Supplementary Online Content
|
|
|
- Violet Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Online Content Rodger AJ, Cambiano V, Bruun T, et al; PARTNER Study Group. Sexual activity without condoms and risk of HIV transmission in serodifferent couples when the HIVpositive partner is using suppressive antiretroviral therapy: the PARTNER Study. JAMA. doi:./jama emethods etable. Partners Sample Type (Either Plasma or PBMCs) and pol HIV- Subtype etable 2. Pairwise Genetic Distances of pol and env Sequences From Partners and Positive Controls (Comprising Replicate Partners Sequences and Sequences From Confirmed Transmission Pairs Obtained in a Separate Study [ref: Beloukas Virus Res 22]) efigure. Phylogenetic Tree of pol Sequences From Couples, Including Couple 5 and Couple 6 With Subtype-Discordant Infection efigure 2. Phylogenetic Tree of pol Sequences From Nine Couples With Subtype B Infection etable 3. Sensitivity Analysis Including and Excluding Follow-up Time in Which the HIV-RNA was Suppressed at the Beginning of the Period but Became Elevated etable 4. Hierarchical Approach to Classifying Types of Sex etable 5. Baseline Characteristics in Participants Who Contributed to the Eligible Couple-Years of Follow-up and Participants Who Did Not (Either Because They Dropped Out or Because the Couple-Years of Follow-up They Contributed Were Not Eligible) 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
2 emethods Virological Methods. HIV- pol and env sequencing and analysis Viral sequences were obtained from either HIV- RNA recovered from plasma (n=4) or HIV- DNA recovered from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (n=3) (Supplementary Table ). HIV- RNA was extracted with NucliSENS easymag (biomérieux, France), reverse transcribed with Invitrogen SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis SuperMix (Life Technologies, CA, USA), and amplified by nested PCR with Invitrogen Platinum PCR SuperMix High Fidelity (Life Technologies). HIV- DNA was extracted with QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit (Qiagen, Netherlands), and input into a first round PCR with Invitrogen Platinum Taq DNA Polymerase High Fidelity (Life Technologies) followed by nested PCR with Invitrogen Platinum PCR SuperMix High Fidelity (Life Technologies). Sequencing was carried out with the BigDye Terminator v3. Cycle Sequencing Kit (Life Technologies) on the ABI 373xl DNA analyzer (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA). Sequences spanning amino acids -44 of pol (HXB nt) and of env (HXB nt) were aligned and manually edited using MUSCLE ( and MEGA 6. software [ref: Tamura, 23], respectively. Subtyping of pol sequences was performed using the online automated subtyping tool COMET (Context-based Modeling for Expeditious Typing) [ref: Struck, 24] and the REGA HIV- Subtyping Tool v3. [ref: Pineda-Pena, 23]. Automated subtyping results were confirmed by phylogenetic analysis with 26 reference sequences representing pure HIV- subtypes (A D, F H, J, and K) and 49 circulating recombinant forms (CRFs), as previously described [ref: Paraskevis, 25]. 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
3 For the analysis of linkage between the partners viral sequences, phylogenetic analyses included either all available sequences (regardless of HIV- subtype) or only those sequences that were typed as subtype B. Codons associated with antiretroviral drug resistance [ref: Wensing, 24] were removed from the partners alignments prior to analysis. jmodeltest2 [ref: Darriba, 22] was used to identify the best fitted substitution model under both AICc and BIC criteria, allowing searches across the three main substitution models and all possible Generalised Time Reversible (GTR) submatrices. GTR+I+G and 222+I+G+F were identified as the best fitted models. Maximumlikelihood (ML) estimates with bootstrap values were obtained with RaxML-HCP2 v8 using GTR+I+G [Ref: Stamatakis,24]. Bayesian Markov Chain Monte-Carlo (MCMC) inference with posterior probabilities was obtained with MrBayes v3.2.6 [ref: Ronquist, 22] using GTR+I+G and 222+I+G+F, for 7 generations sampling every th tree, as previously described [Beloukas, 22]. Convergence of the MCMC procedure was assessed by calculating the effective sampling size (ESS) with Tracer v..6 [Rambaut, 24], with a target ESS >. Analyses showing an initial ESS < were expanded (up to 5 7 generations) until efficient mixing of the Markovian chains was achieved. Each run consensus tree was implied and the Tree visualization and annotation was performed using FigTree v.4. Pairwise genetic distances were calculated using MEGA 6. under the Maximum Composite Likelihood model and the rate variation among sites was modeled with a gamma distribution (shape=4) [ref: Tamura, 23]. Analyses were run on the CIPRES Science Gateway [Ref: Miller 2] 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
4 References for Virological Methods. Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.. Mol Biol Evol 23;3: Struck D, Lawyer G, Ternes AM, Schmit JC, Bercoff DP. COMET: adaptive contextbased modeling for ultrafast HIV- subtype identification. Nucleic Acids Res 24;42: e Pineda-Pena AC, Faria NR, Imbrechts S, et al. Automated subtyping of HIV- genetic sequences for clinical and surveillance purposes: performance evaluation of the new REGA version 3 and seven other tools. Infect Genet Evol 23;9: Paraskevis D, Kostaki E, Beloukas A, et al. Molecular characterization of HIV- infection in Northwest Spain (29-23): Investigation of the subtype F outbreak. Infect Genet Evol 25;3: Wensing AM, Calvez V, Gunthard HF, Johnson VA, Paredes R, Pillay D, et al. 24 Update of the drug resistance mutations in HIV-. Top Antivir Med 24,22: Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D. jmodeltest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 22;9: Stamatakis A. RaxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 24;3: Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, et al. MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. System Biol 22;6: American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
5 9. Beloukas A, Magiorkinis E, Magiorkinis G, Zavitsanou A, Karamitros T, Hatzakis A, Paraskevis D. Assessment of phylogenetic sensitivity for reconstructing HIV- epidemiological relationships. Virus Res. 22;66: Rambaut A, Suchard M, Xie D, Drummond A. Tracer v.6. Available from Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE); 2; New Orleans, LA; 2. Pp American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
6 Calculation of Number of HIV Transmission Expected in the absence of ART We calculated the number of HIV transmissions that we would have expected in this study if the positive index partners were not on ART, based on the numbers of condomless sex acts reported during follow-up. The assumptions regarding the probability of HIV transmission per condomless sex act (in the absence of ART) come from two meta-analyses: Boily MC, Baggaley RF, Wang L, Masse B, White RG, Hayes RJ, et al. Heterosexual risk of HIV- infection per sexual act: systematic review and metaanalysis of observational studies. Lancet Infect Dis. 29;9(2):8-29. Baggaley RF, White RG, Boily MC. HIV transmission risk through anal intercourse: systematic review, met a-analysis and implications for HIV prevention. Int J Epidemiol. 2;39(4):48-63 The first (Boily 29) estimated the rate of transmission per heterosexual sex act in high income countries to be.8 (95% CI:.6-.) for male to female and.4 (95% CI:.-.4) for female to male. The second (Baggaley 2) estimated the probability of transmission per receptive anal sex act to be.4 (95%CI:.2-.25). No separate estimates for anal and vaginal sex were available for heterosexuals. For MSM, we conservatively only accounted for sex acts in which the negative partner was receptive. In order to estimate the number of HIV transmission expected to observe in absence of ART, we calculate separately for heterosexual couples with a male index partner, couples 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
