The patients attended the sickle cell clinic of the. University Hospital of the West Indies in Kingston
|
|
|
- Griffin McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, Non-gouty arthritis in sickle cell disease: report of 37 consecutive cases K. de CEULAER, M. FORBES, D. ROPER, AND G. R. SERJEANT From the Medical Research Council Laboratories (Jamaica), University of the West Indies, Mona, Kingston 7, Jamaica SUMMARY Arthritis in association with sickle cell disease was seen in 37 patients in a 2½/2-year period. Cases of gout and of avascular necrosis of the femoral head were excluded. In 12 patients a non-inflammatory effusion occurred during the course of a painful crisis, in 12 patients an ankle effusion occurred in association with spontaneous development or deterioration of leg ulceration, and in 13 patients there was a group of miscellaneous arthritides. Ankle arthritis with leg ulceration has not been previously recognised, and its association with spontaneous ulceration, which is presumed to have a vaso-occlusive origin, is compatible with ischaemic synovial damage. The aetiology may therefore be similar to that believed to account for effusions in association with the painful crisis. The incidence and pattern of true arthritis in sickle cell disease is largely unknown. Well established causes of arthritis include joint damage associated with avascular necrosis of the femoral head1 2 and gout secondary to hyperuricaemia.35 Less common causes include infective arthritis,6-9 migratory polyarthritis,'t 11 and systemic lupus erythematosus,12-14 although it is unclear whether these are causally linked or occur coincidentally with sickle cell disease. Pains related to the joints commonly occur in the painful crisis, but these are generally attributable to avascular necrosis of bone marrow in the juxtaarticular areas of the long bones.''5 A true arthritis may also occur in association with the painful crisis, " '7'' although little is known of its frequency, characteristics, or outcome. At a large sickle cell clinic in Jamaica 37 patients with sickle cell disease and arthritis unassociated with gout or avascular necrosis of the femoral head have been assessed in a 21/2-year period. These have included 12 patients developing arthritis during a painful crisis, 13 with miscellaneous arthritides, and 12 with a newly recognised syndrome of ankle arthritis associated with recent leg ulceration. The characteristics of these groups are presented. Correspondence to Professor G. R. Serjeant, Medical Research Council Laboratories, University of the West Indies, Kingston 7, Jamaica, WI. Acccptcd for publication 2(0 January Patients and methods The patients attended the sickle cell clinic of the University Hospital of the West Indies in Kingston and a group of peripheral sickle cell clinics operated by the staff of the Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratories during the period March 1980 to November Patients with arthritis associated with gout or with avascular necrosis of the femoral head were excluded, as were patients with painful limitation of the hip in which early avascular necrosis of the femoral head could not be ruled out. There remained 37 patients in whom the diagnosis of haemoglobinopathy was made by standard criteria. " Thirty-one had homozygous sickle cell (SS) disease, five had sickle cell-haemoglobin C (SC) disease, and one had sickle cell-beta' thalassaemia (S3p thal). The diagnosis of arthritis was based on objective signs which included warmth, swelling, effusion, and limitation of movement in at least one joint. When possible, joint fluid was aspirated and examined for total white blood cell and differential counts, under polarised light for crystals, and by bacterial culture. If only limited amounts of fluid were obtained, examination was confined to culture and presence of crystals. The viscosity of synovial fluid was assessed semiquantitatively by observing it dropping from the aspiration needle. Haematological investigations including red cell indices, reticulocyte and irreversibly sickled cell 599
2 600 Ceulaer, Forbes, Roper, Serjeant (ISC) counts, and estimations of bilirubin and fetal haemoglobin (HbF) were performed as previously described.2' Certain of these haematological indices were not normally distributed, and comparison of their distributions in the different groups was performed after transformation to obtain a more normal distribution. These transformations were considered appropriate for HbF, red cell count (RBC), reticulocytes, total bilirubin, and ISC count and the following transformations were used: loge (HbF + 1), loge RBC, loge (retic + 1), loge (total bilirubin + 1), and loge (ISC + 10). Other tests included serum urate and creatinine, VDRL, liver function tests, and tests for latex fixation, antinuclear antibodies, DNA binding, serum complement C3, C4, factor B, and immunoglobulins. Radiographs of affected joints were taken, including the sacroiliac joint where indicated. Results During the period of the study approximately 1100 patients with SS disease of which seven were known to have gout and 55 were known to have avascular necrosis of the femoral head attended these clinics. Since these complications and the arthritides described in this report were almost confined to patients over the age of 10 years, the population at risk would be of the order of 700 patients with SS disease. These gross assumptions would approximate assessments of the prevalence of gout at 1%, avascular necrosis of the femoral head at 8%, and of other arthritides at 4% of this patient sample. Of the 37 patients with arthritis, 12 had arthritis in association with the painful crisis (group I), 12 had arthritis of the ankle associated with leg ulceration (group II), and 13 had a systemic, infectious, or degenerative type of arthritis (group III). Group I. Arthritis associated with painful crisis. Arthritis during the course of a painful crisis was observed in 12 patients (11 SS, 1 SC) of which 6 were male and 6 were female with a mean age of 26*9 years (range years). A monoarthritis affected the knee in eight, and the ankle in two, one patient had an oligoarthritis involving both knees and one ankle, and the other a polyarthritis involving elbows knees, and ankles. These 12 patients were all seen by one observer (K. de C.) during a period when the same observer assessed 64 patients in painful crisis suggesting a prevalence of arthritis of approximately 20% in those attending clinic for painful crises. All patients had typical painful crises with symptoms maximal around the affected joint. The involved joints were swollen, but with only slight limitation of movement, and the point of maximal tenderness was over the epiphyses rather than the joint space. Radiographs at the time of pain did not reveal changes different from those in the steady state and on convalescence there were no radiological features of avascular