STATE TOXINOLOGY SERVICES Toxinology Dept., Women s & Children s Hospital, North Adelaide SA 5006 AUSTRALIA
|
|
|
- Malcolm Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Family Viperidae record number Common name Western Diamond Rattlesnake SN0419 Scientific name combined Global region in which snake is found North America + Central America CLINICAL OVERVIEW is amongst the most dangerous of all North American rattlesnakes, with a high probability of causing envenoming, either local, or local and systemic. Bites cause local swelling, which may be severe, pain, bruising, blistering and sometimes necrosis. In cases with severe swelling, fluid shifts into the bitten limb can cause secondary shock and its sequelae. In addition to local effects, systemic effects are can occur, though are not commonly severe, though both non-specific symptoms and coagulopathy, bleeding and paralytic features are possible. Neurotoxic envenoming is usually minor and is uncommon to rare, but major paralysis, including respiratory paralysis is possible, though is exceptionally rare. Coagulopathy is more common, however, as is persistent thrombocytopenia. In all except minor cases, antivenom therapy is the mainstay of treatment. CroFab is the current prefered product. Antivipmyn remains unproven in clinical practice, though holds promise.
2 (continued) First aid 1. After ensuring the patient and onlookers have moved out of range of further strikes by the snake, the bitten person should be reassured and persuaded to lie down and remain still. Many will be terrified, fearing sudden death and, in this mood, they may behave irrationally or even hysterically. The basis for reassurance is the fact that many venomous bites do not result in envenoming, the relatively slow progression to severe envenoming (hours following elapid bites, days following viper bites) and the effectiveness of modern medical treatment. 2. The bite wound should not be tampered with in any way. Wiping it once with a damp cloth to remove surface venom is unlikely to do much harm (or good) but the wound must not be massaged. 3. All rings or other jewellery on the bitten limb, especially on fingers, should be removed, as they may act as tourniquets if oedema develops. 4. The bitten limb should be immobilised as effectively as possible using an extemporised splint or sling; if available, crepe bandaging of the splinted limb is an effective form of immobilisation. 5. If there is any impairment of vital functions, such as problems with respiration, airway, circulation, heart function, these must be supported as a priority. In particular, for bites causing flaccid paralysis, including respiratory paralysis, both airway and respiration may be impaired, requiring urgent and prolonged treatment, which may include the mouth to mask (mouth to mouth) technique of expired air transfer. Seek urgent medical attention. 6. Do not use Tourniquets, cut, suck or scarify the wound or apply chemicals or electric shock. 7. Avoid peroral intake, absolutely no alcohol. No sedatives outside hospital. If there will be considerable delay before reaching medical aid, measured in several hours to days, then give clear fluids by mouth to prevent dehydration. 8. If the offending snake has been killed it should be brought with the patient for identification (only relevant in areas where there are more than one naturally occurring venomous snake species), but be careful to avoid touching the head, as even a dead snake can envenom. No attempt should be made to pursue the snake into the undergrowth as this will risk further bites. 9. The snakebite victim should be transported as quickly and as passively as possible to the nearest place where they can be seen by a medically-trained person (health station, dispensary, clinic or hospital). The bitten limb must not be exercised as muscular contraction will promote systemic absorption of venom. If no motor vehicle or boat is available, the patient can be carried on a stretcher or hurdle, on the pillion or crossbar of a bicycle or on someone's back. 10. Most traditional, and many of the more recently fashionable, first aid measures are useless and potentially dangerous. These include local cauterization, incision, excision, amputation, suction by mouth, vacuum pump or syringe, combined incision and suction ("venom-ex" apparatus), injection or instillation of compounds such as potassium permanganate, phenol (carbolic soap) and trypsin, application of electric shocks or ice (cryotherapy), use of traditional herbal, folk and other remedies including the ingestion of emetic plant products and parts of the snake, multiple incisions, tattooing and so on.
3 (continued) Clinical summary With the exception of the neurotoxic specimens of Crotalus scutulatus, Mojave rattlesnake, envenoming by all North American rattlesnakes is similar in overall effects, but with differences in likely severity, depending on size, and other, often subtle differences between species. These latter are often not well documented. is a large snake and one of the more common causes of both bites and severe envenoming. In general rattlesnake bites cause both local and systemic effects. The bite is usually associated with local pain, which can be severe, but may also be trivial, at least for some species. The fangs are generally at least moderate sized and bite marks are almost always obvious, as double or single punctures. Occasionally other non-fang teeth may make contact, resulting in more complex bite marks. The same may occur if there have been multiple bites. A concentric half-ring of teeth marks is more suggestive of a python bite, while parallel sets of teeth marks without clear fang marks at the anterior extent might indicate a colubrid bite. In addition to local pain, swelling may develop. In almost all cases with envenoming there will be at least some swelling present, usually within minutes post bite, certainly within 1 hour. The complete absence of local swelling (and any other local or systemic effects) at 2hrs post bite is strongly suggestive of a dry bite, EXCEPT if the bite might have been caused by a Mojave rattlesnake (which has a limited geographic range). The extent of swelling may be restricted, but can also be severe and extensive, sometimes involving all of the bitten limb and beyond. The rapidity of swelling is closely related to the severity of the bite. In addition to swelling, there may be local blistering (bleb formation) which may be restricted to the bite area, or far more widespread on the bitten limb, the latter indicating a severe bite in most cases, as does bloody content of blisters. Blisters often take several hours to become evident, usually 8-36hrs post bite. They may not develop at all in cases given antivenom early. Local necrosis can develop at the bite site or more widely. Necrosis is more likely in tight areas, such as fingers or toes, but even quite severe local haemorrhagic blisters of fingers are not always associated with ultimate necrosis of the finger. At least one expert believes that early antivenom therapy, in sufficient doses, may greatly reduce the chance of necrosis developing. There may be major fluid shifts into the bitten limb, potentially causing hypovolaemic shock. Bruising can develop in the bite area or whole limb and can be associated with active bleeding. Massive swelling can cause temporary nerve dysfunction. True compartment syndrome, though it does occur, is uncommon to rare and muscle necrosis is as likely to be due to direct venom toxicity as to compartment syndrome. If compartment syndrome is suspected on clinical grounds, then it should be confirmed by intracompartment pressure measurement, before considering fasciotomy. Systemic effects of rattlesnake bites include both general and specific effects. General symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, metallic taste in the mouth, fasciculations of muscles (especially of face), dizziness, weakness (not true flaccid paralysis), fever, chills, collapse, rarely convulsions. A metallic taste in the mouth is particularly a feature of envenoming by Crotalus viridis and Crotalus adamanteus and is thought to be absent after envenoming by Crotalus ruber and Crotalus scutulatus according to one expert, who suggests this may help distinguish between bites by these snakes. Similarly, fasciculations are a feature of rattlesnake bites, but not Agkistrodon (copperhead, cottonmouth) or Sistrurus (massasauga, pygmy rattlesnake) bites. Specific systemic effects are principally those associated with coagulopathy. Most rattlesnake venoms contain toxins affecting haemostasis, including procoagulants, fibrinogenases, haemorrhagins and platelet-active toxins. Thus there may be abnormalities of coagulation blood tests, including prolonged PT and aptt, decreased fibrinogen, increased FDP/d-dimer and thrombocytopenia. Active bleeding can occur, especially from blisters on the bitten limb, and other spontaneous bleeding may manifest as bleeding gums, haematemesis, haematuria, melena, but major bleeding, though it can occur, is uncommon and limited to severe cases of envenoming. Severe coagulopathy is not a feature of Agkistrodon or Sistrurus envenoming. Rattlesnakes are generally considered to be non-neurotoxic, so true paralysis is often considered very unlikely. However, it appears that in addition to the Mojave rattlesnake, Crotalus scutulatus, some (but not all) specimens of which can cause flaccid paralysis, often without the severe local and coagulopathic effects of other rattlesnakes, quite a number of non-neurotoxic species can, on occasion, cause at least some paralytic effects. These vary from very local effects, usually involving cranial nerves (ptosis, facial weakness etc), to major generalised paralysis, though the latter is rare. It is most likely after bites by Crotalus adamanteus (in addition to Crotalus scutulatus), but should be considered an exceptional feature.
