ASTHMA EXACERBATION PEDIATRIC
|
|
|
- Betty Underwood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEFINITION Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by repeated episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, and cough due to reversible airflow obstruction and bronchial hyper-responsiveness. In this situation, the client has a preexisting diagnosis of asthma. Exacerbations are considered a progression of asthma beyond good control of symptoms and/or severe enough to require an increase in medication. Pediatric includes 1 to 17 years, 11 months, 29 days of age. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Acute respiratory distress (moderate to severe exacerbation) as indicated by: o Difficulty speaking (unable to complete sentences) o Marked use of accessory muscles of respiration o Breath sounds decreased in intensity o Diffuse, high-pitched wheezes (inspiratory, expiratory or both) o Sp02 < 90% Agitated, diaphoretic, and lethargic No prior relief afforded by ß2-agonists Status asthmaticus: beware of the silent chest (poor air entry, no wheezing) in a client with a history of asthma that presents in acute respiratory distress CAUSES Although the exact cause is unknown, three principle triggers for exacerbation of asthma have been identified: 1. Allergies and environmental factors a. Allergens may include inhaled substance (e.g., molds, pollens, dust, animal danders, cosmetics, tobacco smoke). b. Medications, particularly beta-blockers, aspirin, or aspirin containing drugs. 2. Infections a. Upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) are common precursors to an asthma attack. b. Viral infections commonly precede an asthma attack. 1 P age
2 i. In children < 6 years of age, wheezing episodes are commonly associated with a viral respiratory illness. ii. In children < 2 years of age, the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is commonly associated with wheezing. 3. Psychological factors a. Stressful events at work or home or a series of crises may precipitate an asthma attack. Many times, the stressor is overlooked or dismissed. Inflammation of the airways contributes to bronchial hyperreactivity, airflow limitation, and the resultant signs and symptoms of asthma: wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and cough. PREDISPOSING AND RISK FACTORS Severe or recurrent RSV infection Recurrent pneumonia Familial tendency Poorly controlled asthma o Frequent asthma attacks (> two per week) o Recent severe attack o Recent visit to emergency room or admission to hospital or ICU for asthma o Duration of current symptoms > 24 hours o Non-adherence to pharmacological treatment (inhaler usage) Long delay in seeking medical care Overcrowded housing Dust/mold/poor status of housing (e.g., exposed walls, insulation, increased humidity) Environmental factors such as cigarette smoke, wood smoke, forest fires, cold air Exercise Emotions (e.g., fear, anger, crying) Allergens o Recent exposure to known allergens (e.g., pollen) o Eczema (current or history of) o Frequent nose rubbing (crease across nose) o Watery eyes and nose 2 P age
3 HISTORY Table 1 Elements to Consider when Assessing Asthma Exacerbation Cough History Recurrent wheeze (absence does not rule out asthma) Recurrent episodic dyspnea Recurrent chest tightness Compliance and/or frequency of medication use Absence from school Admission to hospital Symptoms worsen in relation to specific factors Airborne chemicals or dust Animals with fur or feathers Changes in weather Exercise Gastroesophageal reflux Sensitivity to ASA, NSAIDs, and sulfites Dust mites in house (mattresses, furniture, carpets) Menses Mold/pollen Night time (client awakens) Smoke (tobacco, wood, etc.) Strong emotional expression (laughing, crying hard) Viral infection/rhinitis/sinusitis Note. Adapted from Primary care: The art and science of advanced practice nursing (4th ed.), p. 249, by L. M. Dunphy, J. E. Winland-Brown, B. O. Porter, & D. J. Thomas, 2015, Philadephia: F.A. Davis. 3 P age
4 PHYSICAL FINDINGS Determining Severity The severity of asthma is determined by the frequency and chronicity of symptoms, the presence of persistent airflow limitations, and the medication needed to maintain control of the condition. Mild Exacerbation Exertion-related dyspnea, no acute distress Cough Respiratory rate normal or minimally elevated Low-pitched wheezes (inspiratory or expiratory, or both, or none) Good response (usually) to short-acting ß2-agonists Moderate Exacerbation Dyspnea at rest Congested cough Tightness of the chest Nocturnal symptoms ß2-agonists needed > q4h Preceding or current URTI Allergy history Symptoms over previous 2-4 weeks Frequency of bronchodilator use (> 2 times per week) Activity level changes (e.g., missed work, sedentary activity) Hospital admissions for acute exacerbations Short of breath Respiratory rate elevated Some use of accessory muscles of respiration Audible wheeze High-pitched wheezes in all lung fields (inspiratory or expiratory, or both) ß2-agonists provide only partial relief Severe Exacerbation Signs and symptoms as per those indicated in the Immediate Consultation Required in the Following Situations section 4 P age
