Toilet Training. A Parent s Guide
|
|
|
- Shon Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Toilet Training A Parent s Guide These materials are the product of on-going activities of the Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network, a funded program of Autism Speaks. It is supported by cooperative agreement UA3 MC through the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration, Maternal and Child Health Research Program to the Massachusetts General Hospital. p. 1
2 Toileting training can be challenging for children with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). There are many reasons why it can take a long time. Many children with ASD learn to use the toilet at a late age. Most children with ASD learn to urinate and have bowel movements in the toilet later than other children (Tsai, Stewart, & August, 1981). Each child with an ASD is different. Children with ASD have some common problems that can make toileting hard. Knowing about these problems can help you come up with different ways to meet your child s needs. Here are some ideas to think about: Physical: There may be a physical or medical reason for toileting difficulties. Discuss these issues with your child s pediatrician. Language: Children with ASD have trouble understanding and using language. Do not expect a child with autism to ask to use the toilet. Dressing: Some children with ASD have difficulty pulling their pants down or pulling them back up. Fears: Some children with ASD are afraid of sitting on toilet seats or hearing toilets flush. Getting used to the toilet by using a visual schedule and making it part of the routine can make it less scary. Body cues: Some children with ASD may not be aware that they need to go or that their clothes are wet or soiled. Need for sameness (aka routine): Many children with ASD already have their own ways of urinating and having bowel movements. Learning new ways to toilet may be hard. It s a marathon, not a sprint. - Gary Heffner A study by Dalrymple and Ruble (1992) found that, on average, children with ASD require 1.6 years of toilet training to stay dry during the day and sometimes more than 2 years to achieve bowel control. It can be a few years journey but to achieve a lifetime of toileting independence is worth the wait! Using different toilets: Some children with ASD learn a toileting routine at home or school, but have a hard time going in other places such as public restrooms. Never Give Up! The ideas included in this handout may help teach toileting skills to young children, teenagers and adults with ASD. While the problems listed above may make you unsure about how to start toilet training, it is a task within your control; there is always something a child with autism can do to become more independent in toileting. Just remember that toilet training tips for typically developing children often need to be changed for children with ASD. p. 2
3 WHERE DO I START? Trip Training or Schedule Training helps children learn toileting skills without placing other demands on them. Adults set the schedule and help train the child s body to follow the schedule. Sit for 6. Set a goal for 6 toilet sits per day. At first, trips will be short (as little as 5 seconds per trip), with one longer trip each day to work on bowel movements. Over time, toilet sits can be long (e.g., up to 10 minutes). Setting a timer can be a helpful way to let your child know when the toilet sit can end. Your child also is allowed to get up from the toilet immediately if s/he urinates or has a bowel movement. Boys are taught to sit on the toilet to urinate until they regularly have bowel movements on the toilet. Don t Ask. Tell. Do not wait for children to tell you they need to use the bathroom or to say yes when asked if they need to go. Tell them it is time for a toilet trip. Schedule. Make toilet trips part of your everyday life. Plan toilet trips around your usual routine. Stick with the same times of the day or the same daily activities. Communicate. Use the same simple words, signs or pictures during each trip. This helps a child learn toileting language. Keep Trying. They say it takes 3 weeks to make a habit. Once you outline the routine and methods, keep working towards the same goal for 3 weeks. Make a Visual Schedule. Pictures may help your child know what to expect during toilet trips (see Appendix 2: Example Visual Schedule on page 9). Take pictures of items in your bathroom (e.g., toilet, toilet paper). Place the pictures in order on a piece of paper to show your child each step of the toilet trip. There also are websites with toileting pictures that you can print out. Please see page 7 for the website information. If your child does not yet understand pictures, you may show your child actual objects (e.g., a roll of toilet paper) for each step. Quick Points to Practice Be Supportive. Use encouraging language whenever you are talking with children about toileting. Use positive words if they are nearby. Praise your child s effort and cooperation-no matter how large or small. Be calm and matter of fact when you approach toilet training. Stick to a schedule. Establish a time when toileting is practiced both in and outside of the home. Use the same words about toileting. Make sure everyone is using the same plan. Talk with other people who work with your child. Share the toileting plan with them and request they stick to the same routine and language. Identify Rewards. Make a list of your child s favorite things, like foods, toys, and videos. Think of which ones will be easiest to give your child as soon as he/she urinates or has a bowel movement in the toilet. A small food item (e.g., fruit snack, cracker, chocolate chip) often works well. In addition to giving a reward for going in the toilet, you also can give your child time to do a favorite activity (e.g., watch a video, play with a toy) after the toilet trip is over. The Key to Success: Keep language simple and keep toileting routines the same. p. 3
4 TIPS TO INCREASE TOILETING SUCCESS! For 3- typical days, document your child s routine. To help you write your child s toileting program, track how long it takes between when your child drinks and when he or she is wet. Checking your child s diaper frequently for wetness (e.g., every 15 minutes) will help you decide when to schedule toilet trips. Consider your child s diet. Dietary changes, such as increasing the fluids and fiber your child eats and drinks, may help your child feel the urge to use the toilet. Make small changes in daily habits. Dress your child in easy-to-remove clothing. Change your child as soon as he or she becomes wet or soiled. Change diapers in or near the bathroom. Involve your child in the cleanup process. Have your child put waste from the diaper in the toilet when possible. This will also help your child understand that waste goes in the toilet. Have your child flush the toilet and wash hands after each diaper change. Make sure toilet trips are comfortable. Your child should be comfortable while sitting on the toilet. Use a smaller potty seat and/or provide a footstool. If your child will not sit on the toilet, work on sitting before beginning a toilet training program. Think about your child s sensory needs. If your child does not like certain sounds, smells, or things he or she touches in the bathroom, change these as much as you can. Have many pairs of underwear ready. During toilet training it is important for children to wear underwear during the day. They need to feel when they are wet. Your child may wear rubber pants or a pull-up over underwear if necessary. Diapers or pull-ups may be used when your child is sleeping or is away from the home. Use a visual schedule. Pictures showing each step of the potty routine may help your child learn the routine and know what will happen. During toilet trips, show your child the visual schedule you have created. Label each step as you go along (see Appendix 2: Example Visual Schedule on page 9). Use rewards. Give your child a reward immediately after he or she urinates or has a bowel movement in the toilet. The more quickly you reward a behavior, the more likely that behavior will increase. Toileting rewards are special. Rewards used for toileting should only be used for toileting. Practice in different bathrooms. Using different bathrooms helps your child know he or she can use different toilets in different places. p. 4
5 CREATING YOUR CHILD S TOILETING PLAN Many different people may help your child with toileting. Different family members, teachers, aids, and day program staff may help. Everyone working with your child should use the same language and the same routine. This will help make toilet training a success. A written toileting plan may help your child with ASD make progress. If it is in writing, everyone will be able to use the same language and the same routine. Toileting plans may include these details: Goals: Let your child s helper know your goals. Outline for the helper, what it is you are trying to achieve for the given period of time. For example, The goal is to have Tommy visit the restroom 15 minutes after the meal and sit on the toilet for 5 seconds. Routine: How often? Include how often or what time the child should visit the rest room. Some examples include, every hour on the hour or 15 minutes after drinking / meals. For how long? Be sure to include how long your child is able to tolerate the bathroom trips-it may start with only 5 seconds. Language: Words: Use words that work for your child. For example, are there any code words that you use for urination? What words do you use to tell your child to go to the bathroom? Places: Where? Where does your child go to the bathroom? What? Think about the lights, are they bright or dim? How does light affect your child? What about noises in the bathroom (e.g., a fan)? What about the type of toilet paper? Should the door be open or closed? Who? Who goes with your child to the bathroom? Is someone with your child or just nearby? Tools: What tools are you using? Do you use a visual schedule? Does your child like to listen to music or read a book? Rewards: What activities earn a reward? What activities do not? How do you reward your child for a job well done? What happens if your child does not earn a reward? p. 5