4 (continued) Treatment summary North American rattlesnake bites are generally managed as a group, without specific differences between species, except for Crotalus scutulatus bites (potential for significant neurotoxicity). While this approach will be listed here, it should be noted that each species of rattlesnake is likely to have individual characteristics of envenoming, which, where known and well documented, might justify subtle adjustments in management approach. The often poor documentation of such species specific information makes it currently impractical to list such subtleties here. Around 20% of all rattlesnake bites will be dry bites, without significant local or systemic effects. If no local or systemic effects have developed by 12 hrs (some would suggest 6hrs as sufficient), then the bite is almost certainly a dry bite, UNLESS it is or just might be by a neurotoxic species/specimen (principally some specimens of the Mojave rattlesnake, Crotalus scutulatus). If the latter can be excluded, then these non-envenomed cases can usually be allowed to go home, providing there is a responsible adult available to observe them until the following day. Such an approach should be carefully discussed with the patient/relatives, before proceeding. For cases showing clear evidence of local effects, ± systemic symptoms, insert an IV line and give an initial IV fluid load. If there is evidence of major local swelling, with the potential for fluid shifts and shock, monitor BP closely and consider giving further IV fluids to maintain adequate BP and renal perfusion. In such cases, beware later resolution of the swelling resulting in circulatory overload and pulmonary oedema, especially in children. Both local necrosis and compartment syndrome are a potential risk, but the latter is uncommon to rare, and can be confused with direct venom-induced muscle necrosis. If clinically it appears there may be a developing compartment syndrome, confirm this with pressure measurement before considering fasciotomy, otherwise unnecessary long term limb dysfunction and deformity may well result. Fasciotomy is rarely justified for snakebite. Unless the compartment syndrome is severe and well established, it is usually advisable to first try adequate antivenom therapy before proceeding to fasciotomy. Risks versus benefits must be carefully weighed for each individual case before deciding whether to first give antivenom, or proceed directly to fasciotomy. In all cases with significant local or systemic effects, consider antivenom therapy. Not all cases of envenoming by Crotalus species will require antivenom therapy. In North America it is common practice to grade the degree of envenoming and use this to determine the need for intervention (antivenom etc). While this process is not accepted by all, it does form a basis of common care guidelines and therefore its use should be considered, at least by those working in the USA. The grading is based on experience with rattlesnake (Crotalus) bites and any grading should be subject to reassessment, in a dynamic fashion, reflecting the dynamic nature of envenoming. It should be emphasised that this grading is for North American rattlesnake bites (excluding neurotoxic Crotalus scutulatus bites). Grade 0: Non-envenoming (a dry bite); there may be fang puncture marks, but no other local effects or systemic effects. Grade 1: Mild envenoming; local effects (pain, swelling) limited to bite area, no systemic effects or blood test abnormalities. Grade 2: Moderate envenoming; local effects extend beyond the bitten area, but not the whole bitten limb, systemic effects present (such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, metallic taste in mouth, fasciculations of isolated muscle groups, especially the face), blood tests abnormal (may include thrombocytopenia, hypofibrinogenaemia, prolonged prothrombin time, elevated CK). Grade 3: Severe envenoming; rapidly evolving swelling, blistering or ecchymosis or swelling extending to involve the whole bitten limb or beyond, potential for compartment syndrome, major systemic effects (including those seen in moderate envenoming, plus some or all of shock, widespread or severe bleeding, renal failure, respiratory problems, altered conscious state) and blood test abnormalities (severe thrombocytopenia, abnormal coagulation tests, myolysis with grossly elevated CK, myoglobinuria/anaemia, renal failure). Antivenom would not be required or appropriate for Grade 0 cases, would not necessarily be required for Grade 1 cases, but if used would be at a low dose, while all Grade 2 & 3 cases require antivenom. Grade 3 cases will require a higher initial dose, and often require larger subsequent doses of infusions. At least in North America (USA) the only approved antivenom for Crotalus species envenoming is the new ovine F(ab) Crofab, as the Wyeth Polyvalent Crotalidae antivenom is now either unavailable for restocking or out of production. It is unclear if this older product will again become available. Crofab is a safe, expensive, but effective antivenom which has only a short half life, owing to the small molecular size, compared to IgG antivenoms (eg Wyeth), so repeat doses or infusions are often required. The initial dose is usually suggested as 4-6 vials, followed by a further 6+ vials, either stat or, preferably, as an
5 infusion. The common regime suggested is 4-6 vials (each vial is reconstituted with 10mls sterile water) diluted in normal saline (250mls), given IV, initially at a slow rate (20-60ml/min) until it is clear no adverse reaction is occurring, then increase the rate to around 250ml/hr, until the whole initial dose is given. A slower rate or less volume might be required in small children, but still the same dose of antivenom. On completion, reassess to determine if antivenom has been effective. If there is still significant envenoming (eg advancing swelling, major systemic symptoms etc), consider further antivenom, at a similar dose and rate. Thereafter, it is often advisable to maintain antivenom levels by a continuous infusion, at a rate of 2 vials every 6hrs, up to 18+hrs, longer if major envenoming present. Higher doses may be justified in severe cases. Always have epinephrine & resuscitation equipment readily available prior to commencing antivenom therapy, in case of adverse reactions In the past in the USA it was common practice to perform a skin sensitivity test prior to starting antivenom. This dangerous and ineffective procedure is not appropriate and is not advocated by the producer of Crofab; DO NOT USE SKIN SENSITIVIT TESTING! The Mexican antivenom, Antivipmyn, is F(ab)2, not Fab, so is expected to have a longer half life and will not require such frequent doses to maintain levels. However, a higher initial dose is likely to be required, at least vials (producer, Bioclon, suggests 5-16 vials initially in adults, depending on severity, with double this dose in children), and further doses may be needed to neutralise all circulating venom. The indication for further doses is unclear, but consider worsening local swelling or effects, or worsening or developing systemic effects, especially coagulopathy or thrombocytopenia (uncertain if this antivenom will affect the latter). Note that while this antivenom has been recommended for use in North American snakebite, it has only rarely been used in this role and does not yet have US FDA approval; the immunising snake species are central-south American, not North American. In general, if there is a major coagulopathy or bleeding, antivenom will be the most effective treatment and should always be tried first, before considering blood product replacement therapy, except if there is life-threatening bleeding. If antivenom in adequate amounts fails to reverse coagulopathy sufficiently, over a reasonable period of time (allow several hours for such an effect, not minutes), then replacement therapy may be considered. Depending on the nature of the clinical problem or lab test abnormality, FFP, cryoprecipitate, platelet concentrate or whole blood might all be considered. All patients receiving antivenom or suffering any significant local or systemic effects should be followed up after discharge, particularly looking for delayed reactions to the antivenom (serum sickness) and functional problems affecting the bitten limb, as a result of venom-induced tissue injury. It should be stressed that even with the best treatment possible, full pre-injury function and appearance of the bitten limb cannot be guaranteed. Therefore, any such defect is not automatically an indication of malpractice, nor should it occasion legal action by the patient. It is best to advise patients/relatives from the outset that snakebite is a potentially severe injury, with a potential for adverse outcomes beyond the control of modern medical practice. Honest early discussion of the potential short and long term risks of both the bite and its treatment (ie anaphylactoid or serum sickness reactions to antivenom) are in the interests of both the patient and those offering treatment and may reduce the chance of later dissatisfaction or litigation. Few doctors see snakebite cases frequently. Unless the treating doctors see many cases and feel justifiably confident in treating envenoming, they should consider early discussion with colleagues expert in this area of medicine. Such expert advice may be available through the regional poisons centre, who will likely have a list of on-call experts. Early consultation may well avoid unpleasant problems developing later.