5 Consultation with a physician/rn(np) is recommended for treatment plan and evacuation Partial relief achieved with frequent inhaled short acting ß2-agonists The following table provides further clarification: Table 2 Pediatric Respiratory Assessment Measure (PRAM): Signs Suprasternal Absent Present Indrawing indrawing Scalene retractions* Absent Present Retractions Wheezing Absent Expiratory Inspiratory and expiratory Air Entry Normal Decreased/absent Decreased at bases widespread Oxygen > 95% 92-95% < 92% Interpreting total scores: 0-4 points: Mild Asthma 5-8 points: Moderate Asthma 9-12 points: Severe Asthma * Scalene retractions suprasternal retractions Audible without stethoscope Absent Note. Adapted from First Nations and Inuit health: Pediatric clinical guidelines for nurses in primary care, p. 10-6, by Health Canada, 2011, Ottawa, ON: Author. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS The younger the child, the greater likelihood that a diagnosis other than asthma may explain current wheezes. Wheezing does not always mean asthma, while asthma may be present without wheeze. Allergy 5 P age
6 Aspiration Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Congenital anomalies/disease (e.g., heart, intrathoracic) Cystic fibrosis Foreign body aspiration Gastroesophageal reflux Immune system disorders Pertussis Tuberculosis Recurrent viral lower respiratory infection COMPLICATIONS Restrictions in physical activity Psychological impact of chronic illness Localized bronchiectasis Status asthmaticus Death INVESTIGATIONS AND DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Pulse oximetry Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) - can be attempted in an older child, if he or she is not too distressed MAKING THE DIAGNOSIS Suspect asthma exacerbation in the presence of signs and symptoms listed under Physical Findings. An exacerbation that leads to the emergency department (or clinic in an emergent/urgent situation) is an indication of inadequate long-term asthma control or inadequate plans for handling exacerbations. MANAGEMENT AND INTERVENTIONS Goals of Treatment Relieve symptoms (reverse airflow obstruction, correct hypoxemia) Prevent complications (early bronchodilators and systemic corticosteroids) 6 P age
7 Prevent recurrence (adjust baseline therapy) Appropriate Consultation Consult a physician/rn(np) for: any child with previously undiagnosed (suspected) asthma with symptoms, such as: o Breathlessness o Chest tightness o Wheezing o Cough any child with known asthma who is experiencing severe acute symptoms. any child receiving long-term prophylaxis whose symptoms are not well controlled with the current medication regimen. Non-Pharmacological Interventions Education Education is an important part of the successful management of asthma and should be provided to all parents/caregivers and clients. Allergen and trigger avoidance Prevention/management of respiratory infections Avoidance of tobacco smoke and smoking Minimize exposure to pollens (from trees, grass, weeds) and outdoor mold Indoor mold o Fix all leaks and eliminate water sources associated with mold growth o Attempt to keep indoor humidity at less than 50% Animal dander o Remove animals from the home or keep animals out of the client s room o Air ducts should be covered with a dense filter (e.g., HEPA air cleaner) o Vacuum frequently House dust mites o Essential to encase mattress and pillows in an allergen-impermeable cover and wash bed sheets, pillow cases, and blankets weekly in hot water o Wash stuffed toys o If possible, remove carpets from the bedroom and avoid lying or sleeping on 7 P age
8 upholstered furniture Cockroaches o Use poison bait or traps to control o Do not leave food or garbage exposed o Fix leaky faucets and pipes Food o Avoid sulfites and other foods that exacerbate symptoms Medications o Avoid ASA and NSAIDS as risk of exacerbation is high with use of these medications Client Self-Monitoring Consider use of PEF monitoring if compliance is indicated No study has shown improved outcomes with PEF monitoring and compliance has been poor Use of inhalation devices Review proper use of inhalers and spacers Pharmacological Interventions In a case of acute asthma, it is strongly recommended that consultation take place with a physician/rn(np) to determine the treatment plan prior to giving any medication to a child. The two primary agents used in the treatment of acute asthma exacerbations are inhaled beta agonists and systemic glucocorticoids. Additional agents are used as needed depending upon the severity of the exacerbation. Inhaled bronchodilators (ß2-agonists) Salbutamol (Ventolin) 100 mcg/puff MDI (metered dose inhaler) with spacer (AeroChamber) 6-10 puffs/dose q20 minutes x 3 doses Or Nebulized salbutamol (Ventolin) q20 minutes x 3 doses: o Children < 10 kg: mg/dose o Children kg: 2.5 mg/dose 8 P age