necrosis of bone. Synovial fluid was generally non-inflammatory and without crystals (Table 1). The arthritis usually resolved within 2-3 weeks, though it persisted for four months in one patient. The prognosis was excellent, all patients healing without residual functional impairment. Group HI. Arthritis associated with leg ulceration. Arthritis limited to the ankle and which affected the same area as a typical malleolar ulcer occurred in 12 patients. All had SS disease. There were 4 males and 8 females with a mean age of 27*2 years (range years). The arthritis appeared simultaneously or shortly after the development of a spontaneous leg ulcer in seven patients or at the same time as the spontaneous deterioration of an existing ulcer in five patients. In two patients ulceration and arthritis were bilateral. There was usually extreme limitation of ankle movement which impaired walking. Joint fluid was typically non-inflammatory, with predominantly mononuclear cells, sterile, and without urate crystals (Table 1). In one patient the synovial fluid leucocyte count was 15-3 x 109/l, but only 2% were polymorphonuclear cells, the serum urate was 0-56 mmol/l, and no crystals were seen in the joint fluid. The diagnosis of gout was considered unlikely and rapid resolution of the arthritis attended healing of the leg ulcer. Radiology in this group failed to show any acute changes. Arthritis associated with leg ulceration was usually chronic (mean duration 7-7 months, range 1-26 months) and resolved with improvement of the leg ulcer. Swelling and limitation of movement markedly improved with conventional non-steroid Table 1 Synovial fluid analysis in arthritis in SS disease Normal Arthritis with Arthritis with painful crisis leg ulceration (n=8) (n=7) Appearance Clear, Yellow Yellow colourless Abnormal viscosity 0 0/8 3/7 Nucleated cells (x 109/l) < (mean-range) ( ) ( ) % polymorphonuclear leucocytes < (mean range) (0-18) (2-34) Crystals Culture Sterile Sterile Sterile
3 anti-inflammatory drugs. Resolution was usually complete with full function and without radiological abnormalities. Group III. Miscellaneous arthritides. Thirteen patients (8 SS, 4 SC, 1 Sp' thal) presented with a variety of systemic arthritic disorders. All were female and the mean age was 29 years (range 7-69 years). Typical systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with non-deforming arthritis, erythematous skin rash, alopecia, high DNA binding, and low serum complement occurred in one patient, and in two others there was a chronic non-deforming polyarthritis with positive antinuclear antibody test (ANA) but without other features of SLE. Other causes included seropositive erosive rheumatoid arthritis in one, arthritis associated with ulcerative colitis in one, osteoarthrosis of the knee in two, gonococcal arthritis in one, self-limiting flitting polyarthritis with negative antistreptolysin 0 titre and negative bacteriology in two, and chronic seronegative monoarthritis of the knee with quadriceps atrophy in two. One patient with SC disease had severe rheumatic heart disease and a chronic arthritis of the right hip. The patient with ulcerative colitis received systemic corticosteroids and developed severe recurrent painful crises until the treatment was stopped. The gonococcal arthritis responded dramatically to intravenous penicillin. The non-infectious polyarthritides were well controlled on ibuprofen. Investigations. Synovial fluid findings in the group with arthritis associated with painful crises and with leg ulceration are shown in Table 1. The haematology in individuals during the period of arthritis showed no consistent differences when compared with their own steady state values. The steady state haematology in patients developing arthritis did not differ from that in SS controls of similar age (Table 2). Non-gouty arthritis in sickle cell disease 601 Serum immunoglobulin and complement components also showed no significant differences in the groups with arthritis. Discussion The symptoms of sickle cell disease are not infrequently misdiagnosed as 'rheumatism' or arthritis, because the painful crisis, a characteristic manifestation of the disease, usually causes pain referred to the joint areas. It is now recognised that the painful crisis generally results from a limited avascular necrosis of bone marrow in the intermediate zone, a 'watershed' of blood supply between the distribution of branches of the main nutrient artery and the small perforating synovial vessels. Pain in the painful crisis is therefore maximal in the juxta-articular areas of the long bones, and patients frequently refer to joint pains affecting the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists, although on examination the point of maximal tenderness overlies the bone rather than the joint space. A true arthritis is recognised in association with the painful crisis, 7-19 but is thought to be uncommon. Part of the reason for this is that the joint swelling may be minimal and that the symptoms of the effusion are overshadowed by the clinical features of the painful crisis. The present study suggests that such an arthritis may be much commoner than previously recognised, since it occurred in one-fifth of patients seen with painful crises. No assessments of the prevalence of arthritis in the painful crisis has been possible in previously reported cases. Three out of five cases described by Hanissian and Silverman"' were in association with a painful crisis, and one of these had unusual features with bilateral avascular necrosis of the femoral heads at the age of 9 years, a reticulocyte count of Table 2 Comparison of steady-state haematological values in controls (aged years) and in patients developing arthritis associated with the painful crisis and with leg ulceration. Bracketed figures refer to means re-expressed in original units Conitrol values Arthritis with A rthritis w ith painful crisis leg ulcerationi n mneani SD n mean SD ii tneai SD Log,. (% Hb F + 1) (3-6) (4-3) I8 (5-1) 0(4 Total Hb (g/dl) ' MCHC (g/dl) '4 Log, (RBC x 1012/1) (2-9) () (2-9) (-I (2-6) 0*2 MCV (fl) ( Log, (% reticulocytes + 1) (9-9) (9-1) 0( (120-0) (-6 Platelets (x 109/l) Log, (total bilirubin + 1) (3-3) (2-1) 0(5 11 1*3 (2 7) 0-3 Log, (% ISC + 10) (7-3) (6-3) (7-8) 0)-2
