Journal Club: COPD and Rehospitalization Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1
|
|
|
- Deborah Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 791 Journal Club: Rehospitalization Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club: COPD and Rehospitalization Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD; Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, CMS; Roflumilast and Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-Acting β2-agonist on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations, RE(2)SPOND; inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting beta-agonists, ICS/LABA; long-acting muscarinic antagonists, LAMA; phosphodiesterase-4, PDE4; Roflumilast and Exacerbations in Patients receiving Appropriate Combination Therapy, REACT Citation: Balkissoon R. Journal Club: COPD and Rehospitalization. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis (Miami). 2016;3(4): doi: dx.doi.org/ /jcopdf Denver, Colorado Address correspondence to: Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC balkissoonr@njhealth.org Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; COPD; rehospitalization COPD and Rehospitalization Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations may account for up to 75% of direct costs associated with care for these patients. 1 Hospitalization of COPD patients accounts for a substantial part of that economic burden. It is estimated that medical costs attributable to COPD in the United States may reach $49 billion by As the paper by Roberts and colleagues, (included below), points out, 20% of Medicare patients hospitalized for COPD have an all cause rehospitalization within 30 days of discharge and 30% of these readmissions are for COPD-related events. In 2012, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) implemented the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program, that penalizes hospitals that have excessive hospital readmissions within 30 days by reducing their Medicare payments. In 2014 this program was expanded to include COPDrelated exacerbation readmissions. Unfortunately while these penalties are being implemented there is a dearth of evidence-based guidance as to strategies that are likely to reduce early rehospitalization. (See also the 2nd National Readmissions Summit Report in this issue.) In this Journal Club we focus on studies that are examining factors that may predict and or influence the rates of COPD-related rehospitalization. The first article by Roberts et al is a retrospective analysis of data from a national U.S. health claims data base and identifies factors that predict increased risk of rehospitalization in addition to early (<30 days) versus late (>30 days) rehospitalization. The 2 following articles look at the potential efficacy of roflumilast in reducing exacerbations and/or rehospitalization. The Roflumilast and Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-Acting β2-agonist on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations (RE(2)SPOND) study has been eagerly anticipated as the counterpart to the European study Roflumilast and Exacerbations in Patients receiving Appropriate Combination Therapy (REACT) 3 to look at the benefit of roflumilast added to inhaled corticosteroid/longacting beta-agonists (ICS/LABA) and/or long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA). The study suggests that a phenotype of patients that have a history of frequent hospitalization may predict individuals likely to benefit from treatment with roflumilast. The second study presents interesting data regarding the relationships between rehospitalization rates and early versus late institution of roflumilast therapy post hospital discharge. Finally, the last 2 articles examine the efficacy of 2 different approaches to health coaching programs and reducing early rehospitalization rates. It is likely that the economic burden related to COPD will continue to grow for at least the next few decades and it is prudent to initiate efforts to try to control costs related to the treatment of this patient population. Recognition of the complexity of this COPD cohort in terms of different phenotypes and their multiple comorbidities is critical to developing approaches that improve health care quality while also reducing costs.
2 792 Journal Club: Rehospitalization Abstract 1 A retrospective analysis to identify predictors of COPD-related rehospitalization Roberts MH, Clerisme-Beaty E, Kozma CM, Paris A, Slaton T, Mapel DW. BMC Pulm Med. 2016; 16(1):68. doi: BACKGROUND: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is often associated with recurrent hospitalizations. This study aimed to identify factors related to COPD rehospitalization. A national US claims database was used to identify patients, aged 40 years, hospitalized for COPD. Their first COPD-related hospital admission date in 2009 was set as the index date, with post-discharge COPD-related rehospitalization assessed for 180 days post-index date. Data were analyzed for: 1) all eligible patients in whom early COPD-related rehospitalization was evaluated (1-30 days post discharge; all-patient cohort) and 2) a patient subset not rehospitalized early in whom late COPD-related rehospitalization was evaluated (>30 days post discharge to 180 days post-index date; late cohort). Logistic regressions controlling for age and sex assessed potential COPDrelated rehospitalization predictors. Variables from the 360-day pre-index period and index hospitalization were evaluated for each cohort, and 30-day postdischarge variables evaluated for the late cohort. RESULTS: Of 3612 patients with an index hospitalization, 4.8 % (174) had an early COPD-related rehospitalization, and of the remaining 3438 patients, 13.7 % (471) had a late COPD-related rehospitalization. Several pre-index variables were predictive of early COPDrelated rehospitalization including: pneumonia; comorbidities; COPD-related drug therapies; and prior hospitalizations. In patients not rehospitalized early, the strongest predictor of late COPD-related rehospitalization was pre-index COPD-related hospitalization (OR = 3.64 [P < 0.001]). The strongest index hospitalization factors predictive of late COPDrelated rehospitalization were use of steroids (any route: OR = 1.62 [P = 0.007]) and nebulizers (OR = 1.65 [P = 0.007]); neither predicted early COPD-related rehospitalization. Generally, factors predicting COPDrelated rehospitalization were similar in both cohorts. CONCLUSIONS: Several pre-index variables were associated with COPD-related rehospitalization. A strong predictor of COPD-related rehospitalization was prior hospitalization during the pre-index period, particularly with a primary COPD diagnosis, whilst other predictive factors related to increased COPD severity; these may be useful indicators for COPDrelated rehospitalization risk assessment. Some factors, e.g., recurrent pneumonia and exacerbations, may be modifiable. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); Comorbidity; Exacerbations; Readmission predictors; Rehospitalization; Utilization This retrospective analysis had a relatively unique data source that contained data from inpatient pharmacies, as well as medical and outpatient pharmacies. Perhaps it is no surprise that prior hospitalization in the previous year and pneumonia were predictive of early rehospitalization. Other comorbidities that were associated with early rehospitalization included anxiety, asthma, diabetes, hypoxia, ischemic heart disease and dyspnea while notably, hypertension, pulmonary vascular disease, stroke, depression and congestive heart failure were not. Late rehospitalization seemed to be associated with the same comorbidities as early rehospitalization in addition to congestive heart failure, depression, hypertension and osteoporosis and pulmonary vascular disease. Drug-related therapies looked at antibiotics, inhaled steroids, non-inhaled steroids, long-acting beta-agonists and short-acting beta-agonists and anticholinergics. Interestingly pre-index inhaled steroid use was not predictive of an early rehospitalization but was predictive of a late COPD-related hospitalization. All the other classes of medications were predictive of both late and early hospitalizations. One interpretation of this data could be that inhaled steroid use may be protective against early rehospitalization. Interestingly, pre-index influenza or pneumonia vaccines were also predictive of early COPD hospitalization. The findings
