Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast as Monotherapy in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma. Gautam Ghosh, Arun Kumar Manglik and Subhasis Roy
|
|
|
- Justin McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Efficacy and Safety of Montelukast as Monotherapy in Children with Mild Persistent Asthma Gautam Ghosh, Arun Kumar Manglik and Subhasis Roy From the Shree Jain Hospital & Research Center, Howrah and South Point Asthma Clinic, Shibpur, Howrah, West Bengal, India. Correspondence to: Dr. Gautam Ghosh, 6B Gopal Banerjee Street, Kolkata , India. Manuscript received: April 20, 2005; Initial review completed: June 6, 2005; Revision accepted: February 24, Objective: To study the efficacy and tolerability of montelukast as monotherapy in the treatment of mild persistent bronchial asthma. Design: Open, non-comparative, prospective, 12-month study. Setting: Asthma clinic in urban multi-speciality trust hospital. Methods: Children (age 3-11 yrs) with mild persistent asthma, not on any prophylactic drugs were enrolled consecutively (from January to December 2003) and started on 4 mg (2-4 yrs) or 5mg (>4 yrs) montelukast for a period of 12 weeks. Efficacy was assessed by improvements in clinical score, peak expiratory flow rates (PEFR), spirometry measurements and reduction in reliever drug requirement after 4 and 12 weeks of therapy. Side effects were also judged after 12 weeks of therapy. Results: 50 children (mean age 5.41 ± 2.11 years) completed the study. There was association with positive family history (92%), allergic rhinitis (64%), exercise induced asthma (40%), cough variant asthma (24%), seasonal asthma (80%) and high IgE (12%) levels. Clinical scores, viz, activity, wheeze and cough, improved effectively from (1.64 ± ) at baseline to (0.7 ± ) and (1.72 ± 0.701) to (0.92 ± ) and (1.5 ± ) to (0.88 ± ) respectively after 12 weeks of therapy. Significant clinical improvement (p <0.001) was also noted after 4 weeks of therapy. Peak expiratory flow rates (done in 19 cases) documented improvement from ( ± 12.23) at baseline to ( ± 23.34) after 12 weeks. FEV 1 / FVC (done in 11 cases) improved from (71.44 ± 1.35%) to (87.10 ± 8.34%) after 12 weeks. Mean improvement in all the parameters demonstrated P value less than < A total of 19 of 50 cases showed mild side-effects as anorexia (16%), elevated liver function tests (18%) and headache (10%). Conclusion: The clinical outcome showed significant improvement (p <0.01) after 4 and 12 weeks. Key words: Mild persistent asthma, Montelukast, Monotherapy. ASTHMA is the most common chronic illness of childhood affecting approximately 10% of children(1). Persistent asthma is managed pharmacologically by the daily use of a preventer medication and a short acting betaagonist for relief of exacerbations. Inhaled corticosteroids are often used as daily preventer therapy for patients with persistent asthma(2). However, long term inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) exhibit dose related systemic side-effects(3). Moderate to high doses have been associated with a transiently decreased rate of growth in children and decreased bone mineral density(4,5). Inhaled cromolyn or nedocromil have a better safety profile and may be considered in children, but these drugs require upto 6-8 hourly administration making compliance a big problem particularly so in children(6). Leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) are the first new class of asthma therapy which block selectively the leukotriene pathways involved in the pathophysiology of asthma. Cysteinyl leukotrienes cause bronchoconstriction, mucus secretion, increased vascular permeability and eosinophil INDIAN PEDIATRICS 780 VOLUME 43 SEPTEMBER 17, 2006
2 GHOSH, ET AL. migration to the airways, as well as promote smooth muscle proliferation(7,8). Their synthesis and release appear not to be blocked by corticosteroid therapy(9). Montelukast is a potent, specific LTRA. Administered once daily in tablet form, Montelukast reduces the signs and symptoms of persistent asthma in children as young as 2 years of age, with a tolerability profile similar to that of placebo(10,11). Additionally, Montelukast has been shown to attenuate exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in these children. Western studies have shown the beneficial effects of LTRAs in children with persistent asthma(12,13). GINA guidelines clearly recommend the use of LTRAs (montelukast) as a single drug prophylaxis in mild persistent asthma(14). Considering the inhibition among parents about inhaled therapy in their children and side-effects of long-term use of inhaled steroids in children, this trial was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of montelukast in children with mild persistent asthma. Subjects and Methods It was a prospective, open, noncomparative study in an urban childhood asthma clinic in a multi-speciality hospital in Howrah, West Bengal. Prior ethical approval of the Institutional Review Board of the Hospital and written informed consent of the legal guardians of all participating parents was obtained. Children (age 3-11 yrs) with mild persistent asthma and not on any prophylactic drugs were enrolled consecutively (January to December 2003). Exclusion criteria were active upper respiratory infection within three weeks, acute sinus disease requiring antibiotic treatment within one week, emergency treatment of asthma within one month or hospitalization for asthma within three months before enrolment. Children