4 602 Ceulaer, Forbes, Roper, Serjeant 40%, and a recurrent arthritis even involving the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Uric acid levels were not available. The case described by Orozco- Alcala and Baum18 had a synovial fluid leucocyte count of 176 x 109/l with 97% polymorphonuclear cells, and, although septic arthritis could not be confirmed on culture, the rapid improvement in synovial fluid cell count following antibiotic therapy was compatible with that diagnosis. The report by Espinoza et al.11 is difficult to evaluate, since not all patients had sickle cell disease, and the report concerned joint symptoms rather than effusions or other evidence of arthritis. In seven patients in whom effusions occurred in association with a painful crisis the leucocyte count in synovial fluid exceeded 20 x 109/l in four, two of whom had raised uric acid levels, and in two levels were not recorded. Although no crystals were seen, a diagnosis of gout was possible in these cases, since crystals are not always present on single synovial fluid examination in this condition Of the seven patients reported by Schumacher et al. 17 five developed arthritis during the course of a painful crisis, and synovial fluid in the four sampled cases was of a noninflammatory character. As in the cases in the present report, there is a pattern of non-inflammatory effusions in association with some painful crises. The term 'sympathetic effusion' has been applied, but it is unclear whether this represents a passive synovial response to adjacent bone damage or whether there is a primary ischaemic involvement of the synovium. The blood supply to the bone marrow is compromised during the painful crisis, and it is possible that a similar avascular process affects the synovium. Synovial histology in arthritis during the painful crisis is usually normal or shows only local lining cell proliferation and minimal inflammatory cell infiltration." 1(0 Congestion and occlusion of small synovial blood vessels has been observed, 17 and such damage could increase permeability of capillaries, leakage of plasma into the synovium, and a secondary inflammatory reaction. The extent of such vessel obstruction could determine the degree of synovitis and hence the variable findings in synovial fluid of arthritis associated with the painful crisis. In this context the newly recognised arthritis occurring in association with spontaneous leg ulceration is of interest. Leg ulceration presents two basically different patterns in sickle cell disease, some lesions being clearly traumatic and others spontaneous. These latter ulcers are assumed to result from skin infarction, the evidence for this being the absence of trauma, their natural history, and the fact that these ulcers occur more frequently than expected in patients with high vaso-occlusive indices.24 The association of arthritis with this type of ulceration therefore supports the possibility of synovial ischaemia. The longer duration of ankle arthritis would also be compatible with this, since lymphoedema and the higher venous pressure at this site probably contribute to vaso-occlusion. Confirmation of the aetiology of the arthritis with leg ulceration must await pathological studies or the development of diagnostic techniques capable of detecting localised synovial ischaemia or necrosis. The miscellaneous arthritides represent a heterogenous group of conditions some of which occur coincidentally with sickle cell disease. The association with gout is well established because of the tendency to hyperuricaemia in SS disease, but such cases were excluded from the present report. The susceptibility to some infections suggested that an increased prevalence of septic arthritis might occur, but such events appear to be uncommon. A chronic synovitis leading to joint destruction has been reported in sickle cell disease,25 and two patients in the present study had a chronic monoarthritis, but it is unclear whether the complication was aetiologically related. Systemic lupus erythematosus also occurs in sickle cell disease, but there are insufficient data to determine whether this association is coincidental. SLE-like syndromes occur in patients with genetic complement deficiencies, and abnormal complement function in SS disease26 raises the possibility of an immune basis for arthritis.27 Immune complex disease such as poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis28 and autologous immune complex nephritis29 have both been described in sickle cell disease. Establishment of any statistical association between these conditions and sickle cell disease must await more extensive data on their prevalence. References 1 Diggs L W. Bone and joint Iesions in sickle-cell disease. Clin Orthop 1967; 52: Chung S M K, Ralston E L. Necrosis of the femoral head associated with sickle-cell anemia and its genetic variants. A review of the literature and study of thirteen cases. J Bone Joint Surg 1969; 51A: Gold M S, Williams J C, Spivack M, Grann V. Sickle cell anemia and hyperuricemia. JAMA 1968; 206: Ball G V, Sorensen L B. The pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and gout in sickle cell anemia. Arthritis Rheum 1970; 13: Rothschild B M, Sienknecht C W, Kaplan S B, Spindler J S. Sickle cell disease associated with uric acid deposition disease. Ann Rheum Dis 1980; 39: Barrett-Connor E. Bacterial infection and sickle cell anemia. Medicine (Baltimore) 1971; 50: Ebong W W. The treatment of severely ill patients with sickle cell anemia and associated septic arthritis. Clin Orthop 1980; 149: Palmer D W, Ellman M H. Septic arthritis and Reiter's syndrome in sickle cell disorders: case reports and implications for management. South Med J 1976; 69:
5 9 Nelson J D. Sickle-cell disease and bacterial bone-and-joint infection. N Engl J Med 1975; 292: Hanissian A S, Silverman A. Arthritis of sickle cell anemia. South Med J 1974; 67: Espinoza L R, Spilberg I, Osterland C K. Joint manifestations of sickle cell disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1974; 53: Wilson F M, Clifford G 0, Wolf P L. Lupus erythematosus associated with sickle cell anemia. Arthritis Rheum 1964; 7: Wilson W A, Nicholson G D, Hughes G R V, Amin S, Alleyne G A 0, Serjeant G R. Systemic lupus erythematosus and sickle-cell anaemia. Br Med J 1976; i: Karthikeyan G, Wallace S L, Blum L. SLE and sickle cell disease. Arthritis Rheum 1978; 21: Charache S, Page D L. Infarction of bone marrow in sickle cell disorders. Ann Intern Med 1967; 67: Alavi A, Bond J P, Kuhl D E, Creech R H. Scan detection of bone marrow infarcts in sickle cell disorders. J Nucl Med Allied Sci 1974; 15: Schumacher H R, Andrews R, McLaughlin G. Arthropathy in sickle-cell disease. Ann Intern Med 1973; 78: Orozco-Alcala J, Baum J. Arthritis during sickle-cell crisis. N Engl J Med 1973; 288: Alavi A, Schumacher H R, Dorwart B, Kuhl D E. Bone marrow scan evaluation of arthropathy in sickle cell disorders. Arch Intern Med 1976; 136: Serjeant G R. The clinical features of sickle cell disease. Amsterdam: North Holland, Hayes R J, Beckford M, Grandison Y, Mason K, Serjeant B E, Non-gouty arthritis in sickle cell disease 603 Serjeant G R. The haematology of steady state homozygous sickle cell disease. l. Frequency distribution, longitudinal observations, effects of age and sex. Br J Haematol in press. 