INTENSIVE TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: 1. Describe the criteria used
TB CASE MANAGEMENT AND CONTACT INVESTIGATION INTENSIVE TUBERCULOSIS CONTACT INVESTIGATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: 1. Describe the criteria used
SUBJECT: ISOLATION PRECAUTIONS REFERENCE #6003 PAGE: 1 DEPARTMENT: REHABILITATION SERVICES OF: 6 EFFECTIVE:
 PAGE: 1 STANDARD PRECAUTIONS: Precautions which are designed for care of all patients, regardless of diagnosis or presumed infection status to reduce the risk of transmission from both recognized and unrecognized
PAGE: 1 STANDARD PRECAUTIONS: Precautions which are designed for care of all patients, regardless of diagnosis or presumed infection status to reduce the risk of transmission from both recognized and unrecognized
Worker Protection and Infection Control for Pandemic Flu
 Factsheet #2 What Workers Need to Know About Pandemic Flu Worker Protection and Infection Control for Pandemic Flu An influenza pandemic will have a huge impact on workplaces throughout the United States.
Factsheet #2 What Workers Need to Know About Pandemic Flu Worker Protection and Infection Control for Pandemic Flu An influenza pandemic will have a huge impact on workplaces throughout the United States.
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis. Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis. Mycobacteria. Introduction to the pathogen Transmission
 Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis
 Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
Transmission and Pathogenesis of Tuberculosis Adithya Cattamanchi MD, MAS Associate Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Slides adapted from James Watts, Phil Hopewell Transmission
New Standards for an Old Disease:
 New Standards for an Old Disease: Practical Implications of the TB Standards TB Prevention and Control Saskatchewan September 16, 2015 Practical Implications of the TB Standards Learning Objectives At
New Standards for an Old Disease: Practical Implications of the TB Standards TB Prevention and Control Saskatchewan September 16, 2015 Practical Implications of the TB Standards Learning Objectives At
HEALTHWEST PROCEDURE. No Revised by: Effective: December 1, 1995 Revised: April 19, 2017 Environment of Care Committee
 HEALTHWEST PROCEDURE Revised by: Effective: December 1, 1995 Revised: April 19, 2017 Environment of Care Committee Approved by: Subject: Tuberculosis Infection Control Julia Rupp, Executive Director I.
HEALTHWEST PROCEDURE Revised by: Effective: December 1, 1995 Revised: April 19, 2017 Environment of Care Committee Approved by: Subject: Tuberculosis Infection Control Julia Rupp, Executive Director I.
Respirators: One Way of Protecting Workers Against Pandemic Flu
 Factsheet #3 What Workers Need to Know About Pandemic Flu Respirators: One Way of Protecting Workers Against Pandemic Flu When a person infected with pandemic flu coughs, sneezes, or talks, very small
Factsheet #3 What Workers Need to Know About Pandemic Flu Respirators: One Way of Protecting Workers Against Pandemic Flu When a person infected with pandemic flu coughs, sneezes, or talks, very small
Minutes required for removal efficiency ACH 99% 99.9% <1 1
 List Major Errata in Order Importance from the Guidelines for Preventing the Transmission Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Health-care Settings, 2005 http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5417.pdf. Major Errata
List Major Errata in Order Importance from the Guidelines for Preventing the Transmission Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Health-care Settings, 2005 http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5417.pdf. Major Errata
CDC Health Advisory 04/29/2009
 H1N1 (Swine Flu) is a sub-type of Influenza A. Wexford Labs disinfectants are effective against Influenza A. Current CDC Recommendations for Environmental Control in the Healthcare Setting: CDC Health
H1N1 (Swine Flu) is a sub-type of Influenza A. Wexford Labs disinfectants are effective against Influenza A. Current CDC Recommendations for Environmental Control in the Healthcare Setting: CDC Health
Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016. Table of Contents
 Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016 Table of Contents Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016... 1 What is Tuberculosis?... 2 Any required definitions/explanations... 2 NHFT... 2 Tuberculosis (TB)... 3 Latent TB...
Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016 Table of Contents Tuberculosis Procedure ICPr016... 1 What is Tuberculosis?... 2 Any required definitions/explanations... 2 NHFT... 2 Tuberculosis (TB)... 3 Latent TB...
Intensified TB case finding among PLHIV and vulnerable population Identifying contacts Gunta Kirvelaite
 Intensified TB case finding among PLHIV and vulnerable population Identifying contacts Gunta Kirvelaite Riga East Clinical hospital, Centre for tuberculosis and lung diseases. Head of outpatient department.
