HAS DONOR PRIORITIZATION OF HIV/AIDS CONTROL DISPLACED AID FOR OTHER HEALTH CAUSES?
|
|
|
- Edith Shaw
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HAS DONOR PRIORITIZATION OF HIV/AIDS CONTROL DISPLACED AID FOR OTHER HEALTH CAUSES? DRAFT ONLY: PLEASE DO NOT CITE WITHOUT PERMISSION OF THE AUTHOR Jeremy Shiffman, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Public Administration The Maxwell School of Syracuse University Syracuse, NY Paper to be presented at 2006 Population Association of America Conference February 28 th, 2006
2 It is an unfortunate reality that budgeting procedures too often may mean that new funds for HIV and AIDS can draw resources away from other activities, either at country level, or at donor level. Therefore, all parties need to commit themselves to the principle that additional funding for HIV and AIDS is to be used for additional spending, otherwise displacement is inevitable to the detriment of overall development. -- from 2004 UNAIDS Report 1 Introduction As attention by bilateral and multilateral donors to the prevention, control and treatment of HIV/AIDS increases, advocates for other health issues affecting the poor have expressed concern that this prioritization may have adversely affected funding for and attention to other health and population causes. Such concerns have been particularly prominent among reproductive health and population scholars and advocates, 2 although not limited to this group. Those involved with tobacco control, tuberculosis and child immunization, among other causes, have also expressed the same concern. 3 Even organizations dedicated to HIV/AIDS prevention and control have acknowledged a potential problem, as the excerpt above from a 2004 UNAIDS report indicates. A number of analysts have suggested that such competition and funding for scarce resources is counter-productive, 4 arguing that interventions to address HIV/AIDS such as condom promotion can serve a variety of health causes, champions of different issues ought to work collaboratively, and the deeper aim should be to build health systems capacities so that all major health problems of the poor can be addressed. 5 Collaboration has not been so easy to generate, however, as networks of advocates have mobilized around specific health causes that have competed for scarce donor funding, resources that have been allocated based not just on need but also on political considerations.
3 While many concerns have been raised, the precise effects of donor prioritization of HIV/AIDS prevention and control on donor funding for other health causes have not been examined. In this paper I consider funding for health and population from major bilateral and multilateral donors over the past decade in an initial attempt to investigate this issue. I take no normative position on how donor health and population resources should be allocated, save to note that there are very good reasons each of the causes discussed in this paper deserve significantly greater attention than they receive, including HIV/AIDS. This research, rather, has empirical rather than normative aims. Presumably, though, empirical conclusions from this paper and other research on donor funding may be useful for future policy decision-making. Background A number of dynamics may contribute to displacement. Donors have hard-budget constraints. If a donor chooses to augment funding for one cause, it must decrease funding for other causes unless it can secure additional resources. 6 Also, bandwagon effects may occur among donors. As influential donors prioritize a particular cause, others may follow, leading to the neglect of other issues. 7 In addition, national health systems must manage donor resources, diverting scarce capacity away from other causes. 8 On the other hand, if some donors prioritize one cause, others may divert resources to additional issues. National authorities may do the same, a fungibility effect. 9 Also, funds provided for a particular cause may build national infrastructure that can support other causes, as advocates of global polio eradication have argued concerning vaccination for other diseases. In addition, global attention to a major health issue such as HIV/AIDS may have helped galvanize international support for the general issue of addressing the health causes of the poor, benefiting other health issues. 2
4 This paper considers only aggregate donor funding, so one must be cautious in drawing broad inferences on HIV/AIDS displacement effects from these data alone. I do not analyze national health funding so we can draw no conclusions about donor effects on country-level resources. Also, many factors besides HIV/AIDS prioritization influence funding levels for other health causes, including the burden of particular conditions and the advocacy effectiveness of their champions. A complete analysis of HIV/AIDS displacement effects requires controlling for these factors. In addition, the HIV/AIDS agenda may be influencing other health causes in ways not revealed by funding trends, for instance by diverting donor and national human resources toward HIV/AIDS and away from other issues. To investigate displacement fully we need studies of multiple kinds, including examination of the national and bureaucratic politics of aid provision in industrialized countries and of interactions among donors themselves. Methods I calculated the amount of funding for major health and population causes in constant US dollars over the past decade from large bilateral and multilateral donors. I used the Credit Reporting System (CRS) database of the Development Assistance Committee (DAC), an organization that monitors and assesses aid from the world s major bilateral and multilateral donors. I analyzed the years 1992 to 2003 since my primary concern was recent rather than historical priorities, and since records for these but not earlier or later years were relatively comprehensive for each of the donors considered. CRS categories 120 and 130 cover health and population funding, and include contributions to the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria. These categories are divided into fifteen sub-categories. I grouped these sub-categories into six broad health agendas that historically have been prominent among donors: HIV/AIDS prevention and control, reproductive health and population, the control of infectious 3
5 diseases other than HIV/AIDS, basic healthcare, health sector capacity development, and nutrition. 10 I then examined annual funding figures, comparing HIV/AIDS trends with those of the other agendas. CRS data have a number of well-known limitations. I therefore supplemented these data with information from other sources, including UNAIDS reports, U.S. government documents and independent research on donor funding. Among the limitations of the CRS database are that it is incomplete as donors do not report all grants and loans to the DAC; each grant is assigned to only one category according to its primary purpose, even if it includes funding for multiple causes; the CRS records commitments rather than disbursements; and the category for HIV/AIDS also includes funding for the control of other sexually-transmitted diseases. This being said, the CRS in recent years is relatively complete, 11 and there is no reason to believe that reporting omissions vary systematically by cause, so comparisons across causes may be reasonably valid. Also, other studies have concluded that nearly all funding in the STD/HIV category is for HIV/AIDS, and even funding geared toward the control of other sexuallytransmitted diseases is likely to benefit HIV/AIDS prevention and control. 12 Results Total donor funding for health and population The health and population sector has fared well relative to other sectors in recent years. In the mid-1970s health made up approximately 6 percent of total overseas development assistance; by the turn of the millennium it constituted more than 10 percent. 13 Funding for health and population grew three percent per year over the period 1973 to 1998, a trend that continued even during a trough in total aid during the 1990s. 14 4
6 In constant dollar terms, funding for health and population nearly tripled from 1992 to 2003, rising from $2.60 billion to $7.58 billion (figure 1). Figure 1: Total donor funding for health and population in constant dollars Funding (thousands of constant US dollars) 8,000,000 7,000,000 6,000,000 5,000,000 4,000,000 3,000,000 2,000,000 1,000, Year Source: CRS database. United States funding The United States has been by far the largest donor for health and population among DAC countries over the past decade, providing approximately one-third of total bilateral aid. 15 Within US budgets the percentage for HIV/AIDS increased markedly from 1992 to 2003, from 4.8 to 43.1, overtaking all other categories (figure 2). Over the same period, the percentage for population dropped from 55.2 to Funding for health sector capacity development nearly vanished, dropping from 37.0 percent to 1.1 percent. Total US government funding for HIV/AIDS reported in the CRS rose from $26 million in 1992 to $938 million in 2003 (figure 3). One reason for the steep rise may be the initiation of funding for anti-retroviral therapy which began only after Population funding has been stagnant at just over $500 million, while funding for all 5
