Charcot Neuroarthropathy
|
|
|
- Kory Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLINICAL VIGNETTE Charcot Neuroarthropathy Spencer R. Adams, MD, Roger M. Lee, MD and Matthew Leibowitz, MD Acute Charcot foot (Charcot neuroarthropathy (CN)) is an often overlooked complication in diabetic patients with neuropathy. The diagnosis is frequently missed or delayed by months to years leading to increased morbidity and mortality in affected patients. In the early stages, patients with CN present with a red, hot, swollen foot and are often misdiagnosed as having cellulitis or gout. Later stages are characterized by joint dislocation and permanent foot deformities. The pathogenesis of CN is thought to involve pain insensitivity, altered blood flow from autonomic dysfunction, and repetitive trauma ultimately leading to joint destruction and deformity. Initial treatment involves prompt recognition and immobilization and bracing to preserve a functioning foot and avoid complications. Physicians must consider the diagnosis of CN in all patients with diabetes and peripheral neuropathy who present with erythema, edema and elevated temperature. Early identification and treatment helps prevent deformity and functional loss of the lower extremity as well as possible subsequent amputation. Case Report A 64 year-old woman with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus, peripheral neuropathy, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and recurrent urinary tract infections (UTI) complained of having left foot/ankle swelling for a several days. She denied trauma to the left foot. The patient was employed as an attorney and denied illicit drug use. She was already being treated with an oral antibiotic (cefpodoxime) for a recent UTI. Doppler ultrasound of the left leg was negative for deep vein thrombosis. Subsequently, she developed left foot pain, erythema, subjective fever and chills. In addition to cefpodoxime, home medications included repaglinide, levemir insulin, atenolol and hydrochlorothiazide. Vital signs showed temperature 37.2 C, blood pressure 116/65 mmhg, pulse 63 beats per minute, respiration rate 17 breaths per minute with normal oxygen saturation. Physical examination was unremarkable except for her left low extremity. The left leg was edematous to mid shin with taut and shiny skin in addition to erythema on the lateral foot with bruising on the 2 nd and 3 rd toes. The foot was also slightly warm to touch. There was no ulceration, fluctuance or crepitance. Initial laboratory evaluation showed white blood cell count of 10.4 x 10 3 /μl, hemoglobin of 9.8 g/dl, creatinine kinase of 144 U/L, creatinine of 0.9 mg/dl, erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 40 mm/hr and elevated C- reactive protein of 10.7 mg/dl. Initial left foot X-ray showed no evidence of osteomyelitis or foot deformity (Figure 1A). The patient was admitted to the hospital with presumed left foot cellulitis and was empirically treated with intravenous daptomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam. Despite antibiotics, the patient had persistent left foot pain and the erythema only slightly improved. On hospital day four, the patient was ambulating and developed acute worsening of the foot pain along with a deformity at the dorsum of the left foot. Repeat left foot X-ray showed multiple subluxations involving the midfoot and tarsometatarsal articulations with small cortical fractures involving the navicular and likely the medial cuneiform bone (Figure 1B). Computed tomography (CT) of the left foot showed small bony fragments projected from the navicular bone, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform bones and cuboid bone. The navicular, intermediate and lateral cuneiform bones were subluxed dorsally. These findings were consistent with Charcot foot (Figure 2). Podiatry consultation was obtained and patient was placed on strict non-weight bearing of the left foot and was discharged with a controlled ankle motion (CAM) boot and crutches. In follow up, the patient was transitioned to a Charcot restraint orthotic walker (CROW) boot and eventually to diabetic orthotic shoes (Figure 3). Surgical options were discussed, but the patient elected to be treated conservatively. A repeat left foot X-ray three years later showed a similar deformity as at the time of diagnosis. Discussion CN is a progressive deterioration of the weightbearing joints, most commonly in the foot or ankle, characterized by painful or painless bone and joint destruction 1. It occurs most often as a complication of diabetes mellitus and diabetic neuropathy, but other diseases associated with neuropathy (alcohol abuse,
2 spinal cord lesions, etc.) can also predispose to this condition 2,3. The first description of neuropathic arthritis was recorded in the 1700s as a complication of syphilis 4. In the mid-1800s, an American physician, John Kearsley Mitchell, reported cases of hot, swollen, and asymmetrical joints in patients with spinal cord injuries 5,6. In 1868, Jean-Martin Charcot, a French neurologist, identified neuropathic joints with an unusual pattern of destruction in patients with tabes dorsalis caused by syphilis and published his findings 2. At the Seventh International Medical Congress in London, Sir James Paget recognized the discovery by Charcot as a distinct pathological entity and declared that the disease be known as Charcot s disease 7. However, it was not until 1936, that the link between Charcot arthropathy and diabetes mellitus was recognized 8. Unfortunately, diagnosis is often delayed or missed as the acute Charcot foot can clinically mimic other conditions such as cellulitis or gout 3,4. A high index of suspicion is required in all patients with diabetes and neuropathy. Treatment involves immobilization and prompt consultation with orthopedic or podiatric foot specialists to preserve the ability to walk and quality of life 2. CN severely reduces the quality of life and increases morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus and neuropathy. The pathophysiologic mechanism of Charcot foot has long been debated, but it is thought to begin with peripheral neuropathy 3. Several theories have been proposed. Of these, the neurotraumatic theory and the neurovascular theory are foremost. The neurotramatic theory points to the loss of pain sensation and proprioception combined with repetitive trauma to the foot (the midfoot most commonly) leading to a complex series of