with a history of hypersensitivity to montelukast were excluded, only by asking the parents whether this drug was used previously and the child had any side-effects. Children fulfilling the inclusion criteria were given 4 mg (3 to 4 yrs) / 5 mg (>4 yrs) tablets of montelukast in the evening regularly for 12 weeks. Children were considered to be compliant with the study medication if at least 80% of the study medications were taken according to the prescribed regimen. Short acting beta-agonists, either oral or inhaled (salbutamol or terbutaline) were used as needed during the study. The frequency and duration of their use were also noted. The use of oral theophylline, ICS, nasal steroid and inhaled or nasal cromolyn were not permitted. However, oral antihistamines, cough suppressants or expectorants, nasal decongestants (but not nasal steroids or nasal steroids or nasal cromolyn) were allowed. Appropriate treatment of acute asthma attacks were done according to hospital protocol and were documented. Children were called for a pre-study screening just for enrollment in the study. After inclusion, a detailed history and clinical examination were completed for each child. For assessment, the physician examined the patient, recorded the adherence therapy, and any adverse effect and the clinical response on the following visits: Visit I: Start of therapy; Visit II: Four weeks after; and Visit III: Twelve weeks after therapy. Patients were advised to report at any time if there was exacerbation of asthma symptoms. Efficacy assessment 1. Clinical assessment score (Table I): was evaluated at entry (baseline), at 4 weeks INDIAN PEDIATRICS 781 VOLUME 43 SEPTEMBER 17, 2006
3 GHOSH, ET AL and at 12 weeks respectively as per NHLBI guidelines(1). 2. The frequency of use of beta agonists, intensity of acute attacks, need for oral steroids, nebulization or hospitalization during the study period was recorded. 3. Pulmonary function testing (wherever possible): Peak expiratory flow rates (PEFR) at 8 am and 8 pm and spirometry (by any one author) were done regularly in some patients. FEV1 / FVC percentage was chiefly evaluated. Children were closely monitored for any clinical adverse effects in each visit. Laboratory examinations (serum SGPT in selected subjects) were done at 12 weeks only. Results A total of 65 children were enrolled in the study, but 50 children finally completed the study (6 excluded for non-compliance of the treatment and 9 excluded as they were in moderate persistent group on re-analysis). There were 28 boys and 22 girls with a mean age of 5.41 ± 2.11 yr (range 3-11 yrs). Demographic profile of these patients is presented in Table II. Short acting bronchodilators were required for symptomatic relief for 3.84 ± 0.92 days, 2.52 ± 0.56 days, and 1.64 ± 0.23 days a week (on average) at baseline, after 4 weeks of therapy and after 12 weeks of therapy, respectively. No patient required hospitalization during therapy. Short course of oral steroids and nebulization was needed in 5 cases only (within 4 weeks). Of total 40 cases with seasonal asthma, 22 cases started therapy one month before the season. Fourteen (63.67%) out of these 22 cases responded with improvement of symptoms (upgrading in all the scores with reduced use of beta-agonists) than the previous season. 18 cases started therapy during the season and only 6 (33.33%) of them responded favorably after 12 weeks. Fourteen (43.7%) out of 32 cases with allergic rhinitis showed clinical response for rhinitis symptoms within 4 weeks, while 18 (56.25%) cases did so after 12 weeks. Improvement of clinical scores were significant in all the three parameters (Table III) e.g., activity, wheeze and cough after 4 weeks and 12 weeks of therapy (P <0.001). PEFR (done in 19/50 cases) and FEV 1 (done in 11/50 cases) documented mild improvement (P <0.05) after 4 weeks while significant improvement (P <0.001) occurred after 12 weeks of therapy. A total of 19 out of 50 cases showed mild side-effects as anorexia (16%), elevated liver TABLE I Clinical Assessment Score Parameter Wheeze None Some Medium Severe Cough None Occasional Frequent Continous Activity None Can run short distance Can walk only Missed school/work or or climb 3 flights of stayed indoors stairs Sleep Fine Slept well, slight Awake 2-3 times, Bad night, awake all the wheeze or cough wheeze and/or cough time INDIAN PEDIATRICS 782 VOLUME 43 SEPTEMBER 17, 2006
4 GHOSH, ET AL. TABLE II Demographic Profile Parameter Segments Distribution Population Rural 10 (20%) Urban 40 (80%) History of allergic rhinitis Negative 18 (36 %) Positive 32 (64 %) Family history of asthma Negative 04 (8 %) Positive 46 (92 %) History of exercise induced asthma Negative 30(60 %) Positive 20 (40%) Cough variant asthma Negative 12(24 %) Positive 38(76 %) Seasonal asthma Negative 10 (20 %) Positive 40 (80 %) Serum total IgE level Negative (normal) 44 (88 %) Positive (high) 6 (12 %) TABLE III Overall Clinical Response Scores Bameline After 4 weeks P value After 12 weeks P value Mean (SD) Mean (SD) Mean (SD) Activity 1.64 ± (0.52) 1.18 ± (0.69) < ± (0.70) <0.001 Wheeze 1.72 ± (0.70) 1.28 (0.64) < ± (0.69) <0.001 Cough 1.50 ± (0.61) 1.06 ± (0.71) < ± (0.82) <0.001 PEFR ± (12.23) ± (16.34) < ± (23.34) <0.001 FEV ± (1.35) ± (3.45) < ± (8.34) <0.001 function tests (18%) and headache (10%). However, they were not excluded from the study. Discussion In the present study, it was observed that once daily treatment with montelukast (as a single preventer agent) in mild persistent asthma in children showed significant efficacy. Montelukast showed significant (P <0.001) improvement in activity, cough and wheeze scores while PEFR and FEV 1 also improved (P <0.001) in the selected cases where it could be done. The response was evident within 4 weeks and continued till 12 weeks. This study results matches that of the National Montelukast survey 2005 conducted in 56 centers in United Kingdom which also confirmed that a significant proportion of children have their symptoms dramatically improved (41.3%) as compared to adults (33.5%)(15). Moreover, the use of short-acting bronchodilators as rescue therapy was significantly reduced following montelukast therapy as evidenced in other studies too(13). INDIAN PEDIATRICS 783 VOLUME 43 SEPTEMBER 17, 2006
