A sthma and sinusitis are inflammatory diseases of respiratory epithehal tissue. and the association of asthma with sinusitis has long been known.
|
|
|
- Joseph McDowell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scott E. Crater1 Edward J. Peters1 C. Douglas Phillips2 Thomas A. E. Platts-M111s1 Received June 29, 1998; accepted after revision January4, Supported by National Institutes of Health (NlHl grant AI and NIH Asthma Center grant U19-Al Asthma & Allergic Diseases Center, University of Virginia Health Sciences Center, Box 225, Charlottesville, VA Address correspondence to S. E. Crater. 2Department of Radiology, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA AJI9 1999:173: X/99/ American Roentgen Ray Society Prospective Analysis of CT of the Sinuses in Acute Asthma OBJECTIVE. Asthma and sinusitis are both inflammatory diseases of the respiratory epithelium, but to our knowledge no prospective analyses of CT of the sinuses in patients with acute asthma have been performed. The purpose of this study was to investigate the type and extent of abnormalities found on CT of the sinuses in patients with acute asthma. SUBJECTS AND METHODS. Sixty-five patients with acute asthma and 62 age-. race-, and sex-matched control subjects were enrolled in the emergency department. Limited coronal sinus CT was performed and scans were interpreted by a radiologist who was unaware of the patient s clinical condition. Scans were analyzed for the presence of mucosal thickening in the sinuses. ostiomeatal complexes. and nasal cavities. Scans were also assigned a CT score for total mucosal thickening. A CT score of 12 or more points indicated extensive disease. RESULTS. Mucosal thickening in the nasal passages (p <.001 ). ostiomeatal complexes (j <.05), and ethmoidal (p <.05) and sphenoidal sinuses (p <.05) was associated with acute asthma. but maxillary mucosal thickening was not (p =.44). CT scores differed significantly between asthmatic patients (7.7 ± 0.8 points) and control subjects (4.1 ± 0.4 points) (p <.001). Nineteen of the 65 asthmatic patients had extensive disease compared with two of the 62 control subjects (p <.001 ). Thirteen asthmatic patients with extensive disease underwent follow-up CT 5 months later, and I I of the 13 patients showed improvement in CT score without having undergone specific therapy for sinusitis. CONCLUSION. Mucosal thickening in the nasal passages and sphenoidal. ethmoidal. and frontal sinuses is more common in patients with acute asthma than in control subjects. However. maxillary sinus mucosal thickening is no more common in asthmatic patients than in control subjects. A sthma and sinusitis are inflammatory diseases of respiratory epithehal tissue. and the association of asthma with sinusitis has long been known. In I 925, Gottleib [ 11observed that 3 1 of a series of I I 7 asthmatic patients complained of sinus symptoms. Since then. several studies have examined the relationship between asthma and sinusitis using conventional sinus radiographs. Estimates of the incidence of sinusitis in asthmatic patients based on conventional sinus radiographs range from 3 1 % to 87% [2-41. Such variability reflects the difficulty of accurately diagnosing sinus disease using conventional radiographs. Although CT offers superior sensitivity in detecting sinus abnormalities, no study has used sinus CT to assess prospectively the extent of disease in acute asthmatic patients compared with nonasthmatic control subjects [5-7]. The purpose of this study was to document the type and extent of sinus abnormalities detected by CT in patients with acute asthma compared with random control subjects. CT scans were evaluated fbr both specific anatomic features (i.e.. polypoid mucosa and ostiomeatal complex occlusion) and total mucosal thickening in the paranasal sinuses and nasal passages. Subjects and Methods Subjects Sixty-nine acute asthmatic patients and 70 age-. race-. and sex-matched control subjects between the ages of I 8 and 50 years were recruited in the emergency department of a university hospital between August 1997 and March Subjects were enrolled under a protocol approved by the human investigations committee. All subjects provided informed consent befre enrollment. AJR:173, July
2 Crater et al. Control subjects were enrolled at random from the emergency department during the same period as the asthmatic patients. The exclusion criterion for control subjects was acute breathlessness at the time of the study. No exclusions were made on the basis of either cold or sinusitis symptoms or a history of asthma or sinus surgery. The most common complaints among control subjects were orthopedic injuries (,z = 29) followed by lacerations (ii = 10) and toothaches (n = 10). Five control subjects presented with symptoms consistent with an upper respiratory infection. One control subject complained of rhinitis; two, of a sore throat: and two, of an earache. The remaining 26 had a variety of complaints ranging from an animal bite to syncope. Eight control subjects reported a history of asthma, but none were wheezing at the time of the study. In addition, two control subjects and three asthmatic patients had undergone functional endoscopic sinus surgery in the past. For the purposes of this study. asthma was defined as acute breathlessness, wheezing on physical examination, and a history of similar episodes. All subjects were judged to need treatment for asthma by the emergency department physician. and all subjects received nebulized albuterol (l U). The race of study subjects was noted because asthma morbidity and mortality are markedly higher among blacks than whites. Spirometry Technique All subjects performed three vital capacity maneuvers into a portable spirometer (Renaissance model; Puritan-Bennett, Wilmington, MA). according to the American Thoracic Society guidelines [8], before enrollment. CT Technique After enrollment in the emergency department, subjects were scheduled to return for outpatient CT. Seven asthmatic patients were admitted and scanned as inpatients. The CT protocol was a modification of the method originally described by Phillips [9] and has previously been described. All subjects were scanned after administration of a nasal decongestant and clearing of the nose. CT Evaluation and Scoring Cr scans were interpreted by a neuroradiologist who was unaware of the subject s clinical condition. CT scans were evaluated using a previously published scoring system [10, 1 1]. Maximal amount of single-wall mucosal thickening in millimeters was measured in all the paranasal sinuses, and a range of from 0 to 3 points was assigned for each sinus (Table 1). For evaluating the ostiomeatal complexes and nasal