9 o Children > 20 kg: 5 mg/dose If a full response is achieved, consult a physician/rn(np) for continuing management at home: Salbutamol by MDI 1-2 puffs q2-4h prn for relief depending on severity Salbutamol by nebulizer as per weight in kg, q2-4h for relief depending on severity And Prednisone 1-2 mg/kg/day orally for 3-5 days to a maximum dose of 60 mg. No tapering required. For those who are of adult dimension (usually > 12 years of age), the following may be added to treatment with MDI or nebulizer: Prednisone mg/day orally for 7-14 days. No tapering required. If a partial response is achieved, consult a physician/rn(np). In consultation, it may be decided to: Continue the ß2-agonists q20 minutes as above and add the following: o Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) MDI 5 puffs/dose q1h (same dose for all weights) Or o Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent) 250 mcg by nebulizer q1h And o Prednisone 1-2 mg/kg/day orally daily for 5 days (maximum dose of 50 mg) Or o MethylPREDNISolone (SoluMEDROL) 2 mg/kg bolus IV (to a maximum dose of 125 mg) then 0.5 mg/kg q6h. Initial dose may be given prior to consultation with a physician/rn(np). The RN(AAP) will ensure clients have the following medications prior to discharge from the clinic. If the client does not have, the RN(AAP) will prescribe and dispense: Fluticasone (Flovent) MDI and spacer 50 micrograms/puff, 1-2 puffs bid for 1 month Salbutamol (Ventolin) MDI and spacer 100 micrograms/puff, 1 puffs qid for 1 month 9 P age
10 Client and Caregiver Education Home management of asthma exacerbation is an integral part of asthma management. It is recommended that there is a written action plan which includes guided selfmanagement. An Action Plan based on symptoms and use of the stop light analogy is recommended and is available at: Provide instructions (preferably written) to the parents or caregiver on symptoms and signs of respiratory distress. Advise parents or caregiver to bring the child back to the clinic if there is no response to ß2-agonists or the response lasts < 2 hours. Counsel about appropriate use of drugs including dosages, administration techniques (e.g., use of MDI with spacer), effects, and side effects. Explain strategies to prevent further attacks by identifying the precipitating factor and counselling parents to avoid such factors. Prophylactic medication regimen as required. If any change in pharmacologic therapy is initiated, reassess the client in 1-4 weeks. Monitoring and Follow-Up Monitor ABCs, pulse oximetry, hydration, and level of consciousness while awaiting transport or discharge. Referral Child is critically ill (moderate to severe airway obstruction with respiratory distress) Poor response to emergency therapy: needs more than 3 or 4 salbutamol (Ventolin) treatments, post-treatment Sp02 < 95% on room air. Consider non-urgent consult with physician regarding Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT). DOCUMENTATION As per employer policy 10 P age
11 REFERENCES Asthma Society of Canada. (n. d.). Asthma action plan. Retrieved from Bass Iii, P. F. (2016). Rethinking asthma. Contemporary Pediatrics, 33(3), Dunphy, L. M., Winland-Brown, J. E., Porter, B. O., & Thomas, D. J. (2015). Primary care: The art and science of advanced practice nursing (4th ed.). Philadelphia: F.A. Davis. DynaMed. (2014). Asthma exacerbation in children. Retrieved from DynaMed. (2014). Asthma in children. Retrieved from Health Canada (2011). First Nations and Inuit health: Pediatric clinical practice guidelines for nurses in primary care. Ottawa, ON: Author. Retrieved from Humphery, D. A. (2013, March 23). Asthma. Retrieved from Klostranec, J. M., & Kolin, D. L. (Eds). (2012). Toronto notes: Comprehensive Medical Reference and Review For MCCQE1 &USMLE11. Toronto, ON: Toronto Notes for Medical Students Inc. ER31, FM14. Lawlor, R. (2015). Management of asthma in children. Practice Nursing, 26(7), Pollart, S. M., Compton, R. M., & Elward, K. S. (2011). Management of-acute-asthmaexacerbation. American Family Physician, 84(1), Respiratory Review Panel. (2011 Update). Respiratory (Asthma/COPD) Guidelines for family practice. Toronto, ON: MUMS Guideline Clearinghouse. Rx Files Academic Detailing Program. (2014). Rx Files: Drug comparison charts. Saskatoon, SK: Saskatoon Health Region. 11 P age
12 Sarfone, R. J. (2014, March 3). Acute asthma exacerbations in children: Emergency department. Retrieved from Sarfone, R. J. (2013, February 19). Acute asthma exacerbations in children: Outpatient management. Retrieved from NOTICE OF INTENDED USE OF THIS This SRNA Clinical Decision Tool (CDT) exists solely for use in Saskatchewan by an RN with additional authorized practice as granted by the SRNA. The CDT is current as of the date of its publication and updated every three years or as needed. A member must notify the SRNA if there has been a change in best practice regarding the CDT. This CDT does not relieve the RN with additional practice qualifications from exercising sound professional RN judgment and responsibility to deliver safe, competent, ethical and culturally appropriate RN services. The RN must consult a physician/rn(np) when clients needs necessitate deviation from the CDT. While the SRNA has made every effort to ensure the CDT provides accurate and expert information and guidance, it is impossible to predict the circumstances in which it may be used. Accordingly, to the extent permitted by law, the SRNA shall not be held liable to any person or entity with respect to any loss or damage caused by what is contained or left out of this CDT. SRNA This CDT is to be reproduced only with the authorization of the SRNA. 12 P age
ASTHMA EXACERBATION ADULT
 DEFINITION Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by repeated episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, and cough due to reversible airflow obstruction and bronchial hyper-responsiveness.
