Citation for published version (APA): Coevorden, A. M. V. (2005). Hand eczema: clinical efficacy of interventions, and burden of disease s.n.
|
|
|
- Valentine Richardson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Groningen Hand eczema Coevorden, Anthony Marco van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Publication date: 2005 Link to publication in University of Groningen/UMCG research database Citation for published version (APA): Coevorden, A. M. V. (2005). Hand eczema: clinical efficacy of interventions, and burden of disease s.n. Copyright Other than for strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Downloaded from the University of Groningen/UMCG research database (Pure): For technical reasons the number of authors shown on this cover page is limited to 10 maximum. Download date:
2 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
3 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION Hand eczema is defined as an inflammation of the skin ( dermatitis ) confined to the hand(s). We define the hands as the part of the arm, distal of the wrist, including the fingers. The point where the wrist ends and the hand starts, is visible as a fold in the skin. Hand eczema may spread to the wrists and the forearms, or occur in conjunction with foot eczema. However, in cases with eczema predominantly on other parts of the body than the hands, it would be best to use the term eczema with hand involvement. 1 The word eczema is derived from the Greek word εκζεμα: to boil out. Its first use is attributed to Aëtius of Amida, who was writer and physician to the Byzantine Court, and who lived from 502 to 575. It is said to have been the name given by ancient physicians to any fiery pustule on the skin. 2 This inaccuracy continued to some extent for centuries and prompted the writer Norman Walker to refer to the word eczema in 1913 as a chaotic conglomeration and a cloak for ignorance. 3 In the following decades nomenclature has gained more precision, although confusingly the term dermatitis is now frequently used interchangeably with eczema, especially in the USA. Dermatitis however, is a broader descriptive term that implies an inflammation of the skin and therefore encompasses more than eczema alone. In Europe the term hand dermatitis is preferred for those cases in which the eczema is caused by contact with irritants or allergens. In this thesis only the term hand eczema will be used, regardless of the clinical manifestation or aetiology. The special interest for eczema of the hands is justified because it is common and long lasting with a chronic relapsing course, and because it may have severe consequences to the patient and others. In the next paragraphs these points will be addressed, in addition to other general aspects of hand eczema. Epidemiology Hand eczema is a common disease. Exact prevalences however, are unknown. There are many reasons for this: it is not a notifyable disease, there is no universally accepted definition, no clear delineation from slightly damaged skin and not all patients seek medical attention. Research on the topic has usually focused on the prevalence in certain populations, especially with an occupational interest, e.g. hairdressers and nurses. The value of populationbased questionnaires is limited by the imprecision in the definition of hand eczema and the self-assessment by those in the sample. Finally, comparing point prevalences, one-year prevalences and life-time prevalences may be difficult. Exemplary for the fact that most hand eczema prevalence studies are from the Nordic countries, the 1987 paper of Meding reported a one-year prevalence 12
4 Introduction of 9% for men and 15% for women among a random sample from the Gothenburg population (Sweden). The point prevalence in 1983 was 5.4%. 4 The same population was examined again in This follow-up showed a decrease in one-year prevalence to 7.0% for men and 12.3% for women. 5 In Stockholm in 1997 the self-diagnosed one-year prevalence was 6% for men and 10% for women. 6 A self-reported life-time prevalence of hand eczema among Danish twins was 12% for men and 21% for women. 7 This rise in prevalence over the decades, in contrast to Meding s findings, was confirmed by Nielsen, who reported a rise in self-diagnosed hand eczema in the 1990 s. 8 The life-time prevalence was 10.1% for men and 23.3% for women in 1990; in 1998 these numbers were 18.4% and 32.4% respectively. The incidence of hand eczema was 4.0 new cases per 1000 person-years for men and 7.1 for women. Interestingly, there was no difference in incidence between men and women over the age of 30 years. 9 The male to female ratio seems to be slightly under 1:2. However, a 2000 paper from St. John s contact dermatitis clinic reported a male to female ratio of 4:5. 10 Given the practical limitations of a medical examination of large populations, many of these studies combine the validity of a clinical diagnosis with the easy applicability of self-administered questionnaires. In (another) example of such a study, a set of three questions was developed, asking about symptoms of hand eczema, their duration and whether these were recurrent. 11 The validity was evaluated among 109 nurses and compared with a medical diagnosis made by a dermatologist. A diagnosis of hand eczema, defined as one or more symptoms with a recurrent character or lasting for more than three weeks, had a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 64%, resulting in a positive predictive value of 31%. This indicates that use of a questionnaire alone would result in a significant overestimation of the prevalence. This might explain the wide range of prevalences found in the above-mentioned studies, including some very high prevalences. Medical examination of only those who responded positively, to exclude false-positive cases, would, however, increase the specificity while maintaining the high sensitivity. A Swedish study showed that the use of the self-diagnosis term hand eczema seems to be valid, although it was difficult for the individual to identify skin signs compatible with the clinical diagnosis of hand eczema. 12 Aetiology The aetiology of hand dermatitis is usually multifactorial and can be divided in endogenous and exogenous causes. 13 Rarely, hand eczema is caused by one single factor. 13
5 Chapter 1 In 1953, the typical patient with hand eczema was described as a young matron, who must keep house, cook, wash dishes, do the laundry, raise her children and hold her husband. 14 This clearly illustrates the importance of a few commonly encountered irritants: water, food products, soaps and detergents. Other examples are chemicals, dry and cold air and friction. A sequence of repetitive insults with contact irritants may disrupt the epidermal barrier and inhibit its repair, thus leading to hand eczema after repeated exposure. 15 Irritants are the commonest exogenous cause of hand eczema. 16 Sweat, due to hyperhidrosis, can also be an irritant. Although the reasons for the different prevalence in hand eczema between men and women are unknown, the greater exposure of women to wet work is probably significant. The other exogenous cause of hand eczema are contact allergens. These substances result in a type IV delayed type cell mediated hypersensitivity. They can be related to occupation, to hobbies or to domestic work. The role of oral ingestion of allergens remains controversial. 17 Alternatively, type I immediate type IgE mediated hypersensitivity to proteins may provoke hand eczema in certain individuals. 18 Atopy may be both the cause and a contributing risk factor for hand eczema. 19 Similar to atopic eczema of the body, lesions limited to the hands may develop. More commonly, the increased susceptibility of atopics to contact irritants will result in irritant contact eczema of the hands. 20 Occupational factors, both irritant and allergic, can precipitate and perpetuate hand eczema, especially in atopics. Hand eczema now accounts for an estimated 90% of occupational skin diseases. 21 Bryld observed in a population-based twin cohort hereditary factors despite a presumable substantial individual-specific environmental variation. 7 Although the significance of psychosomatic factors to hand eczema remains speculative at best, there is considerable interest in them. 1 Probably there is no aetiological relation, although emotional factors and psychological stress may aggravate hand eczema. One case report proposes an aetiological relation between waterpipe smoking and hand eczema. 22 In contrast to what has been proposed in the past, there is no dysfunction of the acrosyringium and no relationship with sweat gland obstruction or hyperhidrosis in vesicular hand eczema. 23 Therefore, dyshidrotic hand eczema is actually a misnomer. It is also frequently referred to as pompholyx (from the Greek word for bubble ). Clinical features Itching, and to a lesser extent burning, stinging, and pain, may be the most prominent and disturbing symptoms. In acute hand eczema signs are erythema, oedema, papules and vesicles, sometimes with superimposed weeping and 14