3 793 Journal Club: Rehospitalization from this study can provide useful information in the design of prospective studies with regard to parameters that should be included for developing risk stratification systems and specific interventions that will reduce the rate of COPD rehospitalizations. Abstract 2 Effect of roflumilast and inhaled corticosteroid/long-acting β2-agonist on chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations (RE(2) SPOND). A randomized clinical trial Martinez FJ, Rabe KF, Sethi S, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016; 194(5): doi: RATIONALE: Moderate and severe exacerbations are incompletely prevented by maximal inhalation therapy in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. OBJECTIVES: To determine whether roflumilast reduces moderate and/or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations in patients at risk for exacerbations despite treatment with inhaled corticosteroid/longacting β2-agonist with or without a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA). In this 52-week, phase 4, double-blind, placebocontrolled RE(2)SPOND (Roflumilast Effect on Exacerbations in Patients on Dual [LABA/ICS] Therapy) trial (NCT ), participants aged 40 years or older with severe/very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic bronchitis, two or more exacerbations and/or hospitalizations in the previous year, and receiving inhaled corticosteroid/ long-acting β2-agonist with or without LAMA daily for 3 or more months were equally randomized to once-daily roflumilast, 500 μg (n = 1,178), or placebo (n = 1,176). Stratification was based on LAMA use. MEASUREMENTS AND MAIN RESULTS: Although rate of moderate or severe exacerbations per patient per year (primary endpoint) was reduced by 8.5% with roflumilast versus placebo, the between- group difference was not statistically significant (rate ratio, 0.92; 95% confidence interval, ; P = 0.163). However, roflumilast improved lung function, and in a post hoc analysis roflumilast significantly reduced the rate of moderate or severe exacerbations in participants with a history of more than three exacerbations and/or one or more hospitalizations in the prior year. Adverse eventrelated discontinuations occurred in 11.7% roflumilasttreated and 5.4% placebo-treated participants. Deaths occurred in 2.5% roflumilast and 2.1% placebo participants. CONCLUSIONS: Roflumilast failed to statistically significantly reduce moderate and/or severe exacerbations in the overall population. Roflumilast improved lung function and reduced exacerbations in participants with frequent exacerbations and/or hospitalization history. The safety profile of roflumilast was consistent with that of previous studies. Clinical trial registered with www. clinicaltrials.gov (NCT ). bronchodilators; clinical trial; hospitalization; phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor PMID: Roflumilast is a phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor that had been shown in earlier trials to reduce the risk of exacerbations in patients with COPD not on other maintenance medications reported to reduce exacerbations such as ICSs/LABAs and/or LAMAs. The trial Roflumilast and Exacerbations in Patients Receiving Appropriate Combination Therapy (REACT) trial was a European study published last year that used the enteric coated version of roflumilast and demonstrated the efficacy of roflumilast in combination with ICS/LABA with or without LAMA in reducing moderate to severe exacerbations in patients with 2 or more exacerbations and/or hospitalizations in the prior 12 months. The Food and Drug Administration-approved formulation of roflumilast is not film (enteric) coated and thus required a separate study of efficacy with the similar study design. The authors for the RESPOND trial provide a very thoughtful discussion of possible factors that may contribute to why the REACT trial met the primary endpoint (reduction in moderate to severe exacerbations)
4 794 Journal Club: Rehospitalization whereas the RESPOND trial did not. The investigators point to the fact that RESPOND had 10% more patients with very severe airflow obstruction and a higher proportion of patients with more than 2 exacerbations (24%-25%) versus in the REACT trial (10%-11%). There were also differences in the definitions of exacerbations and definitions of end of exacerbations. Further, the highest dose of ICS/LABA allowed in the REACT was fluticasone/salmeterol 500/50 whereas in RESPOND only the 250/50 dose was allowed. The RESPOND trial did not initially allow patients to be on LAMA but later amended the protocol to allow LAMA use, and this may explain the lower percentage of patients that were on triple therapy (ICS/LABA/LAMA) in the RESPOND trial. The difference in the formulations with regard to film coating was felt to not likely contribute to the difference as studies have shown bioequivalence between the formulations and there were no differences between the studies in bioequivalence. Two subgroups (men and those on fluticasone/salmeterol 250/50) did show statistically significant reductions in rates of moderate and severe exacerbations for roflumilast versus placebo in the RESPOND study. About 65% of participants in both treatment arms were on fluticasone/ salmeterol and 35% on budesonide/formoterol. Also, the authors report that there was a lower number of patients with 3 or more prior exacerbations in the RESPOND study compared to the REACT study. Hence, there are several study design issues that may provide plausible explanations and insights as to why there were differences in results for RESPOND versus REACT. While the RESPOND trial did not meet its primary endpoint for a broad population of COPD patients it perhaps helped to further refine our definition of a subphenotype (i.e., previous history of hospitalization and/ or frequent [4 or more] exacerbations in the previous 12 months) that are likely to experience a significant reduction in moderate to severe exacerbations. Abstract 3 Benefits of early roflumilast treatment after hospital or emergency department discharge for a COPD exacerbation Lee Q, Mocarski M, Sun SX. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2016; 9(3): BACKGROUND: Chronic lower respiratory disease, which includes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), is the third leading cause of death in the United States. Roflumilast is an oral, once-daily, selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor approved for reducing the risk for COPD exacerbations in patients with severe COPD associated with chronic bronchitis and a history of exacerbations. OBJECTIVES: To evaluate the effects of roflumilast treatment timing on COPD exacerbation rates (primary objective) and on resource utilization and healthcare costs (secondary objective) after hospital or emergency department discharge associated with a COPD exacerbation. In this retrospective cohort study, claims data from March 2011 to March 2013 were extracted from Truven Health MarketScan combined commercial healthcare claims and Medicare supplemental claims databases and were analyzed to compare the exacerbation rates and the healthcare resource utilization and costs between the early roflumilast treatment (treatment initiation 30 days after hospital or emergency department discharge) and the delayed roflumilast treatment (treatment initiation days after discharge) cohorts. Multivariate logistic regression and generalized linear models with loglink function and gamma distribution were adjusted for age, sex, insurance plan type, COPD disease complexity, and comorbidities. RESULTS: A total of 995 patients (N = 280 early roflumilast treatment, N = 715 delayed roflumilast treatment) were included. Compared with the delayed roflumilast treatment group, patients in the early roflumilast treatment group were 39% less likely to have an exacerbation after hospital discharge (P =.004). The patients receiving early roflumilast treatment also had 42% (P =.003) and 37% (P =.005) lower risks for COPD-related and all-cause rehospitalizations, respectively, than patients in the delayed roflumilast treatment group. Significantly fewer patients receiving early roflumilast treatment had moderate (P =.013) or severe (P =.002) exacerbations. Early roflumilast treatment also was associated with reduced annualized COPD-related (P =.012) and allcause (P =.009) rehospitalizations, outpatient visits per patient (P <.001 for COPD-related and all-cause), and procedures or therapies (COPD-related, P =.016; all-cause, P =.009). The early treatment group had
5 795 Journal Club: Rehospitalization fewer COPD-related emergency department visits per patient than the delayed roflumilast treatment group (P =.035), and the total mean annualized COPDrelated and all-cause costs were reduced by $7273 (P =.014) and $14,111 (P =.002), respectively. Multivariate analyses showed that early treatment was associated with lower COPD-related and all-cause annualized health services costs per patient annually (P <.001 for both). CONCLUSION: In this real-world study, the patients with COPD who initiated roflumilast treatment 30 days after a hospital or emergency department discharge for a COPD-related exacerbation experienced fewer subsequent exacerbations and rehospitalizations, reduced healthcare utilizations, and lower healthcare costs than the patients who delayed their roflumilast treatment. chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; exacerbations; healthcare costs; healthcare utilization; hospital discharge; rehospitalization; roflumilast PMID: This is a retrospective data base analysis that compares early versus late initiation of roflumilast therapy post discharge and suggests that early institution of therapies in the first 30 days post discharge was associated with a reduction in early readmissions. Patients with asthma were not excluded from this analysis and this clearly influences how one should evaluate the data. While one must be mindful of the limitations of a retrospective study like this with regard to such factors as misdiagnosis between asthma and COPD and that patients were not randomly and evenly assigned to early versus late institution of roflumilast, it certainly provides enough food for thought as to the merits of examining this question in a prospective study. Abstract 4 Health coaching and COPD rehospitalization: A randomized study Benzo R, Vickers K, Novotny PJ, et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med Mar 8. [Epub ahead of print] RATIONALE: Hospital readmission in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) has attracted attention due to the burden to patients and the Health Care system. There is a knowledge gap on approaches to reduce COPD readmissions. OBJECTIVE: Determine the effect of comprehensive Health Coaching, on the rate of COPD readmissions. 