Target Cell. Physical stress, inflammation and infection with specific microorganisms trigger the immune response
|
|
|
- Nickolas Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spondyloarthritis Diseases A group of autoimmune diseases that in common appear mediated by activation of autoreactive CD8 T cells CD8 T-cell Cognitive Recognition Target Cell TCR Unknown Self Antigenic Peptide Presented by class I MHC Physical stress, inflammation and infection with specific microorganisms trigger the immune response Primarily affect joints, skin, eyes and mucous membranes Autoantibodies such as ANA or RF are absent Spondylitis Diseases Ankylosing spondylitis (ASp) Reiter s syndrome (RS) / reactive arthritis (ReA) Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) Undifferentiated spondyloarthritis (USpA) Enteropathic arthritis (ulcerative colitis, regional enteritis) Psoriasis 1
2 Spondyloarthritis Diseases-features common to all 1. Clinical:- Affect joints, skin, eyes and mucous membranes in varying proportions with characteristic joint involvement: Spondylitis (inflammation of vertebral discs), sacroiliitis (sacroiliac joints) and enthesitis (tendon insertions). All with granulomatous fibrosis and new bone formation 2. Genetic:- Susceptibility to develop disease is associated with inheritance of certain MHC class I alleles, notably HLA-B27 3. Pathogenesis:- Effector/ memorycd8 T cells are activated and clonally expanded while CD4 T cells or B cells are not involved as shown by increased occurrence of these diseases in AIDS Spondylitis leads to the development of syndesmophytes and ankylosis ASp T cells invade the junction of annulus fibrosis and vertebral body forming granulation tissue (activated macrophages, T cells and fibroblasts) Annulus fibers are eroded, then replaced by fibrocartilage that ossifies to form a syndesmophyte. Subperiosteal new bone formation ensues Progressive cartilaginous and periosteal ossification forms a bamboo spine, osteoporosis develops 2
3 Sacroiliitis The subchondral regions of the synarthrotic SI joints are invaded by T cells leading to the formulation of granulation tissue The cartilage on the iliac side is eroded first, causing bone plate blurring, joint space widening and reactive sclerosis. Ultimately the resultant fibrous ankylosis is replaced by bone, obliterating the SI joint Enthesitis (enthesopathy) the central inflammatory unit of spondyloarthritis Entheses are the specialized fibrocartilagenous region of bone where ligaments, tendons, fascia or joint capsules insert Infiltration of entheses by T cells, enthesitis, produces a combination of bone erosions and heterotopic new bone formation. Calcaneal spurs at insertion of plantar fascia and Achilles ligament are classic examples (Lover s heel). 3
4 Inflammatory back pain Due to the initial inflammation of enthesitis, spondylitis or sacroiliitis Onset before age 40 Insidious persistent (> 3 mo) dull deep buttock or low back pain Poorly localized, does not follow nerve root Stiffness/pain upon arising in the morning, or during sleep Improvement with exercise Spondylitis Disorders Genetic epidemiology Strong familial aggregation, identical twin concordance HLA-B27 increased, but unevenly, among spondylitis diseases Ankylosing spondylitis Reiter s syndrome (reactive arthritis) Psoriatic arthritis Ethnically matched controls HLA-B27 frequency (%) Other class I alleles may also be involved, especially in PsA 4
5 Spondylitis Disorders CD8 T cell effector mechanisms of tissue injury CD8 T-cell Cognitive Recognition The identity of autologous peptides /proteins driving the response is still unknown aggrecan? Macrophages activated by γ-ifn release cytokines (TNF-α) TCR Self Antigenic Peptide Chondrocyte or Fibroblast Activated CD8 T cells injure target cell and release cytokines including γ-ifn that reprogram gene expression of nearby cells CD8 T cells are CD28-negative, memory / effector cells that receive a signal 2 from engagement of NK receptors by stress-induced ligands Fibroblasts usually have fibrogenic and osteoblastic program activated Specific Spondyloarthritis Diseases Ankylosing spondylitis First disease shown to be related to occurrence of a particular HLA allele Uniquely high relationship of susceptibility and HLA- B27 5
6 Ankylosing spondylitis A progressive autoimmune inflammatory disease characterized by Onset, age with dull pain in lumbar or gluteal regions Hip, shoulder knee arthritis in ~30% Epidemiology: >95% of those affected are positive for HLA-B27 Disease prevalence follows distribution of HLA-B27 alleles, highest in circumpolar regions in Europe and Asia Affects 1-3% of HLA-B27 individuals, No evidence for triggering by microorganisms widespread spondylitis and sacroiliitis Male: female =3-10:1 Culminates in boney ankylosis of spine Ankylosing spondylitis - Course Begins with sacroiliitis Inflammatory back pain and tenderness or pain at central entheses (iliac crests, ischeal tuberosities) progresses and ascends over several months to ~10 years, with increasing stiffness and loss of mobility Postural changes include loss of lumbar lordosis, buttock atrophy and thoracocervical kyphosis, chest expansion compromised Peripheral joints, notably the hips may develop flexion contractures or ankylosis. Compensatory knee flexion Peripheral arthritis (~30%) and peripheral enthesopathy (~30%) may dominate the early phase of disease, while bony ankylosis predominates in the latter 6