6 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS FROM PARENTS Q Our child will use the potty at school, but he refuses to use it at home. What should we do? A Something your son with a diagnosis of ASD learns to do at school may be hard for him to do at home. It might help to have your son learn to use different bathrooms at school. Use the words and ideas that his teachers use at school. You may need to start with simple steps at home. Start by walking into the bathroom. Add steps one at a time until he is using the toilet at home. Practice potty trips in different bathrooms. Use the bathroom in stores and other people s houses. Q We thought we had a good toileting program for our daughter, but it isn t working. What are our next steps? A There are a number of steps you may want to take. (1) Be sure there is not a medical reason. Talk with your daughter s doctor to see if she is constipated or to get ideas about changes in diet. (2) Look at your daughter s toileting schedule and make sure you are taking her when she is likely to urinate or have a bowel movement. (3) Think about changing rewards. Make sure your daughter likes the reward. It is often helpful to think about what type of reward you are using at least every 3 months, but you may have to do so more often. Q I worked on toileting all weekend with my son, but we didn t make any progress. How long should the process take? A Toileting takes a long time for many people. It helps to be relaxed and have patience. There isn t a deadline for toileting. Toilet training should be a small part of your life. You can take a break and try again when you have more energy or when your son seems ready. Remember that it can be hard to learn to go to the toilet. Practice toileting when it is a good time for you and your family. That way you will have the energy to work on this important skill over the long haul. Q Our family has tried to help our son become toilet trained, but he is still wearing diapers. What should we do? A It may be time to seek help from someone who has special training. There are physicians, psychologists, special educators, speech/language pathologists, behavioral analysts / specialists, and occupational therapists that can help children with ASD become toilet trained. These professionals may be able to help your family in intensive toilet training. This is a method that may work well for children diagnosed with ASD, but needs to be monitored by a professional. Remember that it can take a long time to learn this complicated and important skill. Please see Appendix 2 on page 8 for an Example Toileting Plan that you can print and complete. p. 6
7 RESOURCES The Autism Speaks Family Services Department offers resources, tool kits, and support to help manage the day-to-day challenges of living with autism If you are interested in speaking with a member of the Autism Speaks Family Services Team contact the Autism Response Team (ART) at 888-AUTISM2 ( ), or by at familyservices@autismspeaks.org. ART En Español al References 1. Dalrymple, N.J. & Ruble, L.A. (1992). Toilet training and behaviors of people with autism: Parent views. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 22 (2), Tsai, L., Stewart, M.A., & August, G. (1981). Implication of sex differences in the familial transmission of infantile autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 11(2), Websites The National Autistic Society: Toilet Training: lfhelp_toileting.htm is a great resource for picture schedules Tips for Daily Life Toilet Training: Bright Tots: Toilet Training and Autism: m.html DVDs Potty Power Elmo s Potty Time Books Self-help Skills for People with Autism: A Systematic Teaching Approach by Anderson, S.R., Jablonski, A.L., Thomeer, M.S., & Knapp, M. (2007). The Potty Journey: Guide to Toilet Training Children with Special Needs, Including Autism and Related Disorders by Coucouvanis, J. (2008). Toilet Training for Children with Special Needs by Hepburn, S. (2009). Toilet Training for Individuals with Autism or other Developmental Issues: A Comprehensive Guide for Parents and Teachers by Wheeler, M. (2007). Once Upon a Potty by Frankel, A. (2007). Going to the Potty by Rogers, F. (1997). ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This publication was developed by members of the Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network / Autism Intervention Research Network on Physical Health-Behavioral Health Sciences Committee. Special thanks to Nicole Bing, Psy.D. (Cincinnati Children s Hospital), Dylan Carelli, BSW (JFK Partners, University of Colorado Denver), Susan Hepburn, Ph.D. (JFK Partners, University of Colorado Denver), Terry Katz, Ph.D. (JFK Partners, University of Colorado Denver), Patti LaVesser, Ph.D., OT ( JFK Partners, University of Colorado Denver), Laura Srivorakiat, M.A. (Cincinnati Children s Hospital), and Amanda Santanello, Psy.D. (Kennedy Krieger Institute) for their work on the publication. It was edited, designed, and produced by Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network / Autism Intervention Research Network on Physical Health communications department. We are grateful for review and suggestions by many, including by families associated with the Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network.This publication may be distributed as is or, at no cost, may be individualized as an electronic file for your production and dissemination, so that it includes your organization and its most frequent referrals. For revision information, please contact atn@autismspeaks.org. These materials are the product of on-going activities of the Autism Speaks Autism Treatment Network, a funded program of Autism Speaks. It is supported by cooperative agreement UA3 MC through the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Health Resources and Services Administration, Maternal and Child Health Research Program to the Massachusetts General Hospital. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the MCHB, HRSA, HHS. Images for this tool kit were purchased from istockphoto. Written May p. 7
8 APPENDIX 1: EXAMPLE TOILETING PLAN Goal: The goal is to have Tommy visit the restroom 15 minutes after the meal and sit on the toilet for 5 seconds. Routine: How often? Tommy goes to the restroom 15 minutes after every meal and drink. How long doing what behavior? Tommy visits the restroom for 5 seconds. He sits on the toilet. Language: Now we go to the bathroom ; Pee-Pee = urinate. Place: Helper stands outside the door. Door is open. Lights and fan on. Tools: Tommy reads Where the Wild Things Are in the bathroom. Rewards: Tommy receives 5 minutes of ipad time for every visit to the bathroom p. 8
9 APPENDIX 2: EXAMPLE VISUAL SCHEDULE Visual Schedule A visual schedule is a display of what is going to happen throughout the day or during an activity. A visual schedule is helpful during toilet trips to decrease anxiety and difficulty with transitions by clearly letting your child know when certain activities will occur. 1) Decide the activities that you will put on the schedule. Try to mix in preferred activities with nonpreferred ones. 2) Put the visuals that stand for the activities that you have identified on a portable schedule (on a binder or clipboard). The schedule should be available to your child from the beginning of the first activity. It should continue to be visible through all of the activities. 3) When it is time for an activity on the schedule to occur, let your child know with a brief verbal instruction before the next activity begins. When that task is completed, give your child praise. Then refer to the schedule and label the next activity. 4) Provide praise and/or other rewards for following the schedule and completing the activities. Put a preferred activity at the end of the schedule to give your child something positive to look forward to after completing all the items on the schedule. VISUAL SCHEDULE p. 9
Strategies to Improve Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders
 Strategies to Improve Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders A Parent s Guide Z AUTISM SPEAKS A~N :::: Autism Treatment Network Autism Intervention Research Network on Physical Health These materials
Strategies to Improve Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders A Parent s Guide Z AUTISM SPEAKS A~N :::: Autism Treatment Network Autism Intervention Research Network on Physical Health These materials
Walk In My Autism. Video. Cynthia Brouillard, Psy.D. Evaluation Clinic Director, LFCA Patti Boheme, M.S., LCPC Executive Vice President, LFCA
 Little Friends Center for Autism is an affiliate of Little Friends, Inc. Little Friends, Inc. is a non-profit, social service agency that services over 800 children and adults with developmental disabilities.
