Study of dynamic lung parameters in bronchial Asthma
|
|
|
- Barrie Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 20; 4(1): ISSN Print: ISSN Online: Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): Received: Accepted: Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate Professor, Department of Physiology, VIMSAR, Burla, Sambalpur, Dr. Tanmoy Mohanty Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, SCB Medical College, Cuttack, Dr. Sunil Kumar Jena Assistant Professor, Department of Physiology, VIMSAR, Burla, Sambalpur, Study of dynamic lung parameters in bronchial Asthma Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik, Dr. Tanmoy Mohanty and Dr. Sunil Kumar Jena Abstract Introduction: Bronchial asthma is a chronic disease of airways which affects children as well as adults. Pulmonary function test is an easy and non-invasive technique to diagnose and assess the severity of the disease. Our aim was to assess the severity of the disease by spirometry. Material and method: Spirometry was done in forty bronchial asthma patients and equal number of healthy individuals of similar age range of 20-60yr. Dynamic lung parameters like FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC%, PEFR, MEFR, MMEFR were recorded. Tests were repeated after inhalation of 2 puffs of salbutamol in asthma patients and improvement were recorded. Statistical analysis was done by SPSS 16. Result: There was marked improvement in the values of all parameters as compared to the control group. After bronchodilator inhalation there was significant improvement in the parameters specially marked in case of FEV1(38.5%), PEFR(40%), MMEFR(25.5%). Conclusion: Pulmonary function test is a simple non-invasive method to diagnose and assess the improvement during treatment in patients of bronchial asthma. Keywords: Pulmonary function test, Spirometry, Bronchial asthma, salbutamol Introduction The NHLBI defined asthma in 2002 as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which many cells and cellular elements play a role. The chronic inflammation causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness chest tightness and coughing, particularly at night and in the early morning. These episodes are usually associated with widespread but variable airflow obstruction that is often reversible either spontaneously or with treatment [1]. PREVALENCE-Asthma is one of the most common chronic diseases globally and currently affects approximately 300 million people worldwide. The prevalence of asthma has risen in affluent countries over the last 30 years but now appears to have stabilized with approximately 10-20% of adults and 15% of children affected by the disease. In developing countries where the prevalence of asthma had been much lower, there is a rising prevalence of, which is associated with increased urbanization. The prevalence of atopy and other allergic diseases has also increased at the same time, suggesting that the reasons for the increase are likely to be systemic rather than confined to the lungs. Most patients with asthma in affluent countries are atopic, with allergic sensitization to the house dust mite, other environmental allergens such as animal fur & pollens. Asthma can present at any age, with a peak age of 3 years. In childhood, more males are affected, but by adulthood sex ratio has equalized. Several risk factors that predisposes to asthma have been identified like [2] Correspondence Dr. Tanmoy Mohanty Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, SCB Medical College, Cuttack, Endogenous Factors Environmental Factors Genetic predisposition Indoor allergens Atopy Outdoor allergens Airway hyper responsiveness Occupational sensitizers Gender Passive smoking Ethnicity Respiratory infections Obesity Diet ~ 312 ~
2 Pulmonary function test: The diagnosis of asthma is usually apparent from the symptoms of variable and intermittent airways obstruction, but must be confirmed by objective measurements of lung functions. CIBA Guest Symposium in1959 accepted the following tests as essential in any case of obstructive pulmonary disease [3]. 