OSTEOARTHRITIS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research
|
|
|
- Jeffery Warner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 infoaging guides DISEASES OF AGING OSTEOARTHRITIS An introduction to aging science brought to you by the American Federation for Aging Research
2 WHAT IS OSTEOARTHRITIS? Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disease and involves damage to and loss of cartilage as well as overgrowth of bone within the joints. This overgrowth often takes the form of bony spurs. Some people with OA can also have synovitis, an inflammation in the joint lining. In the knee joint, there can be damage to the meniscus and joint ligaments. Damage to the cartilage, meniscus, ligament, and bone, as well as the synovitis can cause pain, deformities, and even disability. Indeed, osteoarthritis is the leading cause of disability among older adults. Most of us will develop the early cellular changes of OA in our knees by age 60. Fortunately, not all of us will have changes severe enough to cause symptoms. As we age, the total number of our cartilage cells decreases. Further, these cells ability to repair joint damage declines. If a proper balance between joint damage and joint repair is not maintained, the cartilage becomes worn or ragged. The cartilage cells, called chondrocytes, release cytokines, chemical messengers that activate neighboring chondrocytes as well as bony cells, or osteoblasts, and the joint lining cells. The bone cells respond by creating small bits of new bone that can irritate the joint. Likewise, the bone cells and joint lining cells release cytokines and growth factors, which can act on the chondrocytes and cause further destruction. And if you use a joint lined with ragged cartilage and bony spurs, you feel pain. Eventually, you may also experience chronic swelling that limits the joint s movement. OA is distinct from rheumatoid arthritis, which involves Aging, by itself, does not cause Osteoarthritis (OA), but the changes that take place in cells and joints as we age allow OA to develop more easily. disturbances in an individual s immune system. These disturbances can cause the person s body to have an inappropriate immune response to its own tissue. DIAGNOSING OSTEOARTHRITIS Patient history and a physical examination provide most of the information needed to make a diagnosis of OA. Joint pain generally comes on gradually and may involve only a single joint. OA can produce morning stiffness, which usually lasts only 15 to 30 minutes and typically improves with movement. Over time, the mobility of the affected joints decreases, and they can become tender to the touch. Cracking and crackling can be heard. Overgrowth of bone as well as the surrounding tissues can produce permanent swelling and joint enlargement. There are no blood tests to diagnose OA, distinguishing it from rheumatoid arthritis and gout, for 2 Infoaging Guide to Osteoarthritis
3 which confirmatory blood tests are available. Some imaging tests can confirm the suspicion of OA. They include: X-Rays. X-rays of the bones and joints in a patient suspected of having OA will show narrowing of the spaces that should be seen in joints, thickening of the bone that lines the joints and the formation of bone spurs. X-rays can also show bone changes indicative of OA, even in persons who report none of the usual symptoms. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). MRI studies are very sensitive tests. They are generally done to diagnose acute injuries but can often detect early signs of OA long before symptoms appear. Ultrasound. Ultrasound scans of osteoarthritic joints are particularly good at finding effusions, or fluid collections that might be too small to produce obvious swelling. Despite the sensitivity of ultrasounds and MRI, radiologists generally believe that ordinary X-rays are sufficient to make a diagnosis of OA. CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS The causes of OA include: Age. The risk of OA increases with age, but after the age of 80 to 85, the risk falls a bit for reasons that are not clear. Gender. After the age of 55 to 60, women have a higher incidence of OA of the knee than men do. Some studies suggest that the decline in native estrogen after menopause might play a role in women s greater risk, particularly since estrogen replacement therapy is associated with decreased risk. Obesity. In the Framingham OA Study, the risk of OA of the knees in women increased 40 percent for each ten-pound weight gain. Some researchers have estimated that if obesity were eliminated, the incidence of OA of the knee in both men and women would fall by 25 to 50 percent. Previous injury. Joint injury, such as a tear in a ligament or in the meniscus in the knee, increases the risk of developing OA. OA occurs more rapidly in older adults with joint injuries than in younger people. People who have held jobs requiring much physical labor, such as knee bending with heavy loads, can suffer chronic joint damage that leads to OA. Muscle weakness. Studies have shown that weakness in the quadriceps muscle that runs from the front of the thigh across the knee and down to the shin is associated with OA of the knee in people over 65. A decline in the stability of the knee with age also appears to increase the risk of OA. Congenital abnormalities. Congenital hip dysplasia, a structural abnormality, can lead to OA in later life, due to changes in the shape of the joint. Joint infections. Although it is unusual, joints can be infected by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and mycobacteria (the organisms that cause tuberculosis), all of which can penetrate joint spaces. This causes acute damage and paves the way for chronic damage and future OA. Some of the most well known microbes that infect joints are the Lyme disease and gonorrhea bacteria. Metabolic and hormonal