Bronchial Asthma and Acupuncture
|
|
|
- Cecilia McBride
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BRIEFING PAPER No 8 Bronchial Asthma and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council February 2002
2 The Evidence Series of Briefing Papers aims to provide a review of the key papers in the literature, which provide evidence of the effectiveness of acupuncture in the treatment of specific conditions. The sources of evidence will be clearly identified ranging from clinical trials, outcome studies and case studies. In particular this series of briefing papers will seek to present, discuss and critically evaluate the evidence. BRONCHIAL ASTHMA AND ACUPUNCTURE: THE EVIDENCE FOR EFFECTIVENESS Summary This paper reviews a number of clinical trials and outcome studies on the use of acupuncture to treat asthma. None of the trials had a large sample size and they suffer from the problems common to all acupuncture trials, such as what constitutes appropriate treatment and a suitable control. The outcome studies avoid some of these problems but many lack rigour or adequate description of measurements used. This paper reviews the trials that appeared most sound in methodological terms, together with those outcome studies that had relatively large samples. The trials are divided into two groups: those treating patients as part of normal clinical management and those treating patients suffering an induced asthma attack. The findings for the first group are inconsistent, particularly as regards objective measures of lung function. There is, however, evidence that acupuncture can improve patients subjective experience of their symptoms, reduce their use of medication and improve immunological parameters. The smaller number of trials of induced asthma is more consistently positive. The majority of trials provide an inadequate rationale for the acupuncture points used and few bear any relationship to the way acupuncture is actually practised by British Acupuncture Council members. The outcome studies generally provide a much better picture of the diagnostic criteria used and show more consistently positive results than the trials, but their methodology is often weak. The paper concludes by discussing some of the issues that need to be addressed in developing clinically relevant and methodologically sound research. Introduction. It is estimated that asthma affects approximately 10% of the population. Both incidence of the disease and resulting mortality are increasing (Howell, 2000). The definition of asthma is not, however, clear-cut. Howell (2000) identified three elements: reversible airways obstruction with episodic attacks of breathlessness accompanied by wheezing; responsiveness to asthma drugs (cromoglycate and/or corticosteroids); bronchial hypersensitiveness. In practice, however, none of these provides an absolute criterion for distinguishing asthma from other breathing problems and asthmatics are defined as those with reversible airways obstruction and/or clear responsiveness to asthma medication. The management of asthma often requires daily use of medication on a prophylactic basis. Severe attacks may require hospitalisation and can lead to death. Asthma thus has high economic and personal costs. Lewith and Watkins (1996) suggested that asthma costs the NHS about 400 million per annum; the Department of Social Security, in the form of sickness benefits, 60 million; the economy as a whole, in terms of lost productivity, 350 million.
3 Literature Search A search was carried out using the ARRCBASE, the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre database of articles drawn from the British Library s AMED and the US MEDLINE, using the terms asthma, breathlessness and acupuncture. Sixty-one references were identified and an additional twenty-two were derived from citations in these papers. Papers were excluded for variety of reasons: no English translation was available; the paper was unobtainable from the British Library; the paper was not primarily concerned with presenting or reviewing clinical evidence; the study involved therapies other than acupuncture or did not use needles. The remainder could be grouped into three categories: reviews, descriptions of a randomised controlled trial (RCT) and descriptions of an outcome study. Reviews were only included if they had been published after 1990, on the grounds that earlier publications would have been superseded. Some RCTs were excluded on the grounds of their weak methodology. For trials prior to 1990, the system of evaluating methodological quality set out by Kleijnen et al (1991) was used to exclude those which scored below 40. Trials since 1990 were included if fully randomised. Outcome studies were included if they used significantly larger sample sizes than the RCTs. The papers finally selected comprise 6 reviews, 11 controlled trials, and four outcome studies. Reviews Two of the reviews (Kleijnen et al (1991) and Linde et al (2000)) focused on the methodological quality of the trials reviewed. Kleijnen et al (1991) reviewed 13 trials, which were evaluated against 18 predefined methodological criteria and scored out of 100. Only 8 studies scored above 50 and no paper scored above 72, leading the authors to conclude that no conclusion as to acupuncture s effectiveness could be drawn due to the poor quality of the trials. A similar conclusion was reached in the most recent review carried out by Linde, Jobst and Panton (Linde et al 2001) as part of the Cochrane Collaboration. This review involved tight selection criteria: of 21 trials identified, only seven were regarded as worthy of inclusion. The aim of the Cochrane collaboration is to provide overall analyses that can show conclusively whether there is evidence in favour of particular medical interventions. The authors argued that the heterogeneous nature of the acupuncture trials precluded such an analysis. Both these reviews proposed that there was no conclusive evidence that acupuncture has a significant effect on the course of the condition - but equally there is no evidence that it does not. In effect, these reviews are an argument for more rigorous research. Until then, the jury is out. The remaining four reviews (Linde et al (1996), Jobst (1995, 1996), Lewith and Watkins (1996)) analysed a range of individual trials, all of which involved some comparison of a treatment group receiving true acupuncture with a control group receiving sham acupuncture. Table 1 summarises their findings. These reviews highlight the difficulty in reaching agreement, partly because of the heterogeneous nature of the trials themselves and partly because of differences in the subjective interpretation of the reviewers. For example, Linde et al (1996) used a set of assessors to evaluate both the methodological validity of the trials and the appropriateness of
