The relationship between
|
|
|
- Karin McCarthy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Use of antiseptics for wound cleansing a literature review There is no doubt that clinical infection causes death, distress and costs the NHS. There is a long history in the fight against bacterial contamination of wounds and there is still debate on how that fight should continue. Nevertheless, there are great strides in the knowledge of bacteria and their biofilms, and how antiseptics may help to reduce the NHS cost of 1 billion each year. Antibacterials can certainly make a difference as they quickly remove odour from a wound, which indicates that bacteria is also being removed, as this article shows. Interest in the use of antiseptics in the management of wound infection has re-emerged in recent years as a result of ongoing and escalating problems with resistance and allergy to topical and systemic antibiotics. SYLVIE HAMPTON Independent Tissue Viability Consultant Nurse, UK 70 Wound Essentials 2017, Vol 12 No 1 The relationship between wound, host and bacteria is continuously changing as a result of local, environmental and systemic factors (Templeton, 2014). One of these factors may be the use of antibiotics. However, due to the emergence of many resistant bacteria, the routine use of topical and oral antibiotics is not justified for colonised or infected wounds and should only be considered for wounds that are clinically infected and showing signs of spreading erythema and pyrexia, or if the patient is feeling generally unwell. Therefore, as bacterial colonisation of the wound does not necessarily indicate infection, it should be clear that antibiotics should not be the first choice, although removal of bacteria before it can critically colonise a wound is very important. This places antibacterials in an important position for wound healing if they are effective in reducing colonisation. Antiseptics are chemicals that can slow or stop the growth of micro-organisms on external surfaces of the body and are mainly used to reduce levels of microorganisms on the skin and mucous membranes. However, even though it is inevitable that chronic wounds are colonised by micro-organisms, many go on to heal successfully, despite the colonisation. Nevertheless, sometimes bacteria will multiply and invade the tissues and the host, causing damage to tissues, delaying healing and potentially causing systemic illness (International Wound Journal, 2008). Therefore, it is important that any bacteria in a wound is carefully monitored and managed accordingly. Interest in the use of antiseptics in the management of wound infection has re-emerged in recent years as a result of ongoing and escalating problems with resistance and allergy to topical and systemic antibiotics (World Union of Wound Healing Societies [WUWHS], 2008). However, although antiseptics are commonly used, surprisingly few studies have been conducted to examine the effect on the wound-healing process and efficacy of wound antiseptics. Many of the references in this article are considered older studies but, nevertheless, are relevant to a review such as this. History of antimicrobials The earliest documented records of topical wound treatments were found
2 in Mesopotamia; these inscriptions on clay tablets have been dated to approximately 2500 BC (Cooper, 2004), and between 14AD and 37AD there is documentary evidence that Cornelius Celsus (a Roman physician) described the four principal signs of inflammation and used antiseptic solutions. Claudius Galen ( AD) had such an influence on the management of wounds that he is still thought of, by many today, as the father of surgery. He instigated the laudable pus theory, which incorrectly considered the development of pus in a wound as a positive part of the healing process and he would remove pus from one man s wound and place it in another in order to promote this laudable pus theory. Louis Pasteur was a French chemist and microbiologist renowned for his discoveries of the principles of vaccination, microbial fermentation and pasteurisation. He invented the process of pasteurisation, which is widely used today for milk and beer. The rapid heating process, which kills harmful germs, still bears his name. The importance of antimicrobials has been in the forefront of wound healing since the 19th century. The use of carbolic acid administered by Joseph Lister in operating theatres from 1865 significantly reduced mortality rates associated with surgical procedures (Cooper, 2004). Lister was a British surgeon who was heavily influenced by Louis Pasteur s work on bacteria. Certainly, his greatest contribution to medicine was the promotion of the use of carbolic acid as an antiseptic. Lister published the results of his studies in a series of articles in the British Medical Journal and The Lancet, in which he urged surgeons to wash their hands and instruments with a 5% carbolic solution and to wear clean gloves. Background to wound antiseptics Infection is one of the key reasons why wound healing may stall, leading to increased risks of patient morbidity and mortality with increased treatment costs (NICE, 2008). In the compromised host, there is always an increased risk of wound infection due to the host s inability to mount a robust immune response to the presence of multiplying micro-organisms within the wound (Vowden et al, 2011). Therefore, infection control is particularly important. In addition to infection control measures, effective cleansing of the wound is important to reduce bacterial loading and contamination, of the surrounding skin (Bradbury and Fletcher, 2010). Before new granulation tissue and blood vessels can form, the wound microenvironment must be sufficiently clean and organised to facilitate fibroblast migration and interaction via signals sent from the existing fibrin matrix. In addition, keratinocyte migration and proliferation following release of their attachment to the basement membrane is necessary a course facilitated by matrix metalloproteases (MMPs; Chen and Parks, 2009). Despite the lack of research on the subject, the practice of wound cleansing or antiseptic management has a dichotomous history anchored in tradition and science (Smith 2005). Nevertheless, history has demonstrated that quality of care is a critical requirement for wound healing and good care of wounds has been synonymous with topical prevention and management of microbial contamination. There is a debate in clinical circles about the potential advantages and disadvantages of cleansing wounds of bacterial contamination because the exudate itself may contain growth elements and chemokines, which contribute to wound healing and for that reason it is not always necessary (Atiyeh et al, 2009). However, if healing is not present, as in a chronic wound, then there are no growth factors present. Therefore, applying something that is slightly irritant to the tissues may increase the inflammatory process and may stimulate the wound to heal. Atiyeh et al (2009) suggested that, when applied at the proper times and concentrations, some classes of antiseptics may provide a tool for the clinician to drive the wound bed in desired directions. Moscati et al (1998; 2007) suggested that wound cleansing helps to optimise the healing environment and decrease the potential for infection; tap water is recommended as it has the advantages of being efficient, cost effective and accessible (Angeras et al, 1992; Fernandez et al, 2008). Angeras et al (1992) actually found a higher rate of infection in those wounds irrigated with saline. However, this was on a small number the study population was unknown although a second study of a population of 715 demonstrated similar findings (Moscati et al, 2007). Even where wounds are not clearly clinically infected, they usually have populations of micro-organisms present. It is thought these wounds may heal better if these populations are reduced by antibacterial agents. However, the relationship between infection and micro-organism populations in wounds and wound healing is not very clear (Norman et al, 2016a). Debridement is an extremely important part of wound cleansing but when debridement of the wound bed is not sufficient to reduce bacterial loads, the application of broad-spectrum antiseptics may be indicated (Thomas et al, 2009). In two seminal pieces of work, antiseptics directly applied to cultured human fibroblasts were found to be cytotoxic. All of the cytotoxic agents except hydrogen peroxide were subsequently found to adversely affect wound healing in an animal model (Van Den Broek, 1982; Lineaweaver et al, 1985). At the same time, hydrogen Wound Essentials 2017, Vol 12 No 1 71