pathological processes culminating in bone and joint destruction and subsequent deformity 1,9,10. However, the precise role of trauma in CN remains unclear. The Charcot process is known to progress rapidly after trauma in humans and a precipitating minor traumatic event is reported in as many as 50% of patients with Charcot foot 2. Notably, however, CN sometimes develops in non-weight bearing joints as well. A further complicating factor is that patients with neuropathy often do not recall painless trauma 1,4. The neurovascular theory proposes that the bony destruction is due to an autonomically stimulated vascular reflex that leads to increased blood flow and bone resorption and osteopenia. Combined with repetitive trauma, this eventually leads to joint and bony destruction 1,10. It is likely that a number of mechanisms operating simultaneously result in the pathology leading to CN. While multiple diseases associated with neuropathy can cause CN, diabetes mellitus is the most common cause 3,4. Most patients with CN have had poorly controlled diabetes mellitus for years. It is estimated that ~ 1-7% of diabetics with neuropathy have neuropathic arthropathy, with ~10-30% of these affected patients having bilateral involvement. The distribution of arthropathy is 70% in the midfoot and 15% at the forefoot and midfoot. The tarsometatarsal (Lisfranc s) joint is the most common site for arthropathy 2. The Eichenholtz classification system has been used to define the four stages of CN (Table 1). Each stage is associated by specific characteristics and treatment strategies 10,11. Stage 0, or the inflammation stage, is the clinical (prefracture) stage when early diagnosis and intervention are critical to prevent long-range sequelae. However, the diagnosis at this stage is commonly missed leading to progression of CN into the active destructive phase 9,12. Stage 0 is characterized by erythema, edema, and heat but no structural changed. This stage can progress if weight bearing and inflammation persist. Stage 1, or the development stage, is characterized by bone resorption and fragmentation, and joint dislocation leading to an unstable, deformed foot. Stage 2, or the coalescence stage, involves bony consolidation and fusion after bony destruction. Absorption of small bone fragments, joint fusion, and bony sclerosis are seen 2,3. Stage 3, or the reparative stage (chronic Charcot), is associated with re-stabilization of the foot with progressive fusion of the involved fragments and leads to the return of a stable, although permanently deformed, foot (rocker bottom foot deformity) 2,4,13. In patients with long-standing diabetes and peripheral neuropathy, a red, hot, swollen foot should raise the suspicion of CN 3,4. Early recognition and prompt treatment can preserve a functioning foot. Unfortunately, due to the mimicking presentations, many patients with CN are diagnosed initially with cellulitis or gout. The diagnosis of CN is missed initially 25 to 79% of the time and diagnosis is delayed on average up to 29 weeks 12. Most patients are years old and often present 2-3 months after initial symptoms, because pain is often not pronounced in half of patients 3. The earliest manifestation of CN is typically persistent swelling and discomfort 1. Approximately 50% of patients with Charcot foot remember a minor traumatic precipitating event. While trauma is not a prerequisite for CN, it can develop very rapidly after minor trauma in patients with diabetes and
3 neuropathy. A high index of suspicion for acute Charcot foot is needed for any patient with diabetes and neuropathy 2. On examination during the active stage, the foot is warm, swollen, and tender and can have marked erythema 1. The differential diagnosis includes cellulitis, osteomyelitis, acute gout, deep vein thrombosis, or neuropathic fracture 3,4,10. Infection is rare without the presence or history of an open ulceration as most diabetic foot infections began with a direct inoculation through a skin opening. Patients with CN are typically afebrile, have a normal white blood cell count, and often have no skin ulcerations making infection less likely. Ulcers frequently complicate CN, so that even in patients with plantar ulcers, it is critically important to keep the patient non-weight bearing until an acute Charcot process has been ruled out. A careful medical history is key to the diagnosis, but it is important to remember that many patients with neuropathy and altered pain sensation may be unaware of trauma or injury to the foot. In patients with a plantar ulcer, the physician should determine whether probing to the bone is possible as this is strongly correlated with osteomyelitis. While there are no laboratory criteria for the diagnosis of CN, lab testing can help narrow the differential diagnosis. Leukocytosis, and elevated C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) suggest possible infection. Bilateral weight-bearing radiographs should be obtained to determine stability. Even if there is no radiographic evidence of joint dislocation (as in stage 0 disease), CN should still be suspected so that treatment, if indicated, can be started promptly 3. In the event that the patient is neuropathic and there is no radiographic evidence of osteomyelitis, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a tagged white blood cell scan should be done. MRI can show changes in stage 0 and is extremely sensitive for osteomyelitis, but the presence of osteoarthropathy can lead to false-positive results. MRI has the highest diagnostic accuracy and is increasingly being recommended as the test of choice for diagnosing Charcot neuroarthropathy, especially in the early stages 10,14. Positron emission tomography (PET) combined with computed tomography (CT) is also gaining support and is very reliable for differentiating CN from osteomyelitis 15. Despite all these tests, differentiating CN from Charcot with infection remains difficult and bone biopsies may be necessary for a definitive diagnosis. Prompt podiatry consultation is often warranted not only for diagnostic purposes, but also to aide in treatment decisions, casting and close follow-up. The main goals of treatment include creation and maintenance of a stable foot, wound and bone healing, elimination of infection if present and prevention of deformity 3,10. For the hospitalist or primary care physician, the most important initial treatment is immediate immobilization and avoidance of weight bearing and the prompt referral to a foot and ankle specialist for further recommendations. 