The potential implication of eosinophil activation in the pathogenesis of childhood asthma
|
|
|
- Hugh Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Egypt J Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2004; 2(1): Original article The potential implication of eosinophil activation in the pathogenesis of childhood asthma Background: Asthma is now recognized as an eosinophil mediated inflammation of the airways. Pulmonary function tests are less easily performed in young children. So, measuring markers of eosinophil activation is of special importance in pediatric practice. Objective: This study aimed at evaluating the role of eosinophil protein X (EPX) as a marker for assessment of asthma attack severity and control of the exacerbation. Methods: Serum EPX was measured in 35 asthmatic Egyptian children aged between 7 and 10 and 35 age and sex matched healthy children using radioimmunoassay technique (RIA). Asthmatic patients were graded according to severity of the attack into mild, moderate and severe and the measurement was performed during and after the resolution of acute asthma attack. In addition, complete hemogram, total serum IgE, arterial blood gases and stool analysis were performed and peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) was assessed in asthmatic children during and after acute exacerbation. Results: Serum concentrations of EPX, total serum IgE and absolute eosinophilic count (AEC) were significantly higher in asthmatic children than healthy controls (P<0.001). Serum EPX and AEC were significantly higher in all studied groups before treatment compared to the corresponding levels of the same patients after treatment (P<0.001). Total serum IgE was significantly higher only in mild and moderate asthma before treatment (P<0.001). Serum EPX level was significantly elevated among patients with severe attacks (84.70 ± 7.18 μg/l) than those with moderate attacks (67.2 ± 5.31 μg/l) and patients with mild attacks (53.47 ± μg/l)(p<0.001). It was negatively correlated to PEFR measurement during attacks (r=-0.75, P<0.05). A significant reduction in serum EPX and AEC was observed after the resolution and improvement of pulmonary function. while, total serum IgE decreased after treatment with the resolution of asthma attack, yet it remained significantly higher than that of controls (P<0.001). Conclusion: Our findings support the concept that EPX may be implicated in the pathogenesis of asthma and highlights its importance in monitoring the severity and control of asthma exacerbation. Hence, it might represent an objective guide of treatment efficacy. Key words: EPX, Childhood asthma, pathogenesis, eosinophil activation. INTRODUCTION Asthma is recognized as an eosinophil mediated inflammation of the airways 1. Eosinophils are major contributors to the damage in the airways of asthmatic patients which when activated, degranulate and release granules that contain cytotoxic cationic proteins including the major basic protein, eosinophil peroxidase, eosinophil cationic protein, eosinophil protein "X" (EPX), and membrane lipid mediators. These products have deleterious effects on the airway tissues and result in destruction of mucosal and smooth muscle layers Nayera I. Attia, Wafaa I. Rashid* Institute of Postgraduate Childhood Studies (Medical Department), Ain Shams University and National Research Center*, Cairo-Egypt. Correspondence: Dr. Nayera I. Attia Institute of Postgraduate Childhood Studies (Medical Department), Ain Shams University Abbassiah, Cairo, Egypt. nayera@ hotmail.com which lead to the inability to clear bronchial secretions and the production of constrictor factors that cause bronchoconstriction, increased vascular permeability and development of airway hyperresponsiveness. Also, these products influence the accumulation and maintenance of eosinophilic responses at the site of inflammation 2. So, measuring these proteins in blood to monitor inflammation in bronchial asthma patients is of a special importance in pediatric practice because lung function tests are less easily performed in young children 3. Several studies have been done to 52
2 Eosinophil activation in childhood asthma. measure the eosinophil granule proteins in children with bronchial asthma and the results of these studies suggest that serum markers of eosinophil activation correlate with airway function in childhood asthma and may be of value in assessing the severity of the disease 4. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of eosinophil protein X as a marker for assessment of asthma attack severity and control of exacerbation. METHODS Patients group: This follow up case-control study was carried out on 35 Egyptian asthmatic children (20 boys and 15 girls) aged between 7 and 10 years with a mean of 8.3±1.2 years. These patients were recruited from the Outpatient Pediatric Chest Clinic, Children's Hospital, Ain Shams University during the period from January to December Patients were assessed for asthma severity according to GINA guidelines 5 and were categorized as mild (n=10), moderate (n= 15) and severe asthmatics (n= 10). The patients were evaluated during acute asthmatic attacks and were followed up until the attack subsided clinically and then re-evaluated after 2 weeks of treatment (bronchodilators and short term inhaled steroids). Among these patients, 80% had family history of allergy and parental smoking. Exclusion criteria for the patients were: the presence of acute lower respiratory tract infection, fever, parasitic infestation (by stool analysis) and treatment with long-term corticosteroids whether inhaled or systemic. Control group: thirty-five age and sex matched healthy children were included in this study to serve as controls. They had no personal or family history of allergic diseases. Methods: All the studied children were subjected to the following: Clinical evaluation as regards family history of atopy, the duration and severity of symptoms, records of drug therapy as well as assessment of asthma severity. PEFR was measured by a Mini- Wright peak flow meter (Clement Clarke International Ltd, Edinburgh, Essex CM202 DE, England). Laboratory investigations included complete hemogram including total and differential leukocytic counts (Coulter counter T660, Coultronics, France), blood gas analysis (blood gas analyzer Mod. 995, Hb-Trust Medical Company), stool analysis, total serum IgE level using ELISA technique (Medix Biotech Inc., Agenzyme Company, San Carios CA, USA). Serum eosinophil protein X (EPX) was measured by radioimmunoassay technique (RIA) (4) using a commercially available kits supplied by Pharmacia Company, (100 Route 206 North Peapack, New Jersey 07977, USA). Serum "EPX", total serum IgE, absolute eosinophilic count (AEC) and PEFR were measured twice for each