Quick Reference Guide
|
|
|
- Jasper Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents Alert Check List... 3 CARDIAC ALERT CHECKLIST-For Inclusion... 3 STROKE ALERT CHECKLIST-For inclusion... 3 SEPSIS ALERT... 3 COOLING CRITERIA-passive cooling only... 4 APGAR... 5 Medications and Doses... 5 Acetaminophen (Tylenol)... 5 ASA... 5 Activated Charcoal... 5 Adenosine... 6 Albuterol... 6 Amiodarone... 6 Ativan... 6 Atropine... 6 Calcium gluconate... 6 Celox... 7 Dextrose... 7 Mixing Guide for D10% (neonate)... 7 Mixing Guide for D25%... 7 Diazepam... 7 Diltiazem... 7 Diphenhydramine... 8 Dopamine... 8 Epinephrine (Adrenalin) Dosing Adult... 8 Dosing Pediatric... 8 Epinephrine Drip chart... 8 Etomidate (Amidate)... 9 Fentanyl(Sublimaze)
2 Glucagon... 9 Haloperidol (Haldol) Insta-Glucose... 9 Hydroxocobalamin(Cyanokit) Ipratropium Bromide/Albuterol(Duo-Neb) Ketamine Lidocaine (Xylocaine) Magnesium Sulfate Methylprednisolone (Solumedrol) Midazolam (Versed) Morphine Sulfate Naloxone (Narcan) Nitroglycerin Ondansetron (Zofran) Oxytocin (Pitocin) waivered medication Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) Promethazine (Phenergan) Sodium Bicarbonate Terbutaline (Brethine) Tetracaine Hydrochloride Rocuronium (Zemuron) Vecuronium (Norcuron) EMS Trauma Bay Report EMS Trauma Radio Report Faces Pain Scale Prehospital Trauma Team Activation Criteria RSI Paralytic Dosing Chart-Revised 07/05/ RSI Sedation and Assisting Medication Dosing Chart-Updated Ventilator Initial Setting Ideal Weight Tidal Volume Chart. 6-8 ml/kg
3 Alert Check List CARDIAC ALERT CHECKLIST-For Inclusion Does not have DNR 90 years old or less Characteristic cardiac presentation Pain less than 12 hours old No LBBB or paced rhythm 1 mm ST elevation in two contiguous limb leads 2 mm ST elevation in two contiguous V-leads Tx per cardiac chest pain protocol. Notify hospital within 5 minutes of identifying alert. Transport to Hospital of choice. Obtain serial 12 leads. Start two IV s. Additional information-nursing home status, Contrast dye allergy, anticoagulant therapy. STROKE ALERT CHECKLIST-For inclusion I.B.F.A.S.T. I.-Eyes. Sudden difficulty seeing or visual field deficits B.-Balance-Sudden dizziness or inability to walk straight F.-Facial droop (have pt. show teeth) Normal-both sides of face move equal. A.-Arm drift-pt closes eyes and hold both arms out. Normal-both arms move the same. S.-Speech-Have the patient say you can t teach an old dog new tricks. Normal-pt uses correct words without slurring. T.-Time-Last known well time within 6 hours Additional information-no Hx of brain tumors. Presence of clotting or bleeding disorder. BGL within Presence of intracranial hemorrhage. Surgery within 14 days. New head trauma. Seizure disorders. No active bleeding. SEPSIS ALERT A. Must have two or more SIRS criteria (the following) 3
4 1. Temp < 96.8 or > Resp rate > HR > WBC < 4000 or > 12, 000 (if lab values are available) Pediatric VS parameters for sepsis Age BP HR Resp < 90 > 110 > < 83 > 130 > < 75 > 140 > 30 < 2 < 75 > 180 > 40 B. Must suspect an infection of some sort. C. Must have one of more of the following. 1. Hypoximia-spO2 < Altered mental status Hypo-perfusion-BP < 90 systolic or a MAP < Lactate > 4 mmol/l (if lab values are available) COOLING CRITERIA-passive cooling only Less than 15 minutes of down time 15 years old or greater Initial temperature is > 34 C ETCO2 > 20 mmhg ROSC Non traumatic cardiac arrest 4
5 APGAR A Sign 0 Points 1 Point 2 Points Activity (Muscle Tone) Absent Arms and Legs Flexed Active Movement P Pulse Absent Below 100 bpm Above 100 bpm G Grimace (Reflex Irritability) No Response Grimace Sneeze, cough, pulls away A Appearance (Skin Color) Blue-gray, pale all over Normal, except for extremities Normal over entire body R Respiration Absent Slow, irregular Good, crying Medications and Doses Acetaminophen (Tylenol)-I = relief of Fever in pediatric patients or adult patients. C=repeated use with anemia, renal, or hepatic diseases. Not recommended in the anti-inflammatory setting. Dose = 15 mg/kg. Dosing Chart < 24 lbs or 2 years old. 15 mg/kg lbs ( kg) or 2-3 years old. 5 ml (1 tsp) equal to 160 mg lbs ( kg) or 4-5 years old. 7.5 ml (1.5 tsp) equal to 240 mg lbs ( kg) or 6-8 years old. 10 ml (2 tsp) equal to 320 mg lbs ( kg) or 9-10 years old ml (2.5 tsp) equal to 400 mg lbs ( kg or 11 years old. 15 ml (3 tsp) equal to 480 mg Adult or greater than 95 lbs (42.75 kg) 15 mg/kg 3. ONSET: Minutes DURATION: 3-4 Hours Doses may be given PO or feeding tube Dosing Chart Supplied 160 mg/5ml(32 mg/ml) ASA-I= suspected AMI. C=Decreased LOC, Dysphagia, Allergy. Dose = mg Activated Charcoal-I= Drug ingestion, OD. C= No absolute contraindications other than oral administration in patient without gag reflex or unconscious. Dose = Adult 50 gram single dose years old 1 gm/kg. 5
6 Adenosine-I = # 1 Med for PSVT, Used diagnostically before amiodarone in Wide complex tachycardias, can be used in the Dig toxic pt. C = 2 nd and 3 rd degree blocks, sick sinus syndrome, hypersensitivity to adenosine, A-fib with WPW. Dose = Pedi 0.1mg/kg IV or IO followed by 20ml bolus. Double once, max 12mg. Adult 6 mg rapid push IV/IO followed by 20ml bolus. Second dose 12 mg to a max of 30mg. Albuterol-I= Acute Asthma and COPD with bronchospasm, Anaphylaxis with bronchospasm with poor response to Epi. Pulmonary Edema, Dyspnea secondary to pneumonia, Hyperkalemia after Calcium and Bicarb. C = Sensitivity to albuterol. Dose = Adult and Pedi-2.5mg (0.5ml) over minutes for resp. issues mg over 15 min for Hyper K+. Amiodarone-I=Refractory VF-pulseless VT when defibrillation fails. Symptomatic A-fib/flutter if diltiazem fails. Stable V-Tach/wide beat tachycardias. Ustable V-Tach refractory to Cardioversion. C= Hypersensitivity, Cardiogenic shock, sinus bradycardia, 2 nd and 3 rd degree heart blocks unless pt. has a functioning internal pacemaker. No ETT administration. P = precipitates with Bicarb. May cause hypotension. Dose = PEDS=5 mg/kg over several minutes for ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. Repeat to max of 15mg/kg in 24 hours. Adult = VF/pulseless VT 300 mg rapid IVP with 10ml bolus. Repeat at 150 mg RIVP. VT with pulse/wide complex Tach/Afib/flutter 150mg/100ml over 10 min or slow IVP over 10 min. Ativan-I= Status epilepticus or active SZ. Continued sedation in intubated Pt. Chemical restraint with hysterical or combative pt. FX, dislocations with muscle spasms or contractions. Sedation for cardioversion or pacing. Symptomatic sinus tach (rate > 150) secondary to amphetamine or stimulant abuse in alert patients. C = sensitivity to benzodiazepines or it s vehicle, glaucoma, severe respiratory insufficiency, Breast feeding women. Dose PEDI = 0.1 mg/kg IV/IM/IO max 3 doses. Adult = 2-4 mg IV/IO/IM/ MAD x 3 doses. 