Tolerance induction to bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (BIAP) prevents immunotoxicity after intravenous BIAP treatment in mice
|
|
|
- John Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5 Tolerance induction to bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (BIAP) prevents immunotoxicity after intravenous BIAP treatment in mice In preparation Chantal Beumer Daniëlle Fiechter Willem Raaben Ruud Brands Marianne Bol Lydia Kwast Rob Bleumink Raymond Pieters Willem Seinen Marty Wulferink 93
2 Abstract It has previously been demonstrated that bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (BIAP) attenuates the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated inflammatory response in mice and piglets and might therefore represent a novel therapeutic drug in the treatment of LPS-mediated diseases like Gram-negative sepsis. Safety studies performed in multiple species demonstrated that single dose BIAP administration is safe. Although BIAP administration according to a multiple-dose regimen did not result in any adverse effects in piglets and dogs, mice were prone to anaphylactic shock. In the present study it was investigated if this species difference in immune reactivity towards BIAP is due to a lack of tolerance to bovine proteins in mice. Since mice do not consume bovine products with their food whereas other species used in the safety studies do, oral tolerance may explain the species differences in immunogenicity. In order to induce tolerance, mice were given BIAP in their drinking water for 20 consecutive days. Thereafter, an immunization protocol was used consisting of daily iv administration of BIAP. The level of tolerance was read by the inability to mount a BIAP-specific antibody response. Mice that had received long-term oral BIAP administration showed decreased levels of BIAP-specific antibodies after immunization when compared to orally untreated mice. Furthermore, orally BIAP treated mice did not develop anaphylactic shock reactions whereas orally placebo treated mice did. We therefore conclude that oral administration of BIAP to mice resulted in tolerization, which was characterized by the absence of clinically relevant toxicity and decreased levels of BIAP-specific antibodies upon intravenous BIAP administration. 94
3 Introduction Alkaline phosphatases are dimeric membrane-bound ectoenzymes common to most organisms and can be found in many tissues throughout the body. In mammals, four isoforms are distinguished: placental (PLAP), germ cell (GCAP) and intestinal (IAP), being tissue-specific isoenzymes, and the bone-liver-kidney (BLK) isoenzyme, which is also called tissue non-specific 1. Alkaline phosphatases catalyze the hydrolysis of phosphomonoesters with release of anorganic phosphate at alkaline ph in vitro 2 and have been ascribed several biological functions In 1997, it was shown that human placental alkaline phosphatase (HPLAP) dephosphorylates and thereby detoxifies LPS at physiological ph levels 11. It was also shown that HPLAP reduces mortality in mice lethally infected with Gram-negative bacteria, thereby suggesting a role for alkaline phosphatase in protection against endotoxin insult typical for Gramnegative bacteria 12,13. More recently, we have demonstrated that bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (BIAP), like HPLAP, attenuates LPS-induced TNF! levels and hematological changes in piglets and reduces mortality in mice after a lethal E. coli infection 14. Based on these results it was concluded that BIAP could represent a novel therapeutic drug for the treatment of Gramnegative sepsis and other LPS-mediated diseases. In a previous safety study it was demonstrated that the immunogenic potential of BIAP depends on the species used (Beumer et al., i n preparation). Multiple intravenous dosing of BIAP resulted in anaphylaxis in mice and guinea pigs, but not in piglets and dogs. In mice, renal lesions were observed as well. A hypothesis that may explain the species differences in immunotoxicity might be the presence of bovine products in the food of piglets and dogs, which may have made them tolerant to BIAP. The diet of most animals contains a wide variety of proteins of animal or vegetable origin, most of which are potentially antigenic. However, when protein antigens are administered orally, antigen-specific non-responsiveness (also known as oral tolerance) is induced 15. The present study was initiated to test whether the immunotoxicity of BIAP observed in earlier safety studies in mice and guinea pigs could be explained by a lack of (oral) tolerance. First, the antibody response after multiple intravenous BIAP dosing was studied. Thereafter it was studied if drinking water supplemented with BIAP would induce tolerance and prevent anaphylaxis in mice after multiple BIAP challenge. The results of this study clearly show that oral administration of BIAP can prevent BIAP-specific antibody induction and anaphylaxis in mice after multiple intravenous BIAP challenge. 95
4 Materials and methods Test material, chemicals and reagents Bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (BIAP; GMP-processed, purity ALPIXG: 675 U/mg) was from Biozyme (Blaenavon, UK).C3c-complement/FITC was from Dako (Glostrup, Denmark). Purified rat anti-mouse IgE (clone R35-72) was obtained from Pharmingen (San Diego, USA). Purified goat anti mouse IgG1 was from Southern Biotech Ass Inc. (Birmingham, AL, USA). Immuno Fluore Mounting Medium was from MP Biomedicals Inc (Aurora, Ohio) and p-nitrophenylphosphate was from Acros (Geel, Belgium). Costar high-binding ELISA plates were from Corning B.V. Life Sciences (Schiphol-Rijk, The Netherlands). Animal study design Animals Female BALB/c mice (8-9 week old) were obtained from Charles River (The Netherlands) and housed at the animal facilities (Gemeenschappelijk Dierenlaboratorium, GDL) of Utrecht University. Mice were kept under conventional conditions in filter-topped macrolon cages (four to six mice per cage) at a temperature of 22 ± 3 C and a 12 h light/dark cycle. Animals received SDS D3 food pellets and acidified drinking water ad libitum. Mice were randomly assigned to the study groups and allowed to acclimatize to the laboratory conditions for 13 days before the start of the experiments. Treatment All experiments were conducted according to the guidelines of the Animals Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicin, Utrecht University (Utrecht, The Netherlands). Intravenous toxicity study with BIAP BIAP was diluted in sterile 0.9% saline and administered in the tail vein at 75, 200 or 750 U/kg body weight once daily for 28 consecutive days. Up to two hours after dosing, mice were observed for signs of toxicity. When signs of toxicity occurred, animals were observed for a longer period of time until signs disappeared. Body weight, and food and water consumption were recorded daily. Body temperature was assessed daily until day 11, thereafter it was checked twice a week. At necropsy (days 10 and 28) blood was drawn by heart puncture, after which sera were prepared and screened for BIAP specific IgE and IgG1. Liver, lung, kidney and spleen were preserved for immuno-histopathological examination. 96
