How useful are our present statistics on sexuallytransmitted diseases?
|
|
|
- Julie Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brit.J. vener. Dis. (1975) 51, 153 How useful are our present statistics on sexuallytransmitted diseases? KEVIN WOODCOCK Southampton Special Treatment Centre, Bullar Street, Southampton S02 ONH In order to preserve patient anonymity venereal infections are not notifiable as such, but, since the establishment of 'special clinics' as a result of the 'Venereal Diseases Act, 1916', these clinics have provided annual reports of the number of cases treated. It is impossible to know, in retrospect, how complete a picture of the incidence of venereal diseases was provided by these statistics during the inter-war years, but by 1950 two changes had occurred which had a dramatic effect on the figures. The first was the discovery that penicillin provided a rapid and effective cure for both gonorrhoea and syphilis and the second was the introduction of the National Health Service in General practitioners also had penicillin at their disposal, and the free treatment of venereal disease no longer depended on attendance at the 'special clinics' which were, and still are, the only source of venereal disease statistics. Furthermore, the ability to cure gonorrhoea rapidly had led to the possibility of a few patients repeatedly becoming re-infected and so distorting the 'new cases' figures. In 1951 the clinics first reported the number of cases of 'non-gonococcal urethritis' diagnosed; these figures are even more complicated by the additional problem of deciding whether a late recurrence of symptoms represents a re-infection, or a relapse of the condition previously considered cured. Also, the desire for more information about patients attending the clinics with 'other conditions' led to the addition, in 1971, of seven more categories to the list of diseases to be specifically reported; thus the increased possibility of multiple diagnoses and of variations in diagnostic criteria, as well as the problem of distinguishing relapses from re-infections, has added further to the complexity of interpreting the statistics. Previous work Unfortunately information on cases treated outside the clinics is scanty: on the basis of a 35 per cent. Received for publication October 11, 1974 Paper presented at a meeting of the MSSVD on April 26, Previously unpublished data used in this paper are taken from a report on V.D. statistics presented by the author for the M.Sc. Social Medicine examination, University of London, response to a postal survey it was concluded that gonorrhoea must be under-reported by at least 15 per cent. and syphilis by 25 per cent. (British Cooperative Clinical Group, 1959); a similar survey in East Scotland produced an 85 per cent. response and indicated a 10 to 12 per cent. under-reporting of gonorrhoea (British Co-operative Clinical Group, 1968); more recently, but on what evidence is not stated, it has been suggested that all the figures may be 25 per cent. too low (Wigfield, 1971); in N. Humberside it was calculated that the proportion of cases treated outside the clinics was unlikely to have exceeded 20 per cent., even allowing for a possible 25 per cent. under-recording by the G.Ps surveyed (Heywood and Bacon, 1973). The 'Study of Morbidity Statistics in General Practice' found that gonorrhoea and venereal disease other than syphilis accounted for 2 per cent. of consultations, and 1 per cent. of patients consulting (Logan and Cushion, 1958); from N. Wales comes the information that, of 508 consecutive patients, 0.8 per cent. had male genital problems and 8.4 per cent. gynaecological problems (Bebbington, 1969); from Scotland that 11 years' practice with nearly 1,000 patients aged 15 to 44 produced four cases of gonorrhoea (Mc- Gregor, 1969); from the R.A.F. that 8,018 consultations led to 288 referrals to hospital of which 2.1 per cent. were for V.D. (Beeton, 1969); and at the Belfast Venereal Disease Clinic it was found that, of patients with symptoms, 50 per cent. had consulted their family doctor before attending the clinic (Mahoney, 1972); but nowhere can be found data, comparable with the clinic figures, about the number of cases diagnosed, treated, and not referred to a clinic. There is no published information about possible variations in laboratory techniques and standards over time and between places, nor any information on possible variations of criteria for diagnosing 'new cases', relapses, or re-infections. There is, however, some evidence that the statistics can be confusing: a study in Belfast reported that in 25 per cent. of both male and female patients attending the Venereal Disease clinic no disease was found, and that 1,753 patients codtributed 2,093 diagnoses (Pemberton,
