Primary Care Paramedic
|
|
|
- Hector Wright
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Primary Care Paramedic Pocket Reference Guide 2017 v and 4.1 Page 0 of 48
2 For Reference Only PCP This pocket reference guide has been formatted to align with the ALS PCS version with an in force date of July 17 th, This guide also contains the revised materials applicable to the ALS PCS version 4.1 with an in force date of December 11 th, As always, this guide is intended to support the ALS PCS and is for reference only. Refer to the current medical directives for all treatment decisions. If there are inconsistencies between this reference guide and the current directives always refer to the medical directives. For questions, comments, or suggestions for improvements, please contact us at: Website (follow contact us link): Administration Office 95a Simcoe Street South Oshawa, ON Mailing Address Central East Prehospital Care Program Lakeridge Health 1 Hospital Court Oshawa, ON L1G 2B9 Phone: Fax: Toll Free: Page 1 of 48
3 For Reference Only - PCP Patching... 3 Neonatal Resuscitation... 5 Medical Cardiac Arrest... 7 Foreign Body Airway Obstruction Cardiac Arrest... 9 Hypothermia Cardiac Arrest Trauma Cardiac Arrest Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC) Endotracheal and Tracheostomy Suctioning Supraglottic Airway Bronchoconstriction Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Croup Opioid Toxicity IV and Fluid Therapy Cardiac Ischemia Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Cardiogenic Shock Hypoglycemia Moderate to Severe Allergic Reaction Nausea / Vomiting Adult Analgesia Emergency Childbirth Suspected Adrenal Crisis Home Dialysis Emergency Disconnect Electronic Control Device (ECD) Probe Removal Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid Exposure Cyanide Exposure Headache (Special Events Only) Minor Abrasion (Special Events Only) Minor Allergic Reaction (Special Events Only) Musculoskeletal Pain (Special Events Only) Primary Care Paramedic Scope of Practice NOTES: Page 2 of 48
4 For Reference Only PCP Patching Primary Care Paramedics are required to PATCH to the Base Hospital Physician for the following: Core Directives Medical Cardiac Arrest Directive: If considering a Medical TOR, PATCH after the 3 rd rhythm interpretation Trauma Cardiac Arrest Directive: PATCH for authorization to apply the Trauma TOR if applicable Auxiliary Directives Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Directive: PATCH for authorization to administer IV NaCl bolus to a hypotensive patient greater than or equal to 2 years of age and less than 12 years of age with suspected Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) NOTE: A patch to the Base Hospital Physician may be made at any time to discuss patient care that does not fall within an existing medical directive but is within your scope of practice. Patch failure: is defined as the inability to make contact with a BHP after reasonable attempts. This is to be documented on the ACR in the procedures section using the relevant codes. If the failure resulted in a patient care issue, the Paramedic must contact CEPCP as soon as possible as well as document (with explanation) the failure on their ACR. Patching Page 3 of 48
5 For Reference Only - PCP Page 4 of 48
6 For Reference Only PCP Neonatal Resuscitation Newborn less than 30 days Neonatal Resuscitation Page 5 of 48
7 For Reference Only - PCP Neonatal Resuscitation Page 6 of 48
8 For Reference Only PCP Medical Cardiac Arrest Non-traumatic cardiac arrest Adult Interpret (and print) the rhythm every 2 min For Zoll and LP12 / LP15 use adult settings Adult Doses Epinephrine 1:1,000 - IM (for suspected anaphylaxis) 0.01 mg/kg max 0.5 mg N/A N/A 1 dose BHP PATCH following the 3 rd analysis/rhythm interpretation to consider a Medical TOR (if applicable) Medical TOR 18 years Presumed cardiac origin Arrest not witnessed by EMS 3 rhythm interpretations with no shocks delivered No ROSC at any time NOTE a Heart rate of 60 or less in a child is an ominous finding and CPR is indicated if signs of poor perfusion are present. Pediatric Doses Epinephrine IM (for suspected anaphylaxis) Defibrillation 30 days to < 8 years 0.01 mg/kg 1:1,000 N/A N/A N/A 2 J/kg 2 min 4 J/kg 4 King LT should be inserted where more than OPA/BVM is required, without interrupting CPR. Once inserted, begin continuous compressions and ventilate asynchronously at 1 breath every 6 8 seconds and monitor ETCO 2 : mmhg poor prognosis, check quality of CPR and improve where possible mmhg improved prognosis, indicates good CPR quality > 35 mmhg excellent CPR / prognosis, consider pulse check at next interpretation Large spike to above normal values probable ROSC, consider pulse check at next interpretation Medical Cardiac Arrest Page 7 of 48
9 For Reference Only - PCP King LT Reference Size Colour Patient Amount of Air in Cuff #3 Yellow 4 5 ft tall ml #4 Red 5 6 ft tall ml #5 Purple 6 ft tall ml 6 Confirmation Methods Primary Secondary Confirm advanced (supraglottic) airway placement Medical TOR Patch ETCO 2 (waveform capnography) ETCO 2 (non-waveform capnography) Auscultation Chest rise This is (your name) a Primary Care Paramedic on vehicle (number) patching for a Termination of Resuscitation for a cardiac arrest. Patient is a (age) year old (estimate if needed)gender (male or female) State the three TOR Guidelines : we did not witness the arrest defibrillation has not been indicated, and there has been no return of a carotid pulse. Brief past medical history, history of current presentation The patient was last seen at And was at that time complaining of The patient has a history of My interpretation of the TOR guideline is that we could consider stopping resuscitation at this time. Ask the BHP if further information is required? Would you like any further clinical information? Questions that may be asked: Estimated number of minutes to the arrival on scene from the time you were notified. Whether or not the cardiac arrest was witnessed by a bystander Whether or not bystander CPR was done. Extrication problems, if any, that may delay initiating transport. Estimated number of minutes for ambulance transport to the receiving hospital. Medical Cardiac Arrest Page 8 of 48
10 For Reference Only PCP Foreign Body Airway Obstruction Cardiac Arrest Cardiac arrest secondary to an airway obstruction Not obviously dead as per BLS standards No DNR Interventions Attempt to clear the airway with BLS maneuvers Defibrillate once if the patient is in VF/pVT 30 days to < 8 years old - 2 joules / kg 8 years old adult setting If the obstruction cannot be removed, transport to the closest appropriate facility without delay following the first rhythm interpretation If the patient is in cardiac arrest following removal of the obstruction, initiate management as a medical cardiac arrest Foreign Body Airway Obstruction Cardiac Arrest Page 9
11 For Reference Only - PCP Hypothermia Cardiac Arrest Cardiac arrest secondary to severe hypothermia Not obviously dead as per BLS standards No DNR Interventions Defibrillate once if the patient is in VF/pVT 30 days to < 8 years old - 2 joules / kg 8 years old adult settings Transport to the closest appropriate facility without delay following the first rhythm interpretation Hypothermia Cardiac Arrest Page 10 of 48
