Ranaviruses: Past, Present, and Future. Outline
|
|
|
- Arthur Toby Spencer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ranaviruses: Past, Present, and Future 1 st Intl. Symposium of Ranaviruses, Minneapolis, MN July 7, 2011 Outline Past: 100+ years of iridoviruses Present: Molecular Virology: Elucidation of FV3 gene function Ecology: Understanding the role of ranaviruses in die offs and extinctions Future: Molecular, Genetic and Ecological studies. 1
2 Iridovirus/Ranavirus Timeline: 100+ years of Iridoviruses Lymphocystis disease identified First Insect Iridovirus Identified FV3 identified Xeros (1954) Granoff et al., 1965 (NY Acad. Sci.) St. Jude Childrens Research Hospital, Division of Virology, circa 1980 Allan Granoff, Rakesh Goorha, Dawn Willis, Raj Raghow, Gopal Murti, Greg Chinchar 2
3 Other early ranavirus workers Molecular Studies: Aubertin, Drillien, Kirn (FR) McAuslan (USA) Elliot and Kelly (UK) Identification and Virus Characterization Karzon, Clark Wolf Iridovirus/Ranavirus Timeline: 100+ years of Iridoviruses mid 1980 s 2011 Lymphocystis disease identified First Insect Iridovirus Identified FV3 identified FV3 Life Cycle Elucidated Identification and characterization of ranaviruses and other iridoviruses infecting many different species of fish, amphibians, 3
4 A Ranavirus Renaissance Langdon and Humphrey (1987) Redfin perch [AU EHNV] Ahne et al. (1989) Sheatfish [DE ESV] Kanchanakhan (1989) R. tigrina i [SE Asia] Ai] Pozet et al. (1992) Ictalurus melas [FR ECV] Speare and Smith (1992) ornate burrowing frog [AU BIV] Bloch and Larsen (1993) Turbot [Scandinavia] Chua et al. (1994) and Qin et al. (2001) brown spotted grouper [Singapore/Taiwan/PRC SGIV/GIV] Cunningham et al. (1996) R. tempora [UK] Plumb et al., (1996) largemouth bass [USA/SC LMBV] Mao et al., (1997) doctor fish [SE Asia DFV] Jancovich et al. (1999) Ambystoma tigrinum [USA/AZ ATV] Chen et al. (1999) soft shell turtle [PRC STIV] Allender et al. (2006) box turtles [USA] Family: Iridoviridae Subfamily: Invertiridovirinae Genus: Iridovirus Genus: Chloriridovirus Subfamily: Chordiridovirinae Genus: Lymphocystivirus wart like disease in freshwater and marine fish, disfigurement, but low mortality Genus: Megalocytivirus life threatening infections in >52 species of marine and freshwater fish in SE Asia Genus: Ranavirus systemic disease in fish, reptiles, and amphibians accompanied by variable mortality. FV3, ATV, BIV, EHNV, ECV, SCRV, SGIV, RCV Z 8 4
5 Phylogenetic Tree: MCP 9 Allen et al., (2006) Virology J 3:15. Nuclear Cytoplasmic Large DNA containing Viruses (NCLDV) 5
6 Enveloped Virus Non enveloped FV3 11 Ranavirus Virion Morphology 12 6
7 Nucleus showing chromatin condensation Virions within viral assembly sites Virions within para crystalline array Mitochondria Alex Hyatt (AAHL) 14 7
8 ~100 ORFs: 19 RED (Replication) 5 Blue/Gray (structural) 51 Black (UNKNOWN) 15 Yellow (FV3 specific) Tan et al., genes common to all iridovirids; 13 common to amphibian ranaviruses Eaton et al., 2007 Virology J 4:11 and Jancovich et al.,
9 Replicative Genes DNA/RNA Pol Major capsid protein DNA repair Integrase Myristylated membrane protein FV3 Genes Immune evasion, HR, Virulence vif 2 Steroid synthesis (β HSD) vcard TNF receptor Bak like, IAP like dttp synthesis: RR, TK, dutpase 13 amphibian RVspecific genes; 27 RVspecific genes 17 FV3 ts mutants Naegele and Granoff, Virology 44: , 1971 Purifoy et al., Virology 54: , 1973 Chinchar and Granoff, J. Virology 58: , mutants placed into 19 complementation groups and 4 classes Class I: 12 CG, 16 mutants E+ L+ DNA+ AS+ [Assembly] Class II: 4 CG, 5 mutants E+ L DNA+ AS+/ Class III: 1 CG, 1 mutant E+ L DNA+ AS Class IV: 2 CG, 5 mutants E+ L DNA AS [DNA] 9
10 Knock Down: Antisense Morpholino Oligonucleotides (asmos) asmos are single stranded 25 mers, which If complementary to the region surrounding, or upstream of, the translational start site, block protein synthesis by inhibiting ribosomal movement. 19 Structure of asmos 20 10
11 21 Mock infected FHM FV3 infected FHM AE FV3 infected + asmo 22 11
12 Knock down of 18K synthesis does not affect virion formation or viral infectivity FV3 + anti 18K MO FV3 + anti 18K MO 23 Knock Down Studies: Summary KD of MCP, vpol II alpha, 53R, 46K, and 32R resulted in a marked kddrop in viral replication. KD distinguishes essential from non essential genes. KD studies are limited by inability to detect some viral proteins by SDS PAGE inability to detect some viral proteins by SDS PAGE, sequence of target mrna, inability to function in vivo. 12
