Original Article Diagnostic Immunology INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Jocelin Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Diagnostic Immunology Ann Lab Med 2012;32: ISSN eissn Clinical Relevance of Pretransplant HLA Class II Donor-specific Antibodies in Renal Transplantation Patients with Negative T-cell Cytotoxicity Crossmatches Eun Young Song, M.D. 1, Yu-joo Lee, M.S. 1, Jungwon Hyun, M.D. 1, Yon Su Kim, M.D. 2, Curie Ahn, M.D. 2, Jongwon Ha, M.D. 3, Sang Joon Kim, M.D. 3, and Myoung Hee Park, M.D. 1 Departments of Laboratory Medicine 1, Internal Medicine 2, and Surgery 3, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Background: We evaluated the clinical relevance of pretransplant donor-specific HLA antibodies (DSA) in renal transplantation patients who had negative T-cell cytotoxicity crossmatches. Methods: From 328 consecutive renal transplant recipients, we selected 28 patients who had positive pretransplant (historical or at the time of transplantation) flow cytometry crossmatches, but negative T-cell cytotoxicity crossmatches at the time of transplantation. The presence of DSA and its level at the time of transplantation were retrospectively tested using Luminex single antigen assays. Results: DSA was present in 16 (57.1%) of 28 patients. Biopsy-proven acute rejection (9 patients) occurred more frequently in patients with DSA than in those without DSA (56.3% vs. 0.0%; P =0.003). The positivity rate of class II DSA was significantly higher in patients with antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) than in those without AMR (100% vs. 21.7%; P = 0.003). However, the positivity rate of class I DSA was not different between the two groups (40% vs. 40.9%). Among patients with class II DSA, those with AMR tended to have higher antibody levels (median fluorescence intensity, MFI) than those without AMR (16,359 vs. 5,910; P =0.056). A cut-off MFI value of 4,487 for class II DSA predicted the occurrence of AMR with good sensitivity and specificity (100% and 87.0%). Conclusions: In patients with negative T-cell cytotoxicity crossmatches, the presence of class II DSA and its level at the time of transplantation were associated with the occurrence of AMR. Pretransplant DSA measurement with Luminex single antigen assay would be useful in renal transplantation. Key Words: Donor-specific HLA antibodies, Renal transplantation, Antibody-mediated rejection Received: April 14, 2011 Revision received: October 17, 2011 Accepted: November 25, 2011 Corresponding author: Myoung Hee Park Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 101 Daehak-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul , Korea Tel: Fax: parkmhee@snu.ac.kr The Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. INTRODUCTION Identifying acceptable donors for recipients with anti-hla antibodies is one of the most difficult problems in kidney transplantation. Recently, solid-phase assays, such as the Luminex assay, have become available. These assays detect and quantify donor-specific HLA antibodies (DSA) to a degree that was not possible using cell-based crossmatch tests [1, 2]. When single HLA antigen-coated beads are used, these assays provide a relative indication of DSA level through the median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the beads. Although the presence of pretransplant DSA has generally been considered to be a risk factor for antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) and graft loss [3-6], the clinical relevance of low levels of DSA is still debated [7, 8]. The clinical 139
2 significance of DSA detected solely by using more sensitive assays, such as solid phase assays, or flow cytometry crossmatch (FCXM), are not certain. Some researchers have reported that high levels of DSA at baseline (prior to initiation of desensitization), in historical peak sera, or after desensitization therapy are associated with increased risk of AMR [9-11]. However, other researchers found no association between the level of DSA and occurrence of AMR [4, 7, 8]. Renal transplantation is usually performed in patients with a negative T-cell complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) crossmatch at the time of transplantation. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the risk of acute graft injury and graft loss is related to the level of DSA in these patients at the time of transplantation. METHODS 1. Study design We selected 28 patients with positive FCXM (T and/or B) results at the time of transplantation or in their historical sera from 328 consecutive ABO-compatible renal transplants performed between June 2005 and May 2009 at the Seoul National University Hospital. The demographics and clinical characteristics of the study patients are shown in Table 1. Twelve of the 28 patients underwent pretransplant desensitization therapy, and all 28 patients had negative T-cell CDC crossmatch at the time of transplantation. Serum samples taken at the time of transplantation were retrospectively screened for the presence of class I and class II HLA antibodies with Luminex screening assay kits. Serum from the 12 patients who received desensitization therapy was also tested with Luminex screening assays using samples taken just before the initiation of desensitization therapy and samples taken at the time of transplantation. Sera that were obtained at the time of transplantation and tested positive in the Luminex screening assay (19 HLA class I and 13 HLA class II) were tested with Luminex single antigen assay kits to determine the level of class I and class II DSA. We evaluated the relationship between the presence of DSA and its level and the occurrence of biopsy-proven acute rejection (AR) and graft survival. All clinical data available through June 2010 were included in this analysis, and patients were followed for a median of 33.3 ± 14.6 months (1-58 months). 2. HLA crossmatch test T-cell CDC crossmatch was performed according to the National Institutes of Health Basic and additional Antiglobulin-enhanced Table 1. Demographics and clinical characteristics of the study patients Recipient All (N=28) DSA (+) (N=16) DSA ( ) (N=12) Gender, males, n (%) 8 (29) 3 (19) 5 (42) NS Age, median (range) 47 (14-67) 47 (29-67) 44 (14-57) NS Donor Deceased donor, n (%) 3 (11) 3 (19) 0 (0) NS Gender, males, n (%) 16 (57) 9 (56) 7 (58) NS Age, median (range) 36 (18-62) 34 (18-62) 37 (20-55) NS Sensitizing events*, n (%) 20 (71) 12 (75) 8 (67) NS Desensitization therapy, n (%) 12 (43) 7 (44) 5 (42) NS Induction therapy, n (%) None 8 (29) 4 (25) 4 (33) NS Basiliximab 20 (71) 12 (75) 8 (67) NS Immunosuppression, n (%) Tac-MMF-Pd 20 (71) 11 (69) 9 (75) NS CsA-MMF-Pd 8 (29) 5 (31) 3 (25) NS HLA-A/B mismatches, n (%) 0 0 (0) 0 (0) 0 (0) NS 1 4 (14) 3 (19) 1 (8) NS 2 18 (64) 10 (63) 8 (67) NS 3 3 (11) 3 (19) 0 (0) NS 4 3 (11) 0 (0) 3 (25) NS HLA-DR mismatches, n (%) 0 5 (18) 2 (13) 3 (25) NS 1 17 (61) 9 (56) 8 (67) NS 2 6 (21) 5 (31) 1 (8) NS T-CDC crossmatches (+), n (%) Historical 2/25 (8) 2/13 (15) 0/12 (0) NS Current 0/28 (0) 0/16 (0) 0/12 (0) NS Flow crossmatches (+), n (%) Historical: T and/or B 20/25 (80) 10/13 (77) 10/12 (83) NS T 18/25 (72) 8/13 (62) 10/12 (83) NS B 8/22 (36) 4/11 (36) 4/11 (36) NS Current: T and/or B 14/28 (50) 8/16 (50) 6/12 (50) NS T 7/28 (25) 3/16 (19) 4/12 (33) NS B 8/28 (29) 6/16 (38) 2/12 (17) NS *Prior transplants, blood transfusion, or pregnancies; including 2 cases in DSA (+) group and 2 cases in DSA ( ) group, which were not interpretable due to the interference of rituximab. Abbreviations: DSA, donor-specific HLA antibodies; NS, not significant (P > 0.05); CDC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity. P 140
3 Methods. FCXM was performed using a pronase-treated T/B single tube assay, as previously described [12]. T and B lymphocytes were stained with peridinin chlorophyll protein (PerCP)- conjugated and phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for human CD3 and CD19, respectively (BD Bioscience, San Jose, CA, USA). The presence of bound antibodies was determined using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-human IgG (Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratories Inc., West Grove, PA, USA). Fluorescence was analyzed using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (BD Bioscience). FCXM results are expressed as the ratio of test serum MFI to normal human AB type serum MFI. T-cell and B-cell FCXMs were considered to be positive when the MFI ratio was 2.0. At the time of transplantation, all patients had negative T- cell CDC crossmatches, and FCXM assays indicated, 6 patients were positive for T-cell only, 7 patients for B-cell only, and 1 patient for both T- and B-cell antibodies. The B-cell FCXM results of 2 patients who were positive for DSA and 2 patients negative for DSA were not interpretable due to rituximab interference (Table 1). 3. Detection of DSA HLA antibody screening was performed with LIFECODES Life- Screen Deluxe kit (Gen-probe, Stamford, CT, USA). We performed HLA antibody identification in 28 HLA antibody-positive sera that were obtained at the time of transplantation (19 HLA class I and 13 HLA class II), using LIFECODES LSA class I and class II kits (Gen-probe) according to the manufacturer s instructions. Briefly, 10 µl of serum sample were added to microplate well, then 40 µl of HLA class I or class II single antigen Luminex beads were added, and incubated in the dark for 30 min at room temperature. After washing with wash buffer, 50 µl of goat anti-human IgG secondary antibody conjugated with phycoerythrin was added to the beads and samples were again incubated for 30 min in the dark at room temperature. After washing, the samples were read using the Luminex 200 TM system (Luminex Corp. Austin, TX, USA). The cut-off MFI of positive reaction for each DSA bead was defined as 500. DSA levels were determined by the sum of MFI values for each DSA class: class I (HLA-A, HLA-B), class II (HLA-DR, HLA-DQ), and total (class I+II). HLA-DQ typing of donors was performed to determine donor-specificity when DQ antibodies were detected. 