1-2 mg for stimulant abuse, muscle spasms, and combative patients. Repeat to 4 mg if needed. Atropine-I=Symptomatic Bradycardia. Pacemaker failure. Pre-treatment in RSI patients with bradycardia. Hypersalivation associated with ketamine use. Antidote for muscarinic effects of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides and nerve gas ezposures. C= A-fib/flutter. Tachycardia. Glaucoma. None when used for exposures. Dose PEDI = 0.02mg/kg IV/IO Minimum of.1mg. Max.5mg. (1mg max for adolescent). ETT dose 3 times IV dose. Adult-(No longer recommended for asystole or PEA). Bradycardia and hypersalivation.5mg IV/IO push q 3-5 min max 3mg while waiting for pacemaker. ETT 2-2 1/2 times IV dose. PEDI = 0.02 mg/kg minimum dose os 0.1mg. 4. Child max is 0.5mg, adolescent is 1.0 mg max. For exposures use 2 mg/kg every minutes until symptoms reverse. Calcium gluconate-i=calcium channel blocker toxicity (OD) with symptomatic shock. Beta blocker toxicity. Hyperkalemia with EKG changes, cardiac arrest with etiology of hyperkalemia (first line choice), Magnesium infusion that fails to respond to fluids, Hydrofluoric acid burns, magnesium toxicity. Hypotension associated with magnesium infusion that does not respond to fluids. Hydrofluoric acid burns. Magnesium toxicity. Pediatrics = hypocalcemia, septic shock, Hyperkalemia, hypermagnesemia, 6
7 calcium channel OD. C= VF. Precipitates with Bicarb. Dose-Not for IM or SQ administration. PEDI= 2-5mL slow IV/IO repeated once in 10 min. Pedi max is 5mL and infant max is 2 ml. Adult = 5-20 ml over 2-5 min. repeated q 10. For Hydrofluoric acid burns mix with a water based lubricant and apply liberally to burn area then cover with adaptic dressing, celaphane, or exam glove. Celox-I + Animal use only- arterial or venous bleeding after direct pressure and CAT tourniquet. Pour package contents into wound and pack tightly with guaze. Apply pressure for 5 minutes. Dextrose (D-50)-I= BS < 70 (<40 in neonate) with signs and symptoms. Hypoglycemia with diabetes. Unconscious hypothermic patients with focal or partial neurologic deficits or altered states of consciousness if glucometer is not available. C = questionable IV or know brain injury (trauma or CVA) if glucose levels are above 60. Dose NEONATE = 0.5 to 1gm/kg D-10 (5:1mix with NS) IV/IO/Rectal. PEDI= 0.5 to 1 gm/kg of D-25(dilute to 1:1 with NS) IV/IO/rectal. Adult = g IV/IO/rectal. Mixing Guide for D10% (neonate) 1 Draw up 6g (12 ml) of Dextrose 50 % into 60 ml syringe 2 Add 48 ml of saline to bring the total to 60 ml in the syringe 3 Administer 2-4 ml/kg IV bolus Mixing Guide for D25% 1 Draw up 15g (30 ml) of Dextrose 50 % into 60 ml syringe 2 Add 30 ml of saline to bring the total to 60 ml in syringe 3 Administer 2-4 ml/kg IV bolus Dextrose (D-10)-Indicated to treat hypoglycemia when D-50 is not available. Same indications and contraindications. Diazepam-I= Active SZ, sedation for pacing or carcioversion, continued sedation for RSI, uncontrollable patients needing intubation, excited delirium, in pulseless arrest when trismus is present to facilitate ventilation and intubation. C = recent ETOH intake, patients with resp depression or hypotension, glaucoma, induction for RSI. Dose PEDI = 0.2 mg/kg over 1 min. Double in ETT administration. Rectal dose 0.5mg/kg via small feeding tube. Adult = 5-10 mg slow IV/IO push mg for continued sedation in the intubated pt. 5. Diltiazem-I= symptomatic A-fib/flutter with rapid ventricular response. Stable PSVT refractory to adenosine and vagal maneuvers. C = Sic sinus syndrome except in the presence of a functioning pacemaker. Hypersensitivity. Severe hypotension or CHF, in the presence of Asystole, 1 st 2 nd and 3 rd degree blocks, junctional rhythms. VF, VT, bradycardia. Do not use in the same line as lasix, diazepam, 7
8 or bicarb. Caution with beta-blockers. Dose Adult = 0.25 mg/kg over 2 min. repeat at0.35 mg/kg after 15 min. Diphenhydramine-I= Anaphylaxis, Dystonic reactions, Simple allergic reactions with itching or hives. C = Lower respiratory tract symptoms. Dose PEDI = -1-2 mg/kg IV/IO/IM repeat as needed. Adult = mg slow IV/IO/IM repeat as needed. Dopamine-I= Cardiogenic shock (BP with signs and symptoms of shock) not responding to fluid. Any hypotension after hypovolemia has been treated. Symptomatic Bradycardia refractory to atropine, Hypotension post ROSC. C = Hypovolemic shock, uncorrected tachyarrhythmias or VF. Dose PEDI =mix 200 mg in 250 ml NS ( 800 mcg/ml) infuse at mcg/kg/min. Adult = 400mg in 250 ml (1600 mcg/ml)(26.6mcg/gtt) infuse at 2-20 mcg/kg/min Duo-Dote-I = Suspected nerve agent or organophosphate exposure with signs and symptoms of poisoning. C = none in acute setting. Dose-One to Three auto injector doses depending on severity. Epinephrine (Adrenalin)-I =Pulseless VT, VF, Asystole, PEA, Anaphylaxis, Severe croup, Symptomatic bradycardia. C = In non-arrest situations. HTN, hyperthyroidism, Ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular insufficiency, and childbirth. Dosing Adult Arrest 1mg q 3-5min 1:10,000 IV/IO Double down ETT Anaphylaxis/asthma-mild 0.3mg q 3-5min 1:000 IM Anaphylaxis/asthma-severe 0.3mg q 3-5min 1:10,000 IV/IO-slow push Bradycardia 2-10mcg/min 2mg/250ml IVD Dosing Pediatric Bradycardia 0.01 mg.kg 1:10,000 IV/IO Arrest 0.01 mg/kg 1:10,000 IV/IO Arrest 0.1/mg/kg 1:1000 ETT Anaphylaxis/asthma 0.01mg/kg 1:1000 IM Croup 0.5 ml/kg max of 5 ml 1:1000 Nebulize 6. Epinephrine Drip chart 2 mg in 250 ml = 8 mcg/ml 8