Little Friends Center for Autism is an affiliate of Little Friends, Inc. Little Friends, Inc. is a non-profit, social service agency that services over 800 children and adults with developmental disabilities.
Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling
 Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Patient and Family Education Constipation: Treatment of Chronic Constipation and Soiling While it is normal for a child to be constipated now and then, ongoing problems are not. This handout gives a treatment
Lesson 9 Anxiety and Relaxation Techniques
 The following presentation was originally developed for individuals and families by Achieva (a Western PA service provider). Now offered as a webcast production, ODP is providing this valuable resource
The following presentation was originally developed for individuals and families by Achieva (a Western PA service provider). Now offered as a webcast production, ODP is providing this valuable resource
Meeting a Kid with Autism
 What s up with Nick? When school started, we had a new kid named Nick. He seemed a little different. My friends and I wondered, What's up with Nick? Turns out, Nick has autism. What is Autism This year,
What s up with Nick? When school started, we had a new kid named Nick. He seemed a little different. My friends and I wondered, What's up with Nick? Turns out, Nick has autism. What is Autism This year,
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE, DEMENTIA & DEPRESSION
 ALZHEIMER S DISEASE, DEMENTIA & DEPRESSION Daily Activities/Tasks As Alzheimer's disease and dementia progresses, activities like dressing, bathing, eating, and toileting may become harder to manage. Each
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE, DEMENTIA & DEPRESSION Daily Activities/Tasks As Alzheimer's disease and dementia progresses, activities like dressing, bathing, eating, and toileting may become harder to manage. Each
CARING FOR PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA:
 CARING FOR PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA: LESSON PLAN Lesson overview Time: One hour This lesson teaches useful ways to work with patients who suffer from dementia. Learning goals At the end of this session,
CARING FOR PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA: LESSON PLAN Lesson overview Time: One hour This lesson teaches useful ways to work with patients who suffer from dementia. Learning goals At the end of this session,
Keeping Home Safe WHAT CAN YOU DO?
 Keeping Home Safe or dementia may have trouble knowing what is dangerous or making safe decisions. By helping him or her feel more relaxed and less confused at home, you can help stop accidents. trip because
Keeping Home Safe or dementia may have trouble knowing what is dangerous or making safe decisions. By helping him or her feel more relaxed and less confused at home, you can help stop accidents. trip because
My Family-Hygiene Tips
 My Family-Hygiene Tips 1 Table of Contents Page 3 Hand washing Page 4 Showering, Bathing Hair washing Page 5 Oral Hygiene \fingernails Page 6 Haircuts 2 Hygiene How can I get my child to take a bath or
My Family-Hygiene Tips 1 Table of Contents Page 3 Hand washing Page 4 Showering, Bathing Hair washing Page 5 Oral Hygiene \fingernails Page 6 Haircuts 2 Hygiene How can I get my child to take a bath or
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
SERVING STUDENTS WITH AUTISM IN SCHOOLS 1
 SERVING STUDENTS WITH AUTISM IN SCHOOLS 1 Serving Students with Autism in Schools Beth Kost Abnormal Psychology (PSY 406) SERVING STUDENTS WITH AUTISM IN SCHOOLS 2 Serving Students with Autism in Schools
SERVING STUDENTS WITH AUTISM IN SCHOOLS 1 Serving Students with Autism in Schools Beth Kost Abnormal Psychology (PSY 406) SERVING STUDENTS WITH AUTISM IN SCHOOLS 2 Serving Students with Autism in Schools
Living Well with Diabetes. Meeting 12. Welcome!
 12-1 Welcome! Welcome back and congratulations! Today is a time to celebrate all of your accomplishments. For the past few months we have learned a great deal about managing diabetes. Today, we will talk
12-1 Welcome! Welcome back and congratulations! Today is a time to celebrate all of your accomplishments. For the past few months we have learned a great deal about managing diabetes. Today, we will talk
Autism 101: An Introduction to Understanding Autism
 Autism 101: An Introduction to Understanding Autism What is Autism? Autism is a disorder that affects the brain s normal development of social and communication skills. ~ Autism Society of Colorado The
Autism 101: An Introduction to Understanding Autism What is Autism? Autism is a disorder that affects the brain s normal development of social and communication skills. ~ Autism Society of Colorado The
Smoking and Quitting Assessment
 Smoking and Quitting Assessment A. Which of the following describes you? q I m not interested in trying to quit smoking. q I know I need to quit smoking, but I m not quite ready yet. q I m ready to quit
Smoking and Quitting Assessment A. Which of the following describes you? q I m not interested in trying to quit smoking. q I know I need to quit smoking, but I m not quite ready yet. q I m ready to quit
Inclusive Education. De-mystifying Intellectual Disabilities and investigating best practice.
 Inclusive Education De-mystifying Intellectual Disabilities and investigating best practice. Aims for this session: To understand what the term Intellectual Defiency means To understand the broad spectrum
Inclusive Education De-mystifying Intellectual Disabilities and investigating best practice. Aims for this session: To understand what the term Intellectual Defiency means To understand the broad spectrum
Quick guide to autism
 Quick guide to autism What it looks like and how you can help What is autism? Autism is a lifelong neurodevelopmental disorder We don t know what causes autism but we do know genetics plays a role 1 in
Quick guide to autism What it looks like and how you can help What is autism? Autism is a lifelong neurodevelopmental disorder We don t know what causes autism but we do know genetics plays a role 1 in
A Guide to Help New Mothers Stay Smoke-Free
 A Guide to Help New Mothers Stay Smoke-Free 1 Welcome to motherhood! You have just been through a life-changing experience pregnancy and child birth. Having a plan to stay smoke-free is an important step.