7 Ankylosing spondylitis - systemic involvement Acute anterior uveitis may occur at any time (25%). High potential for syncheae and glaucoma Apical pulmonary fibrosis often with cavitation, uncommon (<<5%) Restrictive pulmonary disease due to costovertebral ankylosis,~ 10% Symptomatic complete heart block due to interventricular septum inflammation and /or aortic insufficiency due to granulomatous aortitis occurring in ~5% of patients. These may appear early, even developing in HLA-B27 individuals without detectable spondylitis Ankylosing spondylitis- different types of HLA-B27 HLA-B27 alleles differ from one another in polymorphic amino acids, in ethnic distribution and, importantly, whether they determine disease susceptibility Allele B*2701 B*2702 B*2703 B*2704 B*2705 B*2706 B*2707 B*2708 B*2709 Features Rare 10% of AS in Europe and Middle East Rare West African allele Major HLA-B27 allele in China and India 90% of AS, circumpolar Caucasians & Asians SE Asia Minor allele in SE Asia, China and India Rare, UK and Azores Sardinia, Italy Ank.Spon No No 7
8 A clue to the identity of a driving peptide HLA-B27 alleles share the same P2 B pocket, but differ from one another in the F P9 pocket Allele B*2701 B*2702 B*2703 B*2704 B*2705 B*2706 B*2707 B*2708 B* Tyr Tyr His Tyr Tyr Tyr Tyr Tyr Tyr 77 Agn Agn Ser Ser Ser P9 Pocket 80 Thr Ile Thr Thr Thr Thr Thr Ile Thr 116 Tyr His 114 His His His His His His His His Ank.Spon No No Current theories of why HLA-B27 predisposes to Ankylosing Spondylitis Peptide binding properties of HLA-B27 Distinctive chemical state of HLA-B27 molecules Transgenic rats expressing >100 copies of HLA-B27 develop a disease with some features of ankylosing spondylitis HLA-B27 may misfold and elicit an altered protein stress response 8
9 Specific Spondyloarthritis Diseases Reiter s syndrome /Reactive arthritis Directly triggered by specific pathogenic microorganisms in susceptible persons that carry HLA- B27 Reiter s syndrome /Reactive arthritis On August 21, 1916 a lieutenant in the Prussian army developed abdominal pain and diarrhea. This episode last 48 hours and was followed by a latent period of 7 days at which time urethritis and conjunctivitis occurred. The following day he developed polyarthralgias and arthritis of the knees, ankles, elbows, wrists and several interphalangeal joints. Within a few days the symptoms remitted and the patient remained well for 3 weeks. A relapse followed with a recurrence of urethritis and uveitis. H. Reiter (Andre Calin) Triad of Reiter s syndrome 9
10 Reiter s syndrome /Reactive arthritis - features Onset 7-30 days after self limited specific enteric or venereal infection Course-Initial episode usually regresses completely after weeks to months, but occasionally can return in a series of sometimes increasingly intense recrudescences and become sustained Peripheral arthritis: acute, highly inflammatory asymmetric arthritis involving knees, ankles, toes, and fingers. - All affected joints usually synchronous in abrupt fulminant onset - Usually an oligoarthritis with 2-4 joints involved Enthesitis - notably plantar fascia and Achilles tendon (40%) Dactylitis (Sausage digit) (40%) Sacroiliitis, stuttering spondylitis with asymmetric involvement of only one or two vertebral units (50%). More extensive vertebral squaring Reiter s syndrome-reactive arthritis Sub periosteal new bone formation a major feature Infiltration of lymphocytes followed by fluffy reactive new bone formation, similar to process occurring in entheses. May produce square vertebrae and other features of paravertebral ossification Some similarities to ankylosing spondylitis, but different 10
11 Reiter s syndrome /Reactive arthritis - Clinical features Onychodystrophy with hyper- and para-keratosis. Often subungual Conjunctivitis (often first manifestation). Uveitis may appear in recurrent disease Non specific urethritis Painless circinate balanitis and mucosal ulcers, prostatitis Heart - 10% of chronic phase patients develop heart block (1 o ) from IV septum inflammation and /or aortic valve insufficiency due to granulomatous aortitis at aortic ring Reiter s syndrome vs. Reactive arthritis Reiter s syndrome - triad of usually explosive arthritis, conjunctivitis and urethritis with keratodermic skin and nail lesions Reactive arthritis - a somewhat milder and more self-limited post infectious arthritis without evidence of skin or eye involvement or urethritis 11