2 154 British Journal of Venereal Diseases McCann, Mahoney, Mackenzie, Dougan, and Hay, 1972). Similarly, in Aberdeen, 1,603 female patients contributed 2,093 diagnoses, of which 1,052 were non-venereal, and 265 were infants with no abnormality being checked for congenital venereal disease before adoption (Thompson and Rutherford, 1972). Yet two recent publications have contained graphs entitled 'New patients attending clinics in England and Wales' whilst using figures for total diagnoses made-which include not only multiple diagnoses on the same patients but also diagnoses of 'no abnormality' (Catterall and Morton, 1970; Catterall, 1973). Objectives The objectives of this paper are: (1) To enumerate, with specific examples, some of the ways in which the present STD statistics are deficient; (2) To suggest practical ways in which adjustments may make the statistics more useful. DEFECTS (i) Data are available from no source other than STD clinics. Table I shows the results of a survey of a Gynaecology outpatient department and a General Practice in S. Kensington aimed at discovering what proportion of patients attending had histories suggesting the possibility of a sexually-transmitted disease (mainly vaginal or urethral discharge or a history of contact with a known case). Although the numbers were small, if this situation were reflected in every Gynaecology clinic and General Practice in the country, the total numbers involved would completely eclipse the STD clinic figures. (ii) 'Cases' are not 'spells of infection' nor 'persons infected' but only diagnoses made. A sample of records of patients attending the St. Mary's Hospital Special Clinic during 1971 were examined to discover what contribution these patients had made to the annual case statistics. The sample consisted of all female patients and alternate male patients attending the clinic on days chosen from a random number table to fill a sample frame stratified to include one day from each week, from each quarter of the year. From the results, shown in Table II, it can be seen that there were 80 per cent. more 'cases' than persons; that nevertheless, 55 per cent. of the patients contributed only a single 'case'; but that 8 per cent. of the patients had four or more diagnoses made and contributed 22 per cent. of the total 'cases'. (iii) A different aspect is demonstrated in Table III: gonorrhoea was diagnosed 2 5 times more often in male patients than in female patients, which might be considered useful information for policy decisions of one kind or another. However, homosexual males accounted for 13 9 cases per 100, while ten females per 100 were treated as contacts of gonorrhoea without waiting for a diagnosis to be made. Hence treatment for gonorrhoea was given only 1 1 times more often to heterosexual males than to females, which fact, undetectable from the routine statistics, might lead to different decisions. TABLE I A comparison between Gynaecology, General Practice, and Venereology departments of new STD presentations as a percentage of total attendances and as an estimated number seen per week New attendances Estimated number of new possible S TD Department surveyed Duration of Total Per cent. with attendances per week survey (wks) number possible S TD St. Mary's Hospital, W.2 Professorial Gynaecology Department (2 O.P. sessions/week) S. Kensington General Practice (Drs Lefever, Trevelyan, and West) St. Mary's Hospital, W.2 Venereology Departnent Referred Unreferred TABLE II Number of patients providing the specified number of cases during 1971, by sex Total number of cases contributed Sex Total persons Male ,017 Female Both ,071 1,909 Total cases
3 TABLE III Effect on male/female gonorrhoea ratio of excluding homosexual cases and including cases treated 'epidemiologically' Column Sex Male Female M/F ratio Column (1) Gonorrhoea cases diagnosed per 100 persons in sample (2) As 1, but excluding homosexually acquired infections (3) As 2, but including cases treated for gonorrhoea because of history, without waiting for a diagnosis to be made (iv) No information is available about the site or severity of infection. The distribution of anal and urethral infections amongst 121 homosexual patients statistics, but some indication of whether an organism was isolated from purulent urethral discharge, an inflamed throat, the bloodstream of a patient with septicaemia, or an apparently healthy cervix, would clearly be desirable. Use of statistics on sexually-transmitted diseases 155 in the case records survey is shown in Table IV. This format is too complex for routinely published (v) The available information does not relate to local populations. By going through the case registers for 1971 of nine clinics in and around W. London and by recording information about all patients with gonorrhoea giving an address in W.2 or W.9 an attempt was made to relate information about gonorrhoea to the 1971 Census Data on residents in W.2 and W.9. The result is shown in the Figure; in epidemiological language this should represent the age/sex specific incidence (spells). The obvious next step would be to compare this information with similar information from elsewhere, but none is available. Even the national figures, shown in Table V, cannot be used directly: not only are the age groupings used rather irregular, but for ages under 16 and over 25 the case figures have been related to total populations-which include both babies