passages, a score of 0 was given for no disease; 1, for mild disease; 2, for moderate or scattered disease; and 3, for severe mucosal disease. To quantify total mucosal thickening, the scores for the individual sinuses, nasal passages. and ostiomeatal complexes were summed. The range of possible scores was from 0 to 30 points. As in earlier studies using this scoring system, a score of 12 or more points indicated extensive disease [1 1]. Attention was paid to specific features including polypoid-appearing (focally thickened) mucosa, air-fluid levels, and bony changes consistent with chronic sinusitis. Finally, the bony architecture of the sinuses including the agger nasi cells, HaIler cells (infraorbital air cells), concha bullosa, and deviated septa was noted. These abnormal bony structures result in apposition of healthy mucosal surfaces, thus impeding normal mucociliary transport. Altered mucociliary transport may lead to stagnation of mucous, which can cause postobstructive sinusitis [ 12]. Statistics A statistical program (True Epistat; Epistat Services, Richardson, TX) was used for data analysis. The prevalence of specific sinus CT features in asthmatic patients was compared with that in control subjects using chi-square analysis. The CT score values are presented as a mean ± SEM. Mean Cr scores in asthmatic patients and control subjects were compared using the Mann-Whitney test for nonparametric data. Results The demographics of the study population are presented in Table 2. Mean forced expiratot) volume in 1 sec was 55% of predicted in asthmatic patients versus 103% of predicted in control subjects (p <.0001). The mean duration of asthma symptoms was 14.7 years. Before presentation to the emergency department, 27 (42%) of the 65 asthmatic patients were using Scoring System for di. aes Note-V limeters. Mod = moderate. a Maximum total score for mucosal thickening is 30 points. inhaled steroids, seven (I 1%) of the 65 were using oral steroids, and three (5%) of the 65 were using steroid nasal sprays for treatment of allergic rhinitis. None were taking antibiotics for treatment of bacterial sinusitis. Only three (5%) of the 65 asthmatic patients had been referred to an otolaryngologist for evaluation of sinus disease in the past. compared with two (3%) of the 65 control subjects. Sixty-five of 69 asthmatic patients and 62 of the 70 control subjects returned for CT, and mean CT scores of asthmatic patients and control subjects are presented in Table 2. Asthmatic patients underwent scanning 0-9 days (mean, 3.4 ± 0.4 days) after presentation to the emergency department. The emergency department physician treated the study subjects for acute asthma, but no subjects received topical nasal steroids, decongestants, or antihistamines for treatment of sinus symptoms in the emergency department. Specific anatomic features on CT were associated with acute asthma exacerbations: mucosal thickening of the nasal passages. the ostiomeatal complexes, and the sphenoidal and ethmoidal sinuses (Table 3). More severe mucosal thickening (i.e., 6 mm) in these areas was also associated with acute asthma (Table 4). On the other hand, because the incidence of maxillary sinus abnormalities was the same in asthmatic patients (65%) and control subjects (73%), mucosal thickening in the maxillary sinuses was not associated with asthma (Table 3). Polypoid-appearing (focally thickened) tissue anywhere on the.haracterlstlcs Of ACute..sthmadc Patients and :ontrol Subjects at bbecause ofthe smaller size ofthe ethmoidal sinuses rel- versus asthmatic patients was performed usin9 the Mannative to the other sinuses, the same number of points was Whitneytestfornonparametric data; p< 001. given for lesser degrees ofthickening. avalues are expressed as a mean ± SEM. 128 AJR:173, July 1999
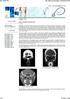
3 CT of the Sinuses in Acute Asthma scan was more common in asthmatic patients, but this finding did not reach statistical significance (Table 3). One asthmatic patient reported a history of aspirin sensitivity: 1 year earlier she had received aspirin at an outside hospital and subsequently required intubation for respiratory distress. This patient had extensive sinus disease Chi-square analysis: p<.001. bchi.square analysis: p <.05. CpOlypOjd mucosa refers to the presence of polypoid-appearing tissue anywhere on the scan. These lesions may represent either true polyps or mucous-retention cysts. Fig year-old black woman with Samter s syndrome (asthma, nasal polyps, aspirin sensitivity). Patient presented with 2-week history of wheezing and rhinorrhea and 10- year history of asthma and sinus problems. Coronal CT scan shows involvement of all paranasal sinuses. CT score = 25 points. Scores for total mucosal thickening in the asthmatic patients ranged from 0 to 25 points of a possible 30 points (Figs. 2 and 3); scores for control subjects ranged from 0 to 14 points. As in previous studies using this system, a score of I 2 or more points indicated extensive sinus disease [10, 1 1j. Extensive disease corre- with polypoid features (Fig. 1). lated significantly with acute asthma by chi-. d Abnormalities Found on CT ofthe Sinuses ofasthmatic Patlnts and Conol Subjects square analysis; 19 of the 65 asthmatic patients had extensive disease, compared with two of the 62 control subjects (p <.001). Follow-up sinus CT scores were obtained for 13 of 19 individuals with extensive sinus disease. Partial to near-complete improvement was seen in I I of the 13 asthmatic patients during a 5-month period, although none of the I I subjects who improved had received any specific therapy for sinus disease (Figs. 4 and 5). Bony thickening suggestive of chronic sinusitis was observed in only three of the 65 asthmatic patients and one of the 62 control subjects (p =.64). Other structural abnormalities commonly associated with sinusitis such as HaIler cells, agger nasi cells, concha bullosa, and deviated septa were not significantly different between asthmatic patients and control subjects. Discussion This study, to our knowledge. is the first controlled. prospective analysis of sinus abnormalities detected by CT in an unselected population of patients with acute asthma and control subjects. Earlier reports of CT findings in asthmatic patients with sinus disease were drawn from retrospective analyses of highly selected populations referred for surgical treatment of chronic sinusitis and not acute asthma [ 10, 1 11.The available studies of sinus abnormalities in patients with acute asthma used conventional sinus radiographs [2-4]. These studies are flawed because conventional sinus radiographs are much less sensitive than CT scans for detecting sinus abnormalities [5-7J. In