13 Knock Out targeted gene Viral Genomic DNA EGFP Puro 18K prom to FV3 [wtfv3] Plasmid transfer vector EGFP Puro 18K prom Sequential selection and purification by puromycin and plaque assay [recombinant FV3] Chen and Robert (University of Rochester Medical Center) Confirmation of PuroR/GFP insertion and 18K and vif 2 deletion A vif 2α PuroR/GFP 18K Kb B WT 18K vif 2 GFP 18K (484) vif 2 (235) DNApol (378) 13
14 FV3 PuroR/GFP FV3 vif 2α FV3 18K 1.0E+07 BHK cells (MOI=5) 1.0E+6 FHM cells (MOI=0.01) Virus Titer (PFU/ml) 1.0E E+05 WT FV3 FV3 PuroR/GFP FV3 18K FV3 vif2α 1.0E Hours Post Infection 1.0E+5 1.0E+4 1.0E+3 1.0E Hours Post Infection 14
15 Challenge of Xenopus tadpoles with control and KO mutants A vdna Pol at 3 dpi B vdna Pol at 6 dpi Fold increase * * ** ** 10 WT vif2 18k 10 WT GFP vif2 18k P<
16 KO mutants One KI and 5 KO mutants have been generated FV3 PuroR/GFP (KI) positive control FV3 18K, vif 2α, βhsd, dutpase, vcard KOs can be used both in vitro and in vivo, and should be constant in their phenotype. Identify non essential genes that may play key roles in virulence, host range, and immune evasion. Ecological/Population Studies RVs and species declines (Gray, Storfer, et al.) Viral transmission and persistence (Brunner, Jensen, Picco) Host susceptibility and pathology (Hoverman, Green, Miller) Pesticides and RV infections (Kirby) Host shifts among RVs (Jancovich) Host Pathogen co evolution (Lesbarreres, Storfer) Host anti viral immunity (Robert) and viral anti host immunity i (Robert, Chinchar) h Identify viruses from various hosts and geographic regions (Balseiro, Schock, Duffus, Mazzoni, Une, Kanchankhan, Waltzek, Marschang, Allender, Ariel) 16
17 Ranaviruses: Past and Present The old view RVs are relatively harmless viruses that provide insight into a poorly characterized virus family and are useful molecular models for DNA methylation and its effect on transcription, hostshutoff, etc. The new realization RVs are responsible for localized die offs among ecologically and commercially important ectothermic animals. The die off trigger is not known, but likely involves interplay between intrinsic viral functions and extrinsic factors (e.g., host immunity, stress, etc.) The Future Understand the role of viral genes in virulence Immune evasion, host range Identify host and reservoir species Is FV3 really a frog virus? Is LMBV an isolate of DFV? Understand what host, viral, and environmental factors trigger disease/persistence/recrudescence FV1 and FV2 were isolated from healthy frogs; what makes LMBV pathogenic? Determine if susceptible species can be protected by vaccination with KO mutants? Does the genus Ranavirus consist of 6+ unique species, or are there fewer species but multiple isolates displaying various host preferences and degrees of pathology? A Regulatory/Taxonomic issue? 17
Amphibian ranavirus transmission and persistence. With an emphasis on ecological relevance. Jesse Brunner
 Amphibian ranavirus transmission and persistence With an emphasis on ecological relevance Jesse Brunner Amphibian ranaviruses 1) Transmission " Routes of transmission How does ranavirus get around? " Function
Amphibian ranavirus transmission and persistence With an emphasis on ecological relevance Jesse Brunner Amphibian ranaviruses 1) Transmission " Routes of transmission How does ranavirus get around? " Function
RANAVIRUSES IN AMPHIBIANS
 RANAVIRUSES IN AMPHIBIANS Ranaviruses are a genus of the Iridoviridae family of viruses. Ranaviruses are capable of causing diseases with formidable mortality in amphibians (Speare et al 2001). Ranaviral
RANAVIRUSES IN AMPHIBIANS Ranaviruses are a genus of the Iridoviridae family of viruses. Ranaviruses are capable of causing diseases with formidable mortality in amphibians (Speare et al 2001). Ranaviral
Ranaviruses: Detection, differentiation and host immune response
 Ranaviruses: Detection, differentiation and host immune response Riikka Holopainen Finnish Food Safety Authority Evira Veterinary Virology Research Unit Helsinki, Finland and Department of Veterinary Biosciences
Ranaviruses: Detection, differentiation and host immune response Riikka Holopainen Finnish Food Safety Authority Evira Veterinary Virology Research Unit Helsinki, Finland and Department of Veterinary Biosciences