6 (continued) Available antivenoms Antivipmyn Instituto Bioclon Calzada de Tlalpan No Toriello Guerra C.P Mexico, D.F., Mexico Phone: Fax: Website: Polyvalent crotalid antivenom ( CroFab ), Ovine, Fab Protherics Inc. (US) th Avenue South Suite 103, Nashville Tennessee U.S.A. Phone: Fax: info@prothetics.com Website:
7 (continued) Management Flowchart
STATE TOXINOLOGY SERVICES Toxinology Dept., Women s & Children s Hospital, North Adelaide SA 5006 AUSTRALIA
 Family Viperidae www.toxinology.com record number Common name Eyelash Palm Pit Viper SN0379 Scientific name combined Global region in which snake is found Central America + South America CLINICAL OVERVIEW
Family Viperidae www.toxinology.com record number Common name Eyelash Palm Pit Viper SN0379 Scientific name combined Global region in which snake is found Central America + South America CLINICAL OVERVIEW
STATE TOXINOLOGY SERVICES Toxinology Dept., Women s & Children s Hospital, North Adelaide SA 5006 AUSTRALIA
 Family Elapidae www.toxinology.com record number SN0170 Scientific name combined Common name Black Mamba, Black-mouthed Mamba Global region in which snake is found CLINICAL OVERVIEW Mambas are amongst
Family Elapidae www.toxinology.com record number SN0170 Scientific name combined Common name Black Mamba, Black-mouthed Mamba Global region in which snake is found CLINICAL OVERVIEW Mambas are amongst
STATE TOXINOLOGY SERVICES Toxinology Dept., Women s & Children s Hospital, North Adelaide SA 5006 AUSTRALIA
 Family Viperidae www.toxinology.com record number SN0200 Scientific name combined Common name Puff Adder, Common Puff Adder, African Puff Adder ( B. a. arietans ), Somali Puff Adder ( B. a. somalica )
Family Viperidae www.toxinology.com record number SN0200 Scientific name combined Common name Puff Adder, Common Puff Adder, African Puff Adder ( B. a. arietans ), Somali Puff Adder ( B. a. somalica )
STATE TOXINOLOGY SERVICES Toxinology Dept., Women s & Children s Hospital, North Adelaide SA 5006 AUSTRALIA
 Family Elapidae www.toxinology.com record number SN0184 Scientific name combined Common name Mocambique Spitting Cobra, m Fezi, Mozambique Spitting Cobra Global region in which snake is found Sub-Saharan
Family Elapidae www.toxinology.com record number SN0184 Scientific name combined Common name Mocambique Spitting Cobra, m Fezi, Mozambique Spitting Cobra Global region in which snake is found Sub-Saharan
STATE TOXINOLOGY SERVICES Toxinology Dept., Women s & Children s Hospital, North Adelaide SA 5006 AUSTRALIA
 Family Elapidae www.toxinology.com record number SN0045 Scientific name combined Common name Thai Spitting Cobra, Isan Spitting Cobra Global region in which snake is found Southeast Asia CLINICAL OVERVIEW
Family Elapidae www.toxinology.com record number SN0045 Scientific name combined Common name Thai Spitting Cobra, Isan Spitting Cobra Global region in which snake is found Southeast Asia CLINICAL OVERVIEW
SNAKEBITE / CROTALID ANTIVENOMS
 DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department. Clinical Module. Clinical features of envenoming: Major toxin syndromes 1 :
 Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Module Toxicology Review Officer: Toxicology registrar Version no: 1 Approval date: February 2017 Review date: February 2019 Approving Officer
Princess Alexandra Hospital Emergency Department Clinical Module Toxicology Review Officer: Toxicology registrar Version no: 1 Approval date: February 2017 Review date: February 2019 Approving Officer
Key Points. Snakebites. Background
 Snakebites Guideline developed by Branson Bolden, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team, August 16, 2013. Last revised by Branson Bolden, MD, August 30, 2016. Key Points Pit viper (rattlesnake, cottonmouth,
Snakebites Guideline developed by Branson Bolden, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team, August 16, 2013. Last revised by Branson Bolden, MD, August 30, 2016. Key Points Pit viper (rattlesnake, cottonmouth,
Product Information BROWN SNAKE ANTIVENOM AUST R 74897
 Product Information APPROVED NAME BROWN SNAKE ANTIVENOM AUST R 74897 DESCRIPTION BROWN SNAKE ANTIVENOM is prepared from the plasma of horses immunised with the venom of the brown snake (Pseudonaja textilis).
Product Information APPROVED NAME BROWN SNAKE ANTIVENOM AUST R 74897 DESCRIPTION BROWN SNAKE ANTIVENOM is prepared from the plasma of horses immunised with the venom of the brown snake (Pseudonaja textilis).
POLYVALENT SNAKE ANTIVENOM Product Information 1(5) Product Information POLYVALENT SNAKE ANTIVENOM (AUSTRALIA - PAPUA NEW GUINEA) AUST R 74899
 POLYVALENT SNAKE ANTIVENOM Product Information 1(5) Product Information NAME OF THE MEDICINE POLYVALENT SNAKE ANTIVENOM (AUSTRALIA - PAPUA NEW GUINEA) AUST R 74899 DESCRIPTION POLYVALENT SNAKE ANTIVENOM
POLYVALENT SNAKE ANTIVENOM Product Information 1(5) Product Information NAME OF THE MEDICINE POLYVALENT SNAKE ANTIVENOM (AUSTRALIA - PAPUA NEW GUINEA) AUST R 74899 DESCRIPTION POLYVALENT SNAKE ANTIVENOM
American Journal oftoxicology
 American Journal of Toxicology Sliesoraitis S et al. American Journals of Toxicology 2015, 1:1-7 American Journal oftoxicology http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajt Page 1 of 7 Vol 1 Article ID 20150679, 7
American Journal of Toxicology Sliesoraitis S et al. American Journals of Toxicology 2015, 1:1-7 American Journal oftoxicology http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajt Page 1 of 7 Vol 1 Article ID 20150679, 7
Snake bite: a current approach to management
 Snake bite: a current approach to management Geoffrey K Isbister, Senior Research Fellow, Tropical Toxinology Unit, Menzies School of Health Research, Charles Darwin University, Northern Territory, Clinical
Snake bite: a current approach to management Geoffrey K Isbister, Senior Research Fellow, Tropical Toxinology Unit, Menzies School of Health Research, Charles Darwin University, Northern Territory, Clinical
CBC with Differential. PHYSICIAN SIGNATURE DATE TIME DRUG ALLERGIES WT: KG
 DRUG AND TREATMENT Non Categorized SUB ED Snakebite Protocol (SUB)* Non Categorized ***(NOTE)*** This plan is designed to be used as part of a larger plan, not independently. Please do NOT order individually.
DRUG AND TREATMENT Non Categorized SUB ED Snakebite Protocol (SUB)* Non Categorized ***(NOTE)*** This plan is designed to be used as part of a larger plan, not independently. Please do NOT order individually.