A Guide to Help New Mothers Stay Smoke-Free 1 Welcome to motherhood! You have just been through a life-changing experience pregnancy and child birth. Having a plan to stay smoke-free is an important step.
A guide to creating. Relaxed Performances. for people with Autism. Page 1 of 12
 A guide to creating Relaxed Performances for people with Autism Page 1 of 12 What is Autism? Research suggests that currently 1.1% of the population have a diagnosis of autism. This statistic does not
A guide to creating Relaxed Performances for people with Autism Page 1 of 12 What is Autism? Research suggests that currently 1.1% of the population have a diagnosis of autism. This statistic does not
Cancer and Relationships
 Cancer and Relationships Being given a diagnosis of cancer can be very emotionally difficult. It is very common for both you and the people around you to find this upsetting or hard to cope with. This
Cancer and Relationships Being given a diagnosis of cancer can be very emotionally difficult. It is very common for both you and the people around you to find this upsetting or hard to cope with. This
Does anxiety cause some difficulty for a young person you know well? What challenges does this cause for the young person in the family or school?
 John Walker, Ph.D. Department of Clinical Health Psychology University of Manitoba Everyone has the emotions at times. Signal us to be careful. Help us to stay safe. Most children and adults have mild
John Walker, Ph.D. Department of Clinical Health Psychology University of Manitoba Everyone has the emotions at times. Signal us to be careful. Help us to stay safe. Most children and adults have mild
Helping your Child with ASD Adjust to New Siblings. Af ter the baby s birth
 Helping your Child with ASD Adjust to New Siblings Af ter the baby s birth 2 Table of Contents Af ter the baby s birth 5 Why might it be dif ficult for my child with ASD? 6 Communication: 8 Managing Change:
Helping your Child with ASD Adjust to New Siblings Af ter the baby s birth 2 Table of Contents Af ter the baby s birth 5 Why might it be dif ficult for my child with ASD? 6 Communication: 8 Managing Change:
Controlling Worries and Habits
 THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
Breakspeare School Provision for Pupils with Autism
 Breakspeare School Provision for Pupils with Autism Provision for pupils with Autistic Spectrum Disorders at Breakspeare School Breakspeare School is a special school for children with severe learning
Breakspeare School Provision for Pupils with Autism Provision for pupils with Autistic Spectrum Disorders at Breakspeare School Breakspeare School is a special school for children with severe learning
Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community
 2 CHAPTER Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community 9 Old people can remember when there were fewer problems with teeth and gums. Children s teeth were stronger and adults kept their teeth longer.
2 CHAPTER Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community 9 Old people can remember when there were fewer problems with teeth and gums. Children s teeth were stronger and adults kept their teeth longer.
Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version
 Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? People with ADHD have brains that may function a little differently in some
Information on ADHD for Children, Question and Answer - long version What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder or ADHD? People with ADHD have brains that may function a little differently in some
Posted July 31, 2015 uwreadilab.com
 VISUAL SUPPORTS For Home and School This booklet was created in 2003 by Wendy Stone, PhD and colleagues at Vanderbilt University Treatment and Research Institute for Autism Spectrum Disorders (TRIAD).
VISUAL SUPPORTS For Home and School This booklet was created in 2003 by Wendy Stone, PhD and colleagues at Vanderbilt University Treatment and Research Institute for Autism Spectrum Disorders (TRIAD).
Autism Spectrum Disorder. A Basic Introduction for Families
 Autism Spectrum Disorder A Basic Introduction for Families 2 INTRODUCTION Your child has been diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD). You may have mixed feelings relieved to know that the concerns
Autism Spectrum Disorder A Basic Introduction for Families 2 INTRODUCTION Your child has been diagnosed with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD). You may have mixed feelings relieved to know that the concerns
A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco
 Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
Pain Notebook NAME PHONE. Three Hole Punch Here Three Hole Punch Here. Global Pain Initiative 2018 Ver 1.0
 Pain Notebook Three Hole Punch Here Three Hole Punch Here NAME EMAIL PHONE Global Pain Initiative 2018 Ver 1.0 What is pain? Pain is a bad sensation that tells you something is wrong. Pain falls into two
Pain Notebook Three Hole Punch Here Three Hole Punch Here NAME EMAIL PHONE Global Pain Initiative 2018 Ver 1.0 What is pain? Pain is a bad sensation that tells you something is wrong. Pain falls into two
Good Communication Starts at Home
 Good Communication Starts at Home It is important to remember the primary and most valuable thing you can do for your deaf or hard of hearing baby at home is to communicate at every available opportunity,
Good Communication Starts at Home It is important to remember the primary and most valuable thing you can do for your deaf or hard of hearing baby at home is to communicate at every available opportunity,
The 3 P s (Pain, Poop, Physical Therapy) for Post-Op Spinal Fusions
 The 3 P s (Pain, Poop, Physical Therapy) for Post-Op Spinal Fusions Pain control is a key part of your care after surgery. It can help speed recovery and improve the results of your surgery. This handout
The 3 P s (Pain, Poop, Physical Therapy) for Post-Op Spinal Fusions Pain control is a key part of your care after surgery. It can help speed recovery and improve the results of your surgery. This handout
Introduction. Today we hope to provide tips and resources to help balance the challenges of caregiving and ensure that everyone is being cared for.
 Caregiver Wellness Introduction Being a caregiver can be both rewarding and challenging. It s easy to forget to tend to your own needs while caring for your loved one, but it is incredibly important. Today
Caregiver Wellness Introduction Being a caregiver can be both rewarding and challenging. It s easy to forget to tend to your own needs while caring for your loved one, but it is incredibly important. Today
I give special thanks to Ed Sbardellati, who has been a pivotal support, during this study, and throughout my career as a behavior analyst.
 Toileting Program for a Child with an Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Sequential Withdrawal Comparison of Cueing and Reinforcement Dana Seidler, Cliff Hickman, Erin Russell The purpose of this study was to
Toileting Program for a Child with an Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Sequential Withdrawal Comparison of Cueing and Reinforcement Dana Seidler, Cliff Hickman, Erin Russell The purpose of this study was to
Delirium: Information for Patients and Families
 health information Delirium: Information for Patients and Families 605837 Alberta Health Services, (2016/11) Resources Delirium in the Older Person Family Guide: search delirium at viha.ca Go to myhealth.alberta.ca
health information Delirium: Information for Patients and Families 605837 Alberta Health Services, (2016/11) Resources Delirium in the Older Person Family Guide: search delirium at viha.ca Go to myhealth.alberta.ca
Pharmacy Advisor Program. Specialized Health Support
 Pharmacy Advisor Program Specialized Health Support Contents Your Health and Your CVS Caremark Pharmacy Advisor Pharmacist...3 Keys to Your Health....4 Getting the Most from Your Medication...6 Feeling
Pharmacy Advisor Program Specialized Health Support Contents Your Health and Your CVS Caremark Pharmacy Advisor Pharmacist...3 Keys to Your Health....4 Getting the Most from Your Medication...6 Feeling
Students with social communication difficulties may/or may not have a formal diagnosis of ASD (autistic spectrum disorder).