4 the acupuncture treatments used. Whilst their assessors reached a high level of agreement on the internal validity of the trials, there was little agreement amongst them as to whether the acupuncture treatments given were appropriate; also, the outcome measures used varied Table 1: Reviews of Acupuncture Author Number of trials reviewed Conclusions Linde et al (1996) Jobst (1995, 1996) Lewith and Watkins (1996) 14 True acupuncture superior to sham: 5 Trend in favour of true acupuncture: 2 No difference between true and sham: 6 Sham acupuncture superior: 1 16 True acupuncture superior: 10 No difference: 3 Equivocal: positive on at least some outcome measures considerably. Furthermore they disagreed with Kleijnen et al (1991) in some of their assessments as to whether or not individual trials showed positive results. Similarly, Jobst (1995,1996) differs from Linde et al (1996) in the interpretation of the results of two trials. In summary, three of the reviews, Kleijnen et al (1991), Linde et al (1996) and Linde et al (2000), argued that the trials did not enable us to come to any conclusions about acupuncture s effectiveness, whilst three, Jobst (1995,1996) and Lewith and Watkins (1996), considered that there was evidence of effectiveness. Jobst (1995,1996) suggested that acupuncture might be used as an addition to conventional medical management of asthma and could lead to a reduction in the need for medication, particularly corticosteroids. Lewith and Watkins (1996) concluded that acupuncture could be useful in the alleviation of short term, acute airways obstruction but that evidence for its long-term efficacy was more open to question - largely, however, because the majority of the trials failed to include any long-term follow-up. The next sections will review in more detail some of the RCTs discussed in the above reviews as well as outcome studies, which, being uncontrolled, are rarely considered in systematic reviews. Randomised Controlled Trials Eleven trials were selected, of which four concern acupuncture administered shortly after the onset of induced asthma, whilst the remainder cover acupuncture provided under normal
5 clinical conditions. Clearly, the latter are of greatest interest to practitioners since most asthmatics encountered in the treatment room will have their asthma managed through drugs and practitioners may very rarely treat a severe acute attack. Of more interest will be issues such as whether acupuncture can lead to a reduction in medication. Nevertheless, the studies of induced asthma are of interest if they can demonstrate whether acupuncture has an effect. Trials of treatment given under normal clinical conditions. Characteristics of trials The trials detailed in Table 2 all involved patients with a diagnosis of chronic asthma, apart from Jobst et al (1986) where the diagnosis was Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, and only four of the subjects had signs of asthma. This paper was included since it appears in all the reviews of trials of asthma. The outcome measures used in the studies varied. All but Joos et al (2000) included measures of lung function. Other measures included: medication use immunological parameters heart rate and blood pressure walking distance (Jobst et al (1986) only) subjective relief of symptoms subjective well-being, quality of life measures. The details of the outcome measurements used are included in the footnote to Table 2.
6 Christensen et al (1984) Dias et al (1982) Design type Double Double Table 2: Controlled Trials for Chronic Asthma Sample Number Treatment Outcome Conclusion size of tx (appropriate Measures acupuncture listed first) over Ren 17, LI4, Lung function: MPEFR, Modest effect of appropriate acupuncture on both five weeks Dingchuan, Bl EPEFR Medication: no. of objective and subjective measures of lung function 13 vs sham. puffs of β-agonist and one immunological parameter. More substantial Subjective: DSA, WSA effect on medication use. Immunological: IgE, IgG, IgA, IgM 20 Variable Ren 22, Lung function: PEFR Improvements in both groups but control group better Dingchuan, Lu 7 Level of medication usage than appropriate acupuncture. vs GB 5 & 6 Jobst et al Single over Individual TCM Lung function: PEFR, FEV 1, No change in lung function. Significant improvement (1986) three treatments vs FVC in well being and walking distance for appropriate weeks sham Subjective well-being acupuncture. Subjective measures of breathlessness. Walking distance: six minute walk.
7 Mitchell & Single 31 8 over 12 Ren 17, Bl 13, Lung function: PEFR Improvements in both groups. No statistically Wells weeks Liv 3 vs Sp 8, Ki Medication use significant difference between them. Appropriate (1989) 9,GB37. Asthma symptoms: patient acupuncture group had no asthma episodes compared report with four in control. No. of Asthma episodes Tashkin et Single 25 8 LI 4, St 36, Du Lung function: SG aw, Trend to improvement in both groups but not al (1985) over 4 week s, then 14, Lu 7, Dingchuan, Waidingchuan vs sham. spirometry. Diaries of medication use & subjective symptoms. Heart rate and BP. statistically significant. cross over Biernacki & Double 23 1 Ren 17 vs sham Lung function: FEV 1, FVC. No improvement in lung function, both groups had Peake treatment point on the Medication use improved quality of life and reduced medication. (1998) followed chest wall. Quality of life questionnaire. by crossover.
8 Joos et al Single Bl 13, 17, Ren Immunological parameters: 14 Significant improvement in general well-being and (2000) treatments 17, LI 4, Lu7 measures used. most immunological parameters for appropriate over 4 plus General well-being (patient acupuncture. weeks individualised report). points vs inappropriate points * * The inappropriate points also included both a set of basic points for all patients (TE3, 19, GB 8, 34) and randomly assigned flexible points (Bl 38, 55, St 4, 6, 32, TE 14, 23, SI 5). Key to abbreviations: MPEFR (morning peak expiratory flow rate), EPEFR (evening peak expiratory flow rate), PEFR (peak expiratory flow rate), FEV 1 (forced expiratory volume in one second), FEF 50 or 75 (forced expiratory flow after 50% or 75% vital capacity exhaled), R aw (airway resistance), SG aw (specific airway conductance), DSA (daily severe asthma scale), WSA (weekly severe asthma scale), BP (blood pressure).
