Characterisation of patients with frequent exacerbation of asthma
|
|
|
- Pauline Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, Characterisation of patients with frequent exacerbation of asthma Takeharu Koga, Yuichi Oshita, Tomoko Kamimura, Hideyuki Koga, Hisamichi Aizawa First Department of Internal Medicine, Kurume University School of Medicine, 67 Asahimachi, Kurume , Japan Received 28 December 2004; accepted 21 May 2005 KEYWORDS Exacerbation; Irreversible airflow limitation; Airway remodelling; Chronic sinusitis; Aspirin-intolerant asthma Summary Background: Exacerbation is one of the most significant problems in patients with asthma. Although subpopulation of patients is more susceptible to exacerbations than others, which clinical features characterise susceptibility to exacerbation are not well understood. Methods: Consecutive non-smoking adult patients with asthma who had multiple exacerbations (ME) despite regular maintenance treatment were compared with those who had at most single exacerbation as control during the previous 1 year. Exacerbation of asthma is defined initiations or escalations of systemic corticosteroid as part of the management for aggravated asthma condition. Results: Patients with ME (n ¼ 32, male: 6, mean age: 46.7 years) were characterised by intensive current maintenance treatment (dose of inhaled corticosteroid; vs mg, P ¼ 0:0005, proportion of oral corticosteroid users; 28.1% vs 2.7%, P ¼ 0:008), severe episodes of exacerbation (asthma-related hospitalisations; 71.9% vs 23.4%, P ¼ 0:0002, arrival on ambulance; 37.5% vs 8.1%, P ¼ 0:008), concomitant chronic sinusitis (34.4% vs 10.8%, P ¼ 0:038) and intolerance to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (34.4% vs 5.4%, P ¼ 0:006) in comparison with controls (n ¼ 37, male:11, mean age:44.4). Pulmonary function in patients with ME was characterised by persistent airflow limitation and reduced reversibility. Conclusion: Patients with ME are at increased risk for severe exacerbation despite more intensive maintenance anti-inflammatory treatment. Persistent irreversible airflow limitation and complications of chronic sinusitis and/or NSAIDs intolerance are characteristics to this subpopulation. & 2005 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: address: kogat@med.kurume-u.ac.jp (T. Koga) /$ - see front matter & 2005 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /j.rmed
2 274 Introduction With the advent of potent anti-inflammatory medications such as inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) and practical guidelines for their appropriate applications, majority of patients with asthma benefit by attaining favourable control over the disease. 1 However, it is becoming increasingly clear that subpopulation of asthmatics are still having compromised quality of life due to frequent exacerbations 2,3 regardless of currently available treatment. 4 They are at greater risk to develop severe exacerbations that convey time off work, admission to hospitals, and more importantly, life-threatening episodes. 5 Frequent medical resource utilisation produces disproportionately high health care expenditure by this population relative to remaining patients with controlled disease, 3 who account for majority of whole patients of asthma. Furthermore, there remains much room for improvement in the treatment and prevention of acute attacks 2 in terms of efficacy. Despite these critical situations, little is known about underlying pathophysiology of these patients who remain susceptible to exacerbations. Since currently available treatment options are limited and not promising, 6 these patients should be identified and managed with special attention to minimise socioeconomic burden and severe, especially lethal attacks. In this context, it is urgent to characterise patients who have frequent exacerbations not only for identifying affected individuals to deliver optimised management but also for gaining insight into the underlying pathophysiology of the condition. Thus, we conducted the present investigation to characterise patients with asthma who had multiple exacerbations (ME) in a year despite maintenance treatment by comparing patients with stable asthma. Methods Subjects Non-smoking adult patients with asthma were consecutively recruited during April 2002 to March 2003 at Kurume University Hospital with informed consent to the investigation. All subjects were regular attendants to outpatient clinic of the hospital for at least previous two consecutive years where care was given by asthma specialist based on a practice guideline (global initiative for asthma (GINA)). 5 The diagnosis of asthma was established by reversible airflow obstruction that occurs naturally or after treatment, and/or airway hyperresponsiveness. 5 Patients who have coexisting conditions that may compromise lung functions, such as dust exposure, bronchiectasis or parenchymal lung diseases were not included in the study. Patients who were considered by the physicians to comply poorly with treatment were excluded. All subjects were recruited when their asthma condition was stable without change in medications for at least 2 months and free of sings of respiratory infections. Asthma exacerbations were defined as initiations of or escalations of systemic corticosteroid required for aggravated asthma condition judged by the physicians. 7 Patients who had exacerbations more than twice during the previous 1 year of the recruitment were compared with those with at most one exacerbation. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the ethical committee of Kurume University Hospital. Questionnaire T. Koga et al. A structured questionnaire was used to obtain information on asthma-related histories (age of onset, family history of asthma, hospital admission and emergency visit on ambulance ever due to asthma), current medications, and concomitant allergic conditions (allergic rhinitis, chronic sinusitis/nasal polyps, and histories of intolerance to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)). The age of asthma onset was based on patient s own report, or if not available, was inferred from the clinical history suggestive of asthma. Childhood asthma was defined by asthma started before 10 years of age. Pulmonary function test and laboratory tests Pulmonary function test (PFT) was performed as directed previously. 8 All measurements were made in the sitting position between 8:30 and 10:30 in the morning. Baseline measurement was evaluated after discontinuation of all forms of b2 adrenergic agonist for 12 h. Forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV 1 ) and forced vital capacity (FVC) were obtained using a dry spirometer (Chestak-33, Chest MI Inc. Tokyo, Japan) before and 30 min after administration of 400 mg of salbutamol by pressurised metered-dose inhaler. The largest values from the first three technically satisfactory forced expirations were selected in each occasion. BDR was expressed as the absolute change volume in FEV 1 (dfev 1 ) and its normalised value to predicted FEV 1 (%dfev 1 ). 9,10 Complete blood count and serum IgE were determined at the same time as the performance of PFT.