 ASD/ social communication difficulties Introduction Students with social communication difficulties may/or may not have a formal diagnosis of ASD (autistic spectrum disorder). Students with ASD are individuals
ASD/ social communication difficulties Introduction Students with social communication difficulties may/or may not have a formal diagnosis of ASD (autistic spectrum disorder). Students with ASD are individuals
Copyright 2016, University of Rochester 1. Anxiety in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Rochester Regional Center for Autism Spectrum Disorder (RRCASD)
 Anxiety in Autism Spectrum Disorder Suzannah Iadarola, Ph.D., BCBA-D Rochester Regional Center for Autism Spectrum Disorder Strong Center for Developmental Disabilities Rochester Regional Center for Autism
Anxiety in Autism Spectrum Disorder Suzannah Iadarola, Ph.D., BCBA-D Rochester Regional Center for Autism Spectrum Disorder Strong Center for Developmental Disabilities Rochester Regional Center for Autism
EP04: The Friendship Game
 EP04: The Friendship Game Here s what you ll find in this guide: The Friendship Game Episode Notes Great Resources! Deeper Thinking Activity As discussed in some of the previous episodes, children with
EP04: The Friendship Game Here s what you ll find in this guide: The Friendship Game Episode Notes Great Resources! Deeper Thinking Activity As discussed in some of the previous episodes, children with
Active Living with Arthritis Podcast #9 Being a Caregiver: Caring for Someone and Managing Your Arthritis
 Active Living with Arthritis Podcast #9 Being a Caregiver: Caring for Someone and Managing Your Arthritis Karen: Welcome to another Active Living with Arthritis podcast, presented by ENACT center at Boston
Active Living with Arthritis Podcast #9 Being a Caregiver: Caring for Someone and Managing Your Arthritis Karen: Welcome to another Active Living with Arthritis podcast, presented by ENACT center at Boston
Coach on Call. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics.
 Coach on Call It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your
Coach on Call It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your
Bowel health and screening: carers guide. A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials
 Bowel health and screening: carers guide A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials Contents Page 3: About this booklet Page 4: What is the bowel? Page 5: Helping someone to have good bowel
Bowel health and screening: carers guide A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials Contents Page 3: About this booklet Page 4: What is the bowel? Page 5: Helping someone to have good bowel
Wellness along the Cancer Journey: Palliative Care Revised October 2015
 Wellness along the Cancer Journey: Palliative Care Revised October 2015 Chapter 3: Addressing Cancer Pain as a part of Palliative Care Palliative Care Rev. 10.8.15 Page 360 Addressing Cancer Pain as Part
Wellness along the Cancer Journey: Palliative Care Revised October 2015 Chapter 3: Addressing Cancer Pain as a part of Palliative Care Palliative Care Rev. 10.8.15 Page 360 Addressing Cancer Pain as Part
Agenda and Objectives
 Agenda and Objectives Session 2 Handout: Activity Session One 1. Welcome & outline review today s agenda 2. Benefits of and barriers to regular exercise 3. Review of exercise homework and planning ahead
Agenda and Objectives Session 2 Handout: Activity Session One 1. Welcome & outline review today s agenda 2. Benefits of and barriers to regular exercise 3. Review of exercise homework and planning ahead
The road to recovery. The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke
 The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline on 0303 3033
The road to recovery The road to recovery The support available to help you with your recovery after stroke We re for life after stroke Need to talk? Call our confidential Stroke Helpline on 0303 3033
To learn more, visit the website and see the Find Out More section at the end of this booklet.
 Loving Your Child, Learning How to Help Congratulations! As a parent of a precious baby or young child, you have a wonderful journey ahead. The fact that your child has a hearing loss is only one part
Loving Your Child, Learning How to Help Congratulations! As a parent of a precious baby or young child, you have a wonderful journey ahead. The fact that your child has a hearing loss is only one part
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
Session 15 Leader Guide: Mindful Eating, Mindful Movement
 Session 15 Leader Guide: Mindful Eating, Mindful Movement Objectives In this session, the participants will: Analyze and describe current eating and activity behaviors. Define mindful eating and mindful
Session 15 Leader Guide: Mindful Eating, Mindful Movement Objectives In this session, the participants will: Analyze and describe current eating and activity behaviors. Define mindful eating and mindful
Session 14: Overview. Quick Fact. Session 14: Make Social Cues Work for You. The Power of Social Cues. Dealing with Social Cues
 Session 14: Overview The Power of Social Cues Social cues are occasions that trigger us to behave in a certain way when we re around other people. For example, watching a football game with friends is
Session 14: Overview The Power of Social Cues Social cues are occasions that trigger us to behave in a certain way when we re around other people. For example, watching a football game with friends is
Making Life Easier. Tip:
 Making Life Easier By Pamelazita Buschbacher, Ed.D. Illustrated by Sarah I. Perez Bedtime and Naptime M any families find bedtime and naptime to be a challenge for them and their children. It is estimated
Making Life Easier By Pamelazita Buschbacher, Ed.D. Illustrated by Sarah I. Perez Bedtime and Naptime M any families find bedtime and naptime to be a challenge for them and their children. It is estimated
Moving from primary to secondary school
 Moving from primary to secondary school Supporting pupils on the autism spectrum The transition from primary to secondary school is a major change in any child s life, and pupils on the autism spectrum
Moving from primary to secondary school Supporting pupils on the autism spectrum The transition from primary to secondary school is a major change in any child s life, and pupils on the autism spectrum
Practical Strategies to Address Challenging Behavior. Bridget A. Taylor, Psy.D., BCBA-D, Alpine Learning Group
 Practical Strategies to Address Challenging Behavior Bridget A. Taylor, Psy.D., BCBA-D, Alpine Learning Group Today * Common behavior problems * Conditions that may occasion behavior problems * Assessment
Practical Strategies to Address Challenging Behavior Bridget A. Taylor, Psy.D., BCBA-D, Alpine Learning Group Today * Common behavior problems * Conditions that may occasion behavior problems * Assessment
Learning to use a sign language
 85 Chapter 8 Learning to use a sign language It is easy for a young child to learn a complete sign language. A child will first begin to understand the signs that others use, especially for people and
85 Chapter 8 Learning to use a sign language It is easy for a young child to learn a complete sign language. A child will first begin to understand the signs that others use, especially for people and
Meeting someone with disabilities etiquette
 Meeting someone with disabilities etiquette Many people unsure how to go about meeting someone with a disability because they don t want to say or do the wrong thing. Here are a few tips to keep in mind
Meeting someone with disabilities etiquette Many people unsure how to go about meeting someone with a disability because they don t want to say or do the wrong thing. Here are a few tips to keep in mind
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS
 SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
Autism 101. Training Packet 2016
 Autism 101 Training Packet 2016 Thank you for participating in the Autism Society of Colorado s Autism 101 Training! Autism 101 is a training offered by the Autism Society of Colorado (ASC) to organizations
Autism 101 Training Packet 2016 Thank you for participating in the Autism Society of Colorado s Autism 101 Training! Autism 101 is a training offered by the Autism Society of Colorado (ASC) to organizations
When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip
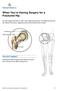 When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip The hip includes the head or ball of the thigh bone (femur). The thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Ligaments and muscles hold the joint in place.