5 Oral tolerance study with BIAP Mice in the oral BIAP groups (four mice per cage) were given non-acidified drinking water supplemented with BIAP at a concentration of 1 mg BIAP/animal/day for 20 consecutive days. Since in a previous study analysis of drinking water consumption resulted in 4 ml/animal/day, 5 mg BIAP was dissolved in 20 ml drinking water. Stability tests showed that enzymatic activity of BIAP in drinking water decreased with a maximum of 10% within 24 hours after preparation. Oral placebo groups received non-acidified drinking water alone. Drinking water of both groups was replaced every day. After this 20-day period, animals were iv challenged once daily for 11 consecutive days. For this purpose, BIAP was diluted in sterile 0.9% saline and administered in the tail vein at 200 or 750 U/kg bodyweight. Iv placebo group animals received saline only. Up to two hours after dosing, mice were observed for signs of anaphylaxis. Body weight, and food and water consumption were recorded daily. Body temperature was assessed daily until the last day of treatment (day 11). At necropsy (day 14), blood was drawn by heart puncture, after which sera were prepared and screened for BIAP specific IgG1. Methods (Immuno)-histopathological examination Samples of liver, kidney and spleen were preserved in formalin (4 % in PBS). Also, part of kidney, spleen and lungs were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen for future immunohistological analysis. Lungs were carefully filled with a solution of 1.5% (w/v) glycerine in PBS to expand the vacuoles and allow for optimal preparation of organ sections. Kidneys were also embedded in paraffin wax, sectioned at 5!m and stained with haematoxylin and eosin. Periodic Acid Schiff (PAS) staining was also performed. Since in a previous safety study with multiple dose BIAP in mice the kidney was found the target organ, histopathological examination was restricted to the kidneys. All other tissues were stored to allow future analysis when necessary. Analysis of immune complex formation in kidneys Cryopreserved kidneys were sectioned at 7!m. From each kidney 3 different sections, !m apart, were stained with C3c-complement/FITC for 1 hour at room temperature. After being rinsed with PBS and covered with anti-fading Immuno Fluore Mounting Medium, slides were visualized by fluorescence microscopy and screened for complement deposits. Analysis of BIAP specific IgE and IgG1 antibodies BIAP-specific antibodies were measured in serum obtained at day 10 and 28 in the immunotoxicity study and day 14 in the oral tolerance study. The assay was performed in Costar high-binding ELISA plates coated overnight at 4 ± 2 C with 100!l carbonate buffer containing either 2!g/ml purified rat anti-mouse IgE or 2!g/ml purified goat anti mouse IgG1. Washing steps were performed with TBS/0.05%Tween (TBST). After blocking with 150!l TBST/BSA for 2 hours, 97
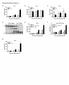
6 plates were washed and sera (diluted in TBST/BSA; first dilution = 2 3 ) were added and incubated for 1 h at 37 ± 2 C. After washing, plates were incubated with 100!l TBST/BSA containing 10!g/ml BIAP. Finally, plates were washed 3 times with TBST and 1 time with diethanolamine buffer. 100!l alkaline phosphatase substrate [pnpp, 1 mg/ml in diethanolamine buffer (9.7 % diethanolamine (v/v) and 0.02 % MgCl 2 (w/v) in distilled water, ph 9.8)] was added per well. After 30 minutes, the reaction was stopped using 50!l of a 10% (w/v) EDTA solution and plates were read at 405 nm on a microplate reader. Samples with an OD smaller than the OD measured for the first sample dilution (2 3 ) were below the detection limit. Samples with an OD higher than the OD measured for the blanc sample + 3 x SD were designated positive. Statistical analysis of the results Statistical analysis on log-transformed anti-alkaline phosphatase antibody titers was performed using one-way ANOVA with Dunnet post-test (Prism 3.00, Graphpad Software Inc.). Data were considered significant when p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**) or p<0.001 (***). Results Immunotoxicity study with BIAP As demonstrated in a previous safety study (Beumer et al., in preparation), anaphylaxis and renal lesions were observed in mice intravenously given BIAP doses of 750 and 7500 U/kg body weight (bw) once dailly for 10 consecutive days. In contrast, animals once daily dosed with 75 U/kg bw for 28 consecutive days did not show any sign of immunotoxicity. In the present study the safety experiments with mice were repeated in order to investigate the antibody response after multiple intravenous BIAP dosing. For this purpose, animals were once daily intravenously dosed with BIAP doses of 75, 200 or 750 U/kg, or saline for 28 consecutive days followed by observation for clinical signs of toxicity and antibody determination in serum. On day nine of the study, intravenous administration of high-dose BIAP (750 U/kg bw) resulted in apathy, cyanosis, and shortness of breath in all five animals of this dose group. These anaphylactic reactions started approximately min after treatment and disappeared approximately 1 hour after the symptoms started. On day 10 of the study, again all animals of the high-dose group suffered from severe anaphylactic reactions. For animal welfare reasons, highdose group animals were not treated any further whereas treatment of control, low-dose (75 U/kg bw) and mid-dose (200 U/kg bw) animals was continued. Intravenous administration of low- or mid-dose BIAP for 28 consecutive days did not result in any behavioural changes. No differences were observed in bodyweight gain, body temperature and food and water consumption in all animals during the entire study (data not shown). High titers of BIAP-specific IgG1 were found on day 10 in all mice of the low-dose and high-dose groups and in one out of five mice of the mid-dose group after multiple iv dosing with 98