12 For Reference Only PCP Trauma Cardiac Arrest Cardiac arrest secondary to severe blunt or penetrating trauma Confirm Trauma Cardiac Arrest Protect C-spine Begin chest compressions Attach pads 30 days of age Begin PPV with BVM Rhythm Determination VF / pvt PEA Asystole Defibrillate once 30 days to < 8 years 2 joules/kg 8 years adult setting Yes Drive-time is < 30 min to nearest hospital? Yes No Patient age < 16 years Continue CPR Transport to hospital PATCH fails, or order not given No PATCH to BHP for Trauma TOR Trauma Cardiac Arrest Page 11 of 48
13 For Reference Only - PCP Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC) ROSC after resuscitation was initiated Adult SBP < 90 mmhg Pediatric SBP < 70 mmhg + (2 x age in years) Bolus: (ONLY if authorized in Autonomous IV) Clear chest / no fluid overload Adult Doses ( 12 years of age) Bolus IV only Pediatric Doses ( 2 years) 10 ml/kg Reassess every 250 ml N/A 1,000 ml Bolus IV only 10 ml/kg Reassess every 100 ml N/A 1,000 ml Titrate oxygenation to 94 to 98% Avoid hyperventilation and target an ETCO 2 of mmhg with continuous waveform capnography Consider 12 lead ECG Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC) Page 12 of 48
14 For Reference Only PCP Endotracheal and Tracheostomy Suctioning Patient with an ETT or trach tube AND The airway is obstructed or increased secretions are present N/A Suction Patient Initial Suction pressure Infant mmhg 1 min Child mmhg 1 min Adult mmhg 1 min Q Repeat Max Same as initial Same as initial Same as initial Before each suctioning procedure, pre-oxygenate with 100% oxygen Do not exceed 10 seconds duration of suction application 5 doses 5 doses 5 doses Endotracheal and Tracheostomy Suctioning Page 13 of 48
15 For Reference Only - PCP Supraglottic Airway Need for ventilatory assistance OR airway control AND Other airway management is ineffective Patient in cardiac arrest Able to clear the airway (with suctioning etc.) No active vomiting No airway edema No stridor No caustic ingestion Confirmation Methods Primary Secondary ETCO 2 (non-waveform Confirm advanced (supraglottic) ETCO 2 (waveform capnography) airway placement capnography) Auscultation Chest rise Maximum number of supraglottic attempts is two An attempt is defined as the insertion of the supraglottic airway into the mouth Must use ETCO 2 (waveform capnography) or at least 2 secondary methods King LT Reference Size Colour Patient Amount of Air in Cuff #3 Yellow 4 5 ft tall ml #4 Red 5 6 ft tall ml #5 Purple 6 ft tall ml Supraglottic Airway Page 14 of 48
16 For Reference Only PCP Bronchoconstriction Respiratory distress AND Suspected bronchoconstriction No allergy or sensitivity to any medication considered Salbutamol: Epinephrine: Patient does not have an actual or suspected BVM ventilation is required fever and there is not a declared FRI outbreak for nebulization administration Must have a history of asthma Adult Doses Salbutamol MDI 25 kg 800 mcg (8 puffs) 5-15 min 800 mcg 3 doses Salbutamol Nebulized 25 kg 5 mg 5-15 min 5 mg 3 doses Epinephrine 1:1,000 IM Pediatric Doses 0.01 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.5 mg N/A N/A 1 dose Salbutamol MDI < 25 kg Salbutamol Nebulized < 25 kg Epinephrine IM 600 mcg 5-15 min 600 mcg 3 doses 2.5 mg 5-15 min 2.5 mg 3 doses 0.01 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.5 mg N/A N/A 1 dose Epinephrine should be the first medication administered if the patient is apneic Salbutamol MDI may be administered subsequently using a BVM MDI adapter (if available) Nebulization is contraindicated in patients with a known or suspected fever or in the setting of a declared febrile respiratory illness outbreak by the local medical officer of health When administering Salbutamol MDI, the rate of administration should be 100 mcg approximately every 4 breaths A spacer should be used when administering Salbutamol MDI (if available) Bronchoconstriction Page 15 of 48
17 For Reference Only - PCP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Severe respiratory distress AND Signs and/or symptoms of acute pulmonary edema OR COPD exacerbation Respiratory rate 28 breaths/minute SpO 2 < 90% OR accessory muscle use SBP 100 Able to sit upright and cooperate Not asthma exacerbation Stable or protected airway Not suspected pneumothorax No major trauma or burns to the head or torso No tracheostomy Adult Doses ( 18 years of age) Start at Increase by Q Max 5 cm H 2 O 2.5 cm H 2 O 5 min 15 cm H 2 O If the device has adjustable FiO 2, start at the lower setting and only increase if SpO 2 remains < 92% despite treatment and/or CPAP pressure of 10 cmh 2 O N/A Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Page 16 of 48
18 For Reference Only PCP Croup Severe respiratory distress AND Stridor at rest AND Current history of URTI AND Barking cough or recent history of a barking cough < 8 years old No allergy or sensitivity to Epinephrine Heart rate less than 200 bpm Pediatric Doses Epinephrine 1:1,000 1 year old Epinephrine 1:1,000 < 1 year old AND 5 kg or more Epinephrine 1:1,000 < 1 year old AND < 5 kg 5.0 mg (5 ml) 2.5 mg (2.5 ml) 0.5 mg (mix with 2 ml of saline to make 2.5 ml) The minimum initial volume for nebulization is 2.5 ml N/A N/A 1 dose N/A N/A 1 dose N/A N/A 1 dose Croup Page 17 of 48
19 For Reference Only - PCP Opioid Toxicity Altered LOC AND Respiratory depression AND Inability to adequately ventilate AND Suspected opioid overdose Respiratory rate < 10 breaths/min No allergy or sensitivity to Naloxone No uncorrected hypoglycemia Adult Doses ( 18 yrs of age) Naloxone SC / IM / IN 0.8 mg 10 min 0.8 mg 3 doses Naloxone IV* Up to 0.4 mg immediate Up to 0.4 mg 3 doses *For IV route, consider diluting the medication for more accurate dose control and titrate naloxone only to restore the patient's respiratory status The IV condition only applies to PCPs authorized in Autonomous IV Where possible, account for 0.12 ml dead space in the intranasal (IN) device for more accurate dosing (ensure the correct amount and volume remain in the syringe after zeroing the MAD adapter) Opioid power comparison where Morphine is assigned a strength of 1: Codeine 0.1, Hydromorphone 10; Fentanyl 100, Carfentanil Opioid Toxicity typically presents with: Decreased LOA Slow respirations Pinpoint pupils Some Common Opioids: Morphine Percodan MS Contin Oxycocet Statex Oxycontin Hydromorphone Tylenol #1, #2, #3 Fentanyl Heroin Percocet Codeine Opioid Toxicity Page 18 of 48
20 For Reference Only PCP IV and Fluid Therapy (ONLY if authorized in Autonomous IV) Actual or potential need for IV medication OR fluid therapy 2 years old Cannulation: No fracture proximal to IV insertion site Bolus: No signs of fluid overload Adult SBP < 90 mmhg Pediatric SBP < 70 mmhg + (2 x age in years) Adult Doses ( 12 years of age) TKVO IV ml/hr N/A N/A N/A Bolus IV only 20 ml/kg Reassess every 250 ml N/A 2,000 ml Pediatric Doses ( 2 years) TKVO IV 15 ml/hr N/A N/A N/A Bolus IV only 20 ml/kg Reassess every 100 ml PATCH to the BHP for authorization to administer IV NaCl bolus to a hypotensive patient greater than or equal to 2 years of age and less than 12 years of age with suspected Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) N/A 2,000 ml IV and Fluid Therapy Page 19 of 48