Isolation of Frog Virus 3 from Pallid Sturgeon (Scaphirhynchus albus) Suggests an Interclass Host Shift
 Isolation of Frog Virus 3 from Pallid Sturgeon (Scaphirhynchus albus) Suggests an Interclass Host Shift Thomas B. Waltzek, Debra L. Miller, Bruce Drecktrah, Jeff T. Briggler, Beth MacConnell, Crystal Hudson,
Isolation of Frog Virus 3 from Pallid Sturgeon (Scaphirhynchus albus) Suggests an Interclass Host Shift Thomas B. Waltzek, Debra L. Miller, Bruce Drecktrah, Jeff T. Briggler, Beth MacConnell, Crystal Hudson,
Ranavirus Ecology and Evolution: From Epidemiology to Extinction
 Ranavirus Ecology and Evolution: From Epidemiology to Extinction Jesse L. Brunner, Andrew Storfer, Matthew J. Gray, and Jason T. Hoverman 1 Introduction Ranaviruses were thought to have little impact on
Ranavirus Ecology and Evolution: From Epidemiology to Extinction Jesse L. Brunner, Andrew Storfer, Matthew J. Gray, and Jason T. Hoverman 1 Introduction Ranaviruses were thought to have little impact on
Rana grylio virus (RGV) envelope protein 2L: subcellular localization and essential roles in virus infectivity revealed by conditional lethal mutant
 Journal of General Virology (2014), 95, 679 690 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.058776-0 Rana grylio virus (RGV) envelope protein 2L: subcellular localization and essential roles in virus infectivity revealed by conditional
Journal of General Virology (2014), 95, 679 690 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.058776-0 Rana grylio virus (RGV) envelope protein 2L: subcellular localization and essential roles in virus infectivity revealed by conditional
Identification of lymphocystis disease virus from paradise fish Macropodus opercularis (LCDV-PF)
 rch Virol (2014) 159:2445 2449 DOI 10.7/s00705-014-2060-0 RIEF REPORT Identification of lymphocystis disease virus from paradise fish Macropodus opercularis () Liwen Xu Juan Feng Youhua Huang Received:
rch Virol (2014) 159:2445 2449 DOI 10.7/s00705-014-2060-0 RIEF REPORT Identification of lymphocystis disease virus from paradise fish Macropodus opercularis () Liwen Xu Juan Feng Youhua Huang Received:
Sensitivity of a Diagnostic Test for Amphibian Ranavirus Varies with Sampling Protocol
 Sensitivity of a Diagnostic Test for Amphibian Ranavirus Varies with Sampling Protocol Authors: Amy L. Greer, and James P. Collins Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 43(3) : 525-532 Published By: Wildlife
Sensitivity of a Diagnostic Test for Amphibian Ranavirus Varies with Sampling Protocol Authors: Amy L. Greer, and James P. Collins Source: Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 43(3) : 525-532 Published By: Wildlife
Fact Sheet. Introductory statement. Aetiology. Natural hosts
 Ranaviral disease in wild Australian amphibians Fact Sheet Introductory statement Ranaviruses have been associated with disease outbreaks causing significant mortality and morbidity in wild amphibians,
Ranaviral disease in wild Australian amphibians Fact Sheet Introductory statement Ranaviruses have been associated with disease outbreaks causing significant mortality and morbidity in wild amphibians,
Isolation and characterization of a ranavirus from koi, Cyprinus carpio L., experiencing mass mortalities in India
 doi:10.1111/jfd.12246 Isolation and characterization of a ranavirus from koi, Cyprinus carpio L., experiencing mass mortalities in India M R George, K R John, M M Mansoor, R Saravanakumar, P Sundar and
doi:10.1111/jfd.12246 Isolation and characterization of a ranavirus from koi, Cyprinus carpio L., experiencing mass mortalities in India M R George, K R John, M M Mansoor, R Saravanakumar, P Sundar and
MARK. Virology. From fish to frogs and beyond: Impact and host range of emergent ranaviruses
 Virology 511 (2017) 272 279 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Virology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro From fish to frogs and beyond: Impact and host range of emergent ranaviruses
Virology 511 (2017) 272 279 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Virology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/yviro From fish to frogs and beyond: Impact and host range of emergent ranaviruses
VIRUSES. 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart.