ANTIVIPMYN TREATMENT PACKAGE
 The Ontario Massasauga Rattlesnake Antivenom Depot Dr. T. J. Fargher, MB. Ch.B., F.C.P (SA), F.R.C.P(C) Medical Director 705-746-9321 ANTIVIPMYN TREATMENT PACKAGE FOR EASTERN MASSASAUGA RATTLESNAKE BITES
The Ontario Massasauga Rattlesnake Antivenom Depot Dr. T. J. Fargher, MB. Ch.B., F.C.P (SA), F.R.C.P(C) Medical Director 705-746-9321 ANTIVIPMYN TREATMENT PACKAGE FOR EASTERN MASSASAUGA RATTLESNAKE BITES
Snake Bites Sept 2014
 Bites Sept 2014 Epidemiology 1000-300 snake bites/ye, 1-4 deaths/yr in Australia. 5-10% envenomation rate Most deaths due to haematological problems Clinical envenoming Local effects (pain, swelling, bruising)
Bites Sept 2014 Epidemiology 1000-300 snake bites/ye, 1-4 deaths/yr in Australia. 5-10% envenomation rate Most deaths due to haematological problems Clinical envenoming Local effects (pain, swelling, bruising)
SNAKEBITE / CROTALID ENVENOMATION
 DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were prepared by the Department of Surgical Education, Orlando Regional Medical Center. They are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care
Brandon. A 38-year-old victim. Pit viper envenomation. Bitten at: Tyler, Texas Treated at: Emergency room at regional medical center
 Brandon Pit viper envenomation A 38-year-old victim Bitten at: Tyler, Texas Treated at: Emergency room at regional medical center History 0 1 hour after bite A man was bitten on a toe on his right foot
Brandon Pit viper envenomation A 38-year-old victim Bitten at: Tyler, Texas Treated at: Emergency room at regional medical center History 0 1 hour after bite A man was bitten on a toe on his right foot
Specific treatment: Antivenom (AV) Therapy
 Specific treatment: Antivenom (AV) Therapy It is never too late to give antivenom provided the indications are present: Only if features of systemic envenoming are present for bites of snakes in the red
Specific treatment: Antivenom (AV) Therapy It is never too late to give antivenom provided the indications are present: Only if features of systemic envenoming are present for bites of snakes in the red
Target Audience: Emergency Medicine Residents (junior and senior level postgraduate learners), Medical Students
 Rattlesnake Bite Authors: Laura Morrison, MD / Ryan Chuang, MD Reviewers: Shawn M. Varney, MD Target Audience: Emergency Medicine Residents (junior and senior level postgraduate learners), Medical Students
Rattlesnake Bite Authors: Laura Morrison, MD / Ryan Chuang, MD Reviewers: Shawn M. Varney, MD Target Audience: Emergency Medicine Residents (junior and senior level postgraduate learners), Medical Students
Eloxatin Oxaliplatin concentrated solution for injection
 Eloxatin Oxaliplatin concentrated solution for injection Consumer Medicine Information Please read this leaflet before you are given this medicine. What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common
Eloxatin Oxaliplatin concentrated solution for injection Consumer Medicine Information Please read this leaflet before you are given this medicine. What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common
CROFAB Crotalidae Polyvalent Immune Fab (Ovine) Lyophilized Powder for Solution for Injection For Intravenous Use Only. Initial U.S.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CROFAB safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CROFAB. CROFAB Crotalidae Polyvalent
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CROFAB safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CROFAB. CROFAB Crotalidae Polyvalent
OV United Soccer Club
 Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Biological Hazards. J. Wesley Graham Field Biologist
 Biological Hazards J. Wesley Graham Field Biologist GOOD MORNING!! Snakes 55 species of snakes in Mississippi Six are venomous Five of the six are pit vipers Pit refers to the sensory organ just below
Biological Hazards J. Wesley Graham Field Biologist GOOD MORNING!! Snakes 55 species of snakes in Mississippi Six are venomous Five of the six are pit vipers Pit refers to the sensory organ just below
Allergic Reactions and Envenomations. Chapter 16
 Allergic Reactions and Envenomations Chapter 16 Allergic Reactions Allergic reaction Exaggerated immune response to any substance Histamines and leukotrienes Chemicals released by the immune system Anaphylaxis
Allergic Reactions and Envenomations Chapter 16 Allergic Reactions Allergic reaction Exaggerated immune response to any substance Histamines and leukotrienes Chemicals released by the immune system Anaphylaxis
Does the traditional snakebite severity score correctly classify envenomated patients?
 Clin Exp Emerg Med 216;3(1):34-4 http://dx.doi.org/1.15441/ceem.16.123 Does the traditional snakebite severity score correctly classify envenomated patients? Seungho Kang, Jeongmi Moon, Byeongjo Chun Department
Clin Exp Emerg Med 216;3(1):34-4 http://dx.doi.org/1.15441/ceem.16.123 Does the traditional snakebite severity score correctly classify envenomated patients? Seungho Kang, Jeongmi Moon, Byeongjo Chun Department
Merkblatt 8 - E CROFAB TM CROTALIDAE POLYVALENT IMMUNE FAB (OVINE)
 Serum-Depot Berlin e. V. Merkblatt 8 - E CROFAB TM CROTALIDAE POLYVALENT IMMUNE FAB (OVINE) Englisch (Stand: 2000) DESCRIPTION CroFab TM [Crotalidae Polyvalent Immune Fab (Ovine)] is a sterile, nonpyrogenic,
Serum-Depot Berlin e. V. Merkblatt 8 - E CROFAB TM CROTALIDAE POLYVALENT IMMUNE FAB (OVINE) Englisch (Stand: 2000) DESCRIPTION CroFab TM [Crotalidae Polyvalent Immune Fab (Ovine)] is a sterile, nonpyrogenic,
Consumer Medicine Information March 2009
 March 2009 50 (oxaliplatin 50mg power for injection vial) 100 (oxaliplatin 100mg power for injection vial) What is in this leaflet? This leaflet answers some common questions about Powder for injection.
March 2009 50 (oxaliplatin 50mg power for injection vial) 100 (oxaliplatin 100mg power for injection vial) What is in this leaflet? This leaflet answers some common questions about Powder for injection.