21 For Reference Only - PCP Cardiac Ischemia Suspected cardiac ischemia No allergies or sensitivity to medication considered Unaltered LOA Nitroglycerin: Prior Nitroglycerin use and/or IV established HR bpm SBP 100 mmhg. Discontinue if SBP drops more than 1/3 of the initial reading No *phosphodiesterase inhibitor in past 48 hrs No right ventricular MI ASA: Able to chew and swallow Prior use of ASA if asthmatic No allergy to ASA or NSAIDs No current active bleeding No CVA or TBI in past 24 hrs Adult Doses ( 18 years of age) Nitroglycerin (non-stemi) 0.4 mg S/L 5 min 0.4 mg 6 doses Nitroglycerin (STEMI) 0.4 mg S/L 5 min 0.4 mg 3 doses ASA mg PO N/A N/A mg Perform 12 lead prior to NTG administration and a 15 lead (V4R) if ST elevation is present in the inferior leads (two or more of II, III and avf) The IV condition only applies to PCPs authorized in Autonomous IV *Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (including but not limited to): Sildenafil: Viagra, Revatio (for pulmonary hypertension) Tadalafil: Cialis, Adcirca (for pulmonary hypertension) Vardenafil: Levitra, Stazyn Cardiac Ischemia Page 20 of 48
22 For Reference Only PCP A 15 lead ECG should be obtained: When a 12 lead shows an inferior wall MI (assess V4R) When there is ST depression in V1-V4 (assess V8 and V9) When the 12 lead is normal but the patient is exhibiting signs or symptoms of cardiac ischemia (assess V8 and V9) V4R The V4R lead is obtained by moving V4 to the same location but on the right chest wall. (5th intercostal space, mid clavicular line) V4R is considered anatomically contiguous with II, III and avf ST elevation in V4R indicates an infarct of the right ventricle and NTG is to be withheld V8 and V9 The V8 lead is obtained by moving V5 around to the posterior, left chest wall and placing it on the mid-scapular line just below the scapula The V9 lead is obtained by moving V6 around to the back and placing it between V5 and the vertebral column ST elevation in V8 and V9 indicates an infarct in the posterior wall of the left ventricle Infarcts in the posterior wall often show up as ST depression in leads V1-V4 or as a normal 12 lead Cardiac Ischemia Page 21 of 48
23 For Reference Only - PCP Common Imitators of MI s Interpreting ST segment s is not possible in the following rhythms (not a complete list other imitators exist) LBBB Characterised by a supraventricular rhythm (identified by the presence of P waves and a 1:1 occurrence with QRS waves) & a wide (> 120 ms) QRS complex. A LBBB will have a -ve terminal deflection in V1 and typically a secondary R wave in V6 (seen as a notched complex seen as RsR below). A STEMI cannot be determined in the field in the presence of a LBBB. A RBBB will have a +ve terminal deflection in V1 typically with a notched complex & a slurred or prolonged S wave in V6. A RBBB does not preclude the ability to interpret a STEMI in the field. Ventricular Paced Rhythm A pacer spike is typically seen immediately preceding the QRS complex which will be wide. Pacer detect may need to be activated on the cardiac monitor Electrical capture is the presence of a QRS following the pacer spike. Mechanical capture is the presence of a pulse matching the electrical rate of the paced rhythm. Cardiac Ischemia Page 22 of 48
24 For Reference Only PCP LVH (Left Ventricular Hypertrophy) Look at the RS complex in either V1 or V2 and count the small boxes of the -ve deflection Then do the same with either V5 or V6, counting the small boxes of the +ve deflection Add the two numbers together, if they equal 35 mm s then it s likely LVH A STEMI cannot be determined in the field in the presence of LVH Pericarditis A condition in which inflammation of the pericardial sac produces electrical abnormalities in the 12 lead ECG Men aged years of age are most susceptible Often produces global ST elevation, or elevation in leads that are not anatomically contiguous and that is not consistent with the patient s clinical presentation A STEMI cannot be determined in the field in the presence of pericarditis Cardiac Ischemia Page 23 of 48
25 For Reference Only - PCP Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Moderate to severe respiratory distress AND Suspected acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema No allergy or sensitivity No *phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the past 48 hours If SBP < 140 mmhg, patient must have prior Nitroglycerin use or an IV established Vital Sign Parameters HR bpm SBP 100 mmhg SBP drops no more than 1/3 of the initial reading Adult Doses ( 18 years of age) Nitroglycerin SBP mmhg WITH an IV or History of use Nitroglycerin SBP 140 mmhg and NO History or IV Nitroglycerin SBP 140 mmhg WITH History or IV 0.4 mg S/L 5 min 0.4 mg 6 doses 0.4 mg S/L 5 min 0.4 mg 6 doses 0.8 mg S/L 5 min 0.8 mg 6 doses Consider 12 /15 lead The IV condition only applies to PCPs authorized in Autonomous IV *Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (including, but are not limited to): Sildenafil: Viagra, Revatio (for pulmonary hypertension) Tadalafil: Cialis, Adcirca (for pulmonary hypertension) Vardenafil: Levitra, Stazyn Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema Page 24 of 48
26 For Reference Only PCP Cardiogenic Shock (ONLY if authorized in Autonomous IV) STEMI positive AND Cardiogenic Shock SBP < 90 mmhg Bolus: Clear Chest / no fluid overload Adult Doses ( 18 years of age) Bolus IV 10 ml/kg Reassess every 250 ml The IV condition only applies to PCPs authorized in Autonomous IV N/A 1,000 ml Cardiogenic Shock Page 25 of 48
27 For Reference Only - PCP Hypoglycemia Agitation OR altered LOA OR seizure OR symptoms of stroke No allergy or sensitivity to any medication considered Dextrose: N/A Glucagon: No Pheochromocytoma Vital Sign Parameters Hypoglycemia: 2 yrs < 4.0 mmol/l < 2 yrs < 3.0 mmol/l Adult Doses D10W D50W 50 kg Dextrose IV 50 kg Dextrose IV 10 g (100 ml) 10 min 10 g 2 doses 25 g (50 ml) 10 min 25 g 2 doses Glucagon IM 25 kg 1 mg 20 min 1 mg 2 doses Pediatric Doses D10W D50W 2 yrs to < 50 kg Dextrose IV 2 yrs to < 50 kg Dextrose IV 2 ml/kg 0.2 g/kg Max 10 g (100 ml) 1 ml/kg 0.5 g/kg Max 25 g (50 ml) 10 min 10 min same as initial same as initial 2 doses 2 doses Glucagon IM < 25 kg 0.5 mg 20 min 0.5 mg 2 doses If the patient responds to Dextrose or Glucagon, he/she may receive oral glucose or other simple carbohydrates If only mild signs or symptoms are exhibited, the patient may receive oral glucose or other simple carbohydrates instead of Dextrose or Glucagon If an IV is established after Glucagon is administered, reassess and consider glucometry and administering Dextrose IV immediately The IV condition only applies to PCPs authorized in Autonomous IV Hypoglycemia Page 26 of 48
28 For Reference Only PCP Dextrose 50% in Water Reference Age 2 years Blood Initial dose Repeat dose(s) Dextrose Sugar Dose Vol. Amt Dose Vol. Amt prep mmol/l g/kg ml/kg ml g/kg ml/kg ml < 4.0 D50W Weight kg > Hypoglycemia Page 27 of 48
29 For Reference Only - PCP Moderate to Severe Allergic Reaction Exposure to a probable allergen AND Signs and/or symptoms of a moderate to severe allergic reaction (including anaphylaxis) No allergy or sensitivity to any medication considered Epinephrine: Use for anaphylaxis only Diphenhydramine: Weight 25 kg Adult Doses Epinephrine 1:1,000 IM Diphenhydramine IV / IM (IV ONLY if authorized in Autonomous IV) Pediatric Doses 0.01 mg/kg Max 0.5 mg 50 mg if 50 kg 25 mg if kg Minimum 5 min same as initial 2 doses N/A N/A 1 dose Epinephrine IM Diphenhydramine IV / IM (IV ONLY if authorized in Autonomous IV) 0.01 mg/kg Max 0.5 mg Minimum 5 min same as initial 2 doses 25 mg if kg N/A N/A 1 dose Epinephrine should be the first medication administered in anaphylaxis The Epinephrine dose may be rounded to the nearest 0.05 mg Diphenhydramine is commonly referred to as Benadryl Moderate to Severe Allergic Reaction Page 28 of 48