4 Early recognition of the Charcot syndrome and prompt treatment can minimize potential foot deformity, ulceration, and loss of function 2. Patient and family education regarding compliance are crucial. Most cases of acute Charcot foot can be treated non-surgically with pressure-relieving methods such as total contact casting (TCC) 10. The goal of TCC is to evenly distribute forces across the plantar surface of the foot. TCC is utilized until the erythema and edema have resolved, the temperature of the foot has normalized, and radiographs show stabilization (generally 8-12 weeks but maybe longer) 16. Foot ulcers may require surgical debridement and antibiotic therapy prior to the application of TCC. After initial radiographs, surveillance films should be taken at 4-6 weeks intervals. When the active phase of the Charcot process is complete, as evidenced by resolution of swelling and erythema and radiographic stability, the TCC is often converted to a Charcot restraint orthotic walker (CROW) boot for a total of 4-6 months of treatment 16. Protective footgear with orthotics may also be needed at a later time. Some studies have reported that the use of a bisphosphonate (pamidronate) results in symptomatic relief with decreased erythema, decreased temperature and decreased Charcot activity 1,17. Surgical treatment is sometimes necessary but is typically reserved for acute fracture or dislocation, severe deformity, or recurrent ulceration 3. Complications are common and include recurrent ulceration, need for prolonged bracing and even amputation 10. All physicians should be vigilant and consider the diagnosis of Charcot foot in neuropathic patients who present with foot or ankle erythema, edema, and elevated temperature. Any minor injury in patients with diabetes and neuropathy requires careful observation because of the tendency of the limb to proceed to a Charcot process. Early identification and treatment of the Charcot process helps prevent deformity and decreased function of the lower extremity, as well as possible subsequent amputation. Patients with an established neuropathic foot should
4 be seen regularly and physicians should provide continuous education about the proper care of the foot and the use of orthotic devices. A multidisciplinary approach with podiatry consultation and co-management is necessary whenever CN is suspected. REFERENCES 1. Rajbhandari SM, Jenkins RC, Davies C, Tesfaye S. Charcot neuroarthropathy in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia Aug;45(8): Epub 2002 Jul 11. Review. PubMed PMID: Sommer TC, Lee TH. Charcot foot: the diagnostic dilemma. Am Fam Physician Nov 1;64(9): Review. Erratum in: Am Fam Physician 2002 Jun 15;65(12): PubMed PMID: Botek G, Anderson MA, Taylor R. Charcot neuroarthropathy: An often overlooked complication of diabetes. Cleve Clin J Med Sep;77(9): doi: /ccjm.77a Review. PubMed PMID: Wukich DK, Sung W. Charcot arthropathy of the foot and ankle: modern concepts and management review. J Diabetes Complications Nov-Dec;23(6): doi: /j.jdiacomp Epub 2008 Oct 17. Review. PubMed PMID: Mitchell JK. On a new practice in acute and chronic rheumatism. American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 1831;1: Mitchell SW, Morehouse GR, Keen WW, editors. Gunshot wounds and other injuries of the nerves. Philadelphia: J.B. Lippincott & Co; p MacCormac W, Klockmann JW, editors. Transaction of the international medical congress: seventh session held in London, August 2-9, London: Balantyne, Hanson & Co. 8. Jordan WR. Neuritic manifestations in diabetes mellitus. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1936;57: Chantelau E. The perils of procrastination: effects of early vs. delayed detection and treatment of incipient Charcot fracture. Diabet Med Dec;22(12): PubMed PMID: Schon L, Shatby W. What is the best treatment for a Charcot foot and ankle? In: Wright JG, editor. Evidencebased orthopaedics: the best answers to clinical questions. Chapter 74. Saunders Elsevier; Kelikian AS. Operative treatment of the foot and ankle. Stamford, Conn.: Appleton & Lange,1999: Wukich DK, Sung W, Wipf SA, Armstrong DG. The consequences of complacency: managing the effects of unrecognized Charcot feet. Diabet Med Feb;28(2): doi: /j x. PubMed PMID: Eichenholtz SN. Charcot joints. Springfield, Ill.: Thomas, Tan PL, Teh J. MRI of the diabetic foot: differentiation of infection from neuropathic change. Br J Radiol Nov;80(959): Epub 2006 May 10. Review. PubMed PMID: Basu S, Chryssikos T, Houseni M, Scot Malay D, Shah J, Zhuang H, Alavi A. Potential role of FDG PET in the setting of diabetic neuro-osteoarthropathy: can it differentiate uncomplicated Charcot's neuroarthropathy from osteomyelitis and soft-tissue infection? Nucl Med Commun Jun;28(6): PubMed PMID: Frykberg RG, Zgonis T, Armstrong DG, Driver VR, Giurini JM, Kravitz SR, Landsman AS, Lavery LA, Moore JC, Schuberth JM, Wukich DK, Andersen C, Vanore JV; American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons. Diabetic foot disorders. A clinical practice guideline (2006 revision). J Foot Ankle Surg Sep- Oct;45(5 Suppl):S1-66. PubMed PMID: Selby PL, Young MJ, Boulton AJ. Bisphosphonates: a new treatment for diabetic Charcot neuroarthropathy? Diabet Med Jan-Feb;11(1): PubMed PMID: Submitted on February 13, 2014 Table 1. Charcot Foot Classification, Description * A. Stage 0 Clinical, inflammation a. Warm, erythematous, edematous foot b. No structural changes B. Stage 1 Fragmentation, development a. Periarticular fractures, joint dislocation, unstable, deformed foot b. Radiographic changes evident C. Stage 2 Coalescence a. Reabsorption of bone debris b. Joint fusion, bony sclerosis seen D. Stage 3 Reparative, chronic Charcot a. Stable foot with deformities b. Progressive fusion, decreased sclerosis *adapted from Sommer TC, Lee TH. Charcot foot: The diagnostic dilemma. American Family Physician Nov 1;64(9): and Wukich DK, Sung W. Charcot arthropathy of the foot and ankle: Modern concepts and management review. Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications. 2009;23:
5 Figure 2: CT of left foot showed subluxations confirming the diagnosis of Charcot foot Figure 1A: Left foot x-ray on admission. Figure 3: Controlled Ankle Motion (CAM) boot (left) and Charcot Restraint Orthotic Walker (CROW) boot (right). Figure 1B: Left foot x-ray 4 days later showing subluxations at the dorsum of mid foot.