4. Desensitization protocol The 12 patients who received desensitization treatment began taking mycophenolate mofetil (MMF, 750 mg twice daily, p.o.) and tacrolimus (0.05 mg/kg twice daily, p.o., target trough level ng/ml) two days before their first plasmapheresis treatment (one plasma volume exchange with 4% albumin and/or fresh frozen plasma). Plasmapheresis was performed 3 to 7 times preoperatively, every other day. Intravenous immunoglobulin (100 mg/kg) was administered immediately after each plasmapheresis treatment. Methylprednisolone 1,000 mg i.v. was started at the time of the surgery, and the steroid dose was tapered to an oral dose of prednisolone. Combined immunosuppression with MMF, tacrolimus and prednisolone was continued through the post-transplantation period. The first 2 desensitization patients received 10 days of OKT3 (muromonab-cd3; 5 mg daily, i.v.) after transplantation. The remaining 10 patients received rituximab (375 mg/m 2 of body surface area, i.v.) instead of OKT3. Rituximab was administered 3 days before the first plasmapheresis treatment and again 1 day before transplantation. 5. Detection and treatment of rejection Biopsies were performed for all recipients with suspected rejection episodes. The biopsies were graded using the Banff 97 classification [13]. AMR was defined by C4d deposition [14]. Acute cellular rejection (ACR) was treated with methylprednisolone pulse therapy (1,000 mg/day for 3 days). AMR was treated with plasmapheresis followed by intravenous immunoglobulin (100 mg/kg), rituximab (375 mg/m 2 of body surface area, i.v.), and methylprednisolone pulse therapy. 6. Statistical analysis Quantitative variables were expressed as the mean (standard deviation) for normally distributed data or the median (interquartile range, IQR) for non-normally distributed data. Categorical variables were expressed as absolute and relative frequencies. Continuous variables were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests and categorical variables using chi-square tests or Fisher s exact tests, as appropriate. ROC curve analysis was computed for each predictor. All tests were 2-sided and used a significance level of Data handling and analysis were performed with SPSS software for Windows, version 12.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). RESULTS The HLA antibody levels of patients undergoing desensitization therapy were tested before therapy and at the time of transplantation using the MFI values of pooled antigen beads from Luminex screen tests. Patients had significantly lower levels of HLA 141
4 class I after therapy than before the start of desensitization therapy (median [IQR], 1,971 [1,355-3,599] vs. 645 [461-2,754]; P < 0.01). There was a similar, though non-significant, tendency for HLA class II levels to be lower at the time of transplantation than they were before desensitization therapy began (median [IQR], 3,604 [1,652-5,788] vs. 1,711 [1,141-3,471]). Of the 28 patients tested, 16 (57.1%) had DSA at the time of transplantation. The relationship between pretransplant DSA and occurrence of acute rejection and graft survival was analyzed in 27 patients (Table 2). One patient negative for DSA was excluded from the analysis, because the graft loss that occurred within 24 hr of transplantation was due to a clinically suspected vascular problem rather than to antibody mediated hyperacute rejection. Pathologic findings of extensive ischemic necrosis, subcapsular hemorrhage and congestion were observed in this patient. Nine patients had biopsy-proven acute rejection: 4 ACR, 3 AMR, 2 ACR+AMR. There was a significantly higher rate of biopsy-proven acute rejection among patients with DSA at the time of transplantation than among those without DSA (56.3% vs. 0.0%; P =0.003). The incidence of AMR (±ACR) tended to be higher in patients with DSA than in those without DSA (31.3% vs. 0.0%; P =0.060). However, 3 yr graft survival was not significantly different between the two groups of patients (83.3% vs %). The relationship between pretransplant DSA and occurrence of AMR is shown in Table 3. Among the 27 patients evaluated, 6 patients had only class I DSA, 5 patients had only class II DSA, and 5 patients had both class I and class II DSA. The proportion of patients positive for class II DSA at the time of transplantation was significantly higher in patients with AMR than in those without AMR (100% vs. 22.7%; P =0.003). However, the proportion of patients positive for class I DSA was not different between the Table 2. Relationship between DSA at the time of transplantation and biopsy-proven acute rejection DSA (+) (N=16) DSA ( ) (N=11)* AR 9 (56.3%) 0 (0.0%) AMR±ACR 5 (31.3%) 0 (0.0%) ACR only 4 (25.0%) 0 (0.0%) yr GS 14/15 (93.3%) 11/11 (100.0%) yr GS 5/6 (83.3%) 7/7 (100.0%) *One case in the DSA ( ) group was excluded, because graft loss within 24 hr of transplantation was due to clinically suspected vascular problem rather than antibody-mediated hyperacute rejection. Abbreviations: DSA, donor-specific HLA antibodies; AR, acute rejection; ACR, acute cellular rejection; AMR, antibody-mediated rejection; GS, graft survival. P two groups (40% vs. 40.9%). The number of DSA was significantly higher in patients with AMR than in those without AMR (median [IQR], 3 [ ] vs. 0 [0-1]; P =0.001). In patients with class II DSA, the antibody level (MFI sum value) tended to be higher in patients with AMR than in those without AMR (median [IQR], 16,359 [12,061-20,538] vs. 5,910 [3,687-6,555]; P =0.056; Table 3, Fig. 1). However, class I DSA level was not significantly different between the two groups. Pretransplant (at the time of transplantation) class II DSA levels that were associated with the occurrence of AMR were evaluated by ROC curve analysis. The occurrence of AMR was predicted with good sensitivity and specificity (100% and 87.0%) using a cut-off MFI value of 4,487 for class II DSA. The area under the curve (AUC) was (95% CI, ). DISCUSSION In this study, pretransplant DSA was significantly associated with the occurrence of acute rejection in T-cell cytotoxicity crossmatch-negative patients (Table 2). Specifically, the presence of HLA class II DSA at the time of transplantation was significantly associated with the occurrence of AMR (Table 3). This finding is Table 3. Relationship between DSA at the time of transplantation and antibody-mediated rejection DSA positivity AMR (N = 5) No AMR (N = 22) Class I 2 (40.0%) 9 (40.9%) Class II 5 (100.0%) 5 (22.7%) Class I only 0 (0.0%) 6 (27.3%) Class II only 3 (60.0%) 2 (9.1%) Class I + II 2 (40.0%) 3 (13.6%) Class I or II 5 (100.0%) 11 (50.0%) Number of DSA* 3 ( ) 0 (0-1) Level of DSA Class I 2,957 (2,954-2,960) 3,127 (2,067-7,232) Class II 16,359 (12,061-20,538) 5,910 (3,687-6,555) Flow crossmatch (+) T and/or B 4 (80.0%) 10 (45.5%) T 0 (0.0%) 7 (31.8%) B 4 (80.0%) 4 (18.2%) *Median (interquartile range); MFI sum value, median (interquartile range); Including 2 cases that were not interpretable due to the interference of rituximab. Abbreviations: AMR, antibody-mediated rejection; DSA, donor-specific HLA antibodies. P 142
5 Class II DSA (MFI sum) 30,000 20,000 10,000 in accordance with the results of several recent studies, which have shown the importance of class II DSA in the outcome of renal transplantation in T-cell crossmatch (flow cytometry or cytotoxicity) negative patients [15-17]. The presence of HLA class II DSA in patients with negative T-cell FCXM was associated with the occurrence of AMR or poor graft survival [15, 16]. Higher levels of class II DSA in patients with negative T-cell cytotoxicity (AHG) crossmatches were related to increased risk of developing transplant glomerulopathy and the presence of C4d in peritubular capillaries [17]. AMR (N=5) 16,359 No AMR (N=22) 5,910 Fig. 1. Class II donor-specific HLA antibody (DSA) levels at the time of transplantation in patients with or without antibody mediated rejection (AMR). Filled and open circles represent DSA positive and negative cases, respectively. MFI sum values of DSA are plotted. Bars indicate median DSA value of the positive cases in each group. In the present study, positive rate of class I DSA or its level was not different between patients with AMR and those without AMR (Table 3). Although a high level of class I DSA is detrimental to allograft survival, low levels of anti-hla class I antibodies result in signaling cascades in endothelial cells that include survival proteins and induce accommodation of human allografts [18-20]. All studies showing the clinical impact of class II DSA, including the present study, were performed using patients with negative T-cell crossmatches (flow cytometry or cytotoxicity). Therefore, patients with high levels of class I antibodies were probably not included in any of these studies. Even if some of the patients in these studies had low levels of HLA class I antibodies, the antibodies might have assisted allograft accommodation, rather than adversely affect allografts. Such an effect may partially explain the lack of association of HLA class I antibodies with poor graft outcome in the patients in our study. Further studies of the effects of low levels of HLA class II antibodies on signaling cascades in endothelial cells are needed to clarify the roles of both HLA class I and class II antibodies in renal transplantation. In the present study, the level of pretransplant class II DSA was associated with the occurrence of AMR (Table 3, Fig. 1). In ROC curve analysis, the cut-off MFI value of 4,487 for class II DSA at the time of transplantation predicted the occurrence of AMR with good sensitivity and specificity. In patients undergoing desensitization therapy, high levels of DSA both before and after desensitization therapy, have been reported to be associated with increased risk of AMR [9, 11]. Very high levels of baseline DSA has been reported to be associated with an increased risk of AMR and poor long-term allograft survival [9]. After desensitization therapy, patients who have