Intensified TB case finding among PLHIV and vulnerable population Identifying contacts Gunta Kirvelaite Riga East Clinical hospital, Centre for tuberculosis and lung diseases. Head of outpatient department.
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB)
 Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Chapter 7 Tuberculosis (TB) TB infection vs. TB disease Information about TB TB skin testing Active TB disease TB risk factors Role of Peel Public Health in TB prevention and control Environmental and
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
TB the basics. (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ)
 TB the basics (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ) Question 1 The scientist who discovered M. tuberculosis was: A: Louis Pasteur B: Robert Koch C: Jean-Antoine Villemin D: Calmette and Guerin Question 2
TB the basics (Dr) Margaret (DHA) and John (INZ) Question 1 The scientist who discovered M. tuberculosis was: A: Louis Pasteur B: Robert Koch C: Jean-Antoine Villemin D: Calmette and Guerin Question 2
Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard
 Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard Welcome to Infection Prevention This course is intended to present a brief overview of various infection control topics.
Infection Prevention To navigate, click the Page Up or Page Down keys on your keyboard Welcome to Infection Prevention This course is intended to present a brief overview of various infection control topics.
TB Contact Investigation
 Ann Raftery, RN, PHN, MS Curry International TB Center Overview Contact investigation as a core TB control and elimination activity Components of TB Contact Investigation TB Control Priority Strategies.
Ann Raftery, RN, PHN, MS Curry International TB Center Overview Contact investigation as a core TB control and elimination activity Components of TB Contact Investigation TB Control Priority Strategies.
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010 TB Pathogenesis and Transmission Lynn Horvath, MD; TCID December 1, 2010 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn L. Horvath, MD, FACP, FIDSA Associate Professor
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010 TB Pathogenesis and Transmission Lynn Horvath, MD; TCID December 1, 2010 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn L. Horvath, MD, FACP, FIDSA Associate Professor
TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of
 TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene TODAY S PRESENTATION Epidemiology
TUBERCULOSIS IN HEALTHCARE SETTINGS Diana M. Nilsen, MD, FCCP Director of Medical Affairs, Bureau of Tuberculosis Control New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene TODAY S PRESENTATION Epidemiology
July 13, 1990 / 39(RR-10);7-20
 July 13, 1990 / 39(RR-10);7-20 Prevention and Control of Tuberculosis in Facilities Providing Long-Term Care to the Elderly Recommendations of the Advisory Committee for Elimination of Tuberculosis These
July 13, 1990 / 39(RR-10);7-20 Prevention and Control of Tuberculosis in Facilities Providing Long-Term Care to the Elderly Recommendations of the Advisory Committee for Elimination of Tuberculosis These
New Tuberculosis Guidelines. Jason Stout, MD, MHS
 New Tuberculosis Guidelines Jason Stout, MD, MHS Two New Sets of Guidelines Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Clinical Infectious Diseases 2016; 63(7): e147-e195 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Adults
New Tuberculosis Guidelines Jason Stout, MD, MHS Two New Sets of Guidelines Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis Clinical Infectious Diseases 2016; 63(7): e147-e195 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis in Adults
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis
 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
결핵 전남대학교병원 호흡기내과 권용수
 결핵 전남대학교병원호흡기내과 권용수 History of TB Skeletal TB Prehistoric humans in 8000 B.C. Egyptian mummies in 2500-1000 B.C. From Tuberculosis 2007. Classification of Mycobacterial Species M. tuberculosis complex
결핵 전남대학교병원호흡기내과 권용수 History of TB Skeletal TB Prehistoric humans in 8000 B.C. Egyptian mummies in 2500-1000 B.C. From Tuberculosis 2007. Classification of Mycobacterial Species M. tuberculosis complex
Contact Investigation
 Tuberculosis Ann Raftery, RN, PHN, MSc GHS Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: Describe the criteria used and method for determining the infectious period
Tuberculosis Ann Raftery, RN, PHN, MSc GHS Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session, participants will be able to: Describe the criteria used and method for determining the infectious period
Pandemic Flu: Non-pharmaceutical Public Health Interventions. Denise Cardo,, M.D. Director Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion
 Pandemic Flu: Non-pharmaceutical Public Health Interventions Denise Cardo,, M.D. Director Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Pandemic Influenza Planning Challenges Cannot predict from where or when
Pandemic Flu: Non-pharmaceutical Public Health Interventions Denise Cardo,, M.D. Director Division of Healthcare Quality Promotion Pandemic Influenza Planning Challenges Cannot predict from where or when
