HEAVY METALS : Review
|
|
|
- Cecil Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HEAVY METALS : Review
2 INHALED TOXINS Dr. Tawfiq Almezeiny MBBS FRCPC (CCM)
3
4
5
6 Introduction Airborne toxins typically produce local noxious effects on the airways and lungs. Examples of Inhalational exposure: Asbestos Urban exposure to photochemical smog
7 Introduction There are wide spectrum of possible toxic inhalants identification of a specific inhalant is generally unnecessary Therapy is based on the clinical manifestations.
8
9 FIRST : SIMPLE ASPHYXIANTS The vast majority of simple asphyxiations are workplace related and usually occur : During the use of liquefied gas While breathing through airline respirators While working in confined spaces. Deaths from the inhalation of automotive exhaust result from simple asphyxiation not carbon monoxide poisoning.
10 Principles of Disease Most simple asphyxiants are inert and produce toxicity only by displacing oxygen and lowering the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO 2 ) Exposed patients remain asymptomatic if the Fio 2 is normal. CO2 and N2 : constituents of air produce narcosis at elevated levels
11 Clinical Features Acute effects occur within minutes of onset of asphyxia: manifestations of hypoxia A fall in the FiO 2 from 21% to 15% Autonomic stimulation (e.g., tachycardia, tachypnea, and dyspnea) Cerebral hypoxia (e.g., ataxia, dizziness, incoordination, and confusion). Stimulator: hypoxemia or hypercarbia?
12 Clinical Features If FiO 2 falls below 10% : Cerebral Edema and Lethargy. FiO 2 below 6%: is Fatal! *Removal from exposure terminates the hypoxia and results in clinical improvement. * Most patients present with resolving symptoms. *Failure to improve suggests complications of ischemia (e.g., seizures, coma, and cardiac arrest) That is poor prognosis.
13 Diagnostic Strategies and Differential Considerations Consistent history Spectrum of complaints Rapid resolution on removal from exposure Minimally symptomatic or asymptomatic patients do not require any tests. Scene investigation(csi): will yield the causative agent ;by a trained and suitably outfitted team.
14 Diagnostic Strategies and Differential Considerations Determination of the exact nature of the gas is of limited clinical value It may have important public health implications. The presenting complaints :nonspecific (e.g., dizziness, syncope, and dyspnea) The differential diagnosis is extensive.
15 Management and Disposition Removal from exposure supportive care: Administration of supplemental oxygen. Neurologic injury or cardiorespiratory arrest should be managed with standard resuscitation protocols. Mildly-poisoning patients: **recover after removal from the exposure **observed briefly and discharged.
16 Management and Disposition Risk for complications of hypoxia : Elderly Pediatrics Coma Seizures Cardiac COPD Prolonged exposure
17 SECOND : PULMONARY IRRITANTS Pulmonary irritant gases large group of agents that produce a common toxicological syndrome when inhaled in moderate concentrations.
18 Principles of Disease 1)Irritant gases dissolve in the respiratory tract mucus. 2)Alter the air-lung interface by inflammatory response. 3)When dissolved, produce an acid or alkaline product. 4)generate oxygen-derived free radicals that produce direct cellular toxicity.
19 Sample reactions of pulmonary irritants reacting with water in the lung
20 Clinical Features Exposure results in immediate irritation, lacrimation nasal burning cough massive or prolonged exposure: laryngeal edema laryngospasm bronchospasm Acute Lung Injury (ALI) noncardiogenic pulmonary edema
21
22 Clinical Features Poorly water-soluble gases do not readily irritate the mucous membranes!! some have pleasant odors (e.g., phosgene's odor is similar to that of hay). Since there are no immediate symptoms, prolonged breathing in the toxic environment allows the gas to reach the alveoli.
23 Weapons of War - Poison Gas ( WMD) : WWI Chlorine Phosgene Mustard gas The German army ended the war as the heaviest user of gas. It is suggested that German use reached 68,000 tons French utilised 36,000 tons British 25,000 tons
24 Clinical Features After 2-24 Hours: Irritation of the lower airway, alveoli, and parenchyma and causes pulmonary endothelial injury. Initial symptoms consistent with ALI may be mild Progress to overt respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome during the ensuing 24 to 36 hours.
25 Diagnostic Strategies and Differential Consideration The evaluation of upper airway : physical examination laryngoscopy normal oropharyngeal or laryngeal evaluation may NOT exclude subsequent deterioration. Radiographic and laboratory studies: not useful.
26 Diagnostic Strategies and Differential Consideration Oxygenation and ventilation are assessed by serial chest auscultation pulse oximetry chest radiography ABGs No clinical tests can identify the specific irritant identification is not generally necessary
27 Management Signs of upper airway dysfunction (e.g., hoarseness and stridor) : visualization of the larynx and immediate airway stabilization ( potential rapidity of airway deterioration)
28 Management Bronchospasm generally responds to Inhaled beta2-adrenergic agonists( Salbutmol) Ipratropium bromide(atrovent). No clearindication for corticosteroids
29 Management Nebulized 2% sodium bicarbonate solution chlorine or hydrogen chloride gas symptomatic relief Patients require extensive discharge instructions for signs and symptoms of pulmonary irritation.