DSA with a standard fluorescence intensity of > 100,000 and with FCXM median channel shift >200 were found to be at higher risk of AMR than those who have lower DSA values [11]. However, the clinical relevance of lower levels of DSA is still debated [7, 8]. Recently, the presence of weak DSA in historical peak sera has been shown to be associated with AMR and poor graft survival [10]. MFI cut-off values of 465 for the highest single, or 820 for total, DSA showed maximal sensitivity and specificity for predicting the occurrence of AMR [10]. Further, 8-yr graft survival decreased progressively with increasing DSA levels: 82.5% in patients with MFI < 465; 78.4% with MFI 466-3,000; 60.6% with MFI >3,000 (P <0.001). DSA levels are not directly comparable between different studies and the differences between the reported levels of DSA with clinical significance may result from many factors. These include lack of standardization of MFI values in Luminex assays, differences in the method of DSA calculation, the extent (DQ, DP) and resolution of HLA typing in donors and recipients, and the density of HLA molecules on single antigen beads [21]. Further efforts are needed to standardize these sources of variability in order to determine the level of DSA that has clinical significance. In conclusion, the presence of class II DSA and its level at the time of transplantation were associated with the occurrence of AMR in renal transplantation patients with negative T-cell cytotoxicity crossmatches. Pretransplant DSA measurement using single antigen Luminex bead assays would be useful for preventing AMR and post-operative follow up in renal transplantation. Authors Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported
6 Acknowledgement This study was supported by a grant number from the SNUH research fund. REFERENCES 1. Gebel HM and Bray RA. Sensitization and sensitivity: defining the unsensitized patient. Transplantation 2000;69: Pei R, Lee JH, Shih NJ, Chen M, Terasaki PI. Single human leukocyte antigen flow cytometry beads for accurate identification of human leukocyte antigen antibody specificities. Transplantation 2003;75: Lefaucheur C, Suberbielle-Boissel C, Hill GS, Nochy D, Andrade J, Antoine C, et al. Clinical relevance of preformed HLA donor-specific antibodies in kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 2008;8: Amico P, Hönger G, Mayr M, Steiger J, Hopfer H, Schaub S. Clinical relevance of pretransplant donor-specific HLA antibodies detected by single-antigen flow-beads. Transplantation 2009;87: Eng HS, Bennett G, Tsiopelas E, Lake M, Humphreys I, Chang SH, et al. Anti-HLA donor-specific antibodies detected in positive B-cell crossmatches by Luminex predict late graft loss. Am J Transplant 2008;8: Gupta A, Iveson V, Varagunam M, Bodger S, Sinnott P, Thuraisingham RC. Pretransplant donor-specific antibodies in cytotoxic negative crossmatch kidney transplants: are they relevant? Transplantation 2008;85: Aubert V, Venetz JP, Pantaleo G, Pascual M. Low levels of human leukocyte antigen donor-specific antibodies detected by solid phase assay before transplantation are frequently clinically irrelevant. Hum Immunol 2009;70: Vlad G, Ho EK, Vasilescu ER, Colovai AI, Stokes MB, Markowitz GS, et al. Relevance of different antibody detection methods for the prediction of antibody-mediated rejection and deceased-donor kidney allograft survival. Hum Immunol 2009;70: Gloor JM, Winters JL, Cornell LD, Fix LA, DeGoey SR, Knauer RM, et al. Baseline donor-specific antibody levels and outcomes in positive crossmatch kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 2010;10: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Hill GS, Andrade J, Nochy D, Antoine C, et al. Preexisting donor-specific HLA antibodies predict outcome in kidney transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol 2010;21: Reinsmoen NL, Lai CH, Vo A, Cao K, Ong G, Naim M, et al. Acceptable donor-specific antibody levels allowing for successful deceased and living donor kidney transplantation after desensitization therapy. Transplantation 2008;86: Vaidya S, Cooper TY, Avandsalehi J, Barnes T, Brooks K, Hymel P, et al. Improved flow cytometric detection of HLA alloantibodies using pronase: potential implications in renal transplantation. Transplantation 2001;71: Racusen LC, Solez K, Colvin RB, Bonsib SM, Castro MC, Cavallo T, et al. The Banff 97 working classification of renal allograft pathology. Kidney Int 1999;55: Racusen LC, Colvin RB, Solez K, Mihatsch MJ, Halloran PF, Campbell PM, et al. Antibody-mediated rejection criteria - an addition to the Banff 97 classification of renal allograft rejection. Am J Transplant 2003;3: Pollinger HS, Stegall MD, Gloor JM, Moore SB, Degoey SR, Ploeger NA, et al. Kidney transplantation in patients with antibodies against donor HLA class II. Am J Transplant 2007;7: Stastny P, Ring S, Lu C, Arenas J, Han M, Lavingia B. Role of immunoglobulin (Ig)-G and IgM antibodies against donor human leukocyte antigens in organ transplant recipients. Hum Immunol 2009;70: Issa N, Cosio FG, Gloor JM, Sethi S, Dean PG, Moore SB, et al. Transplant glomerulopathy: risk and prognosis related to anti-human leukocyte antigen class II antibody levels. Transplantation 2008;86: Jin YP, Fishbein MC, Said JW, Jindra PT, Rajalingam R, Rozengurt E, et al. Anti-HLA class I antibody-mediated activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and induction of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL expression in endothelial cells. Hum Immunol 2004;65: Narayanan K, Jaramillo A, Phelan DL, Mohanakumar T. Pre-exposure to sub-saturating concentrations of HLA class I antibodies confers resistance to endothelial cells against antibody complement-mediated lysis by regulating Bad through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Eur J Immunol 2004;34: Salama AD, Delikouras A, Pusey CD, Cook HT, Bhangal G, Lechler RI, et al. Transplant accommodation in highly sensitized patients: a potential role for Bcl-xL and alloantibody. Am J Transplant 2001;1: Warner PR, Youngs D, Nelson KA. HLA density on microparticles versus antibody detection sensitivity: implications for crossmatch prediction. Hum Immunol 2007;68(S):S
Pre-transplant donor specific antibody and its clinical significance in kidney transplantation
 Original article Pre-transplant donor specific antibody and its clinical significance in kidney transplantation Duangtawan Thammanichanond, 1 Atiporn Ingsathit, 2,3 Tasanee Mongkolsuk, 1 Sasivimol Rattanasiri,
Original article Pre-transplant donor specific antibody and its clinical significance in kidney transplantation Duangtawan Thammanichanond, 1 Atiporn Ingsathit, 2,3 Tasanee Mongkolsuk, 1 Sasivimol Rattanasiri,
Renal transplantation in sensitized recipients with positive luminex and negative CDC (complement-dependent cytotoxicity) crossmatches
 Transplant International ISSN 0934-0874 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Renal transplantation in sensitized recipients with positive luminex and negative CDC (complement-dependent cytotoxicity) crossmatches Kyu Ha Huh,
Transplant International ISSN 0934-0874 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Renal transplantation in sensitized recipients with positive luminex and negative CDC (complement-dependent cytotoxicity) crossmatches Kyu Ha Huh,
Clinical Study Different Impact of Pretransplant Anti-HLA Antibodies Detected by Luminex in Highly Sensitized Renal Transplanted Patients
 BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 738404, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/738404 Clinical Study Different Impact of Pretransplant Anti-HLA Antibodies Detected by Luminex in Highly
BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 738404, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/738404 Clinical Study Different Impact of Pretransplant Anti-HLA Antibodies Detected by Luminex in Highly
Desensitization in Kidney Transplant. James Cooper, MD Assistant Professor, Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Program, Renal Division, UC Denver
 Desensitization in Kidney Transplant James Cooper, MD Assistant Professor, Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Program, Renal Division, UC Denver Organ Shortage Currently there are >90,000 patients on the kidney
Desensitization in Kidney Transplant James Cooper, MD Assistant Professor, Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Program, Renal Division, UC Denver Organ Shortage Currently there are >90,000 patients on the kidney
Transplantation in highly sensitised patients treated with intravenous immunoglobulin and Rituximab
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Advance Access publication 1 February 2010 Transplantation in highly sensitised patients treated with intravenous immunoglobulin and Rituximab Ana Carina Ferreira 1, Sandra Brum 1, Vasco
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Advance Access publication 1 February 2010 Transplantation in highly sensitised patients treated with intravenous immunoglobulin and Rituximab Ana Carina Ferreira 1, Sandra Brum 1, Vasco
Application of Calculated Panel Reactive Antibody Using HLA Frequencies in Koreans
 Original Article Diagnostic Immunology Jang J-Y, et al. Ann Lab Med 2012;32:66-72 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Application of Calculated Panel Reactive Antibody Using HLA Frequencies in Koreans Ji-Young
Original Article Diagnostic Immunology Jang J-Y, et al. Ann Lab Med 2012;32:66-72 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Application of Calculated Panel Reactive Antibody Using HLA Frequencies in Koreans Ji-Young
Posttransplant Human Leukocyte Antigen Antibodies in Stable Kidney Transplant Recipients
 Trends in Transplant. 2014;8:3-9 Gregor Bartel, Georg A. Böhmig: Alloantibodies and Graft Function Posttransplant Human Leukocyte Antigen Antibodies in Stable Kidney Transplant Recipients Gregor Bartel
Trends in Transplant. 2014;8:3-9 Gregor Bartel, Georg A. Böhmig: Alloantibodies and Graft Function Posttransplant Human Leukocyte Antigen Antibodies in Stable Kidney Transplant Recipients Gregor Bartel