215 hospitalized for a COPD exacerbation were randomized at hospital discharge to Motivational Interviewing based Health Coaching plus a written action plan for exacerbations and a brief exercise advice versus usual care. Measures Rate of COPD related hospitalization during the year-followup. RESULTS: The Absolute Risk Reduction of COPD related rehospitalization by health coaching was 7.5% p=0.01, 11.0% p=0.02, 11.6% p=0.03, 11.4% p=0.05 and 5.4% p=0.24 at 1, 3, 6, 9, and 12 months compared to the control group. The Odds Ratio for COPD Hospitalization on the Intervention Arm Compared to the Control was 0.08 (CI ) at 1 month post discharge, 0.35 (CI ) at 3 months post discharge, 0.30 (CI ) at 6 months and 0.49 (CI ) at 1 year post discharge. Missing value rate for the primary outcome was 0.4% (1 patient). Disease specific quality of life improved significantly in the health coaching group compared to the control group at 6 and 12 months by the Chronic Respiratory Questionnaire (CRQ) Emotional Score (Emotion- Mastery) and Physical Score (Dyspnea-Fatigue) p<0.05. There were no differences in the physical activity measured at any time points between groups. Conclusion Health Coaching may represent a feasible and possibly effective intervention to reduce COPD readmissions. Clinical trial registration available at ID NCT COPD; Motivational Interviewing; Quality of Life; health coaching; self-management PMID: This study points out the value of early follow up, discharge education and patient empowerment as being very effective in reducing hospital readmissions.
6 796 Journal Club: Rehospitalization In particular, it did show a significant impact on 30 day readmission rate as well as readmissions at 3 months and 6 months. It is also relatively low cost. It is interesting to note that it is reported that there was no difference in the rate of use of antibiotics and steroids between the 2 groups suggesting that it wasn t simply the factor of having easier access to medications or greater use of these medications in the intervention group. It would have been interesting to have more information on this particular aspect of the study. It is not explicitly stated that the control group were also given an action plan with a package containing 5 days of prednisone and antibiotics. This is encouraging data presenting a relatively affordable intervention that does seem to reduce early rehospitalization. Abstract 5 The E-coach technology-assisted care transition system: a pragmatic randomized trial Ritchie CS, Houston TK, Richman JS, et al. Transl Behav Med. 2016;6(3): Care transitions from the hospital to home remain a vulnerable time for many patients, especially for those with heart failure (CHF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Despite regular use in chronic disease management, it remains unclear how technology can best support patients during their transition from the hospital. We sought to evaluate the impact of a technology-supported care transition support program on hospitalizations, days out of the community and mortality. Using a pragmatic randomized trial, we enrolled patients (511 enrolled, 478 analyzed) hospitalized with CHF/COPD to E-Coach, an intervention with condition-specific customization and in-hospital and post-discharge support by a care transition nurse (CTN), interactive voice response post-discharge calls, and CTN followup versus usual post-discharge care (UC). The primary outcome was 30-day rehospitalization. Secondary outcomes included (1) rehospitalization and death and (2) days in the hospital and out of the community. E-Coach and UC groups were similar at baseline except for gender imbalance (p = 0.02). After adjustment for gender, our primary outcome, 30-day rehospitalization rates did not differ between the E-Coach and UC groups (15.0 vs %, adjusted hazard ratio [95 % confidence interval]: 0.94 [0.60, 1.49]). However, in the COPD subgroup, E-Coach was associated with significantly fewer days in the hospital (0.5 vs. 1.6, p = 0.03). E-Coach, an IVR-augmented care transition intervention did not reduce rehospitalization. The positive impact on our secondary outcome (days in hospital) among COPD patients, but not in CHF, may suggest that E-Coach may be more beneficial among patients with COPD.NIH trial registry number: NCT Trial Protocol: /j.cct Care transitions; Self-management; Telehealth PMID: PMCID: PMC I added this recently published study that looked at an interactive telephonic system that included motivational coaching before discharge but then was followed with an interactive voice response system that would ask set questions and based on responses might prompt preset educational responses for the patient or send red flag alerts that would lead to a nurse contacting the patient. They did not receive any package of medications to self administer at early signs of an exacerbation. This was a study of both cardiac patients and COPD patients and was negative for the primary outcome of rehospitalization within 30 days, though the COPD group did have few days in hospital overall. These 2 studies may point to some of the limitations of E-coaching versus live coaching systems and/or the impact of having an emergency package of medications to take home and start at the earliest signs of an exacerbation.
7 797 Journal Club: Rehospitalization References American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. Standards for the diagnosis and management of patients with COPD. Version 1.2. American Thoracic Society website. www. thoracic.org/copd-guidelines. Published Accessed April 30, Ford ES, Murphy LB, Khavjou O, Giles WH, Holt JB, Croft JB. Total and state-specific medical and absenteeism costs of COPD among adults aged 18 years in the United States for 2010 and projections through Chest. 2015; 147(1): doi: dx.doi.org/ /chest Martinez FJ, Calverley PMA, Goehring U-M, Brose M, Fabbri LM, Rabe KF. Effect of roflumilast on exacerbations in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease uncontrolled by combination therapy (REACT): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015; 385(9971):
Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984]
![Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984]](/thumbs/85/91889043.jpg) Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background & Clinical Effectiveness John McMurray 11 th January 2016 For
Lead team presentation: Roflumilast for treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ID984] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background & Clinical Effectiveness John McMurray 11 th January 2016 For
Re-Submission. roflumilast, 500 microgram, film-coated tablet (Daxas ) SMC No 635/10 AstraZeneca UK Ltd. Published 11 September
 Re-Submission roflumilast, 500 microgram, film-coated tablet (Daxas ) SMC No 635/10 AstraZeneca UK Ltd 4 August 2017 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
Re-Submission roflumilast, 500 microgram, film-coated tablet (Daxas ) SMC No 635/10 AstraZeneca UK Ltd 4 August 2017 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
The Journal Club: COPD Exacerbations
 252 The Journal Club: COPD Exacerbations Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club The Journal Club: COPD Exacerbations Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations:
252 The Journal Club: COPD Exacerbations Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club The Journal Club: COPD Exacerbations Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations:
Journal Club: Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1
 693 Journal Club: Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club: Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC
693 Journal Club: Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club: Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC
Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice. Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital
 Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital Therapy at each stage of COPD I: Mild II: Moderate III: Severe IV: Very severe
Turning Science into Real Life Roflumilast in Clinical Practice Roland Buhl Pulmonary Department Mainz University Hospital Therapy at each stage of COPD I: Mild II: Moderate III: Severe IV: Very severe
Journal of the COPD Foundation. Journal Club. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases:
 85 Journal Club Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations: inhaled corticosteroid, ICS; long acting β 2 -agonist,
85 Journal Club Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations: inhaled corticosteroid, ICS; long acting β 2 -agonist,
Outcomes: Initially, our primary definitions of pneumonia was severe pneumonia, where the subject was hospitalized
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk. NICE All rights reserved.