7 BIAP (see Figure 1a). In control animals (placebo), no BIAP-specific IgG1 was detected. On day 28 (see Figure 1b), BIAP-specific IgG1 levels were further increased in the low- and mid-dose groups (continued iv exposure to BIAP), but not in the high-dose group (discontinued iv BIAP exposure). In addition, low BIAP-specific IgE titers were present in 4 out of 10 mice of the low-dose group, 3 out of 10 mice of the mid-dose group and 1 out of 10 mice of the high-dose group after iv BIAP administration. In control animals (placebo), no BIAP-specific IgG1 or IgE was detected. Figure 1 also shows that BIAP administration on the day of sacrifice does not interfere with the presence of circulating antibodies. a below limit of detection p < p < control 75 U/kg 200 U/kg 750 U/kg treated on day no no no no yes of necropsy b below limit of detection control p < p < p < U/kg 200 U/kg 750 U/kg treated on day no yes no yes no yes no yes of necropsy Figure 1: BIAP specific IgG1 (dots) and IgE (triangles) titers in serum after 10 (a) or 28 (b) days of i.v. BIAP treatment. Limit of detection equals no measurable IgG1 or IgE in the first dilution (2 3 = 1:8) tested. Data of individual mice are depicted. P-values denote statistical significance in IgG1 titers of BIAP-treated groups in comparison to the control group. 99
8 Gross examination at necropsy did not reveal macroscopic pathological changes in any of the test and control animals. No histopathological changes were observed in HE- and PAS-stained paraffin sections of the kidneys. Frozen kidney sections stained with C3c-complement/FITC showed that multiple intravenously dosing with BIAP did not result in complement deposits in the kidneys. Oral tolerance study with BIAP This study was developed to investigate if drinking water supplemented with BIAP would induce tolerance and thereby prevent anaphylaxis in mice after multiple BIAP challenge. For this purpose, animals were given BIAP in their drinking water or drinking water alone for 20 consecutive days. After this period, mice were once daily intravenously challenged with 0, 200 or 750 U BIAP/kg bw for 11 consecutive days. Placebo tolerized/biap challenged animals developed anaphylactic signs on day 10 and 11, whereafter challenge was stopped. In contrast, BIAP tolerized/biap challenged animals did not show any behavioural changes after multiple challenging with BIAP, which was reflected in low BIAP-specific IgG1 titers on day 14 (see Figure 2). In contrast, placebo tolerized/biap challenged animals showed high titers of BIAP-specific IgG1 in 2 out of 4 mice of the mid-dose group and 4 out of 4 mice of the high dose group after multiple intravenous dosing with BIAP. In animals of both control groups (placebo tolerized/placebo challenged and BIAP tolerized/placebo challenged), no behavioural changes were observed and no BIAP-specific antibodies were detected. below limit of detection p < oral treatment: aphos placebo aphos placebo aphos placebo i.v. treatment: saline 200 U/kg 750 U/kg Figure 2: BIAP specific IgG1 titers in serum after 20 days of oral BIAP administration, followed by 11 days of BIAP challenge. Limit of detection equals no measurable IgG1 in the first dilution (2 3 = 1:8) tested. Data of individual mice are depicted. P-values denote statistical significance in IgG1 titers of BIAPtreated groups in comparison to the placebo groups. 100
9 Discussion The medical use of proteins started more than a century ago when immune sera from animal origin were introduced for the prevention or treatment of infections, followed by the use of insulin of bovine and porcine origin some decades later. These products were often immunogenic in patients, sometimes even leading to serious anaphylactic reactions 16. Initially, the foreign nature of the protein was considered the main cause of immunogenicity. Later on, it was found that products purified from human sera, such as factor VIII, also induced immunologic responses 17. It is now clear that nearly all biopharmaceuticals derived from both human and non-human sources can induce antibodies 18, although the incidence is much higher in animal-derived than in humanized protein drugs. Many factors such as protein structure, glycosylation, contaminants, formulation, degradation products, route of administration and the dosing regimen influence the immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins 19. In many cases the antibodies have no or little biological consequences. Problems arise when the antibody neutralizes an endogenous protein with essential biological activity or, even worse, induces anaphylactic shock. A life-threatening situation occurs when antigen administration induces IgE antibodies. Re-exposure to the antigen will now result in cross-linking of the antigen to IgE molecules, followed by the activation and degranulation of mast cells or basophils within seconds to minutes. This response can cause profound organ dysfunction of the cardiac, respiratory, gastrointestinal, dermal and neural system and is known as anaphylactic shock 20. Antibodies (including IgM and IgG) can also react with antigen and form immune complexes in the circulation that can be deposited in tissues like the renal glomerulus, skin venules or lungs. Once deposited, immune complexes can trigger the classical complement pathway, resulting in the generation of the anaphylatoxins C3a, C4a and C5a which have potent effects on smooth muscle and the vascular system and can also induce degranulation of mast cells and basophils 20. Complement-containing immune complexes also generate an influx of polymorphonuclear leukocytes into the vessel wall, resulting in inflammation and tissue damage 21. It has previously been demonstrated that bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (BIAP) is able to detoxify lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in vivo 14. Recent safety studies with BIAP in various animal species as well as human volunteers showed that single dose BIAP administration to mice, rats, dogs and humans, and multiple-dose BIAP administration to piglets and dogs did not result in any adverse effects, whereas multiple-dosing of BIAP to mice and guinea pigs resulted in anaphylaxis (Beumer et al., in preparation). In the first part of the present study the safety experiments with mice were repeated in order to study the antibody response after multiple intravenous BIAP dosing. For this purpose, animals were once daily intravenously dosed with BIAP or vehicle for 28 consecutive days. The clinical symptoms observed at day 10 in high dosed mice, but not in low- and mid-dosed animals, combined with time of onset of these symptoms and the presence of BIAP specific IgG1 in day 10 serum samples led us to conclude that animals suffered from anaphylactic shock reactions. Development of anaphylaxis has long been regarded to be mediated by IgE, however, no BIAP- 101