12 Reiter s syndrome- role of specific infection Induction by particular pathogens Develops 7-30 days after enteric infection with certain Gram neg. rods Salmonella typhimurium, and occasionally S. paratyphi or S. heidelbergii Shigella flexneri 2a and 2b, but not after S. sonnei Yersinea enterocoliticas Campylobacter jejuni or C. fetus These organisms typically invade intestinal and other cells, perhaps resulting in the expression of arthritogenic peptides in class I MHC Develops 7-30 days after venereal infection with Chlamydia trachomatis or C. psittaci Epidemiology Reiter s syndrome /Reactive arthritis Two situations: 1. In previously healthy individuals, disease increasingly common as proceed North in Europe and Asia with highest prevalence circumpolar HLA-B27 marks the most susceptible individuals; 7% of Northern European Caucasoids, increasing in frequency in Northern peoples; 25-40% of Alaskan Inuit and Northern Asians, e.g. Chuckchis 2. Poorly treated HIV-1 infection, Subsaharan Africa HLA-B27 O% in Zimbabwe, where reactive arthritis is a major health problem in setting of HIV 12
13 Reiter s syndrome /Reactive arthritis Penetrance high: > 50% of HLA-B27 individuals develop RS / RA during major epidemics of dysentery by arthritogenic organisms HLA-B7 and HLA-B22 are the non HLA B-27 alleles in Northern European Caucasoids most often associated with susceptibility The 7-30 day delay in disease development after infection suggests clonal expansion and induction of a memory/effector T cell population Reiter s syndrome-reactive arthritis -Mechanism Disruption of tolerance of autoreactive CD8 T cells likely occurs through a combination of mechanisms: Activation of dendritic cells in initial immune response to infection provides co-stimulatory signals that may disrupt tolerance of other intrinsically self-reactive T cells Molecular mimicry - The same T cell clones involved in attack on microorganisms expand and initiate attack on body cells expressing target proteins that contain peptides that mimic the amino acid sequence found in the microorganisms Activation of memory / effector T cells -inflammation provides danger signals that foster the expression of NK and other innate immune system receptors on CD8 T cells, as well as upregulating expression of ligands for these receptors 13
14 HIV and the spondylitis diseases Early in the course of the HIV epidemic, a marked increase in instances of very severe Reiter s syndrome or psoriatic arthritis-psoriasis appeared in North America in patients with frank AIDS This is still a major problem in Africa and parts of Asia Ankylosing spondylitis not seen with AIDS Sometimes the Reiter s syndrome was the first evidence of HIV-1 infection and therapy with immunosuppressant drugs accelerated AIDS The paradox of a disease treated with immunosuppression appearing de novo in a profound immune deficiency state was an experiment of nature that eliminated the role of CD4 T cells from the pathogenesis of RS /PsA It suggested that these spondylitis diseases arise from clones of previously expanded memory rather than from naïve CD8 T cells ( Rheumatoid arthritis and SLE are ameliorated in advanced AIDS) Reiter s syndrome in the setting of AIDS Keratodermia blenorrhagicum- pustular psoriasis-like lesions of palms and soles Psoriasis - like lesions ( T cell infiltration, keratinocytes HLA-DR + with delayed differentiation, parakeratosis, sterile microabsesses 14
15 Reiter s syndrome Progression to psoriasis pattern of skin disease in AIDS Possible events in advanced HIV-infection that foster development of Reiter s syndrome / psoriatic arthritis Increased microbial persistence, and difficulty clearing enteric infections, e.g. Salmonella colonization Increased cytokines, including IL-15 that enhance expression of NK receptors and ligands Increased T cell activation Diminished regulatory cell numbers 15
16 Specific Spondyloarthritis Diseases Psoriatic Arthritis Often triggered by physical stress or injury, and non specific inflammation Psoriasis / Psoriatic Arthritis Psoriasis: T cells driven by keratinocyte peptides infiltrate basal layers of skin and retard kertinocyte differentiation resulting in formation of plaque-type lesions of immature keratinocytes Psoriatic arthritis: an often clinically distinctive complex of enthesitis and arthritis that occurs in the setting of psoriasis It may involve the spine or peripheral joints in a variety of patterns, and is initiated or exacerbated by stress or non specific infection Psoriasis Onset age yrs Prevalence ~3% 10-30% 10 years Psoriatic arthritis ~15% no prior psoriasis 16
17 Psoriatic arthritis Dactylitis (Sausage digit) Enthesopathy, fasciitis, tenosynovitis Spondylitis or sacroiliitis (40%) Conjunctivitis (20%) Anterior uveitis (10%) Systemic features:leukocytosis, fever, night sweats, anemia Patterns of Peripheral Arthritis (any peripheral joint) Symmetric polyarthritis generally similar to rheumatoid arthritis Asymmetric oligoarthritis of small and medium-sized joints DIP arthritis joints, where it characteristically also involves nails Arthritis mutilans Psoriatic arthritis-patterns Symmetric polyarthritis generally similar to rheumatoid arthritis Affects hands, wrists, ankles, and feet Generally milder than RA, more stiffness less tenderness Differentiated from RA by presence of enthesopathy, onychodystrophy, dactylitis, and DIP joint involvement, absence of subcutaneous nodules, or rheumatoid factor (negative RF test) 17