disturbances. A host of disorders feature OA as a complication. They include Paget s disease (in which bone is remodeled inappropriately), acromegaly (from excessive circulating growth hormone), and hemochromatosis (an iron storage disease). Diet. Studies have shown that diets deficient in vitamin C or vitamin D and perhaps vitamin K can increase the risk of progressive OA. In one study, evidence of continuing joint damage was reduced three-fold in those people with the highest dietary intake of vitamins C and D. PREVENTING OSTEOARTHRITIS No studies have been done that can give a definitive solution to the challenge of preventing osteoarthritis. Maintaining an appropriate weight can decrease the risk of developing OA. Finding the correct balance between regular exercise and physical activity and allowing the joints to rest and recover from that activity may prevent OA. Avoidance of jobs and hobbies that require repetitive movements of the joints can also help. Interestingly, running does not lead to OA in people who have not experienced a joint injury. OSTEOARTHRITIS AND AGING Aging, by itself, does not cause OA, but the changes that take place in cells and joints as we age allow OA to develop more easily. Infoaging Guide to Osteoarthritis 3
4 Gout, repetitive trauma associated with jobs or other physical activities, and metabolic disorders are often associated with OA. Aging can influence the choice of treatments for OA, since certain classes of pain relievers have adverse effects that can disproportionately affect older adults. For example, drugs such as ibuprofen, which belong to the category of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs, can produce kidney damage, gastrointestinal bleeding, and rarely, central nervous system and personality changes. TREATMENT With the high cost of prescription (and over the counter) medications and possibility of adverse effects from medications, the American College of Rheumatology recommends beginning treatment for OA with non-drug methods. Studies support the value of carefully planned exercise programs in improving functional status and decreasing pain once OA has developed. For example, a small Danish study of 25 patients with OA of the knees looked at the effects of a coordinated training program focusing on fitness, balance, coordination, and muscle strength. At the end of one year, the patients experienced up to a 20% improvement in strength, a significant decrease in pain, and an increase of 13% in walking speed. Another small study of 113 patients at the Veterans Administration Hospital in Philadelphia compared an exercise program to an OA education program (talks on non-drug treatment of pain, preservation of joint function, and joint protection strategies). This study demonstrated that those who exercised had decreased pain, but both groups had improved strength, suggesting that patient education could play a role in improving quality of life for OA sufferers. The Wake Forest School of Medicine in North Carolina, in conjunction with the University of Tennessee School of Medicine, conducted a larger study of 439 patients with OA of the knee, enrolling them in either an aerobic exercise program, a resistance exercise program, or an education program. Those who had entered the aerobic program had the largest improvements in strength and endurance and the greatest decrease in pain. Those in the resistance training group derived intermediate benefits, and those in the education group had the smallest improvements. Other studies have shown, however, that participation in OA education programs can reduce pain in some sufferers. In a follow-up study, recently published in the Archives of Internal Medicine, researchers at Wake Forest University examined the utility of exercise in improving OA. 250 persons with OA of the knee but no interference as yet in their activities of daily living (ADLs) were assigned to either a resistance exercise program, an aerobic exercise program, or a control group. They were followed for 18 months to determine what impact, if any, there was on their ADLs with either exercise program or with no exercise. Benefits were found with both forms of exercise. The likelihood of developing impediments in ADLs was 37 percent for those who exercised (either resistance or aerobic) and 52 percent for those in the control group. Physicians recommend that people with OA rest their joints about every four to six hours. Exercise X-rays of the bones and joints in a patient suspected of having OA will show narrowing of the spaces that should be seen in joints, thickening of the bone that lines the joints and the formation of bone spurs. 4 Infoaging Guide to Osteoarthritis Infoaging Guide to Osteoarthritis
5 effectively squeezes the water out of the cartilage, and rest allows it to seep back in. A number of tissue studies in animal cartilage have demonstrated this mechanism. These joint rest treatments are aimed at both reducing pain and improving function. Weight loss will certainly benefit those with OA. In the Framingham OA Study, an average of 10 pounds of weight loss over a 10-year period decreased the risk of OA of the knee by 50%. Another study, called the Arthritis, Diet, and Activity Promotion Trial (ADAPT) demonstrated that exercise combined with moderate weight loss could improve function and reduce pain in knee OA. In ADAPT, patients with knee OA followed an 18-month program comprising physical exercise and a calorie-restricted diet. Results showed an average improvement of 24 percent in physical function and a 30.3 percent decrease in knee pain. MEDICATIONS FOR OA Most painful conditions, including OA, involve some degree of inflammation. Inflammation is a complex immune response the body makes to injury, infection, or other damage. It includes the recruitment of various chemical substances in the body to combat the injury or infection. Though