9 Methodologically, it is extremely problematic to design a double trial in which both patient and practitioner are ed. If the treatment is provided by a trained practitioner, even if they are given sets of points to needle by a different practitioner, they may be able to identify whether points are inappropriate or appropriate for the condition being treated. Where sham points are used, the problem is insurmountable. In practice, therefore, the trials described in Table 2 as double have ed the patients and used a ed evaluator but the practitioner providing the treatment is not necessarily ed. There may therefore be little difference between trials which describe themselves as double or single. The majority of the trials involved some sort of period during which baseline measurements of parameters such as lung function were drawn up, followed by a treatment period, followed by further measurements. The majority did not involve any long-term follow-up of patients. Two trials (Biernacki and Peake (1998), Tashkin (1985)) used a crossover design, whereby patients were randomly assigned to real or placebo acupuncture, followed by a washout period, followed by a second treatment phase during which they received the alternate form of acupuncture to the one received in the previous treatment phase. As for the actual treatment given, it is unfortunate that the RCT design has come to be associated with the idea of standard treatments. Whilst this constraint has been more open to question in recent years, only two of the trials below included any individualisation of treatment. In one (Jobst et al (1986)) treatment was fully individualised according to TCM (Traditional Chinese Medicine) syndromes whilst in the other (Joos et al (2000)) both standard and individualised points were used. The control group received either sham acupuncture (points with no defined energetic effect) or what were defined as inappropriate acupuncture points. Researchers differed as to whether they thought the control points should be located reasonably close to the real points or at some distance. All trials except Dias et al (1982) gave a standard number of treatments, which varied from one (real) treatment in Biernacki and Peake (1998) to thirteen in the Jobst et al (1986) study. The number of treatments in the Dias et al (1982) study varied from 2 to 8 (median 6) in the control group and 4 to 12 (median 6) in the treated group. Findings As regards objective outcome measurements, six of the seven trials measured lung function, and, in four, patients experienced improvements in lung function. However, one of these favoured inappropriate acupuncture over appropriate acupuncture and two failed to show a statistically significant change. Only one, therefore, unequivocally favoured appropriate acupuncture. Two of the trials looked at immunological parameters, both of which demonstrated positive benefits for appropriate acupuncture. Joos et al (2000) reported positive changes in a number of immunological parameters, although only the increase in in vitro lymphocyte proliferation rates reached statistical significance when comparing the TCM group with the control group. Christensen et al (1984) reported reduced levels of IgE in the true acupuncture group. Turning to subjective indicators, six of the trials used measures such as general well-being, quality of life or subjective experience of symptoms. All showed patients experiencing
10 benefits, with three showing appropriate acupuncture superior to inappropriate and three showing improvements in both groups. The relative importance of objective and subjective measures is debated: Jobst et al (1986) argued that acupuncture was helpful in reducing disability since the subjective experience of breathlessness and ability to walk for six minutes improved significantly even without there being a corresponding change in objective measures of lung function. In relation to all these trials we should bear in mind that they had small sample sizes and only two made any attempt to include some element of individual diagnosis. Both of these (Jobst et al (1986), Joos et al (2000)) included positive outcomes. The problem of diagnosis and point choice will be discussed further later. Trials of acupuncture for induced asthma attacks. Three trials looked at the effects of acupuncture on people with a history of asthma, but where bronchospasm had been induced, either by exercise (Fung et al (1986), Chow et al (1983)) or by inhalation of methacholine (Tashkin et al (1977)). A fourth (Yu & Lee (1976)) looked at acupuncture as a treatment for spontaneous asthma attacks, but a sub-group of four patients had an attack induced by histamine inhalation whilst in remission. Table 3 summarises the trial characteristics.
11 Chow et al (1983) Tashkin et al (1977) Fung et al (1986) Yu & Lee (1976) Design Single Double, crossov er Single Single Table 3: Controlled Trials for Induced Asthma Sampl No of tx Treatment Outcome measures Conclusion e size 16* 1 before Auricular points: Lung function: FEV 1, FVC. Neither gave protection against asthma. exercise* lung area vs lumbago area after LI4, Du14, Lung function: FVC, FEV 1, Real acupuncture better than sham although induced Dingchuan, FEF 25-75, FVC, Sg aw, R aw, V tg. isoproterenol was most effective. broncho Waidingchuan, Blood pressure. spasm St36, Lu7 vs Heart rate. sham acupuncture 19** 1 before Dingchuan, L6, Lung function: FEV 1, FVC, Real acupuncture gave greater protection than sham. exercise K3 vs SI14, P4, PEFR. GB during St 36 (both Lung function: FEV1, FVC, Dingchuan showed significant benefit compared with spontaneou groups) vs PaCo 2 both sham and St36 during spontaneous asthma s attack. Dingchuan, vs Subjective breathlessness attack. 1 before sham Heart rate and 1 after Expiratory wheeze. induced attack * all aged Needles left in during exercise. ** all aged years Abbreviations: as Table 3 + PaCo2 (arterial carbon dioxide pressure) and Vtg (thoracic volume at functional residual capacity).