6 Introduction crusting due to secondary bacterial infection. Secondary viral infection, usually in atopics, is less common. The vesicles may coalesce to form bullae. Chronic forms usually present with less erythema, no vesicles and more scaling, sometimes even significant hyperkeratosis with fissuring (tylotic hand eczema or eczema hyperkeratoticum et rhagadiforme). The palmar epidermis is thicker than the skin of the back of the hands and the fingers. Therefore, the first signs may be visible on the latter parts of the hands Hand eczema tends to run a long lasting and chronic relapsing course, probably due to its multifactorial origin. Only in those relatively few cases where there is a single, easily avoidable contact factor, the prognosis is good. Classification The classification of hand eczema is complex, leading to considerable confusion. In addition, no single classification is satisfactory. The simplest is into acute, subacute and chronic. As this is usually not refined enough for clinical use, more commonly a combination of morphology (e.g. dyshidrotic hand eczema), aetiology (e.g. allergic contact eczema) and sometimes anatomical localisation (e.g. palms or fingers) is used. The commonest aetiological hand eczema category is irritant contact eczema (35%), followed by atopic hand eczema (22%) and allergic contact eczema (19%). 4 It is important to realise that a single cause can sometimes produce different morphological patterns. Reversely, a certain clinical pattern, does not necessarily imply one single cause. 18 Making the diagnosis In most cases the diagnosis can be made upon evaluation of clinical features and symptoms, such as itch, or pain in cases of fissuring hyperkeratotic hand eczema. Sometimes there is a history of provoking factors, such as irritants (e.g. detergents) or allergens (e.g. nickel). However, some patients do not report such factors, even when explicitly asked. Therefore, epicutaneous allergy tests (patch tests) for type IV delayed type cell mediated hypersensitivities, the gold standard for determining contact allergens, is an essential part of the diagnostic work-up. Finding an allergen holds the tantalising promise of a cure. Unfortunately, when allergies are found, the relevance is not always clear. Scrutinous anamnesis, based upon the test s results, is then needed. In some selected cases, a visit to the work place may elucidate the role and relevance of these allergies. A (family) history of asthma, childhood eczema or hay fever may suggest an atopic diathesis. This can be confirmed by measuring total or specific IgE antibodies and eosinophilic granulocytes in the serum, and by performing intracutaneous allergy tests. 15
7 Chapter 1 The main differential diagnostic points are psoriasis and tinea manuum. Examination of other parts of the body may hold evidence for psoriasis or tinea manuum: especially the feet and toes for tinea manuum, and the elbows, knees, scalp and nails for psoriasis. In addition, family history of psoriasis should be taken, as well as skin scrapings for fungal examination. In rare cases, lichen planus and discoid lupus erythematosus may mimic hyperkeratotic hand eczema. An unusual presentation of bullous pemphigoid limited to the hands may be confused with dyshidrotic hand eczema. 26 Differentiation between dyshidrotic hand eczema and pustulosis palmaris can be facilitated by the presence of the characteristic brown marks, which remain after resolution of the pustules in pustulosis palmaris. Finally, those cases with mild signs and symptoms, such as only mild chapping, can pose a problem. Should they be classified as hand eczema or as a variation in the condition of otherwise normal skin? Do those cases require treatment? As there is no universally accepted definition for hand eczema, these questions are hard to answer. It is in fact up to the individual clinician to make an assessment, in which other signs and symptoms, a previous history of eczema, a possible role of irritants and allergens and an atopic diathesis should be taken into account. 18 Histopathology In hand eczema spongiosis in the lower epidermal layers can be seen, with the possibility of confluence, resulting in intraepidermal vesicles. These can be visible clinically as vesicles or papules, the latter especially on the palms of the hands due to its characteristically thick stratum corneum. There is a sparse, superficial infiltrate of lymphocytes with some exocytosis. 23 In allergic contact dermatitis mild spongiosis adjacent to the vesicles may be present, in combination with eosinophilic granulocytes in the inflammatory infiltrate. The histopathology of hyperkeratotic hand eczema is similar to other forms of hand eczema. But in addition, it shares psoriasiform hyperplasia with compact hyperkeratosis and focal parakeratosis with psoriasis. Hand eczema usually lacks, however, neutrophilic granulocytes in the infiltrate. 27 Management As hand eczema is an inflammatory dermatosis, anti-inflammatory agents are the mainstay of therapy. Topical corticosteroids have replaced coal tar derivatives as the first-line of treatment in the mid 1900s. Other important measures are avoidance of irritants and allergens, and frequent application of bland emollients to restore the disruption of the skin barrier. 1 A supportive measure in cases with vesiculation is soaking the hands in water with added 16
8 Introduction disinfectant. For hyperkeratotic hand eczema keratolytic agents (salicylic acid, lactic acid, urea in petrolatum) may provide relief. Short bursts of oral steroids are useful in a few severe cases only. Other second-line treatments are phototherapies with UVB, UVA, or UVA with psoralens (PUVA) either oral or as soak, and ciclosporin. They have proven to be effective and are relatively frequently used. The following therapies have or are being been used for hand eczema: retinoids, methotrexate, ionising radiation, mycophenolate mofetil, iontophoresis, azathioprine, diets or chelating agents, and intradermal botulinum toxin. The efficacy of some, but not all of them, has been evaluated in randomised controlled trials. Topical calcineurin inhibitors, tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are the latest addition to the dermatologist s therapeutic arsenal. 28 Preventive measures are important, especially for those at high risk, such as hairdressers and those with an atopic diathesis. 13 Organisational adaptations are required for occupational cases. Obviously, protective measures such as protective gloves, barrier creams and emollients, are recommended. Outcome parameters The outcome parameters in intervention studies for hand eczema are usually based on a clinical assessment (severity). There are many ways to make this assessment, none of which are validated. Examples are: clinical judgement, objective signs only (e.g. vesiculation, scaling, erythema), subjective signs only (e.g. itch and pain), both objective and subjective signs, combination of area and severity, and treatment related (e.g. grams of corticosteroids used per week). Rarely one will find a paper in which the patient is asked if he feels better. Other outcomes may include an economical evaluation, or other burden of disease related parameters. These also, are rarely the primary outcome. Recently, two studies investigated, respectively, the value of a photographic scale and a numerical scale as instruments to rate the overall severity of hand eczema; they found high levels of intra- and interobserver reliability They did not validate these scales (content, construct, criterion validity). At present, a validated instrument to assess the severity of hand eczema is still lacking. So, rigorous validation studies are needed. 31 Consequences The hands are the organs of doing things with things. They pick at, pry at, rub and investigate. 14 In addition, the hands are important tools for communication and expression. It is therefore easy to understand that any impairment in form and function may result in major psychosocial problems, e.g. anxiety, low selfesteem and social phobia. The itching is another major problem. It may interfere 17