3 Frequent exacerbation of asthma 275 Statistical analysis Comparisons were performed using w 2 test or Mann Whitney U-test where appropriate. A P value less than 0.05 was considered significant. The program used for the analyses was JMP software (SAS Institute Inc. Cary, NC, USA). Results Table 1 summarises characteristics of the subjects. There were no significant differences in age ( vs years, P ¼ 0:55), gender (proportion of male: 27.3 vs 34.4%, P ¼ 0:44). There was a significant difference in the maintenance treatment of the subjects; the dose of ICS was significantly higher ( vs mg, P ¼ 0:0005) and the proportion of regular user of oral corticosteroid user was significantly higher (7 (31.8%) vs 1 (0.4%), P ¼ 0:016) in patients with ME than in control patients. Duration of asthma was significantly longer in patients with ME than in control patients ( vs years, P ¼ 0:008). There were no significant differences in family history of asthma (53.1 vs 32.4%, P ¼ 0:32) and childhood asthma (25.0 vs 18.9%, P ¼ 0:75). Asthma-related hospital admission was significantly more frequent (71.9 vs 24.3%, P ¼ 0:0002) in patients with ME than in control patients. Likewise, 12 out of 32 patients (37.5%) have ever utilised ambulance for emergency visit in patients with ME, whereas three out of 37 (8.1%) have in control patients (P ¼ 0:008). Among concomitant allergic conditions, the prevalence allergic rhinitis was not different (50.0 vs 64.9%, P ¼ 0:31), whereas that of chronic sinusitis was significantly higher in patients with ME (34.4%) compared with control patients (10.8%, P ¼ 0:038). The prevalence of allergic reactions to NSAIDs was significantly higher in patients with ME (34.4%) than in control patients (5.4%, P ¼ 0:006). Table 2 presents the results of PFT. Although there was no significant difference in %FEV 1 ( vs %, P ¼ 0:17), there was a significant difference in FEV 1 /FVC ( vs %, P ¼ 0:004) between patients with ME and control patients. %FEV 1 after administration of bronchodilator tends to be lower in patients with ME than in control patients ( vs %, P ¼ 0:051). As was baseline value, there was a significant difference in FEV 1 /FVC, being lower in patients with ME than in control patients ( vs %, P ¼ 0:002). Reversibility of FEV 1 in response to the administration of bronchodilator was significantly reduced in patients with ME than in control patients. ( vs ml, P ¼ 0:007) Normalisation of the reversibility to predicted value of FEV 1 presented the same tendency ( vs %, P ¼ 0:018). Comparison of peripheral blood counts and serum IgE were presented in Table 3. Patients with ME had significantly increased numbers of WBC ( vs /ml, P ¼ 0:024) and neutrophils ( vs /ml, P ¼ 0:016) compared with control patients. Number of eosinophils did not differ significantly ( vs /ml, P ¼ 0:13). There was no significant difference in serum IgE between patients with ME ( U/ml) and control patients ( U/ml, P ¼ 0:13). Table 1 Comparison of patient characteristics. ME Control P n Age Male (%) 6 (27.3) 11 (34.4) 0.44 Duration of asthma (years) Family history of asthma (%) 17 (53.1) 12 (32.4) 0.13 Childhood asthma (%) 8 (25.0) 7 (18.9) 0.75 Admissions (%) 23 (71.9) 9 (24.3) Visit on ambulance (%) 12(37.5) 3 (8.1) ICS (mg/day) Oral steroid (%) 9 (28.1) 1 (2.7) Nasal allergy (%) 16 (50.0) 24 (64.9) 0.31 Chronic sinusitis (%) 11 (34.4) 4(10.8) NSAIDs intolerance (%) 11 (34.4) 2 (5.4) 0.006
4 276 T. Koga et al. Table 2 Comparison of pulmonary functions. ME Control P %FEV 1 (%) FEV 1 /FVC (%) %FEV 1 (post) (%) FEV 1 /FVC (post) (%) dfev 1 (ml) %dfev 1 (%) Table 3 Comparison of peripheral blood count and serum IgE. ME Control P WBC (/ml) Neutrophil (%) Neutrophil (/ml) Eosinophil (%) Eosinophil (/ml) IgE (U/ml) Discussion The present study clarified several characters of patients with ME in comparison with control patients with stable asthma. Current maintenance medications demonstrates that patients with ME require significantly more intense treatment to maintain control compared with patients with stable asthma, indicating that they have more severe disease. 11 It is possible that current medications are not enough in efficacy to suppress airways inflammation in this population, rendering them more susceptible to exacerbation. Sont et al. 12 have demonstrated that management of asthma utilising airway hyperresponsiveness as a supplemental objective parameter to apply medications achieved better control over conventional management based on a practical guideline, suggesting that maintenance treatment was insufficient in some of the patients with ME in the present study. Furthermore, airways inflammation does not seem to respond corticosteroid in a subpopulation of patients with asthma. 