asthmatic patient (during and after resolution of acute asthma attack (with a 2 weeks interval). Sample collection: Blood specimens were obtained under complete aseptic condition from the studied individuals by: Arterial puncture (radial artery): 1 ml blood in heparinized syringe for ph and blood gas analysis (Kept in ice till analyzed). Venipuncture: 1 ml was collected in a test tube containing EDTA for complete hemogram and 3ml in a plain dried tube left to clot at room temperature then centrifuged at 3000 rpm to separate serum for EPX and IgE analysis (serum was frozen at -20 o c till assayed). Statistical methods: Data processing of the results statistical analysis statistically using SSPS soft ware package (Version 8, 1997 USA). Student s t test was used to compare the mean values of parametric data and ANOVA for evaluating quality of several groups. RESULTS The mean serum EPX concentration, total serum IgE and absolute eosinophilic count (AEC) were significantly higher while PEFR was significantly lower in asthmatic children than in healthy controls (P<0.001) (table 1). The serum EPX levels and AEC were significantly dropped whereas PEFR significantly increased with the resolution of the attacks (P<0.001). Total serum IgE was significantly higher only in mild and moderate asthma during the attack compared to the level in remission (P<0.001) (table 2). The relationship of asthma severity to different laboratory parameters was studied by ANOVA test. This revealed a significant direct relationship with EPX, serum total IgE and AEC, whereas the relation with PEFR was a significant inverse one (fig.1). Serum EPX correlated negatively with PEFR (r=- 0.75, P<0.05) and positively correlated with AEC and the mean serum IgE level (r=0.56, r=0.59 respectively, P<0.05). 53
3 Attia and Rashid. No significant correlation could be found between serum EPX and the duration of illness. Serum EPX did not differ significantly between patient with history of other atopic diseases (27±65µg/L) and those with no history of atopic diseases (26±27µg/L). Following treatment and resolution of acute asthma symptoms with therapy the mean serum EPX, AEC and PEFR became insignificantly differed from the control values (P>0.05). The mean total serum IgE level decreased after treatment, yet it remained significantly higher than that of the control group (P<0.001) (table 3). Table 1: Comparison between asthmatic patients during attacks and controls as regard serum EPX, total serum IgE, AEC and PEFR. Control group Asthmatic patients P (n=35) (n=35) mean mean Serum EPX (µg/l) 23.95± ±6.90 P<0.001 Total serum IgE (IU/ml) 34.73± ± P<0.001 AEC 1.82± ±1.40 P<0.001 PEFR 97.36± ±2.24 P<0.001 P<0.001= highly significant Table 2: Serum EPX, total IgE, AEC and PEFR in the study groups during acute attacks and in remission. Mild asthmatics (n = 10) Moderate asthmatics (n=15) Severe asthmatics (n=10) During attack In remission During attack In remission During attack In remission Serum EPX (µg/l) ± ± ± ± ±7.18 Total serum IgE (Iu/ml) ± ± ± ± ± P <0.05 <0.005 >0.05 AEC ± ± ± ± ±1.58 PEFR ± ± ± ± ±1.26 P>0.05= non significant P<0.05=significant P<0.001=highly significant 26.6 ± ± ± ±
4 Eosinophil activation in childhood asthma. (µg/l) (Iu/ml) F= F=23.37 F= F= P<0.001 P<0.001 P<0.001 P<0.001 Figure 1: Relation of the laboratory findings and PEFR to the severity of asthma (P values reflect the differences among the groups by ANOVA test). Table 3: Comparison between patients groups and controls as regards serum EPX, total serum IgE, AEC and PEFR after treatment. Controls Mild asthmatics Moderate asthmatics Severe asthmatics Variants (n = 10) (n=15) (n=10) ±S. D Serum EPX (µg/l) ± ± ± ±3.24 P >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 Total serum IgE (Iu/ml) ± ± ± ± AEC 1.82 ± ± ± ±0.82 P >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 PEFR ± ± ± ±7.44 P >0.05 >0.05 >0.05 P>0.05 = non significant, P<0.001= highly significant DISCUSSION Eosinophils are involved in the inflammatory response in asthma and their basic proteins play a major pathophysiological role in this process as they cause cytoxic damage to the airways epithelium in asthma. The serum levels of these basic proteins have been used to monitor the ongoing asthmatic disease. Assessment of eosinophil derived proteins in various body fluids (serum, urine and nasal lavage) could be used for monitoring disease activity of childhood asthma 7. So, this study aimed at evaluating serum EPX as a marker for assessment of disease severity and prognosis in asthmatic children. The results of this study revealed that 80% of patients had positive family history of allergy and parental smoking. This finding was in agreement with that of Cohen 8 who stated that 75% of asthmatic patients had a positive family of asthma or other atopic disorders. As regards parental smoking, Wright et al 9 found that parental smoking was associated with an increased risk of asthma in children. 55
5 Attia and Rashid. In fact, the role of serum EPX was evident in our results since its concentrations was significantly increased in asthmatic children as compared with the control group. In this regard, Remes et al 10 and Koller et al 7 found that the level of serum EPX was significantly raised in children with bronchial asthma compared with healthy control subjects. Also, Boner et al 11 and Oymar 12 reported that levels of EPX were higher in children with asthma during acute attacks than in controls. An important aim of this study was to evaluate serum EPX in asthmatic children during and after the resolution of an asthma attack. Serum EPX significantly increased in all asthmatic children during exacerbations compared to the values observed with the resolution of the attacks (P<0.001). In support of our results, Labbe et al (1) reported that there was significant reduction in the level of EPX in asthmatic children after treatment when compared to their corresponding value before treatment. Another goal of this study was to evaluate whether the level of serum EPX was influenced by the severity of asthma attack. The results showed that during exacerbations of asthma the more severe the grade of asthma was, the higher was the mean serum EPX. Moreover, serum EPX correlated negatively to PEFR in asthmatic children. These findings denote that EPX production is positively correlated with the degree of bronchospasm. In agreement with our results Breuer et al (13) documented that the levels of EPX in serum and body fluids were correlated with disease activity and severity in atopic respiratory disease. Also, Lugosi et al 14 and Shirakawa et al 15 concluded that levels of EPX in serum and urine were negatively correlated with parameters of pulmonary function in asthmatic children. Recently, Bahceciler et al 16 stated that while EPX