CASE REPORT RENAL FAILURE AND DIC-LIKE SYNDROME FOLLOWING SNAKE BITES
 CASE REPORT RENAL FAILURE AND DIC-LIKE SYNDROME FOLLOWING SNAKE BITES Fransciscus Ginting, Restuti, Endang, Tambar Kembaren, Yosia Ginting, Ricky Rivalino Sitepu Tropical Infenction Medicine - Internal
CASE REPORT RENAL FAILURE AND DIC-LIKE SYNDROME FOLLOWING SNAKE BITES Fransciscus Ginting, Restuti, Endang, Tambar Kembaren, Yosia Ginting, Ricky Rivalino Sitepu Tropical Infenction Medicine - Internal
COAGULATION PROFILE AND ANALYSIS OF OUTCOME OF BLOOD COMPONENT THERAPY IN SNAKE BITE VICTIMS
 COAGULATION PROFILE AND ANALYSIS OF OUTCOME OF BLOOD COMPONENT THERAPY IN SNAKE BITE VICTIMS Dr Aboobacker Mohamed Rafi 1, Dr Susheela J Innah Senior Resident Department of Transfusion Medicine Jubilee
COAGULATION PROFILE AND ANALYSIS OF OUTCOME OF BLOOD COMPONENT THERAPY IN SNAKE BITE VICTIMS Dr Aboobacker Mohamed Rafi 1, Dr Susheela J Innah Senior Resident Department of Transfusion Medicine Jubilee
Basic First Aid. Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police
 Basic First Aid Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police Information given for this lecture is not meant to replace any official training by the American Red Cross, or any other
Basic First Aid Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police Information given for this lecture is not meant to replace any official training by the American Red Cross, or any other
CHAPTER 9. Shock National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 9 Shock Shock Dangerous condition: Not enough oxygen-rich blood reaching vital organs, such as brain and heart Caused by anything that significantly reduces blood flow Life-threatening emergency
CHAPTER 9 Shock Shock Dangerous condition: Not enough oxygen-rich blood reaching vital organs, such as brain and heart Caused by anything that significantly reduces blood flow Life-threatening emergency
IMPROVISATION WORKS BEST WHEN PREPARED FOR WELL IN ADVANCE
 WILDERNESS MEDICINE PEARLS Gary Johnson MD University of Nevada Reno Family Medicine Residency Program NAFP WINTER CME MEETING Copyright, 1996 Dale Carnegie & Associates, Inc. PEARL # 1 IMPROVISATION WORKS
WILDERNESS MEDICINE PEARLS Gary Johnson MD University of Nevada Reno Family Medicine Residency Program NAFP WINTER CME MEETING Copyright, 1996 Dale Carnegie & Associates, Inc. PEARL # 1 IMPROVISATION WORKS
MIAMI-DADE COLLEGE. Common Course Number: HSC Course Title: Basic Emergency Care. Course Catalog Description:
 Common Course Number: HSC 2400 MIAMI-DADE COLLEGE Course Title: Basic Emergency Care Course Catalog Description: Designed to provide opportunities to develop, practice, and display skills concerning emergency
Common Course Number: HSC 2400 MIAMI-DADE COLLEGE Course Title: Basic Emergency Care Course Catalog Description: Designed to provide opportunities to develop, practice, and display skills concerning emergency
Environmental Injury and Illnesses. Dc. Anna Toplaghaltsyan
 Environmental Injury and Illnesses Dc. Anna Toplaghaltsyan Yerevan 2018 BITES AND STINGS Insect bites and stings are a common and an annoying occurrence. Most bites are minor but the potential for a serious
Environmental Injury and Illnesses Dc. Anna Toplaghaltsyan Yerevan 2018 BITES AND STINGS Insect bites and stings are a common and an annoying occurrence. Most bites are minor but the potential for a serious
Blood/Blood Component Utilization and Administration Annual Compliance Education
 Blood/Blood Component Utilization and Administration Annual Compliance Education This course contains annual compliance education necessary to meet compliance and regulatory requirements. Instructions:
Blood/Blood Component Utilization and Administration Annual Compliance Education This course contains annual compliance education necessary to meet compliance and regulatory requirements. Instructions:
Bites, Stings and Venomous Things Amanda Wickman, MBA Southwest Center for Agricultural Health, Injury Prevention and Education
 Bites, Stings and Venomous Things Amanda Wickman, MBA Southwest Center for Agricultural Health, Injury Prevention and Education Midwest Migrant Stream Forum November 2015 Background Objectives 1. Dispel
Bites, Stings and Venomous Things Amanda Wickman, MBA Southwest Center for Agricultural Health, Injury Prevention and Education Midwest Migrant Stream Forum November 2015 Background Objectives 1. Dispel
Shock. Perfusion. The cardiovascular system s circulation of blood and oxygen to all the cells in different tissues and organs of the body
 Shock Chapter 10 Shock State of collapse and failure of the cardiovascular system Leads to inadequate circulation Without adequate blood flow, cells cannot get rid of metabolic wastes The result- hypoperfusion
Shock Chapter 10 Shock State of collapse and failure of the cardiovascular system Leads to inadequate circulation Without adequate blood flow, cells cannot get rid of metabolic wastes The result- hypoperfusion
Thrombolysis Delivery, Care, and Monitoring. 5 Acute Trusts - 6 Primary Care Trusts Ambulance Trust 4 Local Authorities
 Thrombolysis Delivery, Care, and Monitoring Documentation & Pathways Need to follow locally agreed policies and procedures Follow thrombolysis pathway? Need to complete Sits database Weight Dose matters!
Thrombolysis Delivery, Care, and Monitoring Documentation & Pathways Need to follow locally agreed policies and procedures Follow thrombolysis pathway? Need to complete Sits database Weight Dose matters!
Key Words. clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma. Linked Core Abilities
 Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 13 Resuscitation and Preparation for Anesthesia & Surgery Key Points 2 13.1 Management of Emergencies and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation The emergency measures that
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 13 Resuscitation and Preparation for Anesthesia & Surgery Key Points 2 13.1 Management of Emergencies and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation The emergency measures that
Venomous Snakebites in Two Children
 Case Report Crit Care & Shock (2009) 12:53-60 Venomous Snakebites in Two Children Heda Melinda D. Nataprawira, Enny Harliany Alwi, Lesmana Syahrir, Tubagus Ferdi Fadilah, Tri Wahyu Murni Abstract Venomous
Case Report Crit Care & Shock (2009) 12:53-60 Venomous Snakebites in Two Children Heda Melinda D. Nataprawira, Enny Harliany Alwi, Lesmana Syahrir, Tubagus Ferdi Fadilah, Tri Wahyu Murni Abstract Venomous
Stinging Insects, Spiders and Snakes
 Stinging Insects, Spiders and Snakes Stinging Insects Bites and stings happen. The stings and bites from most insects are more often a nuisance than a serious problem. A person s response to a bite or
Stinging Insects, Spiders and Snakes Stinging Insects Bites and stings happen. The stings and bites from most insects are more often a nuisance than a serious problem. A person s response to a bite or
Chapter 7 EMERGENCY PLAN AND INITIAL INJURY EVALUATION
 Chapter 7 EMERGENCY PLAN AND INITIAL INJURY EVALUATION Major Concepts. Proper planning of an emergency response is essential for appropriate first aid management of an injury. Anything that can be done
Chapter 7 EMERGENCY PLAN AND INITIAL INJURY EVALUATION Major Concepts. Proper planning of an emergency response is essential for appropriate first aid management of an injury. Anything that can be done
Management of Common Bites and Stings
 Management of Common Bites and Stings Nicholas E. Kman, MD The Ohio State University Department of Emergency Medicine Mary Jo Bowman, M.D. Nationwide Children's Hospital Columbus, Ohio Case 29 yo man was
Management of Common Bites and Stings Nicholas E. Kman, MD The Ohio State University Department of Emergency Medicine Mary Jo Bowman, M.D. Nationwide Children's Hospital Columbus, Ohio Case 29 yo man was
Recombinant Factor VIIa for Treatment of Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage Following Rattlesnake Envenomation
 Wilderness and Environmental Medicine, 20, 156 160 (2009) CASE REPORT Recombinant Factor VIIa for Treatment of Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage Following Rattlesnake Envenomation Anne-Michelle Ruha, MD; Steven
Wilderness and Environmental Medicine, 20, 156 160 (2009) CASE REPORT Recombinant Factor VIIa for Treatment of Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage Following Rattlesnake Envenomation Anne-Michelle Ruha, MD; Steven
Paclitaxel (Taxol) and carboplatin
 Paclitaxel (Taxol) and carboplatin Paclitaxel (Taxol) and carboplatin This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may
Paclitaxel (Taxol) and carboplatin Paclitaxel (Taxol) and carboplatin This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may
Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors.
 Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Appendix to: Johnston CI, Ryan NM, Page CB, et al. The Australian Snakebite
Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Appendix to: Johnston CI, Ryan NM, Page CB, et al. The Australian Snakebite
1 Chapter 10 Shock 2 Shock Shock: Inadequate State of collapse and failure of the system Leads to inadequate circulation Without adequate blood flow,
 1 Chapter 10 Shock 2 Shock Shock: Inadequate State of collapse and failure of the system Leads to inadequate circulation Without adequate blood flow, cannot get rid of metabolic wastes Results in hypoperfusion
1 Chapter 10 Shock 2 Shock Shock: Inadequate State of collapse and failure of the system Leads to inadequate circulation Without adequate blood flow, cannot get rid of metabolic wastes Results in hypoperfusion
Module Summaries: The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program.
 Module Summaries: Summary - The Emergency Plan The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program. Prior to each season and game, those individuals responsible for the program and athletes
Module Summaries: Summary - The Emergency Plan The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program. Prior to each season and game, those individuals responsible for the program and athletes
Shock Video Shock (3)
 CHAPTER 9 Shock Video Shock (3) Lesson Objectives 1. Explain what happens inside the body with severe blood loss. 2. List common causes of shock. 3. Describe first aid steps for a victim in shock. 4. Describe
CHAPTER 9 Shock Video Shock (3) Lesson Objectives 1. Explain what happens inside the body with severe blood loss. 2. List common causes of shock. 3. Describe first aid steps for a victim in shock. 4. Describe
Administration of blood components. Tina Parker - Transfusion Practitioner
 . Administration of blood components Tina Parker - Transfusion Practitioner Red Cells Each unit contains 250-350mls Preserved with glucose and Mannitol to keep the correct tension Lasts 35 days from midnight
. Administration of blood components Tina Parker - Transfusion Practitioner Red Cells Each unit contains 250-350mls Preserved with glucose and Mannitol to keep the correct tension Lasts 35 days from midnight
Poisoning KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES SKILL OBJECTIVES. 1. List the four ways poisons enter the body.
 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Poisoning 1. List the four ways poisons enter the body. 2. List at least six signs and symptoms of poisoning. 3. Describe the role of a poison centre. 4. Identify the general principles
KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Poisoning 1. List the four ways poisons enter the body. 2. List at least six signs and symptoms of poisoning. 3. Describe the role of a poison centre. 4. Identify the general principles
Rattlesnake Envenomation
 CE Article #3 Rattlesnake Envenomation Laura Najman, DVM, DACVECC Ravi Seshadri, DVM, DACVECC, DAVBP Advanced Critical Care and Internal Medicine Tustin, California ABSTRACT: Snake envenomation has been
CE Article #3 Rattlesnake Envenomation Laura Najman, DVM, DACVECC Ravi Seshadri, DVM, DACVECC, DAVBP Advanced Critical Care and Internal Medicine Tustin, California ABSTRACT: Snake envenomation has been
PDP 406 CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
 PDP 406 CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY Pharm.D Fourth Year ENVENOMATION Mr.D.Raju.M.Pharm., Lecturer POISONING Poisonous substances can be swallowed, injected, inhaled, absorbed. Poisoning and envenomation can be
PDP 406 CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY Pharm.D Fourth Year ENVENOMATION Mr.D.Raju.M.Pharm., Lecturer POISONING Poisonous substances can be swallowed, injected, inhaled, absorbed. Poisoning and envenomation can be
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Recurrent and Persistent Coagulopathy Following Pit Viper Envenomation
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Recurrent and Persistent Coagulopathy Following Pit Viper Envenomation Leslie V. Boyer, MD; Steven A. Seifert, MD; Richard F. Clark, MD; Jude T. McNally, RPh; Saralyn R. Williams,
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Recurrent and Persistent Coagulopathy Following Pit Viper Envenomation Leslie V. Boyer, MD; Steven A. Seifert, MD; Richard F. Clark, MD; Jude T. McNally, RPh; Saralyn R. Williams,
Emergency First Response (EFR) Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017
 Emergency First Response () Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017 Airway management & ventilation Airway management & ventilation Trauma jaw thrust 1 Hand positions 2 Perform jaw thrust / mouth open 3
Emergency First Response () Skills Assessment Sheets V4 June 2017 Airway management & ventilation Airway management & ventilation Trauma jaw thrust 1 Hand positions 2 Perform jaw thrust / mouth open 3
Gemcitabine and Cisplatin (urology)
 Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Gemcitabine and Cisplatin (urology) This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce
Gemcitabine and Cisplatin Gemcitabine and Cisplatin (urology) This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce
Dealing with Bugs and Critters. On the grounds of WSU
 Dealing with Bugs and Critters On the grounds of WSU Checklist for protection Expose as little skin as possible Light colored long pants and long-sleeved shirts One piece suit if possible Wear hat to protect
Dealing with Bugs and Critters On the grounds of WSU Checklist for protection Expose as little skin as possible Light colored long pants and long-sleeved shirts One piece suit if possible Wear hat to protect
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use North American Coral Snake Antivenin (Equine) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use North American Coral Snake Antivenin (Equine) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
October 2016 Newsletter
 October 2016 Newsletter Website About Us Legislative Issues News Calendar NOTICE OF RENEWALS OF PHARMACIST AND NUCLEAR PHARMACIST LICENSES AND NOTICE REGARDING ACTIVE - RENEWAL PENDING STATUS Meetings
October 2016 Newsletter Website About Us Legislative Issues News Calendar NOTICE OF RENEWALS OF PHARMACIST AND NUCLEAR PHARMACIST LICENSES AND NOTICE REGARDING ACTIVE - RENEWAL PENDING STATUS Meetings
Weekly standard dose. Paclitaxel (Taxol) and carboplatin
 paclitaxel (taxol) and carboplatin Paclitaxel (Taxol) and carboplatin This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may
paclitaxel (taxol) and carboplatin Paclitaxel (Taxol) and carboplatin This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may
APPLY FIRST AID ONLINE WORKBOOK
 APPLY FIRST AID ONLINE WORKBOOK STUDENT NAME: ADDRESS: PHONE CONTACT: DATE OF COURSE: Welcome to CYNERGEX GROUP pre-learning package for the APPLY FIRST AID course. This workbook is to be completed in
APPLY FIRST AID ONLINE WORKBOOK STUDENT NAME: ADDRESS: PHONE CONTACT: DATE OF COURSE: Welcome to CYNERGEX GROUP pre-learning package for the APPLY FIRST AID course. This workbook is to be completed in
Carboplatin & weekly paclitaxel (Taxol) (for anal cancer) Carboplatin and weekly paclitaxel (Taxol) (for anal cancer)
 Carboplatin & weekly paclitaxel (Taxol) (for anal cancer) Carboplatin and weekly paclitaxel (Taxol) (for anal cancer) The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce the
Carboplatin & weekly paclitaxel (Taxol) (for anal cancer) Carboplatin and weekly paclitaxel (Taxol) (for anal cancer) The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce the
EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF F(AB)2 ANITVENOM FOR SCORPION ENVENOMATION
 Abstracts Venom Week Sponsored by the University of Arizona Colleges of Medicine and Pharmacy at the Arizona Health Sciences Center September 3 7, 2007, Tucson, Arizona Edited by Steven A. Seifert, MD
Abstracts Venom Week Sponsored by the University of Arizona Colleges of Medicine and Pharmacy at the Arizona Health Sciences Center September 3 7, 2007, Tucson, Arizona Edited by Steven A. Seifert, MD
Northwest Community EMS System Feb 2018 CE: Multiple Patient Incidents/ChemPack Intro Credit Questions
 Northwest Community EMS System Feb 2018 CE: Multiple Patient Incidents/ChemPack Intro Credit Questions Name: EMS Agency/hospital: EMSC/Educator reviewer: Date submitted: Credit awarded (date): Returned
Northwest Community EMS System Feb 2018 CE: Multiple Patient Incidents/ChemPack Intro Credit Questions Name: EMS Agency/hospital: EMSC/Educator reviewer: Date submitted: Credit awarded (date): Returned
Animal caused Injuries פגיעות בעלי חיים כל הזכויות שמורות למד"א מרחב ירושלים
 Animal caused Injuries פגיעות בעלי חיים Snake bite נחש In Israel there are 9 kinds of poisonous snakes. 3 mechanisms of venom action: Vascular Neurological Cardiac Small amount of venom goes through the
Animal caused Injuries פגיעות בעלי חיים Snake bite נחש In Israel there are 9 kinds of poisonous snakes. 3 mechanisms of venom action: Vascular Neurological Cardiac Small amount of venom goes through the
TEXAS CHILDREN S HOSPITAL EVIDENCE-BASED OUTCOMES CENTER Evaluation & Management of Suspected U.S. Pit Viper Snakebites Evidence Summary
 TEXAS CHILDREN S HOSPITAL EVIDENCE-BASED OUTCOMES CENTER Evaluation & Management of Suspected U.S. Pit Viper Snakebites Evidence Summary DATE: April 2017 Inclusion Criteria Patients
TEXAS CHILDREN S HOSPITAL EVIDENCE-BASED OUTCOMES CENTER Evaluation & Management of Suspected U.S. Pit Viper Snakebites Evidence Summary DATE: April 2017 Inclusion Criteria Patients
Instituto Bioclon, S.A. de C.V.