the inflammatory response is appropriate and often necessary, the substances or mediators it produces can worsen the damage. Medications that reduce the detrimental effects of the inflammatory response are often used for OA treatment. But in many individuals, medications that reduce pain without affecting inflammation can be just as effective as the anti-inflammatory medications. This suggests that inflammation may not be the sole cause of pain for patients with OA. Some of the medications used to treat OA include: Traditional pain relievers. Acetaminophen gives effective pain relief to many patients with OA. Because aspirin and medications such as ibuprofen are known to cause occasionally severe gastrointestinal bleeding, acetaminophen can be a safer choice. Acetaminophen can be taken at a dose of 1,000 mg, up to three times per day but should not exceed 3,000 mg in a day. Patients need to be aware of any other medications they are taking that may also contain acetaminophen (for example, some cold medications and some combination pain relievers) and include them when calculating their total dose for a day. Lower doses often give inadequate pain relief; higher doses can cause liver damage. Abusing alcohol while taking acetaminophen increases the risk of liver damage. Patients who try acetaminophen for OA should be aware that effective pain relief may take as long as two weeks. Steroid injections. Traditional treatments for flare-ups of joint pain have included injections of cortisone or other steroids into the joint spaces. These treatments can provide several weeks of reduced pain. Individuals should receive no more than four injections in a single year. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS). Topical or applied NSAIDs are available as creams and ointments and offer some relief from pain when rubbed over joints. Some absorption of the drugs through the skin and into the bloodstream is possible, so the fact that they are applied topically is not a guarantee that they will not cause gastrointestinal bleeding or kidney damage. In fact, a meta-study (review of a large number of studies) published in the June 2010 issue of the Journal of Rheumatology, showed that although topical NSAIDS have fewer severe gastrointestinal adverse effects than the oral versions in older adults, a substantial proportion of these patients report systemic adverse effects from them. Further, about the same number of people (up to 21 percent) withdrew from topical therapy as did from oral therapy (up to 25 percent) because of adverse effects. Overall, however, it appears that topical NSAIDs are safer than the oral versions, particularly in adults over the age of 75 years. Infoaging Guide to Osteoarthritis 5
6 Whether oral or topical, traditional NSAIDS produce these adverse effects because they are not selective. While the medications inhibit inflammatory proteins, they cannot distinguish between those that are useful (cyclooxeganase-1 or COX-1, which protects the stomach and other organs) and those that are damaging (cyclooxeganase-2 or COX-2, which enhances inflammation and produces pain). Thus, they inhibit proteins released during inflammation that would actually prevent ulcers and gastrointestinal bleeding. Although NSAIDs do have potentially dangerous adverse effects, with careful management they can achieve excellent results, particularly in short-term treatment. When they are prescribed for longterm use, many physicians also prescribe an anti-ulcer medication to reduce the likelihood of gastrointestinal bleeding. NSAIDs also include a class of drugs called COX-2 inhibitors, which generally cause fewer gastrointestinal side effects because they specifically target the COX-2 protein. However, they do not lower the risk for other side effects such as kidney failure and cardiovascular events. Currently, the prescription drug celecoxib (Celebrex) is the only COX-2 inhibitor available to patients. Two others were pulled from the market when they were found to increase the risk of heart attacks, blood clots, and stroke. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) now requires that the packaging for celecoxib and other NSAIDs contains a boxed warning indicating the risks associated with using these medications. Hyaluronic acid. Another treatment for OA is injection of hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic acid is a normal component of joint fluid, and injecting it causes few adverse effects, although some individuals have experienced increased pain and swelling after an injection. Some people seem to benefit from these injections, but results from multiple studies show modest effects at best. THE FUTURE OF OSTEOARTHRITIS RESEARCH At a recent American College of Rheumatology (ACR) symposium, presenters noted that the current understanding of OA is based in pathomechanics, which includes body mechanics, genetic factors, and any additional factors in the patient s behavior, lifestyle, or environment that might be contributing to the disease s development. At another ACR meeting, lecturers presented new findings that suggested OA is actually an inflammatory disease, rather than simply a condition of wear and tear. As a result, much of future research will, in all probability, focus on the chemicals that cause inflammation in the body. Other promising research areas include the body s stress response to an accumulation of unfolded or mis-folded proteins, genetic triggers of OA, activation of particular gene pathways to stop the progression of OA, and regeneration of healthy tissue through stem cell therapy. American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) 55 West 39th Street, 16th Floor New York, NY Phone: (212) Toll-free: (888) Fax: (212) info@afar.org Websites: Facebook and Twitter: AFARorg Infoaging American Guide Federation to Osteoarthritis of Aging Research. All rights reserved.