concentrations had increased, pulmonary function tests had decreased significantly in asthmatic children during acute attacks. It is of value also to document that with resolution of the attacks, the levels of EPX became insignificantly different from controls. This could be a reflection of decreased recruited eosinophilis to the site of allergic inflammation. Therefore, it could be a useful marker in the follow up of disease severity and activity. In agreement with our results Vila et al 17 reported that eosinophil products including EPX have been related to bronchial inflammatory reactions and their levels have been shown to decline after treatment and the resolution of an asthma attack. Also, Storm et al 18 stated that measurement of serum EPX is helpful in monitoring therapy in asthmatic children. Moreover, Labbe et al 1 found that EPX levels were higher in children with asthma than in controls and after treatment there were significant reduction in the level of EPX in these asthmatic children, so, they concluded that EPX levels were sensitive and useful to the clinician in the evaluation of manifestations of airway inflammation in asthmatic children. On studying serum IgE level in all asthmatics during and after resolution of an asthma attack, it was found that it increased with increased severity of the disease and in comparison to controls. Similarly, Boner et al. 11 found that there was significant increase in the level of serum IgE in asthmatic children during acute attacks. Also, Khadadah et al 19 recorded that total serum IgE was elevated above 200 IU/L in 63% of asthmatic compared to controls. The results of this study showed that the AEC was increased with increasing asthma severity and also it was higher during the attack compared to the count after the resolution and to controls. Lastly, no significant difference between the three studied groups after treatment and controls as regards the mean value of AEC. In agreement with our results Alvarez et al 20 and Oymer et al 12 found that the AEC was higher in asthmatics than in controls. Jang et al 2 found that moderate and severe asthmatics had significantly higher eosinophilic counts compared with mild asthmatics. Finally, Metso et al 21 stated that the AEC was decreased in asthmatics after treatment compared with controls. In the current study, PEFR decreased significantly in patients as compared to healthy controls and in all studied groups during the attack compared to the corresponding values after the resolution. Also, it decreased significantly with increased asthma severity and it increased with improvement of the clinical condition after treatment Bahceciler et al 16 found that PEFR decreased in asthmatics during acute attacks and improved (increased) with improvement of their condition. In conclusion, serum EPX increases with increased acute asthma severity and correlates negatively with PEFR. Its levels are higher during asthma exacerbations and declines towards normality with the resolution of the attacks. Therefore, EPX may be implicated in the pathogenesis of asthma and reflect the degree of severity of asthma. This highlights the importance of EPX as an inflammatory marker detecting both the evolution and the control of asthma exacerbation. Hence, it might represent an objective guide of treatment efficacy. 56
6 Eosinophil activation in childhood asthma. REFERENCES 1. Labbe A, Aublet CB, Jouaville L. Prospective longitudinal study of urinary eosinophil protein X in children with asthma and chronic cough. Pediatr Pulmonol 2001; 31(5): Jang-AS, Choi IS. Eosinophil activation markers in induced sputum in asthmatics. Korean-J-Inter-Med 2000; 15 (1): Kristiansson S, Strannedard IL, Wenneraren G. Inflammatory markers in childhood asthma. Ann Med 1996; 28 (5): Rao R, Frederick JM, Enander I, Gregson RK, Warner JA, Warner JO. Airway function correlates with circulating eosinophil but not mast cell, markers of inflammation in childhood asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 1996; 26 (7): Gina Guidelines. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. USA National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Bennich HH, Ellerson JR, Karlsson T. Evaluation of basic serum IgE levels and IgE antibody response in the rat by radioimmunoassays. Immunological Rev 1978; 41: Koller DY, Halmerbauer G, Frischer T, Roithner B. Assessment of eosinophil granule proteins in various body fluids. Clin Exp Allergy 1999; 29 (6): Cohen C. Genetic aspect of allergy. Med Clin Immunol 1994; 80: Wright A, Holberg C, Martinez F. Relationship of parental smoking to wheezing and non wheezing lower respiratory tract illnesses in infancy. J Pediatr 1997; 118: Remes S, Korppi M, Remes K, Savolainen K. Serum eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) and eosinophil protein X (EPX) in childhood asthma. Pediatr Pulmonol 1998; 25(3): Boner A L, Peroni DG, Venge P. Influence of allergen avoidance at high altitude on serum markers of eosinophil activation in children with allergic asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 1999; 23 (12): Oymar K. High levels of urinary eosinophil protein X in young asthmatic children predict persistent atopic asthma. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2001; 12(6): Breuer K, Kapp A, Werfel T. Urine eosinophil protein X (EPX) is an in vitro parameter of inflammation in atopic dermatitis of the adult age. Allergy 2001; 56(8): Lugosi E, Halmerbauer G, Koller DY. Urinary eosinophil protein X in relation to disease activity in childhood asthma. Allergy 1997; 52(5): Shirakawa S, Iwasaki E, Baba M. Serum eosinophil cationic protein., urinary eosinophil protein X and urinarymethylhistamine during acute asthma in children. Arerugi 1998; 47 (12): Bahceciler NN, Barlan IB, Nuhoglu Y. Which factors predict success after discontinuation of inhaled budesonide therapy in children with asthma. J Asthma 2002; 39(1): Vila Indurain B, Munoz Lopez F, Martin Mateos M. Evaluation of blood eosinophilia and the eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) in the serum of asthmatic children with varying degree of severity. Clin Exp Allergy 1999; 27(6): Storm Van S, Gravesande K, Mattes J, Kuehr J. Circadian variation of urinary eosinophil protein X in asthmatic and healthy children. Clin Exp Allergy 1999; 29(11): Khadadah M, Onadeko BO, Ezeamuzie CI, Marouf R. The association of skin test reactivity, total serum IgE levels, and peripheral blood eosinophilia with asthma in Kuwait. J Asthma 2000; 37(6): Alvarez MJ, Olaguibel JM, Garcia BE, Tabar AI. Airway inflammation in asthma and perennial allergic rhinitis. Allergy 2000; 55(4): Metso J, Kilipio K, Haahtela T. Detection and treatment of early asthma. Allergy 2000; 55(5):
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in asthmatic children.