5 GHOSH, ET AL Key Messages Oral, montelukast improves multiple clinical efficacy end-points when administered as a single prophylactic drug once daily in children with mild persistent asthma. Montelukast is well tolerated and its compliance is satisfactory. Important issues to consider in treatment of children with asthma are drug administration and long-term adherence. ICS, the mainstay of preventer therapy so far are often difficult to administer, have variable drug delivery, more so in small children, and compliance may become questionable, especially if parents are not co-operative(16,17). In the present study the compliance with the orally used, once daily administered montelukast was satisfactory, with only 6 dropouts out of the initial 65 children enrolled (9.2%) as evidenced in other studies too(11). Moreover, the symptoms of seasonal asthma responded significantly in those who started the drug one month in advance i.e., 14 (63.67%) out of 22 cases. The allergic rhinitis symptoms also improved in 14 (43.75%) out of 32 cases within 4 weeks, and in 18 (56.25%) cases after 12 weeks as evidenced in other studies too(15). In adults too, montelukast has shown its beneficial effects with improvements in multiple parameters of asthma control(11,12). The present study definitely suggests that these benefits of montelukast do extend to children as well. Montelukast has been used in many trials as an add-on therapy with ICS in mild and moderate persistent asthma in children. This study has been targeted to see its effect as a single drug as a starter, preventer therapy in mild persistent asthma and has shown significant benefits as in other studies(8). During this 12 week therapy montelukast was well tolerated and had little side effects. This is similar to the studies in adults and children published before(18). The present study was limited by being a non-randomized controlled one, the placebo effect was not accounted for, and the study of total eosinophil count was not included as it was difficult to have a single laboratory as reference. However, it is a short study report and is being continued for further evaluation later. Acknowledgements The authors thank Dr. Mrs. Soma Roychowdhury and Dr. Debasis Bhattacharya of Indian Institute of Business Management for helping in statistical analysis of the study. Contributors: All authors were involved in the concept and design of the study from the beginning, acquisition of data, its subsequent analysis and interpretation, drafting and critically analyzing and finally approving the article in its present form. Funding: None. Competing interests: None. REFERENCES 1. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma: Expert Panel Report 2. NIH Publication No ; National Heat, Lung and Blood Instititute: Betesda, MD, Li JT, Pearlman DS, Nicklas RA. Algorithm for the diagnosis and management of asthma: A practice parameter update. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 1998; 81: Lipworth BJ. Systemic adverse effects of inhaled corticosteroid therapy: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 1999; 159: Agerloft L. Effect of long term treatment with inhaled budesonide on adult height in children with asthma. N Eng J Med 2000; 343: INDIAN PEDIATRICS 784 VOLUME 43 SEPTEMBER 17, 2006
6 GHOSH, ET AL. 5. Garbe E, LeLorier J, Bovinin JF. Inhaled and nasal glucocorticoids and the risks of ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. JAMA 1997; 277: Kelloway JS, Wyatt RA, Adis SA. Comparison of patients compliance with prescribed oral and inhaled asthma medications. Arch Intern Med 1994; 154: Buse WW. The role of leucotrines in asthma and allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy 1996; 26: Drazen JM, Israel E, O Bryne PM. Treatment of asthma with drugs modifying the leucotriene pathway. N Eng J Med 1999; 340: Dworski R, FitzGerald GA, Oates JA. Effect of oral prednisolone on airway inflammatory mediators in atopic asthma. Am J Respir Crtic Care Med 1994; 149: Reiss TF, Chervinsky P, Dockhorn RJ. Montelukast, a once daily leukotine receptor antagonist, in the treatment of chronic asthma. Arch Intern Med 1998; 158: Knorr B, Matz J, Bernstein JA. Montelukast for chronic asthma: a randomized double blind trial. JAMA 1998; 279; Knorr B, Luis M, Bisgaard H. Montelukast, a leucotriene receptor anatgonist for the treatment of persistent asthma in children aged 2-5 yr. Pediatrics 2001; 108: Bisgaard H, Nielson KG. Bronchoprotection with a leucotriene receptor anatgonist in asthmatic preschool children. Am J Respir Care Med 2000;161: Barnes N, Thomas M, Price D, Tate H. The National Montelukast survey. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005; 115; Edelman JM, Preston SR, Turpin JR. Parent and child preference for montelukast, a leucotriene receptor antagonist compared to inhaled cromolyn in asthmatic children aged 6 to 11 yrs. Eur Respir J 1998;12(suppl 29):18S. 17. Wowciechowska I, Duenas-Meza E, Kosa L. Compliance and preference of montelukast vs. cromolyn in children with asthma. Allergy 1999; 54(suppl): Knorr B, Nooan G, McBurney J. Evaluation of long term effect of montelukast in adult (>15yrs) and pediatric (6-14 yrs) patients. Eur Respir J 1999; 14(suppl): 290S. 19. Garcia MLG, Wahn U, Gilles L, Swern A, Tozzi CA, Polos P. Montelukast compared with fluticasone for control of asthma among 6-14 yr old patients with mild asthma: The MOSAIC study. Pediatrics 116; 2: 2005: INDIAN PEDIATRICS 785 VOLUME 43 SEPTEMBER 17, 2006
Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial
 Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial by Vikram Kumar, a P. Ramesh, a Rakesh Lodha, a R. M. Pandey,
Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial by Vikram Kumar, a P. Ramesh, a Rakesh Lodha, a R. M. Pandey,
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Viral-Induced Asthma:
 Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
Viral-Induced : Sorting through the Studies Malcolm R. Sears, MB, FRACP, FRCPC Presented at the Respirology Update Continuing Education Program, January 2005 Viral-associated wheezing is common and not
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot Malhi, B.R. Srinivas and Lata Kumar
 Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies
 Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies Timothy Craig, DO Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University Hershey Medical Center Objectives 1. Learn the Asthma
Learning the Asthma Guidelines by Case Studies Timothy Craig, DO Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics Distinguished Educator Penn State University Hershey Medical Center Objectives 1. Learn the Asthma
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL
 DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
DR REBECCA THOMAS CONSULTANT RESPIRATORY PHYSICIAN YORK DISTRICT HOSPITAL Definition Guidelines contact complicated definitions Central to this is Presence of symptoms Variable airflow obstruction Diagnosis
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations. Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa
 Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa Asthma exacerbations Predicting exacerbation recognising
Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa Asthma exacerbations Predicting exacerbation recognising
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium montelukast 10mg tablets (Singulair ) No. (185/05) Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd (MSD) New indication: for asthmatic patients in whom montelukast is indicated in asthma, montelukast
Scottish Medicines Consortium montelukast 10mg tablets (Singulair ) No. (185/05) Merck, Sharp & Dohme Ltd (MSD) New indication: for asthmatic patients in whom montelukast is indicated in asthma, montelukast
Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies
 Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg and Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, Head, Pediatric
Controversial Issues in the Management of Childhood Asthma: Insights from NIH Asthma Network Studies Stanley J. Szefler, MD Helen Wohlberg and Herman Lambert Chair in Pharmacokinetics, Head, Pediatric
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit)
 Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Line of Business: All Lines of Business Effective Date: August 16, 2017 Xolair (Omalizumab) Drug Prior Authorization Protocol (Medical Benefit & Part B Benefit) This policy has been developed through review
Asthma Update A/Prof. John Abisheganaden. Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Asthma Update - 2013 A/Prof. John Abisheganaden Senior Consultant, Dept Of Respiratory & Crit Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital Asthma A complex syndrome Multifaceted disease Heterogeneous Genetic and
Monocast Description Indications
 Monocast Tablet Description The active ingredient of Monocast tablet is Montelukast Sodium INN. Montelukast is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl
Monocast Tablet Description The active ingredient of Monocast tablet is Montelukast Sodium INN. Montelukast is a selective and orally active leukotriene receptor antagonist that inhibits the cysteinyl
TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN. Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department
 TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department Literature review current through: Feb 2013. This topic last updated: Aug 14, 2012 INTRODUCTION Wheezing
TREAMENT OF RECURRENT VIRUS-INDUCED WHEEZING IN YOUNG CHILDREN Dr Lại Lê Hưng Respiratory Department Literature review current through: Feb 2013. This topic last updated: Aug 14, 2012 INTRODUCTION Wheezing
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016
 Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
Diagnosis and Management of Asthma in Children based on the British Thoracic Society and Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network September 2016 Diagnosis: There is no lower limit to the age at which
ALLERGIC RHINITIS AND ASTHMA :
 ALLERGIC RHINITIS AND ASTHMA : from the Link to Emerging Therapies Allergic rhinitis and asthma are both chronic heterogeneous disorders, with an overlapping epidemiology of prevalence, health care costs