22 Patel A R. Arthropathy in sickle-cell disease. N Engl J Med 1973; 288: Schumacher H R, Jiminez S A. Gibson T. et al. Acute gouty arthritis without uratc crystals identified on initial examination of synovial fluid: report on nine patients. Arthritis Rheumn 1975; 18: Serjeant G R. Leg ulceration in sickle ccll anemia. Arch Intern Med 1974; 133: Schumacher H R. Dorwart B B. Bond J, Alavi A, Miller W. Chronic synovitis with early cartilage destruction in sickle cell disease. Ann Rhleu,n Dio 1977; 36: Johnston R B, Newman S L. Struth A G. An abnormality of the alternate pathway of complement activation in sickle-cell disease. N Enigl J Med 1973; 288: White L E. Reeves J D. Polyarthritis and positive LE preparation in sickle hcmoglobinopathics: a report of two cases. J Pediatr 1979; 95: Nicholson G D. Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis in adult Jamaicans with and without sickle cell anaemia. West Indian Med J 1977; 26: Strauss J. Pardo V, Koss M N. Griswold W, McIntosh R M. Nephropathy associated with sickle cell anemia: an autologous immune complex nephritis. I. Studies on nature of glomerularbound antibody and antigen identification in a patient with sickle cell diseasc and immunc deposit glomerulonephritis. Amn J Med 1975; 58: Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 August Downloaded from on 3 September 2018 by guest. Protected by
Chronic synovitis with early cartilage destruction in
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 413-419 Chronic synovitis with early cartilage destruction in sickle cell disease H. RALPH SCHUMACHER, BONNIE B. DORWART, JAMES BOND, ABASS ALAVI, AND WALLACE
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 413-419 Chronic synovitis with early cartilage destruction in sickle cell disease H. RALPH SCHUMACHER, BONNIE B. DORWART, JAMES BOND, ABASS ALAVI, AND WALLACE
Markedly raised synovial fluid leucocyte counts
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 404W409 Markedly raised synovial fluid leucocyte counts not associated with infectious arthritis in children ANDREW R. BALDASSARE, FRANK CHANG, AND JACK ZUCKNER
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 404W409 Markedly raised synovial fluid leucocyte counts not associated with infectious arthritis in children ANDREW R. BALDASSARE, FRANK CHANG, AND JACK ZUCKNER
Serum urate concentrations in homozygous sickle
 J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:965-969 Serum urate concentrations in homozygous sickle cell disease K DE CEULAER, AG MORGAN, E CHOO-KANG, WA WILSON, GR SERJEANT From the Department ofmedicine and the Medical Research
J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:965-969 Serum urate concentrations in homozygous sickle cell disease K DE CEULAER, AG MORGAN, E CHOO-KANG, WA WILSON, GR SERJEANT From the Department ofmedicine and the Medical Research
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis
 Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS. Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA. University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014
 SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
DISCUSSION BY: Dr M. R. Shakeebi, MD, Rheumatologist
 Case presentations Related to some Rheumatic Diseases Lab & Clinic i Programs, Tuesday, April 24, 2012 COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD, Immunologist COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD,
Case presentations Related to some Rheumatic Diseases Lab & Clinic i Programs, Tuesday, April 24, 2012 COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD, Immunologist COORDINATOR: Dr M. Mahdi Mohammadi, LMD,PhD,
Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary
 Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism or Arthritis 2. Arthritis Monoarticular Polyarticular - :- (Asymmetrical) (Symetrical) :- -Crystals, Gout - Infective acute
Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism or Arthritis 2. Arthritis Monoarticular Polyarticular - :- (Asymmetrical) (Symetrical) :- -Crystals, Gout - Infective acute
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential. 2. To understand the four stages of gout
 Objectives 1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential GOUT 2. To understand the four stages of gout 3. To develop an approach for the acute treatment of gout Anthony Lim 9/13/12 Cycle 3 4.
Objectives 1. To review the diagnosis of gout and its differential GOUT 2. To understand the four stages of gout 3. To develop an approach for the acute treatment of gout Anthony Lim 9/13/12 Cycle 3 4.
Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa
 Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa Hywel Davies BSc ( ),Andrew J Unwin BSc, Nick P H Morgan BSc Windsor Knee Clinic, Windsor, United Kingdom Correspondence: Hywel Davies, Windsor
Synovial Chondromatosis Associated with Polyarteritis Nodosa Hywel Davies BSc ( ),Andrew J Unwin BSc, Nick P H Morgan BSc Windsor Knee Clinic, Windsor, United Kingdom Correspondence: Hywel Davies, Windsor
(48.5%); aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, 75
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 911-915 Acute osteomyelitis in Nigerians with sickle cell disease WALTON W EBONG From the University College Hospital, Ibadan, Nigeria SUMMARY Acute osteomyelitis
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 911-915 Acute osteomyelitis in Nigerians with sickle cell disease WALTON W EBONG From the University College Hospital, Ibadan, Nigeria SUMMARY Acute osteomyelitis
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis
 Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
Etiology: Pathogenesis Clinical manifestation Investigation Treatment Prognosis JIA is the most common rheumatic disease in childhood and a major cause of chronic disability. Etiology: Unknown, but may
received penicillin before admission, an organism was later grown from the bone at operation. The fifth patient (Case
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 40 Septic arthritis A. S. RUSSELL AND B. M. ANSELL M.R.C. Rheuimatism Research Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, Taplow, Maidenhead, Berks. Joint infection, particularly
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 40 Septic arthritis A. S. RUSSELL AND B. M. ANSELL M.R.C. Rheuimatism Research Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, Taplow, Maidenhead, Berks. Joint infection, particularly
PRELIMINARY CRITERIA FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF THE ACUTE ARTHRITIS OF PRIMARY GOUT
 895 PRELIMINARY CRITERIA FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF THE ACUTE ARTHRITIS OF PRIMARY GOUT STANLEY L. WALLACE, HARRY ROBINSON, ALFONSE T. MASI, JOHN L. DECKER, DANIEL J. McCARTY. and T SAI-FAN Yo The American
895 PRELIMINARY CRITERIA FOR THE CLASSIFICATION OF THE ACUTE ARTHRITIS OF PRIMARY GOUT STANLEY L. WALLACE, HARRY ROBINSON, ALFONSE T. MASI, JOHN L. DECKER, DANIEL J. McCARTY. and T SAI-FAN Yo The American
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Rheumatology Pearls 1) A detailed history is much more useful in the work up of patients with inflammatory peripheral arthritis than any lab tests.