7 with a female index partner and MSM couples, the cumulative probability of HIV transmission (CP) for each couple in the group was calculated, based on the number of sex acts the HIV-negative partner reported, using the formula below: CCCC = (( pp) nn ) where: n is the number of condomless sex acts reported by the negative partner sex act) p is the probability of transmission per condomless sex act (specific to the type of The cumulative probability of HIV transmission was summed across all couples to determine the number of sex acts across all couples in the study. These estimates suggest that we would have expected over transmissions in the MSM group alone if the positive partner had not been on ART. These estimates should be considered with caution because the sexual behaviour could have been different if the positive partner was not on ART and the number of sex acts since the last visit was collected as a categorical variable (,, 2-, -2, 2-4, >4) and we used the mid-point in the category they indicated (for the highest category we used a value of 5). Sensitivity Analysis Sensitivity analysis was conducted including the period of follow-up time in which the HIV-RNA was suppressed at the beginning of the period, but during which became elevated (etable 3). If we include the periods of follow-up time (defined between two 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
8 consecutive HIV tests), in which the HIV-RNA was suppressed at the beginning of the period but during which the HIV-RNA became elevated, the number of within-couple transmissions is still zero, therefore the estimated rate is zero. The estimates / confidence intervals included in the manuscript and the alternative described above are shown in the table below. In a further sensitivity analysis we calculated the rate and confidence interval taking a hierarchical approach to classifying types of sex (etable 4). Having defined such a hierarchy of risk, in referring to a specific sex act, we estimated the upper limit of the rate if this type of sex is the highest risk sex being performed. With the hierarchy (from the highest to the lowest) being: receptive anal sex with ejaculation, receptive anal sex without ejaculation, insertive anal sex, vaginal sex with ejaculation and vaginal sex without ejaculation. Those not indicated in the table below will remain invariate using the hierarchical approach. When considering a hierarchical approach (i.e. the act-specific rate were restricted to person-years of follow-up where that type of act was associated with the highest risk of acquisition), the 95% upper limit of the confidence interval increases: for receptive anal sex without ejaculation it increased from 8.4 to.95 per couple-years-of-follow up for heterosexual women, and from.68 to 3.6 per couple-years-of-follow up for MSM, while for vaginal sex it increased from.59 to.69 per couple-years-offollow up (Heterosexual men and women combined). 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
9 etable. Partners Sample Type (Either Plasma or PBMCs) and pol HIV- Subtype Couple no Initial HIV status Sample HIV- subtype NEGATIVE Plasma B POSITIVE Plasma B 2 NEGATIVE Plasma B 3 NEGATIVE Plasma B 4 NEGATIVE Plasma B 5 NEGATIVE Plasma A 6 NEGATIVE Plasma CRF 4_BG 7 NEGATIVE Plasma B POSITIVE Plasma B 8 NEGATIVE Plasma B 9 NEGATIVE PBMC B NEGATIVE PBMC B 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
10 NEGATIVE PBMC B NEGATIVE Plasma B NEGATIVE Plasma B POSITIVE Plasma B Footnotes: PBMC= Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; CRF = circulating recombinant form. HIV- subtype refers to the HIV positive partner initially and the previously HIV negative partner at follow-up after seroconversion 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
11 etable 2. Pairwise Genetic Distances of pol and env Sequences From Partners and Positive Controls (Comprising Replicate Partners Sequences and Sequences From Confirmed Transmission Pairs Obtained in a Separate Study [ref: Beloukas Virus Res 22]) Source Sequence (subtype) Median genetic distance (IQR) Partners pol (all).7 (.56,.79) Partners pol (B).68 (.56,.76) Partners env (all).28 (.,.43) Partners env (B).25 (.98,.37) Partner replicates pol. (<.,.3) Partner replicates env.24 (.2,.37) Separate study pol.8 (.6,.9) All positive controls pol.4 (<.,.8) IQR= Interquartile range 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
12 efigure. Phylogenetic Tree of pol Sequences From Couples, Including Couple 5 and Couple 6 With Subtype-Discordant Infection. Bayesian Markov Chain Monte-Carlo (MCMC) inference (222+I+G+F model). Branch line weight is proportional to the posterior probability. Partners sequences are in blue; N indicates the initially HIVnegative partner whereas P indicates the initially HIV-positive partner. Control sequences comprised the closest sequences identified through BLAST searches of GenBank. Positive control sequences comprised replicate sequences from study partners (in red) and sequences from confirmed transmission pairs obtained in a separate study (in orange) [Ref: Beloukas, Virus Res, 22]. *Sequences 9N2 and 9N3 were obtained from the same sample in two separate experiments. 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
13 AY6655 AY AY 679 AY GQ GQ GQ HM Couple_9N Couple_9N3.97 Couple_9N EU EU EU AY 6652 AY EU67338 FJ HQ76.9 Couple_5N GQ4235 Couple_6N HM3548 DQ Couple_N EF36323 JN94 EF JN833 Couple_8N JQ65835 JQ6565 HQ2658 EU69373 D2. JN55.54 JN355 AY JQ HM46462 GU3449 GQ39995 GQ39977 FJ64745 EU EF Couple_8P K C6977 JQ65838 JN837 HM46474 K C23842 JQ65848 U M KF379 AY GQ39967 HM35483 HM4649 HQ AF42.59 AF AF AY U U AY U Couple_N.74 AY 9424 AY Couple_P Couple_P HIV HX B2 AF42 JF EF EF36324 EF JN AY HQ26534 JQ363 D HQ26584 JQ3628 K J JQ39523 K J426 AY AB AY AF FJ JQ434 JQ58577 JQ KJ AY9423 AY 9423 GU8755 Couple_9P Couple_9P2 GU EF HQ768 GQ Couple_3P Couple_7P2 Couple_7P EF54993 Couple_5P.67 Couple_4N K C EU8779 EU8772 Couple_7N Couple_6P AF FJ AF3389 EF K3455. K J76758 M992.2 JN97 EU8778 FJ22836 FJ2288 JN7 JN995 GQ432 GQ39953 EU8777 FJ2288 JN58 K C EU8769 Couple_2P Couple_4P EU24853 AY AY M AY DQ GQ33845 AY DQ97739 AY AY AY AY AY AY K C AY 362 JX EF36755 AY 3256 AY AY AF AJ49469 GQ39927 AJ AJ9793 AF46728 Couple_N JN6382 AF Couple_3N JQ L GU8756 K 23. FJ65959 FJ D8669. FJ K 283. JN HM45325 U255. KC34798 K C3477 K C AY 368 AY 3679 AY3678 FJ JQ K F38489 AY FJ GU26438 Couple_2N Couple_9N2 EU24855 EU EU EU Couple_P2 Couple_P GU2646 EU25539 GQ4455 EU24859 EU EU24844 EU24845 EU American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
14 efigure 2. Phylogenetic Tree of pol Sequences From Nine Couples With Subtype B Infection. Maximum-likelihood (ML) inference (GTR+I+G model) from 9 couples with subtype B infection. Branch length is proportional to the genetic distance and line weight is proportional to the posterior probability. Partners sequences are in blue; N indicates the initially negative partner whereas P indicates the initially positive partner. Control sequences comprised the closest sequences identified through BLAST searches of GenBank. Positive control sequences comprised replicate samples from study partners (in red) and sequences from confirmed transmission pairs obtained in a separate study (in orange)[ref: Beloukas, Virus Res, 22]. *Sequences 9N2 and 9N3 were obtained from the same sample in two separate experiments. 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