12 Findings Three of the four trials showed positive findings regarding relief of bronchospasm by acupuncture, although Tashkin et al (1977) found that medication had a stronger effect. Yu and Lee (1976) found acupuncture to be beneficial in terms of both subjective and objective parameters for spontaneous asthma attacks, but not effective for histamine-induced attacks. This study is of particular interest because of the comparison of the effect of the extra point Dingchuan with both St 36 and a non-acupuncture site. Nine of the 10 patients in the group treated with Dingchuan experienced relief from breathlessness. This was superior to the nonacupuncture site, which was located 4 cms lateral to Dingchuan. The point St 36 was least effective, with only one out of 20 patients reporting any benefit. Outcome Studies Four outcome studies have been included. These are summarised in Table 4. Findings Three of the outcome studies are particularly useful because they provided for individualised treatments and explained the diagnostic criteria used in the choice of points. The studies all demonstrated very positive results, but a weakness is that the baseline and outcome measures are often unclear. Where specific measures were referred to, actual statistics were rarely given, instead rather vague categories, such as markedly improved, were used. An exception is the experimental group in the Shao Jingming study. Conclusion Whilst three of the four trials of induced asthma showed the acupuncture conferred statistically significant improvements in objective and subjective symptoms, the findings of the trials for asthma as part of normal clinical practice were more mixed. Nevertheless, they demonstrate evidence for the efficacy of appropriate acupuncture for some immunological parameters, for experience of asthma symptoms, level of medication use and quality of life. Findings are more equivocal for improvements in objective measures of lung function with only one, Christensen et al (1984), finding a statistically significant effect in favour of appropriate acupuncture. One, Dias et al (1982),
13 Table 4: Outcome Studies Zang Junqi (1990) Lai Xinsheng (1993) Shao Jingming (1985) Landa & Fadeeva (1992) Sample size Number of treatments Acupuncture Outcome measures Results 192 Single treatment Lu 6 & Lu 10 with electro acupuncture Clinical observation of symptoms and 76.5% clinical signs such as dyspnoea, wheezing but not remission or marked clear how measured. improvement. 143 Treated for six Bl 13, 20, 23, Du 14, Ren 15, 22 (all) Asthma, chest distress, dyspnoea, cough, 89.8% short-term months Dingchuan or St 40 for excess type. Bl 43, Ren expectoration, wheezing and cyanosis. Not cure or markedly 4 (sometimes with moxa) for deficiency type. clear how measured. effective. 111 Daily then alternate Bl 12, 13, Du 14 (all). Lu 5,9 (cough). Ren 12 Reference to symptoms but not specified. 98.2% were days over ten days. St 36 (sputum). Bl 23, Ren 4, Ki 3 (kidney Lung function tests in experimental group improved or Repeated where deficiency). Moxa used for cold symptoms, * markedly improved necessary. cupping for heat. Dietary restrictions. 2, sessions per Individualised according to eight principles, but Observed improvements in asthma Positive effect for children course. no information on actual points used. symptoms plus various objective 87% of all patients. not all measures: suprarenal and hypophysis had functions, immune status, tryptophan asthma exchange, physical development. * A comparison of the effects of Bl 13, Du 14 and Bl 12 using acupuncture with cupping, acupuncture with moxa and no treatment showed the greatest improvement for acupuncture with cupping. They also compared Bl 13, Du 14 and Bl 12 and found that Bl 13 gave the best results.
14 found in favour of the control group, which received inappropriate acupuncture. This leads some researchers, e.g. Grebski et al (1999), to argue that acupuncture is a useful placebo but that the exact location of the needles is unimportant. Three counter-arguments can be made. Firstly, as Joos et al (2000) point out, inappropriate acupuncture is not a placebo since it has definite physiological effects. True acupuncture would, therefore, have to show a greater effect to achieve statistical significance than if it were being compared with an inert placebo. Secondly, a number of trials showed real acupuncture to be superior and the study by Yu and Lee (1976) indicates that, in an acute attack of asthma, it makes a great deal of difference where the needle is inserted, with the point Dingchuan showing a markedly more positive effect than two other points. Thirdly, the majority of the trials used standardised formulae with no attempt at individual diagnosis. Appropriate points included points on the lung, large intestine, kidney, liver and stomach channels together with Ren 17 and 22 and the Back-shu point of the lung, but there was rarely any clear rationale for the choice. Stomach 36, for example, was used by Tashkin et al (1977, 1985) as a real point whereas Yu and Lee (1976) found that it was no better than a sham point. Most traditional acupuncturists would, therefore, regard these trials as of little help in understanding the potential role of acupuncture as it is actually practised. The outcome studies bear a closer relationship to the practice of traditional acupuncture and also demonstrate very positive results. However, they suffer from poor design. Further studies are clearly needed which combine both rigorous research methods and good quality acupuncture treatment. There is no reason why outcome studies cannot use well-validated tools to clearly specify the base line and outcome measures rather than using vague terms such as significant improvement. It is also argued by many that pragmatic RCTs, where the acupuncture treatment is left to the practitioner s discretion and the control group receives an alternative form of treatment or no treatment at all, are more useful than placebo-controlled trials because they enable acupuncture to be studied as it is actually practised. We think it more important to know if acupuncture is of value for the patient than to know that it is more than placebo (Linde et al, 1996). References Biernacki W, Peake MD (1998) Acupuncture in treatment of stable asthma. Resp. Med. 92: Chow O et al (1983) Effect of acupuncture on exercise induced asthma. Lung, 161: Christensen PA et al (1984) Acupuncture and Bronchial Asthma. Allergy 39, Dias PLR, Subramaniam S, Lionel N D W. (1982) Effects of acupuncture in bronchial asthma: preliminary communication. J. R. Soc. Med. 75: Fung KP, Chow OKW, So SY. (1986) Attenuation of exercise induced asthma by acupuncture. Lancet. December 20-27: Grebski E et al (1999) Long-Term Effects of Real and Sham Acupuncture on Lung Function and Eosiphilic Inflammation in Chronic Allergic Asthma: Randomised, Prospective Study. European Respiratory Journal 14:507s (abstract only). 1