 Bioclon, S.A. de C.V. 1 of 7 Fabotherapic polyvalent snake antivenom DOSAGE FORM AND COMPOSITION: FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION (FPI) lyophilizate for injectable solution is presented in a box containing
Bioclon, S.A. de C.V. 1 of 7 Fabotherapic polyvalent snake antivenom DOSAGE FORM AND COMPOSITION: FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION (FPI) lyophilizate for injectable solution is presented in a box containing
Mitomycin C given by injection into a vein. Cisplatin and hydration (fluids) via a drip over 6 or 18 hours.
 Cisplatin & Mitomycin C Cisplatin & Mitomycin C This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce the risk of the
Cisplatin & Mitomycin C Cisplatin & Mitomycin C This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may reduce the risk of the
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT Kopen Sugar Free 125mg/5ml and 250mg/5ml Powder for Oral Solution Phenoxymethylpenicillin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE PATIENT Kopen Sugar Free 125mg/5ml and 250mg/5ml Powder for Oral Solution Phenoxymethylpenicillin Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine
IRECA BLS Challenge 2015 Scenario 1
 Scenario 1 Team Name Team Number Captain Name Judge 1 # Judge 2 # JUDGE S SHEET Overview: This scenario challenges the competitors to use basic triage techniques and then to do the most good for the most
Scenario 1 Team Name Team Number Captain Name Judge 1 # Judge 2 # JUDGE S SHEET Overview: This scenario challenges the competitors to use basic triage techniques and then to do the most good for the most
SUDDEN ILLNESS. Fainting Diabetes Seizures Stroke
 SUDDEN ILLNESS Fainting Diabetes Seizures Stroke FAINTING When someone suddenly loses consciousness and then reawakens. Fainting is not usually harmful and the person will recover quickly. FAINTING - TREATMENT
SUDDEN ILLNESS Fainting Diabetes Seizures Stroke FAINTING When someone suddenly loses consciousness and then reawakens. Fainting is not usually harmful and the person will recover quickly. FAINTING - TREATMENT
1231 Zoledronic acid in early breast cancer Page 1 of 5
 Zoledronic acid in early breast cancer Zoledronic acid in early breast cancer Zoledronic acid is a bisphosphonate. This is treatment which works by slowing down the rate of bone change. In the bone there
Zoledronic acid in early breast cancer Zoledronic acid in early breast cancer Zoledronic acid is a bisphosphonate. This is treatment which works by slowing down the rate of bone change. In the bone there
All about your anaesthetic
 Patient information leaflet All about your anaesthetic General anaesthesia 2 and associated risks For patients having a surgical procedure at a Care UK independent diagnostic and treatment centre This
Patient information leaflet All about your anaesthetic General anaesthesia 2 and associated risks For patients having a surgical procedure at a Care UK independent diagnostic and treatment centre This
Prof A Pourazar Immunohematologist
 Prof A Pourazar Immunohematologist What is plasma? Plasma is part of blood. It is the liquid that supports the circulation of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Plasma is mainly water and
Prof A Pourazar Immunohematologist What is plasma? Plasma is part of blood. It is the liquid that supports the circulation of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Plasma is mainly water and
Paediatric Shock. Dr Andrew Pittaway Department of Anaesthesia Bristol Royal Hospital for Children Bristol, UK
 Paediatric Shock Dr Andrew Pittaway Department of Anaesthesia Bristol Royal Hospital for Children Bristol, UK Self-assessment: 1. What is the definition of shock? 2. List the different pathophysiological
Paediatric Shock Dr Andrew Pittaway Department of Anaesthesia Bristol Royal Hospital for Children Bristol, UK Self-assessment: 1. What is the definition of shock? 2. List the different pathophysiological
Introduction (1 of 3)
 Chapter 10 Shock Introduction (1 of 3) Shock (hypoperfusion) means a state of collapse and failure of the cardiovascular system. In the early stages, the body attempts to maintain homeostasis. As shock
Chapter 10 Shock Introduction (1 of 3) Shock (hypoperfusion) means a state of collapse and failure of the cardiovascular system. In the early stages, the body attempts to maintain homeostasis. As shock
Case Presentation #4: A Pretty Worm
 Case Presentation #4: Presented by Brent R. King, MD, FAAP, FACEP A three year-old child arrives via EMS with ptosis, stridor, hypersalivation, hypotonia, and poor respiratory effort. The symptoms began
Case Presentation #4: Presented by Brent R. King, MD, FAAP, FACEP A three year-old child arrives via EMS with ptosis, stridor, hypersalivation, hypotonia, and poor respiratory effort. The symptoms began
Health care in PWS 40 + years
 40 + years Introduction There are some unusual features of PWS which require special attention and may not always be evident to those who have little experience of the syndrome or when the unusual features
40 + years Introduction There are some unusual features of PWS which require special attention and may not always be evident to those who have little experience of the syndrome or when the unusual features
Ankle Arthroscopy PATIENT INFORMATION. What is an ankle arthroscopy? Common disorders in which ankle arthroscopy is useful.