10 specific IgE was detected in day 10 serum samples. This was expected as IgE levels normally start to rise 2 weeks after initiation of treatment 22. Literature suggests that the classical IgE-mediated pathway does not account for all anaphylactic responses. Indeed, Strait et al. 23 and Miyajima et al. 24 showed that, in contrast to the human situation, antigen-induced anaphylaxis in the mouse primarily proceeds through the IgG1 pathway, even in an experimental model characterized by strong IgE responses. The main goal of the present study was to investigate if oral treatment with BIAP can prevent anaphylaxis in mice after multiple iv BIAP challenge. To investigate this, mice were orally given BIAP or placebo for 20 consecutive days. After this oral treatment period, mice were once daily intravenously challenged with BIAP or placebo. In contrast to placebo tolerized/biap challenged animals, which responded with anaphylactic signs and elevated levels of BIAP-specific IgG1, multiple intravenous BIAP challenge of BIAP tolerized mice did not result in anaphylactic signs or the induction of BIAP-specific IgG1. In conclusion, this study shows that mice can be orally tolerated to BIAP, thereby preventing the induction of BIAP-specific antibodies and anaphylaxis. Since multiple intravenous BIAP dosing to piglets and dogs did not result in BIAP-specific antibody induction (Beumer et al., in preparation), these species are considered tolerant because of the presence of bovine products in their food. Since humans also consume bovine products in their food, it is expected that also humans tolerate BIAP administration. Indeed, a safety study using human volunteers showed that BIAP-specific antibodies and clinical side-effects were absent. Based on these results, a clinical phase II sepsis trial is currently ongoing. References 1 Fishman WH. Alkaline phosphatase isozymes: recent progress. Clin Biochem 1990; 23: McComb RB, Bowers GN, Posen S. Alkaline phosphatases. New York: Plenum Press, Narisawa S, Wennberg C, Millan JL. Abnormal vitamin B6 metabolism in alkaline phosphatase knock-out mice causes multiple abnormalities, but not the impaired bone mineralization. J Pathol 2001; 193: Beckman G, Beckman L, Holm S, et al. Placental alkaline phosphatase types and transplacental IgG transport. Hum Hered 1995; 45:1-5 5 Beckman G, Beckman L, Magnusson SS. Placental alkaline phosphatase phenotypes and pre-natal selection. Evidence from studies of spontaneous and induced abortions. Hum Hered 1972; 22: Beckman L, Beckman G, Mi MP. The relation between human placental alkaline phosphatase types and some perinatal factors. Hum Hered 1969; 19: Beckman L, Bjorling G, Christodoulou C. Pregnancy enzymes and placental polymorphism. I. Alkaline phosphatse. Acta Genet Stat Med 1966; 16:
11 8 Van Hoof VO, and De Broe. Interpretation and clinical significance of alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme patterns. crit. rev. clin. lab. sci. 1994; 31: Flock E, Bollman J. Alkaline phosphatase in the intestinal lymph of the rat. J.Biol.Chem. 1948; 175: Mahmood A, Yamagishi F, Eliakim R, et al. A possible role for rat intestinal surfactant-like particles in transepithelial triacylglycerol transport. J Clin Invest 1994; 93: Poelstra K, Bakker WW, Klok PA, et al. A physiologic function for alkaline phosphatase: endotoxin detoxification. Lab Invest 1997; 76: Poelstra K, Bakker WW, Klok PA, et al. Dephosphorylation of endotoxin by alkaline phosphatase in vivo. Am J Pathol 1997; 151: Bentala H, Verweij WR, Huizinga-Van der Vlag A, et al. Removal of phosphate from lipid A as a strategy to detoxify lipopolysaccharide. Shock 2002; 18: Beumer C, Wulferink M, Raaben W, et al. Calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase, a novel therapeutic drug for lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated diseases, attenuates LPS toxicity in mice and piglets. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2003; 307: Weiner HL. Oral tolerance, an active immunologic process mediated by multiple mechanisms. J Clin Invest 2000; 106: Schernthaner G. Immunogenicity and allergenic potential of animal and human insulins. Diabetes Care 1993; 16: Jacquemin MG, Saint-Remy JM. Factor VIII immunogenicity. Haemophilia 1998; 4: Kromminga A, Schellekens H. Antibodies against erythropoietin and other protein-based therapeutics: an overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2005; 1050: Schellekens H. Bioequivalence and the immunogenicity of biopharmaceuticals. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2002; 1: Janeway CA, Travers P, Walport M, et al. IMMUNOBIOLOGY. The immune system in health and disease. 4 ed: Current Biology Publications, Johnson KJ, Chensue SW, Ward PA. Pathology. 3rd ed: Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Von Garnier C, Astori M, Kettner A, et al. In vivo kinetics of the immunoglobulin E response to allergen: bystander effect of coimmunization and relationship with anaphylaxis. Clin Exp Allergy 2002; 32: Strait RT, Morris SC, Yang M, et al. Pathways of anaphylaxis in the mouse. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002; 109: Miyajima I, Dombrowicz D, Martin TR, et al. Systemic anaphylaxis in the mouse can be mediated largely through IgG1 and Fc gammariii. Assessment of the cardiopulmonary changes, mast cell degranulation, and death associated with active or IgE- or IgG1-dependent passive anaphylaxis. J Clin Invest 1997; 99:
University of Groningen. Detoxification of LPS by alkaline phosphatase Tuin, Annemarie
 University of Groningen Detoxification of LPS by alkaline phosphatase Tuin, Annemarie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Detoxification of LPS by alkaline phosphatase Tuin, Annemarie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
Chapter 6. Summary and general discussion
 Chapter 6 Summary and general discussion Summary and general discussion 106 Chapter 6 Summary Alkaline phosphatase (AP) is an ubiquitous enzyme in the human body that can be present in four isoforms. There
Chapter 6 Summary and general discussion Summary and general discussion 106 Chapter 6 Summary Alkaline phosphatase (AP) is an ubiquitous enzyme in the human body that can be present in four isoforms. There
Chantal Beumer Safety and efficacy of bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase, a novel therapeutic drug for LPS-mediated diseases
 4 Species differences in safety of bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (BIAP), a potential novel therapeutic drug for attenuating lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated diseases In preparation Daniëlle
4 Species differences in safety of bovine calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (BIAP), a potential novel therapeutic drug for attenuating lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-mediated diseases In preparation Daniëlle
The mouse cholera toxin model for evaluation of allergenicity