When You re Having Surgery for a Fractured Hip The hip includes the head or ball of the thigh bone (femur). The thigh bone fits into the socket of the pelvis. Ligaments and muscles hold the joint in place.
Relaxation Techniques
 Relaxation is needed for good health. It gives your body and mind a chance to rest and recover from high-stress situations. Your heart rate slows down, blood pressure decreases and muscles relax. Relaxation
Relaxation is needed for good health. It gives your body and mind a chance to rest and recover from high-stress situations. Your heart rate slows down, blood pressure decreases and muscles relax. Relaxation
Queensmill School Policy guidance on strategies to reduce pupils stress
 Queensmill School Policy guidance on strategies to reduce pupils stress A caring environment where we respect and value children for what they are, help them to understand the world around them and teach
Queensmill School Policy guidance on strategies to reduce pupils stress A caring environment where we respect and value children for what they are, help them to understand the world around them and teach
ECTA Handouts Keynote Address. Affective Education. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy. Affective Education. Affective Education 19/06/2010
 ECTA Handouts Keynote Address ECTA: International Trends in Behavioural Guidance Approaches 26 th June 2010 Cognitive Behaviour Therapy Affective Development (maturity, vocabulary and repair). Cognitive
ECTA Handouts Keynote Address ECTA: International Trends in Behavioural Guidance Approaches 26 th June 2010 Cognitive Behaviour Therapy Affective Development (maturity, vocabulary and repair). Cognitive
Layout book 4.qxp 3/6/ :03 Page 1
 Layout book 4.qxp 3/6/2548 16:03 Page 1 Layout book 4.qxp 3/6/2548 16:03 Page 2 You Are Special For children living in families affected by HIV/AIDS Funded by The United States Agency for International
Layout book 4.qxp 3/6/2548 16:03 Page 1 Layout book 4.qxp 3/6/2548 16:03 Page 2 You Are Special For children living in families affected by HIV/AIDS Funded by The United States Agency for International
Tips for Youth Group Leaders
 OVERWHELMED Sometimes youth on the Autism Spectrum become so over-whelmed they are unable to function Most situations can be avoided by asking the youth to gauge their own comfort level Because the body
OVERWHELMED Sometimes youth on the Autism Spectrum become so over-whelmed they are unable to function Most situations can be avoided by asking the youth to gauge their own comfort level Because the body
WHAT IS STRESS? increased muscle tension increased heart rate increased breathing rate increase in alertness to the slightest touch or sound
 EXAM STRESS WHAT IS STRESS? Stress is part of the body s natural response to a perceived threat. We all experience it from time to time. When we feel under threat, our bodies go into fight or flight response,
EXAM STRESS WHAT IS STRESS? Stress is part of the body s natural response to a perceived threat. We all experience it from time to time. When we feel under threat, our bodies go into fight or flight response,
David Trickey Consultant Clinical Psychologist & Trauma Specialist, Anna Freud National Centre for Children and Families
 David Trickey Consultant Clinical Psychologist & Trauma Specialist, Anna Freud National Centre for Children and Families Explaining the rationale for trauma-focused work: Why it s good to talk. If a traumatic
David Trickey Consultant Clinical Psychologist & Trauma Specialist, Anna Freud National Centre for Children and Families Explaining the rationale for trauma-focused work: Why it s good to talk. If a traumatic
Here are a few ideas to help you cope and get through this learning period:
 Coping with Diabetes When you have diabetes you may feel unwell and have to deal with the fact that you have a life long disease. You also have to learn about taking care of yourself. You play an active
Coping with Diabetes When you have diabetes you may feel unwell and have to deal with the fact that you have a life long disease. You also have to learn about taking care of yourself. You play an active
Autism, my sibling, and me
 ORGANIZATION FOR AUTISM RESEARCH Autism, my sibling, and me Brothers and sisters come in all shapes and sizes. They have a lot in common, and they can be really different from each other. Some kids even
ORGANIZATION FOR AUTISM RESEARCH Autism, my sibling, and me Brothers and sisters come in all shapes and sizes. They have a lot in common, and they can be really different from each other. Some kids even
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
(p) (f) Echolalia. What is it, and how to help your child with Echolalia?