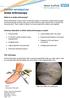 PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthroscopy What is an ankle arthroscopy? Ankle arthroscopy is also known as keyhole surgery or minimally invasive ankle surgery. Ankle arthroscopy involves using very small incisions
PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthroscopy What is an ankle arthroscopy? Ankle arthroscopy is also known as keyhole surgery or minimally invasive ankle surgery. Ankle arthroscopy involves using very small incisions
Surgical Instructions. Wisdom Tooth TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY
 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY Surgical Instructions Wisdom Tooth 1000 North Curtis Road, Suite 103 Boise, ID 83706 Phone: 208-343-0909 Fax: 208-343-6282 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY AFTER
TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY Surgical Instructions Wisdom Tooth 1000 North Curtis Road, Suite 103 Boise, ID 83706 Phone: 208-343-0909 Fax: 208-343-6282 TREASURE VALLEY ORAL & FACIAL SURGERY AFTER
First Aid Fact Sheet 2005 Standards
 First Aid Fact Sheet 2005 Standards Five Leading Causes of Unintentional death: 1. Motor vehicle accidents 2. Falls 3. Poisonings 4. Drownings 5. Choking Good Samaritan Laws laws that give legal protection
First Aid Fact Sheet 2005 Standards Five Leading Causes of Unintentional death: 1. Motor vehicle accidents 2. Falls 3. Poisonings 4. Drownings 5. Choking Good Samaritan Laws laws that give legal protection
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. A Randomized Multicenter Trial of Crotalinae Polyvalent Immune Fab (Ovine) Antivenom
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION A Randomized Multicenter Trial of Crotalinae Polyvalent Immune Fab (Ovine) Antivenom for the Treatment for Crotaline Snakebite in the United States Richard C. Dart, MD, PhD; Steven
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION A Randomized Multicenter Trial of Crotalinae Polyvalent Immune Fab (Ovine) Antivenom for the Treatment for Crotaline Snakebite in the United States Richard C. Dart, MD, PhD; Steven
Unit 7 INJURY MANAGEMENT Review Game
 Unit 7 INJURY MANAGEMENT Review Game Print and cut out the playing cards. Divide the class into groups of 3 or 4. Each group will need a set of playing cards. Directions for the Review game 1. Stack all
Unit 7 INJURY MANAGEMENT Review Game Print and cut out the playing cards. Divide the class into groups of 3 or 4. Each group will need a set of playing cards. Directions for the Review game 1. Stack all
Managing Illness 8/9/2010 1
 Managing Illness 1 Fainting Caused by a temporary drop in blood pressure thus causing a reduction in oxygen to the brain. Insufficient oxygen causes casualty to black out and fall. Consciousness normally
Managing Illness 1 Fainting Caused by a temporary drop in blood pressure thus causing a reduction in oxygen to the brain. Insufficient oxygen causes casualty to black out and fall. Consciousness normally
HAEMATOLOGIC TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
 HAEMATOLOGIC TECHNOLOGIES, INC. Safety Data Sheet SECTION 1: Identification 1.1 Product identifier Product name Product number RVVX-2010, RVVV-2000 1.2 Other means of identification Purified component
HAEMATOLOGIC TECHNOLOGIES, INC. Safety Data Sheet SECTION 1: Identification 1.1 Product identifier Product name Product number RVVX-2010, RVVV-2000 1.2 Other means of identification Purified component
Pentostatin (Nipent )
 Pentostatin (Nipent ) Pentostatin (Nipent ) This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. Your treatment will be fully explained by your doctor or nurse, who will be happy to answer any questions.
Pentostatin (Nipent ) Pentostatin (Nipent ) This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. Your treatment will be fully explained by your doctor or nurse, who will be happy to answer any questions.
Altered Mental Status Basic Emergency Care Course
 Altered Mental Status Basic Emergency Care Course Objectives Recognize key history findings suggestive of different causes of altered mental status Recognize key physical findings suggestive of different
Altered Mental Status Basic Emergency Care Course Objectives Recognize key history findings suggestive of different causes of altered mental status Recognize key physical findings suggestive of different
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials
 Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Cisplatin and radiotherapy to the
 Cisplatin and radiotherapy to the head and neck Cisplatin and radiotherapy to the head and neck This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some
Cisplatin and radiotherapy to the head and neck Cisplatin and radiotherapy to the head and neck This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some
Providing for Players Safety 31. Emergency Plan
 Providing for Players Safety 31 Emergency Plan An emergency plan is the final step in preparing to take appropriate action for severe or serious injuries. The plan calls for three steps: 1. Survey the
Providing for Players Safety 31 Emergency Plan An emergency plan is the final step in preparing to take appropriate action for severe or serious injuries. The plan calls for three steps: 1. Survey the
Gemcitabine and carboplatin (Lung)
 Gemcitabine and carboplatin (Lung) Gemcitabine and carboplatin (Lung) This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may
Gemcitabine and carboplatin (Lung) Gemcitabine and carboplatin (Lung) This leaflet is offered as a guide to you and your family. The possible benefits of treatment vary; for some people chemotherapy may
Transfusion Requirements and Management in Trauma RACHEL JACK
 Transfusion Requirements and Management in Trauma RACHEL JACK Overview Haemostatic resuscitation Massive Transfusion Protocol Overview of NBA research guidelines Haemostatic resuscitation Permissive hypotension
Transfusion Requirements and Management in Trauma RACHEL JACK Overview Haemostatic resuscitation Massive Transfusion Protocol Overview of NBA research guidelines Haemostatic resuscitation Permissive hypotension
Department of Health. Year 8. vaccination program. Important information for parents and students
 Department of Health Year 8 vaccination program Important information for parents and students Contents Why immunise? 1 Vaccination program 1 Schedule of vaccinations 2 Vaccination records 2 Vaccine safety
Department of Health Year 8 vaccination program Important information for parents and students Contents Why immunise? 1 Vaccination program 1 Schedule of vaccinations 2 Vaccination records 2 Vaccine safety
Australian Spider Bites. Dr Sanj Fernando
 Australian Spider Bites Dr Sanj Fernando Funnel Web Spider Atrax robustus Funnel-Web Spider details Large spider - usually seen fangs (4mm long) can penetrate a nail aggressive - bites repeatedly venom
Australian Spider Bites Dr Sanj Fernando Funnel Web Spider Atrax robustus Funnel-Web Spider details Large spider - usually seen fangs (4mm long) can penetrate a nail aggressive - bites repeatedly venom
CHAPTER 10 POISONOUS PLANTS
 CHAPTER 10 POISONOUS PLANTS Successful use of plants in a survival situation depends on positive identification. Knowing poisonous plants is as important to a survivor as knowing edible plants. Knowing
CHAPTER 10 POISONOUS PLANTS Successful use of plants in a survival situation depends on positive identification. Knowing poisonous plants is as important to a survivor as knowing edible plants. Knowing
Clinical focus. Snakebite in Australia: a practical approach to diagnosis and treatment. Clinical focus. Summary. Clinical effects.
 Clinical focus Geoffrey K Isbister BSc, FACEM, MD, Associate Professor, 1 and Clinical Toxicologist 2 Simon G A Brown MB BS, PhD, FACEM, Emergency Physician and Professor 3 Colin B Page MB ChB, FACEM,
Clinical focus Geoffrey K Isbister BSc, FACEM, MD, Associate Professor, 1 and Clinical Toxicologist 2 Simon G A Brown MB BS, PhD, FACEM, Emergency Physician and Professor 3 Colin B Page MB ChB, FACEM,
Skin Anatomy and Physiology
 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Body s largest organ Three layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue 1 2 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Complex system, variety of functions Sensation Control of water loss
Skin Anatomy and Physiology Body s largest organ Three layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue 1 2 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Complex system, variety of functions Sensation Control of water loss
Renal Palliative Care Last Days of Life
 Renal Palliative Care Last Days of Life Introduction This guideline is an aid to clinical decision-making and good practice for patients with stage 4-5 chronic kidney disease (egfr
Renal Palliative Care Last Days of Life Introduction This guideline is an aid to clinical decision-making and good practice for patients with stage 4-5 chronic kidney disease (egfr
Epidemiology of accidental snake poisoning in the pediatric population
 Epidemiology of accidental snake poisoning in the pediatric population Carlos Eduardo Garcia-Willis,* Ricardo Vela-Ortega,* and Maria Elena Maya Leal** *Hospital General de Tampico Dr. Carlos Canseco,
Epidemiology of accidental snake poisoning in the pediatric population Carlos Eduardo Garcia-Willis,* Ricardo Vela-Ortega,* and Maria Elena Maya Leal** *Hospital General de Tampico Dr. Carlos Canseco,