18 Psoriatic arthritis-patterns Asymmetric oligoarthritis of small and medium-sized joints Classic type- e.g. two PIP joints in one hand, a MCP joint in the other Digits of the hands and feet often affected first, characteristically with dactylitis (sausage digits) DIP arthritis, characteristically seen with nail dystrophy Classic and unique to psoriatic arthritis, but found in only ~5% of patients, primarily males Paronychia and swelling of the digital tuft may make appreciation of arthritis difficult; DDx Heberden s nodes Psoriatic arthritis-patterns Arthritis mutilans Osteolytic dissolution of joint with redundant overlying skin and telescoping motion of the digit (opera-glass hand) Distinctive but uncommon Spondylitis (5%) or sacroiliitis (40%) Isolated or can also occur with other patterns of psoriatic arthritis joint involvement Vertebral involvement differs from that of AS: Vertebrae asymmetrically affected with nonmarginal asymmetric syndesmophytes, paravertebral ossification, vertebral fusion with disk calcification, atlantoaxial joint involvement with odontoid erosion and subluxation 18
19 Psoriatic Arthritis Genetics Concordance rate among monozygotic twins of 35-70%, versus 12-20% for dizygotic twins ~40% have strongly positive family histories, most often with first degree relatives affected by psoriasis Sex: Men and women are affected equally Imprinting: If a parent and child are affected, 85% of time the affected parent will be the father Often have psoriasis HLA susceptibility alleles: HLA- Cw*0602, and HLA-B57, HLA-B37, HLA-B13 alleles that are in linkage disequilibrium with HLA-Cw*0602 Additionally HLA-B27, HLA-B38, HLA-B39 Psoriatic arthritis Psoriasis usually precedes or occurs synchronously with arthritis Psoriasis varies from obvious skin lesions to subtle involvement (eg, scalp, umbilicus, intergluteal cleft, ear), or only nail manifestations In ~15%, arthritis appears before psoriasis - a family history of psoriasis or presence of enthesopathy, spondylitis, and characteristic features, e.g. DIP disease suggests diagnosis Onset typically insidious with stiffness predominating, but occasionally may be acute and severe mimicking gout Course: usually characterized by flares and remissions Controversy over percentage progressing to joint destruction ~10%, ankylosis more common (Hallux rigidus) 19
20 Psoriatic Arthritis Progression of DIP arthritis Narrowed joint space & condylar erosions Reactive sub periosteal new bone Pencil in cup appearance Psoriatic Arthritis Nail involvement ~80% Often seen in digit involved with DIP arthritis Onycholysis Transverse ridging Onychodystrophy Pitting Acrokeratosis 20
21 Hypothetical scheme for stages in the pathogenesis of psoriatic arthritis HLA Genes + Unknown Genes Define T cell Repertoire Susceptibility Microorganism, inflammation, trauma? Initiates T cell Response Tolerance Broken? Auto- Antigen Drive Initiated Triggering of effector / memory response in the Joint Cytokine Release Synoviocyte Proliferation Erosions and Fibrosis Enlarged repertoire of effector, autoreactive T cells in blood & skin 21
Spondylitis Diseases. Psoriasis. Spondyloarthritis Diseases. Sacroiliitis. Spondyloarthritis Diseases-features common to all
 Spondyloarthritis Diseases A group of autoimmune diseases that in common appear mediated by activation of autoreactive CD8 T cells CD8 T-cell Cognitive Recognition TCR Unknown Self Antigenic Peptide Presented
Spondyloarthritis Diseases A group of autoimmune diseases that in common appear mediated by activation of autoreactive CD8 T cells CD8 T-cell Cognitive Recognition TCR Unknown Self Antigenic Peptide Presented
Class I Associated Autoimmune Diseases: Class I Associated Autoimmune Diseases: Class I Associated Autoimmune Diseases: Spondylitis Diseases
 Class I Associated Autoimmune Diseases: A group of autoimmune diseases that appear to result almost exclusively from the activation of autoreactive CD8 T cells that recognize self peptides from various
Class I Associated Autoimmune Diseases: A group of autoimmune diseases that appear to result almost exclusively from the activation of autoreactive CD8 T cells that recognize self peptides from various
A group of individually distinctive diseases with common, unifying features
 Spondyloarthritis Diseases A group of individually distinctive diseases with common, unifying features Spondylitis Diseases Ankylosing spondylitis (ASp) Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) Reiter s syndrome (RS)
Spondyloarthritis Diseases A group of individually distinctive diseases with common, unifying features Spondylitis Diseases Ankylosing spondylitis (ASp) Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) Reiter s syndrome (RS)
Spondyloarthritis Diseases. Spondylitis Diseases. Psoriasis. Spondyloarthritis Diseases Uunifying features
 A group of individually distinctive diseases with common, unifying features Spondylitis Diseases Ankylosing spondylitis (ASp) Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) Reiter s syndrome (RS) / reactive arthritis (ReA)
A group of individually distinctive diseases with common, unifying features Spondylitis Diseases Ankylosing spondylitis (ASp) Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) Reiter s syndrome (RS) / reactive arthritis (ReA)