7 other health causes rose, but at a slower pace than that for HIV/AIDS, from $219 million to $705 million. Covering funding only through 2003, these figures largely exclude the substantial increase for HIV/AIDS that has come from President Bush s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), announced in his January 2003 State of the Union address, a five-year, $15 billion global initiative that includes an additional $9 billion above amounts already pledged. It is highly likely therefore that from 2004 on HIV/AIDS has taken on even greater prominence in US funding for health and population. 6
8 Figure 2: US funding for HIV/AIDS, population and all other causes as a percentage of total US health and population funding Percent of health and population funding HIV/AIDS Population All other causes Year Source: CRS database. Figure 3: US funding for HIV/AIDS, population and all other causes in constant dollars Total funding (thousands of constant US dollars) 1,000, , , , , , , , , , HIV/AIDS Population All other causes Year Source: CRS database. 7
9 Other sources also point to the increasing prominence of HIV/AIDS in US health and population budgets. The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) reported an increase in its annual budget for HIV/AIDS from $95.7 million in 1992 to $795.0 million in In 1997 HIV/AIDS constituted only 13 percent of USAID s health and population budget and population 40 percent. 17 By fiscal year 2002 HIV/AIDS comprised 30 percent of the budget, surpassing population s share, which had dropped to 27 percent. 18 A Kaiser Foundation analysis calculated US government commitments of $1,490 million for HIV/AIDS for resource-poor settings in fiscal year 2003, an increase from $1,196 million in It estimated commitments of $2,253 million for 2004, channelled primarily through USAID and the National Institutes for Health. Funding from all donors While HIV/AIDS has been ascendant in US budgets, it never exceeded more than 21.7 percent of total health and population funding from the rest of the world s major donors over the period 1992 to 2003, and in half these years made up less than seven percent (table 1). Population funding also has been less significant among other donors than the United States, making up less than twenty percent every year except 1992 and Health sector capacity development has been central for other donors, exceeding 30 percent of total funding every year except one, and in 2003 standing at 36.9 percent. 8
10 Table 1: Percentage of health and population funding for six causes from all donors other than the United States reporting to the CRS Year HIV/AIDS Population Basic Health care Health sector capacity Infectious disease control Nutrition * * Source: CRS database. * A small number of grants reported in the CRS for 1997 and 2000 were not classified in any of the subcategories that constitute the six health causes reported here; therefore the totals are slightly less than 100 percent. Total When we consider all donors including the United States, the HIV/AIDS and population agendas are less prominent than when the United States is considered alone (figure 4). HIV/AIDS has grown in percentage of funding across time, but still only comprises 23.8 percent of the total, very close to population s share at 23.1 percent. All other causes constitute 53.1 percent of the total, down from 62.8 percent in 1992 but still more than half the total. Among the six agendas, health sector capacity development receives the greatest share at 26.6 percent. In terms of aggregate amounts in constant dollars (figure 5), all three categories showed significant increases over the years 1992 to Funding for all other health causes increased 146 percent to $4.03 billion. Funding for population rose 119 percent to $1.75 billion, other donors compensating for the declining share for population in US budgets. HIV/AIDS showed the sharpest rise at 961 percent to $1.80 billion. A UNAIDS analysis also reported a dramatic rise in HIV/AIDS funding (although noting 9
11 that amounts remain far from adequate) from $300 million in 1996 to $1.7 billion in
12 Figure 4: Funding from all donors for HIV/AIDS, population and all other causes as a percentage of total donor health and population funding Percent of health and population funding HIV/AIDS Population All other health causes Year Source: CRS database. Figure 5: Funding from all donors for HIV/AIDS, population and all other causes in constant dollars 4,500,000 4,000,000 Total funding (thousands of constant US dollars) 3,500,000 3,000,000 2,500,000 2,000,000 1,500,000 1,000, , HIV/AIDS Population All other health causes Year Source: CRS database. 11
13 Discussion HIV/AIDS prioritization by the United States government, the largest bilateral donor for health and population, may have displaced its own funding for other causes in this sector. CRS data indicate that as of 2003 HIV/AIDS comprised nearly half of all U.S. government funding for health and population, and because of PEPFAR, as of 2006 likely constitutes much more than that. Meanwhile, population dropped markedly in percentage terms and stagnated in aggregate amounts over the past decade, while funding for health sector capacity development, a cause formerly prominent among U.S. priorities, nearly vanished. When all donors reporting to the Development Assistance Committee are considered, however, HIV/AIDS possible displacement effects are less apparent. One reason is that health is presently a favored sector for foreign aid, donor resources for health and population having increased significantly in recent years, benefitting most of the health agendas considered in this paper. Also, HIV/AIDS has never figured as prominently in the agendas of other donors as it has in the U.S. agenda. Overall HIV/AIDS occupies a large but not dominant position when all donor aid is considered. This being said, discerning HIV/AIDS displacement effects is a complex and under-researched issue, and considerable additional investigation will be necessary to explore this issue in full. Donor funding is only one among many indicators of priority, and examining this question requires research beyond analysis of aid providers alone, including inquiries into the politics of health in developing countries. In particular, there is a need to examine the issue at the country level, where flows of donor funding for HIV/AIDS prevention and control may be overwhelming health systems targeted by bilateral and multilateral donors. This effect may be even stronger in recent years as 12
14 several new well-financed global programs focused on HIV/AIDS have emerged, including PEPFAR and the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria. A study of aggregate donor funding for health and population reveals broad trends, but is only one dimension of a much larger question concerning displacement effects in the health and population sector. 13
15 Endnotes 1 UNAIDS, 2004 Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic (Geneva: UNAIDS, 2004). 2 A. Yazbeck, Real and perceived threats to reproductive health: a way forward, Reproductive Health Matters 12 (2004): 25-34; M. Berer, HIV/AIDS, sexual and reproductive health: intersections and implications for national programmes, Health Policy and Planning 19 (2004): i62-i70; B. Crossette, Reproductive Health and the Millennium Development Goals: The Missing Link, Report commissioned by the Hewlett Foundation (Hewlett Foundation, 2004). 3 S. Furjuoh, Traffic-related injury prevention interventions for low-income countries, Injury Control and Safety Promotion 10 (2003): ; A. Levin, S. Ram and M. Kaddar, The impact of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative on the financing of routine immunization: case studies in Bangladesh, Cote d Ivoire, and Morocco, Bulletin of the World Health Organization 80 (2002): M.C. Raviglione and A. Pio, Evolution of WHO policies for tuberculosis control, , Lancet 359 (2002): M. Berer, HIV/AIDS, sexual and reproductive health ; B. Crossette, Reproductive Health and the Millennium Development Goals. 5 D. Banerji, Alma-Ata showed the route to effective resource allocations for health, Bulletin of the World Health Organization 82 (2004): S. Feeny and M. McGillivray, Modelling inter-temporal aid allocation: A new application with an emphasis on Papua New Guinea, Oxford Development Studies 32 (2004): I. Périn and A. Attaran, Trading ideology for dialogue: An opportunity to fix international aid for health? Lancet 361 (2003): K. Caines and L. Lush, Impact of Public-private Partnerships Addressing Access to Pharmaceuticals in Selected Low and Middle Income Countries (Geneva: Initiative on Public-Private Partnerships for Health, 2004); R. Brugha, M. Donoghue, M. Starling, P. Ndubani, F. Ssengooba, B. Fernandes, and G. Walt, The Global Fund: Managing great expectations, Lancet, 364 (2004): C. Waddington, Does earmarked donor funding make it more or less likely that developing countries will allocate their resources towards programmes that yield the greatest health benefits? Bulletin of the World Health Organization 82 (2004): ; S. Devarajan and V. Swaroop, The Implications of Foreign Aid Fungibility for Development Assistance (Washington, DC: World Bank, 1998). 14