Charcot Arthropathy of the Foot & Ankle. MTAPA Annual Meeting June 2018 Emily Harnden, MD
 Charcot Arthropathy of the Foot & Ankle MTAPA Annual Meeting June 2018 Emily Harnden, MD Background Disclosures None Learning Objectives Define the disease Recognize presenting signs/symptoms for proper
Charcot Arthropathy of the Foot & Ankle MTAPA Annual Meeting June 2018 Emily Harnden, MD Background Disclosures None Learning Objectives Define the disease Recognize presenting signs/symptoms for proper
Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA
 Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA Charcot 1. What is it? (definition) & Who gets it? (epidemiology
Diabetic Neuropathic Arthropathy (Charcot) Kiwon Young M.D. ( 양기원 ) Eulji Hospital Dept of Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Clinic Seoul, KOREA Charcot 1. What is it? (definition) & Who gets it? (epidemiology
The Charcot Foot. Brian J Burgess, DPM, AACFAS Hinsdale Orthopaedic Assoc. Midwest Podiatry Conference April 19, 2013
 The Charcot Foot Brian J Burgess, DPM, AACFAS Hinsdale Orthopaedic Assoc. Midwest Podiatry Conference April 19, 2013 Brian J Burgess, DPM, AACFAS Associate of Hinsdale Orthopaedics. Doctor of Podiatric
The Charcot Foot Brian J Burgess, DPM, AACFAS Hinsdale Orthopaedic Assoc. Midwest Podiatry Conference April 19, 2013 Brian J Burgess, DPM, AACFAS Associate of Hinsdale Orthopaedics. Doctor of Podiatric
CHARCOT FOOT. What Should we Know?? I Wayan Subawa. Orthopaedi & Traumatology Subdivision Udayana University Sanglah General Hospital, Denpasar-Bali
 CHARCOT FOOT What Should we Know?? I Wayan Subawa Orthopaedi & Traumatology Subdivision Udayana University Sanglah General Hospital, Denpasar-Bali INTRODUCTION Peripheral Neuropathy The most insidious
CHARCOT FOOT What Should we Know?? I Wayan Subawa Orthopaedi & Traumatology Subdivision Udayana University Sanglah General Hospital, Denpasar-Bali INTRODUCTION Peripheral Neuropathy The most insidious
Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora
 Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora 8 ICD-9 CODE 838.03 Lisfranc (Tarsometatarsal) Fracture-Dislocation Key Concepts The Lisfranc joint represents
Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Chapter 194 Lisfranc Injuries Hany El-Rashidy and Anand Vora 8 ICD-9 CODE 838.03 Lisfranc (Tarsometatarsal) Fracture-Dislocation Key Concepts The Lisfranc joint represents
Aetiology Macroangiopathy occurs mainly distally ie Popliteal artery There is arterial wall calcification Microangiopathy is less common
 DIABETIC FOOT Facts 5% of the population is diabetic 12% of diabetic admissions are with foot problems 1/3rd of diabetic foot ulcerations are neuropathic, 1/3rd are ischaemic and 1/3 are of a mixed in
DIABETIC FOOT Facts 5% of the population is diabetic 12% of diabetic admissions are with foot problems 1/3rd of diabetic foot ulcerations are neuropathic, 1/3rd are ischaemic and 1/3 are of a mixed in
Clinical Guideline for: Diagnosis and Management of Charcot Foot
 Clinical Guideline for: Diagnosis and Management of Charcot Foot SUMMARY This guideline outlines the clinical features of Charcot foot (Charcot Neuroarthropathy). It also explains the process of diagnosis
Clinical Guideline for: Diagnosis and Management of Charcot Foot SUMMARY This guideline outlines the clinical features of Charcot foot (Charcot Neuroarthropathy). It also explains the process of diagnosis
Introduction. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment
 Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
 Injury Extra (2008) 39, 291 295 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
Injury Extra (2008) 39, 291 295 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
Diabetic Foot Complications
 Diabetic Foot Complications Podiatry Specialty Clinic YKHC Bethel, Alaska August 1-3, 2017 Charles C. Edwards, DPM Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Peripheral Neuropathy Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Diabetic Foot Complications Podiatry Specialty Clinic YKHC Bethel, Alaska August 1-3, 2017 Charles C. Edwards, DPM Alaska Native Tribal Health Consortium Peripheral Neuropathy Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped
 Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped First Described in 1883 as osteoarthropathy seen in cases of syphilis The typical presentation of the rocker bottom foot As imaging techniques improved the extent of severity
Jack W. Hutter DPM, FACFAS, C.ped First Described in 1883 as osteoarthropathy seen in cases of syphilis The typical presentation of the rocker bottom foot As imaging techniques improved the extent of severity
I also call this lecture
 I also call this lecture GO BUCKS!!! My Background Cornerstone University Grand Rapids, MI Kent State University College of Podiatric Medicine (OCPM) Florida Hospital East Orlando 3 year surgical residency
I also call this lecture GO BUCKS!!! My Background Cornerstone University Grand Rapids, MI Kent State University College of Podiatric Medicine (OCPM) Florida Hospital East Orlando 3 year surgical residency
Anchoring Bias in the Case of Charcot s Foot. By: Vadieh Hamidi. Home for the Summer Program July to August Portage La Prairie, Manitoba
 Anchoring Bias in the Case of Charcot s Foot By: Vadieh Hamidi Home for the Summer Program July to August 2018 Portage La Prairie, Manitoba Supervisor: Dr. Brett Finney 1 Abstract During my six-week Home
Anchoring Bias in the Case of Charcot s Foot By: Vadieh Hamidi Home for the Summer Program July to August 2018 Portage La Prairie, Manitoba Supervisor: Dr. Brett Finney 1 Abstract During my six-week Home
Foot and Ankle Pearls
 Foot and Ankle Pearls Steve Milner Consultant Trauma, Orthopaedic and Foot & Ankle Surgeon Royal Derby Hospital Foot and Ankle PERILS Steve Milner Consultant Trauma, Orthopaedic and Foot & Ankle Surgeon
Foot and Ankle Pearls Steve Milner Consultant Trauma, Orthopaedic and Foot & Ankle Surgeon Royal Derby Hospital Foot and Ankle PERILS Steve Milner Consultant Trauma, Orthopaedic and Foot & Ankle Surgeon
Resection Arthroplasty for Limb Salvage of the Unreconstructable Charcot Foot & Ankle
 Resection Arthroplasty for Limb Salvage of the Unreconstructable Charcot Foot & Ankle Michael Greaser MD and James Brodsky MD Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, TX Resection Arthroplasty for Limb
Resection Arthroplasty for Limb Salvage of the Unreconstructable Charcot Foot & Ankle Michael Greaser MD and James Brodsky MD Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, TX Resection Arthroplasty for Limb
Protected Weight Bearing During Treatment of Acute Charcot Neuroarthropathy: A case series
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Protected Weight Bearing During Treatment of Acute Charcot Neuroarthropathy: A case series by Jeremy
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Protected Weight Bearing During Treatment of Acute Charcot Neuroarthropathy: A case series by Jeremy