fact, Laz.ar et al. [61 documented an error rate of more than 35% when the accuracy of conventional radiographs was compared with that of sinus CT for diagnosing chronic sinusitis. Also, few of the earlier studies compared asthmatic patients with a control population, despite the CT findings of Havas et al. I 131 showing abnormalities in one or more of the paranasal sinuses in more than 40% of control subjects without a history of sinus disease. Like the report by Havas et al. [13]. our study shows a high incidence of sinus mucosal thickening in a random control population. As in the Havas et al. study, the control subjects in our study were randomly selected. No effort was made to exclude subjects with preexisting sinus disease, and five (8%) of the 62 control subjects had some upper respiratory symptoms. We believe that this group of unselected control subjects is representative of the general population at large and that some degree of mucosal thickening in the paranasal sinuses is AJR:173, July
4 Crater et al. a common finding. This hypothesis is especially true for the maxillary sinuses, because the incidence of maxillary mucosal thickening was at least as high in control subjects (45/62 [73%]) as in asthmatic patients (43/65 [66%]). Some degree of maxillary mucosal thickening may be unrelated to any pathologic process because this finding was so common and was not associated with any particular morbidity. It is currently not possible to explain the predominance of sinus disease in the ostiomeatal complexes and sphenoidal and ethmoidal sinuses as opposed to the maxillary sinuses among patients with acute asthma. Practitioners should be aware, however, that maxillary sinus mucosal thickening alone may be clinically insignificant. Therefore, it may be problematic in patients with suspected sinusitis to rely on conventional radiographs, which afford images of the maxillary sinuses and little else. Historically, chronic infection by organisms such as Moraxella catarrhaiis and Haemophilus influenzae has been targeted as the cause of sinusitis. However, abnormalities revealed on CT in this study may have been associated with factors other than bacterial infection of the paranasal sinuses. Community-acquired rhinovinis infection is a common asthma trigger that has been shown to affect the appearance of the nasal passages and paranasal sinuses on a CT scan [14, 15]. Alternatively, acute exposure to high levels of aeroallergens could possibly produce widespread mucosal swelling found on a CT scan. Although the investigations required to support these assertions are beyond the scope of this study, it is significant that 1 1 of the 13 subjects Fig. 5.-Scattergram shows that CT scores in subjects with extensive sinus disease (CT score, 12 points [dotted/mel) improved from mean of 17.5 ± 1.0 points at initial presentation (left) to 11.1 ± 1.5 points at follow-up (right), indicating significant improvement (Mann-Whitney test, p =.003). Fig year-old black woman with 5-day history of wheezing, headache, and rhinorrhea. Coronal CT scan shows absence of mucosal thickening in any paranasal sinuses. CT score = 0 points. Fig year-old white woman with 3-day history of wheezing, rhinorrhea, and frontal headache. Coronal CT scan shows mucosal thickening in both ostiomeatal complexes, mucosal thickening in antenor ethmoidal sinuses, and mild mucosal thickening in maxillary sinuses (not evident on this cut). CT score = 10 points. Fig year-old black woman with acute asthma. A, Coronal CT scan obtained at presentation to emergency department shows severe mucosal thickening in maxillary sinuses. Other cuts revealed severe thickening in anterior ethmoidal sinuses, sphenoidal sinus, and nasal cavity. CT score = 18 points. B, Follow-up coronal CT scan obtained 136 days later, with resolution of asthma symptoms, shows only mild thickening in left ostiomeatal complex (not evident on this cut) and maxillary sinus. CT score = 3 points O U) 18 C (l)ie U) 14 I ! 0 C., I- 06 Initial CT Follow-Up CT 130 AJR:173, July 1999
5 CT of the Sinuses in Acute Asthma with Widespread mucosal thickening (score, 12 points) showed improvement on follow-up CT without receiving additional specific therapy for sinusitis (Figs. 4 and 5). Ofthe two subjects with no improvement shown on CT, one had been seen in the emergency department for acute asthma the day before the follow-up scan was obtained. These results suggest that sinus abnormalities in asthmatic patients may be an episodic part of the illness, with mucosal inflammation that waxes and wanes with respiratory symptoms. Thus, the pathogenesis of the observed mucosal thickening may be related to other inflammatory conditions, rhinovirus infection, or allergic rhinitis [10, 15]. Additional investigations will be required to confirm this hypothesis. This study is the first to show an association between extensive sinus mucosal thickening detected by CT and acute asthma. The identification of transient, acute sinus changes seen on CT differs from the previously published association between chronic sinusitis and asthma [10, 11]. However, the subjects in the earlier studies were selected from a pool of older patients referred to an otolaryngologist for evaluation of chronic severe sinus symptoms, and this group may not be typical ofmost adults with asthma. Furthermore, only one of the asthmatic patients in our study met the criteria for Samter s syndrome, which consists of severe asthma, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyposis, and sensitivity to aspirin (or related compounds) [ 16, 17]. These classic criteria have long been associated with severe adult-onset asthma; however, the mucosal changes seen on CT in this study are mostly unrelated to Samter s syndrome. because only one subject met the criteria (Fig. I). Even when polypoid tissue was identified using CT in the subjects in this study, the incidence of polypoid-appearing mucosa was not significantly higher in the a.sthmatic patients than in the control subjects (Table 3). This finding suggests that polypoid-appearing tissue seen on CT may be unrelated to asthma pathogenesis in most patients. However, the radiologist cannot say with certainty that polypoid-appearing tissue on CT is a polyp, because polyps are a histologic diagnosis. This study shows extensive sinus disease (CT score, 12 points) in almost one third of patients presenting with acute exacerbations of asthma. The sinus abnormalities found in the study subjects probably reflect either an acute or acute-on-chronic process rather than a purely chronic process, because in the patients who underwent CT a second time, the disease appeared to have abated significantly with time. If imaging