16 10 HIV/AIDS is purpose code (STD control including HIV/AIDS); reproductive health and population are purpose codes (population policy and administrative management), (reproductive health care), (family planning) and (personnel development for population and reproductive health); infectious diseases is purpose code (infectious disease control); basic health care is purpose codes (basic health care), (basic health infrastructure), (health education) and (health personnel development); health sector capacity development is purpose codes (health policy and administrative management), (medical education/training), (medical research) and (medical servces); and nutrition is purpose code (basic nutrition). 11 Development Assistance Committee, Comparison of Amounts Reported to the CRS and to the DAC by Sector, Year 2002 (Paris: Development Assistance Committee, 2002). 12 OECD and UNAIDS, Analysis of AID in Support of HIV/AIDS Control, (OECD and UNAIDS, 2004); A. Attaran, A and J. Sachs, Defining and refining international donor support for combating the AIDS pandemic, Lancet, 357 (2001): Development Assistance Committee data file on aid to health. Available at 14 OECD, Recent Trends in Offical Development Assistance to Health (Paris: OECD, 2000). 15 OECD, Recent Trends in Offical Development Assistance to Health. 16 USAID. Data available at: 17 USAID. Data available at: 18 USAID. Data available at: 19 T. Summers and J. Kates, Global Funding for HIV/AIDS in Resource Poor Settings (Menlo Park, CA: The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation, 2003). 20 UNAIDS, 2004 Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic. 15
Financing the Response to AIDS in Low- and Middle- Income Countries: International Assistance from Donor Governments in 2010
 Financing the Response to AIDS in Low- and Middle- Income Countries: International Assistance from Donor Governments in 2010 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation), Adam Wexler (Kaiser Family
Financing the Response to AIDS in Low- and Middle- Income Countries: International Assistance from Donor Governments in 2010 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation), Adam Wexler (Kaiser Family
Key Highlights continued
 Financing the Response to AIDS in Low- and Middle- Income Countries: International Assistance from the G8, European Commission and Other Donor Governments in 2009 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family
Financing the Response to AIDS in Low- and Middle- Income Countries: International Assistance from the G8, European Commission and Other Donor Governments in 2009 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family
Financing the Response to HIV/AIDS in Low and Middle Income Countries: Funding for HIV/AIDS from the G7 and the European Commission
 Financing the Response to HIV/AIDS in Low and Middle Income Countries: Funding for HIV/AIDS from the G7 and the European Commission Presented at: Post G8 Briefing: Future Financing To Address The Global
Financing the Response to HIV/AIDS in Low and Middle Income Countries: Funding for HIV/AIDS from the G7 and the European Commission Presented at: Post G8 Briefing: Future Financing To Address The Global
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RS21181 Updated February 23, 2005 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web HIV/AIDS International Programs: Appropriations, FY2003-FY2006 Raymond W. Copson Specialist in International
Order Code RS21181 Updated February 23, 2005 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web HIV/AIDS International Programs: Appropriations, FY2003-FY2006 Raymond W. Copson Specialist in International
Okinawa, Toyako, and Beyond: Progress on Health and Development
 Okinawa, Toyako, and Beyond: Progress on Health and Development Prof. Michel D. Kazatchkine Executive Director The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria United Nations University, Tokyo,
Okinawa, Toyako, and Beyond: Progress on Health and Development Prof. Michel D. Kazatchkine Executive Director The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria United Nations University, Tokyo,
Renewing Momentum in the fight against HIV/AIDS
 2011 marks 30 years since the first cases of AIDS were documented and the world has made incredible progress in its efforts to understand, prevent and treat this pandemic. Progress has been particularly
2011 marks 30 years since the first cases of AIDS were documented and the world has made incredible progress in its efforts to understand, prevent and treat this pandemic. Progress has been particularly
Financing the Response to AIDS in Low- and Middle- Income Countries: International Assistance from Donor Governments in 2011
 Financing the Response to AIDS in Low- and Middle- Income Countries: International Assistance from Donor Governments in 2011 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation), Adam Wexler (Kaiser Family
Financing the Response to AIDS in Low- and Middle- Income Countries: International Assistance from Donor Governments in 2011 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation), Adam Wexler (Kaiser Family
Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation), Eric Lief (The Stimson Center), Carlos Avila (UNAIDS).
 Financing the response to AIDS in low- and middleincome countries: International assistance from the G8, European Commission and other donor Governments in 2008 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation),
Financing the response to AIDS in low- and middleincome countries: International assistance from the G8, European Commission and other donor Governments in 2008 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation),
Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation), José-Antonio Izazola (UNAIDS), Eric Lief (CSIS).
 Financing the response to AIDS in low- and middleincome countries: International assistance from the G8, European Commission and other donor Governments, 2006 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation),
Financing the response to AIDS in low- and middleincome countries: International assistance from the G8, European Commission and other donor Governments, 2006 Authors: Jennifer Kates (Kaiser Family Foundation),
Overview of development assistance for health trends
 Chapter 1: Overview of development assistance for health trends Since the inception of the first edition of Financing Global Health in 29, IHME has released up-to-date annual estimates of DAH from 199
Chapter 1: Overview of development assistance for health trends Since the inception of the first edition of Financing Global Health in 29, IHME has released up-to-date annual estimates of DAH from 199
Donor Government Funding for HIV in Low- and Middle-Income Countries in 2016
 REPORT Donor Government Funding for HIV in Low- and Middle-Income Countries in 2016 July 2017 Prepared by: Jen Kates & Adam Wexler Kaiser Family Foundation and Eric Lief Consultant and UNAIDS Donor government
REPORT Donor Government Funding for HIV in Low- and Middle-Income Countries in 2016 July 2017 Prepared by: Jen Kates & Adam Wexler Kaiser Family Foundation and Eric Lief Consultant and UNAIDS Donor government
Donor Government Funding for HIV in Low- and Middle-Income Countries in 2017
 July 2018 Donor Government Funding for HIV in Low- and Middle-Income Countries in 2017 Jen Kates & Adam Wexler Kaiser Family Foundation and Eric Lief Georgetown University, Center for Global Health Science
July 2018 Donor Government Funding for HIV in Low- and Middle-Income Countries in 2017 Jen Kates & Adam Wexler Kaiser Family Foundation and Eric Lief Georgetown University, Center for Global Health Science
Financial Resources for HIV: PEPFAR s Contributions to the Global Scale-up of Treatment
 Financial Resources for HIV: PEPFAR s Contributions to the Global Scale-up of Treatment Joint WHO & UNAIDS Consultation with Pharmaceuticals and Stakeholders November 05 2012 Lara Stabinski, MD, MPH Medical
Financial Resources for HIV: PEPFAR s Contributions to the Global Scale-up of Treatment Joint WHO & UNAIDS Consultation with Pharmaceuticals and Stakeholders November 05 2012 Lara Stabinski, MD, MPH Medical
CRS Report for Congress
 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21181 Updated May 2, 2003 HIV/AIDS International Programs: Appropriations, FY2002 - FY2004 Raymond W. Copson Specialist in International