15 JQ65838 K C AY JN58 3 FJ Couple_4P FJ GU2646 AY 368 GU26438 JQ65744 Couple_2N EF EF JN6439 Couple_N Couple_P AY Couple_N Couple_P2 Couple_P EF36323 Couple_5P Couple_3P EF JQ65747 Couple_6P EU GU EU AY3256 GU3449 EU24845 EU EU2484 GQ EU EU EU EU EU EU EU D2. EU69373 JQ6565 JQ65797 JQ65835 KC AY Couple_P AY AF AF42 9 AF42 79 U U U AY9424 JF EF36324 AY AF56824 AY HQ26534 JQ KJ JQ39523 HQ K J JQ3628 AY 9423 HQ2658 AY9423 GU8755 Couple_9P2 Couple_9P KC EF54993 AF D AY AY HM AY AB K J AF JQ58577 AY 336 U FJ JQ434 Couple_9N3 Couple_9N2 Couple_9N4 JX 6277 EF36755 FJ86827 K F AY AF25949 M M992.2 JQ K J Couple_9N GQ39927 JN837 AY 3848 HIVHXB 2 FJ65959 FJ6595 K 283. D8669. FJ65957 K3455. Couple_7P JQ65848 AJ9793 GU8756 L JN HM U AF EF JN FJ Couple_7P2 AY AY GQ33845 K23. K F AY FJ AY AY AY HM46474 DQ DQ M AY EU AJ49469 AF K C6977 GQ AJ GQ39995 JN JN JN995 JN94 EU8779 JN7 GQ39953 EU EU8772 EU8778 JN97 EU8777 GQ432 Couple_2P K C3429 AF46728 EF EU Couple_7N AY 3679 AY 3678 FJ4885 K C34467 Couple_N EF JN833 Couple_8N Couple_8P GQ FJ2288 Couple_3N HQ768 Couple_4N AY K C34798 EU24853 K C American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
16 etable 3. Sensitivity Analysis Including and Excluding Follow-up Time in Which the HIV-RNA was Suppressed at the Beginning of the Period but Became Elevated Rate of within couple transmission (per Upper 95% confidence Couple years of follow-up couple years of follow-up) limit Results presented in the All any sex manuscript HTW any sex HTM any sex MSM any sex Including the periods within which the most recent HIV- RNA load at the beginning of the period was <2 copies/ml, but was subsequently measured as >2 copies/ml during the period All any sex HTM: heterosexual men; HTW: heterosexual women, MSM: men having sex with men; 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
17 etable 4. Hierarchical Approach to Classifying Types of Sex Approach used in the Hierarchical approach manuscript Upper 95% confidence Couple years of Upper 95% confidence Couple years of follow-up limit follow-up limit All vaginal sex All insertive anal sex HTW vaginal sex with ejaculation HTW vaginal sex without ejaculation HTW receptive anal sex without ejaculation HTM vaginal sex MSM insertive anal sex MSM receptive anal sex without ejaculation HTM: heterosexual men; HTW: heterosexual women, MSM: men having sex with men; 26 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
18 etable 5. Baseline Characteristics in Participants Who Contributed to the Eligible Couple-Years of Follow-up and Participants Who Did Not (Either Because They Dropped Out or Because the Couple-Years of Follow-up They Contributed Were Not Eligible) Heterosexuals MSM p-value* Contributed to eligible Contributed to eligible (HT) couple years of follow-up couple years of follow-up Yes (n=96) Age, median (IQR) [ missing] 42.7 ( ) No (n=252) 4.7 ( ) Yes (n=68) 4. ( ) No (n=34) 37.6 ( ) p-value* (MSM).334 <. Ethnicity, n (%) White 837 (78%) 73 (74%) 66 (9%) 245 (9%) Education level, n (%) Black 4 (3%) 37 (6%) 6 (%) 5 (2%) Asian 39 (4%) 5 (2%) 8 (3%) (<%) Other 6 (6%) 2 (9%) 42 (6%) 22 (8%) Missing High school or less 458 (43%) 4 (49%) 4 (2%) 56 (2%) Vocational education College or university 36 (3%) 49 (2%) 9 (28%) 7 (26%) 29 (27%) 7 (3%) 339 (5%) 42(53%) Missing HIV Acquisition Heterosexual 285 (53%) 7 (6) (%) (%) American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
19 route, n (%) [applies only to HIV+] Years of CL sex, median(iqr) Years on ART, median(iqr) [applies only to HIV+] Self-reported ART adherence >9%, n (%) [applies only to HIV+] Informed their partner if they missed doses of ART, n (%) [applies only to HIV+] MSM 23 (4%) (%) 324 (97%) 24 (93%) Shared needles or other injection equipment 97 (8%) 9 (6%) (%) (%) Other 3 (24%) 27 (23%) (3%) (7%) Missing (.7-9.4) 3.4 (.5-.2).5 (.5-4.) Missing ( ) 8. ( ) 4.8 (.9 -.4) Missing (.3-2.5) (.6-9.8) Yes 477 (94%) 98 (89%) 39 (97%) 25 (98%) Missing No 4 (7%) 9 (8%) 3 (4%) 6 (5%) Yes 256 (48%) 6 (52%) 33 (4%) 57 (43%) Did not miss doses 239 (45%) 47 (4%) 9 (57%) 7 (53%) Missing Self-reported Yes 45 (85%) 97 (87%) 39 (94%) (84%) American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
20 undetectable HIV- RNA load, n (%) [applies only to HIV+] CD4 count >35 mm 3, n (%) [applies only to HIV+; missing] Missing Yes 478 (87%) (8%) 39 (9%) 34 (89%) American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Downloaded From: on 6/8/28
The BLAST search on NCBI ( and GISAID
 Supplemental materials and methods The BLAST search on NCBI (http:// www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) and GISAID (http://www.platform.gisaid.org) showed that hemagglutinin (HA) gene of North American H5N1, H5N2 and
Supplemental materials and methods The BLAST search on NCBI (http:// www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) and GISAID (http://www.platform.gisaid.org) showed that hemagglutinin (HA) gene of North American H5N1, H5N2 and
Q and A - the PARTNER Study: new results from PARTNER 2
 Q and A - the PARTNER Study: new results from PARTNER 2 1. Study results What is the PARTNER Study? The PARTNER study is an international two-phase study that looked at whether HIV transmission occurs
Q and A - the PARTNER Study: new results from PARTNER 2 1. Study results What is the PARTNER Study? The PARTNER study is an international two-phase study that looked at whether HIV transmission occurs
(ii) The effective population size may be lower than expected due to variability between individuals in infectiousness.
 Supplementary methods Details of timepoints Caió sequences were derived from: HIV-2 gag (n = 86) 16 sequences from 1996, 10 from 2003, 45 from 2006, 13 from 2007 and two from 2008. HIV-2 env (n = 70) 21
Supplementary methods Details of timepoints Caió sequences were derived from: HIV-2 gag (n = 86) 16 sequences from 1996, 10 from 2003, 45 from 2006, 13 from 2007 and two from 2008. HIV-2 env (n = 70) 21
Fertility Desires/Management of Serodiscordant HIV + Couples
 Fertility Desires/Management of Serodiscordant HIV + Couples William R. Short, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Medicine Division Of Infectious Diseases Jefferson Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University
Fertility Desires/Management of Serodiscordant HIV + Couples William R. Short, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Medicine Division Of Infectious Diseases Jefferson Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University
Cascade of medical care to HIV-infected patients in Europe. Cristina Mussini
 Cascade of medical care to HIV-infected patients in Europe Cristina Mussini UNAIDS: New HIV treatment target 90% of people tested 90% of people diagnosed with HIV on treatment 90% of people on treatment
Cascade of medical care to HIV-infected patients in Europe Cristina Mussini UNAIDS: New HIV treatment target 90% of people tested 90% of people diagnosed with HIV on treatment 90% of people on treatment
HIV & Condomless Sex - What is the Risk? Why Not? Alan J. Taege, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Department of Infectious Disease Cleveland Clinic
 HIV & Condomless Sex - What is the Risk? Why Not? Alan J. Taege, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Department of Infectious Disease Cleveland Clinic Yes No What s Going on Out There? Condomless Sex among
HIV & Condomless Sex - What is the Risk? Why Not? Alan J. Taege, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Department of Infectious Disease Cleveland Clinic Yes No What s Going on Out There? Condomless Sex among
Importance of Viral Suppression to Reduce HIV Transmission: Recent Evidence
 Importance of Viral Suppression to Reduce HIV Transmission: Recent Evidence Toye Brewer, MD Co-Director, Fogarty International Training Program University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Viral suppression
Importance of Viral Suppression to Reduce HIV Transmission: Recent Evidence Toye Brewer, MD Co-Director, Fogarty International Training Program University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Viral suppression
Rajesh Kannangai Phone: ; Fax: ; *Corresponding author
 Amino acid sequence divergence of Tat protein (exon1) of subtype B and C HIV-1 strains: Does it have implications for vaccine development? Abraham Joseph Kandathil 1, Rajesh Kannangai 1, *, Oriapadickal