9 mcg/min ml/hr drops per minute 1 7.5ml/hr or 7.5 drops per minute ml/hr or 15 drops per minute ml/hr or 22.5 drops per minute ml/hr or 30 drops per minute ml/hour or 37.5 drops per minute ml/hr or 45 drops per minute ml/hr or 52.5 drops per minute ml/hr or 60 drops per minute ml/hr or 67.5 drops per minute ml/hr or 75 drops per minute Etomidate (Amidate) wavered medication-i-for initial sedation during RSI. C= Hypersensivitity. Dose = mg/kg IV/IO Fentanyl(Sublimaze)-I=Sedation, Pain relief, Sever chest pain during suspected MI, continued sedation in RSI, Shivering associated with cooling therapy. C= uncorrected respiratory insufficiency, hypersensitivity, Head injuries except during RSI, Not used for induction in RSI. Dose Adult and PEDS = 1-2 mcg/kg IV/IO/IM/MAD q 10 minutes. For RSI 1-3 mcg/kg IV/IO/IM. May nebulizer at 0.75mcg/kg if IV/IO cannot be obtained. Glucagon-I= Hypoglycemia when IV cannot be obtained, Beta Blocker OD, Calcium Channel Blocker OD, Esophageal spasm or obstruction. C = None with listed indications. Dose Adult = 1mg IM. 1mg slow IV/IM/IO. 2 mg for OD. PEDS (<8y/o or 3-18 kg) = 0.5mg kg = 1 mg. Haloperidol (Haldol)-I = psychotic disorders, chemical restraint for uncontrollable, violent, acutely agitated patients, restraint of combative head injury. C = severe toxic CNS depression, coma, allergies to butyrophenone family, parkinson s disease, patients on lithum, patients taking anit-convulsants, severe cardiovascular disorders because of hypotension or angina pain, patients receiving anticoagulant medications. Dose-Adult only- 2-5 mg IV/IM. Insta-Glucose-I = hypoglycemia. C = unconscious patients, patients who cannot control their airway, neonates. Dose-entire contents of tube. Repeat after 10 minutes if no response. 9
10 7. Hydroxocobalamin(Cyanokit)-I= known or suspected cyanide poisoning with unstable vital signs, patients in cardiac arrest or unconscious who were in an enclosed space smoke inhalation or fire. C = None. Dose Adult = 5 g over 15 minutes IVD. Pedi = 70 mg/kg over 15 min. Ipratropium Bromide/Albuterol(Duo-Neb)-I=Acute asthma or COPD with bronchospasm, Anaphylaxis with bronchospasm and poor response to epinephrine, Pulmonary Edema, Dyspnea secondary to pneumonia. C = none with nebulized solution. Supplied.5 mg atropine and 3 mg albuterol per 3 ml. Dose Adult and Adolescent = 0.5mg nebulized. Peds = 0.25 mg nebulized. Ketamine-Waivered Medication-I-Adult patients showing signs of excited delirium and extreme agitation where the safety of the patient and/or provider is of substantial concern. Analgesia after morphine or fentanyl, when longer lasting effects are desired, or in situations when opiates are not desired (addiction, allergy). As an induction agent during RSI. C = relative contraindications for penetrating trauma to the eye and patients with known cardiovascular disease. Dosing. Agitation and excited delirium (adult only) 5 mg/kg IM. Pain control (adult and pedi) 0.3 mg/kg IV/IO up to 3 doses. M.A.D. 0.5 mg/kg up to 3 times. Rapid Sequence Intubation > 12 years old mg/kg IV/IO Lidocaine (Xylocaine)-I= Active or preventative laryngospasm during intubation, pre-treatment for ETT or NG tube if ICP is suspected or patient has a head injury, Analgesia bolus for IO patients who are conscious. C= Bundle branch blocks, AV blocks, A-fib/flutter, SVT with WPW, hypersensitivity. Dose Adult = 1-1.5mg/kg IV/IO for ICP, head injury, or laryngospasm (may spray needed amount on cords as well). 0.5mg/kg slow bolus for IO analgesia. Max adult dose is 3 mg/kg. PEDS mg/kg IV/IO for ICP or head injury. Magnesium Sulfate-I= Torsades de Pointes, A-Fib with rapid ventricular response after diltiazem or amiodarone, eclampsia or pre-eclampsia if > 20 seeks gestation, Asthma with moderate or severe presentation after nebulized medications. Uterine tetany pre partum. C= heart blocks. Dose Adult = 1-2 gm slow IV/IO push for asthma, A-fib, Torsades. 2-4 gm over min for eclampsia. May be given IM for seizing eclamptic patients at a dose of 2 grams, repeat in 5 minutes if needed. PEDS = 50 /kg over 1-3 min for asthma. Methylprednisolone (Solumedrol)-I=Anaphylaxis, severe asthma, or COPD with accessory muscle use, poor airflow, or severe wheezing refractory to Beta agonist use. C = hypersensitivity. Dose Adult = 125 mg IVP over several min. PEDS = 2mg/kg IVP over several minutes Midazolam (Versed)-I= status epilepticus or active SZ, chemical restraint, uncontrollable patients with possible spinal injuries, Sedation for RSI or cardioversion or pacing, Significant FX with contractions or spasm, muscle spasms for chronic back pain, shivering associated with cooling therapy, excited delirium, and pulseless arrest if trismus is present to facilitate ventilation and intubation. C = Glaucoma. Dose Adult = Muscle spasms = mg. SZ, chem. Restraint, uncontrollable or hysterical patients, cardioversion, pacing, shivering = 2-5 mg to a max of 10 mg. RSI initial and re-sedation = mg/kg. May be given IV, IO, IM, and MAD> Pedi = 0.1 mg/kg repeat once if needed to mg/kg. 10