15 Howell J (2000) Asthma: clinical descriptions and definitions in Busse W, Holgate S Asthma and rhinitus Vol 1. Oxford, Blackwell Science. Jobst KA (1995) A Critical Analysis of Acupuncture in Pulmonary Disease: Efficacy and Safety of the Acupuncture Needle. J Alt Compl Med 1: (1) Jobst KA (1996) Acupuncture in Asthma and Pulmonary Disease: An Analysis of Efficacy and Safety. J Alt Compl Med 2 (1): Jobst KA et al (1986) Controlled trial of acupuncture for disabling breathlessness. Lancet Dec ( ): Joos S et al (2000) Immunomodulatory Effects of Acupuncture in the Treatment of Allergic Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Study. J Alt Compl Med 6(6): Kleijnen J, ter Riet G, Knipschild P (1991) Acupuncture and asthma: a review of controlled trials. Thorax 46: Lai Xinsheng (1993) Observation of the Curative Effect of Acupuncture on Type I Allergic Diseases. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 13 (4): Landa N M, Fadeeva M A ( 1992) Acupuncture effect on re-activity and some indices of hormonal systems of children suffering from bronchial asthma, pollinosis, and atopic dermatitis. British Journal of Acupuncture15 (1): 3-8. Lewith GT, Watkins AD. (1996) Unconventional therapies in asthma: an overview. Allergy 51: Linde K et al (1996) Randomised Clinical Trials of Acupuncture for Asthma - a Systematic Review. Forsch Komplementarmed 3 (3): Linde K, Jobst K, Panton J (2001) Acupuncture for the treatment of chronic asthma (Cochrane Review) in The Cochrane Library, Issue 2,2001 Oxford: Update Software Ltd. Mitchell P, Wells JE (1989) Acupuncture for Chronic Asthma: A controlled trial with six months follow-up. Am J. Ac. 17 (pt 1): Tashkin DP et al (1977) Comparison of real and simulated acupuncture and isoproterenol in metacholine-induced asthma. Annals of Allergy. 36 (6) : Tashkin DP et al (1985) A controlled study of real and simulated acupuncture in the management of chronic asthma. J. Allergy and Clin. Immun. 76 (6): Shao Jingming (1985) Clinical Observation on 111 cases of Asthma Treated by Acupuncture and Moxibustion. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 5(1): Yu DYC, Lee SP (1976) Effect of Acupuncture on Bronchial Asthma. Clin. Sci. & Mol. Med. 51:
16 Zang Junqi (1990) Immediate Antiasthmatic Effect of Acupuncture in 192 Cases of Bronchial Asthma. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 10(2): Grateful acknowledgement is made to Jennifer Dale for her work in preparing this briefing paper
Migraine and Acupuncture
 BRIEFING PAPER No 1 Migraine and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council June 1998 The Evidence
BRIEFING PAPER No 1 Migraine and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council June 1998 The Evidence
Chen JC, Mannino DM. Worldwide epidemiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med 1999; 5: 93 9.
 ACUPUNCTURE AND COPD About COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is thought to be the fourth most common cause of death worldwide, and the World Health Organisation anticipates that by 2020
ACUPUNCTURE AND COPD About COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is thought to be the fourth most common cause of death worldwide, and the World Health Organisation anticipates that by 2020
Efficacy of acupuncture in asthma: systematic review and metaanalysis of published data from 11 randomised controlled trials
 Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 846 852 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.00078702 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Efficacy of acupuncture in
Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 846 852 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.00078702 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Efficacy of acupuncture in
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
 Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Ivax Pharmaceuticals UK Sponsor Submission to the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence Clinical and cost-effectiveness of QVAR for the treatment of chronic asthma in adults and children
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016
 Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Patient characteristics Intervention Comparison Length of followup
 ORAL MUCOLYTICS Ref ID: 2511 Bachh AA, Shah NN, Bhargava R et al. Effect oral N- in COPD - A randomised controlled trial. JK Practitioner. 2007; 14(1):12-16. Ref ID: 2511 RCT Single blind; unclear allocation
ORAL MUCOLYTICS Ref ID: 2511 Bachh AA, Shah NN, Bhargava R et al. Effect oral N- in COPD - A randomised controlled trial. JK Practitioner. 2007; 14(1):12-16. Ref ID: 2511 RCT Single blind; unclear allocation
Evolution of asthma from childhood. Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT
 Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications. Potential Conflict Of Interest. Objectives. Rationale: Why Test?
 Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Pulmonary Function Testing: Concepts and Clinical Applications David M Systrom, MD Potential Conflict Of Interest Nothing to disclose pertinent to this presentation BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL Harvard
Asthma: Chronic Management. Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015
 Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
the use of inhaled corticosteroids for at least 3 months preceding the study;
 The cost effectiveness of chlorofluorocarbon-free beclomethasone dipropionate in the treatment of chronic asthma: a cost model based on a 1-year pragmatic, randomised clinical study Price D, Haughney J,
The cost effectiveness of chlorofluorocarbon-free beclomethasone dipropionate in the treatment of chronic asthma: a cost model based on a 1-year pragmatic, randomised clinical study Price D, Haughney J,
DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES:
 TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring
 Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Asthma: diagnosis and monitoring NICE guideline: short version Draft for second consultation, July 01 This guideline covers assessing, diagnosing and monitoring suspected or confirmed asthma in adults,
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Contents. Basic Theory of Acupuncture. (Page 1) Acupuncture Points. (Page 31) Side Effects of Acupuncture. (Page 51)
 VII Contents Basic Theory of Acupuncture (Page 1) Scientific Aspects of Acupuncture..................... 2 Indication and Direction of Action of Acupuncture.................................... 12 Relative
VII Contents Basic Theory of Acupuncture (Page 1) Scientific Aspects of Acupuncture..................... 2 Indication and Direction of Action of Acupuncture.................................... 12 Relative
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Treatment of acute asthmatic exacerbations with an increased dose of inhaled steroid
 12 Paediatrics and Child Health, Dunedin School of Medicine, PO Box 913, University of Otago Medical School, Dunedin, New Zealand J Garrett Preventive and Social Medicine, Dunedin School of Medicine S
12 Paediatrics and Child Health, Dunedin School of Medicine, PO Box 913, University of Otago Medical School, Dunedin, New Zealand J Garrett Preventive and Social Medicine, Dunedin School of Medicine S
Validity of Spirometry for Diagnosis of Cough Variant Asthma
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 6431-6438) Validity of Spirometry for Diagnosis of Cough Variant Asthma Iman Vafaei 1, *Nemat Bilan 2,3, Masoumeh Ghasempour 41 1 Resident of Pediatrics,
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 6431-6438) Validity of Spirometry for Diagnosis of Cough Variant Asthma Iman Vafaei 1, *Nemat Bilan 2,3, Masoumeh Ghasempour 41 1 Resident of Pediatrics,
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma
 Thorax (1973), 28, 574. Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma M. SILVERMAN, P. KONIG, and S. GODFREY' With the technical assistance of Tina Andrea
Thorax (1973), 28, 574. Use of serial exercise tests to assess the efficacy and duration of action of drugs for asthma M. SILVERMAN, P. KONIG, and S. GODFREY' With the technical assistance of Tina Andrea
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
(Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Shirley P.C. Ngai, BSc; Christina W.Y. Hui-Chan, PhD; Alice Y.M. Jones, PhD, FACP
 Research Report A SHORT REVIEW OF ACUPUNCTURE AND BRONCHIAL ASTHMA WESTERN AND TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE CONCEPTS Shirley P.C. Ngai, BSc; Christina W.Y. Hui-Chan, PhD; Alice Y.M. Jones, PhD, FACP Abstract:
Research Report A SHORT REVIEW OF ACUPUNCTURE AND BRONCHIAL ASTHMA WESTERN AND TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE CONCEPTS Shirley P.C. Ngai, BSc; Christina W.Y. Hui-Chan, PhD; Alice Y.M. Jones, PhD, FACP Abstract:
Pulmo-Park Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D
 Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should not perform the
Pom-Pom Shooter: Measuring the Effect of Restricted Breathing on Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) Student Information Page Activity 5D Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should not perform the
HCT Medical Policy. Bronchial Thermoplasty. Policy # HCT113 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016. Policy Statement. Overview
 HCT Medical Policy Bronchial Thermoplasty Policy # HCT113 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016 Medical Policies are developed by HealthyCT to assist in administering plan benefits and constitute neither
HCT Medical Policy Bronchial Thermoplasty Policy # HCT113 Current Effective Date: 05/24/2016 Medical Policies are developed by HealthyCT to assist in administering plan benefits and constitute neither
Predictors of obstructive lung disease among seafood processing workers along the West Coast of the Western Cape Province
 Predictors of obstructive lung disease among seafood processing workers along the West Coast of the Western Cape Province Adams S 1, Jeebhay MF 1, Lopata AL 2, Bateman ED 3, Smuts M 4, Baatjies R 1, Robins
Predictors of obstructive lung disease among seafood processing workers along the West Coast of the Western Cape Province Adams S 1, Jeebhay MF 1, Lopata AL 2, Bateman ED 3, Smuts M 4, Baatjies R 1, Robins
SUMMARY THIS IS A PRINTED COPY OF AN ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT. PLEASE CHECK ITS VALIDITY BEFORE USE.
 i SUMMARY ZENECA PHARMACEUTICALS FINISHED PRODUCT: ACTIVE INGREDIENT: ACCOLATE zafirlukast (ZD9188) Trial title (number): A Dose-ranging, Safety and Efficacy Trial with Zafirlukast (ACCOLATE ) in the Treatment
i SUMMARY ZENECA PHARMACEUTICALS FINISHED PRODUCT: ACTIVE INGREDIENT: ACCOLATE zafirlukast (ZD9188) Trial title (number): A Dose-ranging, Safety and Efficacy Trial with Zafirlukast (ACCOLATE ) in the Treatment
This is the publisher s version. This version is defined in the NISO recommended practice RP
 Journal Article Version This is the publisher s version. This version is defined in the NISO recommended practice RP-8-2008 http://www.niso.org/publications/rp/ Suggested Reference Chong, J., Karner, C.,
Journal Article Version This is the publisher s version. This version is defined in the NISO recommended practice RP-8-2008 http://www.niso.org/publications/rp/ Suggested Reference Chong, J., Karner, C.,
BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY
 BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY UnitedHealthcare Community Plan Medical Policy Policy Number: CS014.E Effective Date: July 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS... 1 COVERAGE
BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY UnitedHealthcare Community Plan Medical Policy Policy Number: CS014.E Effective Date: July 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS... 1 COVERAGE
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
HealthPartners Care Coordination Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide ASTHMA
 The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
2010 Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Asthma Third edition Stephen T Holgate MD DSc FRCP FMedSci MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology School of Medicine Southampton General Hospital Southampton, UK Jo Douglass
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Asthma Third edition Stephen T Holgate MD DSc FRCP FMedSci MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology School of Medicine Southampton General Hospital Southampton, UK Jo Douglass
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Outline FEF Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications?
 Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Gynaecology and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness
 BRIEFING PAPER No 4 Gynaecology and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council September 1999
BRIEFING PAPER No 4 Gynaecology and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council September 1999
Is reslizumab effective in improving quality of life and asthma control in adolescent and adult patients with poorly controlled eosinophilic asthma?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
SCREENING AND PREVENTION
 These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
Running Head: THE PRACTICALITY OF BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY 1. Review of a New Treatment for Severe Asthma: The Practicality of Bronchial Thermoplasty
 Running Head: THE PRACTICALITY OF BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY 1 Review of a New Treatment for Severe Asthma: The Practicality of Bronchial Thermoplasty Jessica Orpen Northeastern University THE PRACTICALITY
Running Head: THE PRACTICALITY OF BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY 1 Review of a New Treatment for Severe Asthma: The Practicality of Bronchial Thermoplasty Jessica Orpen Northeastern University THE PRACTICALITY
Pulmonary Function Tests. Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist
 Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL
 ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL The Role of Acupuncture Treatment with the Management of Threatened Miscarriage: An exploratory study Acupuncture treatment This involves receiving an acupuncture treatment
ACUPUNCTURE AND TOUCH PROTOCOL The Role of Acupuncture Treatment with the Management of Threatened Miscarriage: An exploratory study Acupuncture treatment This involves receiving an acupuncture treatment
BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY
 Review Article 155 BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY Prince James* and Richa Gupta* (Received on 4.5.2010; Accepted after revision on 5.9.2011) Summary: Even with the use of maximum pharmacological treatment, asthma
Review Article 155 BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY Prince James* and Richa Gupta* (Received on 4.5.2010; Accepted after revision on 5.9.2011) Summary: Even with the use of maximum pharmacological treatment, asthma
Gynaecology and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness
 BRIEFING PAPER No 4 Gynaecology and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council September 1999
BRIEFING PAPER No 4 Gynaecology and Acupuncture The evidence for effectiveness Edited and produced by the Acupuncture Research Resource Centre Published by the British Acupuncture Council September 1999
PomPom SHOOTER. Activity Background: Common Obstructive Lung Disorders:
 CAUTION: Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should NOT perform the breathing exercises in this activity because they involve repeated maximal inhalations and exhalations and use of a breathing
CAUTION: Students with asthma or other respiratory problems should NOT perform the breathing exercises in this activity because they involve repeated maximal inhalations and exhalations and use of a breathing
Bronchial asthma. E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics. Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013
 Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Emphysema is a chronic lung disease that
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Known Allergies: Shellfish. Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, or vomiting. congestion, trouble breathing, or wheezing.