 Egypt J Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2003; 1(2): 102-9. Original article Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in asthmatic children. Background: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates the crosstalk
Egypt J Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2003; 1(2): 102-9. Original article Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in asthmatic children. Background: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) regulates the crosstalk
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 75 of Middleton s Allergy Principles and Practice, 7 th Edition, edited by N. Franklin Adkinson, et al. Chapter 75: Approach to Infants and Children with Asthma
RESPIRATORY BLOCK. Bronchial Asthma. Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU
 RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
RESPIRATORY BLOCK Bronchial Asthma Dr. Maha Arafah Department of Pathology KSU marafah@ksu.edu.sa Jan 2018 Objectives Define asthma (BA) Know the two types of asthma 1. Extrinsic or atopic allergic 2.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Impact of Asthma in the U.S. per Year. Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Risk Factors for Asthma. Childhood Asthma Costs of Asthma
 American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
American Association for Respiratory Care Asthma Educator Certification Prep Course Asthma Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Robert C. Cohn, MD, FAARC MetroHealth Medical Center Cleveland, OH Impact of
Immunology of Asthma. Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph. Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy
 Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol 2002; 16(1) : 41-45 Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy Sanjay S. Pawar Shriratna Intensive
Indian J Allergy Asthma Immunol 2002; 16(1) : 41-45 Sensitivity to Sorghum Vulgare (Jowar) Pollens in Allergic Bronchial Asthma and Effect of Allergen Specific Immunotherapy Sanjay S. Pawar Shriratna Intensive
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline
 Pathology of Asthma Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline Bronchial Asthma Definition: chronic, relapsing inflammatory lung disorder characterised by reversible
Pathology of Asthma Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology Anatomical Pathology Discipline Bronchial Asthma Definition: chronic, relapsing inflammatory lung disorder characterised by reversible
EVect of oral glucocorticoid treatment on serum inflammatory markers in acute asthma
 18 Department of Paediatrics, Queen Mary s Hospital, Sidcup, Kent DA14 6LT, UK A Sahid El-Radhi Department of Paediatrics, Royal Brompton Hospital, London SW3 6NP, UK C L Hogg J K Bungre A Bush C J Corrigan
18 Department of Paediatrics, Queen Mary s Hospital, Sidcup, Kent DA14 6LT, UK A Sahid El-Radhi Department of Paediatrics, Royal Brompton Hospital, London SW3 6NP, UK C L Hogg J K Bungre A Bush C J Corrigan
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
M.O. Hoekstra*, H. Hovenga**, J. Gerritsen*, H.F. Kauffman**
 Eur Respir J, 1996, 9, 2231 2235 DOI: 1.1183/931936.96.9112231 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1996 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Eosinophils and eosinophil-derived
Eur Respir J, 1996, 9, 2231 2235 DOI: 1.1183/931936.96.9112231 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1996 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Eosinophils and eosinophil-derived
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 1 Asthma Obstructive & Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Indicate obstruction to flow of air through the airways. As asthma, COPD ( chronic bronchitis
COPD and Asthma: Similarities and differences Prof. Peter Barnes
 and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
and Asthma: Similarities and Differences and Asthma: 1 Imperial College Peter Barnes FRS, FMedSci, National Heart & Lung Institute Imperial College, London, UK p.j.barnes@imperial.ac.uk Royal Brompton
Pathology of Asthma Epidemiology
 Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
Asthma A Presentation on Asthma Management and Prevention What Is Asthma? A chronic disease of the airways that may cause Wheezing Breathlessness Chest tightness Nighttime or early morning coughing Pathology
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss?
 ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
ASTHMA-COPD OVERLAP SYNDROME 2018: What s All the Fuss? Randall W. Brown, MD MPH AE-C Association of Asthma Educators Annual Conference July 20, 2018 Phoenix, Arizona FACULTY/DISCLOSURES Randall Brown,
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma. - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness.