and octogenarians. Recalculating the figures as shown in Table VI allowed some comparison to be made; it can be seen that the incidence in W.2 and W.9 appears to be five to fifteen TABLE Iv Homosexual males' case histories analysed to demonstrate the distribution of proctitis and urethritis episodes during 1971 No. of persons experiencing this number of episodes of urethritis No. of persons experiencing this number of episodes of proctitis (5) 1 Total persons TABLE V Incidence of new cases of gonorrhoea seen at hospital clinics in England, as published by the D.H.S.S. Sex Incidence per 100,000 population aged Under and and Male Female Total TABLE VI Incidence of new cases of gonorrhoea reportedfrom clinics in England and Wales, compared with that calculatedfor London postal districts W.2 and W.9 Incidence of cases of gonorrhoea in persons aged: Total persons All ages Area Sex <20 per 1, per 1, per 1,000 All ages per 1,000 All ages per 1,000 pop. aged pop. aged pop. aged pop. aged total population Male England and Wales Female Total Male London W.2 and Female W.9 Total
4 156 British Journal of Venereal Diseases FIGURE Gonorrhoea cases in W.2 and W.9 per 1,000 population, by age and sex. The histogram baseline for male andfemale cases is the incidence calculated as total cases per totai population, by sex, of all ages times that of the country as a whole, which might have been of interest were it not for the fact that addresses are recorded primarily to ensure that the patient can be contacted. Some patients do not want to be contacted and give a false address; some give the address of a friend; some a business address; some the hotel in which they are staying; and some may have forgotten to mention that they have moved since their address was first recorded. Table VII shows the results of a small survey to discover how reliable the recorded postal district was. TABLE vii Extent of agreement between postal districts of patients as shown in case register and as reported by patients to consulting doctor Total patients Patients Agreement Disagreement (Per cent.) (Per cent.) No. Per cent. New patients Re-attenders Total Thus not only is the information being collected and published incomplete by an unknown amount, and inadequate because it tells only of laboratory diagnoses and nothing about people or their problems, it is also unusable at a local level because it relates to no identifiable population. Any apparent trends shown might be due to variations in laboratory techniques or in diagnostic criteria, to more or less people going to STD clinics instead of other medical agencies, to large differences in the sexual behaviour of a few people, to small differences in the sexual behaviour of many people, or to variations in the population 'at risk', produced, for example, by the tourist industry. SUGGESTIONS (i) The first requirement is the establishment of a working party to decide for what purposes the statistics are required and to endeavour to make the data collected suitable for those purposes. Below is a categorization of different types of health statistics, each of which have different uses; a consideration of these categories might provide the basis for discussion: (a) Demographic and vital (b) Morbidity and disability (c) Health service activity (d) Facilities and resources (e) Health personnel (f) Medical alert (Engel, 1968) (ii) Any statistics collected must relate to populations at risk-at the simplest level this involves no more than recording separately data from visitors and residents. A further step might be to differentiate the patient contactability element from the statistical address element. For the former a telephone number, a business address, or that of a close friend, might actually be more appropriate than the patient's home. For statistical purposes it is not a precise address but an area for which the population structure is known that is important. While it must be accepted that the information obtained will not always be accurate, no longer requiring a routine address should reduce the amount of deliberately false information, and ensure that the information collected is appropriate to the purpose for which it is required. (iii) A distinction must be made between problem and diagnosis. The implications of asymptomatic infection detected during a screening process are clearly different from those of an infection causing symptoms severe enough to require hospitalization; and there are many intermediate situations between those extremes. Furthermore, the laboratory diagnosis may be positively misleading-for example a symptomless patient attending because of a definite history of contact with syphilis in whom the only laboratory finding is Candida albicans. Figures for the number of gonorrhoea and syphilis contacts attending are already collected by the D.H.S.S. (Part G of the quarterly return) but not in a form which would allow them to be incorporated into the main body of case statistics: a problem coding used in conjunction with the diagnostic coding would provide a much better record of what is actually happening.