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21181 Updated May 2, 2003 HIV/AIDS International Programs: Appropriations, FY2002 - FY2004 Raymond W. Copson Specialist in International
DEVELOPMENT. The European Union confronts HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis. A comprehensive strategy for the new millennium EUROPEAN COMMISSION
 DEVELOPMENT The European Union confronts HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis A comprehensive strategy for the new millennium EUROPEAN COMMISSION DE 121 FEB 2004 A global challenge Every minute, 11 people
DEVELOPMENT The European Union confronts HIV/AIDS, malaria and tuberculosis A comprehensive strategy for the new millennium EUROPEAN COMMISSION DE 121 FEB 2004 A global challenge Every minute, 11 people
The U.S. President s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR)
 The U.S. President s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) Although the U.S. has been involved in efforts to address the global AIDS crisis since the mid-1980s, the creation of the President s Emergency
The U.S. President s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) Although the U.S. has been involved in efforts to address the global AIDS crisis since the mid-1980s, the creation of the President s Emergency
World Health Organization. A Sustainable Health Sector
 World Health Organization A Sustainable Health Sector Response to HIV Global Health Sector Strategy for HIV/AIDS 2011-2015 (DRAFT OUTLINE FOR CONSULTATION) Version 2.1 15 July 2010 15 July 2010 1 GLOBAL
World Health Organization A Sustainable Health Sector Response to HIV Global Health Sector Strategy for HIV/AIDS 2011-2015 (DRAFT OUTLINE FOR CONSULTATION) Version 2.1 15 July 2010 15 July 2010 1 GLOBAL
FAO of the UN, WHO and OIE with the collaboration of UNSIC and UNICEF. Background Paper
 FAO of the UN, WHO and OIE with the collaboration of UNSIC and UNICEF Background Paper 3.4 d Ensuring intergovernmental support to national and other stakeholders for integrated action to tackle HPAI and
FAO of the UN, WHO and OIE with the collaboration of UNSIC and UNICEF Background Paper 3.4 d Ensuring intergovernmental support to national and other stakeholders for integrated action to tackle HPAI and
Generation of political priority for global health initiatives:
 Generation of political priority for global health initiatives: A research project, framework, and case study of maternal mortality* Jeremy Shiffman, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Public Administration
Generation of political priority for global health initiatives: A research project, framework, and case study of maternal mortality* Jeremy Shiffman, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Public Administration
The road towards universal access
 The road towards universal access JAN 2006 Issues Paper Requests... that the UNAIDS Secretariat and its Cosponsors assist in facilitating inclusive, country-driven processes, including consultations with
The road towards universal access JAN 2006 Issues Paper Requests... that the UNAIDS Secretariat and its Cosponsors assist in facilitating inclusive, country-driven processes, including consultations with
Post-2015: Innovative Financing of HIV/AIDS. Travis Mitchell Economic Affairs Division
 Post-2015: Innovative Financing of HIV/AIDS Travis Mitchell Economic Affairs Division High Burden (HIV/AIDS) Low Income countries will remain dependent on external funding for decades, creating major financial
Post-2015: Innovative Financing of HIV/AIDS Travis Mitchell Economic Affairs Division High Burden (HIV/AIDS) Low Income countries will remain dependent on external funding for decades, creating major financial
Overview of development assistance for health trends
 Chapter 1 Overview of development assistance for health trends This chapter uses estimates of development assistance for health (DAH) produced by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME)
Chapter 1 Overview of development assistance for health trends This chapter uses estimates of development assistance for health (DAH) produced by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME)
AUGUST 200 JULY Reauthorization of PEPFAR, The United States Leadership Against HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria Act:
 Reauthorization of PEPFAR, The United States Leadership Against HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria Act: JULY 2008 AUGUST 200 A Side-by-Side Comparison to Current Law Reauthorization of PEPFAR, The United
Reauthorization of PEPFAR, The United States Leadership Against HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria Act: JULY 2008 AUGUST 200 A Side-by-Side Comparison to Current Law Reauthorization of PEPFAR, The United
1. The World Bank-GAVI Partnership and the Purpose of the Review
 1. The World Bank-GAVI Partnership and the Purpose of the Review 1.1 The new World Bank Group strategy makes a strong case for an expanded World Bank Group role in global and regional dialogue and collective
1. The World Bank-GAVI Partnership and the Purpose of the Review 1.1 The new World Bank Group strategy makes a strong case for an expanded World Bank Group role in global and regional dialogue and collective
IMPACT OF DEVELOPMENT ASSISTANCE FOR HEALTH ON COUNTRY SPENDING
 CHAPTER 4: IMPACT OF DEVELOPMENT ASSISTANCE FOR HEALTH ON COUNTRY SPENDING As external health aid has grown in importance in recent years, global health experts have discussed the role that development
CHAPTER 4: IMPACT OF DEVELOPMENT ASSISTANCE FOR HEALTH ON COUNTRY SPENDING As external health aid has grown in importance in recent years, global health experts have discussed the role that development
Monitoring of the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals
 SIXTY-THIRD WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY WHA63.15 Agenda item 11.4 21 May 2010 Monitoring of the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals The Sixty-third World Health Assembly, Having considered
SIXTY-THIRD WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY WHA63.15 Agenda item 11.4 21 May 2010 Monitoring of the achievement of the health-related Millennium Development Goals The Sixty-third World Health Assembly, Having considered
AIDS Funding Landscape in Asia and the Pacific
 Agenda 3: Country experiences and plans towards sustainable AIDS financing AIDS Funding Landscape in Asia and the Pacific J.V.R. Prasada Rao United Nations Secretary-General s Special Envoy for AIDS in
Agenda 3: Country experiences and plans towards sustainable AIDS financing AIDS Funding Landscape in Asia and the Pacific J.V.R. Prasada Rao United Nations Secretary-General s Special Envoy for AIDS in
FISCAL YEAR 2020 APPROPRIATIONS REQUESTS (updated ) USAID Global Health Programs (GHP) and State Department
 FISCAL YEAR 2020 APPROPRIATIONS REQUESTS (updated 2.13.19) Contact: Brian Massa, Senior Manager for Global Health Advocacy, Shot@Life (bmassa@unfoundation.org) USAID Global Health Programs (GHP) and State
FISCAL YEAR 2020 APPROPRIATIONS REQUESTS (updated 2.13.19) Contact: Brian Massa, Senior Manager for Global Health Advocacy, Shot@Life (bmassa@unfoundation.org) USAID Global Health Programs (GHP) and State
The Global Fund & UNICEF Partnership
 The Global Fund & UNICEF Partnership Prof Michel D. Kazatchkine Executive Director UNICEF Executive Board February 9 th, 2011 The Global Fund Millennium Development Goals 1. Eradicate extreme poverty and
The Global Fund & UNICEF Partnership Prof Michel D. Kazatchkine Executive Director UNICEF Executive Board February 9 th, 2011 The Global Fund Millennium Development Goals 1. Eradicate extreme poverty and
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund
 United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/BRA/4 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 9 October 2006 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/BRA/4 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 9 October 2006 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
U.S. Response to the Global Threat of HIV/AIDS: Basic Facts
 U.S. Response to the Global Threat of HIV/AIDS: Basic Facts Alexandra E. Kendall Analyst in Global Health February 22, 2011 Congressional Research Service CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and
U.S. Response to the Global Threat of HIV/AIDS: Basic Facts Alexandra E. Kendall Analyst in Global Health February 22, 2011 Congressional Research Service CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and
CONTRACEPTIVES SAVE LIVES
 CONTRACEPTIVES SAVE LIVES Updated with technical feedback December 2012 Introduction In the developing world, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, progress in reducing maternal and newborn
CONTRACEPTIVES SAVE LIVES Updated with technical feedback December 2012 Introduction In the developing world, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, progress in reducing maternal and newborn