13 Therefore, the efficacy of anti-inflammatory treatment is ideally required to be monitored by objective means such as airway hyperresponsiveness and/or induced sputum 14 in addition to subjective symptoms and spirometer or peak flow meter, common measures to evaluate asthma control in practice, 5 in patients who experience frequent or severe exacerbation to ensure that airways inflammation is actually alleviated. Medical histories indicated that patients with ME had more severe exacerbations, which was reflected in the higher rates of asthma-related hospitalisation and emergency visit on ambulance, suggesting that patients with ME have predilection not only to more frequent but also to more intense exacerbations. Thus, these patients should be managed with any possible measures and interventions to prevent exacerbations, which may eventually reduce the risk of fatal events. 15 The present study also demonstrated that patients with ME complicate chronic sinusitis and NSAIDs intolerance significantly more frequently than do control patients with asthma. Although the diagnosis of these conditions are not confirmed by standardised methods such as sinus CT for sinusitis and oral challenge test for NSAIDs intolerance in this investigation, they are known to have a close association with severe form of asthma. 16 These results suggest that some of these patients have aspirin-induced or aspirin-intolerant asthma, which is relatively frequent in Japan. 6 PFT results of the study appear to be relevant to the underlying pathophysiology of the increased susceptibility. The results showed that patients with ME have significantly reduced FEV 1 /FVC and reversibility of airflow obstruction in response to short-acting b2 agonist than do control patients. Since FEV 1 /FVC is a more sensitive parameter to
5 Frequent exacerbation of asthma 277 detect airflow limitation 17 than %FEV 1, these results characterise pulmonary function impairment in patients with ME as a persistent airflow limitation. Although not assessed in the present study, airway responsiveness is shown to correlate negatively with reversibility in airflow limitation, 18 suggesting that patients with ME have increased airway responsiveness. Taken together, persistently narrowed airways that have hypersensitiveness to various bronchoconstricting stimuli can be one of the critical pathologies of patients with ME. A morphometric analysis of airways utilising high-resolution computed tomography revealed that persistent irreversible airflow limitation is associated with airway wall thickening in patients with asthma. 19 It is becoming increasingly clear that several pathological elements contribute to the development of airway wall thickening, including airway wall infiltration of inflammatory cells, thickening of basement membrane, increased airway smooth muscle mass, and edema, which are collectively apprehended as airway remodelling (reviewed in Davies et al. 20 ). Airway remodelling has been documented to have an intimate association with airway responsiveness. 21 Considering the fact that exaggerated airway hyperresponsiveness is a predictor of asthma exacerbation, 22 it can be speculated that susceptibility to exacerbation may be mediated, at least in part, by developed airway remodelling in subgroup of patients with asthma. In this context, it is noteworthy that similarity in pathology between remodelled airways in asthma and upper airways in chronic sinusitis, 23 which has been linked with ME in this investigation, may suggest an intimate association between the two conditions. Peripheral blood count revealed that patients with ME have significantly increased numbers of WBC and neutrophils than do control patients. In contrast there was no significant difference in the number of peripheral blood eosinophils. These results are in concert with the character of severe asthma identified by a multicenter study for severe asthma. 24 Underlying mechanism of the increased number of neutrophils are not known; however, it can be speculated that higher dose of corticosteroid contributes by way of inhibiting apoptosis of neutrophils. 25 The present study is notable in that frequent exacerbations have intimate associations with several clinical characters, which may in turn enable clinicians to identify patients at risk and deliver optimised management, although a limited number of subjects were analysed. Clarification of underlying pathophysiology of these characters may give clues to better understanding of asthma presenting frequent exacerbations. References 1. Schatz M, Cook EF, Nakahiro R, Petitti D. Inhaled corticosteroids and allergy specialty care reduce emergency hospital use for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 111(3): American Thoracic Society. Proceedings of the ATS workshop on refractory asthma: current understanding, recommendations, and unanswered questions. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000; 162(6): Van Ganse E, Laforest L, Pietri G, et al. Persistent asthma: disease control, resource utilisation and direct costs. Eur Respir J 2002;20(2): Walsh LJ, Wong CA, Cooper S, Guhan AR, Pringle M, Tattersfield AE. Morbidity from asthma in relation to regular treatment: a community based study. Thorax 1999; 54(4): Asthma GIf (National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute). Global strategy for asthma management and prevention Barnes PJ, Woolcock AJ. Difficult asthma. Eur Respir J 1998;12(5): Oshita Y, Koga T, Kamimura T, Matsuo K, Rikimaru T, Aizawa H. Increased circulating 92 kda matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) activity in exacerbations of asthma. Thorax 2003;58(9): Quanjer PH, Tammeling GJ, Cotes JE, Pedersen OF, Peslin R, Yernault JC. Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Report Working Party Standardisation of Lung Function Tests, European Community for Steel and Coal. Official Statement of the European Respiratory Society. Eur Respir J Suppl 1993;16: Chhabra SK, Vijayan VK, Gupta R, De S. Expression of bronchodilator response: comparison of four indices. Respir Med 2002;96(8): Quadrelli SA, Roncoroni AJ, Montiel GC. Evaluation of bronchodilator response in patients with airway obstruction. Respir Med 1999;93(9): Cockcroft DW, Swystun VA. Asthma control versus asthma severity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1996;98: Sont JK, Willems LNA, Bel EH. Clinical control and histopathologic outcome of asthma when using airway hyperresponsiveness as an additional guide to longterm treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 159: Louis R, Lau LC, Bron AO, Roldaan AC, Radermecker M, Djukanovic R. The relationship between airways inflammation and asthma severity. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161(1): ten Brinke A, Zwinderman A, Sterk P, Rabe K, Bel E. Factors associated with persistent airflow Limitation in severe asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 164(5): Molfino NA, Nannini LJ, Rebuck AS, Slutsky AS. The fatalityprone asthmatic patient. Follow-up study after near-fatal attacks. Chest 1992;101(3): ten Brinke A, Grootendorst DC, Schmidt JT, et al. Chronic sinusitis in severe asthma is related to sputum eosinophilia. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002;109(4): Enright PL, Lebowitz MD, Cockroft DW. Physiologic measures: pulmonary function tests. Asthma outcome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;149(2 Pt 2):S9 S18 [discussion S19 20]. 18. Rasmussen F, Taylor DR, Flannery EM, et al. Risk factors for airway remodeling in asthma manifested by a low postbronchodilator FEV1/vital capacity ratio: a longitudinal
6 278 T. Koga et al. population study from childhood to adulthood. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165(11): Kasahara K, Shiba K, Ozawa T, Okuda K, Adachi M. Correlation between the bronchial subepithelial layer and whole airway wall thickness in patients with asthma. Thorax 2002;57(3): Davies DE, Wicks J, Powell RM, Puddicombe S, Holgate ST. Airway remodeling in asthma: new insights. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003;111: Chetta A, Foresi A, Del Donno M, Bertorelli G, Pesci A, Olivieri D. Airways remodeling is a distinctive feature of asthma and is related to severity of disease. Chest 1997;111(4): Leuppi JD, Salome CM, Jenkins CR, et al. Predictive markers of asthma exacerbations during stepwise dose reduction of inhaled corticosteroid. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;163(2): Ponikau JU, Sherris DA, Kephart GM, et al. Features of airway remodeling and eosinophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis: is the histopathology similar to asthma? J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003;112(5): European Network for Understanding Mechanisms of Severe Asthma. The ENFUMOSA cross-sectional European multicentre study of the clinical phenotype of chronic severe asthma. Eur Respir J 2003; 22(3), Meagher LC, Cousin JM, Seckl JR, Haslett C. Opposing effects of glucocorticoids on the rate of apoptosis in neutrophilic and eosinophilic granulocytes. J Immunol 1996;156(11):
Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma?