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR VIRUSES 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart. Viral Part Description of Part 2. Some viruses have an envelope
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR VIRUSES 1. Describe the structure of a virus by completing the following chart. Viral Part Description of Part 2. Some viruses have an envelope
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES
 1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
1 of 7 I. Viral Origin. A. Retrovirus - animal lentiviruses. HIV - BASIC PROPERTIES 1. HIV is a member of the Retrovirus family and more specifically it is a member of the Lentivirus genus of this family.
Inactivation of Frog Virus 3 and Channel Catfish Virus by Esculentin-2P and Ranatuerin-2P, Two Antimicrobial Peptides Isolated from Frog Skin
 Virology 288, 351 357 (2001) doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1080, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Inactivation of Frog Virus 3 and Channel Catfish Virus by Esculentin-2P and Ranatuerin-2P, Two
Virology 288, 351 357 (2001) doi:10.1006/viro.2001.1080, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Inactivation of Frog Virus 3 and Channel Catfish Virus by Esculentin-2P and Ranatuerin-2P, Two
Aquaculture and Disease Threats in Australia and an update on EHNV
 Aquaculture and Disease Threats in Australia and an update on EHNV Ellen Ariel, Dean Jerry, Kelly Condon, James Cook University Richard Whittington and Paul Hicks OIE Reference Laboratory for EHNV and
Aquaculture and Disease Threats in Australia and an update on EHNV Ellen Ariel, Dean Jerry, Kelly Condon, James Cook University Richard Whittington and Paul Hicks OIE Reference Laboratory for EHNV and
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
VIROLOGY. Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors
 VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
VIROLOGY Engineering Viral Genomes: Retrovirus Vectors Viral vectors Retrovirus replicative cycle Most mammalian retroviruses use trna PRO, trna Lys3, trna Lys1,2 The partially unfolded trna is annealed
AP Biology Reading Guide. Concept 19.1 A virus consists of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 19: Viruses Overview Experimental work with viruses has provided important evidence that genes are made of nucleic acids. Viruses were also important in working out
AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 19: Viruses Overview Experimental work with viruses has provided important evidence that genes are made of nucleic acids. Viruses were also important in working out
numbe r Done by Corrected by Doctor
 numbe r 5 Done by Mustafa Khader Corrected by Mahdi Sharawi Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh Viral Replication Mechanisms: (Protein Synthesis) 1. Monocistronic Method: All human cells practice the monocistronic
numbe r 5 Done by Mustafa Khader Corrected by Mahdi Sharawi Doctor Ashraf Khasawneh Viral Replication Mechanisms: (Protein Synthesis) 1. Monocistronic Method: All human cells practice the monocistronic
Ebola Virus. Emerging Diseases. Biosciences in the 21 st Century Dr. Amber Rice December 4, 2017
 Ebola Virus Emerging Diseases Biosciences in the 21 st Century Dr. Amber Rice December 4, 2017 Outline Disease emergence: a case study How do pathogens shift hosts? Evolution within hosts: The evolution
Ebola Virus Emerging Diseases Biosciences in the 21 st Century Dr. Amber Rice December 4, 2017 Outline Disease emergence: a case study How do pathogens shift hosts? Evolution within hosts: The evolution
Reoviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Reoviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=13), diameter 60-85 nm Capsid consists of two or three concentric protein
Reoviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=13), diameter 60-85 nm Capsid consists of two or three concentric protein
Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP
 Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP 1 Learning Objectives Recognize hazards associated with viral vectors in research and animal
Viral Vectors In The Research Laboratory: Just How Safe Are They? Dawn P. Wooley, Ph.D., SM(NRM), RBP, CBSP 1 Learning Objectives Recognize hazards associated with viral vectors in research and animal
Slide Organization Good Examples
 Slide Organization Good Examples Slides should be well-balanced, flow logically, and not excessively cluttered Avian Influenza A Viruses 1) Influenza A H5: (H5N1) 9 Subtypes HP or LP 2) Influenza A H7:
Slide Organization Good Examples Slides should be well-balanced, flow logically, and not excessively cluttered Avian Influenza A Viruses 1) Influenza A H5: (H5N1) 9 Subtypes HP or LP 2) Influenza A H7:
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf
 number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
Coronaviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Coronaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Spherical enveloped particles studded with clubbed spikes Diameter 120-160 nm Coiled helical
Coronaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Spherical enveloped particles studded with clubbed spikes Diameter 120-160 nm Coiled helical
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Transmission of Ranavirus between Ectothermic Vertebrate Hosts
 Transmission of Ranavirus between Ectothermic Vertebrate Hosts Roberto Brenes 1 *, Matthew J. Gray 2, Thomas B. Waltzek 3, Rebecca P. Wilkes 4, Debra L. Miller 2,4 1 Department of Biology, Carroll University,