Arthritis of the Knee
 Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of knee arthritis. OA is usually a slowly progressive
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA
 Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA Osteoarthritis: What Is It? Also called "wear and tear" arthritis or degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive breakdown of
Osteoarthritis - An Overview and Visual Guide to OA Osteoarthritis: What Is It? Also called "wear and tear" arthritis or degenerative joint disease, osteoarthritis (OA) is the progressive breakdown of
Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options
 Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options Pinnacle Orthopedics Pinnacle Medical Network About Pinnacle Orthopedics and Pinnacle Medical Network South Louisiana s Premier System for the Delivery of Musculoskeletal
Your Joint Pain and Treatment Options Pinnacle Orthopedics Pinnacle Medical Network About Pinnacle Orthopedics and Pinnacle Medical Network South Louisiana s Premier System for the Delivery of Musculoskeletal
Risk Management Plan Etoricoxib film-coated tablets
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Osteoarthritis (OA): OA is a condition in which the cartilage of the joints is broken down. This causes stiffness, pain and leads
Pain or stiffness in joints after periods of inactivity or excessive use
 Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Arthritis Awareness* Some older adults call it Arthur ; others refer to it as their constant compassion, but most describe it as extremely painful Arthritis is a chronic joint disease It is commonly believed
Arthritis of the Knee
 Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
Copyright 2007 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Arthritis of the Knee There are three basic types of arthritis that may affect the knee joint. Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis
 Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Guide to Understanding and Managing Arthritis The content in this guide is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician
Arthritis. written by Harvard Medical School.
 Arthritis written by Harvard Medical School www.patientedu.org Healthy Joints Your joints are engineering gems. In health, they are strong enough to support your weight, supple enough to let you move about,
Arthritis written by Harvard Medical School www.patientedu.org Healthy Joints Your joints are engineering gems. In health, they are strong enough to support your weight, supple enough to let you move about,
JOYFLEX complete OA line
 JOYFLEX complete OA line NEW Patent formulation* HA 1,6% HA 2,0% *PCT pending What s Osteoarthritis Sometimes called degenerative joint disease or degenerative arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA) is the most
JOYFLEX complete OA line NEW Patent formulation* HA 1,6% HA 2,0% *PCT pending What s Osteoarthritis Sometimes called degenerative joint disease or degenerative arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA) is the most
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS North American Spine Society Public Education Series WHAT IS LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS? The vertebrae are the bones that make up the lumbar spine (low back). The spinal canal runs through
Osteoarthritis. RA Hughes
 Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis This article is also available in Spanish: Estenosis de la columna lumbar (topic.cfm?topic=a00701). A common cause of low back and leg pain is lumbar spinal stenosis. As we age,
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis This article is also available in Spanish: Estenosis de la columna lumbar (topic.cfm?topic=a00701). A common cause of low back and leg pain is lumbar spinal stenosis. As we age,
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis? 1,2 Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. It causes joints to swell and can result
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
ARTHRITIS. What Is Arthritis?
 There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Arthritis of the Shoulder Simply defined, arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. In a diseased shoulder, inflammation causes pain and stiffness. Although there is no cure for arthritis
Joint Health: Arthritis Prevention Non-operative Treatments and Replacement Surgery
 Joint Health: Arthritis Prevention Non-operative Treatments and Replacement Surgery John A. Abraham, MD Orthopedic Oncology Service and Arthroplasty Service, Rothman Institute Director, Jefferson Sarcoma
Joint Health: Arthritis Prevention Non-operative Treatments and Replacement Surgery John A. Abraham, MD Orthopedic Oncology Service and Arthroplasty Service, Rothman Institute Director, Jefferson Sarcoma
Ankle Arthritis PATIENT INFORMATION. The ankle joint. What is ankle arthritis?
 PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
What Is Back Pain? Can Back Pain Be Prevented? When Should I See a Doctor for Pain? How Is Back Pain Diagnosed?
 What Is Back Pain? Back pain can also occur with some conditions and diseases, such as: Scoliosis Spondylolisthesis Arthritis Spinal stenosis Pregnancy Kidney stones Infections Endometriosis Fibromyalgia.
What Is Back Pain? Back pain can also occur with some conditions and diseases, such as: Scoliosis Spondylolisthesis Arthritis Spinal stenosis Pregnancy Kidney stones Infections Endometriosis Fibromyalgia.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis
 Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
 Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. In about
Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. In about
Arthritis. that affects the joints.
 Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
Issue What is Arthritis?