 (p) 406-690-6996 (f) 406-206-5262 info@advancedtherapyclinic.com Echolalia What is it, and how to help your child with Echolalia? Echolalia is repeating or echoing what another person has said. Children
(p) 406-690-6996 (f) 406-206-5262 info@advancedtherapyclinic.com Echolalia What is it, and how to help your child with Echolalia? Echolalia is repeating or echoing what another person has said. Children
Ask the Expert Educator Edition Developing Partnerships with Parents and Caregivers
 www.help4adhd.org (800) 233-4050 Help4ADHD@CHADD.org Ask the Expert Educator Edition Developing Partnerships with Parents and Caregivers Lee Kern, Ph.D. Lehigh University The National Resource Center on
www.help4adhd.org (800) 233-4050 Help4ADHD@CHADD.org Ask the Expert Educator Edition Developing Partnerships with Parents and Caregivers Lee Kern, Ph.D. Lehigh University The National Resource Center on
ADHD. What you need to know
 ADHD What you need to know At Teva, we help to improve the health of 200 million people every day by providing innovative treatments and access to the world s largest medicine cabinet of generic and specialty
ADHD What you need to know At Teva, we help to improve the health of 200 million people every day by providing innovative treatments and access to the world s largest medicine cabinet of generic and specialty
Coping with incontinence
 Coping with incontinence Incontinence can be upsetting and humiliating for the person with dementia and stressful for the carer. But approaching the problem with understanding, matter-of-factness and humour
Coping with incontinence Incontinence can be upsetting and humiliating for the person with dementia and stressful for the carer. But approaching the problem with understanding, matter-of-factness and humour
Mentor training booklet
 Mentor training booklet Goal of ACT: To educate people about autism to protect children from harm, and connect them with education in order to live better lives. WHAT IS AUTISM? Autism is a term used to
Mentor training booklet Goal of ACT: To educate people about autism to protect children from harm, and connect them with education in order to live better lives. WHAT IS AUTISM? Autism is a term used to
Living Life with Persistent Pain. A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain
 Living Life with Persistent Pain A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain Contents What is Persistent Pain? 1 The Science Bit 2 Pain & Stress 3 Coping with Stress 4 The importance of
Living Life with Persistent Pain A guide to improving your quality of life, in spite of pain Contents What is Persistent Pain? 1 The Science Bit 2 Pain & Stress 3 Coping with Stress 4 The importance of
Module 04: Sleep. Module 04:
 Module 04: Sleep Module 04: Sleep Module 04: SLEEP This module includes the following sections: Key Messages Common Sleep Challenges Medications and Sleep Tips from Families for Getting a Good Night s
Module 04: Sleep Module 04: Sleep Module 04: SLEEP This module includes the following sections: Key Messages Common Sleep Challenges Medications and Sleep Tips from Families for Getting a Good Night s
Airline Travel Checklist
 AIRPORT INSTRUCTION & READINESS Airline Travel Checklist um nsu card University of Miami-Nova Southeastern University Center for Autism & Related Disabilities miami-airport.com/miaair.asp 1. Booking Your
AIRPORT INSTRUCTION & READINESS Airline Travel Checklist um nsu card University of Miami-Nova Southeastern University Center for Autism & Related Disabilities miami-airport.com/miaair.asp 1. Booking Your
Penny Williams PARENTING ADHD CHEAT SHEET TIPS AND STRATEGIES TO TAME THE CHAOS OF LIFE WITH ADHD. Parenting Guide. Author. Realist.
 PARENTING ADHD CHEAT SHEET TIPS AND STRATEGIES TO TAME THE CHAOS OF LIFE WITH ADHD ParentingADHDandAutism.com INTRODUCTION Feeling overwhelmed? Helpless? Hopeless? I know the feeling. Really, I do! I ve
PARENTING ADHD CHEAT SHEET TIPS AND STRATEGIES TO TAME THE CHAOS OF LIFE WITH ADHD ParentingADHDandAutism.com INTRODUCTION Feeling overwhelmed? Helpless? Hopeless? I know the feeling. Really, I do! I ve
Running Head: VISUAL SCHEDULES FOR STUDENTS WITH AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER
 Running Head: VISUAL SCHEDULES FOR STUDENTS WITH AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER Visual Schedules for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorder Taylor Herback 200309600 University of Regina VISUAL SCHEDULES FOR
Running Head: VISUAL SCHEDULES FOR STUDENTS WITH AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER Visual Schedules for Students with Autism Spectrum Disorder Taylor Herback 200309600 University of Regina VISUAL SCHEDULES FOR
Leader Guide. Session 8. FOOD is Fuel. Lesson 1: Welcome Back & Warm-up (10 minutes) Lesson 2: FOOD Choices in Your Day (5 Minutes)
 Leader Guide Session 8 FOOD is Fuel Lesson 1: Welcome Back & Warm-up (10 minutes) Lesson 2: FOOD Choices in Your Day (5 Minutes) Lesson 3: FOOD and MOOD Relay (10 Minutes) Lesson 4: Fitness Challenge Circuit
Leader Guide Session 8 FOOD is Fuel Lesson 1: Welcome Back & Warm-up (10 minutes) Lesson 2: FOOD Choices in Your Day (5 Minutes) Lesson 3: FOOD and MOOD Relay (10 Minutes) Lesson 4: Fitness Challenge Circuit
Changing Community Perceptions About Autism
 Changing Community Perceptions About Autism Be Aware, Accept, Include In a world filled with change and diversity I feel it s time to change the views and perceptions of Autism I believe it is something
Changing Community Perceptions About Autism Be Aware, Accept, Include In a world filled with change and diversity I feel it s time to change the views and perceptions of Autism I believe it is something
Explaining the Rationale for Trauma-Focused Work: Why it s Good to Talk
 Explaining the Rationale for Trauma-Focused Work: Why it s Good to Talk David Trickey Consultant Clinical Psychologist Anna Freud National Centre for Children and Families Memories of traumatic events
Explaining the Rationale for Trauma-Focused Work: Why it s Good to Talk David Trickey Consultant Clinical Psychologist Anna Freud National Centre for Children and Families Memories of traumatic events
The KEYHOLE Early Intervention Programme in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Booklet 4. Interaction. Facebook: /AutismNI
 The KEYHOLE Early Intervention Programme in Autism Spectrum Disorder Booklet 4 Interaction Facebook: /AutismNI Twitter: @AutismNIPAPA THE KEYHOLE EARLY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME IN AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER
The KEYHOLE Early Intervention Programme in Autism Spectrum Disorder Booklet 4 Interaction Facebook: /AutismNI Twitter: @AutismNIPAPA THE KEYHOLE EARLY INTERVENTION PROGRAMME IN AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER
Positive Behavior Support in Inclusion. Taylor Singleton, CTRS and Eric Rueger OPRA Conference February 4, 2019
 Positive Behavior Support in Inclusion Taylor Singleton, CTRS and Eric Rueger OPRA Conference February 4, 2019 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to list a strategy for each of the 4 types of
Positive Behavior Support in Inclusion Taylor Singleton, CTRS and Eric Rueger OPRA Conference February 4, 2019 Learning Outcomes Participants will be able to list a strategy for each of the 4 types of
Autism and Physical Education: Strategies for Success JUSTIN A. HAEGELE, PHD, CAPE OLD DOMINION UNIVERSITY
 Autism and Physical Education: Strategies for Success JUSTIN A. HAEGELE, PHD, CAPE OLD DOMINION UNIVERSITY Food for Thought When preparing an activity for children with autism, a teacher should plan to
Autism and Physical Education: Strategies for Success JUSTIN A. HAEGELE, PHD, CAPE OLD DOMINION UNIVERSITY Food for Thought When preparing an activity for children with autism, a teacher should plan to
Mouth care for people with dementia. Good habits for bedtime. Caring for someone with dementia
 Mouth care for people with dementia Good habits for bedtime Caring for someone with dementia 2 Dementia UK Looking after someone with dementia Caring for someone with dementia can be really difficult at
Mouth care for people with dementia Good habits for bedtime Caring for someone with dementia 2 Dementia UK Looking after someone with dementia Caring for someone with dementia can be really difficult at
Talk about Constipation
 This booklet is part of a series for children with bowel and/or bladder problems. The booklets give a simple explanation of the problems the child is having. They give practical advice about how to help.