of the paranasal sinuses is planned for patients with acute asthma, CT should be the preferred technique because CT can detect dinically significant disease in the nasal passages, ostiomeatal complex, and ethmoidal and sphenoidal sinuses. Disease in these areas, not in the maxillary sinuses, appears to be related to the pathogenesis of acute asthma. Unfortunately, CT scans cannot show what proportion of the disease is attributable to allergic inflammation, bacterial infection, or acute viral infection; additional clinical and laboratory investigations that are beyond the scope of this study may be required to identify the cause of sinus abnormalities in patients with acute asthma. References 1. Gouleib Mi. Relation ofintranasal disease in the pmduction ofbronchial asthma JAMA 1925;85:l Zimmerman B, Stringer D, Feanny S. et at. Prevalence ofabnormalities found by sinus x-rays in childhood asthma: lack ofrelation to severity of asthma. JAllergy Clin Immunol 19$7;80: Schwartz HJ, Thompson is, Sher TH, Ross Ri. Occult sinus abnormalities in the asthmatic patient.arrh Intern Med 1987:147: Rossi OVI, Pirila 1, Laitinen I, Huhti E. Sinus aspirates and radiographic abnormalities in severe attacks of asthma. In: Arch Allergy Immuno! 1994: 103: Burke IF, Guertler AT, Timmons JH. Comparison of sinus x-rays with computed tomograpy scans in acute sinusitis. AcadEmerg Med 1994:1: Lazar RH, Younis RT, Parvey LS. Comparison of plain radiographs. coronal CT, and intraoperative findings in children with chronic sinusitis. 0:0- laryngol HeadNeck Surg 1992:107: Zinreich SI. Imaging ofchronic sinusitis in adults: x-ray. computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1992:90: Anonymous. Standardization of spirometry: 1987 update-statement of the American Thoracic Society. Am Rev Respir Dis 1987:136: Phillips CD. Current status and new developments in techniques for imaging the nose and sinuses. 0:o1ar,ngo! Clin NorthAm 1997:30: Hoover GE, Newman Li, Platts-Mills TAE, Phillips CD. Gross CW, Wheatley LM. Chronic sinusitis: risk factors for extensive disease. J Allergy C/in Immunol 1997:100: Newman U, Plans-Mills TAE, Phillips CD. Hazen KC. Gross CW. Chronic sinusitis: relationship of computed tomographic findings to allergy. asthma, and eosinophila. JAMA 1994:271: Evans KL. Diagnosis and management of sinusitis. BMJ 1994:309: Havas TE, Motbey ia. Gullane PJ. Prevalence of incidental abnormalities on computed tomographic scans of the paranasal sinuses. Arch 0:olaryngol HeadNeck Surg 1988:114: Johnston SL, Pattemore PK, Sanderson G, et al. A community study of the role of viral infections in exacerbations ofasthma in 9-11 year old children. BMJ 1995;3l0: Gwaltney IM, Phillips CD, Miller RD. Riker DK. Computed tomographic study of the common cold. N Engi J Med 1994;330: Samter M, Beers RF. Intolerance to aspirin: clinical studies and consideration of its pathogenesis. Ann Intern Med 1968;68: Zeitz Hi. Bronchial asthma, nasal polyps. and aspirin sensitivity: Samter s syndrome. C/in Chest Med 1988:9: AJR:173, July
Sinusitis in Thai Asthmatic Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Sinusitis in Thai Asthmatic Children Nualanong Visitsuntorn 1 Kampanad Balankura 1 Sriprapai Keorochana 2 Suprida Habanananda Pakit Vlchyanond 1 and Montri Tuchlnda 1 Sinusitis has been
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Sinusitis in Thai Asthmatic Children Nualanong Visitsuntorn 1 Kampanad Balankura 1 Sriprapai Keorochana 2 Suprida Habanananda Pakit Vlchyanond 1 and Montri Tuchlnda 1 Sinusitis has been
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE
 PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
PROFESSOR DR SALINA HUSAIN DEPUTY HEAD DEPARTMENT OF OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY-HEAD NECK SURGERY UKM MEDICAL CENTRE MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS IN PRIMARY CARE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES ON MANAGEMENT
Rhinosinusitis. John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD
 Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
Rhinosinusitis John Ramey, MD Joseph Russell, MD Disclosure Statement RSFH as a continuing medical education provider, accredited by the South Carolina Medical Association, it is the policy of RSFH to
SINUSITIS. HAVAS ENT CLINICS Excellence in otolaryngology
 JULY 2015 SINUSITIS WHAT IS IT? WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? WHAT WORKS? THOMAS E HAVAS MBBS (SYD) MD (UNSW) FRCSE, FRACS, FACS CONJOINT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNSW OTOLARNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY HAVAS ENT CLINICS
JULY 2015 SINUSITIS WHAT IS IT? WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? WHAT WORKS? THOMAS E HAVAS MBBS (SYD) MD (UNSW) FRCSE, FRACS, FACS CONJOINT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNSW OTOLARNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY HAVAS ENT CLINICS
Chronic Sinusitis. Acute Sinusitis. Sinusitis. Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses. Sinusitis. Medical Topics - Sinusitis
 1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
Study of correlation between patient symptomatology and incidental paranasal sinus abnormalities detected on CT & MRI Brain imaging
 Original article Study of correlation between patient symptomatology and incidental paranasal sinus abnormalities detected on CT & MRI Brain imaging 1 DR. SHAIKH IMRAN NIZAMUDDIN, 2 DR. Y.P.SACHDEV*, 3
Original article Study of correlation between patient symptomatology and incidental paranasal sinus abnormalities detected on CT & MRI Brain imaging 1 DR. SHAIKH IMRAN NIZAMUDDIN, 2 DR. Y.P.SACHDEV*, 3
Use of Standard Radiography to Diagnose Paranasal Sinus Disease of Asthmatic Children in Taiwan: Comparison with Computed Tomography
 rasian PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (1999) 17. 69-76 Use of Standard Radiography to Diagnose Paranasal Sinus Disease of Asthmatic Children in Taiwan: Comparison with Computed Tomography Li-Chen
rasian PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (1999) 17. 69-76 Use of Standard Radiography to Diagnose Paranasal Sinus Disease of Asthmatic Children in Taiwan: Comparison with Computed Tomography Li-Chen
Review Article The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Pathophysiology and Etiology
 Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS PIDS AND RESPIRATORY DISORDERS 1 PRIMARY IMMUNODEFICIENCIES ABBREVIATIONS COPD CT MRI IG PID Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Computed tomography
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem
 Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Chapter Five. 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM.