1. Forced vital capacity 2. Forced expiratory volume in first second of expiration 3. FEV1/FVC percentage Material & Method: The present study was carried out on forty selected individuals of bronchial asthma attending the outpatients department of Medicine, Pulmonary medicine VIMSAR. Forty healthy adults of the same age group and sex distribution volunteered as control in the present study. Patients having recent respiratory tract infection and having any other medical illness were excluded from study. All subjects were informed about the purpose of the study and tests were done after taking their consent. Pulmonary function test was done on all the subjects using computerised spirometer, which is a precalibrated electronic spirometer. Following dynamic lung parameters were recorded i.e. FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC%, PEFR, MEFR & MMEFR. After the initial reading (premedication reading), 2 puffs of Salbutamol (40 micrograms) was inhaled by each bronchial asthma patient and the test was repeated. Precautions- The patients exposed to this study were instructed to discontinue bronchodilator preceeding eight hours of test to make sure that there is no residual bronchodilator effect. Technique for inhalation from Metered Dose Inhaler: The inhaler is held upright between thumb and forefinger. The mouth piece of the inhaler is brought to about 2-4 cm in front of an open mouth. The person breathes out slowly and completely. The inhaler is activated by pressing down the canister while taking a slow, deep breath in 5-6 seconds. Breath is held at full inspiration for 10 seconds. The person should wait for 1 to 3 minutes before taking next puff. Salbutamol inhaler contains 200 metered doses of salbutamol, each puff releasing 100 micrograms. When the patient follows proper technique nearly 10-20% of the drug (20 microgram) is delivered from the inhaler to the lungs and the remaining part gets deposited in the mouth, pharynx and larynx as observered by Dolovich in 1981 [4]. The post medication values were compared with the premedication values in asthmatics. Statistical analysis was done by statistical software SPSS16. Statistical tests applied were unpaired t test and paired t test. P value <0.05 was considered to be significant. Observation Table 1: Comparison between Age, Height, Weight and BSA of study and control group Age (years) Height (cm) Weight (kg) BSA (Sq mt) study control study control study Control Study control Mean±SD 39.7± ± ± ± ± ± ± ±0.11 the mean age, mean height and mean body surface area (BSA) of subjects of study and control group. SD-Standard Deviation. Sq mt -square meter Table 2: Spirometric Values in Male (mean) Age(yrs) (20-24) (25-34) (35-44) (45-54) (55>) n=2 n=6 n=3 n=3 n=6 FVC (L) FEV1 (L) FEV1/FVC% PEFR (L//min) The above table shows the spirometric values of control male subjects of present study in different age groups Table 3: Spirometric Values Female (mean) Age(yrs) (20-24) (25-34) (35-44) (45-54) (55>) n=2 n=5 n=6 n=5 n=2 FVC (L) FEV1 (L) FEV1/FVC% PEFR (L/min) The above table shows the spirometric values of control female subjects of present study in different age groups. Table 4: Comparison between mean Respiratory Rate, FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC% Respiratory Rate (breath/min) FVC(ml) FEV1(ml) FEV1/FVC% Study Control Study Control Study Control Study Control n=40 n=40 n=40 n=40 n=40 n=40 n=40 n=40 Mean SD SE t test P <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 the study and control groups. The differences between the two groups are statistically highly significant as p value is less than means, t - Unpaired t test, FVC-Force vital capacity, FEV1=Forced expiratory volume in 1 st second, ~ 313 ~
3 Table 5: Comparison between PEFR, MEFR and MMEFR PEFR(L/min) MEFR(L/min) MMEFR(L/min) Study control Study control Study control MEAN SD SE t test P <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 premedication study cases & control groups. The difference between the two groups are statistically highly significant as p value is less than means. t -Unpaired t test PEFR=Peak expiratory flow rate, MEFR=Maximum expiratory flow rate, MMEFR=Maximum mid expiratory flow rate. Table 6: Comparison between Respiratory Rate, FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC% of Post medication study cases and Control Group Resp rate (breath/min) FVC(ml/breath) FEV1(ml/breath) FEV1/FVC % Study control Study control Study control Study control Mean SD SE t test P <0.001 <0.01 <0.001 <0.001 postmedication study cases and control groups. The difference between the two groups are statistically highly significant as the p value is less than means, t - Unpaired t test, FVC-Force vital capacity, FEV1=Forced expiratory volume in 1 st second, Table 7: Comparison between PEFR, MEFR & MMEFR of post-medication study cases and control subjects PEFR(L/min) MEFR(L/min) MMEFR(L/min) Study control Study control Study control Mean SD SE T test P <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 postmedication study cases & control groups. The difference between the two groups are statistically highly significant as p value is less than means. t -Unpaired t test PEFR=Peak expiratory flow rate, MEFR=Maximum expiratory flow