3 peroxide was found to significantly increase the blood flow in ischaemic ulcers in a guinea pig model (Tur, et al, 1995) and subsequently increased acceleration of re-epithelisation in a rat model (Gruber et al, 1975). Macpherson (2004) believed that antiseptics prevent the growth of pathogenic micro-organisms without damaging living tissue. Topical antiseptics are antimicrobial agents that kill, inhibit or reduce the number of micro-organisms and are thought to be essential for wounds infection control. Although certain skin and wound cleansers are designed as topical solutions with varying degrees of antimicrobial activity, concerns have been raised as wound cleansers may affect normal human cells and may be antimitotic, adversely affecting normal tissue repair (Atiyeh et al, 2009). However, in spite of the in vitro demonstrations of inhibition of healing by some antiseptics, there are increasing data to indicate that healing is inhibited by bacterial infection, and that a reduction in bacterial numbers can reduce inflammation and enhance healing (Pierard-Franchimont et al, 1997). These antiseptics are available in many different forms: liquids, pastes, creams, ointments, gels, powders, sprays and impregnated dressings. The method of use and frequency of application may influence the practicality of a particular antiseptic. Some are used for one or more short periods each day, some require reapplication several times per day, and others are left in contact with the wound for up to several days (WUWHS, 2008). The most frequently used topical antimicrobials in modern wound care practice include iodine, silver and honey-containing products. In the past, acetic acid, chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, potassium 72 Wound Essentials 2017, Vol 12 No 1 permanganate and proflavine have been used (Cooper, 2004), but these are rarely used today. In one study comparing cadexomer iodine and silver dressings, all participants showed signs of infection or critical colonisation at baseline. The frequency of complete healing at 12 weeks was similar between treatment groups, with 60% of participants healing in the cadexomer iodine group compared with 61% in the silver-impregnated dressing group (Miller 2010). Therefore, no conclusion can be drawn on whether silver or cadexomer iodine is a more powerful antibacterial, or even if the participants would have healed at the same rate without antimicrobials as there was no control to compare. Certainly, the relative effects of systemic and topical antimicrobial treatments on pressure ulcers are not clear. Where differences in wound healing were found, these sometimes favoured the comparator treatment without antimicrobial properties. The trials are small, clinically heterogenous, generally of short duration, and at high or unclear risk of bias (Norman et al, 2016b). In other studies, hydrogen peroxide and povidone-iodine reduced both migration and proliferation of fibroblasts in a dose-dependent fashion. Treatment with silvercontaining antiseptics and chlorhexidine exhibited reductions in proliferation at high concentrations, but enhanced growth at lower doses. Silver-containing compounds and chlorhexidine also proved to be the least detrimental to migration in these assays. MMP release from the cells was differently affected depending on the dosage and class of antiseptic applied (Thomas et al, 2009). Silver sulfadiazine and chlorhexidine, at levels still proven to be bactericidal, had fewer detrimental effects on fibroblast activity in these assays. The silver-containing antiseptics may even increase the proliferative potential of these cells in culture (Thomas et al, 2009). To become bactericidal, silver atoms must lose an electron and become positively charged silver ions. Silver ions are highly reactive, affecting multiple sites in bacterial cells. They ultimately cause cell death by binding to bacterial cell membranes and causing disruption of the cell wall and cell leakage (Lansdown, 2002). There appears to be no robust evidence on the relative effectiveness of any antiseptic, antibiotic or antibacterial preparation evaluated to date. Where some evidence for possible treatment effects was reported, it stemmed from single studies with small participant numbers and was classed as moderate or low-quality evidence. This means it is likely or very likely that further research will have an important impact on confidence in the estimate of effect, and may change this estimate (Norman et al, 2016a). Current evidence does not support the routine use of honey- or silverbased products and further good quality research is required before definitive conclusions can be drawn about the effectiveness of povidoneiodine, peroxide-based preparations (O Meara et al, 2013). However, evidence from animal studies and some trials has suggested that honey may actually accelerate wound healing (Jull et al, 2015). However, like all research findings, the outcome is only ever as good as the design of the research. In the author s 25-year experience of wound care, antibacterials do make a difference as they quickly remove odour from a wound, which indicates that bacteria is also being removed. Biofilms It is now understood that many medical conditions are the result of
4 biofilm formation: cystic fibrosis, periodontitis, endocarditis, kidney stones, tonsillitis, osteomyelitis, and persistent otitis media, to name a few (Keast et al, 2014) However, though common, the nuances of many of the key issues in infection, such as biofilms, critical colonisation are poorly understood (Swanson and Carville, 2014). After attaching to a surface such as a wound bed, bacteria can encase themselves in a gelatinous matrix known as a biofilm. These complex microbial communities can contain numerous bacterial species, protected against the immune system and antimicrobial agents (WUWHS, 2008). While biofilms can delay wound healing, a routine laboratory test for their detection has not yet been established (Fazli et al, 2009). Nevertheless, there is now strong evidence that biofilms are present in the majority of chronic wounds (Bjarnsholt et al, 2008; James et al, 2008). The physical barrier of the exopolysaccharide shield protects bacteria in biofilms. Furthermore, bacteria in the biofilm especially in the periphery can down regulate their metabolism (a decrease in the number of receptors on the surface of target cells, which makes the cells less sensitive to a hormone or another agent). This makes them less susceptible to antibiotics (Keast et al, 2014) with 60% to 90% of chronic wounds thought to have biofilm formation (Bjarnsholt et al, 2008; James et al, 2008). Both silver- and iodine-releasing dressings have been shown to kill biofilm bacteria (Percival et al, 2008) whereas normal saline and tap water are possibly ineffective for biofilm management (Cutting et al, 2010). The beneficial effects of mechanical debridement in infected wounds may be related partly to the removal of bacterial biofilms (International Wound Journal, 2008) which is why mechanical debridement is popular with surgeons. Conclusion The age of some of the studies reported here means that more recent good quality research is required before definitive conclusions can be drawn about the effectiveness of topical agents, such as povidone iodine, honey-, silver- and peroxidebased products and other topical antiseptics in healing and, in this debate about the role of antiseptics in wound healing, the jury is still out. However, the main arguments are actually between academics who review the research and clinicians who use the products on a daily basis. It is the view of the author that clinicians have a commonsense approach to wound care and if the product did not do what they expected it should do, then they would cease to use the product. This is a simple answer to an ageold question regarding the use of antiseptics. We References Angeras M, Brandberg A, Falk A, Seeman T (1992) Comparison between sterile saline and tap water for the cleaning of acute traumatic soft tissue wounds. Eur J Surg 158(6 7): Akiyama H, Oono T, Saito M, Iwatsuki K (2004) Assessment of cadexomer iodine against Staphylococcus aureus biofilm in vivo and in vitro using confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Dermatol 31(7): Atiyeh BS, Dibo SA, Hayek SN (2009) Wound cleansing, topical antiseptics and wound healing. Int Wound J 6(6): Bianchi J (2000) The cleansing of superficial traumatic wounds. Br J Nurs 9(Suppl 19): S28 38 Bjarnsholt T, Kirketerp-Møller K, Jensen PØ et al (2008) Why chronic wounds will not heal: a novel hypothesis. Wound Repair Regen 16(1): 2 10 Bradbury S, Fletcher J (2011) Prontosan Made Easy. Wounds International 2(2) Carville K, Kapp S, Newell N et al (2008) Predicting Covert and Overt Infection in Venous Leg Ulcers: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Presented at: Australian Wound Management Association 7th National Conference: Dreams, Diversity, Disasters, May 7 10, Darwin, Australia Chen P, Parks WC (2009) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in epithelial migration. J Cell Biochem 108(6): Cooper R (2004) A review of the evidence for the use of topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. World Wide Wounds. Available at: (accessed Cutting K, Wolcott R, Dowd S, Percival S (2010) Biofilms and significance to wound healing. In: Percival S, Cutting K (eds.) Microbiology of Wounds. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL Fazli M, Bjarnsholt T, Kirketerp- Møller K et al (2009) Non-random distribution of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in chronic wounds. J Clin Microbiol 47(12): Fernandez R, Griffiths R, Ussia C (2008) Water for wound cleansing. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 23: CD Gruber RP, Vistnes L, Pardoe R (1975) The effect of commonly used antiseptics on wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 55(4): Wound Essentials 2017, Vol 12 No 1 73