 Obstructive diseases Asthma - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness. - Characterized by Intermittent and reversible (the
Obstructive diseases Asthma - A chronic inflammatory disorder which causes recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, cough and chest tightness. - Characterized by Intermittent and reversible (the
IgE-mediated allergy in elderly patients with asthma
 Allergology international (1997) 46: 237-241 Original Article IgE-mediated allergy in elderly patients with asthma Fumihiro Mitsunobu, Takashi Mifune, Yasuhiro Hosaki, Kouzou Ashida, Hirofumi Tsugeno,
Allergology international (1997) 46: 237-241 Original Article IgE-mediated allergy in elderly patients with asthma Fumihiro Mitsunobu, Takashi Mifune, Yasuhiro Hosaki, Kouzou Ashida, Hirofumi Tsugeno,
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma
 The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
The Asthma Guidelines: Diagnosis and Assessment of Asthma Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Partners Asthma Center Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Objectives Know how the diagnosis of asthma
Induced sputum to assess airway inflammation: a study of reproducibility
 Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 1997. Volume 27. pages 1138-1144 Induced sputum to assess airway inflammation: a study of reproducibility A. SPANEVELLO, G. B. MIGLIORI. A. SHARARA*, L. BALLARDlNIt,
Clinical and Experimental Allergy. 1997. Volume 27. pages 1138-1144 Induced sputum to assess airway inflammation: a study of reproducibility A. SPANEVELLO, G. B. MIGLIORI. A. SHARARA*, L. BALLARDlNIt,
The Link Between Viruses and Asthma
 The Link Between Viruses and Asthma CATHERINE KIER, MD Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division Chief, Pediatric Pulmonary, and Cystic Fibrosis Center Director, Pediatric Sleep Disorders Center SUNY Stony
The Link Between Viruses and Asthma CATHERINE KIER, MD Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Division Chief, Pediatric Pulmonary, and Cystic Fibrosis Center Director, Pediatric Sleep Disorders Center SUNY Stony
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ
 Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Outline FEF Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications?
 Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Plasma concentration of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine in childhood asthma
 Egypt J Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2003; 1(2): 86-92. Original article Plasma concentration of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine in childhood asthma Background: Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine
Egypt J Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2003; 1(2): 86-92. Original article Plasma concentration of thymus and activation-regulated chemokine in childhood asthma Background: Thymus and activation-regulated chemokine
In 2002, it was reported that 72 of 1000
 REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
SCREENING AND PREVENTION
 These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma
 Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Searching for Targets to Control Asthma Timothy Craig Distinguished Educator Professor Medicine and Pediatrics Penn State University Hershey, PA, USA Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma The most important
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO)
 Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Asthma COPD Overlap (ACO) Dr Thomas Brown Consultant Respiratory Physician Thomas.Brown@porthosp.nhs.uk Dr Hitasha Rupani Consultant Respiratory Physician Hitasha.rupani@porthosp.nhs.uk What is Asthma
Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier
 Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Pulmonary Medicine, Washington
Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Pulmonary Medicine, Washington
Evolution of asthma from childhood. Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT
 Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Evolution of asthma from childhood Carlos Nunes Center of Allergy and Immunology of Algarve, PT allergy@mail.telepac.pt Questionnaire data Symptoms occurring once or several times at follow-up (wheeze,
Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast as Monotherapy in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma. Gautam Ghosh, Arun Kumar Manglik and Subhasis Roy
 Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast as Monotherapy in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma Gautam Ghosh, Arun Kumar Manglik and Subhasis Roy From the Shree Jain Hospital & Research Center, Howrah 711 102
Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast as Monotherapy in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma Gautam Ghosh, Arun Kumar Manglik and Subhasis Roy From the Shree Jain Hospital & Research Center, Howrah 711 102
Anti-IgE: beyond asthma
 Anti-IgE: beyond asthma Yehia El-Gamal, MD, PhD, FAAAAI Professor of Pediatrics Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Unit Children s Hospital, Ain Shams University Member, WAO Board of Directors Disclosure
Anti-IgE: beyond asthma Yehia El-Gamal, MD, PhD, FAAAAI Professor of Pediatrics Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Unit Children s Hospital, Ain Shams University Member, WAO Board of Directors Disclosure
Serum eosinophil cationic protein measurements in the management of perennial and periodic asthma: a prospective study
 Eur Respir J 1998; 11: 594 598 DOI:.1183/09031936.98.130594 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1998 European Respiratory Journal ISS 0903 1936 Serum eosinophil cationic protein
Eur Respir J 1998; 11: 594 598 DOI:.1183/09031936.98.130594 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1998 European Respiratory Journal ISS 0903 1936 Serum eosinophil cationic protein
An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease
 An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease Carmen Vidal Athens, September 11, 2014 Pucci S & Incorvaia C, 2008; 153:1-2 1. The major player in driving the immune
An Insight into Allergy and Allergen Immunotherapy Co-morbidities of allergic disease Carmen Vidal Athens, September 11, 2014 Pucci S & Incorvaia C, 2008; 153:1-2 1. The major player in driving the immune
LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE
 LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE Azienda Ospedaliera Pisana Università degli Studi di Pisa Pierluigi Paggiaro GINA International Executive Committee, Chairman GINA ITaly Cardio-Thoracic and Vascular Department,