30 For Reference Only PCP Epinephrine 1:1, mg/kg Rounded to the nearest 0.05 ml 4 kg = 0.04 mg give 0.05 ml 28 kg = 0.28 mg give 0.3 ml 6 kg = 0.06 mg give 0.05 ml 30 kg = 0.3 mg give 0.3 ml 8 kg = 0.08 mg give 0.1 ml 32 kg = 0.32 mg give 0.3 ml 10 kg = 0.1 mg give 0.1 ml 34 kg = 0.34 mg give 0.35 ml 12 kg = 0.12 mg give 0.1 ml 36 kg = 0.36 mg give 0.35 ml 14 kg = 0.14 mg give 0.15 ml 38 kg = 0.38 mg give 0.4 ml 16 kg = 0.16 mg give 0.15 ml 40 kg = 0.4 mg give 0.4 ml 18 kg = 0.18 mg give 0.2 ml 42 kg = 0.42 mg give 0.4 ml 20 kg = 0.2 mg give 0.2 ml 44 kg = 0.44 mg give 0.45 ml 22 kg = 0.22 mg give 0.2 ml 46 kg = 0.46 mg give 0.45 ml 24 kg = 0.24 mg give 0.25 ml 48 kg = 0.48 mg give 0.5 ml 26 kg = 0.26 mg give 0.25 ml 50 kg = 0.5 mg give 0.5 ml Moderate to Severe Allergic Reaction Page 29 of 48
31 For Reference Only - PCP Nausea / Vomiting Nausea and/or Vomiting Unaltered LOA No allergies or sensitivity to Dimenhydrinate or other antihistamines Not overdosed on Antihistamines, Anticholinergics or Tricyclic Antidepressants Adult Doses ( 50 kg) Dimenhydrinate IV / IM 50 mg N/A N/A 1 dose Pediatric Doses (25 50 kg) Dimenhydrinate IV / IM 25 mg N/A N/A 1 dose If administering IV, dilute Dimenhydrinate with 9 ml normal saline to a 50 mg in 10 ml solution. The IV condition only applies to PCPs authorized in Autonomous IV Antihistamines Actifed, Astemazole (Hismanal), Azatdine (Zadine), Cetirizine (Zyrtec, Reactine), Chlorpheniramine (Chlor- Trimeton, chlortripalon), Clemastine, Cyproheptadine (Periactin), Dexchlorpheniramine, Desloratadine (Clarinex), Dimenhydrinate (Dramamine), Diphenhydramine (Benadryl), Fexofenadine (Allegra), Hydroxyzine (Atarax, Vistaril), Loratadine (Claritin, Alavert), Phenothiazines, Promethazine (Phenergan), Piperzanes, Terfenadine (Seldane) Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA) Amitriptyline (Elavil, Ednep, Vanatrip), Clomipramine (Anafranil), Desipramine (Norpramin), Doxepin (Sinequan, Adapin, Silenor), Nortriptyline (Aventyl, Pamelor), Protriptyline (Vivactil), Trimipramine (Surmontil) Anticholinergics Atropine, Hyoscine Glycopyrrolate(Robinul), Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent), Oxybutinin (Ditropan, Lyrinel XL) Oxitropium bromide (Oxivent), Tiotropium (Spiriva) Nausea / Vomiting Page 30 of 48
32 For Reference Only PCP Adult Analgesia Mild Moderate Pain (Acetaminophen / Ibuprofen) OR Mild Severe Pain (Ketorolac) AND Isolated hip or extremity trauma OR Burns OR Renal colic with a prior history OR Acute musculoskeletal back strain OR Current history of cancer related pain Unaltered LOA Acetaminophen / Ibuprofen: N/A Ketorolac: Normotension Restricted to those unable to tolerate oral medications Contraindications Acetaminophen: Use within previous 4 hours Allergy / sensitivity Hx of liver disease Active vomiting Unable to tolerate oral medications Ibuprofen / Ketorolac: NSAID / Ibuprofen use within 6 hours Allergy / sensitivity to ASA or NSAIDs Patient on anticoagulation therapy Current active bleeding Hx of peptic ulcer disease or GI bleeds Pregnant If asthmatic, no prior use of ASA or NSAIDs CVA or TBI in previous 24 hours Known renal impairment Ibuprofen only active vomiting / unable to tolerate oral medications Adult Analgesia Page 31 of 48
33 For Reference Only - PCP Adult Doses ( 18 years of age) Acetaminophen PO mg N/A N/A 1 dose Ibuprofen PO 400 mg N/A N/A 1 dose Ketorolac IM / IV mg N/A N/A 1 dose Consider co-administration of Acetaminophen / Ibuprofen whenever possible If Ketorolac is administered, neither Ibuprofen nor Acetaminophen should be administered Suspected renal colic patients should be considered for Ketorolac The IV condition only applies to PCPs authorized in Autonomous IV Adult Analgesia Page 32 of 48
34 For Reference Only PCP Emergency Childbirth Pregnant patient experiencing labour OR immediately following delivery Child bearing years Delivery Second stage labour and/or imminent birth Umbilical Cord Management Cord complications OR if resuscitation required OR due to transport considerations External Uterine Massage Post placental delivery Emergency Childbirth Page 33 of 48
35 For Reference Only - PCP Suspected Adrenal Crisis Patient with primary adrenal failure who has signs of an adrenal crisis Presented with a vial of Hydrocortisone for that patient AND No allergy or sensitivity to Hydrocortisone AND Patient presents with (any one or more of): o Hypoglycemia o GI symptoms o Syncope o Temperature 38C or suspected fever o Altered LOA o Age related hypotension o Age related tachycardia All Doses Hydrocortisone IM 2 mg/kg Max 100 mg N/A N/A 1 dose Hydrocortisone has a common trade name of Solu-cortef Dose may be rounded to the nearest 10 mg All patients need to be transported Ensure the medication label is examined carefully for its concentration Hydrocortisone may come premixed in a vial or it may be supplied in an ACT-O-VIAL system To use the ACT-O-VIAL : 1. Press down on plastic activator to force diluent into the lower compartment 2. Gently agitate to effect solution 3. Remove plastic tab covering center of stopper 4. Sterilize top of stopper with alcohol 5. Insert needle squarely through center of stopper and withdraw the appropriate dose Suspected Adrenal Crisis Page 34 of 48
36 For Reference Only PCP Home Dialysis Emergency Disconnect Patient connected to home dialysis AND Requires transport to a receiving facility N/A Interventions Disconnect In general, the instructions will be found with the machine Sequence: Ensure the patient side is clamped first, and then the machine side and then the tubing can be disconnected between the clamps Home Dialysis Emergency Disconnect Page 35 of 48
37 For Reference Only - PCP Electronic Control Device (ECD) Probe Removal Electronic control device probe(s) embedded in patient Unaltered LOA Probes not embedded; o Above clavicles, o In the nipple(s), or o In the genital area Interventions ( 18 years of age) Remove probes Police may require preservation of the probe(s) for evidentiary purposes This directive is for removal of ECD only and in no way constitutes a treat and release order, normal principles of patient assessment and care apply Electronic Control Device (ECD) Probe Removal Page 36 of 48
38 For Reference Only PCP Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid Exposure Exposure to vapour and/or liquid Hydrofluoric acid (HF) AND Exhibits signs and symptoms of HF poisoning. No allergy or sensitivity to any medication considered Doses Calcium Gluconate (10% solution) Inhalation exposure Calcium Gluconate (2.5% gel) Skin exposure 100 mg NEB N/A N/A 1 dose N/A Topical N/A Immediate N/A Anaesthetic Eye Drops 2 gtts/eye 10 min 2 gtts/eye N/A For skin contact, ensure thorough irrigation prior to treatment For eye exposure, remove patient s contact lenses, if applicable, prior to initiating treatment. Use Anaesthetic eye drops for comfort and then irrigate eyes with normal saline for at least 15 minutes Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid Exposure Page 37 of 48
39 For Reference Only - PCP Cyanide Exposure Suspected exposure to Cyanide with signs and symptoms of poisoning Altered LOA No allergies or sensitivity to any medication considered Adult Dose ( 18 years of age) Sodium Thiosulfate 25% 12.5 g IV N/A N/A 1 dose OR Hydroxocobalamin 5 g IV over min N/A N/A 1 dose Pediatric Doses Sodium Thiosulfate 25% OR Hydroxocobalamin 1.65 ml/kg IV Max 12.5 g 70 mg/kg over 30 min Max 5 g N/A N/A 1 dose N/A N/A 1 dose Hydroxocobalamin must be reconstituted with 200 ml normal saline prior to administration Cyanide Exposure Page 38 of 48