The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials
 The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials Carmen Lefaucheur 1 2 Banff 2015: Integration of HLA-Ab for improving
The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials Carmen Lefaucheur 1 2 Banff 2015: Integration of HLA-Ab for improving
3/6/2017. Prevention of Complement Activation and Antibody Development: Results from the Duet Trial
 Prevention of Complement Activation and Antibody Development: Results from the Duet Trial Jignesh Patel MD PhD FACC FRCP Medical Director, Heart Transplant Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute Disclosures Name:
Prevention of Complement Activation and Antibody Development: Results from the Duet Trial Jignesh Patel MD PhD FACC FRCP Medical Director, Heart Transplant Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute Disclosures Name:
Eculizumab chez les receveurs de greffe rénal à haut risque immunologique. Mark D. Stegall Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
 Eculizumab chez les receveurs de greffe rénal à haut risque immunologique Mark D. Stegall Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN Disclosure. Dr Mark Stegall. Institution : Mayo Clinic, Rochester. Research contracts
Eculizumab chez les receveurs de greffe rénal à haut risque immunologique Mark D. Stegall Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN Disclosure. Dr Mark Stegall. Institution : Mayo Clinic, Rochester. Research contracts
Antihuman leukocyte antigen (HLA) antibodies can be
 Antihuman Leukocyte Antigen Specific Antibody Strength Determined by Complement-Dependent or Solid-Phase Assays Can Predict Positive Donor-Specific Crossmatches Ibrahim Batal, MD; Adriana Zeevi, PhD; John
Antihuman Leukocyte Antigen Specific Antibody Strength Determined by Complement-Dependent or Solid-Phase Assays Can Predict Positive Donor-Specific Crossmatches Ibrahim Batal, MD; Adriana Zeevi, PhD; John
Quantifying HLA-specific antibodies in patients undergoing desensitization Andrea Zachary a and Nancy L. Reinsmoen b
 Quantifying HLA-specific antibodies in patients undergoing desensitization Andrea Zachary a and Nancy L. Reinsmoen b a John Hopkins University, Immunogenetics Laboratory, Baltimore, Maryland and b Cedars-Sinai
Quantifying HLA-specific antibodies in patients undergoing desensitization Andrea Zachary a and Nancy L. Reinsmoen b a John Hopkins University, Immunogenetics Laboratory, Baltimore, Maryland and b Cedars-Sinai
Kidney Transplantation in Sensitized Recipients; A Single Center Experience
 J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24 (Suppl 1): S143-7 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S143 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Kidney Transplantation in Sensitized Recipients; A Single Center
J Korean Med Sci 2009; 24 (Suppl 1): S143-7 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2009.24.S1.S143 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Kidney Transplantation in Sensitized Recipients; A Single Center
Donor-Specific HLA Class I and CREG Antibodies in Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity-Negative Renal Transplants
 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org 330 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 40, no. 4, 2010 Donor-Specific HLA Class I and CREG Antibodies in Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity-Negative
Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org 330 Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 40, no. 4, 2010 Donor-Specific HLA Class I and CREG Antibodies in Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity-Negative
Why so Sensitive? Desensitizing Protocols for Living Donor Kidney Transplantation
 Why so Sensitive? Desensitizing Protocols for Living Donor Kidney Transplantation Stephen J Tomlanovich MD Objectives of this Talk Define the sensitized patient Describe the scope of the problem for a
Why so Sensitive? Desensitizing Protocols for Living Donor Kidney Transplantation Stephen J Tomlanovich MD Objectives of this Talk Define the sensitized patient Describe the scope of the problem for a
HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management
 HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management Luca Dello Strologo October 29 th, 2016 Hystory I 1960 donor specific antibodies (DSA): first suggestion for a possible role in deteriorating
HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management Luca Dello Strologo October 29 th, 2016 Hystory I 1960 donor specific antibodies (DSA): first suggestion for a possible role in deteriorating
Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies
 Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies Lorita M Rebellato, Ph.D., D (ABHI) Associate Professor Department of Pathology The Brody School of Medicine at ECU Scientific
Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies Lorita M Rebellato, Ph.D., D (ABHI) Associate Professor Department of Pathology The Brody School of Medicine at ECU Scientific
Evaluation of Two New Antibody Detection Techniques in Kidney Transplantation. Doctoral Thesis. Dr. Petra Gombos
 Evaluation of Two New Antibody Detection Techniques in Kidney Transplantation Doctoral Thesis Dr. Petra Gombos Semmelweis University Doctoral School of Pathology Supervisor: Dr. Róbert Langer, Ph.D. Consultant:
Evaluation of Two New Antibody Detection Techniques in Kidney Transplantation Doctoral Thesis Dr. Petra Gombos Semmelweis University Doctoral School of Pathology Supervisor: Dr. Róbert Langer, Ph.D. Consultant:
Transplant Applications of Solid phase Immunoassays Anti HLA antibody testing in solid organ transplantation
 AACC Professional Course BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENTER HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL Transplant Applications of Solid phase Immunoassays Anti HLA antibody testing in solid organ transplantation J. Ryan
AACC Professional Course BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENTER HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL Transplant Applications of Solid phase Immunoassays Anti HLA antibody testing in solid organ transplantation J. Ryan
XM-ONE XM-ONE XM-ONE. References XMO_V4.0_100205_CE.EU
 Transplantation Cross match Transplantation Cross match XMO_V4._125_CE.EU Manufactured by: ABSORBER AB Address: Drottninggatan 33 SE-13 95 Stockholm, Sweden E-mail: info-ssp@olerup.com Tel: +46 8 5 89
Transplantation Cross match Transplantation Cross match XMO_V4._125_CE.EU Manufactured by: ABSORBER AB Address: Drottninggatan 33 SE-13 95 Stockholm, Sweden E-mail: info-ssp@olerup.com Tel: +46 8 5 89
BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience. Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy
 BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy Background BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) has emerged as an important cause of renal graft dysfunction in recent
BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy Background BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) has emerged as an important cause of renal graft dysfunction in recent
Strategies for Desensitization
 Strategies for Desensitization Olwyn Johnston MB, MRCPI, MD, MHSc BC Nephrology Day October 8 th 2010 Pre-transplant crossmatch (CMX) with donor lymphocytes has been standard of practice Positive CDC CXM
Strategies for Desensitization Olwyn Johnston MB, MRCPI, MD, MHSc BC Nephrology Day October 8 th 2010 Pre-transplant crossmatch (CMX) with donor lymphocytes has been standard of practice Positive CDC CXM
Living-Donor Kidney Transplant in T-Cell and B-Cell Flow Cytometry Crossmatch-Positive Patients
 ARTICLe Living-Donor Kidney Transplant in T-Cell and B-Cell Flow Cytometry Crossmatch-Positive Patients Soushi Terasaka, 1 Hidehisa Kitada, 1,3 Yasuhiro Okabe, 1 Sayako Kawanami, 1 Hiroshi Noguchi, 1 Kyoko
ARTICLe Living-Donor Kidney Transplant in T-Cell and B-Cell Flow Cytometry Crossmatch-Positive Patients Soushi Terasaka, 1 Hidehisa Kitada, 1,3 Yasuhiro Okabe, 1 Sayako Kawanami, 1 Hiroshi Noguchi, 1 Kyoko
Supplementary Appendix
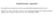 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Loupy A, Lefaucheur C, Vernerey D, et al. Complement-binding
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Loupy A, Lefaucheur C, Vernerey D, et al. Complement-binding
Utility of protocol kidney biopsies for de novo donor- specific antibodies
 Received: 6 June 2017 Revised: 24 July 2017 Accepted: 29 July 2017 DOI: 10.1111/ajt.14466 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Utility of protocol kidney biopsies for de novo donor- specific antibodies Sandesh Parajuli
Received: 6 June 2017 Revised: 24 July 2017 Accepted: 29 July 2017 DOI: 10.1111/ajt.14466 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Utility of protocol kidney biopsies for de novo donor- specific antibodies Sandesh Parajuli
Medicine OBSERVATIONAL STUDY
 Medicine OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Clinical Significance of HLA-DQ Antibodies in the Development of Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Allograft Failure in Kidney Transplant Recipients Hyeyoung Lee, MD,
Medicine OBSERVATIONAL STUDY Clinical Significance of HLA-DQ Antibodies in the Development of Chronic Antibody-Mediated Rejection and Allograft Failure in Kidney Transplant Recipients Hyeyoung Lee, MD,
Long-term prognosis of BK virus-associated nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients
 Original Article Kidney Res Clin Pract 37:167-173, 2018(2) pissn: 2211-9132 eissn: 2211-9140 https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.2.167 KIDNEY RESEARCH AND CLINICAL PRACTICE Long-term prognosis of BK
Original Article Kidney Res Clin Pract 37:167-173, 2018(2) pissn: 2211-9132 eissn: 2211-9140 https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.2.167 KIDNEY RESEARCH AND CLINICAL PRACTICE Long-term prognosis of BK
Steroid Minimization: Great Idea or Silly Move?