Transmission of Ranavirus between Ectothermic Vertebrate Hosts Roberto Brenes 1 *, Matthew J. Gray 2, Thomas B. Waltzek 3, Rebecca P. Wilkes 4, Debra L. Miller 2,4 1 Department of Biology, Carroll University,
USING RAINBOW TROUT CELL LINES AS A MODEL FOR UNDERSTANDING THE INNATE ANTI-FV3 IMMUNE RESPONSE
 Wilfrid Laurier University Scholars Commons @ Laurier Theses and Dissertations (Comprehensive) 2017 USING RAINBOW TROUT CELL LINES AS A MODEL FOR UNDERSTANDING THE INNATE ANTI-FV3 IMMUNE RESPONSE Graeme
Wilfrid Laurier University Scholars Commons @ Laurier Theses and Dissertations (Comprehensive) 2017 USING RAINBOW TROUT CELL LINES AS A MODEL FOR UNDERSTANDING THE INNATE ANTI-FV3 IMMUNE RESPONSE Graeme
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics
 Hepadnaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Hepatitis viruses A group of unrelated pathogens termed hepatitis viruses cause the vast majority
Hepadnaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Hepatitis viruses A group of unrelated pathogens termed hepatitis viruses cause the vast majority
Genome architecture changes and major gene variations of Andrias davidianus ranavirus (ADRV)
 Chen et al. Veterinary Research 2013, 44:101 VETERINARY RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Genome architecture changes and major gene variations of Andrias davidianus ranavirus (ADRV) Zhongyuan Chen 1, Jianfang
Chen et al. Veterinary Research 2013, 44:101 VETERINARY RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Genome architecture changes and major gene variations of Andrias davidianus ranavirus (ADRV) Zhongyuan Chen 1, Jianfang
VIRUSES. Biology Applications Control. David R. Harper. Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
 VIRUSES Biology Applications Control David R. Harper GS Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON vii Chapter 1 Virus Structure and 2.2 VIRUS MORPHOLOGY 26 Infection 1 2.3 VIRAL CLASSIFICATION
VIRUSES Biology Applications Control David R. Harper GS Garland Science Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON vii Chapter 1 Virus Structure and 2.2 VIRUS MORPHOLOGY 26 Infection 1 2.3 VIRAL CLASSIFICATION
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Viruses and hosts Lentivirus from Latin lentis (slow), for slow progression of disease
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Viruses and hosts Lentivirus from Latin lentis (slow), for slow progression of disease
MedChem 401~ Retroviridae. Retroviridae
 MedChem 401~ Retroviridae Retroviruses plus-sense RNA genome (!8-10 kb) protein capsid lipid envelop envelope glycoproteins reverse transcriptase enzyme integrase enzyme protease enzyme Retroviridae The
MedChem 401~ Retroviridae Retroviruses plus-sense RNA genome (!8-10 kb) protein capsid lipid envelop envelope glycoproteins reverse transcriptase enzyme integrase enzyme protease enzyme Retroviridae The
The Veterinary Journal
 The Veterinary Journal 197 (2013) 238 244 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect The Veterinary Journal journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tvjl Long-term study of an infection with ranaviruses
The Veterinary Journal 197 (2013) 238 244 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect The Veterinary Journal journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tvjl Long-term study of an infection with ranaviruses
Causes of Declines. Amphibian Declines 4/25/2009
 Possible Impacts of Predation Risk and Development on Susceptibility of North American Anurans to Ranaviruses Nathan Haislip M.S. Candidate Department of Forestry, Wildlife, and Fisheries Amphibian Declines
Possible Impacts of Predation Risk and Development on Susceptibility of North American Anurans to Ranaviruses Nathan Haislip M.S. Candidate Department of Forestry, Wildlife, and Fisheries Amphibian Declines
Viral reproductive cycle
 Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Large DNA viruses: Herpesviruses, Poxviruses, Baculoviruses and Giant viruses
 Large DNA viruses: Herpesviruses, Poxviruses, Baculoviruses and Giant viruses Viruses are the only obstacles to the domination of the Earth by mankind. -Joshua Lederberg Recommended reading: Field s Virology
Large DNA viruses: Herpesviruses, Poxviruses, Baculoviruses and Giant viruses Viruses are the only obstacles to the domination of the Earth by mankind. -Joshua Lederberg Recommended reading: Field s Virology
Chapter 19: Viruses. 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction. 2. Bacteriophages. 3. Animal Viruses. 4. Viroids & Prions
 Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK. Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV
 LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV In the last two lessons we discussed the how the viral life cycle causes host cell damage. But is there anything we can do to prevent
LESSON 4.6 WORKBOOK Designing an antiviral drug The challenge of HIV In the last two lessons we discussed the how the viral life cycle causes host cell damage. But is there anything we can do to prevent
Lahore University of Management Sciences. BIO 314- Microbiology and Virology (Spring 2018)
 BIO 314- Microbiology and Virology (Spring 2018) Instructor Shaper Mirza Room No. 9-318A Office Hours TBA Email Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu ; shaper.mirza@lums.edu.pk Telephone 8413 Secretary/TA No TA Office
BIO 314- Microbiology and Virology (Spring 2018) Instructor Shaper Mirza Room No. 9-318A Office Hours TBA Email Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu ; shaper.mirza@lums.edu.pk Telephone 8413 Secretary/TA No TA Office
Part I. Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents.
 Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells
 Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
7.014 Problem Set 7 Solutions
 MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 7.014 Problem Set 7 Solutions Question 1 Part A Antigen binding site Antigen binding site Variable region Light chain Light chain Variable
MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 7.014 Problem Set 7 Solutions Question 1 Part A Antigen binding site Antigen binding site Variable region Light chain Light chain Variable
All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction
 Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Infectious Diseases All living creatures share two basic purposes 1. survival 2. reproduction *Organisms must take nutrients essential for growth and proliferation from the environment. *In many conditions
Overview of virus life cycle
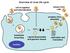 Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Lahore University of Management Sciences. BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015)
 BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015) Instructor Room. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Shaper Mirza and Sadia Hamera Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu Course
BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015) Instructor Room. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Shaper Mirza and Sadia Hamera Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu Course
Virology Introduction. Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment.
 DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
Pathological and microbiological findings from mortality of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus)
 Arch Virol (2014) 159:1403 1412 DOI 10.1007/s00705-013-1962-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pathological and microbiological findings from mortality of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) Yan Meng Jie
Arch Virol (2014) 159:1403 1412 DOI 10.1007/s00705-013-1962-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pathological and microbiological findings from mortality of the Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) Yan Meng Jie
Viruses. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Viruses CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin
Viruses CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin
~Lentivirus production~
 ~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses
 Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
B19, see Parvovirus B19 Bone marrow, gene transfer with parvovirus. Erythrovirus, see Parvovirus B19, Simian parvovirus
 ... Subject Index Adeno-associated virus Cap and genome encapsidation 87 DNA integration homologous recombination 90, 91 latency vs replication 77, 78 mechanism 79 requirements 78, 79 site in human genome
... Subject Index Adeno-associated virus Cap and genome encapsidation 87 DNA integration homologous recombination 90, 91 latency vs replication 77, 78 mechanism 79 requirements 78, 79 site in human genome
Aquaculture 313 (2011) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Aquaculture. journal homepage:
 Aquaculture 313 (2011) 24 30 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Aquaculture journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aqua-online Susceptibility of pike-perch Sander lucioperca to a panel of ranavirus
Aquaculture 313 (2011) 24 30 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Aquaculture journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/aqua-online Susceptibility of pike-perch Sander lucioperca to a panel of ranavirus
VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION
 VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION Paulo Eduardo Brandão, PhD Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health School of Veterinary Medicine University of São Paulo, Brazil I. VIRUS STRUCTURE
VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION Paulo Eduardo Brandão, PhD Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health School of Veterinary Medicine University of São Paulo, Brazil I. VIRUS STRUCTURE
LEC 2, Medical biology, Theory, prepared by Dr. AYAT ALI
 General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Some living things are made of ONE cell, and are called. Other organisms are composed of many cells, and are called. (SEE PAGE 6)
 Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
WHY? Viruses are considered non-living because they do:
 Viruses What is a Virus? Non-living particle WHY? Viruses are considered non-living because they do: NOT Carry out metabolism NOT Grow or develop NOT Replicate without the help of a living cell (host).
Viruses What is a Virus? Non-living particle WHY? Viruses are considered non-living because they do: NOT Carry out metabolism NOT Grow or develop NOT Replicate without the help of a living cell (host).