DEFINITION Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by repeated episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, and cough due to reversible airflow obstruction and bronchial hyper-responsiveness.
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
BRONCHIOLITIS PEDIATRIC
 DEFINITION Bronchiolitis is typically defined as the first episode of wheezing in infants < 24 months of age. It is a viral illness of the lower respiratory tract that causes tachypnea, bronchospasm, and
DEFINITION Bronchiolitis is typically defined as the first episode of wheezing in infants < 24 months of age. It is a viral illness of the lower respiratory tract that causes tachypnea, bronchospasm, and
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C Asthma Statistics 25.6 million Americans diagnosed with asthma 6.8 million are children 10.5 million missed school days per year 14.2 lost work days for adults Approximately 10%
MANAGING ASTHMA. Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C
 MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
MANAGING ASTHMA Nancy Davis, RRT, AE-C What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by episodes or attacks of inflammation and narrowing of small airways in response to asthma
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma. The prevalence of asthma has been increasing worldwide, but why this is happening is not known.
 Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Asthma What is asthma? Asthma is a chronic disorder of the airways of the lungs. The airways are reactive and may be inflamed even when symptoms are not present. The extent and severity of airway irritation
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Breathe Easy. Living with Asthma
 Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
Breathe Easy Living with Asthma Got Asthma? You re Not Alone! More than 300 million people around the world have asthma. But having asthma doesn t have to limit what you can do. With education and treatment,
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER
 MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
Asthma in the Athlete
 Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Breathe Easy ACTIVITIES. A Family Guide to Living with Asthma F O R T H E K ! I D S
 Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
Breathe Easy A Family Guide to Living with Asthma ACTIVITIES FUN & EDUCATIONAL F O R T H E K! I D S What Is Asthma? Asthma is a disease of the lungs. It s a chronic (long-term) condition that affects the
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Teacher Training on Asthma
 Teacher Training on Asthma Understanding Asthma and How It Can Be Managed at School This presentation is made possible by a grant from: Training Objectives Describe the effects of asthma on students Discuss
Teacher Training on Asthma Understanding Asthma and How It Can Be Managed at School This presentation is made possible by a grant from: Training Objectives Describe the effects of asthma on students Discuss
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline
 Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline Inclusion: 1) Children 2 years of age or older with a prior history of wheezing, and 2) Children less than 2 years of age with likely
Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline Inclusion: 1) Children 2 years of age or older with a prior history of wheezing, and 2) Children less than 2 years of age with likely
HealthPartners Care Coordination Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide ASTHMA
 The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and American Academy of Allergy,
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
ASTHMA EXACERBATIONS:
 ASTHMA EXACERBATIONS: IDENTIFYING AND ADDRESSING THE ROOT CAUSES MARCH 20, 2017 Speakers Anna Flattau, MD, MSc, MS, Senior Assistant Vice President Chief Clinical Officer OneCity Health Services/NYC Health
ASTHMA EXACERBATIONS: IDENTIFYING AND ADDRESSING THE ROOT CAUSES MARCH 20, 2017 Speakers Anna Flattau, MD, MSc, MS, Senior Assistant Vice President Chief Clinical Officer OneCity Health Services/NYC Health
AT TRIAGE. Alberta Acute Childhood Asthma Pathway: Evidence based* recommendations For Emergency / Urgent Care
 1 1 Should the child be placed into the Pathway? Asthma Clinical Score (PRAM) Inclusion Children 1 year and 18 years of age who present with wheezing and respiratory distress, and have been diagnosed by
1 1 Should the child be placed into the Pathway? Asthma Clinical Score (PRAM) Inclusion Children 1 year and 18 years of age who present with wheezing and respiratory distress, and have been diagnosed by
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Chalazia can recur, and those that do should be evaluated for malignancy.
 DEFINITION Chalazia (plural of chalazion) are the most common inflammatory lesions of the eye lid. These are slowly enlarging eyelid nodules, formed by inflammation and obstruction of sebaceous glands.
DEFINITION Chalazia (plural of chalazion) are the most common inflammatory lesions of the eye lid. These are slowly enlarging eyelid nodules, formed by inflammation and obstruction of sebaceous glands.
Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health.
 Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health Background: These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and
Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health Background: These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and
Some Facts About Asthma
 Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
Some Facts About Asthma Contents What is asthma? Diagnosing asthma Asthma symptoms Asthma triggers Thanks What is asthma?? Asthma is a chronic lung-disease that inflames and narrows the airways (tubes
Asthma. Permafold Topics. What You Need To Know
 1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
1. What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways to narrow. Airflow is limited due to inflammation in the airways. Asthma What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What Is Asthma?
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Asthma. Guide to Good Health. Healthy Living Guide
 Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
Asthma Guide to Good Health Healthy Living Guide Asthma Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Depression Hyperlipidemia Hypertension
ASTHMA CONTROL. Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms.