 The mouse cholera toxin model for evaluation of allergenicity Joost Smit, ILSI 2012 Of mice and men.(mestas, J Immunol 2004; 172:2731) Mouse Human Neutrophils in blood 10-25% 50-70% Lymphocytes in blood
The mouse cholera toxin model for evaluation of allergenicity Joost Smit, ILSI 2012 Of mice and men.(mestas, J Immunol 2004; 172:2731) Mouse Human Neutrophils in blood 10-25% 50-70% Lymphocytes in blood
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric*
 SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES
 CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES Nitroblue Tetrazolium Chloride (NBT) Reduction test NBT reduction test was evaluated by employing the method described by Hudson and Hay,1989 based upon principle that
CHAPTER 4 IMMUNOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES Nitroblue Tetrazolium Chloride (NBT) Reduction test NBT reduction test was evaluated by employing the method described by Hudson and Hay,1989 based upon principle that
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Reagent Set DAS ELISA, Alkaline phosphatase label SRA 22001, SRA 23203, SRA 27703, SRA & SRA ToRSV, ArMV, GFLV, AnFBV and PDV
 List of contents Lot number Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525
List of contents Lot number Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525
CONTENTS. STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1
 CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
Third line of Defense
 Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
Chapter 15 Specific Immunity and Immunization Topics -3 rd of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities Third line of Defense Specific immunity is a complex interaction of immune cells (leukocytes)
20X Buffer (Tube1) 96-well microplate (12 strips) 1
 PROTOCOL MitoProfile Rapid Microplate Assay Kit for PDH Activity and Quantity (Combines Kit MSP18 & MSP19) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP20 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION MitoProfile Rapid Microplate
PROTOCOL MitoProfile Rapid Microplate Assay Kit for PDH Activity and Quantity (Combines Kit MSP18 & MSP19) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP20 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION MitoProfile Rapid Microplate
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses 12PART B Adaptive Defense System: Third Line of Defense Immune
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
TRACP & ALP Assay Kit
 Cat. # MK301 For Research Use TRACP & ALP Assay Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Introduction...3 Components...4 Materials Required but not Provided...4 V. Storage...4
Cat. # MK301 For Research Use TRACP & ALP Assay Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Introduction...3 Components...4 Materials Required but not Provided...4 V. Storage...4
Complement. History. Chapter 7. Complement Components. Complement Pathways. Pathways of complement activation
 History Chapter 7 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
History Chapter 7 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
MyBioSource.com. Instructions for use. Histamine Release
 Instructions for use Histamine Release Supplementary kit for the determination of the release of histamine from heparinized whole blood (this kit has to be used in combination with the Histamine ELISA,
Instructions for use Histamine Release Supplementary kit for the determination of the release of histamine from heparinized whole blood (this kit has to be used in combination with the Histamine ELISA,
TRACP & ALP double-stain Kit
 Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Instructions for use. Histamine Release
 Instructions for use Histamine Release Supplementary kit for the determination of the release of histamine from heparinized whole blood (this kit has to be used in combination with the Histamine ELISA,
Instructions for use Histamine Release Supplementary kit for the determination of the release of histamine from heparinized whole blood (this kit has to be used in combination with the Histamine ELISA,
neoplastic mast cells (Giarman, Potter & Day, 1960). According to Toh
 J. Phy8iol. (1963), 165, pp. 83-88 83 Printed in Great Britain RELEASE OF HISTAMINE FROM SPLEEN BY KIDNEY EXTRACT, RESERPINE AND COMPOUND 48/80 BY ANNIE B. ELLIOTT From the Department of Physiology, University
J. Phy8iol. (1963), 165, pp. 83-88 83 Printed in Great Britain RELEASE OF HISTAMINE FROM SPLEEN BY KIDNEY EXTRACT, RESERPINE AND COMPOUND 48/80 BY ANNIE B. ELLIOTT From the Department of Physiology, University
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Assessment of leukocyte adhesion in flow chambers
 Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit
 Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0953 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3
Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0953 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3
OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation)
 Product Manual OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation) Catalog Number STA-358 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Product Manual OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation) Catalog Number STA-358 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Mouse GLP-2 EIA. Cat. No. KT-374. For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. For Research Use Only. 1 Rev.
 Mouse GLP-2 EIA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. Cat. No. KT-374 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 11357374 PRODUCT INFORMATION Mouse GLP-2 EIA Cat. No. KT-374 INTENDED
Mouse GLP-2 EIA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. Cat. No. KT-374 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 11357374 PRODUCT INFORMATION Mouse GLP-2 EIA Cat. No. KT-374 INTENDED
IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II
 IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II A. Evolution of the immune system. 1. Figure 1--57.25, p. 1167 from Raven and Johnson Biology 6 th ed. shows how the immune system evolved. Figure 1. How the immune system evolved.
IMMUNITY AND DISEASE II A. Evolution of the immune system. 1. Figure 1--57.25, p. 1167 from Raven and Johnson Biology 6 th ed. shows how the immune system evolved. Figure 1. How the immune system evolved.
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit
 Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Mouse Total IgA Antibody Detection Kit Catalog # 3019 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The total IgA levels in specimens are often determined in mouse disease models involving
Chapter 4. Bovine Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase (BIAP) reduces inflammation after induction of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in mice.