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
TORCH: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate and Survival in COPD
 TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires as measures of the severity and impact of asthma
 Eur Respir J 1999; 1: 591±596 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 1999 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires
Eur Respir J 1999; 1: 591±596 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 1999 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Severe exacerbations predict excess lung function decline in asthma
 ERJ Express. Published on May 30, 2007 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00165106 Severe exacerbations predict excess lung function decline in asthma TR Bai 1, JM Vonk 2, DS Postma 3, HM Boezen 2 1 James Hogg icapture
ERJ Express. Published on May 30, 2007 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00165106 Severe exacerbations predict excess lung function decline in asthma TR Bai 1, JM Vonk 2, DS Postma 3, HM Boezen 2 1 James Hogg icapture
Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment. Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc
 Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc No conflicts to declare Objectives To understand the varied clinical forms of asthma To understand the pathobiologic
Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc No conflicts to declare Objectives To understand the varied clinical forms of asthma To understand the pathobiologic
Research Review. Salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (Seretide ) in COPD. Extended listing for salmeterol/fluticasone propionate in COPD
 Research Review Salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (Seretide ) in COPD Extended listing for salmeterol/fluticasone propionate in COPD In New Zealand, salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (SFC) (Seretide )
Research Review Salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (Seretide ) in COPD Extended listing for salmeterol/fluticasone propionate in COPD In New Zealand, salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (SFC) (Seretide )
Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis
 Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis Kim Hyun Hee, MD, PhD. Dept. of Pediatrics The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine Achieving
Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis Kim Hyun Hee, MD, PhD. Dept. of Pediatrics The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine Achieving
Asthma and COPD in older people lumping or splitting? Christine Jenkins Concord Hospital Woolcock Institute of Medical Research
 Asthma and COPD in older people lumping or splitting? Christine Jenkins Concord Hospital Woolcock Institute of Medical Research Concord Hospital Woolcock Institute of Medical Research Joe has asthma What
Asthma and COPD in older people lumping or splitting? Christine Jenkins Concord Hospital Woolcock Institute of Medical Research Concord Hospital Woolcock Institute of Medical Research Joe has asthma What
KEY WORDS airflow limitation, airway hyperresponsiveness, airway inflammation, airway lability, peak expiratory flow rate
 Allergology International. 2013;62:343-349 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.13-oa-0543 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stratifying a Risk for an Increased Variation of Airway Caliber among the Clinically Stable Asthma Atsushi
Allergology International. 2013;62:343-349 DOI: 10.2332 allergolint.13-oa-0543 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stratifying a Risk for an Increased Variation of Airway Caliber among the Clinically Stable Asthma Atsushi
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO)
 Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Outline FEF Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications?
 Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic adults A long-term correlation study
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2005; 9: 125-131 Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic adults A long-term correlation study R. CARBONE, F. LUPPI *, A. MONSELISE **, G. BOTTINO
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2005; 9: 125-131 Bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic adults A long-term correlation study R. CARBONE, F. LUPPI *, A. MONSELISE **, G. BOTTINO
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 2 Issue 3 July - Sep Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2013 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 23 th May 2013 Revised: 24 th Jun 2013 Accepted:
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 2 Issue 3 July - Sep Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2013 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 23 th May 2013 Revised: 24 th Jun 2013 Accepted:
An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease
 An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease Carmen Vidal Athens, September 11, 2014 Pucci S & Incorvaia C, 2008; 153:1-2 1. The major player in driving the immune
An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease Carmen Vidal Athens, September 11, 2014 Pucci S & Incorvaia C, 2008; 153:1-2 1. The major player in driving the immune
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Definition and Pathology CHAPTER 1. John Rees
 CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP?
 THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma
 Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE
 LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE Azienda Ospedaliera Pisana Università degli Studi di Pisa Pierluigi Paggiaro GINA International Executive Committee, Chairman GINA ITaly Cardio-Thoracic and Vascular Department,
LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE Azienda Ospedaliera Pisana Università degli Studi di Pisa Pierluigi Paggiaro GINA International Executive Committee, Chairman GINA ITaly Cardio-Thoracic and Vascular Department,
Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers?
 Disclosures: Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers? Stanley Fineman, MD Past-President, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Adjunct Associate
Disclosures: Optimal Assessment of Asthma Control in Clinical Practice: Is there a role for biomarkers? Stanley Fineman, MD Past-President, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Adjunct Associate
Peak Expiratory Flow Variability Adjusted by Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second is a Good Index for Airway Responsiveness in Asthmatics