11 Morphine Sulfate-I= Chest pain and anxiety in suspected AMI, Pain associated with FX or burns, Chronic back pain or spasms, General Pain relief. C= shock, hypotension, head injuries, altered mental status, Acute respiratory distress if not associated with pulmonary edema, chest injuries, abdominal injuries. Dose Adult = 2-15 mg slow IVP/IM/IO/<AD/. PEDS = mg/kg Naloxone (Narcan)-I=Coma unknown etiology, reversal of narcotic effects in overdose. C = None. Dose Adult mg IV/IO/ETT/IM/MAD. PEDI = 0.1mg/kg same routes as adult. 8. Nitroglycerin-I= Chest, arm, shoulder, or neck pain or pressure related to possible coronary ischemia. HTN with suspected aortic aneurism or cardiac chest pain, Pulmonary edema, Suspected silent AMI, Esophageal spasms. C= Shock, BP < 90 systolic, patients who have taken erectile dysfunction meds within previous 24 hour period. Dose Adult-0.4 mg spray SL every 3-5 minutes. Do not exceed 3 doses unless patient has showed marked improvement of symptoms. Transdermal Past-When patient needs CPAP but condition warrants nitro apply ½ inch of nitro paste as a single dose. Ondansetron (Zofran)-I= Control of nausea and vomiting, and control of nausea and vomiting with administration of analgesics when further sedation is undesirable. C = Hypersensitivity. Dose Adult = 4 mg IV/IO once. PEDI =.15 mg/kg IV/IO/IM max 4 mg. Oxytocin (Pitocin) waivered medication-i = Postpartum hemorrhage > 1000 ml. C = Hypersensitivity, Potential additional Fetus, prior to delivery of placenta. Dose = 20 units in 1000ml NS wide open IV/IO. If IV is unobtainable may be given 10 units IM. Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine)-I= Prior to nasal intubation, during epistaxis to control bleeding. C = HTN. Dose = two sprays to desired nares. Promethazine (Phenergan)-I= Nausea and vomiting, control of nausea and vomiting associated with the administration of analgesics, allergic reactions to blood or plasma administration. C = ETOH or sedative ingestion, Allergies to phenothiazines, glaucoma, urinary obstruction, Coma, Children under 2 y/o. Dose Adult or = 12.5mg IM/IV/IO. PEDS = mg.kg QuickClot-I = control of severe bleeding. Do not remove packing once wound is packed Sodium Bicarbonate-I= Prolonged cardiac arrest, Tricyclic OD, Hyperkalemia with EKG changes after calcium, crush injuries with prolonged extrication. C = None under previous incidations. Dose Adult 1mEq/kg IV/IOfor suspected or known hyperkalemia. 50 meq IV/IO for arrest. PEDS = 1mEq/kg IV/IO. Second dose ½ if needed. Neonates = 1 meq/kg with a 4.2% solution over 10 min. Terbutaline (Brethine)-I= Asthma, Bronchitis, or COPD. Patients > 40 y/o when epinephrine is not advisable. C = Sensitivity. Dose Adult = 0.25mg IM/SQ. PEDI = 0.01mg/kg SQ max.5mg. 11
12 Tetracaine Hydrochloride-I = Pain relief in eye, to assist with eye irrigation. C = allergies, non intact globe. Dose Adult/PEDS = 1-2 gtts in affected eye. Rocuronium (Zemuron) waivered medication-i= Initial paralytic in RSI C = anaphylaxis, Pediatric patients, Cesarean patients who are in labor. Not for continued muscle relaxation. Use vecuronium. Dose Adult > 12 y/o = mg/kg IV/IO. Defasiculating dose is 1/10 th of standard dose. Vecuronium (Norcuron) waivdred medication-i-for neuro blockade with continuous muscle relaxation is required (long transports). C-patients with hypersensitivity. Dose. 0.1 to 0.15 mg/kg NOTES and Equations 1. Equation for determining Medication dosage. Desired dose in mg divided by supplied concentration = dose in ml. EX: Morphine-supplied as 10mg/ml-you want to give 6 mg mg (desired dose) divided by 10 mg (supplied concentration of 10 mg/ml) =.6 ml 2. MAP calculation-systolic BP minus Diastolic BP. Multiply the result by.33 and add that to the diastolic BP to get the MAP. EX: 120/ = x.33 = = round it to 93 12
13 10. 13
14 EMS Trauma Bay Report *Approximate Age *Gender *Mechanism of injury *VS *Suspected injuries *Changes from pre hospital report
15 Any other information EMS feels is important to patient care should be relayed to the Scribe nurse in the trauma Bay. EMS Trauma Radio Report *Approximate Age *Gender *Mechanism of injury *VS *Suspected injuries *Airway status *Neurologic status 12. *Meds/Procedures performed (including IV access *ETA The purpose of the Bullet is to give clear, actionable information regarding a trauma patient with the least amount of extraneous information that is not immediately important to their care. The Radio bullet contains information from the scene: The trauma Bay bullet is the information given at patient off-load. It is 15
16 suggested that whoever is giving the bullet report should look at the appropriate outline and give information in that order. Using this system, high quality information can be conveyed in less than 30 seconds
17 Faces Pain Scale
18 Prehospital Trauma Team Activation Criteria FULL Trauma Team Criteria Persons who sustain injury with any of the following: PRIMARY SURVEY: PHYSIOLOGIC Adult (15+ yrs) Child (0-14 yrs) Airway Unable to Adequately Ventilate Unable to Adequately Ventilate Intubated or Assisted Ventilation Intubated or Assisted Ventilation Breathing Resp Rate < 10 or > 30/min Any sign of resp insufficiency (hypoxia, acc musc use, grunting) Circulation Systolic BP < 90 mm/hg Any sign of abnormal perfusion (cap refill>2sec, BP low for age) Age SBP (mm/hg) < 1 yr < yrs < 70 +2x age > 10 yrs < 90 Deficit GCS Motor Score 5 AVPU Resp to Pain or Unresp Deterioration of Previously Stable Patient Transfers Requiring Blood Transfusion SECONDARY SURVEY: ANATOMIC Penetrating injuries to the Head, Neck, Torso or Extremities proximal to elbow/knee Open or Depressed Skull Fracture Paralysis or Suspected Spinal Cord Injury Flail Chest Unstable Pelvic Fracture Amputation proximal to the wrist or ankle Two or more Proximal Long Bone Fractures (humerus or femur) Crushed, Degloved or Mangled Extremity LIMITED Trauma Team Criteria Persons who sustain injury with any of the following: 18
19 15. MECHANISM OF INJURY Falls (Adult): > 20 ft; (Child): > 15 ft or 3x ht High Risk auto crash, with: Intrusion of vehicle > 12 in occupant compartment; > 18 other site Ejection (partial or complete) from automobile Death in same passenger compartment Auto vs Ped/Cyclist thrown, run over, or with sig (> 20 mph) impact Motorcycle Crash > 20 mph High Energy Dissipation or Rapid Decelerating Incidents, ie: Ejection from motorcycle, ATV, animal, etc Striking fixed object with momentum Blast or explosion High Energy Electrical Injury Burns > 10% TBSA (2 or 3 ) and/or Inhalation Injury Suspected Non-Accidental Trauma EMS Provider Judgment *Anticoagulated patients require an anticoagulation alert, not a LTTA 19