 Chapter 4 Bovine Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase (BIAP) reduces inflammation after induction of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in mice submitted Daniëlle Fiechter, Suzanne Kats, Ruud Brands, Ben van
Chapter 4 Bovine Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase (BIAP) reduces inflammation after induction of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in mice submitted Daniëlle Fiechter, Suzanne Kats, Ruud Brands, Ben van
Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit
 Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0817 500 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0817 500 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Immunological transfusion reactions
 Immunological transfusion reactions Immunological transfusion reactions can be hemolytic or non-hemolytic in nature. Both types can be separated into acute (those occurring immediately after transfusion)
Immunological transfusion reactions Immunological transfusion reactions can be hemolytic or non-hemolytic in nature. Both types can be separated into acute (those occurring immediately after transfusion)
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity
 Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
Blood and Immune system Acquired Immunity Immunity Acquired (Adaptive) Immunity Defensive mechanisms include : 1) Innate immunity (Natural or Non specific) 2) Acquired immunity (Adaptive or Specific) Cell-mediated
2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory tract sweep out bacteria and particles.
 Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
Lipopolysaccharide, and Outer Membrane in Adults Infected with
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 984, p. 54-58 0095-37/84/54-05$0.00/0 Copyright 3 984, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 0, No. 6 Antibody Responses to Capsular Polysaccharide, Lipopolysaccharide,
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 984, p. 54-58 0095-37/84/54-05$0.00/0 Copyright 3 984, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 0, No. 6 Antibody Responses to Capsular Polysaccharide, Lipopolysaccharide,
OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc.
 OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc. BIOXYTECH pl GPx Enzyme Immunoassay Assay for Human Plasma Glutathione Peroxidase For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog
OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc. BIOXYTECH pl GPx Enzyme Immunoassay Assay for Human Plasma Glutathione Peroxidase For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: Allergy and IgE
 Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: Allergy and IgE Tillie-Louise Hackett Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology James Hogg Research Centre University of British Columbia Short Synopsis This
Pharmacology of the Respiratory Tract: Allergy and IgE Tillie-Louise Hackett Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacology James Hogg Research Centre University of British Columbia Short Synopsis This
History. Chapter 13. Complement Components. Complement Pathways
 History Chapter 13 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
History Chapter 13 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
Hypersensitivity Reactions and Peanut Component Testing 4/17/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Hello everyone. My name is Melissa Snyder, and I am the director of the Antibody Immunology Lab at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, MN. I m so glad you are able to join me for a brief discussion about the
1 Hello everyone. My name is Melissa Snyder, and I am the director of the Antibody Immunology Lab at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, MN. I m so glad you are able to join me for a brief discussion about the
THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM OBJECTIVES:
 Dr Mohammed Al- ani THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: When you finish this section, you should be able to: 1. Describe the effects of complement activation. 2. Outline the Classical, Mannan-Binding (MB)
Dr Mohammed Al- ani THE COMPLEMENT SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: When you finish this section, you should be able to: 1. Describe the effects of complement activation. 2. Outline the Classical, Mannan-Binding (MB)
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE TITLE: TOTAL IGE EIA (HYTEC 288)
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE TITLE: TOTAL IGE EIA (HYTEC 288) INDEX CODE: IC26 (Ver.1) NUMBER OF PAGES: 10 AREA OF APPLICATION: IMMUNOCHEMISTRY PREPARED BY: A. SAMPSON DATE OF IMPLEMENTATION: 2001 MOST
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE TITLE: TOTAL IGE EIA (HYTEC 288) INDEX CODE: IC26 (Ver.1) NUMBER OF PAGES: 10 AREA OF APPLICATION: IMMUNOCHEMISTRY PREPARED BY: A. SAMPSON DATE OF IMPLEMENTATION: 2001 MOST
Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c) Serum IgG1 (a), IgM (b) and IgG2 (c) concentrations in response to papain immediately before primary immunization (day
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Protease allergens induce IgE and IgG1 production. (a-c) Serum IgG1 (a), IgM (b) and IgG2 (c) concentrations in response to papain immediately before primary immunization (day
immunity defenses invertebrates vertebrates chapter 48 Animal defenses --
 defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
Immunotoxicology in Food and Ingredient Safety Assessment: Approaches and Case Studies
 Immunotoxicology in Food and Ingredient Safety Assessment: Approaches and Case Studies April 14, 2015 Toxicology and Food Allergy: Case Study of tbhq Cheryl Rockwell Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacology
Immunotoxicology in Food and Ingredient Safety Assessment: Approaches and Case Studies April 14, 2015 Toxicology and Food Allergy: Case Study of tbhq Cheryl Rockwell Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacology
GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA. For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma
 GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2RT-E01
GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2RT-E01
Human Carbamylated LDL ELISA Kit (CBL-LDL Quantitation)
 Product Manual Human Carbamylated LDL ELISA Kit (CBL-LDL Quantitation) Catalog Number MET-5032 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Product Manual Human Carbamylated LDL ELISA Kit (CBL-LDL Quantitation) Catalog Number MET-5032 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats
 The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Florin Muselin*, Diana Brezovan, Jelena Savici, Romeo T. Cristna, Eugenia
The Use of Sea Buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) and Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) in Alloxan Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Rats Florin Muselin*, Diana Brezovan, Jelena Savici, Romeo T. Cristna, Eugenia
H.pylori IgA Cat #
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Aac Reagent Set ELISA for the detection of Acidovorax avenae subsp. citrulli Catalog number: SRA 14800
 List of contents Lot number Aac Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525
List of contents Lot number Aac Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525
Measles IgM ELISA Kit
 Measles IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2257 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Measles IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2257 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
ANTIBODIES Jiri Mestecky, M.D., Ph.D. - Lecturer
 ANTIBODIES Jiri Mestecky, M.D., Ph.D. - Lecturer Distribution in body fluids: secretions plasma (serum), tears, saliva, milk, genitourinary, and intestinal Cells producing antibodies and their tissue distribution:
ANTIBODIES Jiri Mestecky, M.D., Ph.D. - Lecturer Distribution in body fluids: secretions plasma (serum), tears, saliva, milk, genitourinary, and intestinal Cells producing antibodies and their tissue distribution:
Product Datasheet. HLA ABC Antibody (W6/32) NB Unit Size: 0.25 mg. Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 1 Publications: 22
 Product Datasheet HLA ABC Antibody (W6/32) NB100-64775 Unit Size: 0.25 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 1 Publications: 22 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research
Product Datasheet HLA ABC Antibody (W6/32) NB100-64775 Unit Size: 0.25 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 1 Publications: 22 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research
Third line of Defense. Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization!
 Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
Topic 8 Specific Immunity (adaptive) (18) Topics - 3 rd Line of Defense - B cells - T cells - Specific Immunities 1 3 rd Line = Prophylaxis via Immunization! (a) A painting of Edward Jenner depicts a cow
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Valkenburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1403684111 SI Materials and Methods ELISA and Microneutralization. Sera were treated with Receptor Destroying Enzyme II (RDE II, Accurate) before ELISA
Supporting Information Valkenburg et al. 10.1073/pnas.1403684111 SI Materials and Methods ELISA and Microneutralization. Sera were treated with Receptor Destroying Enzyme II (RDE II, Accurate) before ELISA
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit
 2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
Standard Operating Procedure
 1.0 Purpose: 1.1 Relaxation, dissection, weighing and fixation of heart for histological analysis. Changes in heart weight and wall thickness are linked to cardiovascular phenotypes. This protocol describes
1.0 Purpose: 1.1 Relaxation, dissection, weighing and fixation of heart for histological analysis. Changes in heart weight and wall thickness are linked to cardiovascular phenotypes. This protocol describes
Protocols for the Induction and Evaluation of Systemic Anaphylaxis in Mice
 Chapter 10 Protocols for the Induction and Evaluation of Systemic Anaphylaxis in Mice Elizabeth Doyle, Julia Trosien, and Martin Metz Abstract Mouse models of systemic anaphylaxis are important tools for
Chapter 10 Protocols for the Induction and Evaluation of Systemic Anaphylaxis in Mice Elizabeth Doyle, Julia Trosien, and Martin Metz Abstract Mouse models of systemic anaphylaxis are important tools for
SHRIRAM INSTITUTE FOR INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH
 IN RATS SUB CHRONIC ORAL TOXICITY WITH NHH 44 Bt-COTTON SEEDS Report for: UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION DHARWAD-580007 KARNATAKA Guidelines: DBT, Guidelines for Toxicity
IN RATS SUB CHRONIC ORAL TOXICITY WITH NHH 44 Bt-COTTON SEEDS Report for: UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH STATION DHARWAD-580007 KARNATAKA Guidelines: DBT, Guidelines for Toxicity
Lecture 2. Immunoglobulin
 Lecture 2 Immunoglobulin Objectives; Define secretary IgA Describe structure & functions of IgM Compare the antigenic receptor of B lymphocyte Assess the role of IgE in Atopy Distinguish between Isotype,
Lecture 2 Immunoglobulin Objectives; Define secretary IgA Describe structure & functions of IgM Compare the antigenic receptor of B lymphocyte Assess the role of IgE in Atopy Distinguish between Isotype,
H.Pylori IgG
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
H.Pylori IgG Cat # 1503Z
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Lecture 2. Immunoglobulin
 Lecture 2 Immunoglobulin Objectives; To study the secretary IgA To know the structure & functions of IgM The antigenic receptor of B lymphocyte The role of IgE in Atopy The difference between Isotype,
Lecture 2 Immunoglobulin Objectives; To study the secretary IgA To know the structure & functions of IgM The antigenic receptor of B lymphocyte The role of IgE in Atopy The difference between Isotype,
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens
 How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections
 Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
Direct immunofluorescence of skin using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections SL MERA, EW YOUNG, AND JWB BRADFIELD J Clin Pathol 1980; 33: 365-369 From the University Department ofpathology, University
HSV-1 IgM ELISA. Catalog No (96 Tests) For Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures.
 For Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. INTENDED USE The GenWay, Inc. HSV-1 IgM ELISA Kit is intended for the detection of IgM antibody to HSV-1 in human serum or plasma. SUMMARY AND
For Research Use Only. Not for use in Diagnostic Procedures. INTENDED USE The GenWay, Inc. HSV-1 IgM ELISA Kit is intended for the detection of IgM antibody to HSV-1 in human serum or plasma. SUMMARY AND
Europium Labeling Kit
 Europium Labeling Kit Catalog Number KA2096 100ug *1 Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Europium Labeling Kit Catalog Number KA2096 100ug *1 Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit
 H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3142 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
H. pylori Antigen ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3142 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
For questions 1-5, match the following with their correct descriptions. (24-39) A. Class I B. Class II C. Class III D. TH1 E. TH2
 Questions Made by SI ATTENDEES!! :) Page 1 of 6 Student-Made Practice Exam Activity All questions, answers, and slide numbers are based off of Monday s SI activity, where students/attendees created possible
Questions Made by SI ATTENDEES!! :) Page 1 of 6 Student-Made Practice Exam Activity All questions, answers, and slide numbers are based off of Monday s SI activity, where students/attendees created possible
See external label 2 C-8 C Σ=96 tests Cat # 1505Z. MICROWELL ELISA H.Pylori IgA Cat # 1505Z
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Introduction to Immunopathology
 MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
Chlamydia Trachomatis IgM ELISA Kit
 Chlamydia Trachomatis IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0960 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Chlamydia Trachomatis IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0960 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
H. pylori IgM. Cat # H. pylori IgM ELISA. ELISA: Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. ELISA - Indirect; Antigen Coated Plate
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com H. pylori
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com H. pylori
Blueberry scorch virus Reagent Set DAS ELISA, Alkaline phosphatase label for BlScV Catalog number: SRA 19100
 List of contents Lot number Blueberry scorch virus Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150
List of contents Lot number Blueberry scorch virus Reagent Set Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150
Reagent Set DAS ELISA, Alkaline phosphatase label
 List of contents Lot number Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml
List of contents Lot number Item 96 wells 500 wells 1000 wells 5000 wells Capture antibody 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml Alkaline phosphatase enzyme conjugate 0.150 ml 0.275 ml 0.525 ml 2.525 ml
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Allergy Skin Prick Testing
 Allergy Skin Prick Testing What is allergy? The term allergy is often applied erroneously to a variety of symptoms induced by exposure to a wide range of environmental or ingested agents. True allergy
Allergy Skin Prick Testing What is allergy? The term allergy is often applied erroneously to a variety of symptoms induced by exposure to a wide range of environmental or ingested agents. True allergy
NIS/WW Report 1 1 of 11. Report 1. Testing of Willard s Water for antioxidant capacity and cellular uptake of selected nutrients.