9 Chapter 1 with sleep for patients and also their spouses. A vicious cycle of symptoms and skin damage (the itch/scratch/itch cycle) can aggravate the patient s problems. 32 Painful cracks and blisters can prevent or severely complicate manual work leading to significant disability, economic loss to both individuals and State, and distress to the affected patients. The economic impact may be direct or indirect. Direct costs include medical costs, social security and medical litigation; indirect costs may arise from absence from work and loss of productivity. 13 AIMS OF THIS THESIS As the title of this thesis indicates, it describes studies on two closely related themes: interventions for hand eczema and its burden of disease. First, we shall focus on interventions for hand eczema. Chapter 2 will describe the characteristics of intervention studies for hand eczema and discuss their quality. Chapter 3 will give an overview of the papers dealing with interventions for hand eczema, from a clinical, problem-oriented perspective. Chapter 4 describes a systematic review on interventions for hand eczema. A randomised controlled trial comparing two PUVA treatments for hand eczema will be presented in chapter 5. A case report of a patient with a rare side effect due to one of these PUVA treatments is described in appendix 2. Second, the burden of disease is the central theme in chapter 6 and appendix 1. In chapter 6 data from the study which is described in chapter 5, will be used to compare patient-rated and physician-rated severity scores with a burden of disease questionnaire. As the economic impact of a disease is another component of burden of disease, 33 appendix 1 also uses the data from the study described in chapter 5, to make an economic evaluation of the two PUVA treatments. REFERENCES 1. Epstein E. Hand dermatitis: practical management and current concepts. J Am Acad Dermatol 1984; 10: Wilkinson DS. Introduction, definition and classification. In: Menné T, Maibach HI, editors. Hand eczema. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2000: Walker N. An introduction to Dermatology. 6 th ed. Edinburgh: William Green; Meding B, Swanbeck G. Prevalence of hand eczema in an industrial city. Br J Dermatol 1987; 116: Meding B, Järvholm B. Hand eczema in Swedish adults changes in prevalence between 1983 and J Invest Dermatol 2002; 118:
10 Introduction 6. Meding B, Lidén C, Berglind N. Self-diagnosed dermatitis in adults. Results from a population survey in Stockholm. Contact Dermatitis 2001; 45: Bryld LE, Agner T, Kyvik KO, Brøndsted L, Hindsberger C, Menné T. Hand eczema in twins: a questionnaire investigation. Br J Dermatol 2000; 142: Nielsen NH, Linneberg A, Menné T, Madsen F, Frølund L, Dirksen A, et al. The association between contact allergy and hand eczema in 2 cross-sectional surveys 8 years apart. Contact Dermatitis 2002; 46: Meding B, Järvholm B. Incidence of hand eczema a population-based retrospective study. J Invest Dermatol 2004; 122: Smith HR, Armstrong DKB, Wakelin SH, Rycroft RJG, White IR, McFadden JP. Descriptive epidemiology of hand dermatitis at the St. John s contact dermatitis clinic Br J Dermatol 2000; 142: Smit HA, Coenraads PJ, Lavrijsen AP, Nater JP. Evaluation of a self-administered questionnaire on hand dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis 1992; 26: Svensson Å, Lindberg M, Meding B, Sundberg K, Stenberg B. Self-reported hand eczema: symptom-based reports do not increase the validity of diagnosis. Br J Dermatol 2002; 147: Elston DM, Ahmed DDF, Watsky KL, Schwarzenberger K. Hand dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2002; 47: Sutton RL, Ayres S. Dermatitis of the hands. Arch Dermatol Syph 1953; 68: Malten KE. Thoughts on irritant contact dermatitis. Contact Dermatitis 1981; 7: Meding B, Swanbeck G. Epidemiology of different types of hand eczema in an industrial city. Acta Derm Venereol 1989; 69: Fisher AA. Possible role of diet in pompholyx and nickel dermatitis a critical survey. Cutis 1978; 22: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, Griffiths C, editors. Rook s textbook of dermatology. 7 th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing; Meding B, Swanbeck Predictive factors for hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis 1990; 23: Nassif A, Chan S, Storrs F, Hanifin JM. Abnormal skin irritancy in atopic dermatitis and in atopy without dermatitis. Arch Dermatol 1994; 130: Dickel H, Kuss O, Blesius CR, Schmidt A, Diepgen TL. Occupational skin disease in Northern Bavaria between 1990 and 1999: a population-based study. Br J Dermatol 2001; 145: Onder M, Oztas M, Arnavut O. Nargile (hubble-bubble) smoking-induced hand eczema. Int J Dermatol 2002; 41: Kutzner H, Wurzel R, Wolff HH. Are acrosyringia involved in the pathogenesis of dyshidrosis? Am J Dermatopathol 1986; 8:
11 Chapter Hogan DJ, Dannaker CJ, Lal S, Maibach HI. An international survey on the prognosis of occupational contact dermatitis of the hands. J Am Acad Dermatol 1990; 38: Meding B, Wrangsjö K, Järvholm B. Fifteen-year follow-up of hand eczema: persistence and consequences. Br J Dermatol 2005; 152: Sugimura C, Katsuura J, Moriue T, Matsuoka Y, Kubota Y. Dyshidrosiform pemphigoid: report of a case. J Dermatol. 2003; 30: Weedon D, Strutton G, editors. Skin pathology. 2 nd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; Warshaw E, Lee G, Storrs FJ. Hand dermatitis: a review of clinical features, therapeutic options, and long-term outcomes. Am J Contact Dermat 2003; 14: Coenraads PJ, Van der Walle H, Thestrup-Pedersen K, Ruzicka T, Dreno B, De La Loge C, et al. Construction and validation of a photographic guide for assessing severity of chronic hand eczema. Br J Dermatol 2005; 152: Held E, Skoet R, Johansen JD, Agner T. The hand eczema severity index (HECSI): a scoring system for clinical assessment of hand eczema. A study of inter- and intraobserver reliability. Br J Dermatol 2005; 152: Charman CR, English JS. Getting to grips with hand eczema: measuring skin disease severity objectively. Br J Dermatol 2005; 152: Meding M, Swanbeck G. Consequences of having hand eczema. Contact Dermatitis 1990; 23: Chren MM, Weinstock MA. Conceptual issues in measuring the burden of skin disease. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 2004; 9:
12 Introduction 21
13 Chapter 1 22
Hand eczema classification: a cross-sectional, multicentre study of the aetiology and morphology of hand eczema
 CONTACT DERMATITIS AND ALLERGY BJD British Journal of Dermatology Hand eczema classification: a cross-sectional, multicentre study of the aetiology and morphology of hand eczema T.L. Diepgen, K.E. Andersen,*
CONTACT DERMATITIS AND ALLERGY BJD British Journal of Dermatology Hand eczema classification: a cross-sectional, multicentre study of the aetiology and morphology of hand eczema T.L. Diepgen, K.E. Andersen,*
Citation for published version (APA): Jungbauer, F. H. W. (2004). Wet work in relation to occupational dermatitis s.n.