rate, MMEFR=Maximum mid expiratory flow rate. Table 8: Comparison between Respiratory rate, FVC, FEV1 and FEV1/FVC% of Premedication & Postmedication study cases. Resp. rate (breath/min) FVC(ml/breath) FEV1(ml/breath) FEV1/FVC% Premed Postmed Premed Postmed Premed Postmed Premed Postmed MEAN SD SE t test P <0.01 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 % change 12% % 38.5% 17.7% Premedication and Postmedication study cases. The difference between the two groups are statistically significant as indicated by the p value (< 0.001). means, t - Paired t test, FVC-Force vital capacity, FEV1=Forced expiratory volume in 1 st second Table 9: Comparison between PEFR,,MEFR & MMEFR of premedication and postmedication study cases PEFR(L/min) MEFR(L/min) MMEFR(L/min) Premed Postmed Premed Postmed Premed Postmed MEAN SD SE t test P <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 % change 40.83% 21.67% 21.51% ~ 314 ~
4 Premedication and Postmedication study cases. The difference between the two groups are statistically significant as indicated by the p value(< 0.001),more so in PEFR as there is 40.83% improvement means. t -Paired t test PEFR=Peak expiratory flow rate, MEFR=Maximum expiratory flow rate, MMEFR=Maximum mid expiratory flow rate. Table 10: Normal Expected Spirometric Values (mean±sd) MALE-INDIA Age (yrs) (15-19) (20-24) (25-34) (35-44) (45-54) (55>) FVC SD FEV SD FEV1/FVC% SD PEFR (L/min) SD Table 11: Normal Expected Spirometric Values (Mean±Sd) Female India Age(yrs) (15-19) (20-24) (25-34) (35-44) (45-54) (55>) FVC SD FEV SD FEV1/FVC % SD PEFR(L/min) Table 12: Effect Of Salbutamol on FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC%, PEFR, MEFR & MMEFR (In different age groups) n=40+40 FVC (ml) FEV1 (ml) FEV1/FVC % PERF (L/min) MEFR MMEFR Age Group (20-40 YRS) PRE MED POST MED % Increase ± ± ± ± ±5.90 ± ±71.29 ± ±60.46 ± ±59.58 ± Age Group (41-60 YRS) PRE MED POST MED % Increase ± ± ± ± ±8.93 ± ±80.61 ± ±43.89 ± ±36.56 ± Table 13: Effect of Salbutamol on FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC%, PEFR, MEFR & MMEFR (In different sexes) n=40+40 FVC (ml) FVC1 (ml) FEV1/FVC % PERF (L/min) MEFR MMEFR PRE MED ± ± ± ± ± ±58.88 Male POST MED ± ± ± ± ± ±58.88 % Increase PRE MED 1988 ± ± ± ± ± ±40.92 Female POST MED ± ± ± ± ± ±52.97 % Increase ~ 315 ~
5 Comparison between premedication, Post medication & control FEV1(ml) present study Comparision between Premedication, Post medication & control. PEFR Discussion In the present study, age, height, weight and body surface area of the control group are almost similar to the study group in the age group of years as evident from observation table no-1 Several workers have tried to standardise the pulmonary function parameters in different age groups in India. When compared to the findings of Pande et al. [4] (table-10 & table- 11) in the present study it was found that FVC,FEV1in all age groups (table 2 &3 ) in males is almost similar to their values. The FEV1% was lower in all age groups in males& lower values were found for PEFR. When the parameters in the present study were compared for female control cases, the FVC values were almost similar in all age groups, but higher values were found for FEV1, FEV1% & PEFR. ~ 316 ~ In the study group, the values of mean premedication FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC%, PEFR, MEFR and MMEFR are lower than the mean control values as shown in observation table no-4 & 5.The decrease was statistically significant. These findings correlated to that of Puri et al. (1975) [5], Mahajan et al. [6] and Bhalla et al. (1979) [7]. They observed a significant decrease in the mean FVC, FEV1 and FEV1/FVC% in cases of Bronchial asthma. The mean premedication value of PEFR and MMEFR of the study cases are significantly lower as compared to the mean control values suggesting obstruction of large and small airways respectively. These findings are similar to those of Bhalla et al. (1979) [7]. Who observed similar low values of PEFR & MMEFR. The mean premedication value of MEFR is also significantly lower than the mean control values as seen in