 NIS/WW Report 1 1 of 11 October 18, 2012. Report for: John Willard WW Industries, Inc. PO Box 4040 Rapid City, South Dakota 57709 Phone: (888) 379-4552 Fax: (605) 343-0109 Email: john@drwillard.com Web:
NIS/WW Report 1 1 of 11 October 18, 2012. Report for: John Willard WW Industries, Inc. PO Box 4040 Rapid City, South Dakota 57709 Phone: (888) 379-4552 Fax: (605) 343-0109 Email: john@drwillard.com Web:
Instructions for Use. Tg Antibody ELISA
 Instructions for Use Tg Antibody ELISA Enzyme Immunoassay for the Quantitative Determination of Autoantibodies to Thyroglobulin (Tg) in Serum and Plasma I V D REF EA618/96 12 x 8 2 8 C DLD Gesellschaft
Instructions for Use Tg Antibody ELISA Enzyme Immunoassay for the Quantitative Determination of Autoantibodies to Thyroglobulin (Tg) in Serum and Plasma I V D REF EA618/96 12 x 8 2 8 C DLD Gesellschaft
Mouse Anti-HDM IgG Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-HDM IgG Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3030 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people of
Mouse Anti-HDM IgG Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3030 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects 300 million people of
Phagocytosis of FITC labelled opsonized and non-opsonized E. coli bacteria by monocytes and granulocytes in a whole blood assay
 Phagocytosis of FITC labelled opsonized and non-opsonized E. coli bacteria by monocytes and granulocytes in a whole blood assay APPLICATION NOTE Author: Andreas Spittler, MD, Associate Professor for Pathophysiology
Phagocytosis of FITC labelled opsonized and non-opsonized E. coli bacteria by monocytes and granulocytes in a whole blood assay APPLICATION NOTE Author: Andreas Spittler, MD, Associate Professor for Pathophysiology
Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General
 Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General For the detection and quantitation of human OxLDL in plasma, serum or other biological fluid samples Cat. No. KT-959 For Research Use Only.
Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General For the detection and quantitation of human OxLDL in plasma, serum or other biological fluid samples Cat. No. KT-959 For Research Use Only.
Herpes Simplex Virus 2 IgM HSV 2 IgM
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
GLP-2 ELISA. For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples.
 GLP-2 ELISA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2HU-E01.1 Size: 96 wells Version:
GLP-2 ELISA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2HU-E01.1 Size: 96 wells Version:
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC.
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Product Datasheet. EMMPRIN/CD147 Antibody (MEM-M6/1) NB Unit Size: 0.1 mg. Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 2
 Product Datasheet EMMPRIN/CD147 Antibody (MEM-M6/1) NB500-430 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 2 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images
Product Datasheet EMMPRIN/CD147 Antibody (MEM-M6/1) NB500-430 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Publications: 2 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images
See external label 96 tests HSV 2 IgA. Cat #
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host.
 Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host. Hypersensitivity vs. allergy Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized
Hypersensitivity is the term used when an immune response results in exaggerated or inappropriate reactions harmful to the host. Hypersensitivity vs. allergy Hypersensitivity reactions require a pre-sensitized
Hosta virus X ELISA KIT
 Hosta virus X ELISA KIT Cat. No.:DEIA9256 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use The Hosta virus X ELISA KIT is used to detect HVX in both leaves and roots of hosta plants. Reagents And Materials Provided 1. Capture
Hosta virus X ELISA KIT Cat. No.:DEIA9256 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use The Hosta virus X ELISA KIT is used to detect HVX in both leaves and roots of hosta plants. Reagents And Materials Provided 1. Capture
Immunology. Lecture- 8
 Immunology Lecture- 8 Immunological Disorders Immunodeficiency Autoimmune Disease Hypersensitivities Immunodeficiency 1. Immunodeficiency --> abnormal production or function of immune cells, phagocytes,
Immunology Lecture- 8 Immunological Disorders Immunodeficiency Autoimmune Disease Hypersensitivities Immunodeficiency 1. Immunodeficiency --> abnormal production or function of immune cells, phagocytes,
Chlamydia Trachomatis IgG ELISA Kit
 Chlamydia Trachomatis IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0959 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Chlamydia Trachomatis IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0959 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses
 Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Chapter 21: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses I. 2 main types of body defenses A. Innate (nonspecific) defense: not to a specific microorganism or substance B. Adaptive (specific) defense: immunity to
Quantifying Bordetella-induced Neutrophil Infiltration Using a Myeloperoxidase Assay
 Quantifying Bordetella-induced Neutrophil Infiltration Using a Myeloperoxidase Assay Sandra M. Fuentes, Research Scholar Faculty Mentor: Dr. Eric Harvill The Pennsylvania State University Abstract Bacteria
Quantifying Bordetella-induced Neutrophil Infiltration Using a Myeloperoxidase Assay Sandra M. Fuentes, Research Scholar Faculty Mentor: Dr. Eric Harvill The Pennsylvania State University Abstract Bacteria
History. Chapter 13. Complement Components. Complement Pathways
 History Chapter 13 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
History Chapter 13 Complement Jules Border in 1890 s discovered complement Paul Ehrlich coined the term complement The activity of blood serum that completes the action of antibody Now: Set of serum proteins
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