40 For Reference Only PCP Hydroxocobalamin Dosing Chart Pediatric Weight (kg) Dose Concentration Volume of Administration mg/kg 25 mg/ml 42 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 56 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 70 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 84 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 98 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 112 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 126 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 140 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 154 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 168 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 182 ml mg/kg 25 mg/ml 196 ml > mg/kg 25 mg/ml 200 ml Cyanide Exposure Page 39 of 48
41 For Reference Only - PCP Headache (Special Events Only) Uncomplicated headache conforming to the patient s usual pattern Unaltered LOA No allergy or sensitivity to Acetaminophen No Acetaminophen in the last 4 hours No signs or symptoms of intoxication Adult Doses ( 18 years of age) Acetaminophen PO mg N/A None 1 dose The Special Event Medical Directives are active when they have been preauthorized for use by the Medical Director. Special Event: a preplanned gathering with potentially large numbers of people Consider release from care Advise patient that if the problem persists or worsens that they should seek further medical attention Headache (Special Events Only) Page 40 of 48
42 For Reference Only PCP Minor Abrasion (Special Events Only) Minor abrasions 18 years old Unaltered LOA No allergy or sensitivity to topical antibiotics The Special Event Medical Directives are active when they have been preauthorized for use by the Medical Director. Special Event: a preplanned gathering with potentially large numbers of people Consider release from care Advise patient that if the problem persists or worsens that they should seek further medical attention Minor Abrasion (Special Events Only) Page 41 of 48
43 For Reference Only - PCP Minor Allergic Reaction (Special Events Only) Signs consistent with minor allergic reaction Unaltered LOA SBP 100 mmhg (and other vitals within normal limits) No allergy or sensitivity to Diphenhydramine No antihistamine or sedative use in the previous 4 hours No signs or symptoms of a moderate to severe allergic reaction No signs or symptoms of intoxication No wheezing Adult Doses ( 18 years of age) Diphenhydramine PO 50 mg N/A N/A 1 dose The Special Event Medical Directives are active when they have been preauthorized for use by the Medical Director. Special Event: a preplanned gathering with potentially large numbers of people Consider release from care Advise patient that if the problem persists or worsens that they should seek further medical attention Minor Allergic Reaction (Special Events Only) Page 42 of 48
44 For Reference Only PCP Musculoskeletal Pain (Special Events Only) Minor musculoskeletal pain Unaltered LOA No allergy or sensitivity to Acetaminophen No Acetaminophen use in the previous 4 hours No signs or symptoms of intoxication Adult Doses ( 18 years of age) Acetaminophen PO mg N/A None 1 dose The Special Event Medical Directives are active when they have been preauthorized for use by the Medical Director. Special Event: a preplanned gathering with potentially large numbers of people Consider release from care Advise patient that if the problem persists or worsens that they should seek further medical attention Musculoskeletal Pain (Special Events Only) Page 43 of 48
45 For Reference Only - PCP January 1 st, 2017 Primary Care Paramedic Scope of Practice The Primary Care Paramedic (PCP) is not a part of those members included in the Regulated Health Professions Act, as such they are subject to a scope of practice determined by the Ministry of Health, their Base Hospital Medical Director and their service provider. In general, the scope of practice of the PCP is very similar across the province and may vary within that of an individual Base Hospital. The components of the scope of practice are subject to change from time to time, but the following is based on ALS PCS version dated July 17 th, 2017, and includes Emergency Childbirth that is in force as of December 11 th, 2017, and is restricted in application through the Medical Directives or via direct contact (patch) with a Base Hospital Physician. Skill / Advanced Medical Assessment / Delegated Act - CORE Defibrillation Manual Defibrillation Semi-Automated Endotracheal and Tracheostomy suctioning Cardiac monitoring and interpretation 3 or 4 lead Cardiac monitoring and interpretation 12 and 15 lead Chest auscultation and interpretation Capillary blood sampling and glucometry Utilization and interpretation of SpO 2 monitoring Home Dialysis Disconnect Manage Emergency Childbirth (in force on December 11 th, 2017) Medication administration via IM / IN / SC / PO / NEB / MDI / SL IV line monitoring Skill / Advanced Medical Assessment / Delegated Act - AUXILIARY *Intravenous cannulation *Fluid maintenance and bolus administration Supraglottic Airway placement Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Medication administration via Autoinjector Medication administration via Topical *Medication administration via IV Utilization and interpretation of ETCO 2 monitoring Electronic Control Device (ECD) removal Preparation of ACP pre-loads Primary Care Paramedic Scope of Practice Page 44 of 48
46 For Reference Only PCP Medications and routes Medication Name Core Auxiliary Medical Directive Acetaminophen PO PO PO Adult Analgesia Musculoskeletal Pain Special Event Headache Special event Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) PO - - Cardiac Ischemia **Anaesthetic eye drops - - Topical - - Topical CE Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure CE Symptomatic Riot Agent Exposure Antibiotic - Topical - - Topical Minor Abrasions Special Event **Atropine IM /Auto- injector IM CE Adult Nerve Agent Exposure CE Pediatric Nerve Agent Exposure **, Calcium gluconate - - NEB / Topical CE Hydrofluoric Acid Exposure *Dextrose 10% IV - - Hypoglycemia *Dextrose 50% IV - - Hypoglycemia Dimenhydrinate - - IV* / IM Nausea and Vomiting Diphenhydramine - - Epinephrine 1:1, IM IM IM IV* / IM PO Moderate to Severe Allergic Reaction Minor Allergic Reaction Special Event Medical Cardiac Arrest Bronchoconstriction Moderate to Severe Allergic Reaction Croup NEB - - ***Furosemide - - IV N/A Glucagon IM - - Hypoglycemia Hydrocortisone IM - - Suspected Adrenal Crisis **, ⱡ Hydroxocobalamin - - IV infusion CE Cyanide Exposure Ibuprofen PO - - Adult Analgesia Ketorolac IM IV* Adult Analgesia *NaCl 0.9% IV Naloxone SC / IM / IN IV* Opioid Toxicity Nitroglycerin SL - - SL - - IV IV IV and Fluid Therapy Adult and Pediatric Return of Spontaneous Circulation Adult and Pediatric Cardiogenic Shock Cardiac Ischemia Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema **Obidoxime IM / Autoinjector IM **Pralidoxime - - IM / Autoinjector - - IM Salbutamol MDI / NEB - - Bronchoconstriction ***Sodium Bicarbonate IV - - N/A **Sodium Thiosulfate 25% - - IV infusion CE Cyanide Exposure CE Adult Nerve Agent Exposure CE Pediatric Nerve Agent Exposure CE Adult Nerve Agent Exposure CE Pediatric Nerve Agent Exposure * IV cannulation and IV administration of medication requires the authorization of a PCP to the level of Autonomous IV ** These medications / routes are normally a part of Appendix 5 CBRNE directives and are not authorized for use in the CEPCP catchment area ⱡ Hydroxocobalamin is authorized for use by PCCP paramedics with IV authorization Calcium gluconate is authorized for use by NPS paramedics *** These medications are not currently associated with any medical directives and require a BHP patch for consideration Primary Care Paramedic Scope of Practice Page 45 of 48