 Steroid Minimization: Great Idea or Silly Move? Disclosures I have financial relationship(s) within the last 12 months relevant to my presentation with: Astellas Grants ** Bristol Myers Squibb Grants,
Steroid Minimization: Great Idea or Silly Move? Disclosures I have financial relationship(s) within the last 12 months relevant to my presentation with: Astellas Grants ** Bristol Myers Squibb Grants,
C4d Fixing, Luminex Binding Antibodies A New Tool for Prediction of Graft Failure After Heart Transplantation
 American Journal of Transplantation 27; 7: 289 2815 Blackwell Munksgaard Brief Communication C 27 The Authors Journal compilation C 27 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of
American Journal of Transplantation 27; 7: 289 2815 Blackwell Munksgaard Brief Communication C 27 The Authors Journal compilation C 27 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of
Transfusion support in Transplantation
 Transfusion support in Transplantation Patricia Campbell University of Alberta Hospitals University of Alberta Objectives UofA transplant programs What we do and why? HLA and ABO incompatible transplants
Transfusion support in Transplantation Patricia Campbell University of Alberta Hospitals University of Alberta Objectives UofA transplant programs What we do and why? HLA and ABO incompatible transplants
Approach to Kidney Transplant in Sensitized Potential Transplant Recipients
 RevIew Approach to Kidney Transplant in Sensitized Potential Transplant Recipients Antoine Barbari, Souodod Abbas, Mahassen Jaafar Abstract More than one-third of patients on waiting lists for kidney transplant
RevIew Approach to Kidney Transplant in Sensitized Potential Transplant Recipients Antoine Barbari, Souodod Abbas, Mahassen Jaafar Abstract More than one-third of patients on waiting lists for kidney transplant
Transplant Success in Sensitized Patients Receiving a Standardized Desensitization Therapy: 3 Year Outcomes
 Transplant Success in Sensitized Patients Receiving a Standardized Desensitization Therapy: 3 Year Outcomes INTRODUCTION In patients awaiting a transplant, having antibodies reactive to HLA antigens present
Transplant Success in Sensitized Patients Receiving a Standardized Desensitization Therapy: 3 Year Outcomes INTRODUCTION In patients awaiting a transplant, having antibodies reactive to HLA antigens present
Investigation of Serum Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies at the Time of Renal Allograft Rejection
 Original Article Diagnostic Immunology Ann Lab Med 2015;35:314-320 http://dx.doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.3.314 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Investigation of Serum Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies
Original Article Diagnostic Immunology Ann Lab Med 2015;35:314-320 http://dx.doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.3.314 ISSN 2234-3806 eissn 2234-3814 Investigation of Serum Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies
Virtual Crossmatch in Kidney Transplantation
 Virtual Crossmatch in Kidney Transplantation Shiva Samavat Associate Professor of Nephrology Labbafinejad Hospital SBMU 2018.11.21 All transplant candidates are screened to determine the degree of humoral
Virtual Crossmatch in Kidney Transplantation Shiva Samavat Associate Professor of Nephrology Labbafinejad Hospital SBMU 2018.11.21 All transplant candidates are screened to determine the degree of humoral
Kidney paired donation in the presence of donor-specific antibodies
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 International Society of Nephrology clinical investigation Kidney paired donation in the presence of donor-specific antibodies Jeremy M. Blumberg 1, Hans A. Gritsch
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 International Society of Nephrology clinical investigation Kidney paired donation in the presence of donor-specific antibodies Jeremy M. Blumberg 1, Hans A. Gritsch
Donor-Specific Antibodies Adversely Affect Kidney Allograft Outcomes
 Donor-Specific Antibodies Adversely Affect Kidney Allograft Outcomes Sumit Mohan,* Amudha Palanisamy,* Demetra Tsapepas, Bekir Tanriover,* R. John Crew,* Geoffrey Dube,* Lloyd E. Ratner, David J Cohen,*
Donor-Specific Antibodies Adversely Affect Kidney Allograft Outcomes Sumit Mohan,* Amudha Palanisamy,* Demetra Tsapepas, Bekir Tanriover,* R. John Crew,* Geoffrey Dube,* Lloyd E. Ratner, David J Cohen,*
Research Article The Diagnostic Value of Transcription Factors T-bet/GATA3 Ratio in Predicting Antibody-Mediated Rejection
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 460316, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/460316 Research Article The Diagnostic Value of Transcription Factors T-bet/GATA3 Ratio in Predicting
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 460316, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/460316 Research Article The Diagnostic Value of Transcription Factors T-bet/GATA3 Ratio in Predicting
Background & objectives
 Indian J Med Res 145, February 2017, pp 222-228 DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_222_16 Quick Response Code: Comparative analysis of Luminex-based donor-specific antibody mean fluorescence intensity values with
Indian J Med Res 145, February 2017, pp 222-228 DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_222_16 Quick Response Code: Comparative analysis of Luminex-based donor-specific antibody mean fluorescence intensity values with
Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant
 SDC, Patients and Methods Complement-dependent lymphocytotoxic crossmatch test () Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant donor-specific CXM was
SDC, Patients and Methods Complement-dependent lymphocytotoxic crossmatch test () Serum samples from recipients were obtained within 48 hours before transplantation. Pre-transplant donor-specific CXM was
Understanding crossmatch testing in organ transplantation: A case-based guide for the general nephrologistnep_
 Nephrology 16 (2011) 125 133 Review Article Understanding crossmatch testing in organ transplantation: A case-based guide for the general nephrologistnep_1414 125..133 WILLIAM R MULLEY 1,2 and JOHN KANELLIS
Nephrology 16 (2011) 125 133 Review Article Understanding crossmatch testing in organ transplantation: A case-based guide for the general nephrologistnep_1414 125..133 WILLIAM R MULLEY 1,2 and JOHN KANELLIS
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, et al. Antibody-mediated
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, et al. Antibody-mediated
Mary Keogan, on Mary behalf Keogan of all in NHISSOT On behalf of all in NHISSOT. 4th April 2014
 Solid Organ Transplantation How the Lab Contributes to Improved Patient Outcomes Mary Keogan, on Mary behalf Keogan of all in NHISSOT On behalf of all in NHISSOT 4th April 2014 Solid Organ Transplantation
Solid Organ Transplantation How the Lab Contributes to Improved Patient Outcomes Mary Keogan, on Mary behalf Keogan of all in NHISSOT On behalf of all in NHISSOT 4th April 2014 Solid Organ Transplantation
23/10/2017. Panel Reactive Antibodies and Crossmatch by Flow Cytometry. Antibodies against. Renal transplantation. Antibody mediated rejection (AMR)
 Renal transplantation Panel Reactive Antibodies and Crossmatch by Flow Cytometry Katherina Psarra Immunology Histocompatibility Dept Evangelismos Hospital Athens, Greece In spite of the enormous progress
Renal transplantation Panel Reactive Antibodies and Crossmatch by Flow Cytometry Katherina Psarra Immunology Histocompatibility Dept Evangelismos Hospital Athens, Greece In spite of the enormous progress
SELECTED ABSTRACTS. All (n) % 3-year GS 88% 82% 86% 85% 88% 80% % 3-year DC-GS 95% 87% 94% 89% 96% 80%
 SELECTED ABSTRACTS The following are summaries of selected posters presented at the American Transplant Congress on May 5 9, 2007, in San Humar A, Gillingham KJ, Payne WD, et al. Review of >1000 kidney
SELECTED ABSTRACTS The following are summaries of selected posters presented at the American Transplant Congress on May 5 9, 2007, in San Humar A, Gillingham KJ, Payne WD, et al. Review of >1000 kidney
Outcome of Kidney Transplantations Performed With Preformed Donor-Specific Antibodies of Unknown Etiology
 American Journal of Transplantation 2014; 14: 193 201 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication C Copyright 2013 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
American Journal of Transplantation 2014; 14: 193 201 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication C Copyright 2013 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
ABO. ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO. Key words ABO. Alexandre ABO ABO. double filtration plasmapheresis, DFPP. antibody-mediated rejection, AMR
 ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO.. ABO ABO. ABO. ABO ABO Key words ABO ABO A B antibody-mediated rejection, AMR Alexandre ABO double filtration plasmapheresis, DFPP ABO ABO n ABO n p-value R.....
ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO ABO.. ABO ABO. ABO. ABO ABO Key words ABO ABO A B antibody-mediated rejection, AMR Alexandre ABO double filtration plasmapheresis, DFPP ABO ABO n ABO n p-value R.....
Efficacy and Safety of Thymoglobulin and Basiliximab in Kidney Transplant Patients at High Risk for Acute Rejection and Delayed Graft Function
 ArtIcle Efficacy and Safety of Thymoglobulin and Basiliximab in Kidney Transplant Patients at High Risk for Acute Rejection and Delayed Graft Function Guodong Chen, 1 Jingli Gu, 2 Jiang Qiu, 1 Changxi
ArtIcle Efficacy and Safety of Thymoglobulin and Basiliximab in Kidney Transplant Patients at High Risk for Acute Rejection and Delayed Graft Function Guodong Chen, 1 Jingli Gu, 2 Jiang Qiu, 1 Changxi
Microcirculation Inflammation Associates With Outcome in Renal Transplant Patients With De Novo Donor-Specific Antibodies
 American Journal of Transplantation 2013; 13: 485 492 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication C Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
American Journal of Transplantation 2013; 13: 485 492 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication C Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
2017 BANFF-SCT Joint Scientific Meeting. BARCELONA March 2017
 2017 BANFF-SCT Joint Scientific Meeting BARCELONA 27-31 March 2017 Adriana Zeevi PhD (D) ABHI Professor of Pathology, Surgery and Immunology Director of Histocompatibility Laboratory University of Pittsburgh
2017 BANFF-SCT Joint Scientific Meeting BARCELONA 27-31 March 2017 Adriana Zeevi PhD (D) ABHI Professor of Pathology, Surgery and Immunology Director of Histocompatibility Laboratory University of Pittsburgh
Renal Pathology- Transplantation. Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic
 Renal Pathology- Transplantation Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic eva.honsova@ikem.cz Kidney has a limited number of tissue reactions by which the kidney
Renal Pathology- Transplantation Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic eva.honsova@ikem.cz Kidney has a limited number of tissue reactions by which the kidney
HLA Part II: My Patient Has DSA, Now What?
 2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium HLA Part II: My Patient Has DSA, Now What? James Lan, MD, FRCPC, D(ABHI) Dr. Lan completed his nephrology training at the University of British Columbia.
2017 CST-Astellas Canadian Transplant Fellows Symposium HLA Part II: My Patient Has DSA, Now What? James Lan, MD, FRCPC, D(ABHI) Dr. Lan completed his nephrology training at the University of British Columbia.
Revisiting Traditional Risk Factors for Rejection and Graft Loss After Kidney Transplantation
 American Journal of Transplantation 2011; 11: 2132 2143 Wiley Periodicals Inc. C 2011 The Authors Journal compilation C 2011 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant
American Journal of Transplantation 2011; 11: 2132 2143 Wiley Periodicals Inc. C 2011 The Authors Journal compilation C 2011 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant
Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation. Dr.E Nemati. Professor of Nephrology
 Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation Dr.E Nemati Professor of Nephrology Introductio n Rituximab is a chimeric anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody. The CD20 antigen is a transmembrane nonglycosylated
Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation Dr.E Nemati Professor of Nephrology Introductio n Rituximab is a chimeric anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody. The CD20 antigen is a transmembrane nonglycosylated
APHERESIS FOR DESENSITIZATION OF NON-RENAL TRANSPLANTS
 APHERESIS FOR DESENSITIZATION OF NON-RENAL TRANSPLANTS GOW AREPALLY, MD MEDICAL DIRECTOR DUKE THERAPEUTIC APHERESIS SERVICE ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, MEDICINE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR APHERESIS MAY 25 TH 2013 OVERVIEW
APHERESIS FOR DESENSITIZATION OF NON-RENAL TRANSPLANTS GOW AREPALLY, MD MEDICAL DIRECTOR DUKE THERAPEUTIC APHERESIS SERVICE ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, MEDICINE AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR APHERESIS MAY 25 TH 2013 OVERVIEW
Research Article The Induction of IgM and IgG Antibodies against HLA or MICA after Lung Transplantation
 Pulmonary Medicine Volume 2, Article ID 43269, 9 pages doi:.55/2/43269 Research Article The Induction of IgM and IgG Antibodies against HLA or MICA after Lung Transplantation Annelieke W. M. Paantjens,
Pulmonary Medicine Volume 2, Article ID 43269, 9 pages doi:.55/2/43269 Research Article The Induction of IgM and IgG Antibodies against HLA or MICA after Lung Transplantation Annelieke W. M. Paantjens,
Management of Rejection
 Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Peritubular capillaries C4d deposits in renal allograft biopsies and anti HLA I/II alloantibodies screening Incidence and clinical importance
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Port J Nephrol Hypert 2008; 22(1): 37-42 Peritubular capillaries C4d deposits in renal allograft biopsies and anti HLA I/II alloantibodies screening Incidence and clinical importance Helena
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Port J Nephrol Hypert 2008; 22(1): 37-42 Peritubular capillaries C4d deposits in renal allograft biopsies and anti HLA I/II alloantibodies screening Incidence and clinical importance Helena
Copyright information:
 Posttransplant reduction in preexisting donor-specific antibody levels after belataceptversus cyclosporine-based immunosuppression: Post hoc analyses of BENEFIT and BENEFIT-EXT Robert A Bray, Emory University
Posttransplant reduction in preexisting donor-specific antibody levels after belataceptversus cyclosporine-based immunosuppression: Post hoc analyses of BENEFIT and BENEFIT-EXT Robert A Bray, Emory University
ABO mismatched Renal Transplants
 ABO mismatched Renal Transplants Nicos Kessaris Renal Transplant Surgeon St George s Hospital, London 7 th March 2012 Why? Protocol Risks Experience abroad Experience in UK Experience at St George s Conclusions
ABO mismatched Renal Transplants Nicos Kessaris Renal Transplant Surgeon St George s Hospital, London 7 th March 2012 Why? Protocol Risks Experience abroad Experience in UK Experience at St George s Conclusions
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Antibody Mediated Rejection Post Kidney And Kidney Pancreas Transplant RRCV CMG Renal and Transplant Service
 Diagnosis And Treatment Of Antibody Mediated Rejection Post Kidney And Kidney Pancreas Transplant RRCV CMG Renal and Transplant Service 1. Introduction Transplantation offers better survival and quality
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Antibody Mediated Rejection Post Kidney And Kidney Pancreas Transplant RRCV CMG Renal and Transplant Service 1. Introduction Transplantation offers better survival and quality
10/18/2012. A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why. What?