20 16. RSI Paralytic Dosing Chart-Revised 07/05/14 Zemuron/Rocuronium Initial Paralytic 10 mg/ml 0.6-1mg/kg LBS KG.6-1 mg/kg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg mg Calculation-(Dose in mg to be delivered) divided by (mg/ml) = dose in ml 20
21 RSI Sedation and Assisting Medication Dosing Chart-Updated LBS KG Atropine Etomidate Fentanyl Lidocaine Valium Versed 17. Brady-Adult Initial Sedation Cont. Sedation Susp. Head Inj. Cont. Sedation Initial Sedation 1mg/ml 2mg/ml 50mcg/ml 20mg/ml 5mg/ml 1mg/ml 5mg/mL mg/kg mg/kg 1-3mcg/kg 1-1.5mg/kg 5-15mg mg/kg mg 8-24mg mcg 40-60mg 5-15mg 1.2-4mg mg 9-27mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg mg 10-30mg mcg 50-75mg 5-15mg 1.5-5mg mg 11-33mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg mg 12-36mg mcg 60-90mg 5-15mg 1.8-6mg mg 13-39mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg mg 14-42mg mcg mg 5-15mg 2.1-7mg mg 15-45mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg mg 16-48mg mcg mg 5-15mg 2.4-8mg mg 17-51mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg mg 18-54mg mcg mg 5-15mg 2.7-9mg mg 19-57mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg mg 20-60mg mcg mg 5-15mg 3-10mg mg 21-63mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg mg 22-66mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg mg 23-69mg mcg mg mg mg 24-72mg mcg mg 5-15mg mg Right Drug-Right Dose-Right Indication-Right Patient Calculation- (Dose to Administer in mg) divided by (mg/ml) equals dose in ml. 21
22 Ventilator Initial Setting 18. Tidal Volume: 6-8cc/kg: max of 10cc/kg Ideal Wt. Men-50kg kg/inch above 5 feet Women-45.5 kg kg/inch above 5 feet Resp. Rate: Adult: Peds: 20 and up PIP: Normal Range Adult: Peds: PEEP: Normal is 5 cmh2o Call in > than 10. FiO2 Adjustments Start at 100%. May decrease to 50% depending on pt. need. Allow pt. to adjust to settings before making changes. Ideal Weight Tidal Volume Chart. 6-8 ml/kg Male Female Height Ideal Wt. (kg) Vt Ideal Wt. (kg) Vt
23
24 20. 24
EMS Region Medication List 2010
 EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
EMT-B MEDICATIONS Patient Assisted Medications (PAM) and Ambulance Stock Medications Medication Protocol/Use Dose Auto-injector (Epi-pen) Glucose (Oral) Metered-Dose Inhaler (MDI) Allergic/Anaphylactic
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on this Tetracaine and Morgan lens may be optional in region *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your CS license if required by your region *Midstate will
Contra Costa County Emergency Medical Services Drug Reference. Indication Dosing Cautions Comments
 Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
Drug Adenosine Albuterol Indication Dosing Cautions Comments Narrow complex tachycardia Bronchospasm Crush injury - hyperkalemia Initial 6mg rapid IV Repeat 12mg rapid IV Follow each dose with 20ml NS
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION. 1. Safe scene, standard precautions. 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness. 3. Quick look (monitor)
 LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. Adult Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Adult Treatment Protocols Table of Contents 3.1 Altered Mental Status 3.2 Stroke/Suspected Stroke 3.3 Respiratory Distress 3.4 Seizures 3.5 Sepsis
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02
 PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
PEDIATRIC TREATMENT GUIDELINES - CARDIAC VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION - PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SJ-PO1) effective 05/01/02 Revision #5 04/19/02 Identify Dysrhythmia DEFIBRILLATE: 2 J/kg, 4 J/kg,
Chapter 13. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications
 Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
Chapter 13 Poisonings, Overdoses, and Intoxications Learning Objectives Discuss use of activated charcoal in treatment of poisonings List treatment options for acetaminophen overdose List clinical manifestations
EMS System for Metropolitan Oklahoma City and Tulsa 2018 Medical Control Board Treatment Protocols
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC 14G PATIENT PRIORITIZATION While each patient will receive the best possible EMS care in a humane and ethical manner, proper patient
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC 14G PATIENT PRIORITIZATION While each patient will receive the best possible EMS care in a humane and ethical manner, proper patient
EMS System for Metropolitan Oklahoma City and Tulsa 2019 Medical Control Board Treatment Protocols
 EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC 14G PATIENT PRIORITIZATION While each patient will receive the best possible EMS care in a humane and ethical manner, proper patient
EMERGENCY MEDICAL RESPONDER EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC 14G PATIENT PRIORITIZATION While each patient will receive the best possible EMS care in a humane and ethical manner, proper patient
Z19.2 Cross Reference to Patient Care Maps & Clinical Care Procedures
 2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
2017-04-07 Old version G1 Code of Ethics G2 Scope and Function G3 Scene Assessment G4 Triage G5 Primary Survey G6 Shock G7 Load and Go G8 Secondary Survey G9 Unconscious Patient G10A Obstructed Airway
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL
 CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
PBCFR ALS/BLS Protocols 2009 ALS Pretest
 1. In the patient with a blood glucose of 300mg/dL or higher without signs or symptoms of dehydration should receive how much normal saline? Pg 61 a. 250cc b. 500cc c. 20cc/kg d. None 2. The adult dose
1. In the patient with a blood glucose of 300mg/dL or higher without signs or symptoms of dehydration should receive how much normal saline? Pg 61 a. 250cc b. 500cc c. 20cc/kg d. None 2. The adult dose
In accordance with protocols, this patient should be transported to which medical facility?
 NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
NOTE: Please select the most appropriate answer based on the Westchester Regional On-Line Medical Control Physician (OLMC) Regional System Overview, as well as current regional and state EMS protocols
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services. Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual
 Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
ADENOSINE (Adenocard) VO = Intermediate Paramedic. ALBUTEROL SULFATE VO = EMT, EMT-IV, Intermediate Paramedic
 ADENOSINE (Adenocard) ALBUTEROL SULFATE VO = EMT,, AMIODARONE (Cordarone) -except in cardiac arrest ASPIRIN EMT, ATROPINE SULFATE -except in cardiac arrest 1 ST dose 6 mg IVP, 2 ND dose 12 mg IVP, 3 rd
ADENOSINE (Adenocard) ALBUTEROL SULFATE VO = EMT,, AMIODARONE (Cordarone) -except in cardiac arrest ASPIRIN EMT, ATROPINE SULFATE -except in cardiac arrest 1 ST dose 6 mg IVP, 2 ND dose 12 mg IVP, 3 rd
MICHIGAN. State Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Protocol Name Adult Cardiac Table of Contents General Cardiac Arrest Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulmonary Edema/CHF Chest Pain/Acute Coronary Syndrome
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
PRE-HOSPITAL PATIENT CARE PROTOCOLS BASIC LIFE SUPPORT/ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT
 PRE-HOSPITAL PATIENT CARE PROTOCOLS BASIC LIFE SUPPORT/ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT Board Approved June 2007 Revised December 2009 Revised July 2011 Revised June 2015 435 Hunter Street Fredericksburg, VA 22401
PRE-HOSPITAL PATIENT CARE PROTOCOLS BASIC LIFE SUPPORT/ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT Board Approved June 2007 Revised December 2009 Revised July 2011 Revised June 2015 435 Hunter Street Fredericksburg, VA 22401
Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies):
 Schoolcraft County Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, October 2013 version 1.0 Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies): 1. EMS agencies within the Medical Control Authority
Schoolcraft County Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, October 2013 version 1.0 Name: Level of license: Date: Agency(ies): 1. EMS agencies within the Medical Control Authority
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018 This month we will be looking at a specific ECG Rhythm and its treatments
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Optional CE for EMT-B, Paramedics and PHRN s Bradycardia and Treatments Optional #7 2018 This month we will be looking at a specific ECG Rhythm and its treatments
Drips requiring OLMC. Adult Amiodarone Drip Dose is mg/min
 Step 1 Drips requiring OLMC Adult Amiodarone Drip Dose is 0.5-1 mg/min Determine Concentration Step 2 Determine Rate Mix 90 mg (1.8 ml) of Amiodarone in 50 ml NS (must use 60 drop set) Dose in mg/min 0.5
Step 1 Drips requiring OLMC Adult Amiodarone Drip Dose is 0.5-1 mg/min Determine Concentration Step 2 Determine Rate Mix 90 mg (1.8 ml) of Amiodarone in 50 ml NS (must use 60 drop set) Dose in mg/min 0.5
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Name General Pre-hospital Care Abdominal Pain Nausea
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES. -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
North Carolina College of Emergency Physicians Standards for EMS Medications and Skills Use
 . The baseline medications and skills required in all systems and Specialty Care Transport Programs) with EMS personnel credentialed at the specified level. S. The equipment required in all Specialty Care
. The baseline medications and skills required in all systems and Specialty Care Transport Programs) with EMS personnel credentialed at the specified level. S. The equipment required in all Specialty Care
Protocol Update 2019
 Protocol Update 2019 There have been several questions revolving around protocol updates and how they are to be conducted. As many of you are aware there is a protocol submission process in the appendix
Protocol Update 2019 There have been several questions revolving around protocol updates and how they are to be conducted. As many of you are aware there is a protocol submission process in the appendix
ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS
 THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE NEW YORK CITY PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS Effective September 1, 2017 Version ALS09012017C The Regional
THE REGIONAL EMERGENCY MEDICAL ADVISORY COMMITTEE NEW YORK CITY PREHOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOLS ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT (PARAMEDIC) PROTOCOLS Effective September 1, 2017 Version ALS09012017C The Regional
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
CSI Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment
 CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV OBHG Education Subcommittee
 Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Change in Practice PCP Autonomous IV Intravenous and Fluid Therapy Medical Directive Auxiliary Ability to initiate IV access and Ability to administer fluid and fluid boluses in general IV Therapy Actual
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes
 Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICE
 SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICE PROTOCOL SUPPLEMENT 2018 Contents: 12 Lead EKG Placement Charts Drug Index Adult Drug Charts Pediatric Drug Charts IV Drip Rate Formulas & Examples SUPPLEMENT TABLE
SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICE PROTOCOL SUPPLEMENT 2018 Contents: 12 Lead EKG Placement Charts Drug Index Adult Drug Charts Pediatric Drug Charts IV Drip Rate Formulas & Examples SUPPLEMENT TABLE
The Crashing Pediatric Patient: Stopping the Fall
 The Crashing Pediatric Patient: Stopping the Fall I can t breathe... 4 year old BIBA from school with sudden severe resp distress Hx of asthma, food allergies Judith Klein, MD FACEP Assistant Professor
The Crashing Pediatric Patient: Stopping the Fall I can t breathe... 4 year old BIBA from school with sudden severe resp distress Hx of asthma, food allergies Judith Klein, MD FACEP Assistant Professor
Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice
 Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice Name: Date: Problem 1 Your 4 year old patient weighs 40 pounds. She is febrile. You need to administer acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15mg/kg. How many mg will you administer?
Paramedic Pediatric Medical Math Practice Name: Date: Problem 1 Your 4 year old patient weighs 40 pounds. She is febrile. You need to administer acetaminophen (Tylenol) 15mg/kg. How many mg will you administer?
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters. Dilution not necessary (Available in prefilled syringe)
 Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Drug Max dose approved for IVP Dilution Rate Monitoring Parameters Acetazolamide 500 mg Reconstitute with at least 5ml sterile water (max concentration should not exceed 100mg/ml) 100-500 mg/min Hypotension
Tony L Smith DNP RN ACNP CCRN CFRN EMT-IV Vanderbilt LifeFlight
 Treatment of a Stroke patient: A look at how to care for the Stroke patient in the aeromedical setting Tony L Smith DNP RN ACNP CCRN CFRN EMT-IV Vanderbilt LifeFlight Objectives 1. Discuss the assessment
Treatment of a Stroke patient: A look at how to care for the Stroke patient in the aeromedical setting Tony L Smith DNP RN ACNP CCRN CFRN EMT-IV Vanderbilt LifeFlight Objectives 1. Discuss the assessment
Adenosine. poison/drug induced. flushing, chest pain, transient asystole. Precautions: tachycardia. fibrillation, atrial flutter. Indications: or VT
 Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Adenosine Indications: 1. Narrow complex PSVT 2. Does not convert atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter or VT 1. Side effects include flushing, chest pain, transient asystole 2. May deteriorate widecomplex
Verde Valley Medical Center Orientation Manual and Treatment Guidelines Changes