 Rheumatology Pearls 1) A detailed history is much more useful in the work up of patients with inflammatory peripheral arthritis than any lab tests. Features suggestive of an inflammatory arthritis that
Rheumatology Pearls 1) A detailed history is much more useful in the work up of patients with inflammatory peripheral arthritis than any lab tests. Features suggestive of an inflammatory arthritis that
Rheumatology Cases for the Internist
 Rheumatology Cases for the Internist Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology Vice Chair, Department of Medicine University of Maryland School
Rheumatology Cases for the Internist Marc C. Hochberg, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Head, Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology Vice Chair, Department of Medicine University of Maryland School
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Dr Banu Kaya Consultant Haematologist Barts Health NHS Trust Royal London Hospital, London, UK SICKLE CELL AND THALASSAEMIA OVERVIEW
 Dr Banu Kaya Consultant Haematologist Barts Health NHS Trust Royal London Hospital, London, UK SICKLE CELL AND THALASSAEMIA OVERVIEW Objectives Gain awareness of haemoglobinopathy inheritance, pathophysiology
Dr Banu Kaya Consultant Haematologist Barts Health NHS Trust Royal London Hospital, London, UK SICKLE CELL AND THALASSAEMIA OVERVIEW Objectives Gain awareness of haemoglobinopathy inheritance, pathophysiology
Non-malignant hematologic disorders associated arthropathies: hemoglobinopathy-associated musculoskeletal manifestations, hemophilia
 Non-malignant hematologic disorders associated arthropathies: hemoglobinopathy-associated musculoskeletal manifestations, hemophilia HAEMOGLOBINOPATHIES = inherited disorders of globin divided into: Thalassaemia
Non-malignant hematologic disorders associated arthropathies: hemoglobinopathy-associated musculoskeletal manifestations, hemophilia HAEMOGLOBINOPATHIES = inherited disorders of globin divided into: Thalassaemia
How do polyarthritis, polyarthralgias, and diffuse aches and pains differ?
 Approach to the patient with polyarthritis How do polyarthritis, polyarthralgias, and diffuse aches and pains differ? Polyarthritis is definite inflammation (swelling, tenderness, warmth) of more than
Approach to the patient with polyarthritis How do polyarthritis, polyarthralgias, and diffuse aches and pains differ? Polyarthritis is definite inflammation (swelling, tenderness, warmth) of more than
Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine COPYRIGHT. Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
 Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston MA Case #1 True statement(s) regarding etanercept and leflunomide, for the treatment
Rheumatology Review Update in Internal Medicine Robert H. Shmerling, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Boston MA Case #1 True statement(s) regarding etanercept and leflunomide, for the treatment
A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout
 A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout Nausheen Khan, MB BS, FCRad (D) Irma van de Werke, MB ChB, FRCR Farzanah Ismail, MB ChB, FCRad (D) Department of Radiology, Kalafong Hospital,
A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout Nausheen Khan, MB BS, FCRad (D) Irma van de Werke, MB ChB, FRCR Farzanah Ismail, MB ChB, FCRad (D) Department of Radiology, Kalafong Hospital,
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
THE AUDIO PANCE AND PANRE EPISODE 21
 THE AUDIO PANCE AND PANRE EPISODE 21 To download all the episodes and access 1000 s of questions and interactive online exams join the PANCE and PANRE Academy 1. A 28 year-old female, who has experienced
THE AUDIO PANCE AND PANRE EPISODE 21 To download all the episodes and access 1000 s of questions and interactive online exams join the PANCE and PANRE Academy 1. A 28 year-old female, who has experienced
pathological features
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 185-189 Case report Arthritis in 3 thalassaemia trait: clinical and pathological features BONNIE B. DORWART' AND H. RALPH SCHUMACHER2 From the 'Department of
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 185-189 Case report Arthritis in 3 thalassaemia trait: clinical and pathological features BONNIE B. DORWART' AND H. RALPH SCHUMACHER2 From the 'Department of
Ocular findings in children with sickle
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 644 Ocular findings in children with sickle cell haemoglobin C disease in Jamaica PATRICK I. CONDON, ROBERT GRAY, AND GRAHAM R. SERJEANT From the Medical Research Council,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 644 Ocular findings in children with sickle cell haemoglobin C disease in Jamaica PATRICK I. CONDON, ROBERT GRAY, AND GRAHAM R. SERJEANT From the Medical Research Council,
REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY
 Outpatient Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Clinical Reason for referral Duration of symptoms Essential Referral Content Referring
Outpatient Page 1 1 REFERRAL GUIDELINES: RHEUMATOLOGY Date of birth Demographic Contact details (including mobile phone) Clinical Reason for referral Duration of symptoms Essential Referral Content Referring
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout. György Nagy
 Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout György Nagy Dec 4, 2017 Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic, progressive, autoimmune disorder of the joints with extra-articular
Rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondylarthritides and gout György Nagy Dec 4, 2017 Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Chronic, progressive, autoimmune disorder of the joints with extra-articular
Acute hot swollen joint. Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist
 Acute hot swollen joint Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist Acute monoarthritis: differential diagnosis Septic arthritis Crystal arthritis (gout, pseudogout) Haemarthrosis
Acute hot swollen joint Dr Edward Roddy Senior Lecturer in Rheumatology and Consultant Rheumatologist Acute monoarthritis: differential diagnosis Septic arthritis Crystal arthritis (gout, pseudogout) Haemarthrosis
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011
 Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
Rheumatoid Arthritis Marge Beckman FALU, FLMI Vice President RGA Underwriting Quarterly Underwriting Meeting March 24, 2011 The security of experience. The power of innovation. www.rgare.com Case Study
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Joint Disorders. Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10. Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2011, Article ID 942023, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/942023 Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature Brian P. Oppermann, 1
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2011, Article ID 942023, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/942023 Case Report Pseudoseptic Arthritis: A Case Series and Review of the Literature Brian P. Oppermann, 1
developed in both knees, anikles, radiocarpal joints,
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 1021-1026 Case report Relapsing polychondritis arthritis mimicking rheumatoid P SCHLAPBACH,1 N J GERBER,1 P RAMSER,2 AND F M VAN'T HOOFT2 From the 'Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 1021-1026 Case report Relapsing polychondritis arthritis mimicking rheumatoid P SCHLAPBACH,1 N J GERBER,1 P RAMSER,2 AND F M VAN'T HOOFT2 From the 'Department
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept, for rheumatoid arthritis, 789 Acetaminophen, for low back pain, 735 Acupuncture for fibromyalgia, 753 for low back pain, 738
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abatacept, for rheumatoid arthritis, 789 Acetaminophen, for low back pain, 735 Acupuncture for fibromyalgia, 753 for low back pain, 738
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition
 Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 2 Volume Set. Text with Internet Access Code for Premium Consult Edition Firestein, G ISBN-13: 9781437717389 Table of Contents VOLUME I STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF BONE,
Patient #1. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour
 Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Patient #1 Rheumatoid Arthritis Essentials For The Family Medicine Physician 45 y/o female Morning stiffness in her joints >1 hour Hands, Wrists, Knees, Ankles, Feet Polyarticular, symmetrical swelling
Etiological Profile of Arthritis in Children between 6 Months and 12 Years of Age Admitted in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/241 Etiological Profile of Arthritis in Children between 6 Months and 12 Years of Age Admitted in a Tertiary Care Hospital D Sivakumaran 1, M Krithiga 2 1 Associate
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/241 Etiological Profile of Arthritis in Children between 6 Months and 12 Years of Age Admitted in a Tertiary Care Hospital D Sivakumaran 1, M Krithiga 2 1 Associate
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies
 Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies Directions: Each of the numbered items or incomplete statements in this section is followed by answers or by completions of the statement.