 A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why What? 1 First recognized in mice during 1930 s and 1940 s. Mouse (murine) experiments with tumors Independent observations were made in humans with leukoagglutinating
A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why What? 1 First recognized in mice during 1930 s and 1940 s. Mouse (murine) experiments with tumors Independent observations were made in humans with leukoagglutinating
Treatment of Chronic Antibody Mediated Rejection
 Treatment of Chronic Antibody Mediated Rejection Robert A. Montgomery MD, DPhil Professor of Surgery Director of the NYU Langone Transplant Institute Disclosures: Served on Advisory Boards for Genentech
Treatment of Chronic Antibody Mediated Rejection Robert A. Montgomery MD, DPhil Professor of Surgery Director of the NYU Langone Transplant Institute Disclosures: Served on Advisory Boards for Genentech
Effects of HLA-Matched Blood Transfusion for Patients Awaiting Renal Transplantation
 CLINICAL AND TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH Effects of HLA-Matched Blood Transfusion for Patients Awaiting Renal Transplantation Bernadette A. Magee, 1,4 Jeanie Martin, 1 Miceal P. Cole, 1 Kieran G. Morris, 2
CLINICAL AND TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH Effects of HLA-Matched Blood Transfusion for Patients Awaiting Renal Transplantation Bernadette A. Magee, 1,4 Jeanie Martin, 1 Miceal P. Cole, 1 Kieran G. Morris, 2
Le Rejet Humoral Chronique en 2010: Histoire naturelle et problématiques
 Le Rejet Humoral Chronique en 2010: Histoire naturelle et problématiques CAMR in 2010: natural history and perspectives Alexandre Loupy 1 Introduction 2 CAMR: the missing link 3 Natural history of CAMR
Le Rejet Humoral Chronique en 2010: Histoire naturelle et problématiques CAMR in 2010: natural history and perspectives Alexandre Loupy 1 Introduction 2 CAMR: the missing link 3 Natural history of CAMR
Even in this era of efficient immunosuppression, a positive
 OVERVIEW Enhanced Kidney Allocation to Highly Sensitized Patients by the Acceptable Mismatch Program Frans H. J. Claas, 1 Axel Rahmel, 2 and IIias I. N. Doxiadis 1 Even in this era of efficient immunosuppression,
OVERVIEW Enhanced Kidney Allocation to Highly Sensitized Patients by the Acceptable Mismatch Program Frans H. J. Claas, 1 Axel Rahmel, 2 and IIias I. N. Doxiadis 1 Even in this era of efficient immunosuppression,
Transplantation in Australia and New Zealand
 Transplantation in Australia and New Zealand Matthew D. Jose MBBS (Adel), FRACP, FASN, PhD (Monash), AFRACMA Professor of Medicine, UTAS Renal Physician, Royal Hobart Hospital Overview CKD in Australia
Transplantation in Australia and New Zealand Matthew D. Jose MBBS (Adel), FRACP, FASN, PhD (Monash), AFRACMA Professor of Medicine, UTAS Renal Physician, Royal Hobart Hospital Overview CKD in Australia
IMPACT OF PREFORMED AND DE NOVO ANTI-HLA DP ANTIBODIES
 IMPACT OF PREFORMED AND DE NOVO ANTI-HLA DP ANTIBODIES IN RENAL ALLOGRAFT SURVIVAL Dolores Redondo-Pachón 1, Julio Pascual 1*, María J. Pérez-Sáez 1, Carmen García 2, Juan José Hernández 2, Javier Gimeno
IMPACT OF PREFORMED AND DE NOVO ANTI-HLA DP ANTIBODIES IN RENAL ALLOGRAFT SURVIVAL Dolores Redondo-Pachón 1, Julio Pascual 1*, María J. Pérez-Sáez 1, Carmen García 2, Juan José Hernández 2, Javier Gimeno
Is it safe to transplant against HLA DSA in cardiothoracic patients? development and implementation of national Guidelines
 Is it safe to transplant against HLA DSA in cardiothoracic patients? development and implementation of national Guidelines Dr Martin Howell. Laboratory Director. Department of H&I, NHS Blood and Transplant,
Is it safe to transplant against HLA DSA in cardiothoracic patients? development and implementation of national Guidelines Dr Martin Howell. Laboratory Director. Department of H&I, NHS Blood and Transplant,
Treatment Update of Sensitized Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Review
 RevIew Treatment Update of Sensitized Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Review Hasan Otukesh, 1 Rozita Hoseini, 2 Nahid Rahimzadeh 3 Abstract Sensitization of recipients is an increasing problem
RevIew Treatment Update of Sensitized Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Review Hasan Otukesh, 1 Rozita Hoseini, 2 Nahid Rahimzadeh 3 Abstract Sensitization of recipients is an increasing problem
Predicting Kidney Graft Failure by HLA Antibodies: a Prospective Trial
 American Journal of Transplantation 2004; 4: 438 443 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright C Blackwell Munksgaard 2004 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00360.x Predicting Kidney Graft Failure by HLA Antibodies:
American Journal of Transplantation 2004; 4: 438 443 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright C Blackwell Munksgaard 2004 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00360.x Predicting Kidney Graft Failure by HLA Antibodies:
Blood Group Incompatible Renal Transplantation and Apheresis. Liz Wright Clinical Nurse Specialist Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS FT
 Blood Group Incompatible Renal Transplantation and Apheresis Liz Wright Clinical Nurse Specialist Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS FT Background There is growing interest in transplantation across the
Blood Group Incompatible Renal Transplantation and Apheresis Liz Wright Clinical Nurse Specialist Great Ormond Street Hospital NHS FT Background There is growing interest in transplantation across the
3/6/2017. Treatment of Detected Antibodies. I have financial relationship(s) with: Thoratec/St. Jude/Abbott Consultant CareDx Consultant/Speaker
 Treatment of Detected Antibodies Sean Pinney, MD Director, Advanced Heart Failure & Transplantation Mount Sinai Hospital New York, NY Sean Pinney, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Icahn School of Medicine
Treatment of Detected Antibodies Sean Pinney, MD Director, Advanced Heart Failure & Transplantation Mount Sinai Hospital New York, NY Sean Pinney, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Icahn School of Medicine
Marta Farrero Torres₁, Marcelo Pando₂, Dolly Tyan₂, Hannah Valantine₃, Spenser Smith₃, Kiran Khush₃
 Development of HLA donor specific antibodies after heart transplantation: importance of a new method to detect the first component of the complement cascade Marta Farrero Torres₁, Marcelo Pando₂, Dolly
Development of HLA donor specific antibodies after heart transplantation: importance of a new method to detect the first component of the complement cascade Marta Farrero Torres₁, Marcelo Pando₂, Dolly
DE-MYSTIFYING THE BLACK BOX OF TRANSPLANT IMMUNOLOGY
 2016 DE-MYSTIFYING THE BLACK BOX OF TRANSPLANT IMMUNOLOGY James H Lan, MD, FRCP(C), D(ABHI) Clinical Assistant Professor, University of British Columbia Nephrology & Kidney Transplantation, Vancouver General
2016 DE-MYSTIFYING THE BLACK BOX OF TRANSPLANT IMMUNOLOGY James H Lan, MD, FRCP(C), D(ABHI) Clinical Assistant Professor, University of British Columbia Nephrology & Kidney Transplantation, Vancouver General
Update on Transplant Glomerulopathy
 Update on Transplant Glomerulopathy Miklos Z Molnar, MD, PhD, FEBTM, FERA, FASN Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine University of Tennessee Health Science Center
Update on Transplant Glomerulopathy Miklos Z Molnar, MD, PhD, FEBTM, FERA, FASN Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine University of Tennessee Health Science Center
Review Article Clinical Relevance of HLA Antibody Monitoring after Kidney Transplantation
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Immunology Research Volume 2014, Article ID 845040, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/845040 Review Article Clinical Relevance of HLA Antibody Monitoring
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Immunology Research Volume 2014, Article ID 845040, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/845040 Review Article Clinical Relevance of HLA Antibody Monitoring
6/19/2012. Who is in the room today? What is your level of understanding of Donor Antigens and Candidate Unacceptables in KPD?
 6/19/212 KPD Webinar Series: Part 3 Demystifying the OPTN Kidney Paired Donation Pilot Program Unacceptable HLA antigens: The key to finding a compatible donor for your patient M. Sue Leffell, Ph.D. J.
6/19/212 KPD Webinar Series: Part 3 Demystifying the OPTN Kidney Paired Donation Pilot Program Unacceptable HLA antigens: The key to finding a compatible donor for your patient M. Sue Leffell, Ph.D. J.
Should red cells be matched for transfusions to patients listed for renal transplantation?
 Should red cells be matched for transfusions to patients listed for renal transplantation? Dr M.Willicombe Imperial College Renal and Transplant Centre, Hammersmith Hospital Should red cells be matched
Should red cells be matched for transfusions to patients listed for renal transplantation? Dr M.Willicombe Imperial College Renal and Transplant Centre, Hammersmith Hospital Should red cells be matched
Elevation of Antidonor Immunoglobulin M Levels Precedes Acute Lung Transplant Rejection
 Elevation of Antidonor Immunoglobulin M Levels Precedes Acute Lung Transplant Rejection Kentaroh Miyoshi, MD, Yoshifumi Sano, MD, Masaomi Yamane, MD, Shinichi Toyooka, MD, Takahiro Oto, MD, and Shinichiro
Elevation of Antidonor Immunoglobulin M Levels Precedes Acute Lung Transplant Rejection Kentaroh Miyoshi, MD, Yoshifumi Sano, MD, Masaomi Yamane, MD, Shinichi Toyooka, MD, Takahiro Oto, MD, and Shinichiro
Methodologies for Anti-HLA Antibody Screening in Patients Awaiting Kidney Transplant: A Comparative Study
 ARTiCle Methodologies for Anti-HLA Antibody Screening in Patients Awaiting Kidney Transplant: A Comparative Study Pellegrino B. Minucci, 1 Vincenzo Grimaldi, 1 Amelia Casamassimi, 1 Francesco Cacciatore,
ARTiCle Methodologies for Anti-HLA Antibody Screening in Patients Awaiting Kidney Transplant: A Comparative Study Pellegrino B. Minucci, 1 Vincenzo Grimaldi, 1 Amelia Casamassimi, 1 Francesco Cacciatore,
Donor-Specific HLA Antibodies in a Cohort Comparing Everolimus With Cyclosporine After Kidney Transplantation
 American Journal of Transplantation 2012; 12: 1192 1198 Wiley Periodicals Inc. C Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03961.x
American Journal of Transplantation 2012; 12: 1192 1198 Wiley Periodicals Inc. C Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03961.x
Association between flow cytometric crossmatching and graft survival in Thai cadaveric-donor kidney transplantation
 Original article Association between flow cytometric crossmatching and graft survival in Thai cadaveric-donor kidney transplantation Pawinee Kupatawintu, 1 Araya Tatawatorn, 2 Nalinee Premasathian, 3 Yingyos
Original article Association between flow cytometric crossmatching and graft survival in Thai cadaveric-donor kidney transplantation Pawinee Kupatawintu, 1 Araya Tatawatorn, 2 Nalinee Premasathian, 3 Yingyos
Outcome of Subclinical Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Preformed Donor-Specific Antibodies
 American Journal of Transplantation 2009; 9: 2561 2570 Wiley Periodicals Inc. C 2009 The Authors Journal compilation C 2009 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant
American Journal of Transplantation 2009; 9: 2561 2570 Wiley Periodicals Inc. C 2009 The Authors Journal compilation C 2009 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant
IMMUNOBIOLOGY OF TRANSPLANTATION. Wasim Dar
 IMMUNOBIOLOGY OF TRANSPLANTATION Wasim Dar Immunobiology of Transplantation Overview Transplantation: A complex immunologic process Contributions Innate Immunity Adaptive immunity T Cells B Cells HLA Consequences
IMMUNOBIOLOGY OF TRANSPLANTATION Wasim Dar Immunobiology of Transplantation Overview Transplantation: A complex immunologic process Contributions Innate Immunity Adaptive immunity T Cells B Cells HLA Consequences
CASE REPORT ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Renal transplant was successfully performed after conversion.