Learning Objectives: Case 1 11/12/2015. Tuberculosis: Focus on Transmission and Pathogenesis. TB: Some Important Terms
 A 11/12/2015 Learning Objectives: Tuberculosis: Focus on Transmission and Pathogenesis Henry Fraimow, M ivision of Infectious iseases ooper School of Medicine at Rowan University Medical onsultant, Southern
A 11/12/2015 Learning Objectives: Tuberculosis: Focus on Transmission and Pathogenesis Henry Fraimow, M ivision of Infectious iseases ooper School of Medicine at Rowan University Medical onsultant, Southern
FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF JUVENILE JUSTICE DETENTION SERVICES FACILITY MEDICAL POLICIES
 FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF JUVENILE JUSTICE DETENTION SERVICES FACILITY MEDICAL POLICIES Superintendent Signature Designated Health Authority Signature Effective Date: November 1, 2016 Subject: TUBERCULOSIS
FLORIDA DEPARTMENT OF JUVENILE JUSTICE DETENTION SERVICES FACILITY MEDICAL POLICIES Superintendent Signature Designated Health Authority Signature Effective Date: November 1, 2016 Subject: TUBERCULOSIS
Respiratory Protection and Swine Influenza
 PAGE 1 TechUpdate Respiratory Protection and Swine Influenza Frequently asked Questions The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have recently issued
PAGE 1 TechUpdate Respiratory Protection and Swine Influenza Frequently asked Questions The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have recently issued
Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia
 Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia Philadelphia TB Control Program Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Philadelphia TB Control Program Health Information Portal Website: hip.phila.gov Contains Information On» Disease
Tuberculosis & Refugees in Philadelphia Philadelphia TB Control Program Daniel P. Dohony, MPH Philadelphia TB Control Program Health Information Portal Website: hip.phila.gov Contains Information On» Disease
Using Xpert to discontinue airborne isolation The Consensus Statement
 Using Xpert to discontinue airborne isolation The Consensus Statement Neha Shah, MD MPH Tuberculosis Control California Department of Public Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention NAR February
Using Xpert to discontinue airborne isolation The Consensus Statement Neha Shah, MD MPH Tuberculosis Control California Department of Public Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention NAR February
PANDEMIC INFLUENZA PHASE 6 INFECTION CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS TEMPLATE
 PANDEMIC INFLUENZA PHASE 6 INFECTION CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS TEMPLATE (Updated September 7, 2006) Information and concept courtesy Of the San Francisco Public Health Department Table of Contents Pandemic
PANDEMIC INFLUENZA PHASE 6 INFECTION CONTROL RECOMMENDATIONS TEMPLATE (Updated September 7, 2006) Information and concept courtesy Of the San Francisco Public Health Department Table of Contents Pandemic
Chapter 4 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Disease
 Chapter 4 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Disease Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 75 Introduction.... 77 Medical Evaluation.......................................................... 78 Chapter Summary...
Chapter 4 Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Disease Table of Contents Chapter Objectives.... 75 Introduction.... 77 Medical Evaluation.......................................................... 78 Chapter Summary...
Modes of Transmission of Influenza A H1N1v and Transmission Based Precautions (TBPs)
 Modes of Transmission of Influenza A H1N1v and Transmission Based Precautions (TBPs) 8 January 2010 Version: 2.0 The information contained within this document is for the use of clinical and public health
Modes of Transmission of Influenza A H1N1v and Transmission Based Precautions (TBPs) 8 January 2010 Version: 2.0 The information contained within this document is for the use of clinical and public health
MEMORANDUM. Re: Guidance for follow-up of newly-arrived individual with Class B1 Tuberculosis Pulmonary Tuberculosis, no treatment
 MEMORANDUM To: From: Local Board of Health John Bernardo, MD, Tuberculosis Medical Officer Jennifer Cochran, MPH, Division Director Division of Global Populations and Infectious Disease Prevention Bureau
MEMORANDUM To: From: Local Board of Health John Bernardo, MD, Tuberculosis Medical Officer Jennifer Cochran, MPH, Division Director Division of Global Populations and Infectious Disease Prevention Bureau
Tuberculosis Intensive
 Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department
 Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education 2017 Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department Objectives After you complete this Computer-Based Learning (CBL) module, you should be able
Infection Prevention and Control Annual Education 2017 Authored by: Infection Prevention and Control Department Objectives After you complete this Computer-Based Learning (CBL) module, you should be able
Primary Care and TB Control Dr Helen Booth Consultant Thoracic Physician, UCLH Clinical Lead, Integrated TB NCL-Service