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Peak Expiratory Flow Variability Adjusted by Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second is a Good Index for Airway Responsiveness in Asthmatics Kazuto Matsunaga, Masae Kanda, Atsushi Hayata,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Peak Expiratory Flow Variability Adjusted by Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second is a Good Index for Airway Responsiveness in Asthmatics Kazuto Matsunaga, Masae Kanda, Atsushi Hayata,
Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype. Phenotypes of Severe Asthma. Cellular Phenotypes 12/7/2012
 Subbasement Membrane Thickness(µm) 12/7/212 Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype Phenotypes of Severe Asthma Most mild and to some degree moderate asthmatics respond well to currently available
Subbasement Membrane Thickness(µm) 12/7/212 Current Asthma Therapy: Little Need to Phenotype Phenotypes of Severe Asthma Most mild and to some degree moderate asthmatics respond well to currently available
CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT
 Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): Α A REVIEW
 Volume 23, Issue 3 December 2007 BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): A REVIEW Donna L. Smith, Pharm. D. Candidate More than 22 million people in the United States have asthma according to the Centers
Volume 23, Issue 3 December 2007 BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL (SYMBICORT ): A REVIEW Donna L. Smith, Pharm. D. Candidate More than 22 million people in the United States have asthma according to the Centers
Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 4 Number 2 Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 4 Number 2 Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 07 Contributor Dr David Tan Hsien Yung Definition, Diagnosis and Risk Factors for (COPD) Differential Diagnoses Goals of Management Management of COPD THERAPY AT EACH
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ
 Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Validity of Spirometry for Diagnosis of Cough Variant Asthma
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 6431-6438) Validity of Spirometry for Diagnosis of Cough Variant Asthma Iman Vafaei 1, *Nemat Bilan 2,3, Masoumeh Ghasempour 41 1 Resident of Pediatrics,
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 6431-6438) Validity of Spirometry for Diagnosis of Cough Variant Asthma Iman Vafaei 1, *Nemat Bilan 2,3, Masoumeh Ghasempour 41 1 Resident of Pediatrics,
National Asthma Educator Certification Board Detailed Content Outline
 I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack. Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus
 Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Diagnostic value of post-bronchodilator pulmonary function testing to distinguish between stable, moderate to severe COPD and asthma
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic value of post-bronchodilator pulmonary function testing to distinguish between stable, moderate to severe COPD and asthma Daphne C Richter 1 James R Joubert 1 Haylene Nell
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic value of post-bronchodilator pulmonary function testing to distinguish between stable, moderate to severe COPD and asthma Daphne C Richter 1 James R Joubert 1 Haylene Nell
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Asma, BPCO ed Esercizio Fisico Ferrara, 6 e 7 Novembre Overlap asma BPCO. Dr. Marco Contoli
 Asma, BPCO ed Esercizio Fisico Ferrara, 6 e 7 Novembre 2015 Overlap asma BPCO Dr. Marco Contoli Sezione di Medicina Interna e Cardio-Respiratoria Dipartimento di Scienze Mediche Università di Ferrara (Sept.
Asma, BPCO ed Esercizio Fisico Ferrara, 6 e 7 Novembre 2015 Overlap asma BPCO Dr. Marco Contoli Sezione di Medicina Interna e Cardio-Respiratoria Dipartimento di Scienze Mediche Università di Ferrara (Sept.
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment. John R. Holcomb, M.D.
 Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Asthma Pathophysiology and Treatment John R. Holcomb, M.D. Objectives Definition of Asthma Epidemiology and risk factors of Asthma Pathophysiology of Asthma Diagnostics test of Asthma Management of Asthma
Evolution of asthma from childhood. Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT
 Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Prof Neil Barnes. Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital
 Prof Neil Barnes Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital ASTHMA: WHEN EVERYTHING FAILS WHAT DO YOU DO? South GP CME 2013, Dunedin Saturday 17 th August 2013
Prof Neil Barnes Respiratory and General Medicine London Chest Hospital and The Royal London Hospital ASTHMA: WHEN EVERYTHING FAILS WHAT DO YOU DO? South GP CME 2013, Dunedin Saturday 17 th August 2013
R emodelling of the airway wall in patients with asthma
 242 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between the bronchial subepithelial layer and whole airway wall thickness in patients with asthma K Kasahara, K Shiba, T Ozawa, K Okuda, M Adachi... See end of article
242 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between the bronchial subepithelial layer and whole airway wall thickness in patients with asthma K Kasahara, K Shiba, T Ozawa, K Okuda, M Adachi... See end of article
Clinical Issues Research Implemented April 2010 Asthma Major Recommendations Goals of asthma: - 1) reduction of impairment freedom from symptoms,
 Asthma Major Recommendations Goals of : - 1) reduction of impairment freedom from symptoms, such as cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, and disturbed sleep minimal need (< 2 times per week) of short
Asthma Major Recommendations Goals of : - 1) reduction of impairment freedom from symptoms, such as cough, shortness of breath, wheezing, and disturbed sleep minimal need (< 2 times per week) of short
Usefulness of Bronchial Thermoplasty for Patients with a Deteriorating Lung Function
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8965-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Usefulness of Bronchial Thermoplasty for Patients with a Deteriorating Lung Function Daisuke Minami, Chihiro Ando, Takamasa Nakasuka,
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8965-17 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT Usefulness of Bronchial Thermoplasty for Patients with a Deteriorating Lung Function Daisuke Minami, Chihiro Ando, Takamasa Nakasuka,
NG80. Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80)
 Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/21235
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/21235
Is there any correlation between the ATS, BTS, ERS and GOLD COPD s severity scales and the frequency of hospital admissions?