6 observation table no-5, which suggests that there is obstruction of medium sized airways. This finding correlates with those of Bhalla et al. (1979) [7] who found significant low values of MEFR in bronchial asthma. The study cases showed significant lower values in dynamic lung parameters like FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC%, PEFR & MMEFR as compared to control subjects. This indicates the presence of airway obstruction. After 10 minutes of administration of 2 puffs of Salbutamol, lung parameters were assessed. The post medication values showed statistically significant increase over the premedication values. This confirmed the diagnosis of asthma as per the criteria fixed by Mc Fadden [8]. FVC: Observation table no-8 shows % improvement of mean postmedication FVC as compared to premedication FVC. the finding is similar to Jindal et al. (1989) [9] and Guleria et al. (1991) [10]. FEV1: Study cases showed a significant improvement of 38.5% of mean FEV1 after bronchodilator inhalation. This finding correlates well with Puri et al. (1975) [6], Guleria et al. (1991) & Nissar et al. [11] who also observed more than 15% improvement after bronchodilator inhalation. FEV1/FVC%: In the present study an improvement of 17.7% was seen after Salbutamol inhalation, which was similar to the observations of Jindal et al. (1989) [9] & Guleria et al. (1991) [10]. PEFR: Showed a 40.8% improvement of postmedication values over premedication values. This correlates with the findings of Puri et al. (1975) [6], Banerjee et al. (1975) [12] & Guleria et al. (1991) [10] MEFR: Table -9 shows significant improvement of MEFR of 21.6% after salbutamol. This correlates with the findings of Puri et al. [6] & Guleria et al. (1991) [10] According to Mc Fadden (1981) [8] the diagnosis of asthma is established by observing 25% or greater improvement of at least two parameters after inhalation of a beta agonists in symptomatic asthmatics. In the study subjects there was more than 25% increase in values (FEV1-38.5%, PEFR- 40.8%, MMEFR-25.5%). This confirms the Diagnosis of Asthma. But the parameters were not totally reversible as the postmedication values were lower than control values (Table no-6 &7). Table no-13 gives a comparative study of effect of salbutamol on both the sexes. All the lung parameters showed similar degree of reversibility in both the sexes except FEV1 & FEV1/FVC%. In female subjects they showed higher reversibility. This was explained by the fact that more numbers of mild cases of asthma were included in the female groups. Regarding the reversibility in different age groups, the younger age groups (20-40yrs) showed better reversibility than the older age groups (41-60yrs) as seen in table no-12 in all the three parameters like FEV1, PEFR and MMEFR. This is similar to the findings of Hudon et al. (1997). [13] & Jindal et al. (1996) [9]. They found that progressive decrease in the number & function of beta receptors is the main cause. Pathak et al. & Kenneth et al. (1997) [14]. attributed this to replacement of elastic tissue by fibrous tissues and emphysematous change in alveoli in long standing bronchial asthma. Conclusion The following conclusions have been derived from the present study that airway hyper responsiveness and edema of the bronchial wall are the principal causes of bronchospasm in bronchial asthma. Bronchodilators when administered in aerosol form, relieves bronchospasm with minimum side effects. Pulmonary function tests reflect the severity and document the reversibility of airway obstruction after bronchodilator therapy. Even though other tests are available these simple non-invasive tests will help the clinicians in diagnosis of asthma by differentiating from other conditions with wheeze. References 1. Expert panel report: Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma Update on selected topics, 2002, J. Allergy clin immunology 110:S141-S2, Peter J Barnes, Asthma, 309 Harrison s Textbook of Medicine: 2016; 309: CIBA Guest Symposium: Thorax, 14:286, Dolovich M: Optimal delivery of aerosols from metered dose inhalers., Chest., 80suppl: , Pandey J. Resp Medicine in Tropics, Puri M B, Gupta S, Singh S. J. Assoc. Physiol. India., 1975; 23: Mahajan KK, Maini SK, Mahajan SK: Indian J. Physiol & Pharma., 1978; 22: Mc Fadden ER Jr. An analysis of exercise as a stimulus for production of airway obstruction., Lung. 1981; 3: Jindal SK, Gupta D. Inhalation therapy, Indian J of Chest Dis. & All.Sci., 1996; 38: Guleria R, Behera D, Jindak SK. Indian. J. Med. Res., 1979; 61: Nissar M, Evas JE, Pearson MG, Claverly PM. Bronchodilator trials in COPD, AM. Rev. of Resp. Dis. 1992; 146: Banerjee DK, Lee GS, Malik SK, Dali S. British J. of Dis.Chest, 1987; 81(1): Hudon C. Characteristics of Bronchial Asthma with incomplete reversibility of airflow obstruction, Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunology. 1997; 78(2): Kenneth S Backman, Paul A Greenberger. Airway obstruction in patients with longterm asthma consistent with irreversible asthma, Chest. 1997; 112: ~ 317 ~
Asthma in the Athlete
 Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
SCREENING AND PREVENTION
 These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
SPIROMETRY TECHNIQUE. Jim Reid New Zealand
 Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians 2013/California Academy of Family Physicians
 Family Medicine and Patient-Centered Asthma Care Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians Faculty: Hobart Lee, MD Disclosures: Jeffrey Luther, MD, Program Director, Memorial Family Medicine
Family Medicine and Patient-Centered Asthma Care Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians Faculty: Hobart Lee, MD Disclosures: Jeffrey Luther, MD, Program Director, Memorial Family Medicine
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Differential diagnosis The onset of COPD is insidious. Pathological changes may begin years before symptoms appear. The major differential diagnosis is asthma, and in some cases, a clear distinction between
Asthma Assessment & Review
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
/FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan
 Article FEV 1, FVC, FEV 1 /FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan Meenakshi Sharma 1, Rambabu Sharma 2, Neelam Singh 3, Kusum Gaur 4 Abstract Background: The knowledge of pulmonary
Article FEV 1, FVC, FEV 1 /FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan Meenakshi Sharma 1, Rambabu Sharma 2, Neelam Singh 3, Kusum Gaur 4 Abstract Background: The knowledge of pulmonary
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 2 Issue 3 July - Sep Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2013 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 23 th May 2013 Revised: 24 th Jun 2013 Accepted:
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 2 Issue 3 July - Sep Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2013 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 23 th May 2013 Revised: 24 th Jun 2013 Accepted:
What is Asthma? Chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Night time or early morning coughing
 Asthma What is Asthma? Chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Night time or early morning coughing Episodes are usually associated with widespread, but
Asthma What is Asthma? Chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Night time or early morning coughing Episodes are usually associated with widespread, but
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide.
 Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Q. What is a Peak-Flow Meter? A. It is an instrument that measures Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR). PEFR is the amount of air a person can blow out
 1 2 Q. What is a Peak-Flow Meter? A. It is an instrument that measures Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR). PEFR is the amount of air a person can blow out during a forced expiration after taking in as full
1 2 Q. What is a Peak-Flow Meter? A. It is an instrument that measures Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR). PEFR is the amount of air a person can blow out during a forced expiration after taking in as full
Speaker Disclosure. Identification and Diagnosis of Asthma. Definition of Asthma. Objectives 11/9/2017
 Speaker Disclosure Identification and Diagnosis of Asthma Isabel L. Virella Lowell, MD, Associate Professor, Pulmonology and Sleep Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham Isabel Virella-Lowell, MD
Speaker Disclosure Identification and Diagnosis of Asthma Isabel L. Virella Lowell, MD, Associate Professor, Pulmonology and Sleep Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham Isabel Virella-Lowell, MD
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN BASKET OF CARE SUBCOMMITTEE Report to: Minnesota Department of Health. June 22, 2009
 This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN
This document is made available electronically by the Minnesota Legislative Reference Library as part of an ongoing digital archiving project. http://www.leg.state.mn.us/lrl/lrl.asp ASTHMA CARE FOR CHILDREN
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Research Article STUDY OF ASTHMA QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE: AN INSTRUMENT FOR REVIEWING ASTHMA HEALTH EDUCATION AND PROMOTION
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Research Article STUDY OF ASTHMA QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE: AN INSTRUMENT FOR REVIEWING ASTHMA HEALTH EDUCATION AND PROMOTION
Spirometry: Introduction
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO)
 Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Outline FEF Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications?
 Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Known Allergies: Shellfish. Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, or vomiting. congestion, trouble breathing, or wheezing.