Medical Immunology Practice Questions-2016 Autoimmunity + Case Studies Directions: Each of the numbered items or incomplete statements in this section is followed by answers or by completions of the statement.
Rheumatic disease in Jamaica
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 320-325 Rheumatic disease in Jamaica WENDELL A. WILSON1 AND GRAHAM R. V. HUGHES2 From the 'Department of Medicine, University of the West Indies, Jamaica, and
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 320-325 Rheumatic disease in Jamaica WENDELL A. WILSON1 AND GRAHAM R. V. HUGHES2 From the 'Department of Medicine, University of the West Indies, Jamaica, and
UNUSUAL PRESENTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 UNUSUAL PRESENTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Presenter- Dr. Meghana B S Prof Dr. NAGARAJA B S Prof Dr. NIRMALA A C Dr. SIVARANJANI H Dr. B C PRAKASH Dr. MUMTAZ ALI KHAN A 60 year old lady, k/c/o
UNUSUAL PRESENTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS Presenter- Dr. Meghana B S Prof Dr. NAGARAJA B S Prof Dr. NIRMALA A C Dr. SIVARANJANI H Dr. B C PRAKASH Dr. MUMTAZ ALI KHAN A 60 year old lady, k/c/o
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Acute gout and the accident and emergency department
 Archives of Emergency edicine, 1984, 2, 89-95 Acute gout and the accident and emergency department R. H. HARDY AND B. NATION Department of Accident and Emergency edicine, Hereford General Hospital, and
Archives of Emergency edicine, 1984, 2, 89-95 Acute gout and the accident and emergency department R. H. HARDY AND B. NATION Department of Accident and Emergency edicine, Hereford General Hospital, and
Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all):
 Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Acutely Limping Child and Septic Arthritis Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all): History Careful history of any significant
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Acutely Limping Child and Septic Arthritis Assessment of limping child (beware the child who does not weight bear at all): History Careful history of any significant
JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis. Dr Johan Siebert
 JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis Dr Johan Siebert 1 NORMAL DIARTHRODIAL JOINT Synovial is a thin membrane enclosing the joint space The joint space contains fluid that bathes the joint and reduces friction
JuvenileIdiopathicArthritis Dr Johan Siebert 1 NORMAL DIARTHRODIAL JOINT Synovial is a thin membrane enclosing the joint space The joint space contains fluid that bathes the joint and reduces friction
KAPA 2017 Musculoskeletal Aspiration and Injection Workshop. W. Scott Black, MD Physician Assistant Studies Program University of Kentucky
 KAPA 2017 Musculoskeletal Aspiration and Injection Workshop W. Scott Black, MD Physician Assistant Studies Program University of Kentucky Aspiration Relatively quick and inexpensive Can be performed in
KAPA 2017 Musculoskeletal Aspiration and Injection Workshop W. Scott Black, MD Physician Assistant Studies Program University of Kentucky Aspiration Relatively quick and inexpensive Can be performed in
INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY TESTS IN RHEUMATIC DISEASE
 INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY TESTS IN RHEUMATIC DISEASE Laboratory tests are an important adjunct in the clinical diagnosis of rheumatic diseases and are sometimes helpful in monitoring the activity of
INTERPRETATION OF LABORATORY TESTS IN RHEUMATIC DISEASE Laboratory tests are an important adjunct in the clinical diagnosis of rheumatic diseases and are sometimes helpful in monitoring the activity of
Physical examination of the musculosceletal- and nervous system. Pánczél Pál dr.