 University of Groningen Wet work in relation to occupational dermatitis Jungbauer, Franciscus Henricus Wilhelmus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
University of Groningen Wet work in relation to occupational dermatitis Jungbauer, Franciscus Henricus Wilhelmus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
Hand eczema. Nottingham 17 May Pieter-Jan Coenraads University Medical Center Groningen, NL
 Nottingham 17 May 2017 Hand eczema Pieter-Jan Coenraads University Medical Center Groningen, NL especially on behalf of ms dr Wianda Christoffers PhD Disclosure P.J. Coenraads More than 10 years ago our
Nottingham 17 May 2017 Hand eczema Pieter-Jan Coenraads University Medical Center Groningen, NL especially on behalf of ms dr Wianda Christoffers PhD Disclosure P.J. Coenraads More than 10 years ago our
Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.]
![Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.] Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.]](/thumbs/92/109955334.jpg) University of Groningen Hand eczema Christoffers, Wianda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
University of Groningen Hand eczema Christoffers, Wianda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
Comparison of four methods for assessment of severity of hand eczema Agner, Tove; Jungersted, Jacob Mutanu; Coenraads, Pieter-Jan; Diepgen, Thomas
 University of Groningen Comparison of four methods for assessment of severity of hand eczema Agner, Tove; Jungersted, Jacob Mutanu; Coenraads, Pieter-Jan; Diepgen, Thomas Published in: CONTACT DERMATITIS
University of Groningen Comparison of four methods for assessment of severity of hand eczema Agner, Tove; Jungersted, Jacob Mutanu; Coenraads, Pieter-Jan; Diepgen, Thomas Published in: CONTACT DERMATITIS
Citation for published version (APA): Coevorden, A. M. V. (2005). Hand eczema: clinical efficacy of interventions, and burden of disease s.n.
 University of Groningen Hand eczema Coevorden, Anthony Marco van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Hand eczema Coevorden, Anthony Marco van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen A simple tool with which to study the course of chronic hand eczema in clinical practice van der Valk, Pieter G. M.; van Gils, Robin F.; Boot, Cecile R. L.; Evers, Andrea W. M.;
University of Groningen A simple tool with which to study the course of chronic hand eczema in clinical practice van der Valk, Pieter G. M.; van Gils, Robin F.; Boot, Cecile R. L.; Evers, Andrea W. M.;
Eczema & Dermatitis Clinical features: Histopathological features: Classification:
 Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Patch Testing for Hand Dermatitis-20 years Experience Chun-Hsuan Ho Chee-Ching Sun Mei-Ping Tseng Chia-Yu Chu
 Patch Testing for Hand Dermatitis-20 years Experience Chun-Hsuan Ho Chee-Ching Sun Mei-Ping Tseng Chia-Yu Chu Hand dermatitis is the most frequently recognized occupational skin disease. Comprehensive
Patch Testing for Hand Dermatitis-20 years Experience Chun-Hsuan Ho Chee-Ching Sun Mei-Ping Tseng Chia-Yu Chu Hand dermatitis is the most frequently recognized occupational skin disease. Comprehensive
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 Eczema and Contact Dermatitis John Berth-Jones Consultant Dermatologist University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire NHS Trust, Coventry, UK Eunice Tan Specialist Registrar in Dermatology Norfolk and
Eczema and Contact Dermatitis John Berth-Jones Consultant Dermatologist University Hospitals Coventry and Warwickshire NHS Trust, Coventry, UK Eunice Tan Specialist Registrar in Dermatology Norfolk and
Citation for published version (APA): Coevorden, A. M. V. (2005). Hand eczema: clinical efficacy of interventions, and burden of disease s.n.
 University of Groningen Hand eczema Coevorden, Anthony Marco van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Hand eczema Coevorden, Anthony Marco van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
INVESTIGATIVE REPORT. Scoring of Hand Eczema: Good Reliability of the Hand Eczema Extent Score (HEES)
 INVESTIGATIVE REPORT 193 Scoring of Hand Eczema: Good Reliability of the Hand Eczema Extent Score (HEES) Annica CARLSSON 1,3, Åke SVENSSON 1, Chris D. ANDERSON 2, Irina BARANOVSKAYA 1, Monica HINDSÉN-STENSTRÖM
INVESTIGATIVE REPORT 193 Scoring of Hand Eczema: Good Reliability of the Hand Eczema Extent Score (HEES) Annica CARLSSON 1,3, Åke SVENSSON 1, Chris D. ANDERSON 2, Irina BARANOVSKAYA 1, Monica HINDSÉN-STENSTRÖM
Spoilt for choice evaluation of two different scoring systems for early hand eczema in teledermatological examinations
 Contact Dermatitis 2010: 62: 241 247 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S CONTACT DERMATITIS Spoilt for choice evaluation of two different scoring systems for early hand
Contact Dermatitis 2010: 62: 241 247 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S CONTACT DERMATITIS Spoilt for choice evaluation of two different scoring systems for early hand
My Algorithm. Questions to ask. Do you or your family have a history of?... Allergic rhinitis, Sensitive skin, Asthma Skin Cancer
 Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Contact sensitizers in dyshidrotic eczema
 Contact sensitizers in dyshidrotic eczema Original Article Shobhna Kajal, Sunil Kumar Gupta, Veenu Gupta*, Sukhjot Kaur, Gurpoonam Kaur, Sandeep Kaur Department of Dermatology, Dayanand Medical College
Contact sensitizers in dyshidrotic eczema Original Article Shobhna Kajal, Sunil Kumar Gupta, Veenu Gupta*, Sukhjot Kaur, Gurpoonam Kaur, Sandeep Kaur Department of Dermatology, Dayanand Medical College
Characteristics and Provision of Care in Patients with Chronic Hand Eczema: Updated Data from the CARPE Registry
 Acta Derm Venereol 2014; 94: 163 167 INVESTIGATIVE REPORT Characteristics and Provision of Care in Patients with Chronic Hand Eczema: Updated Data from the CARPE Registry Christian J. Apfelbacher 1,2,
Acta Derm Venereol 2014; 94: 163 167 INVESTIGATIVE REPORT Characteristics and Provision of Care in Patients with Chronic Hand Eczema: Updated Data from the CARPE Registry Christian J. Apfelbacher 1,2,
ATOPIC ECZEMA. What are the aims of this leaflet?
 ATOPIC ECZEMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about atopic eczema. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and where
ATOPIC ECZEMA What are the aims of this leaflet? This leaflet has been written to help you understand more about atopic eczema. It tells you what it is, what causes it, what can be done about it, and where
Prevalence, incidence and predictive factors for hand eczema in young adults a follow-up study
 Johannisson et al. BMC Dermatology 2013, 13:14 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prevalence, incidence and predictive factors for hand eczema in young adults a follow-up study Arne Johannisson 1*, Ann Pontén
Johannisson et al. BMC Dermatology 2013, 13:14 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prevalence, incidence and predictive factors for hand eczema in young adults a follow-up study Arne Johannisson 1*, Ann Pontén
Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV])
![Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV]) Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (Ultraviolet A [PUVA] and B [UBV])](/thumbs/89/99382632.jpg) Origination: 09/27/07 Revised: 08/2/17 Annual Review: 11/2/17 Purpose: To provide Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (PUVA and UBV) guidelines for the Medical Department staff to reference when
Origination: 09/27/07 Revised: 08/2/17 Annual Review: 11/2/17 Purpose: To provide Phototherapy and Photochemotherapy Treatment (PUVA and UBV) guidelines for the Medical Department staff to reference when
This is a repository copy of Treatment of severe, chronic hand eczema. Results from a UK-wide survey..