 Surveillance report 2016 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management (2010) NICE guideline CG101 Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk NICE 2016. All rights
Surveillance report 2016 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in over 16s: diagnosis and management (2010) NICE guideline CG101 Surveillance report Published: 6 April 2016 nice.org.uk NICE 2016. All rights
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Calverley P M A, Anzueto A R, Carter K, et
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Calverley P M A, Anzueto A R, Carter K, et
roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd
 roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd 06 August 2010 (Issued 10 September 2010) The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd 06 August 2010 (Issued 10 September 2010) The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
UPDATE IN CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE
 UPDATE IN CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE Radhika Shah, MD Erlanger Health System University of Tennessee College of Medicine Chattanooga Respiratory, Critical Care, and Sleep medicine No disclosures
UPDATE IN CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE Radhika Shah, MD Erlanger Health System University of Tennessee College of Medicine Chattanooga Respiratory, Critical Care, and Sleep medicine No disclosures
Advances in the management of chronic obstructive lung diseases (COPD) David CL Lam Department of Medicine University of Hong Kong October, 2015
 Advances in the management of chronic obstructive lung diseases (COPD) David CL Lam Department of Medicine University of Hong Kong October, 2015 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) COPD in Hong
Advances in the management of chronic obstructive lung diseases (COPD) David CL Lam Department of Medicine University of Hong Kong October, 2015 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) COPD in Hong
Journal of the COPD Foundation. Impact of the IMPACT Trial Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal Club
 221 Journal Club: The IMPACT Trial Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club Impact of the IMPACT Trial Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations: Global
221 Journal Club: The IMPACT Trial Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Journal Club Impact of the IMPACT Trial Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations: Global
Changing Epidemiology: Quick Facts 9/28/2018. During the year New Treatment Options for COPD: Phenotypes, Endotypes or Treatable Traits?
 New Treatment Options for COPD: Phenotypes, Endotypes or Treatable Traits? Conflict of Interest Statement 2018 Speakers Bureau Astra Zeneca Boehringer Ingelheim Genentech Sunovion Ron Balkissoon MD DIH
New Treatment Options for COPD: Phenotypes, Endotypes or Treatable Traits? Conflict of Interest Statement 2018 Speakers Bureau Astra Zeneca Boehringer Ingelheim Genentech Sunovion Ron Balkissoon MD DIH
THE CHALLENGES OF COPD MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE An Expert Roundtable
 THE CHALLENGES OF COPD MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE An Expert Roundtable This activity is supported by an educational grant from Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. COPD in the United States Third leading cause
THE CHALLENGES OF COPD MANAGEMENT IN PRIMARY CARE An Expert Roundtable This activity is supported by an educational grant from Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. COPD in the United States Third leading cause
A retrospective analysis to identify predictors of COPD-related rehospitalization
 Roberts et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2016) 16:68 DOI 10.1186/s12890-016-0231-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE A retrospective analysis to identify predictors of COPD-related rehospitalization Melissa H. Roberts 1*,
Roberts et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2016) 16:68 DOI 10.1186/s12890-016-0231-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE A retrospective analysis to identify predictors of COPD-related rehospitalization Melissa H. Roberts 1*,
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION
 CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION (FLUTICASONE FUROATE/VILANTEROL) (Breo Ellipta GlaxoSmithKline) Indication: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends
CDEC FINAL RECOMMENDATION (FLUTICASONE FUROATE/VILANTEROL) (Breo Ellipta GlaxoSmithKline) Indication: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Recommendation: The Canadian Drug Expert Committee (CDEC) recommends
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
 Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Temple, TX October
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Temple, TX October
COPD Update. Muhammad Talha Khan MD. COPD Exacerbations. COPD Clinical Importance. COPD Pathophysiology. Overview/Objectives
 Overview/Objectives COPD Update Muhammad Talha Khan MD Pulmonologist St Croix Regional Medical Center, St Croix Falls, WI. Overview of COPD and disease impact Classification of COPD Severity Treatment
Overview/Objectives COPD Update Muhammad Talha Khan MD Pulmonologist St Croix Regional Medical Center, St Croix Falls, WI. Overview of COPD and disease impact Classification of COPD Severity Treatment
Disclosure Statement. Epidemiological Data
 EVALUATION OF THE MEDICATION UTILIZATION OF COPD PATIENTS AT THE MIAMI VA HEALTHCARE SYSTEM Simone Edgerton, PharmD. PGY 1 Pharmacy Resident Miami VA Healthcare System Miami, Florida Simone.edgerton2@va.gov
EVALUATION OF THE MEDICATION UTILIZATION OF COPD PATIENTS AT THE MIAMI VA HEALTHCARE SYSTEM Simone Edgerton, PharmD. PGY 1 Pharmacy Resident Miami VA Healthcare System Miami, Florida Simone.edgerton2@va.gov
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: What s New in Therapeutic Management?
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: What s New in Therapeutic Management? Sabrina Sherwood, PharmD PGY2 Internal Medicine Resident University of Utah Health September 29, 2018 Disclosures Relevant disclosures
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: What s New in Therapeutic Management? Sabrina Sherwood, PharmD PGY2 Internal Medicine Resident University of Utah Health September 29, 2018 Disclosures Relevant disclosures
Choosing an inhaler for COPD made simple. Dr Simon Hart Castle Hill Hospital
 Choosing an inhaler for COPD made simple Dr Simon Hart Castle Hill Hospital 1 Declaration of interests I have received speaker fees, sponsorship to attend conferences, and funding for research from companies
Choosing an inhaler for COPD made simple Dr Simon Hart Castle Hill Hospital 1 Declaration of interests I have received speaker fees, sponsorship to attend conferences, and funding for research from companies
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Roflumilast: Οι κλινικές μελέτες
 Roflumilast: Οι κλινικές μελέτες Επαμεινώνδας Ν. Κοσμάς Δ/ντής Πνευμονολογικού Τμήματος Νοσοκομείου Metropolitan PDE4 PLAYS AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN INFLAMMATION PDE4 inhibition P P P PDE4 P Adapted from Rabe
Roflumilast: Οι κλινικές μελέτες Επαμεινώνδας Ν. Κοσμάς Δ/ντής Πνευμονολογικού Τμήματος Νοσοκομείου Metropolitan PDE4 PLAYS AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN INFLAMMATION PDE4 inhibition P P P PDE4 P Adapted from Rabe
aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A.
 aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A. 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
aclidinium 322 micrograms inhalation powder (Eklira Genuair ) SMC No. (810/12) Almirall S.A. 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product and
What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university
 What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university Management stable COPD Relieve symptoms Improve exercise tolerance Improve health status Prevent
What s new in COPD? Apichart Khanichap MD. Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Thammasat university Management stable COPD Relieve symptoms Improve exercise tolerance Improve health status Prevent
COPD: A Renewed Focus. Disclosures
 COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical Guideline
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Clinical These clinical guidelines are designed to assist clinicians by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation and treatment of patients. They
Disclosure and Conflict of Interest 8/15/2017. Pharmacist Objectives. At the conclusion of this program, the pharmacist will be able to:
 Digging for GOLD Rebecca Young, PharmD, BCACP, Roosevelt University College of Pharmacy Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences Practice Site Advocate Medical Group-Nesset Pavilion Disclosure and Conflict
Digging for GOLD Rebecca Young, PharmD, BCACP, Roosevelt University College of Pharmacy Assistant Professor of Clinical Sciences Practice Site Advocate Medical Group-Nesset Pavilion Disclosure and Conflict
TORCH: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate and Survival in COPD
 TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Changing Landscapes in COPD New Zealand Respiratory Conference
 Changing Landscapes in COPD New Zealand Respiratory Conference Dr Robert Young BMedSc MBChB DPhil (Oxon) FRACP FRCP Associate Professor Consultant Physician Changing Landscapes in COPD: Summary 1. Overview
Changing Landscapes in COPD New Zealand Respiratory Conference Dr Robert Young BMedSc MBChB DPhil (Oxon) FRACP FRCP Associate Professor Consultant Physician Changing Landscapes in COPD: Summary 1. Overview
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) KAREN ALLEN MD PULMONARY & CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE VA HOSPITAL OKC / OUHSC
 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) KAREN ALLEN MD PULMONARY & CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE VA HOSPITAL OKC / OUHSC I have no financial disclosures Definition COPD is a preventable and treatable disease
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) KAREN ALLEN MD PULMONARY & CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE VA HOSPITAL OKC / OUHSC I have no financial disclosures Definition COPD is a preventable and treatable disease
Pharmacotherapy for COPD
 10/3/2017 Topics to be covered Pharmacotherapy for chronic treatment Pharmacotherapy for COPD Dr. W C Yu 3rd September 2017 Commonly used drugs Guidelines for their use Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) in
10/3/2017 Topics to be covered Pharmacotherapy for chronic treatment Pharmacotherapy for COPD Dr. W C Yu 3rd September 2017 Commonly used drugs Guidelines for their use Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) in
Roflumilast for the treatment of respiratory disease: review of the Phase II and III trials
 Roflumilast for the treatment of respiratory disease: review of the Phase II and trials Clin. Invest. (2011) 1(10), 1413 1419 Roflumilast (Daxas [EU], Daliresp [USA]) is the first phospho diesterase 4
Roflumilast for the treatment of respiratory disease: review of the Phase II and trials Clin. Invest. (2011) 1(10), 1413 1419 Roflumilast (Daxas [EU], Daliresp [USA]) is the first phospho diesterase 4
Policy Evaluation: Step Therapy Prior Authorization of Combination Inhaled Corticosteroid / Long-Acting Beta-Agonists
 Drug Use Research & Management Program OHA Division of Medical Assistance Programs 500 Summer Street NE, E35; Salem, OR 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Policy Evaluation: Step Therapy Prior
Drug Use Research & Management Program OHA Division of Medical Assistance Programs 500 Summer Street NE, E35; Salem, OR 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Policy Evaluation: Step Therapy Prior
11/27/18. Challenges in Pulmonary and Critical Care: COPD So Much is New! Faculty. Disclosures
 Challenges in Pulmonary and Critical Care: 2018 COPD So Much is New! 1 Faculty Anas Hadeh, MD, FCCP Director, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Fellowship Program Affiliate Assistant Professor of Clinical
Challenges in Pulmonary and Critical Care: 2018 COPD So Much is New! 1 Faculty Anas Hadeh, MD, FCCP Director, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Fellowship Program Affiliate Assistant Professor of Clinical
Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center
 Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center dtaylor@ochsner.org Observations from Yesterday EPIC is epidemic No EMR No Way!!! Accountability/Benchmarking
Optimum COPD Care in 2010 Why Not Now? David E. Taylor, M.D. Pulmonary/Critical Care Ochnser Medical Center dtaylor@ochsner.org Observations from Yesterday EPIC is epidemic No EMR No Way!!! Accountability/Benchmarking
2/4/2019. GOLD Objectives. GOLD 2019 Report: Chapters
 GOLD Objectives To provide a non biased review of the current evidence for the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD. To highlight short term and long term treatment objectives organized
GOLD Objectives To provide a non biased review of the current evidence for the assessment, diagnosis and treatment of patients with COPD. To highlight short term and long term treatment objectives organized
CARE OF THE ADULT COPD PATIENT
 CARE OF THE ADULT COPD PATIENT Target Audience: The target audience for this clinical guideline is all MultiCare providers and staff including those associated with our Clinically Integrated Network. The
CARE OF THE ADULT COPD PATIENT Target Audience: The target audience for this clinical guideline is all MultiCare providers and staff including those associated with our Clinically Integrated Network. The
April 10 th, Bond Street, Toronto ON, M5B 1W8
 Comprehensive Research Plan: Inhaled long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs; long-acting anticholinergics) for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) April 10 th, 2014 30 Bond
Comprehensive Research Plan: Inhaled long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs; long-acting anticholinergics) for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) April 10 th, 2014 30 Bond
Optum Research Database Proportion of asthma patients with prescription fills for rescue and controller medications by year,
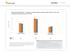 ASTHMA CHART 1 Optum Research Database Proportion of asthma patients with prescription fills for rescue and controller medications by year, 215-216 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 Controller medication 1 Rescue medication
ASTHMA CHART 1 Optum Research Database Proportion of asthma patients with prescription fills for rescue and controller medications by year, 215-216 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 1 Controller medication 1 Rescue medication
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Breathtaking science. Developing respiratory drugs to improve health and quality of life. H.C. Wainwright Global Life Sciences Conference April 2018
 Breathtaking science Developing respiratory drugs to improve health and quality of life H.C. Wainwright Global Life Sciences Conference April 2018 www.veronapharma.com Forward-Looking Statements This presentation
Breathtaking science Developing respiratory drugs to improve health and quality of life H.C. Wainwright Global Life Sciences Conference April 2018 www.veronapharma.com Forward-Looking Statements This presentation
Reducing COPD Exacerbation Readmissions in a Community-Based Teaching Hospital
 Reducing COPD Exacerbation Readmissions in a Community-Based Teaching Hospital Dawn Waddell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Manager Lisa Kingdon, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Dawn Waddell