 Respiratory Medicine (2004) 98, 178 183 Is there any correlation between the ATS, BTS, ERS and GOLD COPD s severity scales and the frequency of hospital admissions? Maria Tsoumakidou, Nikolaos Tzanakis,
Respiratory Medicine (2004) 98, 178 183 Is there any correlation between the ATS, BTS, ERS and GOLD COPD s severity scales and the frequency of hospital admissions? Maria Tsoumakidou, Nikolaos Tzanakis,
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Defining COPD. Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist
 Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
#1 cause of school absenteeism in children 13 million missed days annually
 Asthma Update 2013 Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Disclosures None 2 Objectives Review burden
Asthma Update 2013 Jennifer W. McCallister, MD, FACP, FCCP Associate Professor Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Disclosures None 2 Objectives Review burden
What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university
 What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university Management stable COPD Relieve symptoms Improve exercise tolerance Improve health status Prevent
What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university Management stable COPD Relieve symptoms Improve exercise tolerance Improve health status Prevent
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
COPD and Asthma: Similarities and differences Prof. Peter Barnes
 and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: bronchial_thermoplasty 10/2010 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Bronchial thermoplasty
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: bronchial_thermoplasty 10/2010 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Bronchial thermoplasty
Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot Malhi, B.R. Srinivas and Lata Kumar
 Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Diagnosing Asthma Comparisons between Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurements and Conventional Tests
 Diagnosing Asthma Comparisons between Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurements and Conventional Tests Andrew D. Smith, Jan O. Cowan, Sue Filsell, Chris McLachlan, Gabrielle Monti-Sheehan, Pamela Jackson, and
Diagnosing Asthma Comparisons between Exhaled Nitric Oxide Measurements and Conventional Tests Andrew D. Smith, Jan O. Cowan, Sue Filsell, Chris McLachlan, Gabrielle Monti-Sheehan, Pamela Jackson, and
aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A.
 aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A. 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A. 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University
 Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Adenosine 5 0 -monophosphate increases levels of leukotrienes in breath condensate in asthma
 Respiratory Medicine (2004) 98, 651 655 Adenosine 5 0 -monophosphate increases levels of leukotrienes in breath condensate in asthma E. Bucchioni, Z. Csoma, L. Allegra, K.F. Chung, P.J. Barnes, S.A. Kharitonov*
Respiratory Medicine (2004) 98, 651 655 Adenosine 5 0 -monophosphate increases levels of leukotrienes in breath condensate in asthma E. Bucchioni, Z. Csoma, L. Allegra, K.F. Chung, P.J. Barnes, S.A. Kharitonov*
HCT Medical Policy. Bronchial Thermoplasty. Policy # HCT113 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016. Policy Statement. Overview
 HCT Medical Policy Bronchial Thermoplasty Policy # HCT113 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016 Medical Policies are developed by HealthyCT to assist in administering plan benefits and constitute neither
HCT Medical Policy Bronchial Thermoplasty Policy # HCT113 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016 Medical Policies are developed by HealthyCT to assist in administering plan benefits and constitute neither
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3. Chronic Cough Guidelines
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3 Chronic Cough Guidelines NHS Fife Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Cough in Adults In this section: 1. Introduction 2. Scope Guidelines for Management of Chronic
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3 Chronic Cough Guidelines NHS Fife Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Cough in Adults In this section: 1. Introduction 2. Scope Guidelines for Management of Chronic
Asthma in Day to Day Practice
 Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
Omalizumab (Xolair ) ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September Indication
 ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
Dr Christopher Worsnop
 Dr Christopher Worsnop Respiratory & Sleep Physician Austin Hospital, Melbourne Supported by: Top Tips in Modern Asthma Management Dr Christopher Worsnop Rotorua GPCME Meeting June 2013 Speaker declaration
Dr Christopher Worsnop Respiratory & Sleep Physician Austin Hospital, Melbourne Supported by: Top Tips in Modern Asthma Management Dr Christopher Worsnop Rotorua GPCME Meeting June 2013 Speaker declaration
Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD
 Respiratory Medicine (2003) 97, 1014 1020 Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD J.F. Donohue a, *, S. Menjoge b, S. Kesten b a University of North Carolina School of Medicine, 130
Respiratory Medicine (2003) 97, 1014 1020 Tolerance to bronchodilating effects of salmeterol in COPD J.F. Donohue a, *, S. Menjoge b, S. Kesten b a University of North Carolina School of Medicine, 130
Office Based Spirometry
 Osteopathic Family Physician (2014)1, 14-18 Scott Klosterman, DO; Woodson Crenshaw, OMS4 Spartanburg Regional Family Medicine Residency Program; Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine - Virginia Campus
Osteopathic Family Physician (2014)1, 14-18 Scott Klosterman, DO; Woodson Crenshaw, OMS4 Spartanburg Regional Family Medicine Residency Program; Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine - Virginia Campus
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring
 Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Outcome measures in asthma
 S70 Thorax 2000;55(Suppl 1):S70 S74 Outcome measures in asthma N C Barnes Department of Respiratory Medicine, The London Chest Hospital, London E2 9JX, UK Introductory articles Exacerbations of asthma:
S70 Thorax 2000;55(Suppl 1):S70 S74 Outcome measures in asthma N C Barnes Department of Respiratory Medicine, The London Chest Hospital, London E2 9JX, UK Introductory articles Exacerbations of asthma:
Research in Real Life
 Research in Real Life Study 1: Exploratory study - identifying the benefits of pmdi versus Diskus for delivering fluticasone/salmeterol combination therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Research in Real Life Study 1: Exploratory study - identifying the benefits of pmdi versus Diskus for delivering fluticasone/salmeterol combination therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Comparison of the Effect of Short Course of Oral Prednisone in Patients with Acute Asthma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 7 Number 1 Comparison of the Effect of Short Course of Oral Prednisone in Patients with Acute Asthma E Razi, G Moosavi Citation E Razi, G Moosavi.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 7 Number 1 Comparison of the Effect of Short Course of Oral Prednisone in Patients with Acute Asthma E Razi, G Moosavi Citation E Razi, G Moosavi.