30 Management Diagnosis of ALI ( ARDS) (acute respiratory distress syndrome) aggressive supportive care Advanced ventilation modes in ICU. Exogenous surfactant nitric oxide (NO) ventilation
31 THIRD: SMOKE INHALATION
32 SMOKE INHALATION Principals : 1)Irritant injury: heated particulate matter and adsorbed toxins injure normal mucosa, similar to other irritant gases. 2)Carbon monoxide and Cyanide are systemic toxins.
33 Worst Fire Accidents!
34 Church of the Company Fire (1863) Santiago, Chile More than 2000 :Died
35 Principles of Disease At Temp : 350 C and 500 C, Air has a low heat capacity rarely produces lower airway damage. Heat capacities of steam (approximately 4000 times that of air) plus heated soot suspended in air (i.e., smoke) can transfer heat and cause injury deep within the respiratory tract.
36 Principles of Disease The nature of the fuel determines the composition of its smoke. Irritant toxins produced by the fire are adsorbed onto carbonaceous particles that deposit in the airways. The irritant substances damage the mucosa through mechanisms similar to those of the irritant gases, including generation of acids and free radical formation.
37 Clinical Features morbidity and mortality : respiratory tract damage. Thermal and irritant-induced laryngeal injury *Cough, Stridor, Bronhospasm Then : ARDS *Maybe delayed!
38 Principles of Disease Latency period: variable and dependent on the degree and nature of the exposure. Singed nasal hairs and soot in the sputum suggest substantial exposure but are neither sensitive nor specific
39 Principles of Disease Carbon monoxide (CO) and Cyanide Must be routinely considered in these patients. Exposure to filtered or distant smoke (e.g., in a different room) or (e.g., engine exhaust) inhale predominantly CO, cyanide, and metabolic poisons and do not sustain smoke exposure.
40 Diagnostic Strategies and Differential Considerations Early death: result from 1.asphyxia 2.airway compromise 3.metabolic poisoning (e.g., CO).
41 Management Cyanide : Must suspect : when? Metabolic acidosis!( with serum lactate level greater than 10 mmol/l), suggests concomitant cyanide poisoning. Oxygenation should be assessed by co-oximetry because ABG analysis and pulse oximetry may be inaccurate in CO-poisoned patients.
42 Management : Admission Worrisome clinical findings (e.g., hoarseness and respiratory distress) and those with Identifiers of substantial exposure (e.g., closedspace exposure) Carbonaceous sputum Critical Care Unit or Burn Center
43 Burn Intensive Care Unit
44 Management : Supportive Bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage is frequently recommended to clear debris and toxins from the distal airways. Corticosteroids whether inhaled or systemic, are not indicated and are potentially harmful Antibiotics should be used only in patients with suspected infection.
45 Management : Supportive Management of victims of smoke inhalation and irritant inhalational injuries : similar. Rapid assessment of the airway and early intubation is critical! Inhaled beta-adrenergic agonists Optimal supportive care maintenance of adequate oxygenation (e.g., suctioning and pulmonary toilet) (( most important aspects of care))
46 THANKS
Lecture Notes. Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns
 Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
Lecture Notes Chapter 9: Smoke Inhalation Injury and Burns Objectives List the factors that influence mortality rate Describe the nature of smoke inhalation and the fire environment Recognize the pulmonary
Jeffrey N. Bernstein MD. *Simple asphyxiants *Systemic asyphyxiants *Chemical irritants
 Jeffrey N. Bernstein MD Simple asphyxiants Systemic asyphyxiants Chemical irritants 1746 (est) people killed overnight 3000 Cattle Countless wild animals There was no evidence of bleeding, physical
Jeffrey N. Bernstein MD Simple asphyxiants Systemic asyphyxiants Chemical irritants 1746 (est) people killed overnight 3000 Cattle Countless wild animals There was no evidence of bleeding, physical
Smoke inhalation damages the body by simple asphyxiation (lack of oxygen), chemical irritation, chemical asphyxiation, or a combination of these.
 Print Close 2011 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. Smoke Inhalation Recommend 13 Medical Author: Christopher P Holstege, MD Medical Editor: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Smoke Inhalation Overview Smoke Inhalation
Print Close 2011 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. Smoke Inhalation Recommend 13 Medical Author: Christopher P Holstege, MD Medical Editor: Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD Smoke Inhalation Overview Smoke Inhalation
COBIS Management of airway burns and inhalation injury PAEDIATRIC
 COBIS Management of airway burns and inhalation injury PAEDIATRIC 1 A multidisciplinary team should provide the management of the child with inhalation injury. Childhood inhalation injury mandates transfer
COBIS Management of airway burns and inhalation injury PAEDIATRIC 1 A multidisciplinary team should provide the management of the child with inhalation injury. Childhood inhalation injury mandates transfer
Applicable to. Team Members Performing
 Protocol: Pediatric Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date November 1, 2016 Due for review November 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations
Protocol: Pediatric Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Protocol Number Approval Date November 1, 2016 Due for review November 1, 2018 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose
 Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
Clinical Pathway: Management Of The Life-Threatening Overdose Intravenous access Oxygen Pulse oximetry n-invasive blood pressure monitoring Accu-Check ECG monitoring and ECG Chest x-ray Respiratory depression?