 Issue 4-17. What is Arthritis? Arthritis is very common but can be very confusing for patients to understand. Arthritis is not a single disease, it is a way of referring to joint pain or joint disease.
Issue 4-17. What is Arthritis? Arthritis is very common but can be very confusing for patients to understand. Arthritis is not a single disease, it is a way of referring to joint pain or joint disease.
Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? 2. What are the ingredients of Algaea-X? 3. How does Algaea-X work?
 Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? Algaea-X is a topical cream developed to help relieve pain and inflammation caused by arthritis and helps the regeneration of damaged cartilage. Developed by utilizing
Q&A for Algaea-X 1. What is Algaea-X? Algaea-X is a topical cream developed to help relieve pain and inflammation caused by arthritis and helps the regeneration of damaged cartilage. Developed by utilizing
Basal Joint Arthritis of the Thumb
 Basal Joint Arthritis of the Thumb Cedar Valley Hand Surgery Dr. Johns www.cedarhand.com www.erveytesi.com Anatomy The basal joint of the thumb is also called the CMC joint It is located at the base of
Basal Joint Arthritis of the Thumb Cedar Valley Hand Surgery Dr. Johns www.cedarhand.com www.erveytesi.com Anatomy The basal joint of the thumb is also called the CMC joint It is located at the base of
The Top 3 Herbs That Help Cure Arthritis-A Holistic Approach
 The Top 3 Herbs That Help Cure Arthritis-A Holistic Approach Common Types of Arthritis: organicheirloomplants.com Osteoarthritis: -Cartilage loses its elasticity. If the cartilage is stiff it becomes damaged
The Top 3 Herbs That Help Cure Arthritis-A Holistic Approach Common Types of Arthritis: organicheirloomplants.com Osteoarthritis: -Cartilage loses its elasticity. If the cartilage is stiff it becomes damaged
A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS KNEE PAIN RELIEF THAT JUST CAN T WAIT
 A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS KNEE PAIN RELIEF THAT JUST CAN T WAIT TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR OA KNEE PAIN There are several things you can do to help reduce knee pain due to OA. Lifestyle changes Losing weight, if
A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS KNEE PAIN RELIEF THAT JUST CAN T WAIT TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR OA KNEE PAIN There are several things you can do to help reduce knee pain due to OA. Lifestyle changes Losing weight, if
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing
 A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Rotator Cuff Injuries
 Rotator Cuff Injuries Introduction Shoulder injuries are fairly common, especially for people who tend to exercise a lot. Some of the most common shoulder injuries are called rotator cuff injuries. This
Rotator Cuff Injuries Introduction Shoulder injuries are fairly common, especially for people who tend to exercise a lot. Some of the most common shoulder injuries are called rotator cuff injuries. This
Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions
 Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions MANAGING ARTHRITIS PAIN For people with arthritis, pain management is more complex than just taking aspirin. Arthritis is a chronic disease
Ouch! Managing pain caused by arthritis and related conditions MANAGING ARTHRITIS PAIN For people with arthritis, pain management is more complex than just taking aspirin. Arthritis is a chronic disease
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
Arthritis of the Shoulder In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United States reported that they had been diagnosed with some form of arthritis, according to the National Health Interview Survey.
THAT S PROVEN FOR THE LONG RUN
 A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS KNEE PAIN RELIEF THAT S PROVEN FOR THE LONG RUN TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR OA KNEE PAIN There are several things you can do to help reduce knee pain due to OA. Lifestyle changes Losing
A GUIDE FOR PATIENTS KNEE PAIN RELIEF THAT S PROVEN FOR THE LONG RUN TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR OA KNEE PAIN There are several things you can do to help reduce knee pain due to OA. Lifestyle changes Losing
Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Total Knee Replacement
 Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Total Knee Replacement This is a general information packet for patients undergoing Total Knee Replacement. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Brian P. McKeon MD Jason D. Rand, PA-C, PT Patient Information Sheet: Total Knee Replacement This is a general information packet for patients undergoing Total Knee Replacement. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Dr Doron Sher MBBS MBiomedE FRACS(Orth)
 Dr Doron Sher MBBS MBiomedE FRACS(Orth) Knee, Shoulder, Elbow Surgery Osteoarthritis of the Knee The knee is the largest joint in the body and is the joint most commonly affected by osteoarthritis. There
Dr Doron Sher MBBS MBiomedE FRACS(Orth) Knee, Shoulder, Elbow Surgery Osteoarthritis of the Knee The knee is the largest joint in the body and is the joint most commonly affected by osteoarthritis. There
What Are Shoulder Problems?