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations
 Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations Case Study F: Lisfranc s Midfoot Dislocation Clinical History: J.K. a 28 year old female presents complaining of a painful right foot. She sustained an acute
Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations Case Study F: Lisfranc s Midfoot Dislocation Clinical History: J.K. a 28 year old female presents complaining of a painful right foot. She sustained an acute
Management Of The Diabetic foot
 Management Of The Diabetic foot Aims, Pathways, Treatments Nikki Coates 12/1/18 Diabetic foot pathology Neuropathy Foot deformity Vascular disease Sensory neuropathy Limited Joint Mobility Smoking Autonomic
Management Of The Diabetic foot Aims, Pathways, Treatments Nikki Coates 12/1/18 Diabetic foot pathology Neuropathy Foot deformity Vascular disease Sensory neuropathy Limited Joint Mobility Smoking Autonomic
Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot. Glossary of Terms
 Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Warren Woods, Certified Orthotist, Health Sciences Centre, Rehabilitation Engineering Department What you need to know Glossary of Terms Neuropathic
Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Warren Woods, Certified Orthotist, Health Sciences Centre, Rehabilitation Engineering Department What you need to know Glossary of Terms Neuropathic
Charcot s Neuroarthropathy: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 1 Kotwal N et al. Charcot s Neuroarthropathy: A Case Report and Review of Literature Vimal Upreti *, Narendra Kotwal *, Vishesh Verma *, Shrikant Somani *, Yogesh Kumar * Abstract Charcot s neuroarthropathy
1 Kotwal N et al. Charcot s Neuroarthropathy: A Case Report and Review of Literature Vimal Upreti *, Narendra Kotwal *, Vishesh Verma *, Shrikant Somani *, Yogesh Kumar * Abstract Charcot s neuroarthropathy
Diabetes Mellitus and the Associated Complications
 Understanding and the complications relating to the disease can assist the fitter to better serve patients. and the Associated Complications Released January, 2011 Total: 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of
Understanding and the complications relating to the disease can assist the fitter to better serve patients. and the Associated Complications Released January, 2011 Total: 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of
pedcat Clinical Case Studies
 pedcat Clinical Case Studies C u r v e B e a m 1 7 5 T i t u s A v e, S u i t e 3 0 0 W a r r i n g t o n, P A 1 8 9 7 6 267-4 8 3-8081 w w w. c u r v e b e a m. c o m PedCAT: Clinical Evidence of diagnostic
pedcat Clinical Case Studies C u r v e B e a m 1 7 5 T i t u s A v e, S u i t e 3 0 0 W a r r i n g t o n, P A 1 8 9 7 6 267-4 8 3-8081 w w w. c u r v e b e a m. c o m PedCAT: Clinical Evidence of diagnostic
10/19/2017. Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI. Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis
 Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis Understand the systemic effects of diabetes on the lower extremity The significance of structural and biomechanical
Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis Understand the systemic effects of diabetes on the lower extremity The significance of structural and biomechanical
Charcot Foot: Potential Pearls from Parkland
 Charcot Foot: Potential Pearls from Parkland Javier La Fontaine, D.P.M., M.S. Professor Department of Plastic Surgery UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, Texas Objectives To share the experience from
Charcot Foot: Potential Pearls from Parkland Javier La Fontaine, D.P.M., M.S. Professor Department of Plastic Surgery UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, Texas Objectives To share the experience from
Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태
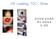 Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태 DMF Protocol VIPS approach V : Vascular I : infection P : Pressure off S : specific wound care Ulcer/Pressure off& Biomechanics PVD vs Peripheral neuropathy NP
Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태 DMF Protocol VIPS approach V : Vascular I : infection P : Pressure off S : specific wound care Ulcer/Pressure off& Biomechanics PVD vs Peripheral neuropathy NP
Increased pressures at
 Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Surgical Off-loading of Plantar Hallux Ulcerations These approaches can be used to treat DFUs. By Adam R. Johnson, DPM Increased pressures at the plantar aspect of the hallux leading to chronic hyperkeratosis
Case 1. July 14, th week wound gel 3 cm x 2.5 cm = 7.5 cm². May 25, st wound gel on 290 days PI treatment 4 cm x 2.4 cm = 9.
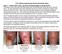 2.5% Sodium Hyaluronate Wound Gel Study Cases Case 1 Patient with Lower Leg Ulcer Not Responding to Compression This patient was a 50-year old male patient with nonhealing right lower leg since January
2.5% Sodium Hyaluronate Wound Gel Study Cases Case 1 Patient with Lower Leg Ulcer Not Responding to Compression This patient was a 50-year old male patient with nonhealing right lower leg since January
Rocker bottom foot in diabetic patients - a severe deformity of the diabetic Charcot s joint with serious sequelae
 Rocker bottom foot in diabetic patients - a severe deformity of the diabetic Charcot s joint with serious sequelae Poster No.: P-0079 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: J. Brtkova, T.
Rocker bottom foot in diabetic patients - a severe deformity of the diabetic Charcot s joint with serious sequelae Poster No.: P-0079 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: J. Brtkova, T.
Page 1 of 6. Appendix 1
 Page 1 Appendix 1 Rotation Objectives and Schedule 1. Introductory Month 4 weeks 2. Total Joints 4 weeks a. Diagnosis and management of hip and knee arthritis b. Indications for surgery c. Implant selection;
Page 1 Appendix 1 Rotation Objectives and Schedule 1. Introductory Month 4 weeks 2. Total Joints 4 weeks a. Diagnosis and management of hip and knee arthritis b. Indications for surgery c. Implant selection;
Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery
 PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
Foot and ankle fractures
 Foot and ankle fractures Some fractures can be managed without surgery, but others require surgery to achieve the best possible outcome. Fractures and injuries to joints have a high risk of developing
Foot and ankle fractures Some fractures can be managed without surgery, but others require surgery to achieve the best possible outcome. Fractures and injuries to joints have a high risk of developing
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Prevalence of Symptomatic Venous Thrombo-Embolism in Patients with Total Contact Cast for Diabetic foot Complications A Retrospective Case Series.