Amino acid sequence divergence of Tat protein (exon1) of subtype B and C HIV-1 strains: Does it have implications for vaccine development? Abraham Joseph Kandathil 1, Rajesh Kannangai 1, *, Oriapadickal
Background. A systematic analysis from previous studies reported the following prevalence:
 High levels of resistance among HIV-1 treatment naive patients in Greece. a nationwide study: Evidence for country and regional level transmission networks D. Paraskevis 1. E. Kostaki 1. G. Magiorkinis
High levels of resistance among HIV-1 treatment naive patients in Greece. a nationwide study: Evidence for country and regional level transmission networks D. Paraskevis 1. E. Kostaki 1. G. Magiorkinis
Phylodynamics of HIV-1 Subtype B among the Men- Having-Sex-with-Men (MSM) Population in Hong Kong
 Phylodynamics of HIV-1 Subtype B among the Men- Having-Sex-with-Men (MSM) Population in Hong Kong Jonathan Hon-Kwan Chen 1,3, Ka-Hing Wong 2, Kenny Chi-Wai Chan 2, Sabrina Wai-Chi To 1, Zhiwei Chen 3,
Phylodynamics of HIV-1 Subtype B among the Men- Having-Sex-with-Men (MSM) Population in Hong Kong Jonathan Hon-Kwan Chen 1,3, Ka-Hing Wong 2, Kenny Chi-Wai Chan 2, Sabrina Wai-Chi To 1, Zhiwei Chen 3,
HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment
 HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment Gabriel Wagner, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Infectious Diseases & Global Public Health UC San Diego HIV-Associated End Organ Damage Antiretroviral
HIV-1 Dual Infection and Neurocognitive Impairment Gabriel Wagner, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Infectious Diseases & Global Public Health UC San Diego HIV-Associated End Organ Damage Antiretroviral
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Goedhals D, Rossouw I, Hallbauer U, Mamabolo
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Goedhals D, Rossouw I, Hallbauer U, Mamabolo
An Analysis of Genital Tract Derived HIV from Heterosexual Transmission Pairs. Debrah Boeras Emory University October 14, 2008
 An Analysis of Genital Tract Derived HIV from Heterosexual Transmission Pairs Debrah Boeras Emory University October 14, 2008 Background A majority of HIV-1 infections occur through heterosexual exposure
An Analysis of Genital Tract Derived HIV from Heterosexual Transmission Pairs Debrah Boeras Emory University October 14, 2008 Background A majority of HIV-1 infections occur through heterosexual exposure
Micropathology Ltd. University of Warwick Science Park, Venture Centre, Sir William Lyons Road, Coventry CV4 7EZ
 www.micropathology.com info@micropathology.com Micropathology Ltd Tel 24hrs: +44 (0) 24-76 323222 Fax / Ans: +44 (0) 24-76 - 323333 University of Warwick Science Park, Venture Centre, Sir William Lyons
www.micropathology.com info@micropathology.com Micropathology Ltd Tel 24hrs: +44 (0) 24-76 323222 Fax / Ans: +44 (0) 24-76 - 323333 University of Warwick Science Park, Venture Centre, Sir William Lyons
Immune pressure analysis of protease and reverse transcriptase genes of primary HIV-1 subtype C isolates from South Africa
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(24), pp. 4784-4793, 6 June, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB10.560 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full Length
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 10(24), pp. 4784-4793, 6 June, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb DOI: 10.5897/AJB10.560 ISSN 1684 5315 2011 Academic Journals Full Length
Three factors were independently associated with a low degree of connectivity in the clusters:
 HIV Transmission Clusters Offer Clues to HIV Risk in Young Black MSM 21st International AIDS Conference (AIDS 2016), July 18-22, 2016, Durban, South Africa Mark Mascolini Phylogenetic analysis of young
HIV Transmission Clusters Offer Clues to HIV Risk in Young Black MSM 21st International AIDS Conference (AIDS 2016), July 18-22, 2016, Durban, South Africa Mark Mascolini Phylogenetic analysis of young
SINCE THE INTRODUCTION OF HIGHLY ACTIVE ANTIRETROVIRAL
 AIDS RESEARCH AND HUMAN RETROVIRUSES Volume 23, Number 1, 2007, pp. 107 115 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/aid.2006.0089 Investigating Signs of Recent Evolution in the Pool of Proviral HIV Type 1
AIDS RESEARCH AND HUMAN RETROVIRUSES Volume 23, Number 1, 2007, pp. 107 115 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/aid.2006.0089 Investigating Signs of Recent Evolution in the Pool of Proviral HIV Type 1
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content El-Sadr WM, Donnell D, Beauchamp G, et al. Financial incentives for linkage to care and viral suppression among HIV-positive patients: a randomized clinical trial (HPTN 065)
Supplementary Online Content El-Sadr WM, Donnell D, Beauchamp G, et al. Financial incentives for linkage to care and viral suppression among HIV-positive patients: a randomized clinical trial (HPTN 065)
SMPD 287 Spring 2015 Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development. Final Examination
 Final Examination You have a choice between A, B, or C. Please email your solutions, as a pdf attachment, by May 13, 2015. In the subject of the email, please use the following format: firstname_lastname_x
Final Examination You have a choice between A, B, or C. Please email your solutions, as a pdf attachment, by May 13, 2015. In the subject of the email, please use the following format: firstname_lastname_x
Chronic HIV-1 Infection Frequently Fails to Protect against Superinfection
 Chronic HIV-1 Infection Frequently Fails to Protect against Superinfection Anne Piantadosi 1,2[, Bhavna Chohan 1,2[, Vrasha Chohan 3, R. Scott McClelland 3,4,5, Julie Overbaugh 1,2* 1 Division of Human
Chronic HIV-1 Infection Frequently Fails to Protect against Superinfection Anne Piantadosi 1,2[, Bhavna Chohan 1,2[, Vrasha Chohan 3, R. Scott McClelland 3,4,5, Julie Overbaugh 1,2* 1 Division of Human
GENETIC STUDY OF VPU VARIANTS AMONG THE HIV-1 INFECTED INTRAVENOUS DRUG USERS OF MANIPUR PREDICTS HIGHLY PATHOGENIC VIRUS
 GENETIC STUDY OF VPU VARIANTS AMONG THE HIV-1 INFECTED INTRAVENOUS DRUG USERS OF MANIPUR PREDICTS HIGHLY PATHOGENIC VIRUS Adhikarimayum Lakhikumar Sharma 1, Thiyam Ramsing Singh 1, Takhellambam Chanu Machathoibi
GENETIC STUDY OF VPU VARIANTS AMONG THE HIV-1 INFECTED INTRAVENOUS DRUG USERS OF MANIPUR PREDICTS HIGHLY PATHOGENIC VIRUS Adhikarimayum Lakhikumar Sharma 1, Thiyam Ramsing Singh 1, Takhellambam Chanu Machathoibi
Evaluation of Dried Blood Spots (DBS) for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1) Drug Resistance Testing
 Evaluation of Dried Blood Spots (DBS) for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1) Drug Resistance Testing Dawit Assefa 2, Woldaregay E.Abegaz 3, Teferi Gedif 2, Belete Tegbaru 1, Dereje Teshome 1, Tesfaye
Evaluation of Dried Blood Spots (DBS) for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1) Drug Resistance Testing Dawit Assefa 2, Woldaregay E.Abegaz 3, Teferi Gedif 2, Belete Tegbaru 1, Dereje Teshome 1, Tesfaye
A new human immunodeficiency virus derived from gorillas
 A new human immunodeficiency virus derived from gorillas Jean-Christophe Plantier, Marie Leoz, Jonathan E Dickerson, Fabienne De Oliveira, François Cordonnier, Véronique Lemée, Florence Damond, David L
A new human immunodeficiency virus derived from gorillas Jean-Christophe Plantier, Marie Leoz, Jonathan E Dickerson, Fabienne De Oliveira, François Cordonnier, Véronique Lemée, Florence Damond, David L
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS. RNA extraction, cdna synthesis and PCR amplification. Since most
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS RNA extraction, cdna synthesis and PCR amplification. Since most patients enrolled in the study had periods of low viral loads in plasma, a sensitive RNA extraction method was used.
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS RNA extraction, cdna synthesis and PCR amplification. Since most patients enrolled in the study had periods of low viral loads in plasma, a sensitive RNA extraction method was used.