 What Are the Parts of the Shoulder? The shoulder joint is made up of bones held in place by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that hold the shoulder muscles to bones. They
What Are the Parts of the Shoulder? The shoulder joint is made up of bones held in place by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that hold the shoulder muscles to bones. They
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? How Are Shoulder Problems Treated? What Are the Most Common Shoulder Problems? What Are Shoulder Problems?
 How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? Doctors diagnose shoulder problems by using: Medical history. Physical examination. Tests such as x rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) How Are Shoulder
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? Doctors diagnose shoulder problems by using: Medical history. Physical examination. Tests such as x rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) How Are Shoulder
Regain your freedom. Authorised Representative Genzyme Europe B.V. Gooimeer DD Naarden The Netherlands
 Regain your freedom Authorised Representative Genzyme Europe B.V. Gooimeer 10 1411 DD Naarden The Netherlands Genzyme Limited 4620 Kingsgate Cascade Way Oxford Business Park South Oxford OX4 2SU Tel: 01865
Regain your freedom Authorised Representative Genzyme Europe B.V. Gooimeer 10 1411 DD Naarden The Netherlands Genzyme Limited 4620 Kingsgate Cascade Way Oxford Business Park South Oxford OX4 2SU Tel: 01865
Arthritis of the Shoulder
 Page 1 of 7 Arthritis of the Shoulder This article is also available in Spanish: Artritis del hombro (Arthritis of the Shoulder) (topic.cfm?topic=a00723). In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United
Page 1 of 7 Arthritis of the Shoulder This article is also available in Spanish: Artritis del hombro (Arthritis of the Shoulder) (topic.cfm?topic=a00723). In 2011, more than 50 million people in the United
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the strong band of tissue that supports the arch of your foot becomes irritated and inflamed.
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Arthritis. Healthy Living with Hand & Wrist Arthritis The Orthopedic Specialty Hospital. ARTH + ITIS = Inflammation (Joint) (Inflammation) of joints
 Healthy Living with Hand & Wrist Arthritis The Orthopedic Specialty Hospital Arthritis Causes Diagnosis Medical treatment Surgical treatment Defining Arthritis ARTH + ITIS = Inflammation (Joint) (Inflammation)
Healthy Living with Hand & Wrist Arthritis The Orthopedic Specialty Hospital Arthritis Causes Diagnosis Medical treatment Surgical treatment Defining Arthritis ARTH + ITIS = Inflammation (Joint) (Inflammation)
What Is Back Pain? Fast Facts: An Easy-to-Read Series of Publications for the Public. Who Gets Back Pain? What Are the Causes of Back Pain?
 Back pain can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that makes it hard to move. It can start quickly if you fall or lift something too heavy, or it can get worse slowly. Who Gets Back
Back pain can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that makes it hard to move. It can start quickly if you fall or lift something too heavy, or it can get worse slowly. Who Gets Back
Understanding your spine and how it works can help you better understand low back pain.
 Low Back Pain Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. This pain can vary from mild to severe. It can be short-lived or long-lasting. However it happens, low back pain
Low Back Pain Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. This pain can vary from mild to severe. It can be short-lived or long-lasting. However it happens, low back pain
Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets , Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
 Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets 23.5.2016, Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg film-coated
Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg, 60 mg, 90 mg and 120 mg film-coated tablets 23.5.2016, Version V1.2 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib STADA 30 mg film-coated
Patellofemoral Replacement
 Patellofemoral Replacement During knee replacement surgery, damaged bone and cartilage is resurfaced with metal and plastic components. Patellofemoral replacement is a type of "partial" knee replacement
Patellofemoral Replacement During knee replacement surgery, damaged bone and cartilage is resurfaced with metal and plastic components. Patellofemoral replacement is a type of "partial" knee replacement
Total hip replacement
 Total hip replacement 2 Hip pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that 1 in 5 people
Total hip replacement 2 Hip pain Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in the United States, and the most frequent cause of discomfort and chronic hip pain. In fact, it s estimated that 1 in 5 people
Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery
 PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
PATIENT INFORMATION Midfoot Arthritis - Midfoot Fusion / Arthrodesis Surgery The Midfoot The midfoot refers to the bones and joints that make up the arch and connect the forefoot to the hindfoot. Metatarsals
WHERE IT HURTS GET RELIEF THAT WORKS GET TARGETED, TOPICAL PENNSAID 2% FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS KNEE PAIN, SELECT IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
 FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS KNEE PAIN, GET RELIEF THAT WORKS WHERE IT HURTS GET TARGETED, TOPICAL PENNSAID 2% PENNSAID (diclofenac sodium topical solution) 2% w/w is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS KNEE PAIN, GET RELIEF THAT WORKS WHERE IT HURTS GET TARGETED, TOPICAL PENNSAID 2% PENNSAID (diclofenac sodium topical solution) 2% w/w is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Understanding treatments for knee pain.