Botswana Private Sector Health Assessment Scope of Work
 Example of a Scope of Work (Botswana) Botswana Private Sector Health Assessment Scope of Work I. BACKGROUND The Republic of Botswana is a stable, democratic country in Southern Africa with an estimated
Example of a Scope of Work (Botswana) Botswana Private Sector Health Assessment Scope of Work I. BACKGROUND The Republic of Botswana is a stable, democratic country in Southern Africa with an estimated
2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS sets world on the Fast-Track to end the epidemic by 2030
 S T A T E M E N T 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS sets world on the Fast-Track to end the epidemic by 2030 World leaders commit to reach three goals and 20 new Fast-Track Targets
S T A T E M E N T 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS sets world on the Fast-Track to end the epidemic by 2030 World leaders commit to reach three goals and 20 new Fast-Track Targets
Ex Post-Evaluation Brief ETHIOPIA: Family Planning and HIV Prevention I and II
 Ex Post-Evaluation Brief ETHIOPIA: Family Planning and HIV Prevention I and II Family Planning and HIV Prevention I and II Programme/Client 1998 65 163, 2002 66 197* Programme executing agency Programming
Ex Post-Evaluation Brief ETHIOPIA: Family Planning and HIV Prevention I and II Family Planning and HIV Prevention I and II Programme/Client 1998 65 163, 2002 66 197* Programme executing agency Programming
10.4 Advocacy, Communication and Social Mobilization Working Group: summary strategic plan,
 10.4 Advocacy, Communication and Social Mobilization Working Group: summary strategic plan, 2006 2015 Introduction A significant scaling-up of advocacy, communication and social mobilization for TB will
10.4 Advocacy, Communication and Social Mobilization Working Group: summary strategic plan, 2006 2015 Introduction A significant scaling-up of advocacy, communication and social mobilization for TB will
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.39 and Add.1)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.39 and Add.1)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.39 and Add.1)]](/thumbs/96/127242235.jpg) United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 7 March 2008 Sixty-second session Agenda item 47 Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.39 and Add.1)]
United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 7 March 2008 Sixty-second session Agenda item 47 Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [without reference to a Main Committee (A/62/L.39 and Add.1)]
Center for Global Health. CDC Global Health Saving Lives Overseas, Protecting Americans at Home
 Center for Global Health CDC Global Health Saving Lives Overseas, Protecting Americans at Home CDC Overview Part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC is the nation s leading public
Center for Global Health CDC Global Health Saving Lives Overseas, Protecting Americans at Home CDC Overview Part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC is the nation s leading public
Global Fund experience on financing the fight against AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria History and lessons learnt Hearings at WHO GCM/NCD working group
 Global Fund experience on financing the fight against AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria History and lessons learnt Hearings at WHO GCM/NCD working group 6 May 2015 Geneva Frederic Goyet, External Relations
Global Fund experience on financing the fight against AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria History and lessons learnt Hearings at WHO GCM/NCD working group 6 May 2015 Geneva Frederic Goyet, External Relations
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/BRA/5 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 26 September
United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/BRA/5 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 26 September
Recipients of development assistance for health
 Chapter 2 Recipients of development assistance for health Both low- and middle-income countries are eligible for development assistance for health (DAH). In addition to income, burden of disease, which
Chapter 2 Recipients of development assistance for health Both low- and middle-income countries are eligible for development assistance for health (DAH). In addition to income, burden of disease, which
Monitoring the Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS & UNGASS indicators
 Monitoring the Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS & UNGASS indicators José Antonio Izazola Chief, AIDS Financing and Economics Division Evidence, Monitoring and Policy Department UNAIDS Assessment 6.3
Monitoring the Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS & UNGASS indicators José Antonio Izazola Chief, AIDS Financing and Economics Division Evidence, Monitoring and Policy Department UNAIDS Assessment 6.3
U.S. Response to the Global Threat of Malaria: Basic Facts
 U.S. Response to the Global Threat of Malaria: Basic Facts Alexandra E. Kendall Analyst in Global Health June 15, 2012 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees of Congress Congressional
U.S. Response to the Global Threat of Malaria: Basic Facts Alexandra E. Kendall Analyst in Global Health June 15, 2012 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees of Congress Congressional
Global Fund Financing of Contraceptives for Reproductive Health Commodity Security
 Global Fund Financing of Contraceptives for Reproductive Health Commodity Security International Conference on Family Planning Kampala, Uganda November 15-18, 2009 Dr. Fidele NGABO Dr NDAHINYUKA Jovith
Global Fund Financing of Contraceptives for Reproductive Health Commodity Security International Conference on Family Planning Kampala, Uganda November 15-18, 2009 Dr. Fidele NGABO Dr NDAHINYUKA Jovith
Working for an International Organization in Public-Private Partnership : The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria
 Working for an International Organization in Public-Private Partnership : The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria Birgit Poniatowski Acting Manager, Board Relations Overview The Global
Working for an International Organization in Public-Private Partnership : The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria Birgit Poniatowski Acting Manager, Board Relations Overview The Global
The Millennium Development Goals. A Snapshot. Prepared by DESA based on its annual Millennium Development Goals Report
 The Millennium Development Goals A Snapshot Prepared by DESA based on its annual Millennium Development Goals Report New York, March 2010 Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger Halve the proportion of people
The Millennium Development Goals A Snapshot Prepared by DESA based on its annual Millennium Development Goals Report New York, March 2010 Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger Halve the proportion of people
Celebrating Life: The U.S. President s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief Annual Report to Congress - Highlights
 Celebrating Life: The U.S. President s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief 2009 Annual Report to Congress - Highlights AIDS. Until recently, many wondered whether prevention, treatment and care could ever make
Celebrating Life: The U.S. President s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief 2009 Annual Report to Congress - Highlights AIDS. Until recently, many wondered whether prevention, treatment and care could ever make
The Strategy Development Process. Global Fund and STOP TB Consultation Istanbul, Turkey 24 July 2015
 The Strategy Development Process Global Fund and STOP TB Consultation Istanbul, Turkey 24 July 2015 Structure of the current 2012-16 Global Fund Strategy The 2012-16 Global Fund Strategy.. States a forward
The Strategy Development Process Global Fund and STOP TB Consultation Istanbul, Turkey 24 July 2015 Structure of the current 2012-16 Global Fund Strategy The 2012-16 Global Fund Strategy.. States a forward
Draft resolution submitted by the President of the General Assembly
 United Nations A/68/L.53 General Assembly Distr.: Limited 7 July 2014 Original: English Sixty-eighth session Agenda item 118 Follow-up to the outcome of the Millennium Summit Draft resolution submitted
United Nations A/68/L.53 General Assembly Distr.: Limited 7 July 2014 Original: English Sixty-eighth session Agenda item 118 Follow-up to the outcome of the Millennium Summit Draft resolution submitted
Bangladesh Resource Mobilization and Sustainability in the HNP Sector
 Bangladesh Resource Mobilization and Sustainability in the HNP Sector Presented by Dr. Khandakar Mosharraf Hossain Minister for Health and Family Welfare Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh
Bangladesh Resource Mobilization and Sustainability in the HNP Sector Presented by Dr. Khandakar Mosharraf Hossain Minister for Health and Family Welfare Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh
Ahimsa Roundtable Cape Town, South Africa June 2015
 A partnership to save lives The critical role of faith-based organizations and faith-inspired communities in Global Health and the fight against AIDS, TB and malaria Ahimsa Roundtable Cape Town, South
A partnership to save lives The critical role of faith-based organizations and faith-inspired communities in Global Health and the fight against AIDS, TB and malaria Ahimsa Roundtable Cape Town, South
Development assistance for HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria by channel
 Chapter 6: Distribution of development assistance for health Building a foundation of knowledge that accurately accounts for the volume of global health funding is crucial, both for those who give aid
Chapter 6: Distribution of development assistance for health Building a foundation of knowledge that accurately accounts for the volume of global health funding is crucial, both for those who give aid
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Coalition C/o American Public Health Association 800 I Street NW Washington, DC,
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Coalition C/o American Public Health Association 800 I Street NW Washington, DC, 20001 202-777-2514 Donald Hoppert, Director of Government Relations, American
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Coalition C/o American Public Health Association 800 I Street NW Washington, DC, 20001 202-777-2514 Donald Hoppert, Director of Government Relations, American
Excerpts from the July 22nd Draft Outcome Document
 The MDGs and Sexual and Reproductive Health E-Bulletin July 28, 2005 Dear Colleagues, As the 2005 World Summit, to be held in September 2005 draws nearer, Family Care International is preparing and distributing
The MDGs and Sexual and Reproductive Health E-Bulletin July 28, 2005 Dear Colleagues, As the 2005 World Summit, to be held in September 2005 draws nearer, Family Care International is preparing and distributing
MEETING OF INTERESTED PARTIES
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION MEETING OF INTERESTED PARTIES GENEVA, 3 TO 7 NOVEMBER 2003 Timetable and annotated agenda Please note that the timetable is indicative and that the timing of discussions may vary
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION MEETING OF INTERESTED PARTIES GENEVA, 3 TO 7 NOVEMBER 2003 Timetable and annotated agenda Please note that the timetable is indicative and that the timing of discussions may vary
Effects of the Global Fund on the health system
 Ukraine: Effects of the Global Fund on the health system Tetyana Semigina 27 Abstract Ukraine has one of the most rapidly growing HIV/AIDS epidemics in Europe, with estimated numbers of people living with
Ukraine: Effects of the Global Fund on the health system Tetyana Semigina 27 Abstract Ukraine has one of the most rapidly growing HIV/AIDS epidemics in Europe, with estimated numbers of people living with
GLOBAL HEALTH SPESIALISERING IN. Austen Davis
 GLOBAL HEALTH SPESIALISERING IN SAMFUNNSMEDISIN 16.02.2016 Austen Davis SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS THE POST 2015 AGENDA Where do we come from? 14 th C quarantine Tropical Health International Health
GLOBAL HEALTH SPESIALISERING IN SAMFUNNSMEDISIN 16.02.2016 Austen Davis SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS THE POST 2015 AGENDA Where do we come from? 14 th C quarantine Tropical Health International Health
Emergency Plan. Pink Ribbon Red. under President. With. screened and Significantly. Commitments: to catalyze. a dynamic, including. of shared.
 Pink Ribbon Red Ribbon Overview Pink Ribbon Red Ribbon is an innovative partnership to leverage public and private investments in global health to combat cervical and breast cancer two of the leading causes
Pink Ribbon Red Ribbon Overview Pink Ribbon Red Ribbon is an innovative partnership to leverage public and private investments in global health to combat cervical and breast cancer two of the leading causes
Toyako Framework for Action on Global Health - Report of the G8 Health Experts Group -
 Toyako Framework for Action on Global Health - Report of the G8 Health Experts Group - 8 July 2008 This report is the recommendation from the G8 Health Experts Group to the G8 leaders. I Introduction 1.
Toyako Framework for Action on Global Health - Report of the G8 Health Experts Group - 8 July 2008 This report is the recommendation from the G8 Health Experts Group to the G8 leaders. I Introduction 1.
TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE CONTROL OF A DUAL EPIDEMIC IN THE WHO AFRICAN REGION. Report of the Regional Director.
 30 August 2007 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-seventh session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 27 31 August Provisional agenda item 7.8 TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE
30 August 2007 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-seventh session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 27 31 August Provisional agenda item 7.8 TUBERCULOSIS AND HIV/AIDS: A STRATEGY FOR THE
Fifth report of Committee A
 SIXTY-EIGHTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY (Draft) A68/73 26 May 2015 Fifth report of Committee A (Draft) Committee A held its twelfth and thirteenth meetings on 25 May 2015 under the chairmanship of Dr Eduardo
SIXTY-EIGHTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY (Draft) A68/73 26 May 2015 Fifth report of Committee A (Draft) Committee A held its twelfth and thirteenth meetings on 25 May 2015 under the chairmanship of Dr Eduardo
Ex post evaluation Tanzania
 Ex post evaluation Tanzania Sector: Health, family planning, HIV/AIDS (12250) Project: Promotion of national vaccination programme in cooperation with GAVI Alliance, Phase I and II (BMZ no. 2011 66 586
Ex post evaluation Tanzania Sector: Health, family planning, HIV/AIDS (12250) Project: Promotion of national vaccination programme in cooperation with GAVI Alliance, Phase I and II (BMZ no. 2011 66 586
GUIDANCE FOR MAKING A COMMITMENT TO EVERY WOMAN EVERY CHILD
 GUIDANCE FOR MAKING A COMMITMENT TO EVERY WOMAN EVERY CHILD Every Woman Every Child is a multi-stakeholder movement to implement the United Nations Global Strategy for Women s and Children s Health, focusing
GUIDANCE FOR MAKING A COMMITMENT TO EVERY WOMAN EVERY CHILD Every Woman Every Child is a multi-stakeholder movement to implement the United Nations Global Strategy for Women s and Children s Health, focusing
This technical paper analyses investments by OECD Development Assistance Committee (DAC) donors in six
 Financing the unfinished business of gender equality and women s rights: priorities for the post-215 framework TECHNICAL BRIEF March 214 This technical paper analyses investments by OECD Development Assistance
Financing the unfinished business of gender equality and women s rights: priorities for the post-215 framework TECHNICAL BRIEF March 214 This technical paper analyses investments by OECD Development Assistance
Latest Funding Trends in AIDS Response
 Latest Funding Trends in AIDS Response 20 th International AIDS Conference Melbourne, Australia J.V.R. Prasada Rao United Nations Secretary-General s Special Envoy for AIDS in Asia and the Pacific 21 July
Latest Funding Trends in AIDS Response 20 th International AIDS Conference Melbourne, Australia J.V.R. Prasada Rao United Nations Secretary-General s Special Envoy for AIDS in Asia and the Pacific 21 July
The HIV Medicine Association (HIVMA) of the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA)
 Written Testimony for the Record to the House Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education and Related Agencies regarding FY 2018 Appropriations for HIV/AIDS Programs Submitted by Dr. Wendy
Written Testimony for the Record to the House Subcommittee on Labor, Health and Human Services, Education and Related Agencies regarding FY 2018 Appropriations for HIV/AIDS Programs Submitted by Dr. Wendy
U.S. Funding for International Family Planning & Reproductive Health
 April 2016 Issue Brief U.S. Funding for International Family Planning & Reproductive Health SUMMARY The U.S. government has supported international family planning and reproductive health (FP/RH) efforts
April 2016 Issue Brief U.S. Funding for International Family Planning & Reproductive Health SUMMARY The U.S. government has supported international family planning and reproductive health (FP/RH) efforts
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RL33485 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web U.S. International HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria Spending: FY2004-FY2008 Updated September 11, 2007 Tiaji Salaam-Blyther Specialist
Order Code RL33485 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web U.S. International HIV/AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria Spending: FY2004-FY2008 Updated September 11, 2007 Tiaji Salaam-Blyther Specialist