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Spondylarthropathies
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA)
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA) Objectives: Introduction SpA disease information Pathogenesis Clinical features Team Members: Ameera Niazi - Lulwah AlShiha - Qaiss Almuhaideb - Abdullah Hashem
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA) Objectives: Introduction SpA disease information Pathogenesis Clinical features Team Members: Ameera Niazi - Lulwah AlShiha - Qaiss Almuhaideb - Abdullah Hashem
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
9 Lecture. Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม
 9 Lecture Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม Spondyloarthritis: SpA Nuntana Kasitanon Division of Rheumatology Department of Medicine Spondyloarthritis: SpA
9 Lecture Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม Spondyloarthritis: SpA Nuntana Kasitanon Division of Rheumatology Department of Medicine Spondyloarthritis: SpA
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling. Rheumatic Diseases
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
Introduction. Natural Progression of AS. Sacroiliac Joint. Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis
 A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Psoriatic Arthritis Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
CLOSER LOOK AT SpA. Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi. Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH
 CLOSER LOOK AT SpA Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH Closer look at SpA I. Categories II. SIGN & SYMPTOMS III. X-RAY IV. MRI V. MANAGMENT Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
CLOSER LOOK AT SpA Dr. Mohamed Bedaiwi Consultant Rheumatologist Rheumatology Unit - KKUH Closer look at SpA I. Categories II. SIGN & SYMPTOMS III. X-RAY IV. MRI V. MANAGMENT Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
8/29/2012. Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 1. Classification-ILAR. 1. Classification-clinical diagnosis. 1. JIA classification
 Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
Requirements in the Development of an Autoimmune Disease Amino Acids in the Shared Epitope
 + T cell MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ Induction of + T H 1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes APC Activated autoreactive +
+ T cell MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ Induction of + T H 1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes APC Activated autoreactive +
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS Division of Rheumatology Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children s Hospital of Chicago Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Medical Social Sciences Northwestern
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kaveh Ardalan, MD, MS Division of Rheumatology Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children s Hospital of Chicago Assistant Professor, Pediatrics and Medical Social Sciences Northwestern
Rheumatology. Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications. Definition of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Spondyloarthropathies
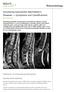 Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Amino acid sequences in the β chain HLA- DRB*0401 molecules dictate susceptibility to RA Amino Acids in the Shared Epitope
 MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ TCR Vβx + Vβx T cell Induction of + TH1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and APC type I diabetes TCR Vβx Activated
MHC/self-peptide MHC/Vβ TCR Vβx + Vβx T cell Induction of + TH1 mediated autoimmunity: A paradigm for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and APC type I diabetes TCR Vβx Activated
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
Disease mechanisms in Spondyloarthritis. Joerg Ermann, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School
 Disease mechanisms in Spondyloarthritis Joerg Ermann, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Disclosures Scientific Advisory Boards: Abbvie, Janssen, Novartis, UCB, Takeda, Eli Lilly Research
Disease mechanisms in Spondyloarthritis Joerg Ermann, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Disclosures Scientific Advisory Boards: Abbvie, Janssen, Novartis, UCB, Takeda, Eli Lilly Research
Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care
 Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
Autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases. Autoantibodies. Autoimmune diseases relatively common
 Autoimmune diseases Fundamental abnormality: the adaptive immune system is triggered by self antigens to initiate a sustained immune response against self molecules that results in tissue injury Specificity
Autoimmune diseases Fundamental abnormality: the adaptive immune system is triggered by self antigens to initiate a sustained immune response against self molecules that results in tissue injury Specificity
Physical examination of the musculosceletal- and nervous system. Pánczél Pál dr.