Reducing COPD Exacerbation Readmissions in a Community-Based Teaching Hospital Dawn Waddell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Manager Lisa Kingdon, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Dawn Waddell
Brand Name: Daliresp. Generic Name: roflumilast. Manufacturer: Forest Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 Brand Name: Daliresp Generic Name: roflumilast 3, 4, 5 Manufacturer: Forest Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 1, 2,4,5,7 Drug Class: Second Generation Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE 4) inhibitor Labeled Uses: prophylaxis
Brand Name: Daliresp Generic Name: roflumilast 3, 4, 5 Manufacturer: Forest Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 1, 2,4,5,7 Drug Class: Second Generation Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE 4) inhibitor Labeled Uses: prophylaxis
Roflumilast for the management of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast for the management of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Issued: January 2012 www.nice.org.uk/ta244 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology
Roflumilast for the management of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Issued: January 2012 www.nice.org.uk/ta244 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology
Roflumilast for the management of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast for the management of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Issued: January 2012 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta244 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology Evaluation
Roflumilast for the management of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Issued: January 2012 guidance.nice.org.uk/ta244 NICE has accredited the process used by the Centre for Health Technology Evaluation
Advancing COPD treatment strategies with evidencebased. 17:15 19:15 Monday 11 September 2017 ERS 2017, Milan, Italy
 Advancing COPD treatment strategies with evidencebased approaches 17:15 19:15 Monday 11 September 2017 ERS 2017, Milan, Italy Increasing understanding of COPD and the effect on guideline evolution. GOLD
Advancing COPD treatment strategies with evidencebased approaches 17:15 19:15 Monday 11 September 2017 ERS 2017, Milan, Italy Increasing understanding of COPD and the effect on guideline evolution. GOLD
Abbreviated Class Review: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Executive summary: Month/Year of Review: February
Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119 Executive summary: Month/Year of Review: February
What s New in Acute COPD? Dr Nick Scriven Consultant AIM President SAM
 What s New in Acute COPD? Dr Nick Scriven Consultant AIM President SAM Covering: Basic Definition New assessment criteria Some newer treatments BiPAP Not Covering: Definitions: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
What s New in Acute COPD? Dr Nick Scriven Consultant AIM President SAM Covering: Basic Definition New assessment criteria Some newer treatments BiPAP Not Covering: Definitions: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
Four of 10 patients with asthma suffer moderate REVIEW DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS II: OBSERVATIONAL DATA. Michael S. Blaiss, MD ABSTRACT
 DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS II: OBSERVATIONAL DATA Michael S. Blaiss, MD ABSTRACT The differences between clinical trials and clinical practice often create difficulty for generalizing results of controlled
DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS II: OBSERVATIONAL DATA Michael S. Blaiss, MD ABSTRACT The differences between clinical trials and clinical practice often create difficulty for generalizing results of controlled
Treatment Responses. Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
 Asthma and COPD: Are They a Spectrum Treatment Responses Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Pharmacological Treatments Bronchodilators Inhaled short-acting β -Agonist (rescue) Inhaled short-acting
Asthma and COPD: Are They a Spectrum Treatment Responses Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Pharmacological Treatments Bronchodilators Inhaled short-acting β -Agonist (rescue) Inhaled short-acting
CLINICAL PATHWAY. Acute Medicine. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 CLINICAL PATHWAY Acute Medicine Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Table of Contents (tap to jump to page) INTRODUCTION 1 Scope of this Pathway 1 Pathway Contacts
CLINICAL PATHWAY Acute Medicine Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Table of Contents (tap to jump to page) INTRODUCTION 1 Scope of this Pathway 1 Pathway Contacts
Potential risks of ICS use
 Potential risks of ICS use Randomised controlled trial Observational study Systematic review Pneumonia Tuberculosis Bone fracture Skin thinning/easy bruising Cataract Diabetes No effect on fracture risk
Potential risks of ICS use Randomised controlled trial Observational study Systematic review Pneumonia Tuberculosis Bone fracture Skin thinning/easy bruising Cataract Diabetes No effect on fracture risk
COPD: Preventable and Treatable. Lecture Outline. Diagnosis of COPD. COPD: Defining Terms
 COPD: Preventable and Treatable Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis and
COPD: Preventable and Treatable Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Lecture Outline I. Diagnosis and
COPD: From Hospital to Home October 5, 2015 Derek Linderman, MD Associate Professor COPD Center Pulmonary Nodule Clinic
 COPD: From Hospital to Home October 5, 2015 Derek Linderman, MD Associate Professor COPD Center Pulmonary Nodule Clinic Learning Objectives Know the adverse effects of COPD exacerbations Know mainstays
COPD: From Hospital to Home October 5, 2015 Derek Linderman, MD Associate Professor COPD Center Pulmonary Nodule Clinic Learning Objectives Know the adverse effects of COPD exacerbations Know mainstays
Reduced lung function in midlife and cognitive impairment in the elderly
 Page 1 of 5 Reduced lung function in midlife and cognitive impairment in the elderly Giuseppe Verlato, M.D. Ph.D Department of Diagnostics and Public Health University of Verona Verona, Italy Mario Olivieri,
Page 1 of 5 Reduced lung function in midlife and cognitive impairment in the elderly Giuseppe Verlato, M.D. Ph.D Department of Diagnostics and Public Health University of Verona Verona, Italy Mario Olivieri,
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary
 Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) October 26 th, 2018 Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Zahava.Picado@va.gov
Three s Company - The role of triple therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) October 26 th, 2018 Zahava Picado, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Resident Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System Zahava.Picado@va.gov
COPD exacerbation frequency and its association with health care resource utilization and costs
 International Journal of COPD open access to scientific and medical research Open Access Full Text Article Original Research COPD exacerbation frequency and its association with health care resource utilization
International Journal of COPD open access to scientific and medical research Open Access Full Text Article Original Research COPD exacerbation frequency and its association with health care resource utilization
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium montelukast 10mg tablets (Singulair ) No. (185/05) Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd (MSD) New indication: for asthmatic patients in whom montelukast is indicated in asthma, montelukast
Scottish Medicines Consortium montelukast 10mg tablets (Singulair ) No. (185/05) Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd (MSD) New indication: for asthmatic patients in whom montelukast is indicated in asthma, montelukast
Aclidinium bromide/formoterol Endpoint category. RR Endpoint. [95% CI 2 ] Study. with event
![Aclidinium bromide/formoterol Endpoint category. RR Endpoint. [95% CI 2 ] Study. with event Aclidinium bromide/formoterol Endpoint category. RR Endpoint. [95% CI 2 ] Study. with event](/thumbs/90/102875145.jpg) Resolution by the Federal Joint Committee on an amendment to the Pharmaceutical Directive (AM-RL): Appendix XII Resolutions on the benefit assessment of pharmaceuticals with new active ingredients, in