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services
 United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 25 April 2014 Original:
United Nations Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme, the United Nations Population Fund and the United Nations Office for Project Services Distr.: General 25 April 2014 Original:
Recognizing noncommunicable diseases as a global health security threat
 Amrita Saha & George Alleyne Noncommunicable diseases: a health security threat This online first version has been peer-reviewed, accepted and edited, but not formatted and finalized with corrections from
Amrita Saha & George Alleyne Noncommunicable diseases: a health security threat This online first version has been peer-reviewed, accepted and edited, but not formatted and finalized with corrections from
This brief analyses investments by OECD Development Assistance Committee (DAC) donors in six policy areas
 Financing the unfinished business of gender equality and women s rights: priorities for the post-215 framework March 214 This brief analyses investments by OECD Development Assistance Committee (DAC) donors
Financing the unfinished business of gender equality and women s rights: priorities for the post-215 framework March 214 This brief analyses investments by OECD Development Assistance Committee (DAC) donors
Mid-term Review of the UNGASS Declaration of. Commitment on HIV/AIDS. Ireland 2006
 Mid-term Review of the UNGASS Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS Ireland 2006 Irish Role in Global Response Just as the HIV/AIDS epidemic is a global threat, addressing the challenge of the epidemic
Mid-term Review of the UNGASS Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS Ireland 2006 Irish Role in Global Response Just as the HIV/AIDS epidemic is a global threat, addressing the challenge of the epidemic
Background. Proposed to develop a framework for action. Address by Foreign Minister Koumura
 July 2008 Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan Background Address by Foreign Minister Koumura Global Health and Japan s Foreign Policy From Okinawa to Toyako (25 November 2007) Special Address by Prime
July 2008 Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan Background Address by Foreign Minister Koumura Global Health and Japan s Foreign Policy From Okinawa to Toyako (25 November 2007) Special Address by Prime
The Economic and Social Council, Recalling the United Nations Millennium Declaration13 and the 2005 World Summit Outcome, 1
 Resolution 2010/24 The role of the United Nations system in implementing the ministerial declaration on the internationally agreed goals and commitments in regard to global public health adopted at the
Resolution 2010/24 The role of the United Nations system in implementing the ministerial declaration on the internationally agreed goals and commitments in regard to global public health adopted at the
1.2 Building on the global momentum
 1.1 Context HIV/AIDS is an unprecedented global development challenge, and one that has already caused too much hardship, illness and death. To date, the epidemic has claimed the lives of 20 million people,
1.1 Context HIV/AIDS is an unprecedented global development challenge, and one that has already caused too much hardship, illness and death. To date, the epidemic has claimed the lives of 20 million people,
Healthy Foreign Policy: Bringing Coherence to the Global Health Agenda
 Healthy Foreign Policy: Bringing Coherence to the Global Health Agenda CGD Policy Brief Healthy Foreign Policy: Bringing Coherence to the Global Health Agenda by Ruth Levine Faced with many urgent challenges,
Healthy Foreign Policy: Bringing Coherence to the Global Health Agenda CGD Policy Brief Healthy Foreign Policy: Bringing Coherence to the Global Health Agenda by Ruth Levine Faced with many urgent challenges,
The Global Economic Crisis and HIV Prevention and Treatment Programmes: Vulnerabilities and Impact. Executive Summary TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
 The Global Economic Crisis and HIV Prevention and Treatment Programmes: Vulnerabilities and Impact Executive Summary TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO October 2009 ACKOWLEDGEMENT The executive summary The Global Economic
The Global Economic Crisis and HIV Prevention and Treatment Programmes: Vulnerabilities and Impact Executive Summary TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO October 2009 ACKOWLEDGEMENT The executive summary The Global Economic
THE Price of a Pandemic 2017
 THE Price of a Pandemic 2017 From 2000-2015: 33 million people died because of TB at a global economic cost of $617bn This report was produced the Global TB Caucus, an international network of over 2,000
THE Price of a Pandemic 2017 From 2000-2015: 33 million people died because of TB at a global economic cost of $617bn This report was produced the Global TB Caucus, an international network of over 2,000
STRATEGIC PLAN AGAINST VIRAL HEPATITIS IN SENEGAL ( ) POLICY BRIEF
 PROGRAMME NATIONAL DE LUTTE CONTRE LES HEPATITES STRATEGIC PLAN AGAINST VIRAL HEPATITIS IN SENEGAL (2019-2023) POLICY BRIEF 1 INVESTING IN THE FIGHT AGAINST HEPATITIS B AND C IN SENEGAL NATIONAL STRATEGIC
PROGRAMME NATIONAL DE LUTTE CONTRE LES HEPATITES STRATEGIC PLAN AGAINST VIRAL HEPATITIS IN SENEGAL (2019-2023) POLICY BRIEF 1 INVESTING IN THE FIGHT AGAINST HEPATITIS B AND C IN SENEGAL NATIONAL STRATEGIC
Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund
 United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/CIV/6 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 6 October 2008 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
United Nations DP/FPA/CPD/CIV/6 Executive Board of the United Nations Development Programme and of the United Nations Population Fund Distr.: General 6 October 2008 Original: English UNITED NATIONS POPULATION
Action Plan on HIV/AIDS in the EU and neighbouring countries:
 Action Plan on HIV/AIDS in the EU and neighbouring countries: 2014-2016 Matthias Schuppe Policy Officer Health Threats Unit DG Health and Consumers European Commission Outline o EU policy framework on
Action Plan on HIV/AIDS in the EU and neighbouring countries: 2014-2016 Matthias Schuppe Policy Officer Health Threats Unit DG Health and Consumers European Commission Outline o EU policy framework on
TOBACCO CONTROL & THE SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
 TOBACCO CONTROL & THE SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS 1 WHAT ARE THE SDGs? The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a United Nations initiative, formally adopted by the United Nations General Assembly
TOBACCO CONTROL & THE SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS 1 WHAT ARE THE SDGs? The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a United Nations initiative, formally adopted by the United Nations General Assembly
Global Funding for HIV/AIDS in Resource Poor Settings
 Global Funding for HIV/AIDS in Resource Poor Settings Todd Summers Progressive Health Partners Jennifer Kates Kaiser Family Foundation December 2003 Global Funding for HIV/AIDS in Resource Poor Settings
Global Funding for HIV/AIDS in Resource Poor Settings Todd Summers Progressive Health Partners Jennifer Kates Kaiser Family Foundation December 2003 Global Funding for HIV/AIDS in Resource Poor Settings
Progress in scaling up voluntary medical male circumcision for HIV prevention in East and Southern Africa
 SUMMARY REPORT Progress in scaling up voluntary medical male circumcision for HIV prevention in East and Southern Africa January December 2012 Table of contents List of acronyms 2 Introduction 3 Summary
SUMMARY REPORT Progress in scaling up voluntary medical male circumcision for HIV prevention in East and Southern Africa January December 2012 Table of contents List of acronyms 2 Introduction 3 Summary
ANALYSIS OF THE ADMINISTRATION S FISCAL YEAR 2004 BUDGET FOR THE CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION
 ANALYSIS OF THE ADMINISTRATION S FISCAL YEAR 2004 BUDGET FOR THE CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION OVERVIEW: On February 20, 2003, President Bush signed the Omnibus Appropriations bill for FY
ANALYSIS OF THE ADMINISTRATION S FISCAL YEAR 2004 BUDGET FOR THE CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION OVERVIEW: On February 20, 2003, President Bush signed the Omnibus Appropriations bill for FY
Project Name Barbados-HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Project ID
 Report No. PID10562 Project Name Barbados-HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control (@)... Project Region Sector Project ID Latin America and the Caribbean (LCR) Other Population; Health & Nutrition BBPE75220 Borrower
Report No. PID10562 Project Name Barbados-HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control (@)... Project Region Sector Project ID Latin America and the Caribbean (LCR) Other Population; Health & Nutrition BBPE75220 Borrower
WHAT ARE DONORS DOING WITH AIDS MONEY?