Receptive Anal Intercourse and HIV Infection
 World Journal of AIDS, 2017, 7, 269-278 http://www.scirp.org/journal/wja ISSN Online: 2160-8822 ISSN Print: 2160-8814 Receptive Anal Intercourse and HIV Infection Gilbert R. Lavoie 1, John F. Fisher 2
World Journal of AIDS, 2017, 7, 269-278 http://www.scirp.org/journal/wja ISSN Online: 2160-8822 ISSN Print: 2160-8814 Receptive Anal Intercourse and HIV Infection Gilbert R. Lavoie 1, John F. Fisher 2
Deep Sequencing Detects V3 loop Forms Present in Functional X4 Viruses Growing in MT 2 assays
 Deep Sequencing Detects V3 loop Forms Present in Functional X4 Viruses Growing in MT 2 assays Christian Pou 1, Rocío Bellido 1, Francisco M. Codoñer 1, Alexander Thielen 3, Cecilia Cabrera 1, Judith Dalmau
Deep Sequencing Detects V3 loop Forms Present in Functional X4 Viruses Growing in MT 2 assays Christian Pou 1, Rocío Bellido 1, Francisco M. Codoñer 1, Alexander Thielen 3, Cecilia Cabrera 1, Judith Dalmau
Viral suppression and HIV transmission in serodiscordant male couples: an international, prospective, observational, cohort study
 Viral suppression and HIV transmission in serodiscordant male couples: an international, prospective, observational, cohort study Benjamin R Bavinton, Angie N Pinto, Nittaya Phanuphak, Beatriz Grinsztejn,
Viral suppression and HIV transmission in serodiscordant male couples: an international, prospective, observational, cohort study Benjamin R Bavinton, Angie N Pinto, Nittaya Phanuphak, Beatriz Grinsztejn,
Evolution of influenza
 Evolution of influenza Today: 1. Global health impact of flu - why should we care? 2. - what are the components of the virus and how do they change? 3. Where does influenza come from? - are there animal
Evolution of influenza Today: 1. Global health impact of flu - why should we care? 2. - what are the components of the virus and how do they change? 3. Where does influenza come from? - are there animal
HIV-1 co-receptor tropism in recently diagnosed patients: correlates of CXCR4-use, impact of subtype and indications for X4/DM virus transmission
 Poster nr. O_26 HIV-1 co-receptor tropism in recently diagnosed patients: correlates of CXCR4-use, impact of subtype and indications for X4/DM virus transmission Kristen Chalmet, Kenny Dauwe, Lander Foquet,
Poster nr. O_26 HIV-1 co-receptor tropism in recently diagnosed patients: correlates of CXCR4-use, impact of subtype and indications for X4/DM virus transmission Kristen Chalmet, Kenny Dauwe, Lander Foquet,
PEP and PREP. Dr David Hawkins Chelsea and Westminster Hospital
 PEP and PREP Dr David Hawkins Chelsea and Westminster Hospital Opportunities for biomedical interventions YEARS HOURS 72 HOURS YEARS Prior to exposure Exposure (pre-coital/ coital) Exposure (pre-coital/
PEP and PREP Dr David Hawkins Chelsea and Westminster Hospital Opportunities for biomedical interventions YEARS HOURS 72 HOURS YEARS Prior to exposure Exposure (pre-coital/ coital) Exposure (pre-coital/
Transmission Fitness of Drug- Resistant HIV Revealed in the United States National Surveillance System
 Transmission Fitness of Drug- Resistant HIV Revealed in the United States National Surveillance System Joel O. Wertheim 1,2, Alexandra M. Oster 3, Jeffrey A. Johnson 3, William M. Switzer 3, Neeraja Saduvala
Transmission Fitness of Drug- Resistant HIV Revealed in the United States National Surveillance System Joel O. Wertheim 1,2, Alexandra M. Oster 3, Jeffrey A. Johnson 3, William M. Switzer 3, Neeraja Saduvala
Transmission of Single and Multiple Viral Variants in Primary HIV-1 Subtype C Infection
 Transmission of Single and Multiple Viral Variants in Primary HIV-1 Subtype C Infection The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Transmission of Single and Multiple Viral Variants in Primary HIV-1 Subtype C Infection The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
High Failure Rate of the ViroSeq HIV-1 Genotyping System for Drug Resistance Testing in Cameroon, a Country with Broad HIV-1 Genetic Diversity
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 1635 1641 Vol. 49, No. 4 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01478-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. High Failure
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 2011, p. 1635 1641 Vol. 49, No. 4 0095-1137/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jcm.01478-10 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. High Failure
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Superinfection with drug-resistant HIV is rare and does not contribute substantially to therapy failure in a large European cohort Bartha, I.; Assel, M.; Sloot, P.M.A.;
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Superinfection with drug-resistant HIV is rare and does not contribute substantially to therapy failure in a large European cohort Bartha, I.; Assel, M.; Sloot, P.M.A.;
Improving the accuracy of demographic and clock model comparison while accommodating phylogenetic uncertainty
 Improving the accuracy of demographic and clock model comparison while accommodating phylogenetic uncertainty Guy Baele Evolutionary and Computational Virology Section, KU Leuven, Belgium June 19th, 2012
Improving the accuracy of demographic and clock model comparison while accommodating phylogenetic uncertainty Guy Baele Evolutionary and Computational Virology Section, KU Leuven, Belgium June 19th, 2012
HIV: Pregnancy in Serodiscordant Couple. Dr Chow TS ID Clinic HPP
 HIV: Pregnancy in Serodiscordant Couple Dr Chow TS ID Clinic HPP Sexual Reproductive Health and Rights The recognition of the sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) of all individuals and couples
HIV: Pregnancy in Serodiscordant Couple Dr Chow TS ID Clinic HPP Sexual Reproductive Health and Rights The recognition of the sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) of all individuals and couples
Women and Viral Load. Together, we can change the course of the HIV epidemic one woman at a time.
 Women and Viral Load Together, we can change the course of the HIV epidemic one woman at a time. #onewomanatatime #thewellproject What Is Viral Load? Viral load is the amount of HIV (number of viruses
Women and Viral Load Together, we can change the course of the HIV epidemic one woman at a time. #onewomanatatime #thewellproject What Is Viral Load? Viral load is the amount of HIV (number of viruses
Evolution of hepatitis C virus in blood donors and their respective recipients
 Journal of General Virology (2003), 84, 441 446 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.18642-0 Short Communication Correspondence Jean-François Cantaloube jfc-ets-ap@gulliver.fr Evolution of hepatitis C virus in blood donors
Journal of General Virology (2003), 84, 441 446 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.18642-0 Short Communication Correspondence Jean-François Cantaloube jfc-ets-ap@gulliver.fr Evolution of hepatitis C virus in blood donors
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Melo AS, Aguiar RS, Amorim MMR, et al. Congenital Zika virus infection: beyond neonatal microcephaly. JAMA Neurol. Published online October 3, 2016. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.3720.
Supplementary Online Content Melo AS, Aguiar RS, Amorim MMR, et al. Congenital Zika virus infection: beyond neonatal microcephaly. JAMA Neurol. Published online October 3, 2016. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.3720.
State of Alabama HIV Surveillance 2014 Annual Report
 State of Alabama HIV Surveillance 2014 Annual Report Prepared by: Division of STD Prevention and Control HIV Surveillance Branch Contact Person: Richard P. Rogers, MS, MPH richard.rogers@adph.state.al.us
State of Alabama HIV Surveillance 2014 Annual Report Prepared by: Division of STD Prevention and Control HIV Surveillance Branch Contact Person: Richard P. Rogers, MS, MPH richard.rogers@adph.state.al.us
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
PrEP for HIV Prevention. Adult Clinical Guideline from the New York State Department of Health AIDS Institute
 PrEP for HIV Prevention Adult Clinical Guideline from the New York State Department of Health AIDS Institute www.hivguidelines.org Purpose of the PrEP Guideline Raise awareness of PrEP among healthcare
PrEP for HIV Prevention Adult Clinical Guideline from the New York State Department of Health AIDS Institute www.hivguidelines.org Purpose of the PrEP Guideline Raise awareness of PrEP among healthcare
Downloaded from:
 Kiwelu, IE; Novitsky, V; Margolin, L; Baca, J; Manongi, R; Sam, N; Shao, J; McLane, MF; Kapiga, SH; Essex, M (2012) HIV-1 subtypes and recombinants in Northern Tanzania: distribution of viral quasispecies.
Kiwelu, IE; Novitsky, V; Margolin, L; Baca, J; Manongi, R; Sam, N; Shao, J; McLane, MF; Kapiga, SH; Essex, M (2012) HIV-1 subtypes and recombinants in Northern Tanzania: distribution of viral quasispecies.