 Physical examination of the musculosceletal- and nervous system in the practice of internal medicine. Pánczél Pál dr. Bursae = sacks of the synovial membrane fulfilled with synovium. Localised between
Physical examination of the musculosceletal- and nervous system in the practice of internal medicine. Pánczél Pál dr. Bursae = sacks of the synovial membrane fulfilled with synovium. Localised between
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Elective Student P. H.
 Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Bones? Did someone say bones? 12/31/2012. W.R Reinus, MD MBA FACR
 William R. Reinus, MD MBA FACR Temple University Medical Center Aug 2012 (55) 1 Bones? Did someone say bones? 2 ABC S OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis: By definition, any disease that is jointcentered: Both sides
William R. Reinus, MD MBA FACR Temple University Medical Center Aug 2012 (55) 1 Bones? Did someone say bones? 2 ABC S OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis: By definition, any disease that is jointcentered: Both sides
Presenter Disclosure Information
 4:15 5:45 pm Diagnostic Challenges of Rheumatologic Disease SPEAKER Peng Thim Fan, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Peng Thim Fan,
4:15 5:45 pm Diagnostic Challenges of Rheumatologic Disease SPEAKER Peng Thim Fan, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Peng Thim Fan,
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis
 Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES
 www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES What is it? The juvenile spondyloarthropathies constitute are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints (arthritis) and
www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHROPATHIES What is it? The juvenile spondyloarthropathies constitute are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints (arthritis) and
Topic (Final-03): Immunologic Tolerance and Autoimmunity-Part II
 Topic (Final-03): Immunologic Tolerance and Autoimmunity-Part II MECHANISMS OF AUTOIMMUNITY The possibility that an individual s immune system may react against autologous antigens and cause tissue injury
Topic (Final-03): Immunologic Tolerance and Autoimmunity-Part II MECHANISMS OF AUTOIMMUNITY The possibility that an individual s immune system may react against autologous antigens and cause tissue injury
Objectives. Joint Pain. Case 1. Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) 12/4/2010
 Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Objectives Rheumatology for the Primary MD (Not just your grandmother s disease) Identify when it is appropriate to refer for rheumatologic evaluation Autoimmune/ Inflammatory v. noninflammatory disease
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination
 History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination Introduction A thorough rheumatologic assessment is performed within the context of a good general evaluation of the patient. The patient should be undressed
History Taking and the Musculoskeletal Examination Introduction A thorough rheumatologic assessment is performed within the context of a good general evaluation of the patient. The patient should be undressed
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Introduction Rheumatoid arthritis is a fairly common joint disease that affects up to 2 million Americans. Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most debilitating forms of arthritis.
HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 504-509 HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis J. C. WOODROW, AND C. J. EASTMOND From the Department of Medicine, Liverpool University SUMMARY One
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 504-509 HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis J. C. WOODROW, AND C. J. EASTMOND From the Department of Medicine, Liverpool University SUMMARY One
Jeopardy. What s the rash? $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400
 Jeopardy Antibodies & more antibodies Aching joints What s the rash? Potpourri Image Challenge $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500
Jeopardy Antibodies & more antibodies Aching joints What s the rash? Potpourri Image Challenge $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500
Axial Spondyloarthritis. Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital
 Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Relation between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A study of 40 patients
 2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
2018 ReachMD Page 1 of 10
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES
 AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis PULMONARY MEDICINE. DR. R. ADITYAVADAN FINAL YEAR PG, DEPT. OF ETIOLOGY AS is a chronic multisystem disease characterized by inflammation of the spine,
Pulmonary Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis PULMONARY MEDICINE. DR. R. ADITYAVADAN FINAL YEAR PG, DEPT. OF ETIOLOGY AS is a chronic multisystem disease characterized by inflammation of the spine,
AUTOIMMUNITY TOLERANCE TO SELF
 AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
AUTOIMMUNITY CLINICAL CORRELATES Pamela E. Prete, MD, FACP, FACR Section Chief, Rheumatology VA Healthcare System, Long Beach, CA Professor of Medicine, Emeritus University of California, Irvine Colonel
Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London
 Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London Background Extraintestinal manifestations of IBD are well recognised. They include:- Arthritis - peripheral and axial Eye complications
Who gets EIMs? Dr Tim Orchard St Mary s Hospital & Imperial College London Background Extraintestinal manifestations of IBD are well recognised. They include:- Arthritis - peripheral and axial Eye complications
JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis. Dr Johan Siebert
 JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis Dr Johan Siebert 1 NORMAL DIARTHRODIAL JOINT Synovial is a thin membrane enclosing the joint space The joint space contains fluid that bathes the joint and reduces friction
JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis Dr Johan Siebert 1 NORMAL DIARTHRODIAL JOINT Synovial is a thin membrane enclosing the joint space The joint space contains fluid that bathes the joint and reduces friction