 WHAT ARE DONORS DOING WITH AIDS MONEY? A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF FUNDING PRACTICES OF THE GLOBAL FUND, WORLD BANK MAP AND PEPFAR IN MOZAMBIQUE, UGANDA AND ZAMBIA Study Objectives 1. To describe the levels
WHAT ARE DONORS DOING WITH AIDS MONEY? A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF FUNDING PRACTICES OF THE GLOBAL FUND, WORLD BANK MAP AND PEPFAR IN MOZAMBIQUE, UGANDA AND ZAMBIA Study Objectives 1. To describe the levels
SCALING UP TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS
 SCALING UP TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS Considerations for countries to set their own national targets for HIV prevention, treatment, and care April 2006 Acknowledgements: The UNAIDS Secretariat would like
SCALING UP TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS Considerations for countries to set their own national targets for HIV prevention, treatment, and care April 2006 Acknowledgements: The UNAIDS Secretariat would like
Suraj Madoori, Treatment Action Group, U.S. and Global Health Policy Director. On behalf of the Tuberculosis Roundtable
 United States House of Representatives Committee on Appropriations Subcommittee on State and Foreign Operations and Related Programs Fiscal Year 2020 Written Testimony Suraj Madoori, Treatment Action Group,
United States House of Representatives Committee on Appropriations Subcommittee on State and Foreign Operations and Related Programs Fiscal Year 2020 Written Testimony Suraj Madoori, Treatment Action Group,
UNIÃO AFRICANA ABUJA CALL FOR ACCELERATED ACTION TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS TO HIV AND AIDS, TUBERCULOSIS AND MALARIA SERVICES IN AFRICA
 AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO AFRICANA ABUJA CALL FOR ACCELERATED ACTION TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS TO HIV AND AIDS, TUBERCULOSIS AND MALARIA SERVICES IN AFRICA AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO
AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO AFRICANA ABUJA CALL FOR ACCELERATED ACTION TOWARDS UNIVERSAL ACCESS TO HIV AND AIDS, TUBERCULOSIS AND MALARIA SERVICES IN AFRICA AFRICAN UNION UNION AFRICAINE UNIÃO
Obama Unveils National AIDS Strategy Amid Praise and Criticism
 SAVE THIS EMAIL THIS Close Obama Unveils National AIDS Strategy Amid Praise and Criticism Dan Robinson White House July 13, 2010 President Barack Obama on Tuesday unveiled what he calls a comprehensive
SAVE THIS EMAIL THIS Close Obama Unveils National AIDS Strategy Amid Praise and Criticism Dan Robinson White House July 13, 2010 President Barack Obama on Tuesday unveiled what he calls a comprehensive
Elaine Zuckerman Embassy of the Republic of Zambia December 1, 2009
 HIV/AIDS and Reproductive Health Spending: Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs ) Elaine Zuckerman Embassy of the Republic of Zambia December 1, 2009 Overview Gender Action is the only organization dedicated
HIV/AIDS and Reproductive Health Spending: Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs ) Elaine Zuckerman Embassy of the Republic of Zambia December 1, 2009 Overview Gender Action is the only organization dedicated
Ex Post-Evaluation Brief CENTRAL AMERICA: HIV/AIDS Prevention
 Ex Post-Evaluation Brief CENTRAL AMERICA: HIV/AIDS Prevention Sector 13040 Combating STDs and HIV/AIDS HIV/AIDS Prevention in Central America - Programme/Client 2002 66 452* Phase I; 2003 66 500 Phase
Ex Post-Evaluation Brief CENTRAL AMERICA: HIV/AIDS Prevention Sector 13040 Combating STDs and HIV/AIDS HIV/AIDS Prevention in Central America - Programme/Client 2002 66 452* Phase I; 2003 66 500 Phase
Follow-up to the high-level meetings of the United Nations General Assembly on health-related issues
 EXECUTIVE BOARD EB44/ 44th session December 08 Provisional agenda item 5.8 Follow-up to the high-level meetings of the United Nations General Assembly on health-related issues Ending tuberculosis Report
EXECUTIVE BOARD EB44/ 44th session December 08 Provisional agenda item 5.8 Follow-up to the high-level meetings of the United Nations General Assembly on health-related issues Ending tuberculosis Report
Six things you need to know
 UNAIDS Report 2010 MDG 6 Six things you need to know about the AIDS response today UNAIDS Report 2010 MDG 6 Six things you need to know about the AIDS response today MDG6: Combat HIV/AIDS, Malaria and
UNAIDS Report 2010 MDG 6 Six things you need to know about the AIDS response today UNAIDS Report 2010 MDG 6 Six things you need to know about the AIDS response today MDG6: Combat HIV/AIDS, Malaria and
Ex Post-Evaluation Brief BURUNDI: Health Sectoral Programme II
 Ex Post-Evaluation Brief BURUNDI: Health Sectoral Programme II Sector 12230 Basic health infrastructure Health sector programme, Phase II - Programme/Client BMZ No. 1995 65 748* incl. accompanying measure,
Ex Post-Evaluation Brief BURUNDI: Health Sectoral Programme II Sector 12230 Basic health infrastructure Health sector programme, Phase II - Programme/Client BMZ No. 1995 65 748* incl. accompanying measure,
in East Asia and the Pacific
 Addressing HIV/AIDS in East Asia and the Pacific The World Bank East Asia and the Pacific Region blic Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized
Addressing HIV/AIDS in East Asia and the Pacific The World Bank East Asia and the Pacific Region blic Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized
Translating Global Health Experiences Into International Policy: Experiments in Public Health, Politics, and Advocacy
 Translating Global Health Experiences Into International Policy: Experiments in Public Health, Politics, and Advocacy Anand Reddi October 27, 2011 University of Colorado School of Medicine Email: anand.reddi@ucdenver.edu
Translating Global Health Experiences Into International Policy: Experiments in Public Health, Politics, and Advocacy Anand Reddi October 27, 2011 University of Colorado School of Medicine Email: anand.reddi@ucdenver.edu
Rudy Giuliani Mike Huckabee Duncan Hunter Alan Keyes John McCain
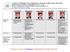 CHART #3: REPUBLICAN CANDIDATES HEALTH CARE PLANS: HIV/AIDS PROPOSALS () By Susan J. Blumenthal, M.D., Beth Louise Hoffman, Yi-An Ko, and Melissa Shive* The Center for the Study of the Presidency Rudy
CHART #3: REPUBLICAN CANDIDATES HEALTH CARE PLANS: HIV/AIDS PROPOSALS () By Susan J. Blumenthal, M.D., Beth Louise Hoffman, Yi-An Ko, and Melissa Shive* The Center for the Study of the Presidency Rudy