 Prevalence of Symptomatic Venous Thrombo-Embolism in Patients with Total Contact Cast for Diabetic foot Complications A Retrospective Case Series. Dr R King, Miss GE Jackson, Mr SR Platt Wirral University
Prevalence of Symptomatic Venous Thrombo-Embolism in Patients with Total Contact Cast for Diabetic foot Complications A Retrospective Case Series. Dr R King, Miss GE Jackson, Mr SR Platt Wirral University
Diabetic charcot neuroarthropathy: prevalence, demographics and outcome in a regional referral centre
 Ir J Med Sci (2017) 186:151 156 DOI 10.1007/s11845-016-1508-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diabetic charcot neuroarthropathy: prevalence, demographics and outcome in a regional referral centre A. O Loughlin 1 E. Kellegher
Ir J Med Sci (2017) 186:151 156 DOI 10.1007/s11845-016-1508-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diabetic charcot neuroarthropathy: prevalence, demographics and outcome in a regional referral centre A. O Loughlin 1 E. Kellegher
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C. Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Objectives Identify Diabetic/Neuropathic
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Objectives Identify Diabetic/Neuropathic
Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Ulcer Assessment Guide South West Regional Wound Care Program Last Updated April 7,
 Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL
 C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
9/22/2017. I am a local. Born at Desert Samaritan
 I am a local Born at Desert Samaritan 1 MOUNTAIN VIEW HIGH SCHOOL ASU U OF IOWA MED SCHOOL PHOENIX FOR RESIDENCY 2 Discuss the 5 most controversial topics in foot and ankle Injuries that are routinely
I am a local Born at Desert Samaritan 1 MOUNTAIN VIEW HIGH SCHOOL ASU U OF IOWA MED SCHOOL PHOENIX FOR RESIDENCY 2 Discuss the 5 most controversial topics in foot and ankle Injuries that are routinely
Index. Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) 865 869 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alpha-lipoic acid, in diabetic neuropathy, 764 Amputation(s), lower-extremity, in diabetes, 791
Foot Ankle Clin N Am 11 (2006) 865 869 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alpha-lipoic acid, in diabetic neuropathy, 764 Amputation(s), lower-extremity, in diabetes, 791
The Charcot Foot. Lee C. Rogers, DPM a,b, *, Robert G. Frykberg, DPM, MPH c
 The Charcot Foot Lee C. Rogers, DPM a,b, *, Robert G. Frykberg, DPM, MPH c KEYWORDS Charcot foot Neuroarthropathy Joints Soft tissues KEY POINTS Charcot foot is primarily a clinical diagnosis at its earliest
The Charcot Foot Lee C. Rogers, DPM a,b, *, Robert G. Frykberg, DPM, MPH c KEYWORDS Charcot foot Neuroarthropathy Joints Soft tissues KEY POINTS Charcot foot is primarily a clinical diagnosis at its earliest
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
The Great Debate: Offloading Diabetic Foot Ulcers: TCC vs. CAM Walkers Gregory A Bohn, MD MAPWCA, ABPM/UHMS
 The Great Debate: Offloading Diabetic Foot Ulcers: TCC vs. CAM Walkers Gregory A Bohn, MD MAPWCA, ABPM/UHMS Department of Surgery Central Michigan School of Medicine Tawas, Michigan Disclosures Medical/Scientific
The Great Debate: Offloading Diabetic Foot Ulcers: TCC vs. CAM Walkers Gregory A Bohn, MD MAPWCA, ABPM/UHMS Department of Surgery Central Michigan School of Medicine Tawas, Michigan Disclosures Medical/Scientific
Surgical Off-loading. Reiber et al Goals of Diabetic Foot Surgery 4/28/2012. The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration
 Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Working Under Pressure is Not Always. a Good Thing. Kathya M. Zinszer, DPM, MPH, MAPWCA. Geisinger Hospital System Orthopedics Department Danville, PA
 Working Under Pressure is Not Always a Good Thing Kathya M. Zinszer, DPM, MPH, MAPWCA Geisinger Hospital System Orthopedics Department Danville, PA Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Working Under Pressure is Not Always a Good Thing Kathya M. Zinszer, DPM, MPH, MAPWCA Geisinger Hospital System Orthopedics Department Danville, PA Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose.
Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities
 Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities The following table provides the description for several foot deformities: hammer toe, claw toe, hallux deformity, pes planus, pes cavus and charcot arthropathy.
Appendix H: Description of Foot Deformities The following table provides the description for several foot deformities: hammer toe, claw toe, hallux deformity, pes planus, pes cavus and charcot arthropathy.