 Understanding treatments for knee pain. 2 Table of Contents Why does my knee hurt? 2 Diagnosis 4 Nonsurgical treatments 5 Surgical treatments 9 Arthroscopy Partial Knee Replacement 10 What is knee replacement?
Understanding treatments for knee pain. 2 Table of Contents Why does my knee hurt? 2 Diagnosis 4 Nonsurgical treatments 5 Surgical treatments 9 Arthroscopy Partial Knee Replacement 10 What is knee replacement?
Arthritis. What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available?
 Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS
 SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
Minimally Invasive Hip and Knee Replacement in the Active Patient
 Minimally Invasive Hip and Knee Replacement in the Active Patient Updates and Emerging Technologies in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Outcomes Ravi K. Bashyal, MD NorthShore University HealthSystem Department
Minimally Invasive Hip and Knee Replacement in the Active Patient Updates and Emerging Technologies in Diagnosis, Treatment, and Outcomes Ravi K. Bashyal, MD NorthShore University HealthSystem Department
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can
Arthritis. Canada s most common chronic health condition. About the Arthritis Society
 About the Arthritis Society The Arthritis Society is a national health charity, fueled by donors and volunteers, with a vision to live in a world where people are free from the devastating effects that
About the Arthritis Society The Arthritis Society is a national health charity, fueled by donors and volunteers, with a vision to live in a world where people are free from the devastating effects that
The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement. Patient Information
 The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement Patient Information Patient Information This patient education brochure is presented by Small Bone Innovations, Inc. Patient results may vary. Please
The S.T.A.R. Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement Patient Information Patient Information This patient education brochure is presented by Small Bone Innovations, Inc. Patient results may vary. Please
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
ARTHRITIS. What happens when Arthritis goes untreated? Often people take arthritis to be a natural part of aging and do not seek medical advice.
 ARTHRITIS Move again with Life ARTHRITIS needn't control your life anymore Now you can control it. Joint pain, restricted joint mobility, joint swelling and inflammation can steal happiness from your life.
ARTHRITIS Move again with Life ARTHRITIS needn't control your life anymore Now you can control it. Joint pain, restricted joint mobility, joint swelling and inflammation can steal happiness from your life.
MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you.
 Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe
 Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub
Bunions / Hallux Valgus deviation of the big toe A bunion (hallux valgus) is a deformity of the base joint of the big toe. The cause is not clear in many cases. The deformity may cause the foot to rub
North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
A Patient s Guide to Osteoarthritis of the Knee. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Osteoarthritis of the Knee Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride
A Patient s Guide to Osteoarthritis of the Knee Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
Are You Living with. Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you.
 Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
Are You Living with Knee Pain? MAKOplasty may be the right treatment option for you. Understanding Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis shouldn t keep you from doing the things you love. Osteoarthritis (OA) is
This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702).
 1 of 5 17 Oct 2015 11:04 AM This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702). Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of
1 of 5 17 Oct 2015 11:04 AM This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702). Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of
WHAT IS ARTHRITIS? PATIENT EDUCATION: HIP & KNEE ARTHRITIS
 KNOWS River Valley Ortho PATIENT EDUCATION: WHAT IS ARTHRITIS? Arthritis literally means joint inflammation. Several forms exist, the most common being osteoarthritis, or wear-and-tear arthritis. Other
KNOWS River Valley Ortho PATIENT EDUCATION: WHAT IS ARTHRITIS? Arthritis literally means joint inflammation. Several forms exist, the most common being osteoarthritis, or wear-and-tear arthritis. Other
Knee Replacement , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. op Last reviewed: 06/01/2017 1
 Knee Replacement Introduction Severe arthritis in the knee can lead to serious pain and loss of motion. Health care providers may recommend surgery for people suffering from severe arthritis in the knee.
Knee Replacement Introduction Severe arthritis in the knee can lead to serious pain and loss of motion. Health care providers may recommend surgery for people suffering from severe arthritis in the knee.
Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent
 Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent ER_OS02 Total Knee Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of November 2018 Local Informa#on For further informa0on locally you can contact the Pa0ent Advice & Liaison Service
Pa#ent Informa#on for Consent ER_OS02 Total Knee Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of November 2018 Local Informa#on For further informa0on locally you can contact the Pa0ent Advice & Liaison Service
REDUCE THE HURT REDUCE THE HARM
 IF YOU HAVE OSTEOARTHRITIS (OA) OR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) REDUCE THE HURT AND REDUCE THE HARM DUEXIS reduces the risk of developing stomach ulcers for patients who are taking ibuprofen for OA/RA INDICATIONS
IF YOU HAVE OSTEOARTHRITIS (OA) OR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA) REDUCE THE HURT AND REDUCE THE HARM DUEXIS reduces the risk of developing stomach ulcers for patients who are taking ibuprofen for OA/RA INDICATIONS
Total Hip Replacement. Find out why Total Hip Replacement may be right for you.