5 Han A, Zenilman JM, Melendez JH, Shirtliff ME et al (2011) The importance of a multifaceted approach to characterizing the microbial flora of chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 19(5): International Wound Journal (2008) Wound infection in clinical practice. An International Consensus. 5: iii 11 James GA, Swogger E, Wolcott R et al (2008) Biofilms in chronic wounds. Wounds Repair Regen 16: Jull AB, Cullum N, Dumville JC et al (2015) Honey as a topical treatment for wounds. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 6: CD Keast D, Swanson T, Carville K (2014) Ten top tips. Understanding and managing wound biofilm. Wounds International 5(2): 20 4 Kirketerp-Møller K, Jenson PO, Fazli M et al (2008) Distribution, organization, and ecology of bacteria in chronic wounds. J Clin Microbiol 46: Lansdown AB (2002) Silver. I: Its antibacterial properties and mechanism of action. J Wound Care 11(4): Lineaweaver W, Howard R, Soucy D et al (1985) Topical antimicrobial toxicity. F Arch Surg 120(3): Macpherson G (2004) Black s Student Medical Dictionary. A & C Black Publishers Limited, London Miller CN, Newall N, Kapp SE et al (2010) A randomized-controlled trial comparing cadexomer iodine and nanocrystalline silver on the healing of leg ulcers. Wound Repair Regen 18(4): Moscati R, Mayrose J, Fincher L, Jehle D (1998) Comparison of normal saline with tap water for wound irrigation. Am J Emerg Med 16(4): Moscati RM, Mayrose J, Reardon RF et al (2007) A multicenter comparison of tap water versus sterile saline for wound irrigation. Acad Emerg Med 14(5): NICE (2008) Surgical Site Infection. Preventing Surgical Site Infection. NICE Clinical Guideline. Available at: (accessed Norman G1, Dumville JC, Mohapatra DP (2016a) Antibiotics and antiseptics for surgical wounds healing by secondary intention. Database Syst Rev 3: CD Norman G, Dumville JC, Moore ZE et al (2016b) Antibiotics and antiseptics for pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev Apr 4: CD O Meara S, Al-Kurdi D, Ologun Y et al (2013) Antibiotics and antiseptics for venous leg ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 23: CD Percival SL, Bowler P, Woods EJ (2008) Assessing the effect of an antimicrobial wound dressing on biofilms. Wound Repair Regen 16(1): 52 7 Pierard-Franchimont C, Paquet P, Arrese JE, Pierard GZ (1997) Healing rate and bacterial necrotizing vasculitis in venous leg ulcers. Dermatology 194(4): Smith RG (2005) A critical discussion of the use of antiseptics in acute traumatic wounds. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 95(2): Swanson T, Carville K (2014) Wound Infection Institute: Leaders in Wound Infection Understanding, Prevention, and Management. Wounds International. Available at: com/media/journals/_/946/files/ content_11312.pdf (accessed ) Templeton S (2014) Infected wounds. In: Swanson T, Asimus M, McGuiness W (eds.) Wound Management for the Advanced Practitioner. IP Communications, Melbourne, Australia Thomas GW, Rael LT, Bar-Or R (2009) Mechanisms of delayed wound healing by commonly used antiseptics. J Trauma 66(1): 82 90; discussion 90 1 Tur E, Bolton L, Constantine BE (1995) Topical hydrogen peroxide treatment of ischemic ulcers in the guinea pig: blood recruitment in multiple skin sites. JAAD 33(2:1): Van Den Broek PJ, Buys LMF, Van Furth R (1982) Interaction of povidone-iodine compounds, phagocytic cells, and microorganisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 22(4): Vowden P, Vowden K, Carville K (2011) Antimicrobial Dressings Made Easy. Wounds International 2(1). Available at: ly/1obtgls (accessed World Union of Wound Healing Societies (2008) Wound Infection in Clinical Practice. An International Consensus. London: MEP Ltd. Available at: bit.ly/1abvwpq (accessed 74 Wound Essentials 2017, Vol 12 No 1
RN Cathy Hammond. Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch
 RN Cathy Hammond Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #141: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know 15:05-16:00 WS #153: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know
RN Cathy Hammond Specialist Wound Management Service at Nurse Maude Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #141: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know 15:05-16:00 WS #153: Wound Infection - What You Need to Know
Biofilms are free floating
 Biofilms: the myths and realities There has been an increasing interest in biofilms and their possible contribution to the non-healing of chronic wounds. Currently, there is no gold standard for identifying
Biofilms: the myths and realities There has been an increasing interest in biofilms and their possible contribution to the non-healing of chronic wounds. Currently, there is no gold standard for identifying
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK
 Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
easy made Biofilm-based wound care with cadexomer iodine
 Biofilm-based wound care with cadexomer iodine made easy Wounds International November 2017 www.woundsinternational.com Introduction Evidence suggests that biofilms are present in most, if not all, chronic,
Biofilm-based wound care with cadexomer iodine made easy Wounds International November 2017 www.woundsinternational.com Introduction Evidence suggests that biofilms are present in most, if not all, chronic,
INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS
 WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION TO WOUND DRESSINGS JEC 2017 Wound Care Successfully completed specialized skills training in Wound Management. WOUND CONDITIONS & SYMBOLS BY COLOURS Yellow Black Necrotic tissue
EWMA Educational Development Programme. Curriculum Development Project. Education Module. Wound Infection
 EWMA Educational Development Programme Curriculum Development Project Education Module Wound Infection Latest revision: February 2014 ABOUT THE EWMA EDUCATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME The Programme is designed
EWMA Educational Development Programme Curriculum Development Project Education Module Wound Infection Latest revision: February 2014 ABOUT THE EWMA EDUCATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME The Programme is designed
Effective Diagnosis of Local Wound Bed Infection. Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust
 Effective Diagnosis of Local Wound Bed Infection Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust Localised Wound Bed Infection is the Result of imbalance between patient s
Effective Diagnosis of Local Wound Bed Infection Julie Hewish Senior Tissue Viability Nurse Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust Localised Wound Bed Infection is the Result of imbalance between patient s
Diagnosing wound infection - a clinical challenge
 Diagnosing wound infection - a clinical challenge Keith F Cutting Merimbula, 5 th November 2010 Wound infection microbial load immune system microbial load + + + immune system infection host response Diagnosing
Diagnosing wound infection - a clinical challenge Keith F Cutting Merimbula, 5 th November 2010 Wound infection microbial load immune system microbial load + + + immune system infection host response Diagnosing
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment. Michelle Greenwood. Lorraine Grothier. Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust
 Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Galen ( A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing
 Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Galen (120-201A.D) Advanced Wound Dressing Wounds heal optimally in a moist environment นพ.เก งกาจ ว น ยโกศล Wound assessment Ideal wound dressing Type of wound Clinical appearance Wound location Measurement
Chronic wounds need an ideal microenvironment. NEXODYN TM can support the physiological healing process.