LINEE GUIDA DELL ASMA: UP TO DATE Azienda Ospedaliera Pisana Università degli Studi di Pisa Pierluigi Paggiaro GINA International Executive Committee, Chairman GINA ITaly Cardio-Thoracic and Vascular Department,
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Potent and Selective CRTh2 Antagonists are Efficacious in Models of Asthma, Allergic Rhinitis and Atopic Dermatitis
 Potent and Selective CRTh2 Antagonists are Efficacious in Models of Asthma, Allergic Rhinitis and Atopic Dermatitis Laura L. Carter, Yoshi Shiraishi, Yooseob Shin, Laurence Burgess, Christine Eberhardt,
Potent and Selective CRTh2 Antagonists are Efficacious in Models of Asthma, Allergic Rhinitis and Atopic Dermatitis Laura L. Carter, Yoshi Shiraishi, Yooseob Shin, Laurence Burgess, Christine Eberhardt,
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes. Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy
 Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Clinical Implications of Asthma Phenotypes Michael Schatz, MD, MS Department of Allergy Definition of Phenotype The observable properties of an organism that are produced by the interaction of the genotype
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Definition and Pathology CHAPTER 1. John Rees
 CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
CHAPTER 1 Definition and Pathology John Rees Sherman Education Centre, Guy s Hospital, London, UK OVERVIEW Asthma is an overall descriptive term but there are a number of more or less distinct phenotypes
Outcome, classification and management of wheezing in preschool children Paul L.P. Brand
 Outcome, classification and management of wheezing in preschool children Paul L.P. Brand Princess Amalia Children s Clinic Isala klinieken, Zwolle the Netherlands p.l.p.brand@isala.nl Valle de la Luna,
Outcome, classification and management of wheezing in preschool children Paul L.P. Brand Princess Amalia Children s Clinic Isala klinieken, Zwolle the Netherlands p.l.p.brand@isala.nl Valle de la Luna,
Add on therapy in asthma. Local experience in context J Paul Dilworth, Nicola Marks, Lauren Geddes
 Add on therapy in asthma Local experience in context J Paul Dilworth, Nicola Marks, Lauren Geddes Programme Omalizumab Evidence and assessment Local Experience Dysfunctional breathing The other effective
Add on therapy in asthma Local experience in context J Paul Dilworth, Nicola Marks, Lauren Geddes Programme Omalizumab Evidence and assessment Local Experience Dysfunctional breathing The other effective
Systems Pharmacology Respiratory Pharmacology. Lecture series : General outline
 Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Systems Pharmacology 3320 2017 Respiratory Pharmacology Associate Professor Peter Henry (Rm 1.34) Peter.Henry@uwa.edu.au Division of Pharmacology, School of Biomedical Sciences Lecture series : General
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention
 Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Immunomodulators: Anti-IgE mab. Thomas B. Casale, MD Professor of Medicine Chief, Allergy/Immunology Creighton University Omaha, NE
 Immunomodulators: Anti-IgE mab Thomas B. Casale, MD Professor of Medicine Chief, Allergy/Immunology Creighton University Omaha, NE Objectives To explain the rationale behind IgE blockade To discuss which
Immunomodulators: Anti-IgE mab Thomas B. Casale, MD Professor of Medicine Chief, Allergy/Immunology Creighton University Omaha, NE Objectives To explain the rationale behind IgE blockade To discuss which
Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot Malhi, B.R. Srinivas and Lata Kumar
 Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Disease spectrum. IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
 Aspergillus & ABPA Disease spectrum IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis ABPA ABPA pathophysiology conidia of Aspergillus trapped in mucous and narrowed airways of asthmatics/cf germinate to form hyphae
Aspergillus & ABPA Disease spectrum IPA Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis ABPA ABPA pathophysiology conidia of Aspergillus trapped in mucous and narrowed airways of asthmatics/cf germinate to form hyphae
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction
 Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Asthma and Vocal Cord Dysfunction Amy L. Marks DO, FACOP Pediatric Allergy and Immunology Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Objectives: Understanding
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange
 Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
Basic mechanisms disturbing lung function and gas exchange Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department, Medical University of Plovdiv Respiratory system 1 Control of breathing Structure of the lungs
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of YourCare Health Plan
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 6 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS
 Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS Asthma Usually acquire before the age of 10 These patients exhibit hyper-reactive airways Spasm Constriction Swelling Secretions are
Asthma- THE most common Pediatric Disease JENNIFER MCDANIEL, RRT- NPS Asthma Usually acquire before the age of 10 These patients exhibit hyper-reactive airways Spasm Constriction Swelling Secretions are
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria. Defining Asthma: Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness
 Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria Atopy 34% Recent wheeze 20% Asthma 11% AHR 19% n = 807 From: Woolcock, AJ. Asthma in Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 2nd ed. Murray, Nadel, eds.(saunders:philadelphia)
Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria Atopy 34% Recent wheeze 20% Asthma 11% AHR 19% n = 807 From: Woolcock, AJ. Asthma in Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 2nd ed. Murray, Nadel, eds.(saunders:philadelphia)
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Recurrent Wheezing in Preschool Children. William Sheehan, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Allergy and Immunology
 Recurrent Wheezing in Preschool Children William Sheehan, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Allergy and Immunology Disclosure I have nothing to disclose related to this talk. Background
Recurrent Wheezing in Preschool Children William Sheehan, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Allergy and Immunology Disclosure I have nothing to disclose related to this talk. Background