 This is a repository copy of Treatment of severe, chronic hand eczema. Results from a UK-wide survey.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/104211/ Version: Accepted
This is a repository copy of Treatment of severe, chronic hand eczema. Results from a UK-wide survey.. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/104211/ Version: Accepted
The epidemiology of hand eczema in the general population prevalence and main findings*
 Contact Dermatitis 2010: 62: 75 87 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S CONTACT DERMATITIS Review Article The epidemiology of hand eczema in the general population prevalence
Contact Dermatitis 2010: 62: 75 87 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S CONTACT DERMATITIS Review Article The epidemiology of hand eczema in the general population prevalence
Eczema. By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University
 Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
6. Contact allergic reactions in patients with atopic eczema
 Acta Derm Venereol 2005; Suppl. 215: 28 32 6. Contact allergic reactions in patients with atopic eczema JOHN MCFADDEN Medicament allergy is a not uncommon problem both with antibiotics and topical corticosteroids.
Acta Derm Venereol 2005; Suppl. 215: 28 32 6. Contact allergic reactions in patients with atopic eczema JOHN MCFADDEN Medicament allergy is a not uncommon problem both with antibiotics and topical corticosteroids.
Skin allergy to chemicals
 Skin allergy to chemicals clinical, epidemiological and public health perspectives Jeanne Duus Johansen National Allergy Research Centre Department of Dermato allergology Copenhagen University Hospital
Skin allergy to chemicals clinical, epidemiological and public health perspectives Jeanne Duus Johansen National Allergy Research Centre Department of Dermato allergology Copenhagen University Hospital
What to do when patch testing is negative?
 What to do when patch testing is negative? Christen M. Mowad MD Clinical Professor of Dermatology Geisinger Medical Center Danville, PA 17821 cmowad@geisinger.edu I have no disclosures. What to do when
What to do when patch testing is negative? Christen M. Mowad MD Clinical Professor of Dermatology Geisinger Medical Center Danville, PA 17821 cmowad@geisinger.edu I have no disclosures. What to do when
Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
 Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment We all know that a healthy immune system is good. But, do you know that an overactive immune system can cause certain conditions like Psoriasis? Read on to find
Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment We all know that a healthy immune system is good. But, do you know that an overactive immune system can cause certain conditions like Psoriasis? Read on to find
Psoriasis. Overview. Epidemiology. Epidemiology 08/08/2015. Dr Nigel Burrows Consultant Dermatologist Addenbrooke s Hospital
 Overview Psoriasis 1. Epidemiology of psoriasis 2. Histology Dr Nigel Burrows Consultant Dermatologist Addenbrooke s Hospital Aug 2015 3. Types of psoriasis 4. Assessing severity 5. Treatments Topical
Overview Psoriasis 1. Epidemiology of psoriasis 2. Histology Dr Nigel Burrows Consultant Dermatologist Addenbrooke s Hospital Aug 2015 3. Types of psoriasis 4. Assessing severity 5. Treatments Topical
What do patients with occupational hand eczema know about skin care?
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis What do patients with occupational hand eczema know about skin care? Maja H. Fisker 1, Niels E. Ebbehøj 1, Jakob M. Jungersted 2 and Tove Agner
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis What do patients with occupational hand eczema know about skin care? Maja H. Fisker 1, Niels E. Ebbehøj 1, Jakob M. Jungersted 2 and Tove Agner
Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology
 Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathogbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University e-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Pathogenesis of allergic
Clinico Pathological Test SCPA605-Essential Pathology Somphong Narkpinit, M.D. Department of Pathogbiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University e-mail : somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Pathogenesis of allergic
Constitutional eczema
 Patient information Constitutional eczema What is constitutional eczema? Constitutional eczema, also called atopic eczema, is a form of eczema that mainly occurs in childhood. Eczema usually starts before
Patient information Constitutional eczema What is constitutional eczema? Constitutional eczema, also called atopic eczema, is a form of eczema that mainly occurs in childhood. Eczema usually starts before
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Psoriasis: the management of psoriasis 1.1 Short title Psoriasis 2 The remit The Department of Health has asked NICE: 'to produce
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Psoriasis: the management of psoriasis 1.1 Short title Psoriasis 2 The remit The Department of Health has asked NICE: 'to produce
Dermatitis. Occupational aspects of management
 Dermatitis Occupational aspects of management Evidence-based guidance for healthcare professionals Introduction This leaflet summarises the findings from a review of the published scientific literature
Dermatitis Occupational aspects of management Evidence-based guidance for healthcare professionals Introduction This leaflet summarises the findings from a review of the published scientific literature
Dermatology elective for yr. 5. Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015
 Dermatology elective for yr. 5 Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015 How to diagnosis and manage eczema and psoriasis. Objectives
Dermatology elective for yr. 5 Natta Rajatanavin, MD. Div. of dermatology Dep. Of Medicine, Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol University 23 rd Feb 2015 How to diagnosis and manage eczema and psoriasis. Objectives
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
DAFTAR PUSTAKA. Dalam: Australian Safety and Compensation Council; h
 DAFTAR PUSTAKA 1. Nixon R, Frowen K. Occupational contact dermatitis in Australia April 2006. Dalam: Australian Safety and Compensation Council; 2005. h. 1-13. 2. Sasseville D. Occupational Contact Dermatitis.
DAFTAR PUSTAKA 1. Nixon R, Frowen K. Occupational contact dermatitis in Australia April 2006. Dalam: Australian Safety and Compensation Council; 2005. h. 1-13. 2. Sasseville D. Occupational Contact Dermatitis.
A*STAR skin examination protocol
 A*STAR skin examination protocol Professor Carsten Flohr Chair in Dermatology and Population Science & Consultant Dermatologist Unit for Population-Based Dermatology Research St John s Institute of Dermatology
A*STAR skin examination protocol Professor Carsten Flohr Chair in Dermatology and Population Science & Consultant Dermatologist Unit for Population-Based Dermatology Research St John s Institute of Dermatology
The hands in health and disease of individuals with filaggrin loss-of-function mutations: clinical reflections on the hand eczema phenotype
 Contact Dermatitis Review Article COD Contact Dermatitis The hands in health and disease of individuals with filaggrin loss-of-function mutations: clinical reflections on the hand eczema phenotype Jeanette
Contact Dermatitis Review Article COD Contact Dermatitis The hands in health and disease of individuals with filaggrin loss-of-function mutations: clinical reflections on the hand eczema phenotype Jeanette
COD. Summary. Contact Dermatitis. Magnus Lindberg 1,2, Kerstin Bingefors 3, Birgitta Meding 4 and Mats Berg 5,6
 Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Hand eczema and health-related quality of life; a comparison of EQ-5D and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) in relation to the hand eczema
Contact Dermatitis Original Article COD Contact Dermatitis Hand eczema and health-related quality of life; a comparison of EQ-5D and the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) in relation to the hand eczema
CHAPTER 1. Eczema Basics
 CHAPTER 1 Eczema Basics Definition Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition, characterised by ichtyosis (dry skin), erythema (redness), excoriation (interruption of the skin), scratching lesions, lichenification
CHAPTER 1 Eczema Basics Definition Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition, characterised by ichtyosis (dry skin), erythema (redness), excoriation (interruption of the skin), scratching lesions, lichenification
Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist. Susan Nedorost, MD
 Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist Susan Nedorost, MD Contact Dermatitis: Challenges for the General Dermatologist Disclosure Statement I, Susan Nedorost, MD, do not have any relevant
Contact Dermatitis Challenges for the General Dermatologist Susan Nedorost, MD Contact Dermatitis: Challenges for the General Dermatologist Disclosure Statement I, Susan Nedorost, MD, do not have any relevant
Grover s disease: A case report.