 Chronic wounds need an ideal microenvironment. can support the physiological healing process. Wound microenvironment of chronic wounds represents a major therapeutic challenge¹ The most relevant factors
Chronic wounds need an ideal microenvironment. can support the physiological healing process. Wound microenvironment of chronic wounds represents a major therapeutic challenge¹ The most relevant factors
Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types. Summary
 Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Biofilm and Advanced Wound Management Strategies
 Biofilm and Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org 1 Objectives What are Biofilms How Biofilms
Biofilm and Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org 1 Objectives What are Biofilms How Biofilms
Appropriate use of silver dressings
 Appropriate use of silver dressings David Keast, Center Director, Aging Rehabilitation and Geriatric Care Research Centre, St Joseph s Parkwood Hospital, London, Ontario, Canada Role of antimicrobial dressings
Appropriate use of silver dressings David Keast, Center Director, Aging Rehabilitation and Geriatric Care Research Centre, St Joseph s Parkwood Hospital, London, Ontario, Canada Role of antimicrobial dressings
Multi-Center Clinical Results with PluroGel PSSD in Chronic Wounds
 Multi-Center Clinical Results with PluroGel PSSD in Chronic Wounds Presented at a Satellite Symposium during the European Wound Management Association (EWMA) 2012 24 May 2012 Vienna, Austria Multi-Center
Multi-Center Clinical Results with PluroGel PSSD in Chronic Wounds Presented at a Satellite Symposium during the European Wound Management Association (EWMA) 2012 24 May 2012 Vienna, Austria Multi-Center
This article is based on a symposium held
 Advances in wound cleansing: an integrated approach LIZ OVENS Independent Tissue Viability Specialist Nurse SALLY IRVING Independent Tissue Viability Nurse Consultant This article is based on a symposium
Advances in wound cleansing: an integrated approach LIZ OVENS Independent Tissue Viability Specialist Nurse SALLY IRVING Independent Tissue Viability Nurse Consultant This article is based on a symposium
Essity Internal. Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues
 Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues Learning objectives 1. Identifying the cost which wound infection can have on both the patient and healthcare organisations 2. Understanding
Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues Learning objectives 1. Identifying the cost which wound infection can have on both the patient and healthcare organisations 2. Understanding
Prontosan. Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing
 Prontosan Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing CoE Infection Control Prontosan the unique combination of Betaine & Polihexanide reduces healing time removes and prevents biofilm prevents infections
Prontosan Clean. Easy Wound Healing. Wound Cleansing CoE Infection Control Prontosan the unique combination of Betaine & Polihexanide reduces healing time removes and prevents biofilm prevents infections
Wound management accounts for
 An audit to determine the clinical effectiveness of a pathway for managing wound infection KEY WORDS Wound management Infection risk Clinical pathway Audit Prevention of wound infection is a key objective
An audit to determine the clinical effectiveness of a pathway for managing wound infection KEY WORDS Wound management Infection risk Clinical pathway Audit Prevention of wound infection is a key objective
Wound management accounts for
 An audit to determine the clinical effectiveness of a pathway for managing wound infection. KEY WORDS Wound management Infection risk Clinical pathway Audit Prevention of wound infection is a key objective
An audit to determine the clinical effectiveness of a pathway for managing wound infection. KEY WORDS Wound management Infection risk Clinical pathway Audit Prevention of wound infection is a key objective
Foam dressings have frequently
 The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
The practical use of foam dressings Efficient and cost-effective management of excessive exudate continues to challenge clinicians. Foam dressings are commonly used in the management of moderate to heavily
easy made Cutimed Sorbact
 PRODUCTS FOR PRACTICE Cutimed Sorbact made easy Volume 3 Issue 2 May 2012 www.woundsinternational.com Introduction Bacterial colonisation and infection may contribute to delayed healing and present a major
PRODUCTS FOR PRACTICE Cutimed Sorbact made easy Volume 3 Issue 2 May 2012 www.woundsinternational.com Introduction Bacterial colonisation and infection may contribute to delayed healing and present a major
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT
 TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
Making the Most of your Dressing Products Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE
 Making the Most of your Dressing Products 2013 Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE What do you need in your dressings cupboard? 2 Skin tear 3 4 Lack Confidence in Selecting Dressings? 5 Appropriate Use of Product
Making the Most of your Dressing Products 2013 Catherine Hammond CNS/CNE What do you need in your dressings cupboard? 2 Skin tear 3 4 Lack Confidence in Selecting Dressings? 5 Appropriate Use of Product
Wound Healing: General Principles. Mansour Dib MD
 Wound Healing: General Principles Mansour Dib MD Normal Wound Healing Chronic Wounds: Stuck Where does it get stuck? Mostly Proliferation Sometimes Remodeling Why? Systemic factors Local factors How do
Wound Healing: General Principles Mansour Dib MD Normal Wound Healing Chronic Wounds: Stuck Where does it get stuck? Mostly Proliferation Sometimes Remodeling Why? Systemic factors Local factors How do
DRESSING SELECTION. Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate
 DRESSING SELECTION Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate Should be individually tailored in conjunction with the patient to meet their individual needs. WOUND MANAGEMENT: Comprehensive health assessment Wound
DRESSING SELECTION Rebecca Aburn MN NP Candidate Should be individually tailored in conjunction with the patient to meet their individual needs. WOUND MANAGEMENT: Comprehensive health assessment Wound
Best practice wound management. Liz Milner Wound Consultant
 Best practice wound management Liz Milner Wound Consultant The goals of wound care: reducing risks that inhibit wound healing, enhancing the healing process, and lowering the incidence of wound infections.
Best practice wound management Liz Milner Wound Consultant The goals of wound care: reducing risks that inhibit wound healing, enhancing the healing process, and lowering the incidence of wound infections.