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Undifferentiated SpA Juvenile SpA Ankylosing Spondylitis Psoriatic Arthritis Arthritis associated with Ulcerative Colitis/ Crohn s Disease Reactive Arthritis Acute anterior
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Undifferentiated SpA Juvenile SpA Ankylosing Spondylitis Psoriatic Arthritis Arthritis associated with Ulcerative Colitis/ Crohn s Disease Reactive Arthritis Acute anterior
Joint Disorders. Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10. Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Where has SARA gone? Prof. David Kane Consultant Rheumatologist Beacon & Tallaght Hospitals. Clinical Professor in Rheumatology Trinity College Dublin
 Where has SARA gone? Prof. David Kane Consultant Rheumatologist Beacon & Tallaght Hospitals Clinical Professor in Rheumatology Trinity College Dublin 1 Reactive Arthritis Seronegative Asymmetrical Arthritis
Where has SARA gone? Prof. David Kane Consultant Rheumatologist Beacon & Tallaght Hospitals Clinical Professor in Rheumatology Trinity College Dublin 1 Reactive Arthritis Seronegative Asymmetrical Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
Rheumatoid Arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation of the joints. Autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly
EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS. Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital
 EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital EIA: Introduction National priority Preventable cause of disability Very common condition High
EARLY INFLAMMATORY ARTHRITIS Cristina Tacu Consultant Rheumatologist Brighton and Sussex University Hospital EIA: Introduction National priority Preventable cause of disability Very common condition High
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW. Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center
 RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
Systemic forms of stiffness
 Systemic forms of stiffness ANNA LITWIC CONSULTANT RHEUMATOLOGIST SALISBURY DISTRICT HOSPITAL CLINICAL RESEARCH FELLOW MRC LIFECOURSE EPIDEMIOLOGY UNIT Overview Rheumatoid arthritis Know it when you see
Systemic forms of stiffness ANNA LITWIC CONSULTANT RHEUMATOLOGIST SALISBURY DISTRICT HOSPITAL CLINICAL RESEARCH FELLOW MRC LIFECOURSE EPIDEMIOLOGY UNIT Overview Rheumatoid arthritis Know it when you see
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R
 The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings
 Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings Poster No.: C-0399 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Persechino 1, L. Cristiano 1, A. Bartoloni 1, C. Cantone 2, A. Keywords: DOI:
Psoriatic arthritis: early ultrasound findings Poster No.: C-0399 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Persechino 1, L. Cristiano 1, A. Bartoloni 1, C. Cantone 2, A. Keywords: DOI:
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Semiology of arthopathies and its complications
 Semiology of arthopathies and its complications Poster No.: C-1029 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Caba Cuevas, E. M. Ocón Alonso, D. M. Castaño Palacio, I. Zabala Martín-Gil,
Semiology of arthopathies and its complications Poster No.: C-1029 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Caba Cuevas, E. M. Ocón Alonso, D. M. Castaño Palacio, I. Zabala Martín-Gil,
Ankylosing Spondylitis. DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017
 Ankylosing Spondylitis DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or
Ankylosing Spondylitis DR. Milt Baker SEA Courses 2017 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form or
Seronegative Arthritis. Dr Mary Gayed 25 th April 2018
 Seronegative Arthritis Dr Mary Gayed 25 th April 2018 Overview Description of the conditions Discussion of symptoms & investigations that may be required Discussion of management and treatment Questions
Seronegative Arthritis Dr Mary Gayed 25 th April 2018 Overview Description of the conditions Discussion of symptoms & investigations that may be required Discussion of management and treatment Questions
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Rheumatoid arthritis and Psoriatic arthritis: a guide for Primary Care. Nina Flavin, MD Rheumatology Confluence Health April 13 th, 2018
 Rheumatoid arthritis and Psoriatic arthritis: a guide for Primary Care Nina Flavin, MD Rheumatology Confluence Health April 13 th, 2018 No Disclosures Objectives Recognize early signs of RA/PsA what to
Rheumatoid arthritis and Psoriatic arthritis: a guide for Primary Care Nina Flavin, MD Rheumatology Confluence Health April 13 th, 2018 No Disclosures Objectives Recognize early signs of RA/PsA what to
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis
 Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2. Inflammatory Diseases. Definition. Imaging Signs
 Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Psoriatic Arthritis Shared Decision Making
 Psoriatic Arthritis Shared Decision Making Disease Modifying Drug Therapy DMARDs Therapy El Miedany et al. Ann Rheum Dis 74(Suppl2): 1002 DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-eular.1410 www.rheumatology4u.com
Psoriatic Arthritis Shared Decision Making Disease Modifying Drug Therapy DMARDs Therapy El Miedany et al. Ann Rheum Dis 74(Suppl2): 1002 DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-eular.1410 www.rheumatology4u.com
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Self-tolerance. Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens. Central Tolerance. Peripheral tolerance
 Autoimmunity Self-tolerance Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens Central Tolerance Peripheral tolerance Factors Regulating Immune Response Antigen availability Properties
Autoimmunity Self-tolerance Lack of immune responsiveness to an individual s own tissue antigens Central Tolerance Peripheral tolerance Factors Regulating Immune Response Antigen availability Properties
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Disclosures. Enteropathic Arthritis. Definition. Outline. Pathogenesis 5/4/2018. How Often do Patients with SpA Have Intestinal Inflammation?