Resolution by the Federal Joint Committee on an amendment to the Pharmaceutical Directive (AM-RL): Appendix XII Resolutions on the benefit assessment of pharmaceuticals with new active ingredients, in
Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy with Combinations of Long-Acting Bronchodilators and Inhaled Steroids for Treatment of COPD
 Collaboration for Outcomes Research and Evaluation University of British Columbia Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy with Combinations of Long-Acting Bronchodilators and Inhaled Steroids for Treatment of COPD
Collaboration for Outcomes Research and Evaluation University of British Columbia Cost-Effectiveness of Therapy with Combinations of Long-Acting Bronchodilators and Inhaled Steroids for Treatment of COPD
Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo,
 Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo, BRONCHODILATORS: Beta Adrenoreceptor Agonists Actions Adrenoreceptor agonists have many of the same actions as epinephrine/adrenaline,
Kirthi Gunasekera MD Respiratory Physician National Hospital of Sri Lanka Colombo, BRONCHODILATORS: Beta Adrenoreceptor Agonists Actions Adrenoreceptor agonists have many of the same actions as epinephrine/adrenaline,
Management of COPD Updates and Evidence
 Management of COPD Updates and Evidence Providence Alaska Medical Center PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Residents Ann-Chee Cheng, PharmD Kaite Kammers, PharmD http://www.fpnotebook.com/_media/lungxsgraybb962.gif
Management of COPD Updates and Evidence Providence Alaska Medical Center PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Residents Ann-Chee Cheng, PharmD Kaite Kammers, PharmD http://www.fpnotebook.com/_media/lungxsgraybb962.gif
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary and secondary
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the management of adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in primary and secondary
UMEC/VI vs. UMEC in subjects who responded to UMEC UMEC/VI vs. VI in subjects who responded to VI
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT - ASTHMA INTERVENTION PROGRAM PREVENTS READMISSIONS IN HIGH HEALTHCARE UTILIZERS
 R2 (REVISED MANUSCRIPT BLUE 200208-877OC) ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT - ASTHMA INTERVENTION PROGRAM PREVENTS READMISSIONS IN HIGH HEALTHCARE UTILIZERS Mario Castro, M.D., M.P.H. Nina A. Zimmermann R.N. Sue
R2 (REVISED MANUSCRIPT BLUE 200208-877OC) ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT - ASTHMA INTERVENTION PROGRAM PREVENTS READMISSIONS IN HIGH HEALTHCARE UTILIZERS Mario Castro, M.D., M.P.H. Nina A. Zimmermann R.N. Sue
AECOPD: Management and Prevention
 Neil MacIntyre MD Duke University Medical Center Durham NC Professor P.J. Barnes, MD, National Heart and Lung Institute, London UK Professor Peter J. Barnes, MD National Heart and Lung Institute, London
Neil MacIntyre MD Duke University Medical Center Durham NC Professor P.J. Barnes, MD, National Heart and Lung Institute, London UK Professor Peter J. Barnes, MD National Heart and Lung Institute, London
COPD: Treatment Update Property of Presenter. Not for Reproduction. Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health
 COPD: Treatment Update Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory board, consultant, multi-center trial, research funding, Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB), or
COPD: Treatment Update Barry Make, MD Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health Disclosures Advisory board, consultant, multi-center trial, research funding, Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB), or
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
0 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Implementing NICE guidance June 2010 NICE clinical guideline 101 What this presentation covers Background Scope Key priorities for implementation Discussion Find
COPD: Current Medical Therapy
 COPD: Current Medical Therapy Angela Golden, DNP, FNP-C, FAANP Owner, NP from Home, LLC Outcomes As a result of this activity, learners will be able to: 1. List the appropriate classes of medications for
COPD: Current Medical Therapy Angela Golden, DNP, FNP-C, FAANP Owner, NP from Home, LLC Outcomes As a result of this activity, learners will be able to: 1. List the appropriate classes of medications for
Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD
 MiCMRC Educational Webinar Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD August 22, 2018 MiCMRC Educational Webinar Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD Expert Presenter: Catherine A. Meldrum PhD RN MS
MiCMRC Educational Webinar Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD August 22, 2018 MiCMRC Educational Webinar Management of Acute Exacerbations of COPD Expert Presenter: Catherine A. Meldrum PhD RN MS
CME/CE QUIZ CME/CE QUESTIONS
 CME/CE QUIZ CME/CE QUESTIONS Continuing Medical Education Accreditation The University of Cincinnati College of Medicine designates this educational activity for a maximum of 2 Category 1 credits toward
CME/CE QUIZ CME/CE QUESTIONS Continuing Medical Education Accreditation The University of Cincinnati College of Medicine designates this educational activity for a maximum of 2 Category 1 credits toward
Journal of the COPD Foundation Stem Cell Therapy for COPD: Where are we?
 148 Journal Club: Stem Cell Therapy Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Stem Cell Therapy for COPD: Where are we? Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations:
148 Journal Club: Stem Cell Therapy Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation Stem Cell Therapy for COPD: Where are we? Ron Balkissoon, MD, MSc, DIH, FRCPC 1 Abbreviations:
David M Kern 1*, Jill Davis 2, Setareh A Williams 3, Ozgur Tunceli 1, Bingcao Wu 1, Sally Hollis 4, Charlie Strange 5 and Frank Trudo 2
 Kern et al. Respiratory Research (2015) 16:52 DOI 10.1186/s12931-015-0210-x RESEARCH Open Access Comparative effectiveness of budesonide/ formoterol combination and fluticasone/ salmeterol combination
Kern et al. Respiratory Research (2015) 16:52 DOI 10.1186/s12931-015-0210-x RESEARCH Open Access Comparative effectiveness of budesonide/ formoterol combination and fluticasone/ salmeterol combination
COPD: GOLD guidelines Ijlal Babar, MD Medical Director Pulmonary CCM, Pulmonary Hypertension Center SRHS
 COPD: GOLD guidelines 2017 Ijlal Babar, MD Medical Director Pulmonary CCM, Pulmonary Hypertension Center SRHS Introduction The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) program was
COPD: GOLD guidelines 2017 Ijlal Babar, MD Medical Director Pulmonary CCM, Pulmonary Hypertension Center SRHS Introduction The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) program was
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #52 (NQF 0102): Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Long-Acting Inhaled Bronchodilator Therapy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL
Quality ID #52 (NQF 0102): Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Long-Acting Inhaled Bronchodilator Therapy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
What is COPD? COPD Pharmacotherapy. COPD Mortality Is Increasing
 COPD Pharmacotherapy Chronic Bronchitis What is COPD? 75% 17.5% Emphysema Laura C. Feemster, MD, MS Assistant Professor University of Washington Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care April 23,2015 COPD
COPD Pharmacotherapy Chronic Bronchitis What is COPD? 75% 17.5% Emphysema Laura C. Feemster, MD, MS Assistant Professor University of Washington Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care April 23,2015 COPD
Research Review. Salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (Seretide ) in COPD. Extended listing for salmeterol/fluticasone propionate in COPD
 Research Review Salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (Seretide ) in COPD Extended listing for salmeterol/fluticasone propionate in COPD In New Zealand, salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (SFC) (Seretide )