 CSTAR CASE STUDIES: BLOCK B Asthma or COPD? Setting: Walk in clinic. Dan: I havi g that cough thi g agai HPI: Dan is a 49-year-old male teacher who reports having had episodes of cough with mucus production
CSTAR CASE STUDIES: BLOCK B Asthma or COPD? Setting: Walk in clinic. Dan: I havi g that cough thi g agai HPI: Dan is a 49-year-old male teacher who reports having had episodes of cough with mucus production
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: bronchial_thermoplasty 10/2010 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Bronchial thermoplasty
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: bronchial_thermoplasty 10/2010 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Bronchial thermoplasty
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO)
 Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires as measures of the severity and impact of asthma
 Eur Respir J 1999; 1: 591±596 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 1999 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires
Eur Respir J 1999; 1: 591±596 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 1999 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 A comparison of global questions versus health status questionnaires
NG80. Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80)
 Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
Bronchial reactions to the inhalation of high-dose tobramycin in cystic fibrosis
 Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 122 126 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.00264002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Bronchial reactions to the
Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 122 126 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.00264002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Bronchial reactions to the
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY
 BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: RESPIRATORY 009.11 T2 Effective Date: August 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY... 1 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: RESPIRATORY 009.11 T2 Effective Date: August 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page BRONCHIAL THERMOPLASTY... 1 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...
COPD/ Asthma. Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer
 COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
COPD/ Asthma Dr Heather Lewis Honorary Clinical Lecturer Objectives To understand the pathogenesis of asthma/ COPD To recognise the clinical features of asthma/ COPD To know how to diagnose asthma/ COPD
NICE guideline Published: 29 November 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng80
 Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management NICE guideline Published: 29 November 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng80 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management NICE guideline Published: 29 November 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng80 NICE 2017. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Study of dynamic lung parameters in bronchial Asthma
 20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
Long term benefits of acupuncture for chronic pain: what makes a difference?
 Long term benefits of acupuncture for chronic pain: what makes a difference? Hugh MacPherson www.hughmacpherson.com 1 Outline 1. Acupuncture for chronic pain the Acupuncture Trialists Collaboration, and
Long term benefits of acupuncture for chronic pain: what makes a difference? Hugh MacPherson www.hughmacpherson.com 1 Outline 1. Acupuncture for chronic pain the Acupuncture Trialists Collaboration, and
National Asthma Educator Certification Board Detailed Content Outline
 I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd
 roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd 06 August 2010 (Issued 10 September 2010) The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
roflumilast 500 microgram tablets (Daxas ) SMC No. (635/10) Nycomed Ltd 06 August 2010 (Issued 10 September 2010) The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT
 Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse
 Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County
 Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County 4400 persons underwent examination 950 persons were given referrals to more detailed investigation 600 persons were examined so far The results of more detailed
Respiratory diseases in Ostrołęka County 4400 persons underwent examination 950 persons were given referrals to more detailed investigation 600 persons were examined so far The results of more detailed
Putting NICE guidance into practice. Resource impact report: Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80)
 Putting NICE guidance into practice Resource impact report: Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) Published: November 2017 Summary This report focuses on the recommendations
Putting NICE guidance into practice Resource impact report: Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) Published: November 2017 Summary This report focuses on the recommendations
Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians 2013/California Academy of Family Physicians
 Family Medicine and Patient-Centered Asthma Care Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians Faculty: Hobart Lee, MD Disclosures: Jeffrey Luther, MD, Program Director, Memorial Family Medicine
Family Medicine and Patient-Centered Asthma Care Presented by the California Academy of Family Physicians Faculty: Hobart Lee, MD Disclosures: Jeffrey Luther, MD, Program Director, Memorial Family Medicine
COPD. Helen Suen & Lexi Smith
 COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
SPIROMETRY TECHNIQUE. Jim Reid New Zealand
 Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of insertion of endobronchial nitinol coils to improve lung function in emphysema
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of insertion of endobronchial nitinol coils to improve lung function in emphysema
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of the Dossier. Volume:
 Final Report M/100977/21Final Version () 2. SYNOPSIS A Title of Study: A PHASE IIa, RANDOMISED, DOUBLE-BLIND, MULTIPLE DOSE, PLACEBO CONTROLLED, 3 PERIOD CROSS-OVER, ASCENDING DOSE CLINICAL TRIAL TO ASSESS
Final Report M/100977/21Final Version () 2. SYNOPSIS A Title of Study: A PHASE IIa, RANDOMISED, DOUBLE-BLIND, MULTIPLE DOSE, PLACEBO CONTROLLED, 3 PERIOD CROSS-OVER, ASCENDING DOSE CLINICAL TRIAL TO ASSESS
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma
 The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
Acupuncture Stops Coughing, Soothes Passages
 Acupuncture Stops Coughing, Soothes Passages 07 JUNE 2017 Researchers find acupuncture effective for the alleviation of chronic coughing. In a controlled clinical investigation, researchers determined