 Disclosures Enteropathic Arthritis Site PI on UCB NR-Ax-SpA trial Site PI on Abbvie AS trial Mark C. Fisher, MD MPH Outline SpA and Colitis IBD and Arthritis Other intestinal processes associated with
Disclosures Enteropathic Arthritis Site PI on UCB NR-Ax-SpA trial Site PI on Abbvie AS trial Mark C. Fisher, MD MPH Outline SpA and Colitis IBD and Arthritis Other intestinal processes associated with
Immunological Tolerance
 Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Immunological Tolerance Introduction Definition: Unresponsiveness to an antigen that is induced by exposure to that antigen Tolerogen = tolerogenic antigen = antigen that induces tolerance Important for
Mary Derlacki, FNP. No financial relationships to disclose. Office Rheumatology for the Nurse Practitioner. Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Office Rheumatology for the Nurse Practitioner Mary Derlacki, FNP Drs. Cassell and Boren Eugene, OR 541-687-0816 mderlacki@comcast.net No financial relationships to disclose Rheumatoid Arthritis 1% of
Office Rheumatology for the Nurse Practitioner Mary Derlacki, FNP Drs. Cassell and Boren Eugene, OR 541-687-0816 mderlacki@comcast.net No financial relationships to disclose Rheumatoid Arthritis 1% of
Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation
 F.A. Davis: Advantage Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation(10.6.15) Page 1 Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation The musculoskeletal system is affected by infections and inflammatory conditions.
F.A. Davis: Advantage Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation(10.6.15) Page 1 Musculoskeletal Infection and Inflammation The musculoskeletal system is affected by infections and inflammatory conditions.
Chapter 09: Musculoskeletal Disorders Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904)
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Rheumatoid Arthritis Manish Relan, MD FACP RhMSUS Arthritis & Rheumatology Care Center. Jacksonville, FL (904) 503-6999. 1 Disclosures Speaker Bureau: Abbvie 2 Objectives Better understand the pathophysiology
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
 EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS ACTIVITY 1: EARLY COLLABORATION IN THE TREATMENT OF PSA Key Slides COMMON COMORBIDITIES OF PSORIATIC DISEASE
EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS ACTIVITY 1: EARLY COLLABORATION IN THE TREATMENT OF PSA Key Slides COMMON COMORBIDITIES OF PSORIATIC DISEASE
Dr Tracey Kain. Associate Professor Ed Gane
 Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
1 Tolerance 2. Regulatory T cells; why tolerance fails Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Regulatory T cells: functions and clinical relevance Pathogenesis of autoimmunity: why selftolerance fails
Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Combined Clinic Electronic Medical Records Form
 Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Combined Clinic Electronic Medical Records Form NAME: AGE: SEX: CHIEF COMPLAINT: HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient presents for the initial evaluation of [psoriasis
Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Combined Clinic Electronic Medical Records Form NAME: AGE: SEX: CHIEF COMPLAINT: HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient presents for the initial evaluation of [psoriasis
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies
 A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
TCR-p-MHC 10/28/2013. Disclosures. Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Autoimmunity: good genes, elegant mechanisms, bad results
 Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Autoimmunity: good genes, elegant mechanisms, bad results The meaning and significance of HLA associations Disclosures No relevant commercial relationships
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Autoimmunity: good genes, elegant mechanisms, bad results The meaning and significance of HLA associations Disclosures No relevant commercial relationships