 320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
320 Case report Thai J Dermatol, October-December 2011 ABSTRACT: Grover s disease: A case report. Supicha Chavanich MD, Praneet Sajjachareonpong MD. CHAVANICH C, SAJJACHAREONPONG P. GROVER S DISEASE: A
Citation for published version (APA): Ebbes, P. (2004). Latent instrumental variables: a new approach to solve for endogeneity s.n.
 University of Groningen Latent instrumental variables Ebbes, P. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Latent instrumental variables Ebbes, P. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Conflicts of interest
 Vulvar Cases 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology)
Vulvar Cases 2 nd PANHELLANIC CONGRESS on Lower Genital Tract Disorders December 14-16 Grand Hyatt Athens Lynette J. Margesson MD FRCPC Assistant Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Surgery(Dermatology)
Citation for published version (APA): Weert, E. V. (2007). Cancer rehabilitation: effects and mechanisms s.n.
 University of Groningen Cancer rehabilitation Weert, Ellen van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Cancer rehabilitation Weert, Ellen van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Access to the published version may require journal subscription. Published with permission from: Blackwell Synergy
 This is an author produced version of a paper published in Contact Dermatitis This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proofcorrections or journal pagination. Citation
This is an author produced version of a paper published in Contact Dermatitis This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proofcorrections or journal pagination. Citation
CLINICAL REPORT. (Accepted December 16, 2003.) Acta Derm Venereol 2004; 84:
 Acta Derm Venereol 2004; 84: 291 295 CLINICAL REPORT Are Adverse Skin Reactions to Cosmetics Underestimated in the Clinical Assessment of Contact Dermatitis? A Prospective Study among 1075 Patients Attending
Acta Derm Venereol 2004; 84: 291 295 CLINICAL REPORT Are Adverse Skin Reactions to Cosmetics Underestimated in the Clinical Assessment of Contact Dermatitis? A Prospective Study among 1075 Patients Attending
Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.]
![Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.] Citation for published version (APA): Christoffers, W. (2014). Hand eczema: interventions & contact allergies [S.l.]: [S.n.]](/thumbs/78/78446206.jpg) University of Groningen Hand eczema Christoffers, Wianda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
University of Groningen Hand eczema Christoffers, Wianda IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version
Frequency of skin diseases among sea fishermen in Basrah
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 1 Frequency of skin diseases among sea fishermen in Basrah K Al Hamdi, M Al-Malikey Citation K Al Hamdi, M Al-Malikey.. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 1 Frequency of skin diseases among sea fishermen in Basrah K Al Hamdi, M Al-Malikey Citation K Al Hamdi, M Al-Malikey.. The Internet Journal
University of Groningen. BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem
 University of Groningen BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen BNP and NT-proBNP in heart failure Hogenhuis, Jochem IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
An Everyday Guide to Eczema
 An Everyday Guide to Eczema By Dr. Kristel Polder, Board-Certified Dermatologist Developed in Partnership with Who is affected by eczema? 32 million people in the US 1 in 5 children 1 in 12 adults *www.eczema.org
An Everyday Guide to Eczema By Dr. Kristel Polder, Board-Certified Dermatologist Developed in Partnership with Who is affected by eczema? 32 million people in the US 1 in 5 children 1 in 12 adults *www.eczema.org
PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE PSORIASIS. Plaque a raised lesion where the diameter is greater than the thickness. Number 2
 Number 2 CORE TUTORIALS IN DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE AYERS ROCK, ULURU NATIONAL PARK, AUSTRALIA PSORIASIS UPDATED PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE 2011 Plaque a raised lesion
Number 2 CORE TUTORIALS IN DERMATOLOGY FOR PRIMARY CARE PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE AYERS ROCK, ULURU NATIONAL PARK, AUSTRALIA PSORIASIS UPDATED PDP SELF-TEST QUESTIONNAIRE 2011 Plaque a raised lesion
Comparative efficacy of topical mometasone furoate 0.1% cream vs topical tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in the treatment of atopic dermatitis
 Original Article Comparative efficacy of topical mometasone furoate 0.1% cream vs topical tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in the treatment of atopic dermatitis Md Alauddin Khan *, Lubna Khondker **, Dilshad
Original Article Comparative efficacy of topical mometasone furoate 0.1% cream vs topical tacrolimus 0.03% ointment in the treatment of atopic dermatitis Md Alauddin Khan *, Lubna Khondker **, Dilshad
Management of Senile Atopic Dermatitis in Geriatric Outpatient Clinic Dermatovenereology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital in
 Global Journal of Medical Research: F Diseases Volume 18 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print ISSN:
Global Journal of Medical Research: F Diseases Volume 18 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print ISSN:
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
If looking for a book Psoriasis Cure: Treatments, Natural Remedies and Best Home Managements (Skin Disease, Skin Problems, Skin Diseases and
 Psoriasis Cure: Treatments, Natural Remedies And Best Home Managements (Skin Disease, Skin Problems, Skin Diseases And Disorders Book 1) By Jeff Kennedy READ ONLINE If looking for a book Psoriasis Cure:
Psoriasis Cure: Treatments, Natural Remedies And Best Home Managements (Skin Disease, Skin Problems, Skin Diseases And Disorders Book 1) By Jeff Kennedy READ ONLINE If looking for a book Psoriasis Cure:
An Evaluation of Patch Test among Hand Eczema Patients Attending Tertiary Care Center in South East Rajasthan
 Original Research Article An Evaluation of Patch Test among Hand Eczema Patients Attending Tertiary Care Center in South East Rajasthan Raghavendra KR 1,*, Jitendra Bhuria 2, Mukul Sharma 3 1 Senior Resident,
Original Research Article An Evaluation of Patch Test among Hand Eczema Patients Attending Tertiary Care Center in South East Rajasthan Raghavendra KR 1,*, Jitendra Bhuria 2, Mukul Sharma 3 1 Senior Resident,
Chronic hand dermatitis often interferes with ability
 32 Practical Dermatology October 2006 Follow these tips on history, exam, and testing in order to make the right diagnosis and institute effective therapy. By Susan Nedorost, MD Chronic hand dermatitis
32 Practical Dermatology October 2006 Follow these tips on history, exam, and testing in order to make the right diagnosis and institute effective therapy. By Susan Nedorost, MD Chronic hand dermatitis
Contact Dermatitis In Atopic Patients
 Contact Dermatitis In Atopic Patients Jenny Murase, MD Palo Alto Foundation Medical Group Director of Patch Testing University of California, San Francisco Associate Clinical Professor Disclosures Consultant
Contact Dermatitis In Atopic Patients Jenny Murase, MD Palo Alto Foundation Medical Group Director of Patch Testing University of California, San Francisco Associate Clinical Professor Disclosures Consultant
Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients.
 Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients. Isaksson, Marléne Published in: Contact Dermatitis DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.00959.x
Corticosteroid contact allergy - the importance of late readings and testing with corticosteroids used by the patients. Isaksson, Marléne Published in: Contact Dermatitis DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.00959.x
Arthrocentesis and viscosupplementation as treatment modalities for arthralgia of the temporomandibular joint Vos, Lukas Matthijs
 University of Groningen Arthrocentesis and viscosupplementation as treatment modalities for arthralgia of the temporomandibular joint Vos, Lukas Matthijs IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the
University of Groningen Arthrocentesis and viscosupplementation as treatment modalities for arthralgia of the temporomandibular joint Vos, Lukas Matthijs IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the
What you need to know about ECZEMA
 What you need to know about ECZEMA The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health and the prevention of skin
What you need to know about ECZEMA The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health and the prevention of skin
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
What you need to know about ECZEMA
 What you need to know about ECZEMA The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health and the prevention of skin
What you need to know about ECZEMA The Irish Skin Foundation is a national charity with a mission to improve quality of life for people with skin conditions, promote skin health and the prevention of skin
Quality of Life of Saudi Patients with Dermatologic Disorders
 Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics 2018, 8(1): 1-6 DOI: 10.5923/j.cmd.20180801.01 Quality of Life of Saudi Patients with Dermatologic Disorders Bassam Ahmed Almutlaq 1, Fatemah Kadhem Aljishi 2, Rawan Ahmed
Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics 2018, 8(1): 1-6 DOI: 10.5923/j.cmd.20180801.01 Quality of Life of Saudi Patients with Dermatologic Disorders Bassam Ahmed Almutlaq 1, Fatemah Kadhem Aljishi 2, Rawan Ahmed
Dr David Orchard MBBS FACD
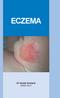 Eczema Dr David Orchard MBBS FACD What is eczema? Eczema is a particular type of inflammatory reaction in the skin. The features include redness, scaling and itch. When it is more severe the skin will
Eczema Dr David Orchard MBBS FACD What is eczema? Eczema is a particular type of inflammatory reaction in the skin. The features include redness, scaling and itch. When it is more severe the skin will
Citation for published version (APA): Westerman, E. M. (2009). Studies on antibiotic aerosols for inhalation in cystic fibrosis s.n.
 University of Groningen Studies on antibiotic aerosols for inhalation in cystic fibrosis Westerman, Elisabeth Mechteld IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen Studies on antibiotic aerosols for inhalation in cystic fibrosis Westerman, Elisabeth Mechteld IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen. Skin disease in paper mill workers Jungbauer, F.H.W.; Lensen, G.J.; Groothoff, J.W.; Coenraads, Pieter
 University of Groningen Skin disease in paper mill workers Jungbauer, F.H.W.; Lensen, G.J.; Groothoff, J.W.; Coenraads, Pieter Published in: Occupational Medicine-Oxford DOI: 10.1093/occmed/kqi022 IMPORTANT
University of Groningen Skin disease in paper mill workers Jungbauer, F.H.W.; Lensen, G.J.; Groothoff, J.W.; Coenraads, Pieter Published in: Occupational Medicine-Oxford DOI: 10.1093/occmed/kqi022 IMPORTANT
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis. Moisture Associated Dermatitis 8/31/2017. Goals of Presentation. Differentiating and Controlling
 Incontinence Associated Dermatitis Moisture Associated Dermatitis Differentiating and Controlling Goals of Presentation This presentation will attempt to: Identify causes and risk factors for IAD and MASD
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis Moisture Associated Dermatitis Differentiating and Controlling Goals of Presentation This presentation will attempt to: Identify causes and risk factors for IAD and MASD
Dupilumab and Crisaborole for Atopic Dermatitis: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks
 Dupilumab and Crisaborole for Atopic Dermatitis: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks Draft Background and Scope November 7, 2016 Background: Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a chronic/chronically-relapsing
Dupilumab and Crisaborole for Atopic Dermatitis: Effectiveness, Value, and Value-Based Price Benchmarks Draft Background and Scope November 7, 2016 Background: Atopic dermatitis (eczema) is a chronic/chronically-relapsing
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
What is atopic dermatitis?
 What is atopic dermatitis? Complex inflammatory skin disorder intense pruritus cutaneous hyperreactivity immune dysregulation Chronic with exacerbations and remissions Affects all ages, but more common
What is atopic dermatitis? Complex inflammatory skin disorder intense pruritus cutaneous hyperreactivity immune dysregulation Chronic with exacerbations and remissions Affects all ages, but more common
Update on emollients
 Update on emollients Amal Mhanna, MD Pediatric Dermatologist Clemenceau Medical Center Disclosure: I was a member of an advisory board y for J&J and received honoraria. Emollients and moisturizers are
Update on emollients Amal Mhanna, MD Pediatric Dermatologist Clemenceau Medical Center Disclosure: I was a member of an advisory board y for J&J and received honoraria. Emollients and moisturizers are
Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory, Prescribing in children
 Psoriasis in children: current approaches to management Laura Proudfoot BSc, MRCP, Elisabeth Higgins MA, FRCP and Judy Davids RGN Our series Prescribing in children gives practical advice for successful
Psoriasis in children: current approaches to management Laura Proudfoot BSc, MRCP, Elisabeth Higgins MA, FRCP and Judy Davids RGN Our series Prescribing in children gives practical advice for successful
Psoriasis And Sensitive Areas READ ONLINE
 Psoriasis And Sensitive Areas READ ONLINE Psoriasis - Drugs.com - Psoriasis Definition. Psoriasis is a common skin condition that changes the life cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis causes cells to build up
Psoriasis And Sensitive Areas READ ONLINE Psoriasis - Drugs.com - Psoriasis Definition. Psoriasis is a common skin condition that changes the life cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis causes cells to build up
Infections, inflammation and venous thrombosis; an epidemiological perspective Tichelaar, Ynse
 University of Groningen Infections, inflammation and venous thrombosis; an epidemiological perspective Tichelaar, Ynse IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen Infections, inflammation and venous thrombosis; an epidemiological perspective Tichelaar, Ynse IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal Vol. 6 No 1: 14, June 2010
 Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
Wells Syndrome H. Gammaz, H. Amer, A. Adly and S. Mahmoud Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 6 (1): 14 Al-Haud Al-Marsoud Hospital, Cairo, Egypt e-mail: hananderma@hotmail.com Submitted: April 15, 2010
University of Groningen. Common mental disorders Norder, Giny
 University of Groningen Common mental disorders Norder, Giny IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Common mental disorders Norder, Giny IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Allergy Medications. Antihistamines. are very safe. Although usually taken as tablets, they may be prescribed as a liquid or syrup for young children