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Orthopaedic Surgery and the Diabetic Charcot Foot
 Orthopaedic Surgery and the Diabetic Charcot Foot Wei Shen, MD, PhD, Dane Wukich, MD* KEYWORDS Diabetes Foot Charcot Orthopaedic surgery KEY POINTS Due to the systemic manifestations of diabetes mellitus
Orthopaedic Surgery and the Diabetic Charcot Foot Wei Shen, MD, PhD, Dane Wukich, MD* KEYWORDS Diabetes Foot Charcot Orthopaedic surgery KEY POINTS Due to the systemic manifestations of diabetes mellitus
H: Orthopedic Nursing
 H: Orthopedic Nursing Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 87 Competency: H-1 Knowledge of H-1-1 H-1-2 H-1-3 H-1-4 H-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge of human anatomy and physiology, specifically
H: Orthopedic Nursing Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 87 Competency: H-1 Knowledge of H-1-1 H-1-2 H-1-3 H-1-4 H-1-5 Demonstrate knowledge of human anatomy and physiology, specifically
AIM OF MASTERCLASS. Overview of the diabetic foot disease. Modern approach to management
 AIM OF MASTERCLASS Overview of the diabetic foot disease Modern approach to management DIABETIC FOOT DISEASE THROUGHOUT THE WORLD, THERE IS AN AMPUTATION EVERY 20 SECONDS MOST OF THESE AMPUTATIONS ARE
AIM OF MASTERCLASS Overview of the diabetic foot disease Modern approach to management DIABETIC FOOT DISEASE THROUGHOUT THE WORLD, THERE IS AN AMPUTATION EVERY 20 SECONDS MOST OF THESE AMPUTATIONS ARE
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Diabetes Metab. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 July 07.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Diabetes Metab. 2013 November 1; 4(9): 310. doi:10.4172/2155-6156.1000310. Foreign Body with Gas Gangrene in an Elderly Patient
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Diabetes Metab. 2013 November 1; 4(9): 310. doi:10.4172/2155-6156.1000310. Foreign Body with Gas Gangrene in an Elderly Patient
bilateral, both before below elbow twice a day below knee bedrest
 Abbreviations Student Name: A approximately assessment assist active active assist abdominal aortic aneurysm active assistive range of motion abduction/adduction acromioclavicular joint anterior cruciate
Abbreviations Student Name: A approximately assessment assist active active assist abdominal aortic aneurysm active assistive range of motion abduction/adduction acromioclavicular joint anterior cruciate
Conservative Management to Restore and Maintain Function in Limb Preservation Patients
 Conservative Management to Restore and Maintain Function in Limb Preservation Patients Tyson Green, DPM Department Chair Imperial Health Center for Orthopaedics Lake Charles, LA Founder & Medical Director
Conservative Management to Restore and Maintain Function in Limb Preservation Patients Tyson Green, DPM Department Chair Imperial Health Center for Orthopaedics Lake Charles, LA Founder & Medical Director
THE DIABETIC FOOT. Nicola Kilburn Diabetes Specialist Podiatrist
 THE DIABETIC FOOT Nicola Kilburn Diabetes Specialist Podiatrist Diabetic foot disease is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Foot screening is effective in identifying an individuals risk
THE DIABETIC FOOT Nicola Kilburn Diabetes Specialist Podiatrist Diabetic foot disease is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Foot screening is effective in identifying an individuals risk
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
out of primary care Taking care of your The Boot? Department of Orthopaedics Erica V. Eshoo, NP SFGH
 The Boot? Taking care of your patient s toes in and out of primary care Erica V. Eshoo, NP Department of Orthopaedics SFGH http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_m64cy 1MMPg Objectives Topics Recognizing and
The Boot? Taking care of your patient s toes in and out of primary care Erica V. Eshoo, NP Department of Orthopaedics SFGH http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_m64cy 1MMPg Objectives Topics Recognizing and
AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION. Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot)
 AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot) Introduction - The Australian Wound Management Association Education & Professional Development Sub Committee-(AWMA
AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot) Introduction - The Australian Wound Management Association Education & Professional Development Sub Committee-(AWMA
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Care for Patients in All Settings
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer. The scope of the standard
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer. The scope of the standard
Pilon Fractures - OrthoInfo - AAOS. Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Pilon Fractures
 Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Pilon Fractures Pilon fractures affect the bottom of the shinbone (tibia) at the ankle joint. In most cases, both bones in the lower leg, the tibia
Copyright 2010 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Pilon Fractures Pilon fractures affect the bottom of the shinbone (tibia) at the ankle joint. In most cases, both bones in the lower leg, the tibia
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER:
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER:
«Foot & Ankle Surgery» 04. Sept THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT. Norman Espinosa, MD
 THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT Norman Espinosa, MD Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich Balgrist Switzerland www.balgrist.ch WHAT TO DO? INTRINSIC > EXTRINSIC ETIOLOGIES Repetitive microtrauma combined
THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT Norman Espinosa, MD Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich Balgrist Switzerland www.balgrist.ch WHAT TO DO? INTRINSIC > EXTRINSIC ETIOLOGIES Repetitive microtrauma combined
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome 950 Breckinridge Lane Suite 220 Louisville, KY 40223 Phone: 502.708.2940 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Pain Management: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome 950 Breckinridge Lane Suite 220 Louisville, KY 40223 Phone: 502.708.2940 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care
 The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Care of the Diabetic Patient
 Care of the Diabetic Patient Aarti Deshpande, CPO Clinic Manager Zuckerberg San Francisco General Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, San Francisco March 16, 2017 Diabetes Diabetes
Care of the Diabetic Patient Aarti Deshpande, CPO Clinic Manager Zuckerberg San Francisco General Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, San Francisco March 16, 2017 Diabetes Diabetes
Minimally Invasive Closing Wedge Osteotomy for Charcot Correction
 AOFAS 2015 Long Beach, California DISCLOSURES* Minimally Invasive Closing Wedge Osteotomy for Charcot Correction Vernois* Miss Ros Miller FRCS Tr&Orth Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Hairmyres Hospital,
AOFAS 2015 Long Beach, California DISCLOSURES* Minimally Invasive Closing Wedge Osteotomy for Charcot Correction Vernois* Miss Ros Miller FRCS Tr&Orth Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Hairmyres Hospital,
Section 6: Preoperative Planning
 Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Management of Charcot Arthropathy
 Review Article Management of Charcot Arthropathy Shahnooshi Javad F* Department of Pharmacy Practice, Krupandhi College of Pharmacy, Chikkabellandur Village, Varthur Hobli, Bangalore 560035, India. J.
Review Article Management of Charcot Arthropathy Shahnooshi Javad F* Department of Pharmacy Practice, Krupandhi College of Pharmacy, Chikkabellandur Village, Varthur Hobli, Bangalore 560035, India. J.