PRODUCTS OF COMBUSTION
 Chemical Hazards and Poisons Division () Incident Summary PRODUCTS OF COMBUSTION DRAFT SUMMARY INFORMATION Key Points Health risks associated with exposure to smoke and toxic substances released in fires
Chemical Hazards and Poisons Division () Incident Summary PRODUCTS OF COMBUSTION DRAFT SUMMARY INFORMATION Key Points Health risks associated with exposure to smoke and toxic substances released in fires
CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch th )
 CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch. 152 9 th ) Episode Overview Key Concepts: Aspiration is the major toxic risk of hydrocarbon poisoning. Hydrocarbons may cause systemic toxicity, burns, seizures, cardiac
CRACKCast Episode Hydrocarbons (Ch. 152 9 th ) Episode Overview Key Concepts: Aspiration is the major toxic risk of hydrocarbon poisoning. Hydrocarbons may cause systemic toxicity, burns, seizures, cardiac
PRODUCTS OF COMBUSTION
 Division of Chemical Hazards and Poisons () Incident Summary PRODUCTS OF COMBUSTION DRAFT SUMMARY INFORMATION Key Points Health risks associated with exposure to smoke and toxic substances released in
Division of Chemical Hazards and Poisons () Incident Summary PRODUCTS OF COMBUSTION DRAFT SUMMARY INFORMATION Key Points Health risks associated with exposure to smoke and toxic substances released in
1 Inhalational Injury: pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment. O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery
 1 Inhalational Injury: pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery 2 At the end of this lecture you should be able to: Describe the physiology of the respiration of the
1 Inhalational Injury: pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery 2 At the end of this lecture you should be able to: Describe the physiology of the respiration of the
Chapter 159 Inhaled Toxins
 Chapter 159 Inhaled Toxins Episode Overview: 1) Define simple asphyxiants and list 5 examples 2) What are pulmonary irritants? Describe their management. 3) Describe the mechanism of cyanide toxicity 4)
Chapter 159 Inhaled Toxins Episode Overview: 1) Define simple asphyxiants and list 5 examples 2) What are pulmonary irritants? Describe their management. 3) Describe the mechanism of cyanide toxicity 4)
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
LUNG-DAMAGING AGENTS AND TOXIC INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS
 Lung-Damaging Agents and Toxic Industrial Chemicals Chapter 4 LUNG-DAMAGING AGENTS AND TOXIC INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS NATO Codes: CG, Cl Summary Signs and Symptoms: Central effects: Eye and airway irritation,
Lung-Damaging Agents and Toxic Industrial Chemicals Chapter 4 LUNG-DAMAGING AGENTS AND TOXIC INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS NATO Codes: CG, Cl Summary Signs and Symptoms: Central effects: Eye and airway irritation,
Applicable to. Team Members Performing
 Protocol: Category Clinical Practice Approval Date March 13, 2019 Due for review March 13, 2021 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG VPH Other All faculty & staff Other: Faculty
Protocol: Category Clinical Practice Approval Date March 13, 2019 Due for review March 13, 2021 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG VPH Other All faculty & staff Other: Faculty
Appendix D An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires:
 Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Formaldehyde (HCHO) C 1
 BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Formaldehyde (HCHO) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients exposed only to formaldehyde gas or vapor do not
BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Formaldehyde (HCHO) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients exposed only to formaldehyde gas or vapor do not
American Osteopathic College of Occupational and Preventive Medicine 2011 Annual Meeting, Orlando, Florida, November 1, 2011
 Occupational Lung Disease Practical Applications of The Respiratory Standard Lance Walker D.O. MPH Objectives 1. Review of Occupational Lung Diseases 2. OSHA Respiratory Standard Refresher 3. Discuss spirometry
Occupational Lung Disease Practical Applications of The Respiratory Standard Lance Walker D.O. MPH Objectives 1. Review of Occupational Lung Diseases 2. OSHA Respiratory Standard Refresher 3. Discuss spirometry
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES. Michael Waters MD April 2004
 RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES Michael Waters MD April 2004 ASTHMA Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways with variable or reversible airway obstruction Characterized by increased sensitivity
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES Michael Waters MD April 2004 ASTHMA Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways with variable or reversible airway obstruction Characterized by increased sensitivity
Applicable to. Team Members Performing MD House Staff APRN/PA RN LPN
 Protocol: Adult Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Approval Date: March 26, 2019 Review Date: March 26, 2020 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG VPH Other All faculty
Protocol: Adult Burn Inhalation Injury Category Clinical Practice Approval Date: March 26, 2019 Review Date: March 26, 2020 Applicable to VUH Children s DOT VMG Off-site locations VMG VPH Other All faculty
Lecture Notes. Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
INDICATIONS FOR RESPIRATORY ASSISTANCE A C U T E M E D I C I N E U N I T P - Y E A R M B B S 4
 INDICATIONS FOR RESPIRATORY ASSISTANCE A C U T E M E D I C I N E U N I T P - Y E A R M B B S 4 RESPIRATORY FAILURE Acute respiratory failure is defined by hypoxemia with or without hypercapnia. It is one