Pharmacodynamic steady state of tiotropium in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Eur Respir J 2002; 19: 639 644 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.00238002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Pharmacodynamic steady state
Eur Respir J 2002; 19: 639 644 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.00238002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Pharmacodynamic steady state
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
Complements asthma therapy NOT a CURE for Severe. Non pharmacologic treatment of asthma. limits the ability of the airways to constrict.
 Bronchial Thermoplasty Karla Provost Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine 2015 What is Bronchial Thermoplasty Non pharmacologic treatment of asthma Outpatient procedure performed over 3 treatment sessions
Bronchial Thermoplasty Karla Provost Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine 2015 What is Bronchial Thermoplasty Non pharmacologic treatment of asthma Outpatient procedure performed over 3 treatment sessions
What is Severe Persistent Asthma? What is Bronchial Thermoplasty Non pharmacologic treatment of asthma
 Objectives BT defined What is Severe Persistent Asthma Case Study introduction How is BT performed Pre-op, PACU and Discharge care Who does it work for the criteria for BT Brief overview of BT results
Objectives BT defined What is Severe Persistent Asthma Case Study introduction How is BT performed Pre-op, PACU and Discharge care Who does it work for the criteria for BT Brief overview of BT results
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Predicting response to triamcinolone in severe asthma by machine learning: solving the Enigma
 Page 1 of 5 Predicting response to triamcinolone in severe asthma by machine learning: solving the Enigma Kian Fan Chung National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College London & Royal Brompton and Harefield
Page 1 of 5 Predicting response to triamcinolone in severe asthma by machine learning: solving the Enigma Kian Fan Chung National Heart & Lung Institute, Imperial College London & Royal Brompton and Harefield
N ational and international guidelines on the treatment
 561 ASTHMA Predictors of therapy resistant asthma: outcome of a systematic evaluation protocol L G Heaney, E Conway, C Kelly, B T Johnston, C English, M Stevenson, J Gamble... See end of article for authors
561 ASTHMA Predictors of therapy resistant asthma: outcome of a systematic evaluation protocol L G Heaney, E Conway, C Kelly, B T Johnston, C English, M Stevenson, J Gamble... See end of article for authors
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
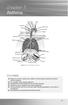 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Is reslizumab effective in improving quality of life and asthma control in adolescent and adult patients with poorly controlled eosinophilic asthma?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Evidence-based recommendations or Show me the patients selected and I will tell you the results
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, S17 S21 Evidence-based recommendations or Show me the patients selected and I will tell you the results Leif Bjermer Department of Respiratory Medicine & Allergology, 221
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, S17 S21 Evidence-based recommendations or Show me the patients selected and I will tell you the results Leif Bjermer Department of Respiratory Medicine & Allergology, 221
2.6 MONITORING ASTHMA
 2.6 MONITORING ASTHMA 2.6.1 MONITORING ASTHMA IN ADULTS In the majority of patients with asthma symptom-based monitoring is adequate. Patients achieving control of symptoms with treatment have a low risk
2.6 MONITORING ASTHMA 2.6.1 MONITORING ASTHMA IN ADULTS In the majority of patients with asthma symptom-based monitoring is adequate. Patients achieving control of symptoms with treatment have a low risk
ALLERGY IN RESPIRATORY AIRWAY DISEASE AND
 Allergy in Respiratory Airway Disease and Beyond Unit No. 2 differentiating asthma from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Dr Lee Pyng ABSTRACT Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Allergy in Respiratory Airway Disease and Beyond Unit No. 2 differentiating asthma from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Dr Lee Pyng ABSTRACT Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control
 Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
MUHAMMAD H. MAEBED, M.D.*; DINA A. EZZAT, M.D.*; ABEER S. MUHAMMAD, M.D.**; OSAMA LAMEI, M.D.*** and ELHAM ABDUL MAGEED, M.Sc.*
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 78, No. 2, June: 89-97, 2010 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Study of Airway Remodeling in Pediatric Patients with Bronchial Asthma Using Chest High Resolution Computed
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 78, No. 2, June: 89-97, 2010 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Study of Airway Remodeling in Pediatric Patients with Bronchial Asthma Using Chest High Resolution Computed