47 For Reference Only - PCP NOTES: NOTES: Page 46 of 48
48 For Reference Only PCP NOTES: NOTES: Page 47 of 48
49 For Reference Only - PCP NOTES: NOTES: Page 48 of 48
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV OBHG Education Subcommittee
 Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Advanced Care Paramedic
 Advanced Care Paramedic Pocket Reference Guide 2017 v. 4.0.1 and 4.1 Page 0 of 65 This pocket reference guide has been formatted to align with the ALS PCS version 4.0.1 with an in force date of July 17
Advanced Care Paramedic Pocket Reference Guide 2017 v. 4.0.1 and 4.1 Page 0 of 65 This pocket reference guide has been formatted to align with the ALS PCS version 4.0.1 with an in force date of July 17
Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards
 This document contains both information and navigation buttons. To read information, use the Down Arrow from a form field. Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards Version 4.4 Comes into force December
This document contains both information and navigation buttons. To read information, use the Down Arrow from a form field. Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards Version 4.4 Comes into force December
Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards
 Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards Version 4.4 Comes into force December 11, 2017 Emergency Health Services Branch Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care To all users of this publication: The
Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards Version 4.4 Comes into force December 11, 2017 Emergency Health Services Branch Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care To all users of this publication: The
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services. Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual
 Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards
 Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards November 2013 Version 3.1 Emergency Health Services Branch Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care To all users of this publication: The information contained
Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards November 2013 Version 3.1 Emergency Health Services Branch Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care To all users of this publication: The information contained
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS
 MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION. 1. Safe scene, standard precautions. 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness. 3. Quick look (monitor)
 LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
Errata and Stickers- Pocketbook 2019
 Errata and Stickers- Pocketbook 2019 Pocketbook Stickers for ALSPCS.5 Emergency Childbirth: Emergency Childbirth: Nuchal Cord: Attempt to slip over head (or shoulder) If tight, leave in situ and somersault
Errata and Stickers- Pocketbook 2019 Pocketbook Stickers for ALSPCS.5 Emergency Childbirth: Emergency Childbirth: Nuchal Cord: Attempt to slip over head (or shoulder) If tight, leave in situ and somersault
Z19.2 Cross Reference to Patient Care Maps & Clinical Care Procedures
 2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02
 PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
ALS. Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards. June Emergency Health Services Branch Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. Version 2.
 ALS Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards June 2007 Version 2.1 Emergency Health Services Branch Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care To all users of this publication: The information contained
ALS Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards June 2007 Version 2.1 Emergency Health Services Branch Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care To all users of this publication: The information contained
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
In accordance with protocols, this patient should be transported to which medical facility?
 NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
Hamilton Health Sciences Base Hospital Program Medical Directives for PCPs and ACPs October 2007
 Hamilton Health Sciences Base Hospital Program Medical Directives for PCPs and ACPs Ontario Base Hospital Group Medical Advisory Committee Table of Contents Topic: Page Introduction: Use of the Protocols
Hamilton Health Sciences Base Hospital Program Medical Directives for PCPs and ACPs Ontario Base Hospital Group Medical Advisory Committee Table of Contents Topic: Page Introduction: Use of the Protocols
App Update: 4.0 will be updated on July 16 th, 2017 update your app (Ontario Paramedic Clinical Guide)
 App Update: 4.0 will be updated on July 16 th, 2017 update your app (Ontario Paramedic Clinical Guide) 1 2 3 No change to the beginning of the cardiac arrest management plan Service specific teaching SAED
App Update: 4.0 will be updated on July 16 th, 2017 update your app (Ontario Paramedic Clinical Guide) 1 2 3 No change to the beginning of the cardiac arrest management plan Service specific teaching SAED
Prehospital Care Bundles
 Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP REFERENCE AND EDUCATIONAL NOTES
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP REFERENCE AND EDUCATIONAL NOTES Companion Document for the Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards February 2017 Version 4.0.1 Medicine is a discipline in which no two
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP REFERENCE AND EDUCATIONAL NOTES Companion Document for the Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards February 2017 Version 4.0.1 Medicine is a discipline in which no two
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
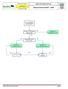 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Advanced Care Paramedic Medical Directives
 Advanced Care Paramedic Medical Directives Regional Medical Director: Dr. M. Lewell Local Medical Director: Dr. A. Dukelow Local Medical Director: Dr. D. Eby Local Medical Director: Dr. P. Bradford Areas
Advanced Care Paramedic Medical Directives Regional Medical Director: Dr. M. Lewell Local Medical Director: Dr. A. Dukelow Local Medical Director: Dr. D. Eby Local Medical Director: Dr. P. Bradford Areas
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. Adult Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
Primary Care Paramedic Medical Directives
 Primary Care Paramedic Medical Directives Regional Medical Director: Dr. M. Lewell Local Medical Director: Dr. A. Dukelow Local Medical Director: Dr. D. Eby Local Medical Director: Dr. P. Bradford Areas
Primary Care Paramedic Medical Directives Regional Medical Director: Dr. M. Lewell Local Medical Director: Dr. A. Dukelow Local Medical Director: Dr. D. Eby Local Medical Director: Dr. P. Bradford Areas
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
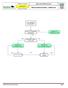 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL
 CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
Pediatric Resuscitation
 Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Naloxone Intranasal EMT OPTIONAL SKILL. Cell Phones and Pagers. Course Outline 09/2017
 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and Overview
EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and Overview
Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off.