Contents. lessmore. 1 of 11 6/2/ :06 PM
 1 of 11 6/2/2010 12:06 PM Background Since its initial detection in April 2009, the A/H1N1pdm influenza virus has spread rapidly in humans, with over 5,700 human deaths. However, little is known about
1 of 11 6/2/2010 12:06 PM Background Since its initial detection in April 2009, the A/H1N1pdm influenza virus has spread rapidly in humans, with over 5,700 human deaths. However, little is known about
Systematic review with multiple treatment comparison metaanalysis. on interventions for hepatic encephalopathy
 Systematic review with multiple treatment comparison metaanalysis on interventions for hepatic encephalopathy Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a reversible neuropsychiatric syndrome associated with severe
Systematic review with multiple treatment comparison metaanalysis on interventions for hepatic encephalopathy Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a reversible neuropsychiatric syndrome associated with severe
Supplementary Fig. S1: E. helvum cytochrome b haplotype Bayesian phylogeny with E. dupreanum used as an outgroup. Three main clades are identified:
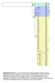 Supplementary Fig. S1: E. helvum cytochrome b haplotype Bayesian phylogeny with E. dupreanum used as an outgroup. Three main clades are identified: A, B and C. Posterior probabilities are shown on the
Supplementary Fig. S1: E. helvum cytochrome b haplotype Bayesian phylogeny with E. dupreanum used as an outgroup. Three main clades are identified: A, B and C. Posterior probabilities are shown on the
Phylodynamics analysis of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1)
 Page 1 of 24 1 Phylodynamics analysis of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope gene in mother and child pairs. Luciane Amorim Santos 1, Rebecca R Gray 3, Joana Paixão Monteiro-Cunha
Page 1 of 24 1 Phylodynamics analysis of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) envelope gene in mother and child pairs. Luciane Amorim Santos 1, Rebecca R Gray 3, Joana Paixão Monteiro-Cunha
HIV transmission in the migrant population. D. Paraskevis
 HIV transmission in the migrant population D. Paraskevis Content Definitions Epidemiology of HIV in migrants Methods to estimate the origin of HIV acquisition Molecular epidemiology Bayes method based
HIV transmission in the migrant population D. Paraskevis Content Definitions Epidemiology of HIV in migrants Methods to estimate the origin of HIV acquisition Molecular epidemiology Bayes method based
Ongoing HIV Replication During ART Reconsidered
 Open Forum Infectious Diseases PERSPECTIVES Ongoing HIV Replication During ART Reconsidered Mary F. Kearney, 1 Ann Wiegand, 1 Wei Shao, 2 William R. McManus, 1 Michael J. Bale, 1 Brian Luke, 2 Frank Maldarelli,
Open Forum Infectious Diseases PERSPECTIVES Ongoing HIV Replication During ART Reconsidered Mary F. Kearney, 1 Ann Wiegand, 1 Wei Shao, 2 William R. McManus, 1 Michael J. Bale, 1 Brian Luke, 2 Frank Maldarelli,
HIV-1 subtype C in Karonga District, Malawi. Simon Travers
 HIV-1 subtype C in Karonga District, Malawi Simon Travers HIV-1; closely related to HIV found in chimps HIV-2; closely related to HIV found in mangabys Worldwide Distribution of HIV-1 group M subtypes
HIV-1 subtype C in Karonga District, Malawi Simon Travers HIV-1; closely related to HIV found in chimps HIV-2; closely related to HIV found in mangabys Worldwide Distribution of HIV-1 group M subtypes
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure. HIV Update Outline. Undetectable = Untransmissable HTPN 052. Partner Opposites attract 9/28/2018
 Faculty/Presenter Disclosure HIV Update 2018 Dr. Joss de Wet Clinical Assistant Professor Family Medicine UBC Faculty: Joss de Wet Relationships with financial sponsors: Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: Gilead,
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure HIV Update 2018 Dr. Joss de Wet Clinical Assistant Professor Family Medicine UBC Faculty: Joss de Wet Relationships with financial sponsors: Speakers Bureau/Honoraria: Gilead,
Inter-country mixing in HIV transmission clusters: A pan-european phylodynamic study
 Inter-country mixing in HIV transmission clusters: A pan-european phylodynamic study Prabhav Kalaghatgi Max Planck Institute for Informatics March 20th 2013 HIV epidemic (2009) Prabhav Kalaghatgi 2/18
Inter-country mixing in HIV transmission clusters: A pan-european phylodynamic study Prabhav Kalaghatgi Max Planck Institute for Informatics March 20th 2013 HIV epidemic (2009) Prabhav Kalaghatgi 2/18
Models of HIV during antiretroviral treatment
 Models of HIV during antiretroviral treatment Christina M.R. Kitchen 1, Satish Pillai 2, Daniel Kuritzkes 3, Jin Ling 3, Rebecca Hoh 2, Marc Suchard 1, Steven Deeks 2 1 UCLA, 2 UCSF, 3 Brigham & Womes
Models of HIV during antiretroviral treatment Christina M.R. Kitchen 1, Satish Pillai 2, Daniel Kuritzkes 3, Jin Ling 3, Rebecca Hoh 2, Marc Suchard 1, Steven Deeks 2 1 UCLA, 2 UCSF, 3 Brigham & Womes
Anti Retroviral Traitment (ARVs)
 Anti Retroviral Traitment (ARVs) IEC material for People With Disabilities UPHLS - 2015 - Anti Retroviral Traitment Booklet Produced by AZ MEDIA No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior
Anti Retroviral Traitment (ARVs) IEC material for People With Disabilities UPHLS - 2015 - Anti Retroviral Traitment Booklet Produced by AZ MEDIA No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior
Principles of phylogenetic analysis
 Principles of phylogenetic analysis Arne Holst-Jensen, NVI, Norway. Fusarium course, Ås, Norway, June 22 nd 2008 Distance based methods Compare C OTUs and characters X A + D = Pairwise: A and B; X characters
Principles of phylogenetic analysis Arne Holst-Jensen, NVI, Norway. Fusarium course, Ås, Norway, June 22 nd 2008 Distance based methods Compare C OTUs and characters X A + D = Pairwise: A and B; X characters
State of Alabama HIV Surveillance 2013 Annual Report Finalized
 State of Alabama HIV Surveillance 2013 Annual Report Finalized Prepared by: Division of STD Prevention and Control HIV Surveillance Branch Contact Person: Allison R. Smith, MPH Allison.Smith@adph.state.al.us
State of Alabama HIV Surveillance 2013 Annual Report Finalized Prepared by: Division of STD Prevention and Control HIV Surveillance Branch Contact Person: Allison R. Smith, MPH Allison.Smith@adph.state.al.us
COMET: Rapid and reliable HCV subtype predictor
 COMET: Rapid and reliable HCV subtype predictor (Context-based Modeling for Expeditious Typing) Daniel Struck CRP-SANTÉ Laboratory of Retrovirology (daniel.struck@crp-sante.lu) Background HCV genotype/subtype
COMET: Rapid and reliable HCV subtype predictor (Context-based Modeling for Expeditious Typing) Daniel Struck CRP-SANTÉ Laboratory of Retrovirology (daniel.struck@crp-sante.lu) Background HCV genotype/subtype
Attendees will be able to:
 A. Kay Kalousek, DO, MS, FACOFP kaysdroid@gmail.com April 21, 2017 Attendees will be able to: List strategies for prevention of HIV infection Explain the pharmacology of TDF/FTC related to PrEP Assess
A. Kay Kalousek, DO, MS, FACOFP kaysdroid@gmail.com April 21, 2017 Attendees will be able to: List strategies for prevention of HIV infection Explain the pharmacology of TDF/FTC related to PrEP Assess
When PrEP fails. Laura Waters MD FRCP Mortimer Market Centre London
 When PrEP fails Laura Waters MD FRCP Mortimer Market Centre London www.aidsunited.org PrEP works If people at risk take it If it s taken in the right way If it s available Commissioned/licensed Affordable
When PrEP fails Laura Waters MD FRCP Mortimer Market Centre London www.aidsunited.org PrEP works If people at risk take it If it s taken in the right way If it s available Commissioned/licensed Affordable
New technologies reaching the clinic
 New technologies reaching the clinic Martin Däumer May 31, 2018 Deep-sequencing Standard Sanger-sequencing...PQIYMDDHTRE... Ultra-deep-sequencing...PQIYMDDHTRE......PQIYMDDHTRE......PQIYVDDHTRE......PQIYMDDHTRE......PQIYMDDHTRE......PQIYMDDHTRE...
New technologies reaching the clinic Martin Däumer May 31, 2018 Deep-sequencing Standard Sanger-sequencing...PQIYMDDHTRE... Ultra-deep-sequencing...PQIYMDDHTRE......PQIYMDDHTRE......PQIYVDDHTRE......PQIYMDDHTRE......PQIYMDDHTRE......PQIYMDDHTRE...
Foot-and Mouth Disease Ecological Studies In Endemic Settings: Ongoing Studies in Vietnam and Pakistan
 Foot-and Mouth Disease Ecological Studies In Endemic Settings: Ongoing Studies in Vietnam and Pakistan Luis Rodriguez (Jonathan Arzt) Research leader, USDA-ARS Plum Island 1 PAKISTAN CHARACTERIZATION OF
Foot-and Mouth Disease Ecological Studies In Endemic Settings: Ongoing Studies in Vietnam and Pakistan Luis Rodriguez (Jonathan Arzt) Research leader, USDA-ARS Plum Island 1 PAKISTAN CHARACTERIZATION OF
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 September 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012 September 1; 61(1): 19 22. doi:10.1097/qai.0b013e318264460f. Evaluation of HIV-1 Ambiguous Nucleotide
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2012 September 1; 61(1): 19 22. doi:10.1097/qai.0b013e318264460f. Evaluation of HIV-1 Ambiguous Nucleotide
HIV-1 acute infection: evidence for selection?