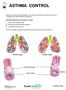 ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
ASTHMA CONTROL Asthma is a chronic airway disease. You cannot cure asthma, but you can control it. Treatment can improve asthma symptoms. Asthma changes the lung airways in 3 ways: 1. Lining of the airways
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
PEDIATRIC ACUTE ASTHMA SCORE (P.A.A.S.) GUIDELINES. >97% 94% to 96% 91%-93% <90% Moderate to severe expiratory wheeze
 Inclusion: Children experiencing acute asthma exacerbation 24 months to 18 years of age with a diagnosis of asthma Patients with a previous history of asthma (Consider differential diagnosis for infants
Inclusion: Children experiencing acute asthma exacerbation 24 months to 18 years of age with a diagnosis of asthma Patients with a previous history of asthma (Consider differential diagnosis for infants
Asthma Education. The Keys to Asthma Prevention and Control. what to do when one s asthma is flared! Lucile Packard Children s Hospital.
 Asthma Education Lucile Packa r d Children s H o spit al Created by Rachel Lawler RN, MSN, cpnp, AE-C, NPAT Pulmonary Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Lucile Packard Children s Hospital The Keys to Asthma
Asthma Education Lucile Packa r d Children s H o spit al Created by Rachel Lawler RN, MSN, cpnp, AE-C, NPAT Pulmonary Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Lucile Packard Children s Hospital The Keys to Asthma
CMS Asthma Education Program
 CMS Asthma Education Program ASTHMA IS Common Chronic Treatable Distressing Misunderstood Potentially Dangerous CMS Prevalence Number one chronic disease Leading cause of Absences 6481 CMS students (2003-04)
CMS Asthma Education Program ASTHMA IS Common Chronic Treatable Distressing Misunderstood Potentially Dangerous CMS Prevalence Number one chronic disease Leading cause of Absences 6481 CMS students (2003-04)
Bronchial asthma. E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics. Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013
 Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Bronchial asthma E. Cserháti 1 st Department of Paediatrics Lecture for english speaking students 5 February 2013 Epidemiology of childhood bronchial asthma Worldwide prevalence of 7-8 and 13-14 years
Clear and Easy. Skypark Publishing. Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line
 Clear and Easy #5 Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line 1-888-275-8750 TTY: 1-866-735-2929 Molina Healthcare Línea de TeleSalud Disponible las 24 Horas 1-866-648-3537 TTY: 1-866-833-4703 Skypark
Clear and Easy #5 Molina Healthcare 24 Hour Nurse Advice Line 1-888-275-8750 TTY: 1-866-735-2929 Molina Healthcare Línea de TeleSalud Disponible las 24 Horas 1-866-648-3537 TTY: 1-866-833-4703 Skypark
Glossary of Asthma Terms
 HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
HealthyKidsExpress@bjc.org Asthma Words to Know Developed in partnership with Health Literacy Missouri Airways (Bronchi, Bronchial Tubes): The tubes in the lungs that let air in and out of the body. Airway
What is Asthma? Chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Night time or early morning coughing
 Asthma What is Asthma? Chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Night time or early morning coughing Episodes are usually associated with widespread, but
Asthma What is Asthma? Chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Night time or early morning coughing Episodes are usually associated with widespread, but
Childhood Asthma. The pathophysiology of asthma is an interplay. CME Case Study. Case Study. By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC
 CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
LivingWith Asthma. A Guide to Understanding Asthma...