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Design and Analysis of Ranavirus Studies: Surveillance and Assessing Risk
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Forestry, Wildlife, and Fisheries Publications and Other Works Forestry, Wildlife, and Fisheries 2015 Design and Analysis
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Forestry, Wildlife, and Fisheries Publications and Other Works Forestry, Wildlife, and Fisheries 2015 Design and Analysis
AP Biology. Viral diseases Polio. Chapter 18. Smallpox. Influenza: 1918 epidemic. Emerging viruses. A sense of size
 Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Discovery of. 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes. 1931: first images of viruses obtained using
 Discovery of (1884: invention of the Chamberland filter with pores smaller than bacteria) 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes a paper in which shows that extracts from diseased tobacco plants
Discovery of (1884: invention of the Chamberland filter with pores smaller than bacteria) 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes a paper in which shows that extracts from diseased tobacco plants
Comparative Genomics of an Emerging Amphibian Virus
 INVESTIGATION Comparative Genomics of an Emerging Amphibian Virus Brendan Epstein and Andrew Storfer 1 School of Biological Sciences, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington 99164 ABSTRACT Ranaviruses,
INVESTIGATION Comparative Genomics of an Emerging Amphibian Virus Brendan Epstein and Andrew Storfer 1 School of Biological Sciences, Washington State University, Pullman, Washington 99164 ABSTRACT Ranaviruses,
Unit 13.2: Viruses. Vocabulary capsid latency vaccine virion
 Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Influenza viruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Influenza viruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped particles, quasi-spherical or filamentous Diameter 80-120 nm Envelope is derived
Influenza viruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped particles, quasi-spherical or filamentous Diameter 80-120 nm Envelope is derived
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Chapter 19: Viruses. 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction. What exactly is a Virus? 11/7/ Viral Structure & Reproduction. 2.
 Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Picornaviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
Ebola virus crisis. Prof. Viktor Volchkov. Molecular basis of viral pathogenicity
 Ebola virus crisis Prof. Viktor Volchkov Molecular basis of viral pathogenicity International Centre for Research in Infectiology (CIRI), INSERM Claude Bernard University Lyon-1, Lyon, France viktor.volchkov@inserm.fr
Ebola virus crisis Prof. Viktor Volchkov Molecular basis of viral pathogenicity International Centre for Research in Infectiology (CIRI), INSERM Claude Bernard University Lyon-1, Lyon, France viktor.volchkov@inserm.fr
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
HIV INFECTION: An Overview
 HIV INFECTION: An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ
HIV INFECTION: An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ
Hands-on Activity Viral DNA Integration. Educator Materials
 OVERVIEW This activity is part of a series of activities and demonstrations focusing on various aspects of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) life cycle. HIV is a retrovirus. Retroviruses are distinguished
OVERVIEW This activity is part of a series of activities and demonstrations focusing on various aspects of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) life cycle. HIV is a retrovirus. Retroviruses are distinguished
III. What are the requirements for taking and passing this course?
 1 Molecular Virology Lecture # 1: Course Introduction I. Instructor and Background Dr. Richard Kuhn rjkuhn@bragg.bio.purdue.edu B-129 Lilly Hall 494-1164 Office Hours - Wednesday 10:30-11:30 II. Objective:
1 Molecular Virology Lecture # 1: Course Introduction I. Instructor and Background Dr. Richard Kuhn rjkuhn@bragg.bio.purdue.edu B-129 Lilly Hall 494-1164 Office Hours - Wednesday 10:30-11:30 II. Objective:
Animal hosts Natural host Laboratory animals Rabbits Mice Rats Hamsters Newborn or suckling rodents Animal models for viral pathogenesis 4 Growth of v
 Principles of Virology Department of Molecular Genetics & Microbiology Univ ersity of Florida, Gainesv ille, FL 1 Outline Virus cultivation Assay of viruses Virus genetics 2 Virus isolation Evidence of
Principles of Virology Department of Molecular Genetics & Microbiology Univ ersity of Florida, Gainesv ille, FL 1 Outline Virus cultivation Assay of viruses Virus genetics 2 Virus isolation Evidence of
Fayth K. Yoshimura, Ph.D. September 7, of 7 RETROVIRUSES. 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
 1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
1 of 7 I. Diseases Caused by Retroviruses RETROVIRUSES A. Human retroviruses that cause cancers 1. HTLV-I causes adult T-cell leukemia and tropical spastic paraparesis 2. HTLV-II causes hairy T-cell leukemia
Running Head: AN UNDERSTANDING OF HIV- 1, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENTS. An Understanding of HIV- 1, Symptoms, and Treatments.