 HIV-1 acute infection: evidence for selection? ROLLAND Morgane University of Washington Cohort & data S6 S5 T4 S4 T2 S2 T1 S1 S7 T3 DPS (days post symptoms) 3 (Fiebig I) 7 (Fiebig I) 13 (Fiebig V) 14 (Fiebig
HIV-1 acute infection: evidence for selection? ROLLAND Morgane University of Washington Cohort & data S6 S5 T4 S4 T2 S2 T1 S1 S7 T3 DPS (days post symptoms) 3 (Fiebig I) 7 (Fiebig I) 13 (Fiebig V) 14 (Fiebig
Analysis of HIV-1 Resistance Mutations from various Compartments of the Peripheral Blood in Patients with Low-Level Viremia
 Andrea Freystetter / Christian Paar / Herbert Stekel / Jörg Berg Analysis of HIV-1 Resistance Mutations from various Compartments of the Peripheral Blood in Patients with Low-Level Viremia 107 - Translationale
Andrea Freystetter / Christian Paar / Herbert Stekel / Jörg Berg Analysis of HIV-1 Resistance Mutations from various Compartments of the Peripheral Blood in Patients with Low-Level Viremia 107 - Translationale
Analysis Plan for Individual-based Model Projections of the HPTN 071 (PopART) Intervention
 Analysis Plan for Individual-based Model Projections of the HPTN 071 (PopART) Intervention William Probert, Rafael Sauter, Anne Cori, Michael Pickles, Sian Floyd, David MacLeod, Ethan A Wilson, Deborah
Analysis Plan for Individual-based Model Projections of the HPTN 071 (PopART) Intervention William Probert, Rafael Sauter, Anne Cori, Michael Pickles, Sian Floyd, David MacLeod, Ethan A Wilson, Deborah
The Latest on HIV Testing. Dominika Seidman, MD MAS
 The Latest on HIV Testing Dominika Seidman, MD MAS Disclosures none 2 Learning objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to Define the window periods for various HIV tests
The Latest on HIV Testing Dominika Seidman, MD MAS Disclosures none 2 Learning objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to Define the window periods for various HIV tests
Antiretroviral therapy for prevention of HIV transmission: implications for Europe
 Review articles Antiretroviral therapy for prevention of HIV transmission: implications for Europe V Cambiano (v.cambiano@ucl.ac.uk) 1, J O Connor 1, A N Phillips 1, A Rodger 1, R Lodwick 2, A Pharris
Review articles Antiretroviral therapy for prevention of HIV transmission: implications for Europe V Cambiano (v.cambiano@ucl.ac.uk) 1, J O Connor 1, A N Phillips 1, A Rodger 1, R Lodwick 2, A Pharris
Mapping of the influenza A hemagglutinin serotypes evolution by the ISSCOR method
 Regular paper Supplementary Materials pp 441 452 Vol. 61, 2014 on-line at: www.actabp.pl Mapping of the influenza A hemagglutinin serotypes evolution by the ISSCOR method Jan P. Radomski 1,4 *, Piotr P.
Regular paper Supplementary Materials pp 441 452 Vol. 61, 2014 on-line at: www.actabp.pl Mapping of the influenza A hemagglutinin serotypes evolution by the ISSCOR method Jan P. Radomski 1,4 *, Piotr P.
Fertility Management in HIV. INTEREST Workshop, 16 Dakar May 2013 Vivian Black, Director Clinical Programmes Wits Reproductive Health & HIV Institute
 Fertility Management in HIV INTEREST Workshop, 16 Dakar May 2013 Vivian Black, Director Clinical Programmes Wits Reproductive Health & HIV Institute What to consider Does HIV affect fertility success?
Fertility Management in HIV INTEREST Workshop, 16 Dakar May 2013 Vivian Black, Director Clinical Programmes Wits Reproductive Health & HIV Institute What to consider Does HIV affect fertility success?
Advances in HIV science and treatment. Report on the global AIDS epidemic,
 HIV biomolecular advances and treatment updates David A Cooper National Centre in HIV Epidemiology and Clinical Research The University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia UNAIDS: global l HIV infections
HIV biomolecular advances and treatment updates David A Cooper National Centre in HIV Epidemiology and Clinical Research The University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia UNAIDS: global l HIV infections
Charles Boucher MD. PhD. HIV Prevention 2.0
 Charles Boucher MD. PhD HIV Prevention 2.0 Prevention A variety of methods exists to prevent transmission of HIV Circumcision Condoms Post-exposure profylaxe (PEP) Treatment as prevention Pre-exposure
Charles Boucher MD. PhD HIV Prevention 2.0 Prevention A variety of methods exists to prevent transmission of HIV Circumcision Condoms Post-exposure profylaxe (PEP) Treatment as prevention Pre-exposure
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Fumagalli D, Venet D, Ignatiadis M, et al. RNA Sequencing to predict response to neoadjuvant anti-her2 therapy: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO randomized clinical trial.
Supplementary Online Content Fumagalli D, Venet D, Ignatiadis M, et al. RNA Sequencing to predict response to neoadjuvant anti-her2 therapy: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO randomized clinical trial.
MANITOBA HIV REPORT 2015
 MANITOBA HIV REPORT 2015 The Manitoba HIV Program provides information, specialized care, treatment, and support to approximately 1,250 people living with HIV across the province. The Program has two Winnipeg-based
MANITOBA HIV REPORT 2015 The Manitoba HIV Program provides information, specialized care, treatment, and support to approximately 1,250 people living with HIV across the province. The Program has two Winnipeg-based
BEAST Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis Sampling Trees
 BEAST Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis Sampling Trees Introduction Revealing the evolutionary dynamics of influenza This tutorial provides a step-by-step explanation on how to reconstruct the evolutionary
BEAST Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis Sampling Trees Introduction Revealing the evolutionary dynamics of influenza This tutorial provides a step-by-step explanation on how to reconstruct the evolutionary
Sample collection. To extend our previous molecular epidemiological survey of
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Methods Sample collection. To extend our previous molecular epidemiological survey of SIV infection in wild-living ape populations 1, 725 additional fecal samples
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Methods Sample collection. To extend our previous molecular epidemiological survey of SIV infection in wild-living ape populations 1, 725 additional fecal samples
HBV. Next Generation Sequencing, data analysis and reporting. Presenter Leen-Jan van Doorn
 HBV Next Generation Sequencing, data analysis and reporting Presenter Leen-Jan van Doorn HBV Forum 3 October 24 th, 2017 Marriott Marquis, Washington DC www.forumresearch.org HBV Biomarkers HBV biomarkers:
HBV Next Generation Sequencing, data analysis and reporting Presenter Leen-Jan van Doorn HBV Forum 3 October 24 th, 2017 Marriott Marquis, Washington DC www.forumresearch.org HBV Biomarkers HBV biomarkers:
The Science behind Preexposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Yunus Moosa Department of Infectious Diseases UKZN
 The Science behind Preexposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Yunus Moosa Department of Infectious Diseases UKZN 1 Ongoing HIV transmission despite expanding access to ART SA 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Treatment exposure
The Science behind Preexposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Yunus Moosa Department of Infectious Diseases UKZN 1 Ongoing HIV transmission despite expanding access to ART SA 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Treatment exposure
Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep)
 Projeto Praça Onze Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep) Mauro Schechter Principal Investigator, Projeto Praça Onze Professor of Infectious Diseases Universidade
Projeto Praça Onze Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro Post-Sexual Exposure Prophylaxis (npep) Mauro Schechter Principal Investigator, Projeto Praça Onze Professor of Infectious Diseases Universidade
HIV and drug resistance Simon Collins UK-CAB 1 May 2009
 HIV and drug resistance Simon Collins UK-CAB 1 May 2009 slides: thanks to Prof Clive Loveday, Intl. Clinical Virology Centre www.icvc.org.uk Tip of the iceberg = HIV result, CD4, VL Introduction: resistance
HIV and drug resistance Simon Collins UK-CAB 1 May 2009 slides: thanks to Prof Clive Loveday, Intl. Clinical Virology Centre www.icvc.org.uk Tip of the iceberg = HIV result, CD4, VL Introduction: resistance