Honey has been used in wound care since the
 Honey as a dressing for chronic wounds in adults Carolyn Fox Carolyn Fox is Clinical Nurse Specialist - Tissue Viability, University Hospital Lewisham, London Series editor: Peter Griffiths Honey has been
Honey as a dressing for chronic wounds in adults Carolyn Fox Carolyn Fox is Clinical Nurse Specialist - Tissue Viability, University Hospital Lewisham, London Series editor: Peter Griffiths Honey has been
INVESTIGATING: WOUND INFECTION
 INVESTIGATING: WOUND INFECTION Diagnosing infection in surgical and other wounds involves nurses being able to observe the clinical signs in a wound rather than simply obtaining positive microbiology results
INVESTIGATING: WOUND INFECTION Diagnosing infection in surgical and other wounds involves nurses being able to observe the clinical signs in a wound rather than simply obtaining positive microbiology results
Many patients with chronic wounds. Case reports. The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series
 Case reports The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series Author: Liezl Naude Many patients with chronic wounds will develop infection (Landis et al, 2007; Sibbald
Case reports The use of Prontosan in combination with Askina Calgitrol : an independent case series Author: Liezl Naude Many patients with chronic wounds will develop infection (Landis et al, 2007; Sibbald
Wound Management. E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP
 Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
New approach to the wounds by moist wound healing in Japan. Yoshihiko Mochizuki Japan
 New approach to the wounds by moist wound healing in Japan. Yoshihiko Mochizuki M.D. @Tokyo Japan What is the meaning of wound healing? I think there are two types of wound healing. 1. True healing moist
New approach to the wounds by moist wound healing in Japan. Yoshihiko Mochizuki M.D. @Tokyo Japan What is the meaning of wound healing? I think there are two types of wound healing. 1. True healing moist
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection
 Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Hemostasis Inflammatory Phase Proliferative/rebuilding Phase Maturation Phase
 The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
The presenters are staff members of the CHI Health St. Elizabeth Burn and Wound Center. Many of the products discussed are used in our current practice but we have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice
 Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice Wound management Conclusion In an observational study of 86
Impregnated tulle dressing containing silver promotes healing of wounds and treats the wound margins Atrauman Ag tested in clinical practice Wound management Conclusion In an observational study of 86
The medicinal use of honey has been known since ancient
 THE JOURNAL OF ALTERNATIVE AND COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE Volume 13, Number 4, 2007, pp. 439 441 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/acm.2007.6366 Bactericidal Activity of Different Types of Honey Against
THE JOURNAL OF ALTERNATIVE AND COMPLEMENTARY MEDICINE Volume 13, Number 4, 2007, pp. 439 441 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/acm.2007.6366 Bactericidal Activity of Different Types of Honey Against
Mean percent reduction in ulcer area from baseline at six weeks 62 % SANTYL Ointment + supportive care* + sharp debridement 1 (P<0.
 Evaluating two common adjuncts to sharp debridement in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers Mean percent reduction in ulcer area from baseline at six weeks 62 % 40 % SANTYL Ointment + supportive care*
Evaluating two common adjuncts to sharp debridement in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers Mean percent reduction in ulcer area from baseline at six weeks 62 % 40 % SANTYL Ointment + supportive care*
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds
 Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed. Closing wounds. Together.
 Closing wounds. Together. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed Sorbact range. A responsible choice. THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. www.bsnmedical.co.uk TOGETHER WE CAN MAKE
Closing wounds. Together. Need safe and efficient infection prevention and management? 1 The Cutimed Sorbact range. A responsible choice. THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. www.bsnmedical.co.uk TOGETHER WE CAN MAKE
Super Bugs vs Super Heroes: A Wound Care Perspective
 Super Bugs vs Super Heroes: A Wound Care Perspective IPAC GTA Annual Education Day October 3 rd 2017 Zaynab Sheraly RN, BScN, MHSC, IIWCC Nicholas Joachimides RN, BScN, CRN(c), IIWCC, MClSc, MSc This document
Super Bugs vs Super Heroes: A Wound Care Perspective IPAC GTA Annual Education Day October 3 rd 2017 Zaynab Sheraly RN, BScN, MHSC, IIWCC Nicholas Joachimides RN, BScN, CRN(c), IIWCC, MClSc, MSc This document
Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection
 Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection Arglaes Controlled-Release Silver Technology Reduce bioburden with Arglaes Silver Barrier Dressings Antimicrobial Arglaes began the
Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection Arglaes Controlled-Release Silver Technology Reduce bioburden with Arglaes Silver Barrier Dressings Antimicrobial Arglaes began the
Wound culture. (Sampling methods) M. Rostami MSn.ICP Rajaei Heart Center
 Wound culture (Sampling methods) M. Rostami MSn.ICP Rajaei Heart Center Infection is a major impairment in delayed and nonhealing chronic wounds. Cultures of chronic wounds are not routinely performed
Wound culture (Sampling methods) M. Rostami MSn.ICP Rajaei Heart Center Infection is a major impairment in delayed and nonhealing chronic wounds. Cultures of chronic wounds are not routinely performed
comfortable healing customizable infection control antimicrobial exudate control evidence conformable biofilm control absorbency tested advanced
 Next generation antimicrobial dressings AQUACEL Ag+ Extra and Ribbon antimicrobial absorbency tested comfortable strength infection control advanced exudate control evidence healing customizable protection
Next generation antimicrobial dressings AQUACEL Ag+ Extra and Ribbon antimicrobial absorbency tested comfortable strength infection control advanced exudate control evidence healing customizable protection
Prepares wounds to allow natural healing
 ADVANCED CARE OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC WOUNDS Prepares wounds to allow natural healing 0373 Medical Device Hyaluronic Acid and Collagenase COMBINED ACTION IN WOUND REPAIR Hyaluronic acid and collagenase promote
ADVANCED CARE OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC WOUNDS Prepares wounds to allow natural healing 0373 Medical Device Hyaluronic Acid and Collagenase COMBINED ACTION IN WOUND REPAIR Hyaluronic acid and collagenase promote
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey
 Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
Disclosures for Tarik Alam. Wound Bed Preparation. Wound Prognosis. Session Objectives. Debridement 4/26/2015
 Disclosures for Tarik Alam Challenges in Managing Bioburden and Devitalized Tissue Tarik Alam RN, BScN, ET, MClSc(WH) Enterostomal Therapy Nurse tarikalam@hotmail.com Clinical Affairs Manager for Hollister
Disclosures for Tarik Alam Challenges in Managing Bioburden and Devitalized Tissue Tarik Alam RN, BScN, ET, MClSc(WH) Enterostomal Therapy Nurse tarikalam@hotmail.com Clinical Affairs Manager for Hollister