Acupuncture Stops Coughing, Soothes Passages 07 JUNE 2017 Researchers find acupuncture effective for the alleviation of chronic coughing. In a controlled clinical investigation, researchers determined
Respiratory Health L O O K, F E E L A N D L I V E B E T T E R
 LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BET TER Respiratory health: hay-fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay-fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body s immune system
LOOK, FEEL AND LIVE BET TER Respiratory health: hay-fever and asthma Airway obstruction and symptoms in asthma and hay-fever alike are the result of inappropriate responses of the body s immune system
Introduction to Acupuncture
 Introduction to Acupuncture The TCM paradigm Objective- To explain the following: Definition of Acupuncture Overview of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Meridian Theory The Eight Principles Pathogenic
Introduction to Acupuncture The TCM paradigm Objective- To explain the following: Definition of Acupuncture Overview of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Meridian Theory The Eight Principles Pathogenic
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
East Meets West: Treating Pain with Acupuncture
 East Meets West: Treating Pain with Acupuncture Lixing Lao, Ph.D., L.Ac. Professor and Director TCM Research Program, Center for Integrative Medicine University of Maryland School of Medicine Center for
East Meets West: Treating Pain with Acupuncture Lixing Lao, Ph.D., L.Ac. Professor and Director TCM Research Program, Center for Integrative Medicine University of Maryland School of Medicine Center for
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600
 Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600 Your responsibility This guidance represents
Endobronchial valve insertion to reduce lung volume in emphysema Interventional procedures guidance Published: 20 December 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg600 Your responsibility This guidance represents
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3. Chronic Cough Guidelines
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3 Chronic Cough Guidelines NHS Fife Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Cough in Adults In this section: 1. Introduction 2. Scope Guidelines for Management of Chronic
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 3 Chronic Cough Guidelines NHS Fife Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Cough in Adults In this section: 1. Introduction 2. Scope Guidelines for Management of Chronic
Public Dissemination
 1. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 18 3 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
1. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 18 3 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY. Evidence Review: Temperature-controlled laminar airflow device for persistent allergic asthma (children)
 Evidence Review: Temperature-controlled laminar airflow device for persistent allergic asthma (children) NHS England Evidence Review: Temperature-controlled laminar airflow device for persistent allergic
Evidence Review: Temperature-controlled laminar airflow device for persistent allergic asthma (children) NHS England Evidence Review: Temperature-controlled laminar airflow device for persistent allergic
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
Asthma Assessment & Review
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
Pulmonary Function Testing
 Pulmonary Function Testing Let s catch our breath Eddie Needham, MD, FAAFP Program Director Emory Family Medicine Residency Program Learning Objectives The Astute Learner will: Become familiar with indications
Pulmonary Function Testing Let s catch our breath Eddie Needham, MD, FAAFP Program Director Emory Family Medicine Residency Program Learning Objectives The Astute Learner will: Become familiar with indications
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
Online Data Supplement. Prevalence of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Korea: Results of a Population-based Spirometry Survey
 Online Data Supplement Prevalence of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Korea: Results of a Population-based Spirometry Survey Dong Soon Kim, MD, Young Sam Kim MD, Kee Suk Chung MD, Jung Hyun Chang
Online Data Supplement Prevalence of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Korea: Results of a Population-based Spirometry Survey Dong Soon Kim, MD, Young Sam Kim MD, Kee Suk Chung MD, Jung Hyun Chang
PCRS-UK briefing document Asthma guidelines. November 2017
 PCRS-UK briefing document Asthma guidelines November 2017 1 1. Background The Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) and British Thoracic Society (BTS) have been collaborating on producing
PCRS-UK briefing document Asthma guidelines November 2017 1 1. Background The Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) and British Thoracic Society (BTS) have been collaborating on producing
Asthma Tutorial. Trainer MRW. Consider the two scenarios, make an attempt at the questions, what guidance have you used?
 Registrar: LG PR RS Topic Asthma and COPD Asthma Tutorial Trainer MRW Date of Tutorial 18 th Jan 2007 Objectives of the tutorial How to diagnose What investigations and when Treatment guidelines QoF Criteria
Registrar: LG PR RS Topic Asthma and COPD Asthma Tutorial Trainer MRW Date of Tutorial 18 th Jan 2007 Objectives of the tutorial How to diagnose What investigations and when Treatment guidelines QoF Criteria
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
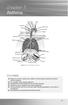 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide.
 Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Methacholine versus Mannitol Challenge in the Evaluation of Asthma Clinical applications of methacholine and mannitol challenges
 Methacholine versus Mannitol Challenge in the Evaluation of Asthma Clinical applications of methacholine and mannitol challenges AAAAI San Antonio Tx February 2013 Catherine Lemière MD, MSc Hôpital du
Methacholine versus Mannitol Challenge in the Evaluation of Asthma Clinical applications of methacholine and mannitol challenges AAAAI San Antonio Tx February 2013 Catherine Lemière MD, MSc Hôpital du
Pathway diagrams Annex F
 Pathway diagrams Annex F Fig 1 Asthma: The patient journey Asthma is diagnosed Making the diagnosis of asthma Confirming the diagnosis may depend on history, response to treatment, measurement of airflow
Pathway diagrams Annex F Fig 1 Asthma: The patient journey Asthma is diagnosed Making the diagnosis of asthma Confirming the diagnosis may depend on history, response to treatment, measurement of airflow
Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot Malhi, B.R. Srinivas and Lata Kumar
 Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