Distinguishing epidemiological dependent from treatment (resistance) dependent HIV mutations: Problem Statement
 Distinguishing epidemiological dependent from treatment (resistance) dependent HIV mutations: Problem Statement Leander Schietgat 1, Kristof Theys 2, Jan Ramon 1, Hendrik Blockeel 1, and Anne-Mieke Vandamme
Distinguishing epidemiological dependent from treatment (resistance) dependent HIV mutations: Problem Statement Leander Schietgat 1, Kristof Theys 2, Jan Ramon 1, Hendrik Blockeel 1, and Anne-Mieke Vandamme
Phylogenetic Relatedness of Circulating HIV-1C Variants in Mochudi, Botswana
 Phylogenetic Relatedness of Circulating HIV-1C Variants in Mochudi, Botswana The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Phylogenetic Relatedness of Circulating HIV-1C Variants in Mochudi, Botswana The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Phylogenesis and Clinical Aspects of Pandemic 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection
 22 The Open Virology Journal, 2011, 5, 22-26 Open Access Phylogenesis and Clinical Aspects of Pandemic 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection Massimo Ciccozzi 1, Muhammed Babakir-Mina 2,3, Alessandra
22 The Open Virology Journal, 2011, 5, 22-26 Open Access Phylogenesis and Clinical Aspects of Pandemic 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection Massimo Ciccozzi 1, Muhammed Babakir-Mina 2,3, Alessandra
Extremely rapid spread of HIV-1 BF recombinants. in Argentina ACCEPTED. Laboratorio de Biología Celular y Retrovirus-CONICET,
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on October 00 J. Virol. doi:0./jvi.00-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved. 0 0 Extremely
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on October 00 J. Virol. doi:0./jvi.00-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved. 0 0 Extremely
Detection of HEV in Estonia. Anna Ivanova, Irina Golovljova, Valentina Tefanova
 Detection of HEV in Estonia Anna Ivanova, Irina Golovljova, Valentina Tefanova National Institute for Health Development Department of Virology Zoonotic pathogens Tick-borne pathogens: TBEV, Borrelia sp.,
Detection of HEV in Estonia Anna Ivanova, Irina Golovljova, Valentina Tefanova National Institute for Health Development Department of Virology Zoonotic pathogens Tick-borne pathogens: TBEV, Borrelia sp.,
Circumcision and penile human papillomavirus prevalence in human immunodeficiency virus-infected men: heterosexual and men who have sex with men
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EPIDEMIOLOGY Circumcision and penile human papillomavirus prevalence in human immunodeficiency virus-infected men: heterosexual and men who have sex with men M. P. Canadas 1,2, L. Darwich
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EPIDEMIOLOGY Circumcision and penile human papillomavirus prevalence in human immunodeficiency virus-infected men: heterosexual and men who have sex with men M. P. Canadas 1,2, L. Darwich
Science Supporting Online Material
 Science Supporting Online Material Cynthia A. Derdeyn, Julie M. Decker, Frederic Bibollet-Ruche, John L. Mokili, Mark Muldoon, Scott A. Denham, Marintha L. Heil, Francis Kasolo, Rosemary Musonda, Beatrice
Science Supporting Online Material Cynthia A. Derdeyn, Julie M. Decker, Frederic Bibollet-Ruche, John L. Mokili, Mark Muldoon, Scott A. Denham, Marintha L. Heil, Francis Kasolo, Rosemary Musonda, Beatrice
Trends in molecular diagnostics
 Trends in molecular diagnostics Detection of target genes of interest Quantification Infectious diseases HIV Hepatitis C & B TB / MAC Cytomegalovirus Herpes simplex Varicella zoster CT/GC HPV Profiling
Trends in molecular diagnostics Detection of target genes of interest Quantification Infectious diseases HIV Hepatitis C & B TB / MAC Cytomegalovirus Herpes simplex Varicella zoster CT/GC HPV Profiling
The cost-effectiveness of expanded testing for primary HIV infection Coco A
 The cost-effectiveness of expanded testing for primary HIV infection Coco A Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each abstract
The cost-effectiveness of expanded testing for primary HIV infection Coco A Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each abstract
Deep-Sequencing of HIV-1
 Deep-Sequencing of HIV-1 The quest for true variants Alexander Thielen, Martin Däumer 09.05.2015 Limitations of drug resistance testing by standard-sequencing Blood plasma RNA extraction RNA Reverse Transcription/
Deep-Sequencing of HIV-1 The quest for true variants Alexander Thielen, Martin Däumer 09.05.2015 Limitations of drug resistance testing by standard-sequencing Blood plasma RNA extraction RNA Reverse Transcription/
Evolutionary Rate of E2 Genes of Classical Swine Fever Virus in China
 Evolutionary Rate of E2 Genes of Classical Swine Fever Virus in China Zhang, H.,* Cao, H.W., Wu, Z.J. and Cui, Y.D. College of Biological Science and Technology, HeiLongJiang BaYi Agricultural University,
Evolutionary Rate of E2 Genes of Classical Swine Fever Virus in China Zhang, H.,* Cao, H.W., Wu, Z.J. and Cui, Y.D. College of Biological Science and Technology, HeiLongJiang BaYi Agricultural University,
Community oriented studies. New perspectives
 Community oriented studies. New perspectives Swiss HIV Cohort Study Increased Viral Load Suppression in HIV+ Persons on ART Cohort size: 4624 4852 5045 5279 5556 5830 6121 6418 6526 100 Percent of individuals
Community oriented studies. New perspectives Swiss HIV Cohort Study Increased Viral Load Suppression in HIV+ Persons on ART Cohort size: 4624 4852 5045 5279 5556 5830 6121 6418 6526 100 Percent of individuals
Biomedical Prevention in HIV
 Biomedical Prevention in HIV CHART - CCAS-CDC 3 RD Joint Meeting Montego Bay, Jamaica August 21-26,2011 Presented by Tina Hylton-Kong, ERTU-CHART Some Slides from Impact of ART on HIV Transmission Wafaa
Biomedical Prevention in HIV CHART - CCAS-CDC 3 RD Joint Meeting Montego Bay, Jamaica August 21-26,2011 Presented by Tina Hylton-Kong, ERTU-CHART Some Slides from Impact of ART on HIV Transmission Wafaa
Modernization of North Carolina s HIV control measures
 Modernization of North Carolina s HIV control measures North Carolina Division of Public Health Victoria Mobley, MD MPH Evelyn Foust, MPH CPM Agenda Introduction Summary of scientific evidence used to
Modernization of North Carolina s HIV control measures North Carolina Division of Public Health Victoria Mobley, MD MPH Evelyn Foust, MPH CPM Agenda Introduction Summary of scientific evidence used to
The PTAP sequence duplication in HIV-1 subtype C Gag p6 in drug-naive subjects of India and South Africa
 Sharma et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:95 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2184-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE The PTAP sequence duplication in HIV-1 subtype C Gag p6 in drug-naive subjects of India and South Africa
Sharma et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2017) 17:95 DOI 10.1186/s12879-017-2184-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE The PTAP sequence duplication in HIV-1 subtype C Gag p6 in drug-naive subjects of India and South Africa
HBV PUBLIC HEALTH IMPLICATIONS
 جزايری دکتر سيد محمد آزمايشگاه ھپاتيت B -دانشکده بھداشت ويروس شناسی- گروه دانشگاه علوم پزشکی تھران کنگره ارتقا کيفيت- ١٣٩٢ HBV PUBLIC HEALTH IMPLICATIONS 2 billion people have been infected by HBV worldwide.
جزايری دکتر سيد محمد آزمايشگاه ھپاتيت B -دانشکده بھداشت ويروس شناسی- گروه دانشگاه علوم پزشکی تھران کنگره ارتقا کيفيت- ١٣٩٢ HBV PUBLIC HEALTH IMPLICATIONS 2 billion people have been infected by HBV worldwide.
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR Generation of molecular standard for quantitative PCR
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
The Synergy between HIV and other STIs
 Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research 2017 Module: Sexually transmitted infections, HIV/AIDS The Synergy between HIV and other STIs Alberto Matteelli Brescia University Sexual Transmission
Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research 2017 Module: Sexually transmitted infections, HIV/AIDS The Synergy between HIV and other STIs Alberto Matteelli Brescia University Sexual Transmission