 CSTAR CASE STUDIES: BLOCK B Asthma or COPD? Setting: Walk in clinic. Dan: I havi g that cough thi g agai HPI: Dan is a 49-year-old male teacher who reports having had episodes of cough with mucus production
CSTAR CASE STUDIES: BLOCK B Asthma or COPD? Setting: Walk in clinic. Dan: I havi g that cough thi g agai HPI: Dan is a 49-year-old male teacher who reports having had episodes of cough with mucus production
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer
 Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Using an Inhaler and Nebulizer Introduction An inhaler is a handheld device that is used to deliver medication directly to your airways. A nebulizer is an electric or battery powered machine that turns
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control
 Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Content Indica c tion Lung v olumes e & Lung Indica c tions i n c paci c ties
 Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Avg PM10. Avg Low Temp
 Geography 532 Geography of Environmental Health Dr. Paul Marr Name: Ex 16- Seasonality, Time Delay, and Disease (10 pts) Below are asthma cases per month for the years 1992-1994. The table also includes
Geography 532 Geography of Environmental Health Dr. Paul Marr Name: Ex 16- Seasonality, Time Delay, and Disease (10 pts) Below are asthma cases per month for the years 1992-1994. The table also includes
HealthPartners Care Coordination Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide ASTHMA
 The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
Bronchial asthma. E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics. Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013
 Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist, District Early Intervention Programme National Health Mission, Ambikapur, Chattisgarh, India
 (Volume2, Issue6) Available online at www.ijarnd.com Evaluation of Peak Expiratory Flow Rate and Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second in Indian Children with Suspected Asthma Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist,
(Volume2, Issue6) Available online at www.ijarnd.com Evaluation of Peak Expiratory Flow Rate and Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second in Indian Children with Suspected Asthma Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist,
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction
 Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C
 MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C Explain the importance of objective measures in the management of asthma Explain the different types of objective measures used in the management
MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C Explain the importance of objective measures in the management of asthma Explain the different types of objective measures used in the management
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring
 Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
File: Spirometry-Vimeo 720p-MP3 for Audio Podcasting.mp3 Duration: 0:07:09 Date: 05/02/2014 START AUDIO
 BMJ LEARNING VIDEO TRANSCRIPT File: Spirometry-Vimeo 720p-MP3 for Audio Podcasting.mp3 Duration: 0:07:09 Date: 05/02/2014 START AUDIO Dr Kevin Gruffyd-Jones: Spirometry is important in several ways. Firstly,
BMJ LEARNING VIDEO TRANSCRIPT File: Spirometry-Vimeo 720p-MP3 for Audio Podcasting.mp3 Duration: 0:07:09 Date: 05/02/2014 START AUDIO Dr Kevin Gruffyd-Jones: Spirometry is important in several ways. Firstly,
Assessment of Bronchodilator Response in Various Spirometric Patterns
 Original Article 2013 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS Assessment of Bronchodilator Response in Various Spirometric Patterns Amir Houshang
Original Article 2013 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS Assessment of Bronchodilator Response in Various Spirometric Patterns Amir Houshang
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh
 BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2005; VOL 29 (3) : 93-98 Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh JU MAZUMDER 1, S AHMED 2, AH MOLLAH 3, ARML KABIR 4,
BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2005; VOL 29 (3) : 93-98 Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh JU MAZUMDER 1, S AHMED 2, AH MOLLAH 3, ARML KABIR 4,
COPD/ Asthma. Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer
 COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems
 Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems Learning Objectives 1. State the parts of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and give the functions of each part. 2. Identify the parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems Learning Objectives 1. State the parts of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and give the functions of each part. 2. Identify the parts of the cardiovascular
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma?
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Evaluation of efficacy and utility of spirometry data in elderly
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20185109 Evaluation of efficacy
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20185109 Evaluation of efficacy
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April-2016 1644 Interpretation of Bronchodilator Response for Assessment of Airway Obstruction. Dr.S. meenakshi ABSTRACT:
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April-2016 1644 Interpretation of Bronchodilator Response for Assessment of Airway Obstruction. Dr.S. meenakshi ABSTRACT:
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Breathing and pulmonary function
 EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
Pathway diagrams Annex F
 Pathway diagrams Annex F Fig 1 Asthma: The patient journey Asthma is diagnosed Making the diagnosis of asthma Confirming the diagnosis may depend on history, response to treatment, measurement of airflow
Pathway diagrams Annex F Fig 1 Asthma: The patient journey Asthma is diagnosed Making the diagnosis of asthma Confirming the diagnosis may depend on history, response to treatment, measurement of airflow
Asthma. Guide to Good Health. Healthy Living Guide
 Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
A Guide for Students and Parents
 A Guide for Students and Parents February 20, 2009 This program was made possible through an unrestricted grant from: Monaghan Medical Corporation, Lupin Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Forest Laboratories Inc.