Case Presentation. The Failure to Diagnose Sepsis. chills. pain out of proportion to mechanism. low-grade fever. tachycardia that does not make sense
 Case Presentation The Failure to Diagnose Sepsis Sepsis is a regular visitor in the news as cases of flesh-eating bacteria and the dramatic speed with which victims deteriorate hit the headlines. The failure
Case Presentation The Failure to Diagnose Sepsis Sepsis is a regular visitor in the news as cases of flesh-eating bacteria and the dramatic speed with which victims deteriorate hit the headlines. The failure
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN EARLY STAGE CHARCOT ARTHROPATHY CORRELATION OF IMAGING FINDINGS AND CLINICAL SYMPTOMS
 September 22, 2008 EU RO PE AN JOUR NAL OF MED I CAL RE SEARCH 409 Eur J Med Res (2008) 13: 409-414 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2008 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN EARLY STAGE CHARCOT ARTHROPATHY CORRELATION
September 22, 2008 EU RO PE AN JOUR NAL OF MED I CAL RE SEARCH 409 Eur J Med Res (2008) 13: 409-414 I. Holzapfel Publishers 2008 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING IN EARLY STAGE CHARCOT ARTHROPATHY CORRELATION
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists
 EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
Lesser metatarsal cuneiform joint fusion for the treatment of midfoot osteoarthritis. Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery
 Lesser metatarsal cuneiform joint fusion for the treatment of midfoot osteoarthritis Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is midfoot osteoarthritis? Midfoot arthritis is 'wear
Lesser metatarsal cuneiform joint fusion for the treatment of midfoot osteoarthritis Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is midfoot osteoarthritis? Midfoot arthritis is 'wear
MRI of Diabetic foot - appearances and mimics, a pictorial review
 MRI of Diabetic foot - appearances and mimics, a pictorial review Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Dutta, M. George; Singapore/SG Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint,
MRI of Diabetic foot - appearances and mimics, a pictorial review Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Dutta, M. George; Singapore/SG Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint,
2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Measure #127 (NQF 0416): Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Ulcer Prevention Evaluation of Footwear National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Measure #127 (NQF 0416): Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Ulcer Prevention Evaluation of Footwear National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2017 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES:
Developing an evidence-based clinical pathway for the assessment, diagnosis and management of acute Charcot Neuro-Arthropathy: a systematic review
 Milne et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2013, 6:30 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH REVIEW Open Access Developing an evidence-based clinical pathway for the assessment, diagnosis and management
Milne et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2013, 6:30 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH REVIEW Open Access Developing an evidence-based clinical pathway for the assessment, diagnosis and management
Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
A Prospective Study on Fractured Tarsal Navicular Bone in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital
 Original article: A Prospective Study on Fractured Tarsal Navicular Bone in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital Mohammad Azmoddin 1, Surender Rao Yadagiri 2 1Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
Original article: A Prospective Study on Fractured Tarsal Navicular Bone in a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital Mohammad Azmoddin 1, Surender Rao Yadagiri 2 1Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Multisciplinary Team and Diabetic Foot Syndrome
 Multisciplinary Team and Diabetic Foot Syndrome Giacomo Clerici MD Roberto Ferraresi MD Amputation Prevention Centre Humanitas Hospitals Group Milan and Bergamo giacomoclerici@me.com Twitter @diabeticfoot1
Multisciplinary Team and Diabetic Foot Syndrome Giacomo Clerici MD Roberto Ferraresi MD Amputation Prevention Centre Humanitas Hospitals Group Milan and Bergamo giacomoclerici@me.com Twitter @diabeticfoot1
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery
 Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery Bunion surgery is generally reserved for bunions that are severe and impacting on function. There most frequent surgical procedure used involves a medial incision
Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery Bunion surgery is generally reserved for bunions that are severe and impacting on function. There most frequent surgical procedure used involves a medial incision
Predicting & Preventing Diabetic Ulcerations Utilizing Computerized Pressure Gait Analysis
 Predicting & Preventing Diabetic Ulcerations Utilizing Computerized Pressure Gait Analysis Jeffrey A. Ross, DPM, MD, FACFAS, FAPWCA Associate Clinical Professor Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas
Predicting & Preventing Diabetic Ulcerations Utilizing Computerized Pressure Gait Analysis Jeffrey A. Ross, DPM, MD, FACFAS, FAPWCA Associate Clinical Professor Baylor College of Medicine Houston, Texas
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Limping in Children 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Ulcer Assessment Guide South West Regional Wound Care Program Last Updated June 10,
 Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
OSTEOMYELITIS. If it occurs in adults, then the axial skeleton is the usual site.
 OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
Diabetes and malleolar fractures
 Diabetes and malleolar fractures Frank Linde Foot and ankle section Department of Orthopaedics University Hospital of Aarhus Diabetic complications and unstable malleolar fractures 40% risk of serious
Diabetes and malleolar fractures Frank Linde Foot and ankle section Department of Orthopaedics University Hospital of Aarhus Diabetic complications and unstable malleolar fractures 40% risk of serious
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #127 (NQF 0416): Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Ulcer Prevention Evaluation of Footwear National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL
Quality ID #127 (NQF 0416): Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Ulcer Prevention Evaluation of Footwear National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL
Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot
 Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot Dane K. Wukich M.D. Chief, Division of Foot and Ankle Surgery Medical Director, UPMC Foot and Ankle Center University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosure
Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot Dane K. Wukich M.D. Chief, Division of Foot and Ankle Surgery Medical Director, UPMC Foot and Ankle Center University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosure
1 of :19
 1 of 8 3-12-2012 12:19 Diabetic foot ulcer classification system for research purposes Introduction Aims of the ulcer research classification system Definitions and categorisation for the ulcer research
1 of 8 3-12-2012 12:19 Diabetic foot ulcer classification system for research purposes Introduction Aims of the ulcer research classification system Definitions and categorisation for the ulcer research
Project I - Background Worksheet. Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu. Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers
 Project I - Background Worksheet Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers 1) Strategic Focus based on the Strategic focus powerpoint presentation and readings a. Team
Project I - Background Worksheet Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers 1) Strategic Focus based on the Strategic focus powerpoint presentation and readings a. Team
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
WHAT IS AN ARTHRODESIS? (FUSION)
 Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS AN ARTHRODESIS? (FUSION) An Arthrodesis or fusion is an operation performed to
Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS AN ARTHRODESIS? (FUSION) An Arthrodesis or fusion is an operation performed to
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS. Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2
 NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