Research Review Salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (Seretide ) in COPD Extended listing for salmeterol/fluticasone propionate in COPD In New Zealand, salmeterol/fluticasone propionate (SFC) (Seretide )
Blood Eosinophils and Response to Maintenance COPD Treatment: Data from the FLAME Trial. Online Data Supplement
 Blood Eosinophils and Response to Maintenance COPD Treatment: Data from the FLAME Trial Nicolas Roche, Kenneth R. Chapman, Claus F. Vogelmeier, Felix JF Herth, Chau Thach, Robert Fogel, Petter Olsson,
Blood Eosinophils and Response to Maintenance COPD Treatment: Data from the FLAME Trial Nicolas Roche, Kenneth R. Chapman, Claus F. Vogelmeier, Felix JF Herth, Chau Thach, Robert Fogel, Petter Olsson,
Is reslizumab effective in improving quality of life and asthma control in adolescent and adult patients with poorly controlled eosinophilic asthma?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
GSK Medicine: Study Number: Title: Rationale: Study Period: Objectives: Indication: Study Investigators/Centers: Research Methods: Data Source
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Clinical and economic outcomes of multiple versus single long-acting inhalers in COPD
 Respiratory Medicine (2011) 105, 1861e1871 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed Clinical and economic outcomes of multiple versus single long-acting inhalers
Respiratory Medicine (2011) 105, 1861e1871 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed Clinical and economic outcomes of multiple versus single long-acting inhalers
COPD: Applying New Guidelines to Optimizing Evaluation and Treatment
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Roflumilast with long-acting b 2 -agonists for COPD: influence of exacerbation history
 Eur Respir J 211; 3: 553 56 DOI: 1.113/9319.1771 CopyrightßERS 211 with long-acting b 2 -agonists for COPD: influence of exacerbation history E.D. Bateman*, K.F. Rabe #,", P.M.A. Calverley +, U.M. Goehring
Eur Respir J 211; 3: 553 56 DOI: 1.113/9319.1771 CopyrightßERS 211 with long-acting b 2 -agonists for COPD: influence of exacerbation history E.D. Bateman*, K.F. Rabe #,", P.M.A. Calverley +, U.M. Goehring
Research in Real Life
 Research in Real Life Study 1: Exploratory study - identifying the benefits of pmdi versus Diskus for delivering fluticasone/salmeterol combination therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Research in Real Life Study 1: Exploratory study - identifying the benefits of pmdi versus Diskus for delivering fluticasone/salmeterol combination therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
Douglas W. Mapel MD, MPH, Melissa Roberts PhD
 Original Article Spirometry, the St. George s Respiratory Questionnaire, and other clinical measures as predictors of medical costs and COPD exacerbation events in a prospective cohort Douglas W. Mapel
Original Article Spirometry, the St. George s Respiratory Questionnaire, and other clinical measures as predictors of medical costs and COPD exacerbation events in a prospective cohort Douglas W. Mapel
CAH Participation and Quality Measure Results for Hospital Compare 2007 Discharges and Trends: National and North Carolina Results
 January 2009 CAH Participation and Quality Measure Results for Hospital Compare Discharges and - Trends: and Results Michelle Casey, MS 1, Michele Burlew, MS 2, Ira Moscovice, PhD 1 1 University of Minnesota
January 2009 CAH Participation and Quality Measure Results for Hospital Compare Discharges and - Trends: and Results Michelle Casey, MS 1, Michele Burlew, MS 2, Ira Moscovice, PhD 1 1 University of Minnesota
Report of the COPD7 Conference Conference Report Sponsored by
 Report of the COPD7 Conference 2010 Conference Report Sponsored by Report of the COPD7 Conference 2010 CONTENTS Burden of COPD Pages 3-4 Current challenges in COPD management Pages 5-6 Overcoming challenges
Report of the COPD7 Conference 2010 Conference Report Sponsored by Report of the COPD7 Conference 2010 CONTENTS Burden of COPD Pages 3-4 Current challenges in COPD management Pages 5-6 Overcoming challenges
Online supplementary material
 Online supplementary material Add-on long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) in a separate inhaler as asthma step-up therapy versus increased dose of inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) or ICS/LABA combination inhaler
Online supplementary material Add-on long-acting β2-agonist (LABA) in a separate inhaler as asthma step-up therapy versus increased dose of inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) or ICS/LABA combination inhaler
EXACERBATION ASSESSMENT FORM
 EXACERBATION ASSESSMENT FORM ID NUMBER: 0a) Form Completion Date... 0b) Staff Code... Administrative Information 1) Date of clinic visit: 2) What type of Event is this?... Participant/HCU-triggered...
EXACERBATION ASSESSMENT FORM ID NUMBER: 0a) Form Completion Date... 0b) Staff Code... Administrative Information 1) Date of clinic visit: 2) What type of Event is this?... Participant/HCU-triggered...
EXACERBATION ASSESSMENT FORM
 EXACERBATION ASSESSMENT FORM ID NUMBER: VERSION: 1.0 05/27/14 0a) Form Completion Date... 0b) Staff Code... Instructions: This form should be completed when a participant comes to the clinical center for
EXACERBATION ASSESSMENT FORM ID NUMBER: VERSION: 1.0 05/27/14 0a) Form Completion Date... 0b) Staff Code... Instructions: This form should be completed when a participant comes to the clinical center for
Clinical and radiographic predictors of GOLD-Unclassified smokers in COPDGene
 Clinical and radiographic predictors of GOLD-Unclassified smokers in COPDGene Emily S. Wan, John E. Hokanson, James R. Murphy, Elizabeth A. Regan, Barry J. Make, David A. Lynch, James D. Crapo, Edwin K.
Clinical and radiographic predictors of GOLD-Unclassified smokers in COPDGene Emily S. Wan, John E. Hokanson, James R. Murphy, Elizabeth A. Regan, Barry J. Make, David A. Lynch, James D. Crapo, Edwin K.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Lee JS, Nsa W, Hausmann LRM, et al. Quality of care for elderly patients hospitalized for pneumonia in the United States, 2006 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. Published online September
Supplementary Online Content Lee JS, Nsa W, Hausmann LRM, et al. Quality of care for elderly patients hospitalized for pneumonia in the United States, 2006 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. Published online September
Patient Care Transitions in COPD: Improving Collaboration Between Inpatient and Outpatient Providers to Reduce Readmissions
 Patient Care Transitions in COPD: Improving Collaboration Between Inpatient and Outpatient Providers to Reduce Readmissions Held in conjunction with Hospital Medicine 2017, SHM s Annual Meeting. Provided
Patient Care Transitions in COPD: Improving Collaboration Between Inpatient and Outpatient Providers to Reduce Readmissions Held in conjunction with Hospital Medicine 2017, SHM s Annual Meeting. Provided
ROBERTO P. BENZO, MD, MS
 COPD PHENOTYPES ROBERTO P. BENZO, MD, MS DIRECTOR, MINDFUL BREATHING LABORATORY MAYO CLINIC ROCHESTER, MN Dr. Benzo is the founding director of the Breathing and Behavior Laboratory, which develops and
COPD PHENOTYPES ROBERTO P. BENZO, MD, MS DIRECTOR, MINDFUL BREATHING LABORATORY MAYO CLINIC ROCHESTER, MN Dr. Benzo is the founding director of the Breathing and Behavior Laboratory, which develops and
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES
 APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 6, Issue 12 Newsletter Date: December 2014 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: COPD Simvastatin for the prevention of exacerbations in moderate-to severe COPD
APSR RESPIRATORY UPDATES Volume 6, Issue 12 Newsletter Date: December 2014 APSR EDUCATION PUBLICATION Inside this issue: COPD Simvastatin for the prevention of exacerbations in moderate-to severe COPD
The National Asthma Education and Prevention Program s
 Long-Acting b-agonist Among Children and Adults With Asthma Elizabeth A. Wasilevich, PhD, MPH; Sarah J. Clark, MPH; Lisa M. Cohn, MS; and Kevin J. Dombkowski, DrPH Managed Care & Healthcare Communications,
Long-Acting b-agonist Among Children and Adults With Asthma Elizabeth A. Wasilevich, PhD, MPH; Sarah J. Clark, MPH; Lisa M. Cohn, MS; and Kevin J. Dombkowski, DrPH Managed Care & Healthcare Communications,