 Physical examination of the musculosceletal- and nervous system in the practice of internal medicine. Pánczél Pál dr. Bursae = sacks of the synovial membrane fulfilled with synovium. Localised between
Physical examination of the musculosceletal- and nervous system in the practice of internal medicine. Pánczél Pál dr. Bursae = sacks of the synovial membrane fulfilled with synovium. Localised between
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS. Synovial Fluid. Synovial Fluid Classification. CLS 426 Urinalysis and Body Fluid Analysis Body Fluid Lecture Session 1
 BODY FLUID ANALYSIS Synovial Fluid Serous fluids the 3 P s Peritoneal Pleural Pericardial Cerebrospinal Fluid Karen Keller, MT(ASCP), SH Synovial Fluid Lubricant and sole nutrient source of joint. Normal
BODY FLUID ANALYSIS Synovial Fluid Serous fluids the 3 P s Peritoneal Pleural Pericardial Cerebrospinal Fluid Karen Keller, MT(ASCP), SH Synovial Fluid Lubricant and sole nutrient source of joint. Normal
Speaker s Disclosure Statement. Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN. Objectives. Risk Factors
 Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN Speaker s Disclosure Statement I have no industry relationships to disclose I will discuss off-label use of medications Dana-Farber/Boston Children
Starvation, Death and Destruction: The Battlefield of AVN Speaker s Disclosure Statement I have no industry relationships to disclose I will discuss off-label use of medications Dana-Farber/Boston Children
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
2) An 87 year old female who is 2 weeks post TKR presents with a sore swollen knee. She has a history of atrial fibrillation. Her vital signs are:
 EMQ - Rheumatology For each clinical vignette match the correct diagnosis. Reiter s syndrome Pseudogout Septic arthritis Gout Haemarthrosis Traumatic effusion Ankylosing spondylitis Rheumatoid arthritis
EMQ - Rheumatology For each clinical vignette match the correct diagnosis. Reiter s syndrome Pseudogout Septic arthritis Gout Haemarthrosis Traumatic effusion Ankylosing spondylitis Rheumatoid arthritis
predicts radiographic change
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS. Ms. Doshi
 CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
CHAPTER 6 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM DISEASES, DISORDERS, AND DIAGNOSTIC TERMS Ms. Doshi Worksheet 1 pp 154-156 Review Exercises Infections Disease cellulitis myocellulitis osteitis osteomyelitis osteochondritis
Acute monoarthritis is a common clinical presentation
 CMAJ Review Acute monoarthritis: What is the cause of my patient s painful swollen joint? Lingling Ma MD PhD, Ann Cranney MD MSc, Jayna M. Holroyd-Leduc MD DOI:10.1503/cmaj.080183 The case Early in the
CMAJ Review Acute monoarthritis: What is the cause of my patient s painful swollen joint? Lingling Ma MD PhD, Ann Cranney MD MSc, Jayna M. Holroyd-Leduc MD DOI:10.1503/cmaj.080183 The case Early in the
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling. Rheumatic Diseases
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING
 AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
ERROR CORRECTION FORM
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Registry Use Only Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic, syngeneic unrelated related
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Registry Use Only Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic, syngeneic unrelated related
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
A CRP B FBC C LFT D blood culture E uric acid
 1 A 39 year old lady with rheumatoid arthritis is admitted to hospital with a hot, swollen and painful right knee. Which is the most important blood test? A CRP B FBC C LFT D blood culture E uric acid
1 A 39 year old lady with rheumatoid arthritis is admitted to hospital with a hot, swollen and painful right knee. Which is the most important blood test? A CRP B FBC C LFT D blood culture E uric acid
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
CIBMTR Center Number: CIBMTR Recipient ID: RETIRED. Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed:
 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Date Received: Registry Use Only Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic,
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Pre-HSCT Data Sequence Number: Date Received: Registry Use Only Today s Date: Date of HSCT for which this form is being completed: HSCT type: autologous allogeneic, allogeneic,
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Oncology Type of Article: Case Report Title:
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Oncology Type of Article: Case Report Title:
HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE
 ORIGINAL PAPER HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE A CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL BY J. A. KIRK AND G. D. KERSLEY Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath
ORIGINAL PAPER HEAT AND COLD IN THE PHYSICAL TREATMENT OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE A CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL BY J. A. KIRK AND G. D. KERSLEY Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Bath
Iris atrophy in sickle cell disease
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1986, 70, 516-521 R W ACHESON,' S M FORD,' G H MAUDE,' R W LYNESS,2 AND G R SERJEANT From the 'Medical Research Council Laboratories (Jamaica), University ofthe West Indies,
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1986, 70, 516-521 R W ACHESON,' S M FORD,' G H MAUDE,' R W LYNESS,2 AND G R SERJEANT From the 'Medical Research Council Laboratories (Jamaica), University ofthe West Indies,
Sickle Cell Disease. Edward Malters, MD
 Sickle Cell Disease Edward Malters, MD Introduction Vaso-occlusive phenomena and hemolysis are the clinical hallmarks of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) Inherited disorder due to homozygosity for the abnormal
Sickle Cell Disease Edward Malters, MD Introduction Vaso-occlusive phenomena and hemolysis are the clinical hallmarks of Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) Inherited disorder due to homozygosity for the abnormal
Relation between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A study of 40 patients
 2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
SICKLE CELL DISEASE. Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH. Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN
 SICKLE CELL DISEASE Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN Objective: The student should be able: To identify the presentation, diagnosis,
SICKLE CELL DISEASE Dr. MUBARAK ABDELRAHMAN MD PEDIATRICS AND CHILD HEALTH Assistant Professor FACULTY OF MEDICINE -JAZAN Objective: The student should be able: To identify the presentation, diagnosis,
Photo Diagnosis. Case 1 The upper lip of this three-year-old boy became swollen and itchy an hour after he had ingested some peanuts.
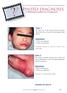 An illustrated quiz on problems seen in everyday practice Case 1 The upper lip of this three-year-old boy became swollen and itchy an hour after he had ingested some peanuts. 2. What is the treatment?
An illustrated quiz on problems seen in everyday practice Case 1 The upper lip of this three-year-old boy became swollen and itchy an hour after he had ingested some peanuts. 2. What is the treatment?
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW. Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center
 RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
RHEUMATOLOGY OVERVIEW Carmelita J. Colbert, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Rheumatology Loyola University Medical Center What is Rheumatology? Medical science devoted to the rheumatic diseases
Dual energy CT in diagnosis of Gout
 Dual energy CT in diagnosis of Gout Poster No.: R-0060 Congress: RANZCR ASM 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Tabatabaie Moghadam, A. Moghaddam, F. Ghazanfari ; 1 1 1 2 2 Brisbane/AU, Melbourne/AU
Dual energy CT in diagnosis of Gout Poster No.: R-0060 Congress: RANZCR ASM 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Tabatabaie Moghadam, A. Moghaddam, F. Ghazanfari ; 1 1 1 2 2 Brisbane/AU, Melbourne/AU
What organ system is involved? What is the pathology? What is the possible etiology?
 Johan van Rensburg What organ system is involved? What is the pathology? What is the possible etiology? Genetic Environmental What are the possible complications? How is the patient s functioning impaired?
Johan van Rensburg What organ system is involved? What is the pathology? What is the possible etiology? Genetic Environmental What are the possible complications? How is the patient s functioning impaired?