 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision
 THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
Mucocele of paranasal sinuses
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 7, 2012 Mucocele of paranasal sinuses Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/57/ Mucoceles of paranasal
Middleton Chapter 43 (pages ) Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps Prepared by: Malika Gupta, MD
 FIT Board Review Corner December 2017 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Amar Dixit, MD, and Christin L. Deal, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In- Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner December 2017 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Amar Dixit, MD, and Christin L. Deal, MD, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In- Training (FITs)
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS
 MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Otorhinolaryngologist - Head & Neck Surgeons (MS)-HNS) Academy of Medicine Malaysia KEY MESSAGES
MANAGEMENT OF RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADOLESCENTS AND ADULTS Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Otorhinolaryngologist - Head & Neck Surgeons (MS)-HNS) Academy of Medicine Malaysia KEY MESSAGES
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Ighodaro O. Emmanuel, Ehigiamusoe O. Festus
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lund-Mackay Scoring of Incidental Paranasal Sinus Collection on Computed Tomography Scan of Head and Neck in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Nigeria Ighodaro O. Emmanuel, Ehigiamusoe
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Lund-Mackay Scoring of Incidental Paranasal Sinus Collection on Computed Tomography Scan of Head and Neck in the University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Nigeria Ighodaro O. Emmanuel, Ehigiamusoe
DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC
 MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS DR ZULKEFLI HUSSEIN CONSULTANT EAR NOSE & THROAT SURGEON PANTAI HOSPITAL PENANG DISCLAIMER Nothing to disclose PENANG ISLAND, MALAYSIA
MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS DR ZULKEFLI HUSSEIN CONSULTANT EAR NOSE & THROAT SURGEON PANTAI HOSPITAL PENANG DISCLAIMER Nothing to disclose PENANG ISLAND, MALAYSIA
Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
Review Article The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Nasal Polyposis. DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore
 Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Nasal Polyposis DEPARTMENT OF ENT K.S.Hegde Medical Academy Deralakatte, Mangalore Def: INTRODUCTION Chronic inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane in the nose & PNS, presenting as pedunculated smooth
Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis
 Original article: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis G.S. Thalor Senior Specialist (MS) (department of Oto Rhino Laryngology), Govt. S.K. Hospital, Sikar, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding
Original article: Retrospective Analysis of Patients with Allergy Sinusitis G.S. Thalor Senior Specialist (MS) (department of Oto Rhino Laryngology), Govt. S.K. Hospital, Sikar, Rajasthan, India. Corresponding
The Relation between Anatomical Variations of Osteomeatal Complex & Nasal Structures and Chronic Sinusitis by Computed Tomography
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2015; 3(2): 16-20 Published online March 6, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20150302.12 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN:
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2015; 3(2): 16-20 Published online March 6, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20150302.12 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN:
SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS
 1. Medical Condition TUEC Guidelines SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS Sinusitis refers to inflammation of the sinuses only while the more clinically relevant term should be Rhinosinusitis which is the inflammation
1. Medical Condition TUEC Guidelines SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS Sinusitis refers to inflammation of the sinuses only while the more clinically relevant term should be Rhinosinusitis which is the inflammation
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections OTITIS MEDIA Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear. There are more than 709 million cases of otitis media worldwide each year; half of these cases occur in
Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief.
 Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
Sinus Sinus Congestion, headache, recurrent infection, post-nasal drip, smell problems? We can find the source and offer solutions for relief. So what is sinusitis? Although many individuals interpret
Original Article. Relieving Symptoms of Chronic Sinusitis in Children By Adenoidectomy
 Original Article Relieving Symptoms of Chronic Sinusitis in Children By Adenoidectomy * C.A.B.M.S/ENT Summary: Background: To determine the efficacy of adenoidectomy in relieving symptoms of chronic sinusitis
Original Article Relieving Symptoms of Chronic Sinusitis in Children By Adenoidectomy * C.A.B.M.S/ENT Summary: Background: To determine the efficacy of adenoidectomy in relieving symptoms of chronic sinusitis
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections / 42
 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Acute tonsillitispharyngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Common cold Acute laryngitis Otitis externa Mastoiditis Acute apiglottis
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections 1 Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Acute tonsillitispharyngitis Acute otitis media Acute sinusitis Common cold Acute laryngitis Otitis externa Mastoiditis Acute apiglottis
Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty
 Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: septoplasty 4/1999 8/2018 8/2019 8/2018 Description of Procedure or Service There are many potential
Corporate Medical Policy Septoplasty File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: septoplasty 4/1999 8/2018 8/2019 8/2018 Description of Procedure or Service There are many potential
The clinical diagnosis of acute purulent sinusitis in general practice a review
 The clinical diagnosis of acute purulent sinusitis in general practice a review Morten Lindbæk and Per Hjortdahl SUMMARY Acute sinusitis is a common illness in primary care. Studies have demonstrated the
The clinical diagnosis of acute purulent sinusitis in general practice a review Morten Lindbæk and Per Hjortdahl SUMMARY Acute sinusitis is a common illness in primary care. Studies have demonstrated the
Prof. Marek L. Kowalski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Immunology, Rheumatology and Allergy, Chair of Immunology, Medical University of Łódź, Poland
 Rhinosinusitis and Asthma Exacerbations Prof. Marek L. Kowalski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Immunology, Rheumatology and Allergy, Chair of Immunology, Medical University of Łódź, Poland Chronic rhinosinusitis
Rhinosinusitis and Asthma Exacerbations Prof. Marek L. Kowalski, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Immunology, Rheumatology and Allergy, Chair of Immunology, Medical University of Łódź, Poland Chronic rhinosinusitis
Disclaimers. Topical Therapy. The Problem. Topical Therapy for Chronic Rhinosinusitis No Disclosures
 Topical Therapy for Chronic Rhinosinusitis No Disclosures Disclaimers Off-label use of multiple steroid and antibiotic medications Large talk, limited time Steven D. Pletcher MD University of California,
Topical Therapy for Chronic Rhinosinusitis No Disclosures Disclaimers Off-label use of multiple steroid and antibiotic medications Large talk, limited time Steven D. Pletcher MD University of California,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Extended Endoscopic Frontal Sinus Surgery to Interrupted Nasofrontal Communication Caused by Scarring of the Anterior Ethmoid
 Extended Endoscopic Frontal Sinus Surgery to Interrupted Nasofrontal Communication Caused by Scarring of the nterior Ethmoid Long-term Results ORIGINL RTICLE Toru Kikawada, MD; Masao Fujigaki, MD; Mikino