 A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
A Guide to Understanding... LivingWith Understanding Diagnosing Treating Frequently Asked Questions [2] A Guide to Understanding... Understanding What Is? (AZ-muh) is a chronic disease that affects your
Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes:
 Dr. W. Wijnant Paediatric Pulmonology Steve Biko Academic Hospital Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes: Viral wheezer Multiple trigger wheezer Transient wheezer Persistent early
Dr. W. Wijnant Paediatric Pulmonology Steve Biko Academic Hospital Most common chronic disease in childhood Different phenotypes: Viral wheezer Multiple trigger wheezer Transient wheezer Persistent early
Outpatient Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Outpatient Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Initial Visit Follow-Up Visits See page 2 Asthma Diagnosis See page 3 Classifying Asthma Severity and Initiating Treatment See pages 2 and
Outpatient Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Initial Visit Follow-Up Visits See page 2 Asthma Diagnosis See page 3 Classifying Asthma Severity and Initiating Treatment See pages 2 and
Get Healthy Stay Healthy
 Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
Asthma Management WHAT IS ASTHMA? Asthma causes swelling and inflammation in the breathing passages that lead to your lungs. When asthma flares up, the airways tighten and become narrower. This keeps the
Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma
 Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma Dr Andrew Tai FRACP, PhD Paediatric Respiratory and Sleep Specialist Women's and Children's Hospital, Adelaide Approaching the patient Check the diagnosis
Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma Dr Andrew Tai FRACP, PhD Paediatric Respiratory and Sleep Specialist Women's and Children's Hospital, Adelaide Approaching the patient Check the diagnosis
Asthma Friendly School Environments
 Asthma Friendly School Environments Our Mission Prevent lung disease and promote lung health in Mississippi through: Education Advocacy Research What is Asthma? Asthma: Is a life-long disease found in
Asthma Friendly School Environments Our Mission Prevent lung disease and promote lung health in Mississippi through: Education Advocacy Research What is Asthma? Asthma: Is a life-long disease found in
Asthma and IAQ. Lani Wheeler, MD, Medical Officer Sarah Merkle, MPH, Program Analyst
 Asthma and IAQ Lani Wheeler, MD, Medical Officer Sarah Merkle, MPH, Program Analyst Division of Adolescent and School Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Asthma is a Major Public Health Problem
Asthma and IAQ Lani Wheeler, MD, Medical Officer Sarah Merkle, MPH, Program Analyst Division of Adolescent and School Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Asthma is a Major Public Health Problem
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes
 Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Asthma Management Protocol
 Asthma Management Protocol USC School of Pharmacy Updated October 2012 08/24/18 USC School of Pharmacy 1 I. Goals and Objectives The goal of the pharmacist-managed Asthma Management Program (AMP) is to
Asthma Management Protocol USC School of Pharmacy Updated October 2012 08/24/18 USC School of Pharmacy 1 I. Goals and Objectives The goal of the pharmacist-managed Asthma Management Program (AMP) is to
ASTHMA AND CHILDCARE PART 1. Presented by: Robin Costley, CRT, AE-C Marion County Public Health Department Manager, Asthma Alliance of Indianapolis
 ASTHMA AND CHILDCARE PART 1 Presented by: Robin Costley, CRT, AE-C Marion County Public Health Department Manager, Asthma Alliance of Indianapolis OBJECTIVES By the end of training, participants will:
ASTHMA AND CHILDCARE PART 1 Presented by: Robin Costley, CRT, AE-C Marion County Public Health Department Manager, Asthma Alliance of Indianapolis OBJECTIVES By the end of training, participants will:
Asthma By Mayo Clinic staff
 MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
MayoClinic.com reprints This single copy is for your personal, noncommercial use only. For permission to reprint multiple copies or to order presentation-ready copies for distribution, use the reprints
Asthma. What Is Asthma? Overview. Asthma
 Asthma What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), chest tightness,
Asthma What Is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic (long-term) lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), chest tightness,
Respiratory Health. Asthma and COPD
 Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Respiratory Health Asthma and COPD Definition of asthma Working definition by AAH 2014: Chronic lung disease Can be controlled not cured Large variation in lung function Large variation in respiratory
Alberta Childhood Asthma Pathway for Primary Care
 Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Asthma Triggers. It is very important for you to find out what your child s asthma triggers are and learn ways to avoid them.
 Asthma s It is very important for you to find out what your child s asthma triggers are and learn ways to avoid them. With asthma, your child s airways are very sensitive. Things, called triggers, may
Asthma s It is very important for you to find out what your child s asthma triggers are and learn ways to avoid them. With asthma, your child s airways are very sensitive. Things, called triggers, may
In case of an urgent concern or emergency, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency department right away.
 Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Asthma Basics Patient and Family Education This teaching sheet contains general information only. Talk with your child s doctor or a member of your child s healthcare team about specific care of your child.
Emergency Department Protocol Initiative
 Emergency Department Protocol Initiative ACUTE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT TOOLKIT March 2006 Provincial Emergency Services Project PHYSICIAN ORDER TEMPLATE FOR CTAS LEVEL 1 ASTHMA ADULT PEDIATRIC Date: Site: Arrival
Emergency Department Protocol Initiative ACUTE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT TOOLKIT March 2006 Provincial Emergency Services Project PHYSICIAN ORDER TEMPLATE FOR CTAS LEVEL 1 ASTHMA ADULT PEDIATRIC Date: Site: Arrival
Asthma. January 2011
 Asthma January 2011 What is Asthma? Asthma is a lung disease that affects the breathing tubes (airways) that allow air to go in and out of the lungs. Normal airways are wide open, so air can go in and
Asthma January 2011 What is Asthma? Asthma is a lung disease that affects the breathing tubes (airways) that allow air to go in and out of the lungs. Normal airways are wide open, so air can go in and
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
You Can Control Your Asthma
 asthma_brochureprint_v2.qxd 9/5/06 9:54 AM Page 2 For More Information on Controlling Asthma: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Environmental Health, MS F52 4770 Buford Highway,
asthma_brochureprint_v2.qxd 9/5/06 9:54 AM Page 2 For More Information on Controlling Asthma: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Environmental Health, MS F52 4770 Buford Highway,
National Asthma Educator Certification Board Detailed Content Outline
 I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
Emergency Department Guideline. Asthma
 Emergency Department Guideline Inclusion criteria: Patients 2 years old with: o Known history of asthma or wheezing responsive to bronchodilators presenting to the ED with cough, wheeze, shortness of breath,
Emergency Department Guideline Inclusion criteria: Patients 2 years old with: o Known history of asthma or wheezing responsive to bronchodilators presenting to the ED with cough, wheeze, shortness of breath,
Breathe Easy. Tips for controlling your Asthma
 Breathe Easy Tips for controlling your Asthma Have you or a family member been told you have asthma? Are you or a family member coughing or wheezing? Do you or a family member have tightness in your chest?