ALLERGIC RHINITIS AND ASTHMA : from the Link to Emerging Therapies Allergic rhinitis and asthma are both chronic heterogeneous disorders, with an overlapping epidemiology of prevalence, health care costs
Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis
 Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis Kim Hyun Hee, MD, PhD. Dept. of Pediatrics The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine Achieving
Clinical efficacy of montelukast in anti-inflammatory treatment of asthma and allergic rhinitis Kim Hyun Hee, MD, PhD. Dept. of Pediatrics The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine Achieving
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
In 2002, it was reported that 72 of 1000
 REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
REPORTS Aligning Patient Care and Asthma Treatment Guidelines Eric Cannon, PharmD Abstract This article describes how the National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Guidelines for the Diagnosis and
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma :
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier
 Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Pulmonary Medicine, Washington
Management of asthma in preschool children with inhaled corticosteroids and leukotriene receptor antagonists Leonard B. Bacharier Department of Pediatrics, Division of Allergy and Pulmonary Medicine, Washington
Pathophysiology of the cysteinyl leukotrienes and effects of leukotriene receptor antagonists in asthma
 Allergy 2001: 56: Suppl. 66: 7 11 Printed in UK. All rights reserved Copyright # Munksgaard 2001 ALLERGY ISSN 0108-1675 Pathophysiology of the cysteinyl leukotrienes and effects of leukotriene receptor
Allergy 2001: 56: Suppl. 66: 7 11 Printed in UK. All rights reserved Copyright # Munksgaard 2001 ALLERGY ISSN 0108-1675 Pathophysiology of the cysteinyl leukotrienes and effects of leukotriene receptor
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes
 Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Improving the Management of Asthma to Improve Patient Adherence and Outcomes Robert Sussman, MD Atlantic Health System Overlook Medical Center Asthma Remains a Serious Health Risk in the US Every day in
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
NG80. Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80)
 Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
Asthma: diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management (NG80) NG80 NICE has checked the use of its content in this product and the sponsor has had no influence on the content of this booklet. NICE
Omalizumab (Xolair ) ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September Indication
 ( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
( Genentech, Inc., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.) September 2003 Indication The FDA recently approved Omalizumab on June 20, 2003 for adults and adolescents (12 years of age and above) with moderate to
Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007
 Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Selecting Initial Therapy
Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Selecting Initial Therapy
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse
 Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
Asthma: Chronic Management. Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015
 Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
Asthma: Chronic Management Yung-Yang Liu, MD Attending physician, Chest Department Taipei Veterans General Hospital April 26, 2015 Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Evidence-based Implementation
Drug Use Criteria: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
 Texas Vendor Drug Program Drug Use Criteria: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists Publication History Developed February 2007. Revised March 2016; June 2014; October 2012; November 2010; October 2010; September
Texas Vendor Drug Program Drug Use Criteria: Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists Publication History Developed February 2007. Revised March 2016; June 2014; October 2012; November 2010; October 2010; September
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
Childhood Asthma. The pathophysiology of asthma is an interplay. CME Case Study. Case Study. By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC
 CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
CME Case Study Childhood Asthma By Moyez B. Ladhani, MD, CCFP, FAAP, FRCPC Case Study A two-year-old child presents to your office with a cough, which has been present for three weeks. It is worse at nighttime
Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007
 Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Selecting Initial Therapy
Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Full Report 2007 TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Inclusion Criterion Exclusion Criterion RECOMMENDATIONS Selecting Initial Therapy
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016?
 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016? GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention GINA: A Brief History Established in 1993 Collaboration between NHLBI and WHO Multiple
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2016? GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention GINA: A Brief History Established in 1993 Collaboration between NHLBI and WHO Multiple
Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you?
 Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you? Joseph Spahn, MD Denver, Colo The primary goal of most clinical trials is an evaluation of the efficacy of the drug being evaluated. Therefore, it
Clinical trial efficacy: What does it really tell you? Joseph Spahn, MD Denver, Colo The primary goal of most clinical trials is an evaluation of the efficacy of the drug being evaluated. Therefore, it
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Leukotriene receptor antagonists in the management of childhood asthma
 Information Paper paper for health Health professionals Professionals LTRAs for childhood asthma Leukotriene receptor antagonists in the management of childhood asthma Key points Introduction This information
Information Paper paper for health Health professionals Professionals LTRAs for childhood asthma Leukotriene receptor antagonists in the management of childhood asthma Key points Introduction This information
Alberta Childhood Asthma Pathway for Primary Care
 Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Asthma Diagnosis Box 1 Diagnosis: Based on symptom pattern, careful and thorough history of symptoms (wheeze, cough, night waking and activity limitations), and assessment of family history of asthma and
Adult asthma management: focus on control
 Adult asthma management: focus on control Jennifer W. McCallister, MD Associate Professor Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Objectives Apply
Adult asthma management: focus on control Jennifer W. McCallister, MD Associate Professor Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Objectives Apply
Efficacy and safety of montelukast in adults with asthma and allergic rhinitis
 Respiratory Medicine (26), 1952 1959 Efficacy and safety of montelukast in adults with asthma and allergic rhinitis J.Chr. Virchow a,, C. Bachert b a Universität Rostock, Ernst-Heydemann-Str. 6, 1857 Rostock,
Respiratory Medicine (26), 1952 1959 Efficacy and safety of montelukast in adults with asthma and allergic rhinitis J.Chr. Virchow a,, C. Bachert b a Universität Rostock, Ernst-Heydemann-Str. 6, 1857 Rostock,
James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren, MD
 Therapeutic Effect of Zafirlukast as Monotherapy in Steroid-Naive Patients With Severe Persistent Asthma* James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren,
Therapeutic Effect of Zafirlukast as Monotherapy in Steroid-Naive Patients With Severe Persistent Asthma* James P. Kemp, MD; Margaret C. Minkwitz, PhD; Catherine M. Bonuccelli, MD; and Marshelle S. Warren,
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
COMPARISON OF MONTELUKAST AND KETOTIFEN AS ADD ON THERAPY IN MODERATE AND SEVERE PERSISTENT BRONCHIAL ASTHMA Dr. Gaurav Chhabra 1, Dr. Shubhakaran Sharma 2* Original research article 1,2 Associate professor,
MODERATE PERSISTENT ASTHMA IN CHILDREN; COMPARISON OF INHALED BECLOMETHASONE WITH ORAL MONTELUKAST IN THE MANAGEMENT
 The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-2495 MODERATE PERSISTENT ASTHMA IN CHILDREN; COMPARISON OF INHALED BECLOMETHASONE WITH ORAL MONTELUKAST IN THE MANAGEMENT 1 2 3 Dr.
The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-2495 MODERATE PERSISTENT ASTHMA IN CHILDREN; COMPARISON OF INHALED BECLOMETHASONE WITH ORAL MONTELUKAST IN THE MANAGEMENT 1 2 3 Dr.
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Guideline topic: Pharmacological management of asthma Evidence table 4.4d: Leukotriene receptor antagonists with short-acting betaagonists
 1 of 5 09/05/2018, 11:12 Guideline topic: Pharmacological management of asthma Evidence table 4.4d: Leukotriene receptor antagonists with short-acting betaagonists Author Year Study type Quality rating
1 of 5 09/05/2018, 11:12 Guideline topic: Pharmacological management of asthma Evidence table 4.4d: Leukotriene receptor antagonists with short-acting betaagonists Author Year Study type Quality rating
31 - Respiratory System
 31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
31 - Respiratory System Asthma 1. Asthma has two components. Name the two components. 2. What are the common triggers of asthma? (LP p319) (e.g., pets) Upper respiratory infections ( ) 3. Describe a normal
Dual-controller therapy, or combinations REVIEW DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS I: DATA FROM RANDOMIZED, CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS.
 DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS I: DATA FROM RANDOMIZED, CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS Samy Suissa, PhD ABSTRACT Dual-controller therapy, or combinations of 2 or more pharmacotherapies with complementary mechanisms
DUAL-CONTROLLER REGIMENS I: DATA FROM RANDOMIZED, CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS Samy Suissa, PhD ABSTRACT Dual-controller therapy, or combinations of 2 or more pharmacotherapies with complementary mechanisms
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma
 Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Clinical Practice Guideline: Asthma INTRODUCTION A critical aspect of the diagnosis and management of asthma is the precise and periodic measurement of lung function both before and after bronchodilator
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Xolair (omalizumab) Page 1 of 15 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Xolair (omalizumab) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management?
 Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management? Ting Fan LEUNG, MBChB, MD, FRCPCH, FAAAAI Professor and Chairman Department of Paediatrics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Asthma and Allergy by
Do We Need Biologics in Pediatric Asthma Management? Ting Fan LEUNG, MBChB, MD, FRCPCH, FAAAAI Professor and Chairman Department of Paediatrics The Chinese University of Hong Kong Asthma and Allergy by
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) What s new in GINA 2017?