 Verde Valley Medical Center Orientation Manual and Treatment Guidelines 2017 Changes Description Page Change Why Orientation Manual changes Verde Valley Provider agencies Application for Medical Direction
Verde Valley Medical Center Orientation Manual and Treatment Guidelines 2017 Changes Description Page Change Why Orientation Manual changes Verde Valley Provider agencies Application for Medical Direction
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PRE-HOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOL EXAM EMT PARAMEDIC FEBRUARY *Minimum Passing Grade is 80%*
 SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PRE-HOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOL EXAM EMT PARAMEDIC FEBRUARY 2013 *Minimum Passing Grade is 80%* 2013 EMT-PARAMEDIC Protocol Exam 1. You are inducing hypothermia
SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PRE-HOSPITAL TREATMENT PROTOCOL EXAM EMT PARAMEDIC FEBRUARY 2013 *Minimum Passing Grade is 80%* 2013 EMT-PARAMEDIC Protocol Exam 1. You are inducing hypothermia
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS
 MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
MEDICAL KIT - ALGORITHMS Page 2 : BRONCHOSPASM / ASTHMA Page 3 : TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX Page 4 : Page 5 : Page 6 : CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE/ PULMONARY EDEMA ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK / ALLERGIC REACTION ANGINA
3. The signs of Compartment Syndrome are listed in the General Crush Protocol. a. True b. False
 Schoolcraft Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, February 2015, Version 1 MFR/EMT/SPECIALIST/PARAMEDIC 1. Schoolcraft County Medical Control Protocols and Procedures can be found
Schoolcraft Medical Control Authority (MCA) Protocol and Procedures Test, February 2015, Version 1 MFR/EMT/SPECIALIST/PARAMEDIC 1. Schoolcraft County Medical Control Protocols and Procedures can be found
Preparing for your upcoming PALS course
 IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
COUNTY OF SAN LUIS OBISPO HEALTH AGENCY PUBLIC HEALTH DEPARTMENT
 COUNTY OF SAN LUIS OBISPO HEALTH AGENCY PUBLIC HEALTH DEPARTMENT Michael Hill Health Agency Director Penny Borenstein, MD, MPH Health Officer/Public Health Director SLO County Emergency Medical Services
COUNTY OF SAN LUIS OBISPO HEALTH AGENCY PUBLIC HEALTH DEPARTMENT Michael Hill Health Agency Director Penny Borenstein, MD, MPH Health Officer/Public Health Director SLO County Emergency Medical Services
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL
 PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL HARBOR-UCLA MEDICAL CENTER PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL SECTION Preface Disclaimer Nonpharmacologic Methods Table of Contents PAGE i ii iii
PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL HARBOR-UCLA MEDICAL CENTER PEDIATRIC ANALGESIA AND SEDATION DRUG MANUAL SECTION Preface Disclaimer Nonpharmacologic Methods Table of Contents PAGE i ii iii
SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICE
 SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICE PROTOCOL SUPPLEMENT 2019 Contents: 12 Lead EKG Placement Charts Drug Index Adult Drug Charts Pediatric Drug Charts IV Drip Rate Formulas & Examples SUPPLEMENT TABLE
SOUTH PLAINS EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICE PROTOCOL SUPPLEMENT 2019 Contents: 12 Lead EKG Placement Charts Drug Index Adult Drug Charts Pediatric Drug Charts IV Drip Rate Formulas & Examples SUPPLEMENT TABLE
UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table
 2014-2016 UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table September 2014 Based on Revision D, 15 September 2014 Implementation Date: 1 October 2014 This document summarizes
2014-2016 UTSW/BioTel Guidelines for Therapy: Treatment Guidelines Cumulative Review Table September 2014 Based on Revision D, 15 September 2014 Implementation Date: 1 October 2014 This document summarizes
SAN LUIS OBISPO COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY PREHOSPITAL POLICY
 SAN LUIS OBISPO COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY PREHOSPITAL POLICY Policy Reference No: 153 [01/08/2013] Formerly Policy No: 201.3 Effective Date: 11/01/2012 Review Date: 03/01/2014 TRAUMA PATIENT
SAN LUIS OBISPO COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY PREHOSPITAL POLICY Policy Reference No: 153 [01/08/2013] Formerly Policy No: 201.3 Effective Date: 11/01/2012 Review Date: 03/01/2014 TRAUMA PATIENT
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information
 Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information Reference Reviewed: Updated: Blood pressure Minimal systolic BP = 70 + (2 x age) Normal systolic BP = 90 + (2 x age) Estimation of Pediatric Weight (2 x age)
Pediatric (BP, weight conversion) Information Reference Reviewed: Updated: Blood pressure Minimal systolic BP = 70 + (2 x age) Normal systolic BP = 90 + (2 x age) Estimation of Pediatric Weight (2 x age)
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
MICHIGAN. Table of Contents. State Protocols. General Treatment Protocols
 MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
MICHIGAN State Protocols General Treatment Protocols Table of Contents Protocol Number Protocol Name 1.1 General Pre-hospital Care: Regional Protocol 1.2 Abdominal Pain 1.3 Nausea and Vomiting: Regional
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update What s New for 2010? 3 CPR. 4 4 Steps of BLS Survey 5 CPR 6 CPR.
 1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CARE GUIDE Child 70mm. Child 70mm
 PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CARE GUIDE Pediatric Parameters & Equipment Age Neonate 3mo 6mo 1 yr 2 yr 3 yr 4 yr 6 yr 8 yr 12 yr 14 yr Wt (kg) 3.5 6 8 10 12 14 16 20 25 40 50 ~ BSA (m 2 ) 0.24 0.34 0.42 0.49 0.56
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CARE GUIDE Pediatric Parameters & Equipment Age Neonate 3mo 6mo 1 yr 2 yr 3 yr 4 yr 6 yr 8 yr 12 yr 14 yr Wt (kg) 3.5 6 8 10 12 14 16 20 25 40 50 ~ BSA (m 2 ) 0.24 0.34 0.42 0.49 0.56
national CPR committee Saudi Heart Association (SHA). International Liason Commission Of Resuscitation (ILCOR)
 2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013
 NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
European Resuscitation Council
 European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
European Resuscitation Council Objectives To know basic elements to evaluate patients with rythm disturbance To know advanced treatment of paediatric cardiac arrest To know emergency treatment of most
CLINICAL MANUAL. Trauma System Activation Trauma Code Criteria
 CLINICAL MANUAL Policy Number: CM T-28 Approved by: Nursing Congress, Management Forum Issue Date: 09/1999 Applies to: Downtown Value(s): Respect, Integrity, Innovation Page(s): 1 of 4 Trauma System Activation
CLINICAL MANUAL Policy Number: CM T-28 Approved by: Nursing Congress, Management Forum Issue Date: 09/1999 Applies to: Downtown Value(s): Respect, Integrity, Innovation Page(s): 1 of 4 Trauma System Activation
SIERRA-SACRAMENTO VALLEY EMS AGENCY PROGRAM POLICY
 SIERRA-SACRAMENTO VALLEY EMS AGENCY PROGRAM POLICY PURPOSE: To identify those patients who are at greatest risk for severe injury and determine the most appropriate facility to transport persons with different
SIERRA-SACRAMENTO VALLEY EMS AGENCY PROGRAM POLICY PURPOSE: To identify those patients who are at greatest risk for severe injury and determine the most appropriate facility to transport persons with different
Requirements to successfully complete PALS:
 The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains these 2010 Guidelines.The 2010
The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains these 2010 Guidelines.The 2010
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
A00.2 Office of the Medical Director
 A00.2 Office of the Medical Director 2017-07-17 Medications Individual license holders are responsible to hold and maintain the appropriate competencies (satisfactory knowledge and appropriate psychomotor
A00.2 Office of the Medical Director 2017-07-17 Medications Individual license holders are responsible to hold and maintain the appropriate competencies (satisfactory knowledge and appropriate psychomotor