 Primary Care and TB Control Dr Helen Booth Consultant Thoracic Physician, UCLH Clinical Lead, Integrated TB NCL-Service North Central London TB Service TBService@nhs.net After Action Review Could we have
Primary Care and TB Control Dr Helen Booth Consultant Thoracic Physician, UCLH Clinical Lead, Integrated TB NCL-Service North Central London TB Service TBService@nhs.net After Action Review Could we have
Improving Tuberculosis Infection Control
 Improving Tuberculosis Infection Control the implementation of HIV/TB collaborative activities in selected African countries Addis Ababa, Nov 13-14, 2008 Nthabiseng Ntlama Deputy TB Program Manager Outline
Improving Tuberculosis Infection Control the implementation of HIV/TB collaborative activities in selected African countries Addis Ababa, Nov 13-14, 2008 Nthabiseng Ntlama Deputy TB Program Manager Outline
AEROSOL TRANSMISSIBLE DISEASE STANDARD. Riverside County Department of Public Health 2010
 AEROSOL TRANSMISSIBLE DISEASE STANDARD Riverside County Department of Public Health 2010 1 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation participants will be able to: 1. Identify at least
AEROSOL TRANSMISSIBLE DISEASE STANDARD Riverside County Department of Public Health 2010 1 Learning Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation participants will be able to: 1. Identify at least
Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB)
 Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB) Information Leaflet For Patients and Visitors Please follow this guidance from the Infection Prevention and Control Team What is Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB)? Pulmonary/respiratory
Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB) Information Leaflet For Patients and Visitors Please follow this guidance from the Infection Prevention and Control Team What is Respiratory Tuberculosis (TB)? Pulmonary/respiratory
Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010
 Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010 What is Latent TB Infection (LTBI)? Traci Hadley, RN October 5, 2010 LTBI or TB Disease? Presented by : Traci Hadley, RN
Understanding and Managing Latent TB Infection Arnold, Missouri October 5, 2010 What is Latent TB Infection (LTBI)? Traci Hadley, RN October 5, 2010 LTBI or TB Disease? Presented by : Traci Hadley, RN
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk
 Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
Tuberculosis Populations at Risk One-third of the world is infected with TB, an average of one new infection per second Two million people died from tuberculosis in 2010, 1 every 20 seconds TB is the leading
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 7 References Related ACA Standards 4 th Edition Standards for Adult Correctional Institutions 4-4350, 4-4355 These guidelines are based on the recommendations of the American Thoracic Society
PAGE 1 of 7 References Related ACA Standards 4 th Edition Standards for Adult Correctional Institutions 4-4350, 4-4355 These guidelines are based on the recommendations of the American Thoracic Society
Changing TB Isolation Practices: Consensus Statement Concerning the Incorporation of Molecular Testing
 Dave Ashkin, MD, FCCP Changing TB Isolation Practices: Consensus Statement Concerning the Incorporation of Molecular Testing 07/20/2016 1 Dave Ashkin, MD, FCCP Staff TST in Four Hospitals with MDR-TB Outbreak
Dave Ashkin, MD, FCCP Changing TB Isolation Practices: Consensus Statement Concerning the Incorporation of Molecular Testing 07/20/2016 1 Dave Ashkin, MD, FCCP Staff TST in Four Hospitals with MDR-TB Outbreak
Module 3 - TB Infection control incbo
 Module 3 - TB Infection control incbo TB Infectioncontrol Sirkku Grierson Numberof slides from: StopTB TB infection control for national managers, 2009 Varvara Ivanchenko, Paul Jensen: TB IC courses in
Module 3 - TB Infection control incbo TB Infectioncontrol Sirkku Grierson Numberof slides from: StopTB TB infection control for national managers, 2009 Varvara Ivanchenko, Paul Jensen: TB IC courses in
Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel
 Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel 2017 A leading cause of death and increased morbidity for hospitalized ptns Hospitals, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, home care settings Higher rate
Infection Control for Anesthesia Personnel 2017 A leading cause of death and increased morbidity for hospitalized ptns Hospitals, nursing homes, long-term care facilities, home care settings Higher rate
Bulleted Recommendations
 Screening and Isolation Guidance for Healthcare Facilities NOTE: This guidance document has been revised to include the issues surrounding swine influenza. 04/27/09 This document provides bulleted recommendations
Screening and Isolation Guidance for Healthcare Facilities NOTE: This guidance document has been revised to include the issues surrounding swine influenza. 04/27/09 This document provides bulleted recommendations
Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of. Latent Tuberculosis. Infection and Tuberculosis Disease
 Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
Self-Study Study Modules on Tuberculosis Targeted Testing and the Diagnosis of Latent Tuberculosis Infection and Tuberculosis Disease 1 Module 3: Objectives At completion of this module, learners will