Asthma. Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital. Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence,
 Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA. Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine)
 Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine) Conventional diagnostic criteria for ABPA Primary Episodic bronchial obstruction (asthma) Peripheral blood eosinophilia
Recent advances in diagnosis and management of ABPA Arindam SR(Pulmonary Medicine) Conventional diagnostic criteria for ABPA Primary Episodic bronchial obstruction (asthma) Peripheral blood eosinophilia
Safety, PK and PD of ARRY-502, a CRTh2 Antagonist, in Healthy Subjects with a History of Seasonal Allergies
 Safety, PK and PD of ARRY502, a CRTh2 Antagonist, in Healthy Subjects with a History of Seasonal Allergies L. Burgess*, L. Anderson, C. Nugent, N. Klopfenstein, C. Eberhardt, L. Carter, C. Kass, S. RojasCaro,
Safety, PK and PD of ARRY502, a CRTh2 Antagonist, in Healthy Subjects with a History of Seasonal Allergies L. Burgess*, L. Anderson, C. Nugent, N. Klopfenstein, C. Eberhardt, L. Carter, C. Kass, S. RojasCaro,
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Asthma and obesity, implications for airway inflammation and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness
 Asthma and obesity, implications for airway inflammation and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness Fernando Holguin MD MPH Asthma Institute University of Pittsburgh Obesity Trends* Among U.S. Adults BRFSS, 1990,
Asthma and obesity, implications for airway inflammation and Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness Fernando Holguin MD MPH Asthma Institute University of Pittsburgh Obesity Trends* Among U.S. Adults BRFSS, 1990,
E-1 Role of IgE and IgE receptors in allergic airway inflammation and remodeling
 E-1 Role of IgE and IgE receptors in allergic airway inflammation and remodeling Ruby Pawankar, MD, Ph.D. FRCP, FAAAAI Prof. Div of Allergy, Dept of Pediatrics Nippon Medical School Tokyo, Japan pawankar.ruby@gmail.com
E-1 Role of IgE and IgE receptors in allergic airway inflammation and remodeling Ruby Pawankar, MD, Ph.D. FRCP, FAAAAI Prof. Div of Allergy, Dept of Pediatrics Nippon Medical School Tokyo, Japan pawankar.ruby@gmail.com
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma
 Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit)
 Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Meeting the Challenges of Asthma
 Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Meeting the Challenge of Asthma SPEAKER Christopher Fanta, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christopher Fanta, MD: No financial
Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment. Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc
 Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc No conflicts to declare Objectives To understand the varied clinical forms of asthma To understand the pathobiologic
Phenotypes of asthma; implications for treatment Medical Grand Rounds Feb 2018 Jim Martin MD DSc No conflicts to declare Objectives To understand the varied clinical forms of asthma To understand the pathobiologic
National Asthma Educator Certification Board Detailed Content Outline
 I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
I. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 20 1 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing
 Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing TSANZ / ANZSRS Masterclass: April 3rd, 2016 13:00 13:30 John D. Brannan PhD Scientific Director - Dept. Respiratory & Sleep Medicine John Hunter Hospital,
Mechanisms of action of bronchial provocation testing TSANZ / ANZSRS Masterclass: April 3rd, 2016 13:00 13:30 John D. Brannan PhD Scientific Director - Dept. Respiratory & Sleep Medicine John Hunter Hospital,
Diagnosis and Management of Fungal Allergy Monday, 9-139
 Diagnosis and Management of Fungal Allergy Monday, 9-139 13-2010 Alan P. Knutsen,, MD Director, Pediatric Allergy & Immunology Director, Jeffrey Modell Diagnostic Center for Primary Immunodeficiencies
Diagnosis and Management of Fungal Allergy Monday, 9-139 13-2010 Alan P. Knutsen,, MD Director, Pediatric Allergy & Immunology Director, Jeffrey Modell Diagnostic Center for Primary Immunodeficiencies
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
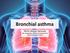 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
2010 Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Asthma Third edition Stephen T Holgate MD DSc FRCP FMedSci MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology School of Medicine Southampton General Hospital Southampton, UK Jo Douglass
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Asthma Third edition Stephen T Holgate MD DSc FRCP FMedSci MRC Clinical Professor of Immunopharmacology School of Medicine Southampton General Hospital Southampton, UK Jo Douglass
SLIT: Review and Update
 SLIT: Review and Update Disclosure Speaker: ISTA Pharmaceuticals Speaker: GlaxoSmithKline Allergen IT - Evidence Based Evaluation: Rescue Medications Meta-analysis Disease IT # of Patients Rescue Medication
SLIT: Review and Update Disclosure Speaker: ISTA Pharmaceuticals Speaker: GlaxoSmithKline Allergen IT - Evidence Based Evaluation: Rescue Medications Meta-analysis Disease IT # of Patients Rescue Medication
Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD. AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07
 Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07 Introduction Diagnosis and course of COPD/Asthma Clinical information Pulmonary function tests Arterial blood gases Chest X-raysX No direct
Exhaled Biomarkers Asthma & COPD AS Paul DM Seminar 30 March 07 Introduction Diagnosis and course of COPD/Asthma Clinical information Pulmonary function tests Arterial blood gases Chest X-raysX No direct
Pro/Con: Pets Prevent Allergies and Asthma
 Slide 1 Pro/Con: Pets Prevent Allergies and Asthma Slide 2 Special thanks to: n Dr. Dennis Ownby n Dr. Matt Perzanowski n Dr. Erica von Mutius and Dr. Charlotte Braun-Fahrlander n Dr. Andy Liu n Colleagues
Slide 1 Pro/Con: Pets Prevent Allergies and Asthma Slide 2 Special thanks to: n Dr. Dennis Ownby n Dr. Matt Perzanowski n Dr. Erica von Mutius and Dr. Charlotte Braun-Fahrlander n Dr. Andy Liu n Colleagues
Public Dissemination
 1. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 18 3 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
1. THE ASTHMA CONDITION 9 18 3 30 A. Pathophysiology 4 6 0 10 1. Teach an individual with asthma and their family using simple language by illustrating the following with appropriate educational aids a.