A Guide for Students and Parents February 20, 2009 This program was made possible through an unrestricted grant from: Monaghan Medical Corporation, Lupin Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Forest Laboratories Inc.
Spirometry: FEVER DISEASE DIABETES HOW RELIABLE IS THIS? 9/2/2010 BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools
 SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists
 Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Respiratory Pharmacology PCTH 400 Asthma and β-agonists Dr. Tillie-Louise Hackett Department of Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics University of British Columbia Associate Director, Centre of
Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District
 Original Research Article Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District V. Sivagangailakshmi 1*,
Original Research Article Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District V. Sivagangailakshmi 1*,
INFLUENCE OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE ON LUNG FUNCTIONS IN ASTHMATIC FEMALES
 INFLUENCE OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE ON LUNG FUNCTIONS IN ASTHMATIC FEMALES *Dimple Arora 1, Parminder Kaur 1, Mohit Arora 2 and Urmil Gupta 3 1 Department of Physiology, Sri Guru Ramdas Institute of Medical Sciences
INFLUENCE OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE ON LUNG FUNCTIONS IN ASTHMATIC FEMALES *Dimple Arora 1, Parminder Kaur 1, Mohit Arora 2 and Urmil Gupta 3 1 Department of Physiology, Sri Guru Ramdas Institute of Medical Sciences
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
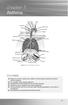 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Pulmonary Function Tests. Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist
 Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests
 6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
Evolution of asthma from childhood. Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT
 Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016
 Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
I have no perceived conflicts of interest or commercial relationships to disclose.
 ASTHMA BASICS Michelle Dickens RN FNP-C AE-C Nurse Practitioner/Certified Asthma Educator Ferrell Duncan Allergy/Asthma/Immunology Coordinator, CoxHealth Asthma Center DISCLOSURES I have no perceived conflicts
ASTHMA BASICS Michelle Dickens RN FNP-C AE-C Nurse Practitioner/Certified Asthma Educator Ferrell Duncan Allergy/Asthma/Immunology Coordinator, CoxHealth Asthma Center DISCLOSURES I have no perceived conflicts
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes
 Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Assessment of reversibility of airway obstruction. disease. in patients with chronic obstructive airways. FEVy after salbutamol occurred in the
 19 Regional Thoracic Unit, Fazakerley Hospital, Liverpool M Nisar M Walshaw J E Earis M G Pearson P M A Calverley Address for reprint requests: Dr P M A Calverley, Fazakerley Hospital, Liverpool, L9 7AL.
19 Regional Thoracic Unit, Fazakerley Hospital, Liverpool M Nisar M Walshaw J E Earis M G Pearson P M A Calverley Address for reprint requests: Dr P M A Calverley, Fazakerley Hospital, Liverpool, L9 7AL.
Defining COPD. Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist
 Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Outpatient Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Outpatient Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Initial Visit Follow-Up Visits See page 2 Asthma Diagnosis See page 3 Classifying Asthma Severity and Initiating Treatment See pages 2 and
Outpatient Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Initial Visit Follow-Up Visits See page 2 Asthma Diagnosis See page 3 Classifying Asthma Severity and Initiating Treatment See pages 2 and
Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement
 Shortness of breath THEME Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement BACKGROUND Respiratory disease is common and amenable to early detection and management in the primary care setting. Spirometric
Shortness of breath THEME Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement BACKGROUND Respiratory disease is common and amenable to early detection and management in the primary care setting. Spirometric
Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol)
 Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol) For inhalation use Important: Read instructions carefully Wash your inhaler once a week and allow to dry What you need
Ventamol CFC-Free 100 micrograms, Pressurised Inhalation, Suspension (Salbutamol) For inhalation use Important: Read instructions carefully Wash your inhaler once a week and allow to dry What you need
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
What do pulmonary function tests tell you?
 Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics
 8 Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics Dr. Nilay A. Kapadia*, Dr. Ashok Goswami**, Dr. Prakash Chaudhari*, Dr. Kalpan Desai*Dr Janardan V Bhatt @ *P.G.Student, Department
8 Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics Dr. Nilay A. Kapadia*, Dr. Ashok Goswami**, Dr. Prakash Chaudhari*, Dr. Kalpan Desai*Dr Janardan V Bhatt @ *P.G.Student, Department
Systems Pharmacology Respiratory Pharmacology. Lecture series : General outline
 Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 3/12/2018
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
EVALUATION OF HIGH SENSITIVITY C REACTIVE PROTEIN LEVELS IN BRONCHIAL ASTHMA
 Bio chemistry Original Article International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 3, Issue 3, May-Jun 2015. Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. EVALUATION OF HIGH SENSITIVITY
Bio chemistry Original Article International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 3, Issue 3, May-Jun 2015. Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. EVALUATION OF HIGH SENSITIVITY
Interpreting Spirometry. Vikki Knowles BSc(Hons) RGN Respiratory Nurse Consultant G & W`CCG
 Interpreting Spirometry Vikki Knowles BSc(Hons) RGN Respiratory Nurse Consultant G & W`CCG Why Spirometry? supports diagnosis classifies defect - obstructive/restrictive assesses -severity of defect -
Interpreting Spirometry Vikki Knowles BSc(Hons) RGN Respiratory Nurse Consultant G & W`CCG Why Spirometry? supports diagnosis classifies defect - obstructive/restrictive assesses -severity of defect -
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 2/5/2019
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
7/7/2015. Somboon Chansakulporn, MD. History of variable respiratory symptoms. 1. Documented excessive variability in PFT ( 1 test)
 Definition of Asthma GINA 2010: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways Airway hyper-responsiveness Recurrent wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing Variable, reversible airflow obstruction
Definition of Asthma GINA 2010: Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways Airway hyper-responsiveness Recurrent wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, coughing Variable, reversible airflow obstruction
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP?
 THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
THE NHLBI GUIDELINES: WHERE DO WE STAND AND WHAT IS THE NEW DIRECTION FROM THE NAEPP? Peter S. Creticos, MD ABSTRACT In 1991 and 1997, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute s National Asthma Education
Play acting Asthma attack
 1 ASTHMA Date: 16/10/06 By: ismile Health Info Inforeach Communications Sdn Bhd. Tel: 03-42946368 You cough, wheeze and feel tightness in your chest. Suddenly, your airways narrow and you gasp for breath.
1 ASTHMA Date: 16/10/06 By: ismile Health Info Inforeach Communications Sdn Bhd. Tel: 03-42946368 You cough, wheeze and feel tightness in your chest. Suddenly, your airways narrow and you gasp for breath.
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma 101. Introduction
 TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek
 Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek 1 in 11 people are currently receiving treatment for asthma (5.4 million people in the UK) Every 10 seconds, someone is having a potentially life-threatening asthma attack
Allwin Mercer Dr Andrew Zurek 1 in 11 people are currently receiving treatment for asthma (5.4 million people in the UK) Every 10 seconds, someone is having a potentially life-threatening asthma attack
To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry
 Original Research Article To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry Dhipu Mathew 1, Kirthana G 2, Krishnapriya R 1, Srinivasan R 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry Dhipu Mathew 1, Kirthana G 2, Krishnapriya R 1, Srinivasan R 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Peak expiratory flow rate and its correlation with body surface area in healthy school children
 2014; 3(4): 397-401 Available online at: www.jsirjournal.com Research Article ISSN 2320-4818 JSIR 2014; 3(4): 397-401 2014, All rights reserved Received: 11-09-2014 Accepted: 22-09-2014 Dr. K. Vijay Krishna
2014; 3(4): 397-401 Available online at: www.jsirjournal.com Research Article ISSN 2320-4818 JSIR 2014; 3(4): 397-401 2014, All rights reserved Received: 11-09-2014 Accepted: 22-09-2014 Dr. K. Vijay Krishna
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