This booklet is part of a series for children with bowel and/or bladder problems. The booklets give a simple explanation of the problems the child is having. They give practical advice about how to help.
Ready to give up. Booklet 3
 Ready to give up Booklet 3 This booklet is written for people who have decided that they want to stop smoking. You can use this booklet on its own or go through it with the person who gave it to you. You
Ready to give up Booklet 3 This booklet is written for people who have decided that they want to stop smoking. You can use this booklet on its own or go through it with the person who gave it to you. You
1. Work on heart health 2. Go nuts about nutrition 3. Have fun with fitness 4. Share your knowledge 5. Be a girl of service
 elcome to the Go Red Girl Scouts Patch Program a patch program for girls who love their hearts. Are you ready to raise awareness of the danger of heart disease as a serious women s health issue? Let s
elcome to the Go Red Girl Scouts Patch Program a patch program for girls who love their hearts. Are you ready to raise awareness of the danger of heart disease as a serious women s health issue? Let s
Simple Strategies for Behavior Change
 Simple Strategies for Behavior Change Successful programs for Students with Severe Language and Learning Deficits Sue Heatter, M.S. BCBA University of West Florida If you don t like the behavior you are
Simple Strategies for Behavior Change Successful programs for Students with Severe Language and Learning Deficits Sue Heatter, M.S. BCBA University of West Florida If you don t like the behavior you are
SELF-ESTEEM AND HUMAN RELATIONSHIPS 9. SELF-ESTEEM AND ADHD
 SELF-ESTEEM AND HUMAN RELATIONSHIPS 9. SELF-ESTEEM AND ADHD 9.1. Self-Esteem in Children with ADHD ADHD stands for Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. It's thought to be caused by developmental differences
SELF-ESTEEM AND HUMAN RELATIONSHIPS 9. SELF-ESTEEM AND ADHD 9.1. Self-Esteem in Children with ADHD ADHD stands for Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. It's thought to be caused by developmental differences
Bonnie Van Metre M.Ed., BCBA Kennedy Krieger Institute Center for Autism and Related Disorders
 Bonnie Van Metre M.Ed., BCBA Kennedy Krieger Institute Center for Autism and Related Disorders Principles of behavior/ functions of behavior Preventive strategies Consequences strategies Aggression Pinching
Bonnie Van Metre M.Ed., BCBA Kennedy Krieger Institute Center for Autism and Related Disorders Principles of behavior/ functions of behavior Preventive strategies Consequences strategies Aggression Pinching
Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included.
 Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Urology Clinic Hospital for Sick Children Please read the following information and have the child follow the bladder retraining protocol included. Information on bladder retraining, urinary tract infections
Ten Strategies to Overcome Procrastination
 Ten Strategies to Overcome Procrastination True confession: I procrastinated on writing this article on procrastination. The irony is funny, right? Actually, it is proof positive that we all procrastinate
Ten Strategies to Overcome Procrastination True confession: I procrastinated on writing this article on procrastination. The irony is funny, right? Actually, it is proof positive that we all procrastinate
EBP s for Transitioning: Implementing with Individuals with Autism. Laura Ferguson, M.Ed, BCBA
 EBP s for Transitioning: Implementing with Individuals with Autism Laura Ferguson, M.Ed, BCBA What is Autism? Autism is a complex developmental disability that has a neurological basis that causes impairments
EBP s for Transitioning: Implementing with Individuals with Autism Laura Ferguson, M.Ed, BCBA What is Autism? Autism is a complex developmental disability that has a neurological basis that causes impairments
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
 Do you feel trapped in a pattern of unwanted and upsetting thoughts? A R E A L I L L N E S S Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder NIH Publication No. 00-4676 Does This Sound
Do you feel trapped in a pattern of unwanted and upsetting thoughts? A R E A L I L L N E S S Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder NIH Publication No. 00-4676 Does This Sound
Beyond Cancer Moving On
 Beyond Cancer Moving On Today, people with cancer have a better chance at living a normal life than ever before in history. In fact, there are more than 10 million survivors people who have, or are living
Beyond Cancer Moving On Today, people with cancer have a better chance at living a normal life than ever before in history. In fact, there are more than 10 million survivors people who have, or are living
a stimulant in coffee, tea, chocolate, and some soft drinks 2. to believe something without knowing the facts 5.
 In this lesson, you will discuss everyone s favorite subject sleep! If you re not a good sleeper, you ll learn five things that could be keeping you awake. If you do sleep well, you can share your tips
In this lesson, you will discuss everyone s favorite subject sleep! If you re not a good sleeper, you ll learn five things that could be keeping you awake. If you do sleep well, you can share your tips
Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER
 Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER A foster child has been placed in your home. You are told that she has been prenatally exposed to alcohol and has a Fetal Alcohol
Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER A foster child has been placed in your home. You are told that she has been prenatally exposed to alcohol and has a Fetal Alcohol
Interviewer: Tell us about the workshops you taught on Self-Determination.
 INTERVIEW WITH JAMIE POPE This is an edited translation of an interview by Jelica Nuccio on August 26, 2011. Jelica began by explaining the project (a curriculum for SSPs, and for Deaf-Blind people regarding
INTERVIEW WITH JAMIE POPE This is an edited translation of an interview by Jelica Nuccio on August 26, 2011. Jelica began by explaining the project (a curriculum for SSPs, and for Deaf-Blind people regarding
Educator s Teaching Teeth Guidebook
 Educator s Teaching Teeth Guidebook This booklet is intended for Community Health Representatives (CHRs), Children s Oral Health Coordinators (COHCs), and other educators or health care workers who want
Educator s Teaching Teeth Guidebook This booklet is intended for Community Health Representatives (CHRs), Children s Oral Health Coordinators (COHCs), and other educators or health care workers who want
Getting Started: Introducing Your Child to His or Her Diagnosis of Autism or Asperger Syndrome
 Getting Started: Introducing Your Child to His or Her Diagnosis of Autism or Asperger Syndrome by Marci Wheeler, Social Worker, Indiana Resource Center for Autism Who, what, when, where, how, and why are
Getting Started: Introducing Your Child to His or Her Diagnosis of Autism or Asperger Syndrome by Marci Wheeler, Social Worker, Indiana Resource Center for Autism Who, what, when, where, how, and why are
keep track of other information like warning discuss with your doctor, and numbers of signs for relapse, things you want to
 Helping you set your brain free from psychosis. www.heretohelp.bc.ca This book was written by Sophia Kelly and the BC Schizophrenia Society, for the BC Partners for Mental Health and Addictions Information.
Helping you set your brain free from psychosis. www.heretohelp.bc.ca This book was written by Sophia Kelly and the BC Schizophrenia Society, for the BC Partners for Mental Health and Addictions Information.