Breathe Easy Tips for controlling your Asthma Have you or a family member been told you have asthma? Are you or a family member coughing or wheezing? Do you or a family member have tightness in your chest?
Asthma. Definition. Symptoms
 Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
Asthma Definition Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath. For some
10/6/2014. Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement. Disclosure. Objectives for this talk.
 Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Asthma and Air Pollution
 Asthma and Air Pollution Health Effects Workshop Nov. 6, 2008 Joann Held with thanks to: Dave Brown Asthma and Airways Asthma Physiology A chronic disease that affects airways. The inside walls of airways
Asthma and Air Pollution Health Effects Workshop Nov. 6, 2008 Joann Held with thanks to: Dave Brown Asthma and Airways Asthma Physiology A chronic disease that affects airways. The inside walls of airways
Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Adults and Children with Asthma
 Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Adults and Children with Asthma - 2005 Criteria that suggest the diagnosis of Asthma: The symptoms of dyspnea, cough and/or wheezing,
Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Adults and Children with Asthma - 2005 Criteria that suggest the diagnosis of Asthma: The symptoms of dyspnea, cough and/or wheezing,
Avg PM10. Avg Low Temp
 Geography 532 Geography of Environmental Health Dr. Paul Marr Name: Ex 16- Seasonality, Time Delay, and Disease (10 pts) Below are asthma cases per month for the years 1992-1994. The table also includes
Geography 532 Geography of Environmental Health Dr. Paul Marr Name: Ex 16- Seasonality, Time Delay, and Disease (10 pts) Below are asthma cases per month for the years 1992-1994. The table also includes
Asthma. If an Ambulance is required - call immediately - do not delay. H & A Training PL RTO No:90871
 Asthma is a reversible breathing problem caused from sudden or progressive narrowing and spasming of the smaller airways and includes mucus production, which interferes with oxygen exchange. People who
Asthma is a reversible breathing problem caused from sudden or progressive narrowing and spasming of the smaller airways and includes mucus production, which interferes with oxygen exchange. People who
Management of Respiratory Issues in the School Setting. Pediatric Indicators of High Risk 8/7/2015. Facts about Pediatric Respiratory Failure
 Management of Respiratory Issues in the School Setting Toni B. Vento, MS, RN, NCSN Supervisor of Health Services Medford Public Schools Pediatric Indicators of High Risk Anatomic features of the immature
Management of Respiratory Issues in the School Setting Toni B. Vento, MS, RN, NCSN Supervisor of Health Services Medford Public Schools Pediatric Indicators of High Risk Anatomic features of the immature
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO
 ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA
 Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Your Guide to MANAGING ASTHMA Asthma affects more than 24 MILLION AMERICANS. It is a chronic disease that causes your airways to become inflamed, making it hard to breathe. There is no cure for asthma.
Home Management Plan. Cover Page
 Home Management Plan Cover Page What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by swelling and irritation in the lining of airways Tightness of the airway muscles Excess mucus in the airways
Home Management Plan Cover Page What is Asthma? Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs caused by swelling and irritation in the lining of airways Tightness of the airway muscles Excess mucus in the airways
Allergies and Asthma 5/21/2013. Objectives. Allergic Rhinitis (AR): Risk Factor for ASTHMA. Rhinitis and Asthma
 Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Allergies and Asthma Presented By: Dr. Fadwa Gillanders, Pharm.D Clinical Pharmacy Specialist May 2013 Objectives Understand the relationship between asthma and allergic rhinitis Understand what is going
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Asthma 101. Introduction
 TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
TRIGGERS Introduction Asthma is a chronic disease of the lungs that makes it difficult for people to breathe. Asthma is extremely common. About 20 million Americans have asthma. About 5,000 die each year
Management of acute asthma in children in emergency department. Moderate asthma
 152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
Asthma Assessment & Review
 ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
ASTHMA RESOURCE PACK Section 5B Asthma Assessment & Review In this section: 1. Primary Care initial assessment and review Asthma Resource Pack Section 5B: Asthma Assessment & Review Version 3.0 Last Updated:
SCREENING AND PREVENTION
 These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in Taking Care of Your Child s Asthma. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather
 Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Dealing with Asthma in Winter Weather Asthma is a chronic disease affecting more that twenty million children and adults in America. It is likely that some of the individuals you support may have asthma.