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Crystal induced arthropathies. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal
 Crystal induced arthropathies Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal 1 Crystal induced Arthropathies Gout Pseudogout Debilitating illnesses; Recurrent episodes of pain and joint inflammation; Formation and deposition of
Crystal induced arthropathies Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal 1 Crystal induced Arthropathies Gout Pseudogout Debilitating illnesses; Recurrent episodes of pain and joint inflammation; Formation and deposition of
Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement
 \>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
\>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
The diagnostic challenge of joint pain part 2
 Musculoskeletal 407 The diagnostic challenge of joint pain part 2 Polyarthralgia is a common presentation in primary care. Because chronic arthritides may present abruptly, they need to be considered in
Musculoskeletal 407 The diagnostic challenge of joint pain part 2 Polyarthralgia is a common presentation in primary care. Because chronic arthritides may present abruptly, they need to be considered in
Selected Issues in Nonneoplastic. Orthopaedic Pathology. Diseases of Diarthrodial Joints and their Complications
 1 2 3 Selected Issues in Nonneoplastic Orthopaedic Pathology Diseases of Diarthrodial Joints and their Complications Biology of articular hyaline cartilage Arthritis Osteonecrosis Prosthetic Joints Metabolic
1 2 3 Selected Issues in Nonneoplastic Orthopaedic Pathology Diseases of Diarthrodial Joints and their Complications Biology of articular hyaline cartilage Arthritis Osteonecrosis Prosthetic Joints Metabolic
Acute Emergencies in Rheumatology
 Acute Emergencies in Rheumatology Clare Higgens Northwick Park hospital and St George s Hospital London Acute Rheumatological Emergencies The Acute Hot joint Inflammatory back pain.. Systemic lupus erythematosus(sle)
Acute Emergencies in Rheumatology Clare Higgens Northwick Park hospital and St George s Hospital London Acute Rheumatological Emergencies The Acute Hot joint Inflammatory back pain.. Systemic lupus erythematosus(sle)
Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS
 February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
Pharmaceutical pathology
 Pharmaceutical pathology Livia Vida 2018 1. Necrosis, types, examples. Apoptosis. 2. Adaptations I. Degeneration, atrophy. 3. Adaptations II. Hypertrophy, hyperplasia. 4. Pigments. Calcification. 5. Inflammation
Pharmaceutical pathology Livia Vida 2018 1. Necrosis, types, examples. Apoptosis. 2. Adaptations I. Degeneration, atrophy. 3. Adaptations II. Hypertrophy, hyperplasia. 4. Pigments. Calcification. 5. Inflammation
Spondyloarthritis: A Gouty Display
 Spondyloarthritis: A Gouty Display Preetam Gongidi 1*, Shawn Gough-Fibkins 2 1. Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA 2. Broward General Medical Center,
Spondyloarthritis: A Gouty Display Preetam Gongidi 1*, Shawn Gough-Fibkins 2 1. Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA 2. Broward General Medical Center,
I nuovi criteri ACR/EULAR per la classificazione dell artrite reumatoide
 I nuovi criteri ACR/EULAR per la classificazione dell artrite reumatoide Pierluigi Macchioni Struttura Complessa di Reumatologia, Ospedale di Reggio Emilia Topics 1987 ACR classification criteria for RA
I nuovi criteri ACR/EULAR per la classificazione dell artrite reumatoide Pierluigi Macchioni Struttura Complessa di Reumatologia, Ospedale di Reggio Emilia Topics 1987 ACR classification criteria for RA
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Introduction reduction in output alter the amino acid sequence combination
 Sickle cell anemia. Introduction Mutations in the globin genes can cause a quantitative reduction in output from that gene or alter the amino acid sequence of the protein produced or a combination of the
Sickle cell anemia. Introduction Mutations in the globin genes can cause a quantitative reduction in output from that gene or alter the amino acid sequence of the protein produced or a combination of the
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
p. 70 p. 94 p. 102 p. 105 p. 108
 European League Against Rheumatism EULAR - a vehicle for communication p. 3 EULAR - a vehicle for communication; the role of ILAR p. 8 Overview on the Scientific Basis of Rheumatic Diseases Molecular and
European League Against Rheumatism EULAR - a vehicle for communication p. 3 EULAR - a vehicle for communication; the role of ILAR p. 8 Overview on the Scientific Basis of Rheumatic Diseases Molecular and
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Use of Serological markers for evaluation of patients with Rheumatoid arthritis
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 61-66 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Use of Serological markers for evaluation of patients with Rheumatoid arthritis G. Sucilathangam*, G.
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 9 (2015) pp. 61-66 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Use of Serological markers for evaluation of patients with Rheumatoid arthritis G. Sucilathangam*, G.
Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient
 Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient Kristina Haley, DO March 10, 2012 Jovita Reyes Memorial Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
Putting some hematology into Pediatric Hematology/Oncology: a review of Hemophilia and Sickle Cell Disease in the Pediatric Patient Kristina Haley, DO March 10, 2012 Jovita Reyes Memorial Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
measuring element was out of the joint. Thirtyone
 INTRA-ARTICULAR TEMPERATURE AS A MEASURE OF JOINT REACTION By STEVEN M. HORVATH AND JOSEPH L. HOLLANDER 1 (From the Department of Physical Medicine and the Arthritis Section of the Hospital of the University
INTRA-ARTICULAR TEMPERATURE AS A MEASURE OF JOINT REACTION By STEVEN M. HORVATH AND JOSEPH L. HOLLANDER 1 (From the Department of Physical Medicine and the Arthritis Section of the Hospital of the University
Approach to Arthritis
 Approach to Arthritis Dr. V. Krishnamurthy M. D., D. M. (Rheumatology) Rheumatologist, Chennai Meenakshi Multispecialty Hospital Rheumatologist, Meenakshi Academy of Higher Education (MAHER), Apollo Specialty
Approach to Arthritis Dr. V. Krishnamurthy M. D., D. M. (Rheumatology) Rheumatologist, Chennai Meenakshi Multispecialty Hospital Rheumatologist, Meenakshi Academy of Higher Education (MAHER), Apollo Specialty
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