 Total Hip Replacement Find out why Total Hip Replacement may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of hip anatomy, arthritis and total hip arthroplasty.
Total Hip Replacement Find out why Total Hip Replacement may be right for you. UNDERSTANDING TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT This brochure offers a brief overview of hip anatomy, arthritis and total hip arthroplasty.
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome
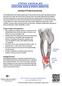 Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis Classification of Knee Arthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis of Knee
 1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE
 Dr C S Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE The knee is the largest joint in the body, and is also the joint most
Dr C S Waller MB BS FRCS(Ed) FRACS FA(Orth)A Specialist Hip and Knee Surgeon NON-SURGICAL TREATMENTS FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS of the KNEE The knee is the largest joint in the body, and is also the joint most
Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis
 Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis Overview Facet joint syndrome is an arthritis-like condition of the spine that can be a significant source of back and neck pain. It is caused by degenerative changes to
Facet Joint Syndrome / Arthritis Overview Facet joint syndrome is an arthritis-like condition of the spine that can be a significant source of back and neck pain. It is caused by degenerative changes to
PATIENT INFORMATION THE DIFFERENCE IS MOVING.
 PATIENT INFORMATION THE DIFFERENCE IS MOVING. THIS BROCHURE IS WRITTEN TO HELP YOU MAKE AN INFORMED DECISION ABOUT YOUR SURGERY. Please read this entire brochure carefully. Keep this brochure. You may
PATIENT INFORMATION THE DIFFERENCE IS MOVING. THIS BROCHURE IS WRITTEN TO HELP YOU MAKE AN INFORMED DECISION ABOUT YOUR SURGERY. Please read this entire brochure carefully. Keep this brochure. You may
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in How to Prevent and Treat Aches and Pains. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
A Patient s Guide to Bipartite Patella
 A Patient s Guide to Bipartite Patella 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Bipartite Patella 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
 Lucas Wymore, MD Sports Medicine 23000 Moakley Street Suite 102 Leonardtown MD 20650 Office Phone: 301-475-5555 Office Fax: 301-475- 5914 Email: lwymore@somdortho.com PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
Lucas Wymore, MD Sports Medicine 23000 Moakley Street Suite 102 Leonardtown MD 20650 Office Phone: 301-475-5555 Office Fax: 301-475- 5914 Email: lwymore@somdortho.com PATIENT GUIDE TO CARTILAGE INJURIES
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Relieving Arthritis Knee Pain Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics
 Arthritis is COMMON Relieving Arthritis Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics 303-622-3172 More than 43 million people have some form of arthritis. It is estimated that the number of
Arthritis is COMMON Relieving Arthritis Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics 303-622-3172 More than 43 million people have some form of arthritis. It is estimated that the number of
Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers
 CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
What Is Spinal Stenosis?
 The spine, a row of 26 bones in your back, allows you to stand up straight and bend over. The spine also protects your spinal cord from being hurt. In people with spinal stenosis, the spine is narrowed
The spine, a row of 26 bones in your back, allows you to stand up straight and bend over. The spine also protects your spinal cord from being hurt. In people with spinal stenosis, the spine is narrowed
Facts About Aging and. Bone Health. A Guide to Better Understanding and Well-Being. This educational information is proudly provided by
 and Bone Health A Guide to Better Understanding and Well-Being This educational information is proudly provided by Aging The fact is, everyone experiences slow loss of bone strength and bone density throughout
and Bone Health A Guide to Better Understanding and Well-Being This educational information is proudly provided by Aging The fact is, everyone experiences slow loss of bone strength and bone density throughout
A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
fitting shoes, or repetitive stress. It also frequently arises from unknown causes.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Morton's Neuroma Morton's Neuroma, also sometimes referred to as plantar Neuroma or intermetatarsal Neuroma,
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Morton's Neuroma Morton's Neuroma, also sometimes referred to as plantar Neuroma or intermetatarsal Neuroma,
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: , VERSION 1.
 RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: 07-10-2016, VERSION 1.2 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib Orion
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (RMP) PUBLIC SUMMARY ETORICOXIB ORION (ETORICOXIB) 30 MG, 60 MG, 90 MG & 120 MG FILM-COATED TABLET DATE: 07-10-2016, VERSION 1.2 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary Etoricoxib Orion