5 (iv) Attendances are more appropriate than diagnoses as a measure of workload, but as recorded at present do not distinguish an attendance with a new and complex problem from a brief visit to confirm a negative blood result. The existing system of recording attendance information can be easily modified by using a numerical indication of the type of visit instead of merely recording the fact of a visit. (v) Precise information must be published on what criteria are required for any particular diagnosis to be made, and under what circumstances relapses or re-infections should be categorized as a new diagnosis. Although the criteria used should be as generally acceptable as possible, it matters less that they should be believed to represent the 'truth' than that they be recognized as providing the uniformity needed for comparisons to be made. (vi) Distinction must be made between diagnoses, spells of infection, and persons involved. Counting and reporting all three individually would involve more work and would not provide any indication of the relationship between them. A much simpler method, and one with the added advantage of incorporating a failsafe for identification of missed defaulters, is to delay statistical diagnosing for 3 months from the initial visit. Very little extra work would be involved since the getting out and refiling of records would merely take place for the patients who had attended 3 months previously instead of currently, and persons, spells, and diagnoses could be recorded and linked at one and the same time. If the consequent delay in getting the traditional annual statistics were considered important, it would be possible to use October to September figures which would be available at the same time as the present January to December ones. Conclusions In a paper of this kind, intended only to give pause for thought and to provoke discussion, conclusions are neither appropriate nor possible. Instead a question-'how useful are our present statistics?' Readers unconvinced by the foregoing may like to answer that question themselves by considering the statistics available in relation to the following quotation from one of the world's experts in health statistical methodology. 'Briefly stated, the usefulness of morbidity statistics lies, in general, in their giving information on the following: (a) How many people suffer from particular diseases, how often, and for how long; (b) What demands these diseases place on the medical and public health resources; and what financial Use of statistics on sexually-transmitted diseases 157 loss they cause; (c) How fatal the different diseases are; (d) To what extent people are prevented by these diseases from carrying on their normal activities; (e) To what extent diseases are concentrated in particular groups of the population, e.g. according to age, ethnic group, occupation, or place of residence; (f ) How far the above factors vary from time to time (variation according to season or from year to year). (g) What is the effect of medical care and health services on the control of disease incidence.' (Swaroop, 1960.) Summary Various aspects of the British statistics relating to sexually-transmitted diseases are examined. Defects in these are illustrated by data from a series of surveys. It is suggested that the information being collected and published is incomplete by an unknown amount, inadequate because it tells only of laboratory diagnoses, and unusable at a local level because it relates to no identifiable population. Some suggestions are made as to how the data collected might be made more useful: the first and most important is that a working party should decide for what purposes the statistics are required. References BEBBINGTON, R. (1969) J. roy. Coll. gen. Practit., 18, 27 BEETON, D. G. (1969) Practitioner, 202, 830 BRITIsH Co-o_muATIVE CLiNCAL GROUP (1959) Brit. J. vener. Dis., 35, (1968) Ibid., 44, 299 (Annex II) CATTERALL, R. D. (1973) Ibid., 49, and MORTON, R. S. (1970) Brit. med. J., 3, 699 ENGEL, A. (1968) 'Perspectives in Health Planning'. Athlone Press, London HEYwOOD, C. P., and BACON, P. M. (1973) Brit. J. vener. Dis., 49, 540 LOGAN, W. P. D., and CUsHION, A. A. (1958) 'Morbidity Statistics from General Practice', vol. 1, Studies on Medical and Population Subjects', No. 14. General Register Office, London McGREGoR, R. M. (1969) 'The Work of a Family Doctor'. Livingstone, Edinburgh MAHONEY, J. D. H. (1972) Brit. J. vener. Dis., 48, 71 PEMBERTON, J., MCCANN, J. S., MAHONEY, J. D. H., MACKENZIE, G., DOUGAN, H., and HAY, I. (1972) Ibid., 48, 391 SwAROOP, S. (1960) 'Introduction to Health Statistics'. Livingstone, Edinburgh THOMPSON, B., and RuTHEFORD, H. W. (1972) Brit. J. vener. Dis., 48, 209 WIGFIELD, A. S. (1971) Brit. med. J., 4, 342
Practices in STD clinics in England and Wales A reassessment based on the numbers of cases seen
 Br J Vener Dis 1981; 57:221-5 Practices in STD clinics in England and Wales A reassessment based on the numbers of cases seen M C KELSON, E M BELSEY, AND M W ADLER From the Academic Department of Genitourinary
Br J Vener Dis 1981; 57:221-5 Practices in STD clinics in England and Wales A reassessment based on the numbers of cases seen M C KELSON, E M BELSEY, AND M W ADLER From the Academic Department of Genitourinary
gonorrhoea in sexually transmitted disease clinics in
 British Journal of Venereal Diseases, 1978, 54, 10-14 Diagnostic treatment and reporting criteria for gonorrhoea in sexually transmitted disease clinics in England and Wales 1: Diagnosis M. W. ADLER From
British Journal of Venereal Diseases, 1978, 54, 10-14 Diagnostic treatment and reporting criteria for gonorrhoea in sexually transmitted disease clinics in England and Wales 1: Diagnosis M. W. ADLER From
DIAGNOSIS OF GONORRHOEA. The diagnosis of gonorrhoea was made if either a smear or a culture was positive for gonococci.