Pediatric Code Blue FOCUS on Medications. Objectives
 Pediatric Code Blue FOCUS on Medications Objectives The learner will be able to: 1. List commonly used pediatric code drugs based on PALS 2015 guidelines 2. Discuss mechanism of action, clinical indications,
Pediatric Code Blue FOCUS on Medications Objectives The learner will be able to: 1. List commonly used pediatric code drugs based on PALS 2015 guidelines 2. Discuss mechanism of action, clinical indications,
Medical First Responder Program Protocols
 Medical Scene Safety Protocol Verify Scene Safety with Police or Dispatch UNKWN Scene Safe? Enter Continue to Appropriate Protocol Possible to Make Safe Make Safe Then Continue Exit Area and Stage Outside
Medical Scene Safety Protocol Verify Scene Safety with Police or Dispatch UNKWN Scene Safe? Enter Continue to Appropriate Protocol Possible to Make Safe Make Safe Then Continue Exit Area and Stage Outside
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac
 Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Utah EMS Protocol Guidelines: Cardiac Version 1 / November 1, 2013 Cardiac Patient Care Guidelines These guidelines were created to provide direction for each level of certified provider in caring for
Drug Profiles Professional Responder
 Entonox Classification Medical Gas Entonox (50% oxygen 50% nitrous oxide) Effects Potent analgesic, weak anesthetic Onset Rapid Peak Immediate Indications Relief of moderate to severe pain Cardiac-related
Entonox Classification Medical Gas Entonox (50% oxygen 50% nitrous oxide) Effects Potent analgesic, weak anesthetic Onset Rapid Peak Immediate Indications Relief of moderate to severe pain Cardiac-related
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
 Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
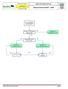 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Prehospital Care Bundles
 Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
Restore adequate respiratory and circulatory conditions. Reduce pain
 Pre-hospital management of the trauma patient is best performed by an integrated team focused on minimizing the time from injury to definitive care at an appropriate trauma center. Dispatchers, first responders,
Pre-hospital management of the trauma patient is best performed by an integrated team focused on minimizing the time from injury to definitive care at an appropriate trauma center. Dispatchers, first responders,
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
Street Level Pharmacology
 Street Level Pharmacology Authored By: ARIELLE Gonzales, FP-C David Berry, FP-C, CCP Rey Ramirez, BSN, CFRN Shane Brown, FP-C Teresa Nystrom Tom McClendon, CFRN Objectives 1. Explain drug choice in association
Street Level Pharmacology Authored By: ARIELLE Gonzales, FP-C David Berry, FP-C, CCP Rey Ramirez, BSN, CFRN Shane Brown, FP-C Teresa Nystrom Tom McClendon, CFRN Objectives 1. Explain drug choice in association
PALS PRETEST. PALS Pretest
 PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
Algorithm Focus. Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Algorithms for the Conscious Patient Prehospital Medication Profiles Algorithm Focus Bradycardia Acute Pulmonary Edema and Shock Hypothermia
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Algorithms for the Conscious Patient Prehospital Medication Profiles Algorithm Focus Bradycardia Acute Pulmonary Edema and Shock Hypothermia
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
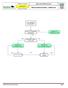 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
Summary of 2017 Protocol Changes
 Table of Contents x Transport to Freestanding Medical Facility Transport to Freestanding Emergency Medical Facility This change also applies to all instances where "Freestanding Medical Facility" appears
Table of Contents x Transport to Freestanding Medical Facility Transport to Freestanding Emergency Medical Facility This change also applies to all instances where "Freestanding Medical Facility" appears
Standardized Nurse Activated Protocols (SNAPs)
 SNAPs by presenting complaint/problem help nurses initiate care before the patient is seen by a physician. SNAPs should be approved by ED team consensus If patient unstable in any way, immediately notify
SNAPs by presenting complaint/problem help nurses initiate care before the patient is seen by a physician. SNAPs should be approved by ED team consensus If patient unstable in any way, immediately notify
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health
 CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
2019 Protocol Roll - OUT
 2019 Protocol Roll - OUT Objectives Discuss participation in the Regional EMS Protocol Outline changes, and discuss how UH will implement Review changes from last year that carry over into this protocol
2019 Protocol Roll - OUT Objectives Discuss participation in the Regional EMS Protocol Outline changes, and discuss how UH will implement Review changes from last year that carry over into this protocol
ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES
 ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Last Revised: July 2017 Cardiac Emergencies Section A 1 CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST NOTE: High quality CPR includes: 1. Chest Compressions at a depth of at least 2 inches 2. Rate of
ADULT CARDIAC EMERGENCIES Last Revised: July 2017 Cardiac Emergencies Section A 1 CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST NOTE: High quality CPR includes: 1. Chest Compressions at a depth of at least 2 inches 2. Rate of
Cleveland Clinic Regional Hospitals EMS Protocol DRAFT Release Notes. Global Changes
 Cleveland Clinic Regional Hospitals EMS Protocol 2014 DRAFT Release Notes Global Changes Added cautions and stops with selected high risk medications / procedures on protocol tree page for safety Individual
Cleveland Clinic Regional Hospitals EMS Protocol 2014 DRAFT Release Notes Global Changes Added cautions and stops with selected high risk medications / procedures on protocol tree page for safety Individual
Intermediate Medications. Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol
 Intermediate Medications Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Needle Handling Precautions Minimize the tasks performed in a moving ambulance Balance the
Intermediate Medications Epinephrine cardiac Epinephrine anaphylaxis Dextrose Atropine Narcan Thiamine Albuterol Needle Handling Precautions Minimize the tasks performed in a moving ambulance Balance the
Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016
 Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016 1. Which of the following is incorrect? a. Each EMS and Fire agency should have protocols in place for evaluation of personnel involved in fire suppression operations
Mesa County EMS Protocol Test 2016 1. Which of the following is incorrect? a. Each EMS and Fire agency should have protocols in place for evaluation of personnel involved in fire suppression operations
Adult Basic Life Support
 Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
Adult Basic Life Support UNRESPONSIVE? Shout for help Open airway NOT BREATHING NORMALLY? Call 112* 30 chest compressions 2 rescue breaths 30 compressions *or national emergency number Fig 1.2_Adult BLS
SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES
 EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
EMS Agency SAN JOAQUIN COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES Pediatric Advanced Life Support Policies Emergency Medical Services TITLE: Pediatric Routine Medical Care EMS Policy No. 5800 Pediatric Routine
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Michigan Adult Cardiac Protocols TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Asystole Section 2-1 Bradycardia Section 2-2 Cardiac Arrest General Section 2-3 Cardiac Arrest ROSC Section 2-4 Chest Pain Acute Coronary Syndrome
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Introduction to the Algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