 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Asthma-COPD overlap The word syndrome has been removed from the previous term asthma-copd overlap syndrome
Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) GINA Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention Asthma-COPD overlap The word syndrome has been removed from the previous term asthma-copd overlap syndrome
Lack of tolerance to the protective effect of montelukast in exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children
 Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 291 295 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00020606 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Lack of tolerance to the protective effect of montelukast in exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children
Eur Respir J 2006; 28: 291 295 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.06.00020606 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2006 Lack of tolerance to the protective effect of montelukast in exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in children
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack. Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus
 Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Asthma in Pediatric Patients. DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP. Disclosures. None
 Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
Asthma in Pediatric Patients DanThuy Dao, D.O., FAAP Disclosures None Objectives 1. Discuss the evaluation and management of asthma in a pediatric patient 2. Accurately assess asthma severity and level
(Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management
 Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Dubai Standards of Care 2018 (Asthma) Diagnosis, monitoring and chronic asthma management Preface Asthma is one of the most common problem dealt with in daily practice. In Dubai, the management of chronic
Role of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction: A Review
 Review Article Role of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction: A Review George S. Philteos, MD, FRCP(C); Beth E. Davis, BSc; Donald W. Cockcroft, MD,
Review Article Role of Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists in the Treatment of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction: A Review George S. Philteos, MD, FRCP(C); Beth E. Davis, BSc; Donald W. Cockcroft, MD,
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention
 Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Current Asthma Management: Opportunities for a Nutrition-Based Intervention Stanley J. Szefler, MD Approximately 22 million Americans, including 6 million children, have asthma. It is one of the most prevalent
Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma. April 21, Spring Managed Care Forum
 Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma April 21, 2016 2016 Spring Managed Care Forum David M. Mannino, M.D. Professor Department of Preventive Medicine and Environmental Health University
Improving Outcomes in the Management & Treatment of Asthma April 21, 2016 2016 Spring Managed Care Forum David M. Mannino, M.D. Professor Department of Preventive Medicine and Environmental Health University
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide.
 Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma
 Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Biologic Agents in the treatment of Severe Asthma Daniel L Maxwell, D.O., FACOI, FAASM Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine College of Human
Abstract Background Theophylline is widely used in the treatment of asthma, and there is evidence that theophylline has antiinflammatory
 Thorax 2000;55:837 841 837 National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College School of Medicine and Royal Brompton Hospital, London SW3 6LY, UK S Lim A Jatakanon K F Chung P J Barnes Napp Laboratories
Thorax 2000;55:837 841 837 National Heart and Lung Institute, Imperial College School of Medicine and Royal Brompton Hospital, London SW3 6LY, UK S Lim A Jatakanon K F Chung P J Barnes Napp Laboratories
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Interventions to improve adherence to inhaled steroids for asthma. Respiratory department
 Interventions to improve adherence to inhaled steroids for asthma Respiratory department Content Overview Research References Overview Asthma is a chronic breathing condition that affects more than 300
Interventions to improve adherence to inhaled steroids for asthma Respiratory department Content Overview Research References Overview Asthma is a chronic breathing condition that affects more than 300
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION
 ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
ASTHMA IN THE PEDIATRIC POPULATION SEARCH Rotation 2 August 23, 2010 Objectives Define asthma as a chronic disease Discuss the morbidity of asthma in pediatrics Discuss a few things that a health center
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ
 Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Amanda Hess, MMS, PA-C President-Elect, AAPA-AAI Arizona Asthma and Allergy Institute Scottsdale, AZ Financial Disclosures Advanced Practiced Advisory Board for Circassia Learning Objectives 1. Briefly
Antileukotrienes and asthma: Alternative or adjunct to inhaled steroids?
 CURRENT DRUG THERAPY MANI S. KAVURU, MD Director, Pulmonary Function Laboratory, Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Cleveland Clinic REVATHI SUBRAMONY, RPH Staff Pharmacist, Metrohealth
CURRENT DRUG THERAPY MANI S. KAVURU, MD Director, Pulmonary Function Laboratory, Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Cleveland Clinic REVATHI SUBRAMONY, RPH Staff Pharmacist, Metrohealth
Bronchial asthma. MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL
 Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Bronchial asthma MUDr. Mojmír Račanský Odd. Alergologie a klinické imunologie FNOL Ústav Imunologie LF UPOL DEFINITION ASTHMA BRONCHIALE = Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways in which
Difficult Asthma Assessment: A systematic approach
 Difficult Asthma Assessment: A systematic approach Dr Naghmeh Radhakrishna Respiratory, Sleep & Allergy Physician Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology Service The Alfred Hospital Melbourne, Australia
Difficult Asthma Assessment: A systematic approach Dr Naghmeh Radhakrishna Respiratory, Sleep & Allergy Physician Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology Service The Alfred Hospital Melbourne, Australia