Evaluation of Mean Thrombocyte Volumes in Asthma Patients During Acute Exacerbations and Stable Periods
 Research Article Evaluation of Mean Thrombocyte Volumes in Asthma Patients During Acute Exacerbations and Stable Periods Uysal Dolap 1, Tuncer Tuğ 2, Suat Konuk 2* 1 Şırnak State Hospital, Şırnak, Turkey
Research Article Evaluation of Mean Thrombocyte Volumes in Asthma Patients During Acute Exacerbations and Stable Periods Uysal Dolap 1, Tuncer Tuğ 2, Suat Konuk 2* 1 Şırnak State Hospital, Şırnak, Turkey
Omalizumab (Xolair ) ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September Indication
 ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Allergen and Environment in Severe Asthma
 Allergen and Environment in Severe Asthma Hye-Ryun Kang MD., PhD. Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital Role of Allergen in Asthma Pathogenesis Early response of allergen
Allergen and Environment in Severe Asthma Hye-Ryun Kang MD., PhD. Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital Role of Allergen in Asthma Pathogenesis Early response of allergen
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria. Defining Asthma: Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness
 Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria Atopy 34% Recent wheeze 20% Asthma 11% AHR 19% n = 807 From: Woolcock, AJ. Asthma in Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 2nd ed. Murray, Nadel, eds.(saunders:philadelphia)
Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria Atopy 34% Recent wheeze 20% Asthma 11% AHR 19% n = 807 From: Woolcock, AJ. Asthma in Textbook of Respiratory Medicine, 2nd ed. Murray, Nadel, eds.(saunders:philadelphia)
Defining Asthma: Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness. Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria. Impaired Ventilation in Asthma. Dynamic Imaging of Asthma
 Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria Defining Asthma: Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness Atopy 34% Recent wheeze 20% Asthma 11% AHR 19% n = 807 From: Woolcock, AJ. Asthma in Textbook of Respiratory Medicine,
Defining Asthma: Clinical Criteria Defining Asthma: Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness Atopy 34% Recent wheeze 20% Asthma 11% AHR 19% n = 807 From: Woolcock, AJ. Asthma in Textbook of Respiratory Medicine,
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
spontaneously or under optimum treatment (2,3). Asthma can be classify as early onset or
 The importance of post exercise peak expiratory flow rate & plasma IgE as a diagnostic tests for Mossa M. Marbut*, Jawad Ali Salih*, Abdul- Ghani M. Al-Samarai**. * Department of physiology, College of
The importance of post exercise peak expiratory flow rate & plasma IgE as a diagnostic tests for Mossa M. Marbut*, Jawad Ali Salih*, Abdul- Ghani M. Al-Samarai**. * Department of physiology, College of
C ough variant asthma, gastro-oesophageal reflux associated
 14 ASTHMA Comparison of atopic cough with cough variant asthma: is atopic cough a precursor of asthma? M Fujimura, H Ogawa, Y Nishizawa, K Nishi... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
14 ASTHMA Comparison of atopic cough with cough variant asthma: is atopic cough a precursor of asthma? M Fujimura, H Ogawa, Y Nishizawa, K Nishi... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Efficacy and safety of montelukast in adults with asthma and allergic rhinitis
 Respiratory Medicine (26), 1952 1959 Efficacy and safety of montelukast in adults with asthma and allergic rhinitis J.Chr. Virchow a,, C. Bachert b a Universität Rostock, Ernst-Heydemann-Str. 6, 1857 Rostock,
Respiratory Medicine (26), 1952 1959 Efficacy and safety of montelukast in adults with asthma and allergic rhinitis J.Chr. Virchow a,, C. Bachert b a Universität Rostock, Ernst-Heydemann-Str. 6, 1857 Rostock,
Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care
 Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care Leonard B. Bacharier, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Clinical Director, Division of Allergy, Immunology, & Pulmonary Medicine
Using Patient Characteristics to Individualize and Improve Asthma Care Leonard B. Bacharier, M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Clinical Director, Division of Allergy, Immunology, & Pulmonary Medicine
Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Ast. Rhinitis: A Risk Factor for Asthma? Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
 Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Ast Rhinitis: A Risk Factor for Asthma? Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Rhinitis and asthma SIT-SLIT Evidence A SIT-SLIT Evidence A? SIT Evidence? Rhinitis
Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Ast Rhinitis: A Risk Factor for Asthma? Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark Rhinitis and asthma SIT-SLIT Evidence A SIT-SLIT Evidence A? SIT Evidence? Rhinitis
Property of Presenter
 Have We Missed A Role For Neutrophils In Asthma? In Steroid-Refractory Asthma? Erwin W. Gelfand, MD Chairman, Department of Pediatrics National Jewish Health Professor of Pediatrics and Immunology University
Have We Missed A Role For Neutrophils In Asthma? In Steroid-Refractory Asthma? Erwin W. Gelfand, MD Chairman, Department of Pediatrics National Jewish Health Professor of Pediatrics and Immunology University
Connecting Health & Housing: Asthma and the Home. Presented by: The California-Nevada Public Health Training Center
 Connecting Health & Housing: Asthma and the Home Presented by: The California-Nevada Public Health Training Center Funded by Grant #UB6HP20202 from the Health Resources and Services Administration, U.S.
Connecting Health & Housing: Asthma and the Home Presented by: The California-Nevada Public Health Training Center Funded by Grant #UB6HP20202 from the Health Resources and Services Administration, U.S.
Physiology. Effect of Aerobic Excersice and Other Variables on Bronchial Hyper Reactivity in Apprantly Healthy Young Adolescents of Central India
 Physiology Effect of Aerobic Excersice and Other Variables on Bronchial Hyper Reactivity in Apprantly Healthy Young Adolescents of Central India KEYWORDS EIBHR- Excersice induced bronchial hyper reactivity,
Physiology Effect of Aerobic Excersice and Other Variables on Bronchial Hyper Reactivity in Apprantly Healthy Young Adolescents of Central India KEYWORDS EIBHR- Excersice induced bronchial hyper reactivity,
A preliminary assessment of nurses asthma education needs and the effect of a training. programme in an urban tertiary healthcare facility.
 A preliminary assessment of nurses asthma education needs and the effect of a training programme in an urban tertiary healthcare facility O O Adeyeye, Y A Kuyinu, R T Bamisile, and C I Oghama Abstract
A preliminary assessment of nurses asthma education needs and the effect of a training programme in an urban tertiary healthcare facility O O Adeyeye, Y A Kuyinu, R T Bamisile, and C I Oghama Abstract
Michael S. Blaiss, MD
 Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine Division of Clinical Immunology and Allergy University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Speaker s Bureau: AstraZeneca,
Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine Division of Clinical Immunology and Allergy University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Speaker s Bureau: AstraZeneca,