made PRODUCTS FOR PRACTICE
 PRODUCTS FOR PRACTICE made BPA easy Wounds International vember 2016 www.woundsinternational.com Introduction The mere presence of bacteria in chronic wounds may not indicate active infection or impair
PRODUCTS FOR PRACTICE made BPA easy Wounds International vember 2016 www.woundsinternational.com Introduction The mere presence of bacteria in chronic wounds may not indicate active infection or impair
Understanding and Managing
 Understanding and Managing MM s in Wound Bed Brock Liden DM, ABM, FAWCA Learning Objectives Review the four sequential phases of normal wound healing and recognize the BENEFICIAL effects of CONTROLLED
Understanding and Managing MM s in Wound Bed Brock Liden DM, ABM, FAWCA Learning Objectives Review the four sequential phases of normal wound healing and recognize the BENEFICIAL effects of CONTROLLED
Advancing the science of wound bed preparation
 Advancing the science of wound bed preparation How Drawtex wound dressing works LevaFiber Technology provides three different types of action. Mechanisms of Action Capillary Action Hydroconductive Action
Advancing the science of wound bed preparation How Drawtex wound dressing works LevaFiber Technology provides three different types of action. Mechanisms of Action Capillary Action Hydroconductive Action
DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED
 10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM. Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS
 BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Contamination Presence of non-replicating microorganisms on the wound surface that evoke no clinical host response - All
BIOBURDEN-BASED WOUND MANAGEMENT: A NEW PARADIGM Ryan H. Fitzgerald, DPM, FACFAS Contamination Presence of non-replicating microorganisms on the wound surface that evoke no clinical host response - All
Objectives. Jeffrey M. Levine MD 3/5/2013. Today s Speaker. MRT Gold STAMP & Outbreak Investigation in a Nursing Home Training Project Webinar
 MRT Gold STAMP & Outbreak Investigation in a Nursing Home Training Project Webinar Infectious Aspects of Chronic Wounds Including Infection Control March 7, 2013 12-1:00 pm ET This project is funded through
MRT Gold STAMP & Outbreak Investigation in a Nursing Home Training Project Webinar Infectious Aspects of Chronic Wounds Including Infection Control March 7, 2013 12-1:00 pm ET This project is funded through
What did we find living under some silver dressings? * NEW in vitro Evidence. Not all silver dressings are created equal. *As demonstrated in vitro
 NEW in vitro Evidence What did we find living under some silver dressings? * Not all silver dressings are created equal.. Micro-contouring, bacteria killing* 1,2 *As demonstrated in vitro Dressing technology
NEW in vitro Evidence What did we find living under some silver dressings? * Not all silver dressings are created equal.. Micro-contouring, bacteria killing* 1,2 *As demonstrated in vitro Dressing technology
Evaluating the use of a topical haemoglobin spray as adjunctive therapy in non-healing chronic wounds a pilot study Liezl Naude
 Evaluating the use of a topical haemoglobin spray as adjunctive therapy in non-healing chronic wounds a pilot study Liezl Naude Abstract Wound Management Specialist Eloquent Health & Wellness Centre, Pretoria,
Evaluating the use of a topical haemoglobin spray as adjunctive therapy in non-healing chronic wounds a pilot study Liezl Naude Abstract Wound Management Specialist Eloquent Health & Wellness Centre, Pretoria,
The Biofilm-forming capacity of staphylococcus aureus from chronic wounds can be useful for determining Wound-Bed Preparation methods
 ienna EWMA 2012 The Biofilm-forming capacity of staphylococcus aureus from chronic wounds can be useful for determining Wound-Bed Preparation methods Science, Practice and Education ABSTRACT Introduction:
ienna EWMA 2012 The Biofilm-forming capacity of staphylococcus aureus from chronic wounds can be useful for determining Wound-Bed Preparation methods Science, Practice and Education ABSTRACT Introduction:
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice.
 Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Assessment & Management of Wounds in primary practice. Nutrition Successful wound management depends on appropriate nutritional support. Poor nutrition is recognised as one of the major causes of poor
Dr. Julia Overstreet, DPM, FAPWCA, FAPMSB
 Evidence Based Wound Care Dr. Julia Overstreet, DPM, FAPWCA, FAPMSB Silver Dressings 1. Understand the mechanisms of action 2. Chose the appropriate times to use a silver dressing 3.What does the research
Evidence Based Wound Care Dr. Julia Overstreet, DPM, FAPWCA, FAPMSB Silver Dressings 1. Understand the mechanisms of action 2. Chose the appropriate times to use a silver dressing 3.What does the research
Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service
 Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service This search summary contains the results of a literature search undertaken by the Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service librarians in January 2010. All
Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service This search summary contains the results of a literature search undertaken by the Lincolnshire Knowledge and Resource Service librarians in January 2010. All
The right dressing does make a difference
 The right dressing does make a difference a A post-operative dressing regimen using Mepore dressing covering AQUACEL dressing was compared to a new dressing regimen of DuoDERM Extra Thin dressing covering
The right dressing does make a difference a A post-operative dressing regimen using Mepore dressing covering AQUACEL dressing was compared to a new dressing regimen of DuoDERM Extra Thin dressing covering
The Triangle of Wound Assessment
 The Triangle of Wound Assessment A simple and holistic framework for wound management CPWSC_TOWA_Brochure_210x210_2018.indd 1 10/01/2018 15.13 ? We asked healthcare professionals around the world about
The Triangle of Wound Assessment A simple and holistic framework for wound management CPWSC_TOWA_Brochure_210x210_2018.indd 1 10/01/2018 15.13 ? We asked healthcare professionals around the world about
I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use!
 I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use! Introduction: Originating from battlefield medicine much of what we use today is an evolution of material science combined with our understanding
I ve a drawer full of dressings i don t know how to use! Introduction: Originating from battlefield medicine much of what we use today is an evolution of material science combined with our understanding
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 03 Page March 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i3.55 Thesis Paper A Prospective Comparative
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i3.55 Thesis Paper A Prospective Comparative
Human skin acts as a physical and
 How effective is wound swabbing? A clinimetric assessment of wound swabs KEY WORDS Clinimetric assessment Validity Wound swabbing The swabbing of wounds is routinely carried out in a number of healthcare
How effective is wound swabbing? A clinimetric assessment of wound swabs KEY WORDS Clinimetric assessment Validity Wound swabbing The swabbing of wounds is routinely carried out in a number of healthcare
Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know?
 Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know? Laura Owen European Specialist in Small Animal Surgery Lecturer in Small Animal Surgery, University of Cambridge The Acute Open Wound PPE
Wound Management for Nurses/Technicians What do we need to know? Laura Owen European Specialist in Small Animal Surgery Lecturer in Small Animal Surgery, University of Cambridge The Acute Open Wound PPE
Chronic wounds: how to kick start healing <Clinical Special>
 Chronic wounds: how to kick start healing Agenda Chronic wounds: How to kick start healing Chronic wounds an overview Chronic wound exudate management Increased bioburden, infection
Chronic wounds: how to kick start healing Agenda Chronic wounds: How to kick start healing Chronic wounds an overview Chronic wound exudate management Increased bioburden, infection
This article is based on a symposium held
 Taking wound cleansing seriously to minimise risk MARK COLLIER Nurse Consultant, Tissue Viability, United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust PAMELA HOFER Medical and Scientific Affairs, B Braun This article
Taking wound cleansing seriously to minimise risk MARK COLLIER Nurse Consultant, Tissue Viability, United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust PAMELA HOFER Medical and Scientific Affairs, B Braun This article
Beyond Wet-to-Dry: A Rational Approach to Treating Chronic Wounds
 Beyond Wet-to-Dry: A Rational Approach to Treating Chronic Wounds Johnson C. Lee, BA, a Swetha Kandula, MD, b,c and Noëlle S. Sherber, MD c a Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD;
Beyond Wet-to-Dry: A Rational Approach to Treating Chronic Wounds Johnson C. Lee, BA, a Swetha Kandula, MD, b,c and Noëlle S. Sherber, MD c a Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD;
Prontosan. Clinical and Scientific Evidence
 Clinical and Scientific Evidence Rationale for the use of Prontosan Millions of people around the world suffer from chronic wounds. Such patients have to come to terms with months of pain and reduced quality
Clinical and Scientific Evidence Rationale for the use of Prontosan Millions of people around the world suffer from chronic wounds. Such patients have to come to terms with months of pain and reduced quality
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Comparative Study on the Effect of Honey and Povidone Iodine Ointment on Pain, Wound Healing
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Comparative Study on the Effect of Honey and Povidone Iodine Ointment on Pain, Wound Healing
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
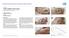 CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
CASE 1: TYPE-II DIABETIC FOOT ULCER DIABETIC FOOT ULCER 48 YEAR-OLD MALE Mr. C., was a 48-year old man with a history of Type-II diabetes over the past 6 years. The current foot ulcer with corresponding
easy made Reactive Oxygen Wounds uk Introduction SETTING THE SCENE INFECTION AND BIOFILM MANAGEMENT
 Wounds uk VOL 14 ISSUE 5 NOV 2018 Reactive Oxygen made easy Introduction Reactive oxygen species () are part of the body s antimicrobial response and have a major role in wound healing. Members of the
Wounds uk VOL 14 ISSUE 5 NOV 2018 Reactive Oxygen made easy Introduction Reactive oxygen species () are part of the body s antimicrobial response and have a major role in wound healing. Members of the
Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy and tolerability
 Treatment of infected and infection-prone wounds with Atrauman Ag Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy and tolerability Wound management Summary More than 600 patients with
Treatment of infected and infection-prone wounds with Atrauman Ag Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy and tolerability Wound management Summary More than 600 patients with
Abilar Questions and Answers
 Abilar Questions and Answers Question Answer Product Information What is Abilar Resin Salve? What are the main properties of Abilar? How is Resin different from colophony (rosin)? Abilar Resin Salve is
Abilar Questions and Answers Question Answer Product Information What is Abilar Resin Salve? What are the main properties of Abilar? How is Resin different from colophony (rosin)? Abilar Resin Salve is
Ivory, John D.; Gethin, Georgina; McIntosh, Caroline
 Provided by the author(s) and NUI Galway in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Antimicrobial dressings for treating local infection in patients
Provided by the author(s) and NUI Galway in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Antimicrobial dressings for treating local infection in patients
Practice development. Ensuring that the correct antimicrobial dressing is selected
 Ensuring that the correct antimicrobial dressing is selected Authors: David Keast, Christina Lindholm This article examines the various tools available to clinicians in the fight against the increase of
Ensuring that the correct antimicrobial dressing is selected Authors: David Keast, Christina Lindholm This article examines the various tools available to clinicians in the fight against the increase of
How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice BY Christine Pearson Christine Pearson, RN, IIWCC, is a wound clinician for Vancouver Coastal Health and has worked in
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E How Wounds Heal: A Guide for the Wound-care Novice BY Christine Pearson Christine Pearson, RN, IIWCC, is a wound clinician for Vancouver Coastal Health and has worked in
Identification and management of biofilm in chronic wounds
 Identification and management of biofilm in chronic wounds Vincent Siaw-Sakyi Evidence suggests that biofilm is present in at least 78% of nonhealing wounds, and it is widely accepted that its presence
Identification and management of biofilm in chronic wounds Vincent Siaw-Sakyi Evidence suggests that biofilm is present in at least 78% of nonhealing wounds, and it is widely accepted that its presence
Conference Report: The Wound Infection Summit. Kings College Hospital, London; March 2013
 Conference Report: The Wound Infection Summit Kings College Hospital, London; March 2013 We report on the first Wound Infection Summit, which took place at Kings College Hospital, London, on 20 th March
Conference Report: The Wound Infection Summit Kings College Hospital, London; March 2013 We report on the first Wound Infection Summit, which took place at Kings College Hospital, London, on 20 th March
White (2015) suggests that in
 Super silver: the answer to wound infection and biofilm management in venous leg ulcers? In order for silver to be biocidal it must be in an ionic form. The higher the ionic state (the more electrons missing)
Super silver: the answer to wound infection and biofilm management in venous leg ulcers? In order for silver to be biocidal it must be in an ionic form. The higher the ionic state (the more electrons missing)
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. NICE Quality Standards Consultation Surgical Site Infection. Closing date: 5pm 17 June 2013
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence NICE Quality Standards Consultation Surgical Site Infection Closing date: 5pm 17 June 2013 Organisation Title (e.g. Dr, Mr, Ms, Prof) Name Job title or
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence NICE Quality Standards Consultation Surgical Site Infection Closing date: 5pm 17 June 2013 Organisation Title (e.g. Dr, Mr, Ms, Prof) Name Job title or
Tissue Viability Service. Medical honey simplified. A patient guide to the role of honey in wound management
 Medical honey simplified A patient guide to the role of honey in wound management Medical honey is a natural, non-toxic agent that has been used to treat wounds for thousands of years. This ancient remedy
Medical honey simplified A patient guide to the role of honey in wound management Medical honey is a natural, non-toxic agent that has been used to treat wounds for thousands of years. This ancient remedy
Introducing Mepilex Transfer Ag It all adds up to undisturbed healing. Antimicrobial wound contact layer with Safetac technology
 Introducing Mepilex Transfer Ag It all adds up to undisturbed healing Antimicrobial wound contact layer with Safetac technology Mepilex Transfer Ag Help the body heal The importance of less pain The body