Extended Endoscopic Frontal Sinus Surgery to Interrupted Nasofrontal Communication Caused by Scarring of the nterior Ethmoid Long-term Results ORIGINL RTICLE Toru Kikawada, MD; Masao Fujigaki, MD; Mikino
Consumer summary. Endoscopic modified Lothrop procedure for the. treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis
 ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Endoscopic modified Lothrop procedure for the treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis (The report
ASERNIP S Australian Safety and Efficacy Register of New Interventional Procedures Surgical Consumer summary Endoscopic modified Lothrop procedure for the treatment of chronic frontal sinusitis (The report
Acute rhinosinusitis is defined as. Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis in Adults: Part I. Evaluation
 This is a corrected version of the article that appeared in print. Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis in Adults: Part I. Evaluation DEWEY C. SCHEID, M.D., M.P.H., and ROBERT. M. HAMM, PH.D. University of Oklahoma
This is a corrected version of the article that appeared in print. Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis in Adults: Part I. Evaluation DEWEY C. SCHEID, M.D., M.P.H., and ROBERT. M. HAMM, PH.D. University of Oklahoma
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i1.116 Nasal Polyps- Causes and Associated Symptoms-
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v5i1.116 Nasal Polyps- Causes and Associated Symptoms-
Rhinosinusitis in severe asthma
 Rhinosinusitis in severe asthma Megon Bresciani, MD, a Louis Paradis, MD, a Anne Des Roches, MD, a Hélène Vernhet, MD, b Isabelle Vachier, PhD, a Philippe Godard, MD, a Jean Bousquet, MD, PhD, a and Pascal
Rhinosinusitis in severe asthma Megon Bresciani, MD, a Louis Paradis, MD, a Anne Des Roches, MD, a Hélène Vernhet, MD, b Isabelle Vachier, PhD, a Philippe Godard, MD, a Jean Bousquet, MD, PhD, a and Pascal
ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
OSTEITIS IN CRS. Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a
 OSTEITIS IN CRS Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a ROAD MAP Definition. pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Grading systems. Clinical implications. Management. OSTEITIS Presence of new bone formation,
OSTEITIS IN CRS Rhinology Chair Meeting presented by Amal Binhazza a ROAD MAP Definition. pathophysiology. Diagnosis. Grading systems. Clinical implications. Management. OSTEITIS Presence of new bone formation,
A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF TÂRGU MUREȘ ROMANIA A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS PhD THESIS ABSTRACT PhD Student Viorel Emanoil
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF TÂRGU MUREȘ ROMANIA A CONTRIBUTION TO THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF SINONASAL INVERTED PAPILLOMAS PhD THESIS ABSTRACT PhD Student Viorel Emanoil
Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis
 Original papers Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis Marcin Frączek 1, A D, F, Marcin Masalski 1, B, B, E, Maciej Guziński 1 Department of Otolaryngology,
Original papers Reliability of computed tomography scans in the diagnosis of chronic rhinosinusitis Marcin Frączek 1, A D, F, Marcin Masalski 1, B, B, E, Maciej Guziński 1 Department of Otolaryngology,
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 05 Page May 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i5.25 Radiologic Variations of Nose and Paranasal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i5.25 Radiologic Variations of Nose and Paranasal
Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/130 Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre B G Prakash 1, Suhasini Biyyapu 2 1 Professor, Department of ENT, JSS Medical College,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/130 Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre B G Prakash 1, Suhasini Biyyapu 2 1 Professor, Department of ENT, JSS Medical College,
What causes abnormal secretions?
 Post-Nasal Drip Glands in your nose and throat continually produce mucus (one to two quarts a day). Mucus moistens and cleans the nasal membranes, humidifies air, traps and clears inhaled foreign matter,
Post-Nasal Drip Glands in your nose and throat continually produce mucus (one to two quarts a day). Mucus moistens and cleans the nasal membranes, humidifies air, traps and clears inhaled foreign matter,
Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults Guideline
 Member Groups Requesting Changes: Lakeview Clinic Marshfield Clinic Mayo Clinic South Lake Pediatrics Response Report for Review and Comment January 2013 Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness
Member Groups Requesting Changes: Lakeview Clinic Marshfield Clinic Mayo Clinic South Lake Pediatrics Response Report for Review and Comment January 2013 Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness
thus, the correct terminology is now rhinosinusitis.
 By: Ibrahim Alarifi Introduction Rhinitis and sinusitis usually coexist and are concurrent in most individuals; thus, the correct terminology is now rhinosinusitis. Mucosa of the nose is a continuation
By: Ibrahim Alarifi Introduction Rhinitis and sinusitis usually coexist and are concurrent in most individuals; thus, the correct terminology is now rhinosinusitis. Mucosa of the nose is a continuation
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP SINUS CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70486, 70487, 70488, 76380
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP SINUS CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70486, 70487, 70488, 76380
CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS
 CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS SCOPE OF THE PRACTICE GUIDELINE This clinical practice guideline is for use by the Philippine Society of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. It covers the diagnosis and
CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS IN ADULTS SCOPE OF THE PRACTICE GUIDELINE This clinical practice guideline is for use by the Philippine Society of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. It covers the diagnosis and
The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction Fatma
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction Fatma
4/7/13 SINUSITIS WHO ARE WE TREATING? AMANDA SAM CONLEY RN, MSN, CFN, LNC, FNP- BC
 SINUSITIS WHO ARE WE TREATING? AMANDA SAM CONLEY RN, MSN, CFN, LNC, FNP- BC 1 DefiniGons Anatomy Review Signs and Symptoms OBJECTIVES Acute Viral vrs. Acute Bacterial Treatment Guidelines ANATOMY REVIEW
SINUSITIS WHO ARE WE TREATING? AMANDA SAM CONLEY RN, MSN, CFN, LNC, FNP- BC 1 DefiniGons Anatomy Review Signs and Symptoms OBJECTIVES Acute Viral vrs. Acute Bacterial Treatment Guidelines ANATOMY REVIEW
Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment
 Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment INFECTION INFLAMMATION Predisposing Factors Anatomical variations Allergic rhinitis Acute sinusitis Immune deficiency Rhinosinusitis Non-allergic rhinitis Chronic sinusitis
Chronic Rhinosinusitis-Treatment INFECTION INFLAMMATION Predisposing Factors Anatomical variations Allergic rhinitis Acute sinusitis Immune deficiency Rhinosinusitis Non-allergic rhinitis Chronic sinusitis
Anatomically, lower respiratory tract is directly connected with the upper one. Ideally, when both specialists manage
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com MANAGEMENT FEATURES OF PATIENT WITH BRONCHIAL ASTHMA AND ACUTE EXACERBATION OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS BY VACUUM DRAINAGE
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com MANAGEMENT FEATURES OF PATIENT WITH BRONCHIAL ASTHMA AND ACUTE EXACERBATION OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS BY VACUUM DRAINAGE
Evaluating Chronic Cough in Children
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/hot-topics-in-allergy/evaluating-chronic-cough-in-children/3914/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/hot-topics-in-allergy/evaluating-chronic-cough-in-children/3914/
Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Pathological l & Radiological i l Evidences in the Pathogenesis es s of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study Prof. Dr. H. ABDEL FATAH, MD A. Prof. Dr. K. NOWEAM, MD Dr. Z.