 CASE REPORT Port J Nephrol Hypert 2007; 21(1): 41-47 Successful live donor kidney transplant in a hypersensitised patient with positive cross-match. A case report and a review of the effectiveness of desensitisation
CASE REPORT Port J Nephrol Hypert 2007; 21(1): 41-47 Successful live donor kidney transplant in a hypersensitised patient with positive cross-match. A case report and a review of the effectiveness of desensitisation
James E. Cooper, M.D. Assistant Professor, University of Colorado at Denver Division of Renal Disease and Hypertension, Kidney and PancreasTransplant
 James E. Cooper, M.D. Assistant Professor, University of Colorado at Denver Division of Renal Disease and Hypertension, Kidney and PancreasTransplant Program Has no real or apparent conflicts of interest
James E. Cooper, M.D. Assistant Professor, University of Colorado at Denver Division of Renal Disease and Hypertension, Kidney and PancreasTransplant Program Has no real or apparent conflicts of interest
Rituximab and Intravenous Immune Globulin for Desensitization during Renal Transplantation
 The new england journal of medicine original article Rituximab and Intravenous Immune Globulin for Desensitization during Renal Transplantation Ashley A. Vo, Pharm.D., Marina Lukovsky, Pharm.D., Mieko
The new england journal of medicine original article Rituximab and Intravenous Immune Globulin for Desensitization during Renal Transplantation Ashley A. Vo, Pharm.D., Marina Lukovsky, Pharm.D., Mieko
Donor-derived Cell-free DNA Improves DSA-informed Diagnosis of ABMR in Kidney Transplant Patients
 Donor-derived Cell-free DNA Improves DSA-informed Diagnosis of ABMR in Kidney Transplant Patients Stanley C. Jordan, MD Director, Division of Nephrology Medical Director, Kidney Transplant Program Medical
Donor-derived Cell-free DNA Improves DSA-informed Diagnosis of ABMR in Kidney Transplant Patients Stanley C. Jordan, MD Director, Division of Nephrology Medical Director, Kidney Transplant Program Medical
The diffuse extent of peritubular capillaritis in renal allograft rejection is an independent risk factor for graft loss
 http://www.kidney-international.org 2015 International Society of Nephrology see commentary on page 218 The diffuse extent of peritubular capillaritis in renal allograft rejection is an independent risk
http://www.kidney-international.org 2015 International Society of Nephrology see commentary on page 218 The diffuse extent of peritubular capillaritis in renal allograft rejection is an independent risk
Posttransplant Prophylactic Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Kidney Transplant Patients at High Immunological Risk: A Pilot Study
 American Journal of Transplantation 2007; 7: 1185 1192 Blackwell Munksgaard C 2007 The Authors Journal compilation C 2007 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant
American Journal of Transplantation 2007; 7: 1185 1192 Blackwell Munksgaard C 2007 The Authors Journal compilation C 2007 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant
AND My presentation does include discussion of off-label or investigational use (empiric therapy)
 Managing Sensitized Patients Pre-Heart Transplantation Patricia P. Chang, MD MHS Associate Professor of Medicine Director, UNC Heart Failure & Transplant Program Patricia P. Chang, MD MHS Associate Professor
Managing Sensitized Patients Pre-Heart Transplantation Patricia P. Chang, MD MHS Associate Professor of Medicine Director, UNC Heart Failure & Transplant Program Patricia P. Chang, MD MHS Associate Professor
ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in elderly patients over 60 years of age
 Int Urol Nephrol (2012) 44:1563 1570 DOI 10.1007/s11255-012-0231-z NEPHROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in elderly patients over 60 years of age Junji Uchida Tomoaki Iwai
Int Urol Nephrol (2012) 44:1563 1570 DOI 10.1007/s11255-012-0231-z NEPHROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in elderly patients over 60 years of age Junji Uchida Tomoaki Iwai
HLA Antibody Complement Based Assays. Howard M. Gebel, PhD, D(ABHI) Robert A. Bray, PhD, D(ABHI) Emory University Hospital Atlanta, GA
 HLA Antibody Complement Based Assays Howard M. Gebel, PhD, D(ABHI) Robert A. Bray, PhD, D(ABHI) Emory University Hospital Atlanta, GA Disclosure Neither presenter has any financial relationships related
HLA Antibody Complement Based Assays Howard M. Gebel, PhD, D(ABHI) Robert A. Bray, PhD, D(ABHI) Emory University Hospital Atlanta, GA Disclosure Neither presenter has any financial relationships related
NAPRTCS Annual Transplant Report
 North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2014 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE II TRANSPLANTATION Section
North American Pediatric Renal Trials and Collaborative Studies NAPRTCS 2014 Annual Transplant Report This is a privileged communication not for publication. TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE II TRANSPLANTATION Section
RevIeWS. Sensitized renal transplant recipients: current protocols and future directions. James Gloor and Mark D. Stegall
 RevIeWS Sensitized renal transplant recipients: current protocols and future directions James Gloor and Mark D. Stegall Abstract The identification of suitable donor kidneys for transplant candidates with
RevIeWS Sensitized renal transplant recipients: current protocols and future directions James Gloor and Mark D. Stegall Abstract The identification of suitable donor kidneys for transplant candidates with
Increased Early Rejection Rate after Conversion from Tacrolimus in Kidney and Pancreas Transplantation
 Increased Early Rejection Rate after Conversion from Tacrolimus in Kidney and Pancreas Transplantation Gary W Barone 1, Beverley L Ketel 1, Sameh R Abul-Ezz 2, Meredith L Lightfoot 1 1 Department of Surgery
Increased Early Rejection Rate after Conversion from Tacrolimus in Kidney and Pancreas Transplantation Gary W Barone 1, Beverley L Ketel 1, Sameh R Abul-Ezz 2, Meredith L Lightfoot 1 1 Department of Surgery
Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection
 Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection Ibrahim Batal MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY, USA Overview Pathophysiology and grading of TCMR TCMR is still a significant
Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection Ibrahim Batal MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY, USA Overview Pathophysiology and grading of TCMR TCMR is still a significant
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. Characteristics of Donor-Specific anti-hla Antibodies (DSA) Impacting different Renal. Allograft Outcomes. Salim S.
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Characteristics of Donor-Specific anti-hla Antibodies (DSA) Impacting different Renal Allograft Outcomes by Salim S. Ghandorah A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Characteristics of Donor-Specific anti-hla Antibodies (DSA) Impacting different Renal Allograft Outcomes by Salim S. Ghandorah A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES
Antibody Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation
 Antibody Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation 2012 Teresa De Marco, MD, FACC Professor of Medicine & Surgery Director Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Program Medical Director, Heart Transplantation
Antibody Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation 2012 Teresa De Marco, MD, FACC Professor of Medicine & Surgery Director Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Program Medical Director, Heart Transplantation
Figure 1. Actuarial survival of patients with ABO I, ABO compatible, and ABO identical grafts.
 New Insights into Antibody Mediated Graft Injury after Pediatric Liver Transplantation S.V. McDiarmid MD Professor of Pediatrics and Surgery David Geffen School of Medicine University of California, Los
New Insights into Antibody Mediated Graft Injury after Pediatric Liver Transplantation S.V. McDiarmid MD Professor of Pediatrics and Surgery David Geffen School of Medicine University of California, Los