 The treatments prescribed for allergy control the symptoms and reactions; they do not cure the condition. However, using treatments as prescribed can show a huge change in a patient s health, mood and
The treatments prescribed for allergy control the symptoms and reactions; they do not cure the condition. However, using treatments as prescribed can show a huge change in a patient s health, mood and
Common Superficial Fungal Infections
 How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
This PDF is available for free download from a site hosted by Medknow Publications
 Net Study Comparison of clinical efficacy of topical tazarotene.1% cream with topical clobetasol propionate.5% cream in chronic plaque psoriasis: A double-blind, randomized, right-left comparison study
Net Study Comparison of clinical efficacy of topical tazarotene.1% cream with topical clobetasol propionate.5% cream in chronic plaque psoriasis: A double-blind, randomized, right-left comparison study
Dermatitis (inflammatory skin condition) Nonallergic. dermatitis. Non-atopic eczema (non- IgE mediated)
 Atopic Eczema Dermatitis (inflammatory skin condition) Allergic dermatitis -eczema Nonallergic dermatitis Atopic eczema (IgE mediated) Non-atopic eczema (non- IgE mediated) Pathophysiology of Eczema Allergy
Atopic Eczema Dermatitis (inflammatory skin condition) Allergic dermatitis -eczema Nonallergic dermatitis Atopic eczema (IgE mediated) Non-atopic eczema (non- IgE mediated) Pathophysiology of Eczema Allergy
Paediatric Eczema. Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012
 Paediatric Eczema Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012 Classification of the principal forms of eczema EXOGENOUS ENDOGENOUS Irritant Allergic contact Photoallergic contact Eczematous
Paediatric Eczema Dr Manjeet Joshi Consultant Dermatologist 16 th May 2012 Classification of the principal forms of eczema EXOGENOUS ENDOGENOUS Irritant Allergic contact Photoallergic contact Eczematous
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Types of Skin Infections
 Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
It is estimated that about 26,000 new cases of
 Focus on CME at Dalhousie University Set On Soothing Psoriasis A. H. Murray, MD, FRCP(C) Presented at the 76th Annual Dalhousie Refresher Course It is estimated that about 26,000 new cases of psoriasis
Focus on CME at Dalhousie University Set On Soothing Psoriasis A. H. Murray, MD, FRCP(C) Presented at the 76th Annual Dalhousie Refresher Course It is estimated that about 26,000 new cases of psoriasis
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Citation for published version (APA): Coevorden, A. M. V. (2005). Hand eczema: clinical efficacy of interventions, and burden of disease s.n.
 University of Groningen Hand eczema Coevorden, Anthony Marco van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Hand eczema Coevorden, Anthony Marco van IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
RELEVANT MEDICAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS
 Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, Bazex syndrome (also known as acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex and acrokeratosis neoplastica) is a cutaneous condition characterized by
Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, Bazex syndrome (also known as acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex and acrokeratosis neoplastica) is a cutaneous condition characterized by
Heritability of Hand Eczema Is Not Explained by Comorbidity with Atopic Dermatitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE See related commentary on pg 1568 Is Not Explained by Comorbidity with Atopic Dermatitis Anne Lerbaek 1,2, Kirsten O. Kyvik 3, Jakob Mortensen 3, Lars E. Bryld 2, Torkil Menné 1,2 and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE See related commentary on pg 1568 Is Not Explained by Comorbidity with Atopic Dermatitis Anne Lerbaek 1,2, Kirsten O. Kyvik 3, Jakob Mortensen 3, Lars E. Bryld 2, Torkil Menné 1,2 and
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY
 WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps
 Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps Dr Carol Hlela Consultant Dermatologist Head of Unit, Department of Dermatology, Paediatrics Red Cross Children s Hospital, UCT Red Cross War Memorial
Atopic Eczema with detail on how to apply wet wraps Dr Carol Hlela Consultant Dermatologist Head of Unit, Department of Dermatology, Paediatrics Red Cross Children s Hospital, UCT Red Cross War Memorial
The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care
 The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care Item type Authors Publisher Journal Article Buckley, David Nursing in General Practice Nursing in general practice Downloaded 16-Sep-2016
The role of the practice nurse in managing psoriasis in primary care Item type Authors Publisher Journal Article Buckley, David Nursing in General Practice Nursing in general practice Downloaded 16-Sep-2016
Allergic versus Contact
 Allergic versus Contact Dermatitis Julie Sterbank, DO Assistant Clinical Professor Allergy/Immunology MetroHealth Medical Center/Case Western Reserve University Disclosure I have no financial disclosures
Allergic versus Contact Dermatitis Julie Sterbank, DO Assistant Clinical Professor Allergy/Immunology MetroHealth Medical Center/Case Western Reserve University Disclosure I have no financial disclosures
Skin lesions & Abrasions
 Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
Skin lesions & Abrasions What Are Skin Lesions? A skin lesion is a part of the skin that has an abnormal growth or appearance compared to the skin around it Types of Skin Lesions Two types of skin lesions
CUTANEOUS SENSORY THRESHOLD STIMULATION WITH HIGH FREQUENCY SQUARE-WAVE CURRENT II. THE RELATIONSHIP OF BODY SITE AND OF SKIN DISEASES TO THE SENSORY
 CUTANEOUS SENSORY THRESHOLD STIMULATION WITH HIGH FREQUENCY SQUARE-WAVE CURRENT II. THE RELATIONSHIP OF BODY SITE AND OF SKIN DISEASES TO THE SENSORY THRESHOLD* HARRY SIGEL, M.D. Potelunas, Meixner and
CUTANEOUS SENSORY THRESHOLD STIMULATION WITH HIGH FREQUENCY SQUARE-WAVE CURRENT II. THE RELATIONSHIP OF BODY SITE AND OF SKIN DISEASES TO THE SENSORY THRESHOLD* HARRY SIGEL, M.D. Potelunas, Meixner and
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES ATOPIC DERMATITIS / ECZEMA MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN
 RELEVANT DISCLOSURES MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN Advisory board member - MEDA (Elidel), Speaking honoraria Bayer (Advantan) Advisory board, consultant, speaker: Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Elli
RELEVANT DISCLOSURES MANAGING ECZEMA IN INFANTS AND CHILDREN Advisory board member - MEDA (Elidel), Speaking honoraria Bayer (Advantan) Advisory board, consultant, speaker: Pfizer, Abbvie, Janssen, Elli
Dermatology Literary Review
 Emollients and ageing skin: optimising effectiveness and safety of Nursing, Vol. 25, No.11, pages 596-598. 6 Article outlines the causes of dryness in ageing skin and concludes that emollients are the
Emollients and ageing skin: optimising effectiveness and safety of Nursing, Vol. 25, No.11, pages 596-598. 6 Article outlines the causes of dryness in ageing skin and concludes that emollients are the
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis
 Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis Dermatological conditions are perhaps the most worrisome diseases in the
Difference Between Seborrheic Dermatitis and Psoriasis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis Dermatological conditions are perhaps the most worrisome diseases in the
Some skin conditions
 Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