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Pathological l & Radiological i l Evidences in the Pathogenesis es s of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Prospective Study Prof. Dr. H. ABDEL FATAH, MD A. Prof. Dr. K. NOWEAM, MD Dr. Z.
Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses
 14. Sommerschule Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses Bettlach 24.08.2018 Christoph Schlegel Conventional Radiology NNH-Status: okzipito-frontal: frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid okzipito-nasal : maxillary
14. Sommerschule Imaging of the Paranasal Sinuses Bettlach 24.08.2018 Christoph Schlegel Conventional Radiology NNH-Status: okzipito-frontal: frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid okzipito-nasal : maxillary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Toru Kikawada, MD; Takeo Nonoda, MD; Mariko Matsumoto, MD; Mikino Kikura, MD; Keiko Kikawada, MD
 ORIGINAL ARTILE Treatment of Intractable iseased Tissue in the Maxillary Sinus After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery With High-Pressure Water Jet and Preservation of the Periosteum Toru Kikawada, M; Takeo Nonoda,
ORIGINAL ARTILE Treatment of Intractable iseased Tissue in the Maxillary Sinus After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery With High-Pressure Water Jet and Preservation of the Periosteum Toru Kikawada, M; Takeo Nonoda,
US Drug Eluting Sinus Stent (DESS) Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts ( ) September 2016
 US Drug Eluting Sinus Stent (DESS) Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts (2016-2021) September 2016 US Drug Eluting Sinus Stent Market Report Scope of the Report The report entitled US Drug Eluting Sinus Stent
US Drug Eluting Sinus Stent (DESS) Market: Size, Trends & Forecasts (2016-2021) September 2016 US Drug Eluting Sinus Stent Market Report Scope of the Report The report entitled US Drug Eluting Sinus Stent
Advances in the Surgical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 Rhinitis and Sinusitis dvances in the Surgical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Erin D. Wright, MDCM, MEd, FRCSC; Saul Frenkiel, MDCM, FRCSC bstract The surgical management of chronic rhinosinusitis
Rhinitis and Sinusitis dvances in the Surgical Management of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Erin D. Wright, MDCM, MEd, FRCSC; Saul Frenkiel, MDCM, FRCSC bstract The surgical management of chronic rhinosinusitis
Epidemiology of nasal polyps in hilly areas and its risk factors
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Nanda MS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;3(1):77-81 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Nanda MS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;3(1):77-81 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Case Report
 Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Destructive Giant Maxillary Sinus Mucocele: A Vahit Mutlu 1, Ozgur Yoruk 1, Ozalkan Ozkan 2 1 Atatürk University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ears, Nose and Throat, Erzurum, Turkey 2 Erzincan University
Boundaries Septum Turbinates & Meati Lamellae Drainage Pathways Variants
 The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
DURATION OF ORAL ANTIBIOTIC IN THE SETING OF MAXIMAL MEDICAL THERAPY FOR CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS. Dr. Ziyad Al-Abduljabbar
 DURATION OF ORAL ANTIBIOTIC IN THE SETING OF MAXIMAL MEDICAL THERAPY FOR CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS Dr. Ziyad Al-Abduljabbar International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, Vol. 5, No. 9, September 2015 INTRODUCTION
DURATION OF ORAL ANTIBIOTIC IN THE SETING OF MAXIMAL MEDICAL THERAPY FOR CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS Dr. Ziyad Al-Abduljabbar International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, Vol. 5, No. 9, September 2015 INTRODUCTION
Consultation for Sinusitis and Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 Consultation for Sinusitis and Endoscopic Sinus Surgery This consultation is part of a series of consultations with Head and Neck Surgery specialists at the University of California, San Diego. The case
Consultation for Sinusitis and Endoscopic Sinus Surgery This consultation is part of a series of consultations with Head and Neck Surgery specialists at the University of California, San Diego. The case
TUEC Guidelines Medical Information to Support the Decisions of TUE Committees Sinusitis/Rhinosinusitis SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS
 1. Medical Condition SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS Sinusitis refers to inflammation of the sinuses only while the more clinically relevant term should be Rhinosinusitis which refers to inflammation of both
1. Medical Condition SINUSITIS/RHINOSINUSITIS Sinusitis refers to inflammation of the sinuses only while the more clinically relevant term should be Rhinosinusitis which refers to inflammation of both
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
Spine MRI and Spine CT MRI is almost always preferred over CT scan; if ordering CT, CLEARLY document why MRI is not appropriate. In cases of back pain without red flags, six weeks of multimodality supervised
Osteomeatal unit OMU
 20074724752 CT Osteomeatal unitomu Assessment of the Relationship between Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis and Findings in the Ostiomeatal Unit on Coronal CT Images Miya Kato, Takashi Kaneda, Masataka Kato,
20074724752 CT Osteomeatal unitomu Assessment of the Relationship between Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis and Findings in the Ostiomeatal Unit on Coronal CT Images Miya Kato, Takashi Kaneda, Masataka Kato,
Sinusitis. What are the sinuses? Who develops sinusitis?
 Sinusitis Health experts estimate that 37 million Americans are affected by sinusitis every year. Americans spend nearly $6 billion each year on health care costs related to sinusitis. Sinusitis is an
Sinusitis Health experts estimate that 37 million Americans are affected by sinusitis every year. Americans spend nearly $6 billion each year on health care costs related to sinusitis. Sinusitis is an
9/18/2018. Disclosures. Objectives
 Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Impact of Sinus Computed Tomography on Treatment Decisions for Chronic Sinusitis. widespread condition, affecting
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Impact of Sinus Computed Tomography on Treatment Decisions for Chronic Sinusitis Yoshimi Anzai, MD; Ernest A. Weymuller, Jr, MD; Bevan Yueh, MD, MPH; Nicole Maronian, MD; Jeffrey G.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Impact of Sinus Computed Tomography on Treatment Decisions for Chronic Sinusitis Yoshimi Anzai, MD; Ernest A. Weymuller, Jr, MD; Bevan Yueh, MD, MPH; Nicole Maronian, MD; Jeffrey G.