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management - Clinical Practice Guideline
 1 Asthma Management - Clinical Practice Guideline 05/2018 Diagnosis and Screening Diagnostic Criteria o Episodic symptoms of airflow obstruction or airway hyperresponsiveness are present o Airflow obstruction
1 Asthma Management - Clinical Practice Guideline 05/2018 Diagnosis and Screening Diagnostic Criteria o Episodic symptoms of airflow obstruction or airway hyperresponsiveness are present o Airflow obstruction
CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA. A guide for parents. childrensmn.org
 CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA A guide for parents childrensmn.org Content Your child has asthma a chronic lung disease. To best control the symptoms of asthma, it is important that you learn all you can about asthma.
CARE AT HOME: ASTHMA A guide for parents childrensmn.org Content Your child has asthma a chronic lung disease. To best control the symptoms of asthma, it is important that you learn all you can about asthma.
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control
 Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma 2015: Establishing and Maintaining Control Webinar for Michigan Center for Clinical Systems Improvement (Mi-CCSI) Karen Meyerson, MSN, APRN, NP-C, AE-C June 16, 2015 Asthma Prevalence Approx. 26
Asthma: Evaluate and Improve Your Practice
 Potential Barriers and Suggested Ideas for Change Key Activity: Initial assessment and management Rationale: The history and physical examination obtained from the patient and family interviews form the
Potential Barriers and Suggested Ideas for Change Key Activity: Initial assessment and management Rationale: The history and physical examination obtained from the patient and family interviews form the
In 2002, it was reported that 72 of 1000
 REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
Appendix D. Sample Draft Clinical Guidelines
 Appendix D. Sample Draft Clinical Guidelines 95 The sample guideline Asthma Chronic Care was drafted by Ronald M. Shansky, M.D., M.P.H., and is presented here in draft form. Once adopted by the National
Appendix D. Sample Draft Clinical Guidelines 95 The sample guideline Asthma Chronic Care was drafted by Ronald M. Shansky, M.D., M.P.H., and is presented here in draft form. Once adopted by the National
MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING Presented by:
 MEDS@Work MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING 2013 Presented by: Lusia Fomuso PharmD candidate 2014 Olivia Sibailly PharmD candidate 2014 Kimberly Biedka PharmD candidate 2014 Dr. Donna Bartlett PharmD CGP RPh
MEDS@Work MANAGEMENT OF ASTHMA SPRING 2013 Presented by: Lusia Fomuso PharmD candidate 2014 Olivia Sibailly PharmD candidate 2014 Kimberly Biedka PharmD candidate 2014 Dr. Donna Bartlett PharmD CGP RPh
Update on management of respiratory symptoms. Dr Farid Bazari Consultant Respiratory Physician Kingston Hospital NHS FT
 Update on management of respiratory symptoms Dr Farid Bazari Consultant Respiratory Physician Kingston Hospital NHS FT Topics The common respiratory symptoms Cough: causes, diagnosis and therapy Update
Update on management of respiratory symptoms Dr Farid Bazari Consultant Respiratory Physician Kingston Hospital NHS FT Topics The common respiratory symptoms Cough: causes, diagnosis and therapy Update
A Guide for Students and Parents
 A Guide for Students and Parents February 20, 2009 This program was made possible through an unrestricted grant from: Monaghan Medical Corporation, Lupin Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Forest Laboratories Inc.
A Guide for Students and Parents February 20, 2009 This program was made possible through an unrestricted grant from: Monaghan Medical Corporation, Lupin Pharmaceuticals Inc., and Forest Laboratories Inc.
Asthma. Basic Information About Asthma. What is asthma? Who is at risk? What are the most common triggers for asthma symptoms?
 In This Issue: } Basic Information About Asthma } 5 Steps for Asthma Self-Management } Treatments for Asthma: Controller Meds and Rescue Meds } Is Your House an Asthma Trigger? Basic Information About
In This Issue: } Basic Information About Asthma } 5 Steps for Asthma Self-Management } Treatments for Asthma: Controller Meds and Rescue Meds } Is Your House an Asthma Trigger? Basic Information About
Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians
 Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Asthma in Adults Melissa Ngai, Pharm.D Candidate Peter J. Hughes, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice McWhorter School of Pharmacy Birmingham,
Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Asthma in Adults Melissa Ngai, Pharm.D Candidate Peter J. Hughes, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor of Pharmacy Practice McWhorter School of Pharmacy Birmingham,
Keys to Breathing Easy
 Keys to Breathing Easy Ways to Manage Your Asthma EHAP Environmental Health Action Project SUPPORTED IN PART BY: Project H17 MC 00170 from Healthy Tomorrows Partnership for Childrens Program, Maternal
Keys to Breathing Easy Ways to Manage Your Asthma EHAP Environmental Health Action Project SUPPORTED IN PART BY: Project H17 MC 00170 from Healthy Tomorrows Partnership for Childrens Program, Maternal