 1 2 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. 3 4 5 6 Course Outline Introduction
1 2 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. 3 4 5 6 Course Outline Introduction
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Primary Care Paramedic
 Primary Care Paramedic Directives ALS PCS 4.4 Introduction Airway/ Breathing Cardiac/ Circulation Level of Conciousness/ Procedural References Medication Information VERSION 1-2018 PRINT DATE 2018-04-01
Primary Care Paramedic Directives ALS PCS 4.4 Introduction Airway/ Breathing Cardiac/ Circulation Level of Conciousness/ Procedural References Medication Information VERSION 1-2018 PRINT DATE 2018-04-01
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
Resuscitation Checklist
 Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
Resuscitation Checklist Actions if multiple responders are on scene Is resuscitation appropriate? Conditions incompatible with life Advanced decision in place Based on the information available, the senior
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Cardiac chest pain or suspected Myocardial Infarction.
 s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
Professional Development Geriatric Care Part II
 Self-Study Spring 2016 Professional Development Geriatric Care Part II 1) An elderly patient falls and is experiencing some groin pain and difficulty walking. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Self-Study Spring 2016 Professional Development Geriatric Care Part II 1) An elderly patient falls and is experiencing some groin pain and difficulty walking. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
** Note: second generation antihistamines cause less drowsiness; may be beneficial in patients that need to drive themselves home.
 Table 5 : Management of Acute Reactions to Contrast Media in Adults HIVES Mild (scattered and/ transient) No treatment often needed; however, if symptomatic, can consider: Diphenhydramine (Benadryl )*
Table 5 : Management of Acute Reactions to Contrast Media in Adults HIVES Mild (scattered and/ transient) No treatment often needed; however, if symptomatic, can consider: Diphenhydramine (Benadryl )*
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses
 Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 5 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General This protocol should be followed for all pediatric cardiac arrests. If an arrest is of a known traumatic origin refer to the Dead on
EMS Region Medication List 2010
 EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care
 Standard Operating Procedure 2.10 Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care Position Responsible: Medical Director Approved: Clinical Governance Committee Related Documents: This document is the intellectual property
Standard Operating Procedure 2.10 Post Resuscitation (ROSC) Care Position Responsible: Medical Director Approved: Clinical Governance Committee Related Documents: This document is the intellectual property
Medical First Responder Program Protocols
 Medical Scene Safety Protocol Verify Scene Safety with Police or Dispatch UNKWN Scene Safe? Enter Continue to Appropriate Protocol Possible to Make Safe Make Safe Then Continue Exit Area and Stage Outside
Medical Scene Safety Protocol Verify Scene Safety with Police or Dispatch UNKWN Scene Safe? Enter Continue to Appropriate Protocol Possible to Make Safe Make Safe Then Continue Exit Area and Stage Outside
San Benito County EMS Agency Section 700: Patient Care Procedures
 Purpose: To outline the steps EMTs & paramedics will take to manage possible life threats in any child or adult patient they encounter. This policy is in effect for all treatment protocols & is to be referred
Purpose: To outline the steps EMTs & paramedics will take to manage possible life threats in any child or adult patient they encounter. This policy is in effect for all treatment protocols & is to be referred
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY. Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose
 SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose Disclaimer: Authorization - EMT Optional Skills Only authorized Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT) who
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Administration of Naloxone for Opiate Overdose Disclaimer: Authorization - EMT Optional Skills Only authorized Emergency Medical Technicians (EMT) who
Primary Care Paramedic Pocket Reference Guide Version 1.1 CEPCP
 Primary Care Paramedic Pocket Reference Guide 2011 Version 1.1 CEPCP 2! This pocket reference guide is to be used for reference only. Refer to the current medical directives for all treatment decisions.
Primary Care Paramedic Pocket Reference Guide 2011 Version 1.1 CEPCP 2! This pocket reference guide is to be used for reference only. Refer to the current medical directives for all treatment decisions.
Drug Profiles Professional Responder
 Entonox Classification Medical Gas Entonox (50% oxygen 50% nitrous oxide) Effects Potent analgesic, weak anesthetic Onset Rapid Peak Immediate Indications Relief of moderate to severe pain Cardiac-related
Entonox Classification Medical Gas Entonox (50% oxygen 50% nitrous oxide) Effects Potent analgesic, weak anesthetic Onset Rapid Peak Immediate Indications Relief of moderate to severe pain Cardiac-related
Consider Treatable Underlying Causes Early
 Page 1 of 8 Cardiac Arrest Timeout Checklist Assign roles for Pit Crew CPR o Compressors x 2 o Airway o Lead responsible for coordinating team, making decisions o Medications Continuous compressions at
Page 1 of 8 Cardiac Arrest Timeout Checklist Assign roles for Pit Crew CPR o Compressors x 2 o Airway o Lead responsible for coordinating team, making decisions o Medications Continuous compressions at
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes
 Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
A00.2 Office of the Medical Director
 A00.2 Office of the Medical Director 2017-07-17 Medications Individual license holders are responsible to hold and maintain the appropriate competencies (satisfactory knowledge and appropriate psychomotor
A00.2 Office of the Medical Director 2017-07-17 Medications Individual license holders are responsible to hold and maintain the appropriate competencies (satisfactory knowledge and appropriate psychomotor
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health
 CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
Head Trauma Protocol
 Injuries to the head may cause underlying brain tissue damage. Increased intracranial pressure from bleeding or swelling tissue is a common threat after head trauma. Common signs and symptoms of increased
Injuries to the head may cause underlying brain tissue damage. Increased intracranial pressure from bleeding or swelling tissue is a common threat after head trauma. Common signs and symptoms of increased
ILS Protocols Content Page
 Altered Mental Status/Coma Asthma Chest Pain CPAP Hypoglycemia Intraosseous Infusion (EZ IO) Adult Intraosseous Infusion (EZIO) Pediatric Poisoning and/or Overdose Seizure Spinal Immob. Decision Tree s
Altered Mental Status/Coma Asthma Chest Pain CPAP Hypoglycemia Intraosseous Infusion (EZ IO) Adult Intraosseous Infusion (EZIO) Pediatric Poisoning and/or Overdose Seizure Spinal Immob. Decision Tree s
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update What s New for 2010? 3 CPR. 4 4 Steps of BLS Survey 5 CPR 6 CPR.
 1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
ADULT TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016
 HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016 CAPABILITIES Airway Management Finger sweep Head-tilt-chin lift Jaw-thrust
HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH AFRICA PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR EMERGENCY CARE CAPABILITIES OF EMERGENCY CARE PROVIDERS: JUNE 2016 CAPABILITIES Airway Management Finger sweep Head-tilt-chin lift Jaw-thrust
Preparing for your upcoming PALS course
 IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
PALS PRETEST. PALS Pretest
 PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS
 EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director ALLERGIC REACTION/ANAPHYLAXIS ADULT BLS TREATMENT
EL DORADO COUNTY EMS AGENCY PREHOSPITAL PROTOCOLS Effective: July 1, 2017 Reviewed: November 9, 2016 Revised: November 9, 2016 EMS Agency Medical Director ALLERGIC REACTION/ANAPHYLAXIS ADULT BLS TREATMENT
Emergency Care Progress Log
 Emergency Care Progress Log For further details on the National Occupational Competencies for EMRs, please visit www.paramedic.ca. Check off each skill once successfully demonstrated the Instructor. All
Emergency Care Progress Log For further details on the National Occupational Competencies for EMRs, please visit www.paramedic.ca. Check off each skill once successfully demonstrated the Instructor. All
PCP Medical Directives Paramedic Handbook 2012
 PCP Medical Directives Paramedic Handbook 2012 Credits Editor in Chief Severo Rodriguez Editor and Project Manager Cathy Prowd Publication Assistant Tracy Gaunt Editor Medical Content Dr. Michael Lewell
PCP Medical Directives Paramedic Handbook 2012 Credits Editor in Chief Severo Rodriguez Editor and Project Manager Cathy Prowd Publication Assistant Tracy Gaunt Editor Medical Content Dr. Michael Lewell
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP REFERENCE AND EDUCATIONAL NOTES
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP REFERENCE AND EDUCATIONAL NOTES Companion Document for the Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards December 2017 Version 4.4 Medicine is a discipline in which no two situations
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP REFERENCE AND EDUCATIONAL NOTES Companion Document for the Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards December 2017 Version 4.4 Medicine is a discipline in which no two situations
They aren t the same thing. Daniel Dunham
 They aren t the same thing Daniel Dunham Capnometry Displays the value (as a number) of the partial pressure of CO2 Capnography Waveform capnography shows (as a wave) the change in CO2 over time Both are
They aren t the same thing Daniel Dunham Capnometry Displays the value (as a number) of the partial pressure of CO2 Capnography Waveform capnography shows (as a wave) the change in CO2 over time Both are
Adult Basic Life Support
 Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice
 Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice Name: Date: Problem 1 Your 4 year old patient weighs 40 pounds. She is febrile. You need to administer acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15mg/kg. How many mg will you administer?
Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice Name: Date: Problem 1 Your 4 year old patient weighs 40 pounds. She is febrile. You need to administer acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15mg/kg. How many mg will you administer?
Clinical Procedures and Guidelines
 Clinical Procedures and Guidelines Pocket Edition 2013-2015 2 foreword These are the Clinical Procedures and Guidelines (CPGs) for the New Zealand ambulance sector. This is the pocket edition of the Clinical
Clinical Procedures and Guidelines Pocket Edition 2013-2015 2 foreword These are the Clinical Procedures and Guidelines (CPGs) for the New Zealand ambulance sector. This is the pocket edition of the Clinical
Clinical Practice Guidelines Edition (Updated February 2018)
 The Formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to support Emergency First Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical Practice Guidelines
The Formulary is published by the Pre-Hospital Emergency Care Council (PHECC) to support Emergency First Responders to be competent in the use of medications permitted under Clinical Practice Guidelines
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies. CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED
 Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Lesson 4-3: Cardiac Emergencies CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Angina, AMI, CHF and AED THREE FAMILIAR CARDIAC CONDITIONS Angina Pectoris Acute Myocardial Infarction Congestive Heart Failure ANGINA PECTORIS Chest
Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016
 Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016 1. Which of the following is incorrect? a. Each EMS and Fire agency should have protocols in place for evaluation of personnel involved in fire suppression operations
Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016 1. Which of the following is incorrect? a. Each EMS and Fire agency should have protocols in place for evaluation of personnel involved in fire suppression operations
CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION
 CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION A. Age delineation: Infant CPR guidelines apply to victims less than one year of age; Child CPR guidelines apply to victims one year of age to the onset of adolescence
CARDIAC ARREST GENERAL CONSIDERATION A. Age delineation: Infant CPR guidelines apply to victims less than one year of age; Child CPR guidelines apply to victims one year of age to the onset of adolescence
Conscious Sedation Permit Evaluation. General Comments Emergency Algorithms
 General Comments Emergency Algorithms These algorithms delineate appropriate responses to the simulated emergencies listed in Article 5, Section 1043.4c of the California Code of Regulations. Each algorithm
General Comments Emergency Algorithms These algorithms delineate appropriate responses to the simulated emergencies listed in Article 5, Section 1043.4c of the California Code of Regulations. Each algorithm
UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table
 2014-2016 UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table September 2014 Based on Revision D, 15 September 2014 Implementation Date: 1 October 2014 This document summarizes
2014-2016 UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table September 2014 Based on Revision D, 15 September 2014 Implementation Date: 1 October 2014 This document summarizes
Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS
 Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS Instructions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Questions 1 and 2 pertain to the following scenario: A 54-year-old man has experienced
Final Written Exam ASHI ACLS Instructions: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Questions 1 and 2 pertain to the following scenario: A 54-year-old man has experienced
Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines. Cardiac Arrest
 Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines Cardiac Arrest Note: These guidelines are based on (or adapted from) the current American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency
Portage County EMS Patient Care Guidelines Cardiac Arrest Note: These guidelines are based on (or adapted from) the current American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency
2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol Medical Newborn/Neonatal. Protocol 8-3 Resuscitation 4. Medical Supraventricular
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SECTION: Pediatric Cardiovascular Emergencies REVISED: 06/2017 Section 8 1. Cardiac Arrest Unknown Rhythm (i.e. Protocol 8-1 BLS) 2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol 8-2 3. Medical Newborn/Neonatal
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SECTION: Pediatric Cardiovascular Emergencies REVISED: 06/2017 Section 8 1. Cardiac Arrest Unknown Rhythm (i.e. Protocol 8-1 BLS) 2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol 8-2 3. Medical Newborn/Neonatal
Skills: Recall the incidence of seizures Recall the causes of seizures Describe types of seizures List signs and symptoms of seizure patients
 Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket
 BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
3. The signs of Compartment Syndrome are listed in the General Crush Protocol. a. True b. False
 Schoolcraft Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, February 2015, Version 1 MFR/EMT/SPECIALIST/PARAMEDIC 1. Schoolcraft County Medical Control Protocols and Procedures can be found
Schoolcraft Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, February 2015, Version 1 MFR/EMT/SPECIALIST/PARAMEDIC 1. Schoolcraft County Medical Control Protocols and Procedures can be found
A silent chest is. Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest. Children are different. Cough variant asthma. Symptoms of severe distress
 Asthma ~21% of all asthma cases are school aged Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest Identify 3 symptoms of an asthma exacerbation Bronchospasm Edema of the bronchi Increased mucus production
Asthma ~21% of all asthma cases are school aged Pediatrics II Asthma, seizures and cardiac arrest Identify 3 symptoms of an asthma exacerbation Bronchospasm Edema of the bronchi Increased mucus production
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines
 table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac
 Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Reference Material. Medical Directives PCP Auxiliary. Medical Directives. Phone Numbers. Introduction PCP Core. BHP Patch. Notes
 Primary Care Paramedic Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards Version 3..3 Introduction PCP Core Medical Directives PCP Auxiliary Medical Directives Reference Material Notes BHP Patch Phone Numbers
Primary Care Paramedic Advanced Life Support Patient Care Standards Version 3..3 Introduction PCP Core Medical Directives PCP Auxiliary Medical Directives Reference Material Notes BHP Patch Phone Numbers
INTUBATION/RSI. PURPOSE: A. To facilitate secure, definitive control of the airway by endotracheal intubation in an expeditious and safe manner
 Manual: LifeLine Patient Care Protocols Section: Adult/Pediatrics Protocol #: AP1-009 Approval Date: 03/01/2018 Effective Date: 03/05/2018 Revision Due Date: 12/01/2018 INTUBATION/RSI PURPOSE: A. To facilitate
Manual: LifeLine Patient Care Protocols Section: Adult/Pediatrics Protocol #: AP1-009 Approval Date: 03/01/2018 Effective Date: 03/05/2018 Revision Due Date: 12/01/2018 INTUBATION/RSI PURPOSE: A. To facilitate
Sierra Sacramento Valley EMS Agency Policy/Protocol Manual Table of Contents
 SECTION 100 STATE LAW AND REGULATION 100 Index 101 California Health And Safety Code, Division 2.5 Emergency Medical Services 102 California Code Of Regulations, Title 22, Division 9 SECTION 200 LEMSA
SECTION 100 STATE LAW AND REGULATION 100 Index 101 California Health And Safety Code, Division 2.5 Emergency Medical Services 102 California Code Of Regulations, Title 22, Division 9 SECTION 200 LEMSA