INDICATIONS FOR RESPIRATORY ASSISTANCE A C U T E M E D I C I N E U N I T P - Y E A R M B B S 4 RESPIRATORY FAILURE Acute respiratory failure is defined by hypoxemia with or without hypercapnia. It is one
Sources of carbon monoxide exposure
 Carbon monoxide Sources of carbon monoxide exposure Mechanism of action Tissue hypoxia Binds to myoglobin and cytochrome oxidase Shift oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve to left Accelerate cellular death
Carbon monoxide Sources of carbon monoxide exposure Mechanism of action Tissue hypoxia Binds to myoglobin and cytochrome oxidase Shift oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve to left Accelerate cellular death
CHLOROPICRIN VAPOR EXPOSURE RESULTING FROM TREATED FIELD VAPOR
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL TREATMENT GUIDE CHLOROPICRIN VAPOR EXPOSURE RESULTING FROM TREATED FIELD VAPOR SYNONYMS: Chloropicrin, Trichloronitromethane, Nitrochloroform (label names such as Tri- Clor and Tri-Pic).
EMERGENCY MEDICAL TREATMENT GUIDE CHLOROPICRIN VAPOR EXPOSURE RESULTING FROM TREATED FIELD VAPOR SYNONYMS: Chloropicrin, Trichloronitromethane, Nitrochloroform (label names such as Tri- Clor and Tri-Pic).
March 2009 CE. Site code # E Carbon Monoxide, Smoke Inhalation, Cyanide Poisoning and Medical Rehab
 March 2009 CE Site code #107200-E-1209 Carbon Monoxide, Smoke Inhalation, Cyanide Poisoning and Medical Rehab Objectives and materials by: F/M Dan Ogurek Countryside Fire Protection Dist. Packet Prepared
March 2009 CE Site code #107200-E-1209 Carbon Monoxide, Smoke Inhalation, Cyanide Poisoning and Medical Rehab Objectives and materials by: F/M Dan Ogurek Countryside Fire Protection Dist. Packet Prepared
Epiglottitis. Bronchitis. Bronchiolitis. Pneumonia. Croup syndrome. Miss. kamlah 2
 Miss. kamlah 1 Epiglottitis. Bronchitis. Bronchiolitis. Pneumonia. Croup syndrome. Miss. kamlah 2 Acute Epiglottitis Is an infection of the epiglottis, the long narrow structure that closes off the glottis
Miss. kamlah 1 Epiglottitis. Bronchitis. Bronchiolitis. Pneumonia. Croup syndrome. Miss. kamlah 2 Acute Epiglottitis Is an infection of the epiglottis, the long narrow structure that closes off the glottis
Toxic Gases from Fermentation
 Toxic Gases from Fermentation รศ.พญ.ส ดา วรรณประสาท ภาคว ชาเภส ชว ทยา หน วยเภส ชว ทยาและพ ษว ทยาคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น Confined space Simple ช องว างหร อบร เวณป ด ท เก
Toxic Gases from Fermentation รศ.พญ.ส ดา วรรณประสาท ภาคว ชาเภส ชว ทยา หน วยเภส ชว ทยาและพ ษว ทยาคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น Confined space Simple ช องว างหร อบร เวณป ด ท เก
Ammonia (NH 3 ) B 1. Information and recommendations for paramedics and doctors at the site. BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines
 BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Ammonia (NH 3 ) B 1 Information and recommendations for paramedics and doctors at the site Before approaching the patient the paramedics and doctors at the site
BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Ammonia (NH 3 ) B 1 Information and recommendations for paramedics and doctors at the site Before approaching the patient the paramedics and doctors at the site
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
Acute respiratory failure
 Rita Williams, NP-C, PA PeaceHealth Medical Group Pulmonary & Critical Care Acute respiratory failure Ventilation/perfusion mismatching Most common cause of hypoxemia Normal is 1:1 ratio or 1 Ventilation
Rita Williams, NP-C, PA PeaceHealth Medical Group Pulmonary & Critical Care Acute respiratory failure Ventilation/perfusion mismatching Most common cause of hypoxemia Normal is 1:1 ratio or 1 Ventilation
Respiratory Failure. Causes of Acute Respiratory Failure (ARF): a- Intrapulmonary:
 Respiratory failure exists whenever the exchange of O 2 for CO 2 in the lungs cannot keep up with the rate of O 2 consumption & CO 2 production in the cells of the body. This results in a fall in arterial
Respiratory failure exists whenever the exchange of O 2 for CO 2 in the lungs cannot keep up with the rate of O 2 consumption & CO 2 production in the cells of the body. This results in a fall in arterial
LUNG-DAMAGING AGENTS: TOXIC INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS
 Lung-Damaging Agents: Toxic Industrial Chemicals Chapter 1 LUNG-DAMAGING AGENTS: TOXIC INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS Summary NATO Codes: CG, Cl Signs and Symptoms: Central effects: eye and airway irritation, dyspnea;
Lung-Damaging Agents: Toxic Industrial Chemicals Chapter 1 LUNG-DAMAGING AGENTS: TOXIC INDUSTRIAL CHEMICALS Summary NATO Codes: CG, Cl Signs and Symptoms: Central effects: eye and airway irritation, dyspnea;
Exercise and Air Pollution
 Exercise and Air Pollution Two Major Groups of Air Pollutants Primary From a single source of pollution CO, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, particulants Secondary Result from an interaction
Exercise and Air Pollution Two Major Groups of Air Pollutants Primary From a single source of pollution CO, sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, particulants Secondary Result from an interaction
Over the last several years various national and
 Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Chapter 13. Respiratory Emergencies
 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Introduction Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in
Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Introduction Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in
PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm.
 PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Bradycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Tachycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M
PALS Pulseless Arrest Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Bradycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M E et al. Circulation 2010;122:S876-S908 PALS Tachycardia Algorithm. Kleinman M
A. Incorrect! The alveolus is where gas exchange takes place. B. Correct! Surfactant is the lipid-rich material that permits lung inflation.
 Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
Toxicology - Problem Drill 13: Respiratory Toxicology No. 1 of 10 1. The lipid-rich material that decreases surface tension of the alveoli, allowing sacs to inflate properly and remain inflated during
COPD Challenge CASE PRESENTATION
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations may make up more than 10% of acute medical admissions [1], and they are increasingly recognised as a cause of significant morbidity and mortality
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations may make up more than 10% of acute medical admissions [1], and they are increasingly recognised as a cause of significant morbidity and mortality
Bronchospasm & SOB. Kim Kilmurray Senior Clinical Teaching Fellow
 Bronchospasm & SOB Kim Kilmurray Senior Clinical Teaching Fellow LEARNING OBJECTIVES Perform a comprehensive respiratory examination & link clinical signs to underlying pathology Identify the spectrum
Bronchospasm & SOB Kim Kilmurray Senior Clinical Teaching Fellow LEARNING OBJECTIVES Perform a comprehensive respiratory examination & link clinical signs to underlying pathology Identify the spectrum
Respiratory Emergencies. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Respiratory Emergencies Lesson Goal Assess and provide timely treatment & transport to patients experiencing respiratory emergencies Lesson Objectives List parts of respiratory system and how they work
Respiratory Emergencies Lesson Goal Assess and provide timely treatment & transport to patients experiencing respiratory emergencies Lesson Objectives List parts of respiratory system and how they work
Wilson County Emergency Management Agency Protocol Manual Protocols
 Carbon Monoxide Monitoring AEMT & Paramedic Standing Order With the technology of the Masmio RAD 57 carbon monoxide detector EMS personnel are now able to determine CO levels with the same simplicity as
Carbon Monoxide Monitoring AEMT & Paramedic Standing Order With the technology of the Masmio RAD 57 carbon monoxide detector EMS personnel are now able to determine CO levels with the same simplicity as
ETCO2 MONITORING NON-INTUBATED PATIENTS
 Although the standard of care in ETC02 is well established for intubated patients, there has been little emphasis on the use of capnography in nonintubated patients till now. In addition to confirming
Although the standard of care in ETC02 is well established for intubated patients, there has been little emphasis on the use of capnography in nonintubated patients till now. In addition to confirming
Oxygenation. Chapter 45. Re'eda Almashagba 1
 Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
COPD is a syndrome of chronic limitation in expiratory airflow encompassing emphysema or chronic bronchitis.
 1 Definition of COPD: COPD is a syndrome of chronic limitation in expiratory airflow encompassing emphysema or chronic bronchitis. Airflow obstruction may be accompanied by airway hyper-responsiveness
1 Definition of COPD: COPD is a syndrome of chronic limitation in expiratory airflow encompassing emphysema or chronic bronchitis. Airflow obstruction may be accompanied by airway hyper-responsiveness
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Appendix E Choose the sign or symptom that best indicates severe respiratory distress.
 Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
Safety Data Sheet. Product Name: Product Number: Product Identity. 2. Hazardous Ingredients. Formaldehyde: CAS: Methanol: CAS:
 Olathe, KS Tel: 913-390-6184 Safety Data Sheet Solution (Formalin, Formol, Methanol, Formaldehyde containing solutions, Formalith) Emergency phone: 800 424 9300 (Chemtrec) NFPA Rating: Health 3, Flammability
Olathe, KS Tel: 913-390-6184 Safety Data Sheet Solution (Formalin, Formol, Methanol, Formaldehyde containing solutions, Formalith) Emergency phone: 800 424 9300 (Chemtrec) NFPA Rating: Health 3, Flammability
Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism.
 Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism. Poisoning= overdose toxicity intoxication= toxicity due to foreign substance
Poison (Toxicant): any substance or agent capable of producing a deleterious response in a biological system or living organism. Poisoning= overdose toxicity intoxication= toxicity due to foreign substance
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 ROLF C. HAGEN INC., 20500 TRANS HWY, A8253 / A8254 /A8255 Page 1 of 4 Section I. Product identification and uses Product name Marine CAS # Mixture Use To adjust alkalinity of aquarium water Supplier Rolf
ROLF C. HAGEN INC., 20500 TRANS HWY, A8253 / A8254 /A8255 Page 1 of 4 Section I. Product identification and uses Product name Marine CAS # Mixture Use To adjust alkalinity of aquarium water Supplier Rolf
Nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) C 1. Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments
 BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients whose clothing or skin is contaminated with
BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments Patients whose clothing or skin is contaminated with
Knowledge Objectives (2 of 2) Skills Objectives. Death Scene Considerations. Introduction 12/20/2013
 Fire and Explosion Deaths and Injuries Knowledge Objectives (1 of 2) Identify the effects of fire and explosion on the human body. Discuss the various issues involved in fire or explosion death investigation.
Fire and Explosion Deaths and Injuries Knowledge Objectives (1 of 2) Identify the effects of fire and explosion on the human body. Discuss the various issues involved in fire or explosion death investigation.
Management of Inhalation Injury in an Adult Burn Patient
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Advanced Nursing Practice Volume 13 Number 1 Management of Inhalation Injury in an Adult Burn Patient D Tubera Citation D Tubera. Management of Inhalation Injury in an
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Advanced Nursing Practice Volume 13 Number 1 Management of Inhalation Injury in an Adult Burn Patient D Tubera Citation D Tubera. Management of Inhalation Injury in an
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator
 Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator Lecture Overview Burn statistics and etiologies Pre-hospital evaluation Anatomy of a burn
Pediatric Burn Management Justin D. Klein, MD Associate Burn Director Lisa C. Vitale, RN Burn Program Coordinator Lecture Overview Burn statistics and etiologies Pre-hospital evaluation Anatomy of a burn
Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. By: Lillian Han
 Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By: Lillian Han Background: Respiratory anesthetic emergencies are the most common complications during the administration of anesthesia
Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By: Lillian Han Background: Respiratory anesthetic emergencies are the most common complications during the administration of anesthesia
Oxygen:..Nothing is without poison.. the poison is in the dose..
 Interdepartmental Division of Critical Care Medicine Mount Sinai Hospital/University Health Network University of Toronto Toronto, Canada Oxygen:..Nothing is without poison.. the poison is in the dose..
Interdepartmental Division of Critical Care Medicine Mount Sinai Hospital/University Health Network University of Toronto Toronto, Canada Oxygen:..Nothing is without poison.. the poison is in the dose..
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv
 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) Rv.8.18.18 ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME (ARDS) SUDDEN PROGRESSIVE FORM OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE ALVEOLAR CAPILLARY MEMBRANE BECOMES DAMAGED AND MORE
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy
 An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
Lecture 2 Chemical and Biological Agents
 Lecture 2 Chemical and Biological Agents In the Chemical ad Biological section, Routes of exposure we will be covering: Forms of Chemical agents Examples of chemical agents Forms of Biological agents Classifications
Lecture 2 Chemical and Biological Agents In the Chemical ad Biological section, Routes of exposure we will be covering: Forms of Chemical agents Examples of chemical agents Forms of Biological agents Classifications
Cystic Fibrosis Complications ANDRES ZIRLINGER, MD STANFORD UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MARCH 3, 2012
 Cystic Fibrosis Complications ANDRES ZIRLINGER, MD STANFORD UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MARCH 3, 2012 INTRODUCTION PNEUMOTHORAX HEMOPTYSIS RESPIRATORY FAILURE Cystic Fibrosis Autosomal Recessive Genetically
Cystic Fibrosis Complications ANDRES ZIRLINGER, MD STANFORD UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER MARCH 3, 2012 INTRODUCTION PNEUMOTHORAX HEMOPTYSIS RESPIRATORY FAILURE Cystic Fibrosis Autosomal Recessive Genetically
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE
 1 PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE DISEASE: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) DEFINITION: COPD can be defined as a disease in which there is a significant damage to the lungs thus reducing
1 PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL PROCESS TEMPLATE DISEASE: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) DEFINITION: COPD can be defined as a disease in which there is a significant damage to the lungs thus reducing
Toxins. Learning Objectives. Chemistry of Carbon Monoxide. Carbon Monoxide
 Toxins Carbon Monoxide Version Date: 2/6/2013 Learning Objectives Upon the completion of this program participants will be able to: 1. Understand the pathophysiology of carbon monoxide (CO)poisoning 2.
Toxins Carbon Monoxide Version Date: 2/6/2013 Learning Objectives Upon the completion of this program participants will be able to: 1. Understand the pathophysiology of carbon monoxide (CO)poisoning 2.