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Asthma in Pregnancy. Asthma. Chronic Airway Inflammation. Objective Measures of Airflow. Peak exp. flow rate (PEFR)
 Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Chronic Airway Inflammation Asthma in Pregnancy Robin Field, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Kaiser Permanente San Francisco Asthma Chronic airway inflammation increased airway responsiveness to a variety of
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
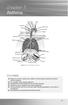 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm. Michael A Lucia, MD, FCCP Asst Clinical Professor, UNR School of Medicine Sierra Pulmonary & Sleep Institute
 Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm Michael A Lucia, MD, FCCP Asst Clinical Professor, UNR School of Medicine Sierra Pulmonary & Sleep Institute EIB Episodic bronchoconstriction with exercise May be an exacerbation
Exercise-Induced Bronchospasm Michael A Lucia, MD, FCCP Asst Clinical Professor, UNR School of Medicine Sierra Pulmonary & Sleep Institute EIB Episodic bronchoconstriction with exercise May be an exacerbation
Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma
 Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma Non-pharmacological options for ALL patients, consider at ALL stages Make sure diagnosis
Greater Manchester Asthma Management Plan 2018 Inhaler therapy options for adult patients (18 and over) with asthma Non-pharmacological options for ALL patients, consider at ALL stages Make sure diagnosis
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications
 The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
Long Term Care Formulary RS -29
 RESTRICTED USE Asthma/COPD Management 1 of 6 PROTOCOL: Asthma Glossary of Medication Acronyms: SABA: short-acting beta agonist (e.g. salbutamol) SABD: short-acting bronchodilator (e.g. ipratropium or SABA)
RESTRICTED USE Asthma/COPD Management 1 of 6 PROTOCOL: Asthma Glossary of Medication Acronyms: SABA: short-acting beta agonist (e.g. salbutamol) SABD: short-acting bronchodilator (e.g. ipratropium or SABA)
Step up if needed (first, check adherence, environmental control and comorbid conditions) Patients ASSESS CONTROL. Step down if possible
 12/9/212 Pharmacogenomics Treating the Individual Asthma Patient Elliot Israel, M.D. Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Brigham & Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Too much of a good thing?
12/9/212 Pharmacogenomics Treating the Individual Asthma Patient Elliot Israel, M.D. Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Brigham & Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Too much of a good thing?
Recurrent Wheezing in Preschool Children. William Sheehan, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Allergy and Immunology
 Recurrent Wheezing in Preschool Children William Sheehan, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Allergy and Immunology Disclosure I have nothing to disclose related to this talk. Background
Recurrent Wheezing in Preschool Children William Sheehan, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Allergy and Immunology Disclosure I have nothing to disclose related to this talk. Background
Management of wheeze in pre-school children. Prof Colin Robertson, Respiratory Medicine, Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne
 Management of wheeze in pre-school children Prof Colin Robertson, Respiratory Medicine, Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne General Practitioner encounters for asthma Asthma in Australia, 2003 Emergency
Management of wheeze in pre-school children Prof Colin Robertson, Respiratory Medicine, Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne General Practitioner encounters for asthma Asthma in Australia, 2003 Emergency
Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy. Joseph Spahn, MD Children s Hospital Colorado & University of Colorado Medical School Aurora, Colorado
 Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy Joseph Spahn, MD Children s Hospital Colorado & University of Colorado Medical School Aurora, Colorado Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy Disclosures/Conflicts of Interest:
Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy Joseph Spahn, MD Children s Hospital Colorado & University of Colorado Medical School Aurora, Colorado Pediatric Asthma: Pharmacotherapy Disclosures/Conflicts of Interest:
SCREENING AND PREVENTION
 These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
These protocols are designed to implement standard guidelines, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical experience for AHC II Integrated Clinical Delivery Network patients and allow
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD
 Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
Pharmacology of drugs used in bronchial asthma & COPD By Prof. Hanan Hagar Pharmacology Unit King Saud University ILOs: The students should be able to 1. Different types of drugs used for treatment of
10/6/2014. Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement. Disclosure. Objectives for this talk.
 Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma?
 Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
Respiratory Medicine (2006) 100, 458 462 Do current treatment protocols adequately prevent airway remodeling in children with mild intermittent asthma? Haim S. Bibi a,, David Feigenbaum a, Mariana Hessen
A review of the current guidelines for allergic rhinitis and asthma
 A review of the current guidelines for allergic rhinitis and asthma Robert F. Lemanske, Jr., MD Madison, Wis. Allergic rhinitis and asthma are common chronic respiratory tract disorders. These disorders
A review of the current guidelines for allergic rhinitis and asthma Robert F. Lemanske, Jr., MD Madison, Wis. Allergic rhinitis and asthma are common chronic respiratory tract disorders. These disorders
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma
 Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Exhaled Nitric Oxide: An Adjunctive Tool in the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma Jason Debley, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatrics Division of Pulmonary Medicine University of Washington School of
Q: Should patients with mild asthma
 1-MINUTE CONSULT CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider prescribing inhaled corticosteroids to their patients who have mild persistent asthma brief answers to specific clinical questions
1-MINUTE CONSULT CME CREDIT EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVE: Readers will consider prescribing inhaled corticosteroids to their patients who have mild persistent asthma brief answers to specific clinical questions