 Running Head: AN UNDERSTANDING OF HIV- 1, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENTS An Understanding of HIV- 1, Symptoms, and Treatments Benjamin Mills Abstract HIV- 1 is a virus that has had major impacts worldwide. Numerous
Running Head: AN UNDERSTANDING OF HIV- 1, SYMPTOMS, AND TREATMENTS An Understanding of HIV- 1, Symptoms, and Treatments Benjamin Mills Abstract HIV- 1 is a virus that has had major impacts worldwide. Numerous
History electron microscopes
 Viruses History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin word- poison) In the 1930s, after the invention of
Viruses History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin word- poison) In the 1930s, after the invention of
Reverse Genetics of RNA Viruses
 Reverse Genetics of RNA Viruses Reverse Genetics (RG) he creation of a virus with a fulllength copy of the viral genome he most powerful tool in modern virology RG of RNA viruses Generation or recovery
Reverse Genetics of RNA Viruses Reverse Genetics (RG) he creation of a virus with a fulllength copy of the viral genome he most powerful tool in modern virology RG of RNA viruses Generation or recovery
Bacteriophage Reproduction
 Bacteriophage Reproduction Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles The following information is taken from: http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/index.html#charvir Bacteriophage Structure More complex
Bacteriophage Reproduction Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles The following information is taken from: http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/index.html#charvir Bacteriophage Structure More complex
Virology. *Viruses can be only observed by electron microscope never by light microscope. The size of the virus: nm in diameter.
 Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
HS-LS4-4 Construct an explanation based on evidence for how natural selection leads to adaptation of populations.
 Unit 2, Lesson 2: Teacher s Edition 1 Unit 2: Lesson 2 Influenza and HIV Lesson Questions: o What steps are involved in viral infection and replication? o Why are some kinds of influenza virus more deadly
Unit 2, Lesson 2: Teacher s Edition 1 Unit 2: Lesson 2 Influenza and HIV Lesson Questions: o What steps are involved in viral infection and replication? o Why are some kinds of influenza virus more deadly
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay
 Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Coronaviruses cause acute, mild upper respiratory infection (common cold).
 Coronaviruses David A. J. Tyrrell Steven H. Myint GENERAL CONCEPTS Clinical Presentation Coronaviruses cause acute, mild upper respiratory infection (common cold). Structure Spherical or pleomorphic enveloped
Coronaviruses David A. J. Tyrrell Steven H. Myint GENERAL CONCEPTS Clinical Presentation Coronaviruses cause acute, mild upper respiratory infection (common cold). Structure Spherical or pleomorphic enveloped
VIRUS & LAST UNIVERSAL COMMON ANCESTOR
 VIRUS & LAST UNIVERSAL COMMON ANCESTOR JOINT GRADUATE SEMINAR 2015 M.PHIL. STUDENT: CHEUNG KA WING, KELTON SUPERVISOR: DR. MARTIN CHAN 15 TH DEC 2015 DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE THE
VIRUS & LAST UNIVERSAL COMMON ANCESTOR JOINT GRADUATE SEMINAR 2015 M.PHIL. STUDENT: CHEUNG KA WING, KELTON SUPERVISOR: DR. MARTIN CHAN 15 TH DEC 2015 DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE THE
33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58
 Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Pro-rich region Trans-membrane region 214 246 359 381 UL50 1 397 211SSRTAS216PPPPPR222 NLS CR1 CR2 CR3 CR4 UL53 1 376 11RERRS15ALRS19LLRKRRR25 33VASTVNGATSANNHGEPPS51PADARPR58 FIG S1. UL97 phosphorylation
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics. AP Biology
 Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
FROG VIRUS 3-LIKE INFECTIONS IN AQUATIC AMPHIBIAN COMMUNITIES
 Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 44(1), 2008, pp. 109 120 # Wildlife Disease Association 2008 FROG VIRUS 3-LIKE INFECTIONS IN AQUATIC AMPHIBIAN COMMUNITIES A. L. J. Duffus, 1,5 B. D. Pauli, 2 K. Wozney, 3
Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 44(1), 2008, pp. 109 120 # Wildlife Disease Association 2008 FROG VIRUS 3-LIKE INFECTIONS IN AQUATIC AMPHIBIAN COMMUNITIES A. L. J. Duffus, 1,5 B. D. Pauli, 2 K. Wozney, 3
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES
 STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
And Current Situation
 African Swine Fever Research And Current Situation Luis L. Rodriguez Research Leader Foreign Animal Disease Research Unit Agricultural Research Service, Plum Island Animal Disease Center African Swine
African Swine Fever Research And Current Situation Luis L. Rodriguez Research Leader Foreign Animal Disease Research Unit Agricultural Research Service, Plum Island Animal Disease Center African Swine
the world and viruses
 More than 5,450 viruses belonging to more than 2,000 species, 287 genera, 73 families and 3 orders are recognized in the 8th ICTVreport report. the world and viruses 1 1889 H2N2 Emerging viruses in the
More than 5,450 viruses belonging to more than 2,000 species, 287 genera, 73 families and 3 orders are recognized in the 8th ICTVreport report. the world and viruses 1 1889 H2N2 Emerging viruses in the