Introducing Mepilex Transfer Ag It all adds up to undisturbed healing Antimicrobial wound contact layer with Safetac technology Mepilex Transfer Ag Help the body heal The importance of less pain The body
Wound Care in the Community. Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts
 Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
Wound Care in the Community Lisa Sutherland MSc Tissue Viability Senior Lead Ipswich Hospital & Community NHS Trusts What are the key elements? What is the patient s goal or aim for the wound? What are
Electromicyn WHO Essential Medicines List
 Electromicyn WHO Essential Medicines List Lance Gravatt PhD Founder Te Arai BioFarma Ltd Finding a Global Partner Oculus Innovative Sciences, Petaluma, CA Launched Microdacyn at NZWCS Conference, Blenheim
Electromicyn WHO Essential Medicines List Lance Gravatt PhD Founder Te Arai BioFarma Ltd Finding a Global Partner Oculus Innovative Sciences, Petaluma, CA Launched Microdacyn at NZWCS Conference, Blenheim
Antibiotic or antimicrobial resistance
 Authors: xxxxx Authors: Valerie Edwards- Jones, Madeleine Flanagan, Randall Wolcott Technological advancements in the fight against antimicrobial resistance Intro Over-prescription and misuse of antibiotics
Authors: xxxxx Authors: Valerie Edwards- Jones, Madeleine Flanagan, Randall Wolcott Technological advancements in the fight against antimicrobial resistance Intro Over-prescription and misuse of antibiotics
Surgical Wounds & Incisions
 Surgical Wounds & Incisions A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist www.woundcarenurses.org 1
Surgical Wounds & Incisions A Comprehensive Review Assessment & Management Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist www.woundcarenurses.org 1
Understanding our report and advice: Antimicrobial wound dressings (AWDs) for chronic wounds
 Understanding our report and advice: Antimicrobial wound dressings (AWDs) for chronic wounds Health technology assessment report 13 December 2015 Healthcare Improvement Scotland 2015 Published December
Understanding our report and advice: Antimicrobial wound dressings (AWDs) for chronic wounds Health technology assessment report 13 December 2015 Healthcare Improvement Scotland 2015 Published December
Haemoglobin. Granulox: TOPICAL HAEMOGLOBIN
 QUICK GUIDE Haemoglobin Granulox: TOPICAL HAEMOGLOBIN OXYGEN AND WOUND HEALING 1 Oxygen is needed at all phases of wound healing Insufficient wound tissue oxygenation is a major risk factor for delayed
QUICK GUIDE Haemoglobin Granulox: TOPICAL HAEMOGLOBIN OXYGEN AND WOUND HEALING 1 Oxygen is needed at all phases of wound healing Insufficient wound tissue oxygenation is a major risk factor for delayed
Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected dressings enhance the body s ability to heal the wound. Progression Towards Healing
 Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Dressings in Wound Care: They Do Matter John S. Steinberg, DPM FACFAS Associate Professor, Department of Plastic Surgery Georgetown University School of Medicine Dressings do not heal wounds properly selected
Conwy & Denbighshire NHS Trust. Ymddiriedolaeth GIG Siroedd Conwy a Dinbych Conwy & Denbighshire NHS Trust
 Ymddiriedolaeth GIG Siroedd Conwy a Dinbych POLICY FOR ANTISEPTICS AND DISINFECTANTS YELLOW 09 Policy Details: Author job title: Senior Nurse - Infection Control Dept/Working Group(s): Infection Control
Ymddiriedolaeth GIG Siroedd Conwy a Dinbych POLICY FOR ANTISEPTICS AND DISINFECTANTS YELLOW 09 Policy Details: Author job title: Senior Nurse - Infection Control Dept/Working Group(s): Infection Control
WOUND CARE UPDATE. -Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products For Wound. -Total Contact Casting. Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C. ped.
 WOUND CARE UPDATE -Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products For Wound Closure -Total Contact Casting Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C. ped. Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products for Wound Closure why are they
WOUND CARE UPDATE -Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products For Wound Closure -Total Contact Casting Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C. ped. Commonly Used Skin Substitute Products for Wound Closure why are they
Abena Antimicrobial Glove
 Abena Antimicrobial Glove Revolutionizing the world of infection prevention The first non-leaching antimicrobial nitrile glove Provides active protection against HAIs Kills up to 99.999% of selected bacteria
Abena Antimicrobial Glove Revolutionizing the world of infection prevention The first non-leaching antimicrobial nitrile glove Provides active protection against HAIs Kills up to 99.999% of selected bacteria
Bactisure Wound Lavage. Advancing Biofilm Removal
 Wound Lavage Advancing Biofilm Removal Wound Lavage Wound Lavage is used to remove debris, including microorganisms, from wounds using pulsed (jet) lavage. The clear, colorless, low-odor solution is a
Wound Lavage Advancing Biofilm Removal Wound Lavage Wound Lavage is used to remove debris, including microorganisms, from wounds using pulsed (jet) lavage. The clear, colorless, low-odor solution is a
Currently, the NHS is facing the challenge of
 Evaluation of a superabsorbent dressing in a primary care organization Jackie Stephen-Haynes and Claire Stephens Jackie Stephen-Haynes is Professor and Nurse Consultant, Practice Development Unit, Birmingham
Evaluation of a superabsorbent dressing in a primary care organization Jackie Stephen-Haynes and Claire Stephens Jackie Stephen-Haynes is Professor and Nurse Consultant, Practice Development Unit, Birmingham
Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds
 Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds Health Improvement Scotland published their 13th Health Technology Assessment (HTA 13) in December 2015 entitled, Antimicrobial
Resources to Guide the Management of Suspected Infection in Chronic Wounds Health Improvement Scotland published their 13th Health Technology Assessment (HTA 13) in December 2015 entitled, Antimicrobial
Wound bed preparation: TIME in practice
 Wound bed preparation: TIME in practice Wound bed preparation is now a well established concept and the TIME framework has been developed as a practical tool to assist practitioners when assessing and
Wound bed preparation: TIME in practice Wound bed preparation is now a well established concept and the TIME framework has been developed as a practical tool to assist practitioners when assessing and
WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets
 AMERIGEL WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets P R O D U C T I N F O R M AT I O N MSDS APPLICATION PROTOCOLS AmeriGel WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets A HYDROGEL WITH A UNIQUE AUTOLYTIC DEBRIDER Diabetic
AMERIGEL WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets P R O D U C T I N F O R M AT I O N MSDS APPLICATION PROTOCOLS AmeriGel WOUND DRESSING Daily Dressing Packets A HYDROGEL WITH A UNIQUE AUTOLYTIC DEBRIDER Diabetic
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease
 Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Clinical evaluation of honey-based products for lower extremity wounds in a home care setting
 Clinical evaluation of honey-based products for lower extremity wounds in a home care setting Abstract Matthew Thomas, Mohammed Filip Hamdan, KegelsSharon Hailes, Michael Walker Aims: To evaluate the efficacy
Clinical evaluation of honey-based products for lower extremity wounds in a home care setting Abstract Matthew Thomas, Mohammed Filip Hamdan, KegelsSharon Hailes, Michael Walker Aims: To evaluate the efficacy
Regenerative Tissue Matrix in Treatment of Wounds
 Regenerative Tissue Matrix in Treatment of Wounds Learning Objectives Differentiate between reparative and regenerative healing Review surgical techniques for applying a regenerative tissue scaffold to
Regenerative Tissue Matrix in Treatment of Wounds Learning Objectives Differentiate between reparative and regenerative healing Review surgical techniques for applying a regenerative tissue scaffold to