RoleofAllergyinNasalPolyposis. Role of Allergy in Nasal Polyposis
 Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 1 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2
 STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Santhosha Kumar B, Manjunath Rao S. V. Study of Correlation between
STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Santhosha Kumar B, Manjunath Rao S. V. Study of Correlation between
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr.V. Krishna Chaitanya
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(1G):508-513 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(1G):508-513 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Evaluation of Ultrasound Efficiency in the Diagnosis of Acute Maxillary Sinusitis in Comparison with CT Scan Findings in Children Aged 5 to 15 Years
 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Sciences 2018, Volume 6, Issue 3, Page No: 363-367 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Evaluation
Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Sciences 2018, Volume 6, Issue 3, Page No: 363-367 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Evaluation
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with rhinosinusitis and the following clinical presentations or diagnoses:
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Rhinosinusitis AUC 12/04/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with rhinosinusitis and the following clinical presentations or diagnoses:
The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their relationship with maxillary sinusitis based on CBCT finding
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 11:152-156 The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 11:152-156 The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page 1390-1394 Anatomical Variations of Nasal Structures in Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Detected by Computed Tomography Scan Omar Adnan Hasan,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page 1390-1394 Anatomical Variations of Nasal Structures in Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Detected by Computed Tomography Scan Omar Adnan Hasan,
Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis. Difficulties in diagnosis and treatment Videler, W.J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Videler, W.
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations
 White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Sponsor Novartis Consumer Health, SA. Generic Drug Name
 Sponsor Novartis Consumer Health, SA Generic Drug Name Xylometazoline Hydrochloride Trial Indication(s) For the symptomatic relief of nasal congestion due to colds, hayfever or other allergic rhinitis,
Sponsor Novartis Consumer Health, SA Generic Drug Name Xylometazoline Hydrochloride Trial Indication(s) For the symptomatic relief of nasal congestion due to colds, hayfever or other allergic rhinitis,
Sinusitis. 12 weeks. Subacute sinusitis: An inflammation lasting 4 to 8 weeks. weeks or longer Re urre t si usitis: Se eral atta ks ithi a year
 Sinusitis 12 weeks. Sinusitis, also known as a sinus infection or rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the sinuses resulting in symptoms. Common signs and symptoms include thick nasal mucous, a plugged nose,
Sinusitis 12 weeks. Sinusitis, also known as a sinus infection or rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the sinuses resulting in symptoms. Common signs and symptoms include thick nasal mucous, a plugged nose,
Katya A. Shpilberg 1 Simon C. Daniel 1 Amish H. Doshi 1 William Lawson 2 Peter M. Som 1. Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Shpilberg et al. CT of Paranasal Sinuses and Nasal Cavity Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Katya A. Shpilberg 1 Simon C. Daniel
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Shpilberg et al. CT of Paranasal Sinuses and Nasal Cavity Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Katya A. Shpilberg 1 Simon C. Daniel
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis.
 DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
CASE REPORTS. Inflammatory Polyp of the Bronchus. V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D.
 CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
CASE REPORTS V. K. Saini, M.S., and P. L. Wahi, M.D. I n 1932 Jackson and Jackson [l] first reported a number of clinical cases under the title Benign Tumors of the Trachea and Bronchi with Especial Reference
Diagnosis and Treatment of Respiratory Illness in Children and Adults
 Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
Page 1 of 9 Main Algorithm Annotations 1. Patient Reports Some Combination of Symptoms Patients may present for an appointment, call into a provider to schedule an appointment or nurse line presenting
Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 29, January-March 2018 ORIGINAL STUDY DOI: 10.2478/rjr-2018-0003 Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities Emilia
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 29, January-March 2018 ORIGINAL STUDY DOI: 10.2478/rjr-2018-0003 Clinical and imagistic correlations in the inflammatory pathology of nasosinusal cavities Emilia
Spheno-Ethmoidectomy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal Ostiomeatal Channels and Paranasal Sinuses
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.192 on 12/22/17 from IP address 37.44.202.192. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.192 on 12/22/17 from IP address 37.44.202.192. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal
Variation in frontal cells in relation to chronic frontal sinusitis
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 244-71 P-ISJN: A472-04, E -ISJN: A472-01 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume, Issue 1-2019 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2019.0.01.00
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 244-71 P-ISJN: A472-04, E -ISJN: A472-01 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume, Issue 1-2019 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2019.0.01.00
Nasal Polyps. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Nasal Polyps must be made in conjunction with your Physician or
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Nasal Polyps must be made in conjunction with your Physician or
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res.2015;6(1):4775-4781 Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International Journal of Biological & Medical Research Journal homepage: www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect
Int J Biol Med Res.2015;6(1):4775-4781 Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International Journal of Biological & Medical Research Journal homepage: www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect
SYNOPSIS. A Multi-center, Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Parallel Group, Phase II Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of RHINOCORT
 Drug product: RHINOCORT AQUA Drug substance(s): Budesonide Edition No.: Final Study code: D5360C00703 Date: 8 November 2005 SYNOPSIS A Multi-center, Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Parallel
Drug product: RHINOCORT AQUA Drug substance(s): Budesonide Edition No.: Final Study code: D5360C00703 Date: 8 November 2005 SYNOPSIS A Multi-center, Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Parallel
Case Report Adult-Onset Woakes Syndrome: Report of a Rare Case
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 857675, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/857675 Case Report Adult-Onset Woakes Syndrome: Report of a Rare Case U. Schoenenberger and A. J. Tasman
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 857675, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/857675 Case Report Adult-Onset Woakes Syndrome: Report of a Rare Case U. Schoenenberger and A. J. Tasman
Spine MRI and Spine CT Test Request Tip Sheet
 Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Spine MRI and Spine CT With/Without Contrast CT, MRI The study considered best for a specific clinical scenario should be ordered. The second study should be done ONLY if the first study does not provide
Sinus Surgery. Middle Meatus
 Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Preventing sinusitis Health24. Page 3
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : TREAT AND PREVENT SINUSITIS WHAT YOUR DOCTOR ISNT TELLING YOU SINUS INFECTION SINUSITIS SYMPTOMS SINUSITIS TREATMENT SINUS CURE CHRONIC SINUSITIS SYMPTOMS TRANSCEND MEDIOCRITY BOOK 35
DOWNLOAD OR READ : TREAT AND PREVENT SINUSITIS WHAT YOUR DOCTOR ISNT TELLING YOU SINUS INFECTION SINUSITIS SYMPTOMS SINUSITIS TREATMENT SINUS CURE CHRONIC SINUSITIS SYMPTOMS TRANSCEND MEDIOCRITY BOOK 35