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
a. Will not suppress respiratory drive in acute asthma
 Status Asthmaticus & COPD with Respiratory Failure - Key Points M.J. Betzner MD FRCPc - NYEMU Toronto 2018 Overview This talk is about the sickest of the sick patients presenting with severe or near death
Status Asthmaticus & COPD with Respiratory Failure - Key Points M.J. Betzner MD FRCPc - NYEMU Toronto 2018 Overview This talk is about the sickest of the sick patients presenting with severe or near death
CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2
 CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2 M1 Objectives To understand how resuscitation techniques should be modified in the special circumstances of: Hypothermia Immersion and submersion Poisoning Pregnancy
CARDIAC ARREST IN SPECIAL CIRCUMSTANCES 2 M1 Objectives To understand how resuscitation techniques should be modified in the special circumstances of: Hypothermia Immersion and submersion Poisoning Pregnancy
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Bronchiolitis: diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis in children. 1.1 Short title Bronchiolitis in children 2 The remit The
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
3. Identify the importance in the prehospital setting for the administration of nebulized bronchodilator.
 TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
TERMINAL OBJECTIVE At the end of this lesson, the EMT-Basic will be able to utilize the assessment findings to formulate a field impression of bronchospasm and understand the administration of nebulized
Paramedic Rounds. Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
INHALANT ABUSE AND RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Chalita Waenlor, MD
 INHALANT ABUSE AND RESPIRATORY FAILURE Chalita Waenlor, MD Inhalants Substances with significant acute and chronic toxicity. Wide variety of chemical structures with the majority being hydrocarbons (aliphatic,
INHALANT ABUSE AND RESPIRATORY FAILURE Chalita Waenlor, MD Inhalants Substances with significant acute and chronic toxicity. Wide variety of chemical structures with the majority being hydrocarbons (aliphatic,
Capnography for Pediatric Procedural Sedation Learning Module Last revised: February 18, 2014
 Capnography for Pediatric Procedural Sedation Learning Module Last revised: February 18, 2014 Capnography 40 Non-invasive device that continually monitors EtCO 2 While pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation,
Capnography for Pediatric Procedural Sedation Learning Module Last revised: February 18, 2014 Capnography 40 Non-invasive device that continually monitors EtCO 2 While pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation,
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
Weapons of Mass Destruction. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Weapons of Mass Destruction Lesson Goal To become familiarize with the concept of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), how these weapons might be used, and the type of treatment that would be appropriate
Weapons of Mass Destruction Lesson Goal To become familiarize with the concept of weapons of mass destruction (WMD), how these weapons might be used, and the type of treatment that would be appropriate
Piratox sheet #5: "Suffocating agents and phosphine
 Piratox sheet #5: "Suffocating agents and phosphine Indicative list of concerned agents: Toxic compounds with suffocating action - Phosgene (CAS number: 75-44-5) - Chlorine (CAS number: 7782-50-5) - Methyl
Piratox sheet #5: "Suffocating agents and phosphine Indicative list of concerned agents: Toxic compounds with suffocating action - Phosgene (CAS number: 75-44-5) - Chlorine (CAS number: 7782-50-5) - Methyl
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET Issue Date: December 14, 2011 Version 5.3
 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET Issue Date: December 14, 2011 Version 5.3 Section 1 Product and Company Information Product Name Vehicle Hygienist Product Use Deodorizing delivery system (pouch) for the generation
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET Issue Date: December 14, 2011 Version 5.3 Section 1 Product and Company Information Product Name Vehicle Hygienist Product Use Deodorizing delivery system (pouch) for the generation
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
BURNS MODULE. In the paediatric population consider non-accidental injury as a mechanism for burn injuries.
 BURNS MODULE INTRODUCTION Burns are a common cause of trauma. Most burn injuries are a result of flame burns, with scalds also occurring commonly. Electrical and chemical burns are less common. 1 Concurrent
BURNS MODULE INTRODUCTION Burns are a common cause of trauma. Most burn injuries are a result of flame burns, with scalds also occurring commonly. Electrical and chemical burns are less common. 1 Concurrent
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Respiratory Disorders. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-17. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 5-1. Identify the characteristics,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Respiratory Disorders. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-17. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 5-1. Identify the characteristics,
ALCO Regulations. Protocol pg. 47
 For the EMT-Basic Objectives Understand ALCO regulations relative to monitoring pulse oximetry by the EMT-B Review the signs and symptoms of respiratory compromise. Understand the importance of adequate
For the EMT-Basic Objectives Understand ALCO regulations relative to monitoring pulse oximetry by the EMT-B Review the signs and symptoms of respiratory compromise. Understand the importance of adequate
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis. Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine
 Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine Asthma Defined National Asthma Education and Prevention
Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine Asthma Defined National Asthma Education and Prevention
2/4/2019. GOLD Objectives. GOLD 2019 Report: Chapters
 GOLD Objectives To provide a non biased review of the current evidence for the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD. To highlight short term and long term treatment objectives organized
GOLD Objectives To provide a non biased review of the current evidence for the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD. To highlight short term and long term treatment objectives organized
People with asthma who smoke. The combination of asthma, a chronic airway disease, and smoking increases the risk of COPD even more.
 COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, cough, sputum (phlegm) production
10/17/16. Acute Respiratory Failure in the Acute Care Setting. Margaret Rosales, APRN-CNP, FNP
 Acute Respiratory Failure in the Acute Care Setting Margaret Rosales, APRN-CNP, FNP Margaret_r1965@yahoo.com 918-448-5887 1 Definition: Respiratory failure is a syndrome in which the respiratory system
Acute Respiratory Failure in the Acute Care Setting Margaret Rosales, APRN-CNP, FNP Margaret_r1965@yahoo.com 918-448-5887 1 Definition: Respiratory failure is a syndrome in which the respiratory system
RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN TGESBIOLOGY ISC 11
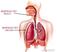 RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN Difference between dry and wet cough Irritation of respiratory tract Due to dust or smoke Accumulation of mucus Due to infections The respiratory tract Tracheal epithelium
RESPIRATORY TRACT RESPIRATORY ORGAN Difference between dry and wet cough Irritation of respiratory tract Due to dust or smoke Accumulation of mucus Due to infections The respiratory tract Tracheal epithelium
... Nitrogen oxides are reactive substances commonly understood to encompass nitric
 Nitrogen oxides Updated: December 2015... Nitrogen oxides are reactive substances commonly understood to encompass nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), referred to
Nitrogen oxides Updated: December 2015... Nitrogen oxides are reactive substances commonly understood to encompass nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and dinitrogen tetroxide (N2O4), referred to
Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD
 MiCMRC Educational Webinar Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD August 22, 2018 MiCMRC Educational Webinar Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD Expert Presenter: Catherine A. Meldrum PhD RN MS
MiCMRC Educational Webinar Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD August 22, 2018 MiCMRC Educational Webinar Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD Expert Presenter: Catherine A. Meldrum PhD RN MS
NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP)
 Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
TOXIC INHALATIONAL INJURY
 Toxic Inhalational Injury Chapter 9 TOXIC INHALATIONAL INJURY JOHN S. URBANETTI, M.D., FRCP(C), FACP, FCCP * INTRODUCTION TOXIC INHALATIONAL INJURY Physical Aspects Clinical Effects Physiology Evaluation
Toxic Inhalational Injury Chapter 9 TOXIC INHALATIONAL INJURY JOHN S. URBANETTI, M.D., FRCP(C), FACP, FCCP * INTRODUCTION TOXIC INHALATIONAL INJURY Physical Aspects Clinical Effects Physiology Evaluation
Chapter 15 - Respiratory Emergencies
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Medicine Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation based on assessment findings for an acutely
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Medicine Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation based on assessment findings for an acutely
Acid anhydrides (e.g. maleic/phthalic anhydride, C 4 H 2 O 3 /C 8 H 4 O 3 ) C 1
 BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Acid anhydrides (e.g. maleic/phthalic anhydride, C 4 H 2 O 3 /C 8 H 4 O 3 ) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments
BASF Chemical Emergency Medical Guidelines Acid anhydrides (e.g. maleic/phthalic anhydride, C 4 H 2 O 3 /C 8 H 4 O 3 ) C 1 Information and recommendations for doctors at hospitals/emergency departments
Capnography 101. James A Temple BA, NRP, CCP
 Capnography 101 James A Temple BA, NRP, CCP Expected Outcomes 1. Gain a working knowledge of the physiology and science behind End-Tidal CO2. 2.Relate End-Tidal CO2 to ventilation, perfusion, and metabolism.
Capnography 101 James A Temple BA, NRP, CCP Expected Outcomes 1. Gain a working knowledge of the physiology and science behind End-Tidal CO2. 2.Relate End-Tidal CO2 to ventilation, perfusion, and metabolism.
The immediate management of burns patients should be similar to management of trauma.
 CATS Clinical Guideline Burns The National Burn Care Review recommends that children with burns should be treated in a Burn Centre. Chelsea and Westminster may take non-ventilated children, Broomfield
CATS Clinical Guideline Burns The National Burn Care Review recommends that children with burns should be treated in a Burn Centre. Chelsea and Westminster may take non-ventilated children, Broomfield
Lecture Notes. Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure
 Lecture Notes Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure Objectives Define respiratory failure, ventilatory failure, and oxygenation failure List the causes of respiratory failure Describe the effects
Lecture Notes Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure Objectives Define respiratory failure, ventilatory failure, and oxygenation failure List the causes of respiratory failure Describe the effects
Supplementary Online Content 2
 Supplementary Online Content 2 van Meenen DMP, van der Hoeven SM, Binnekade JM, et al. Effect of on demand vs routine nebulization of acetylcysteine with salbutamol on ventilator-free days in intensive
Supplementary Online Content 2 van Meenen DMP, van der Hoeven SM, Binnekade JM, et al. Effect of on demand vs routine nebulization of acetylcysteine with salbutamol on ventilator-free days in intensive