 Brit.. vener. Dis. (1974) 51, 41 Gonorrhoea in 1972 A 1-year study of patients attending the VD Unit in Uppsala JOHAN WALLIN From the Department of Dermatology and Venereology, University Hospital, Uppsala,
Brit.. vener. Dis. (1974) 51, 41 Gonorrhoea in 1972 A 1-year study of patients attending the VD Unit in Uppsala JOHAN WALLIN From the Department of Dermatology and Venereology, University Hospital, Uppsala,
ELIMINATION OF CONGENITAL SYPHILIS*
 Brit. J. vener. Dis. (1959), 35, 15. ELIMINATION OF CONGENITAL SYPHILIS* BY S. M. LAIRD St. Luke's Ctthic and V.D. Department, Royal Infirmary, Manchester It has been taught and believed for many years
Brit. J. vener. Dis. (1959), 35, 15. ELIMINATION OF CONGENITAL SYPHILIS* BY S. M. LAIRD St. Luke's Ctthic and V.D. Department, Royal Infirmary, Manchester It has been taught and believed for many years
Detection and treatment of hypertension in an inner London community
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1976), 30, 268-272 Detection and treatment of hypertension in an inner London community RICHARD F. HELLER Lecturer in Epidemiology, St Mary's Hospital Medical School Heller, R.
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1976), 30, 268-272 Detection and treatment of hypertension in an inner London community RICHARD F. HELLER Lecturer in Epidemiology, St Mary's Hospital Medical School Heller, R.
STD Report 2010 Summary St. Charles County Department of Community Health and the Environment Alison Tucker, MSc 802 Figure 1:
 STD Report 2010 Summary St. Charles County Department of Community Health and the Environment Alison Tucker, MSc STD cases include Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis There was a total of 802 reported laboratory
STD Report 2010 Summary St. Charles County Department of Community Health and the Environment Alison Tucker, MSc STD cases include Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis There was a total of 802 reported laboratory
Survey questionnaire on STI. surveillance, care and prevention. in European countries SAMPLE APPENDIX
 European Surveillance of Sexually Transmitted Infections Survey questionnaire on STI surveillance, care and prevention in European countries APPENDIX Detailed questionnaire on clinician and laboratory
European Surveillance of Sexually Transmitted Infections Survey questionnaire on STI surveillance, care and prevention in European countries APPENDIX Detailed questionnaire on clinician and laboratory
The cost-effectiveness of syndromic management in pharmacies in Lima, Peru Adams E J, Garcia P J, Garnett G P, Edmunds W J, Holmes K K
 The cost-effectiveness of syndromic management in pharmacies in Lima, Peru Adams E J, Garcia P J, Garnett G P, Edmunds W J, Holmes K K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
The cost-effectiveness of syndromic management in pharmacies in Lima, Peru Adams E J, Garcia P J, Garnett G P, Edmunds W J, Holmes K K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
 WHO/HIV_AIDS/2001.01 WHO/RHR/01.10 Original: English Distr.: General GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS World Health Organization Copyright World Health Organization 2001.
WHO/HIV_AIDS/2001.01 WHO/RHR/01.10 Original: English Distr.: General GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS World Health Organization Copyright World Health Organization 2001.
Source :
 1 2 Source : www.ecdc.europa.eu 3 Collection Form: What data are needed? At a minimum, the number of diagnosed cases, and the population denominator (to give it a context), geographical location, and an
1 2 Source : www.ecdc.europa.eu 3 Collection Form: What data are needed? At a minimum, the number of diagnosed cases, and the population denominator (to give it a context), geographical location, and an
HPSC SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS IN IRELAND, 2011
 HPSC SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS IN IRELAND, 2011 Health Protection Surveillance Centre, www.hpsc.ie Version 2.1 October, 2012 Table of Contents Acknowledgements... 3 Key Points... 3 Introduction...
HPSC SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS IN IRELAND, 2011 Health Protection Surveillance Centre, www.hpsc.ie Version 2.1 October, 2012 Table of Contents Acknowledgements... 3 Key Points... 3 Introduction...
New Brunswick Report on Sexually Transmitted and Blood Borne Infections, 2016
 New Brunswick Report on Sexually Transmitted and Blood Borne Infections, 6 Table of Contents. Introduction.... Methodology... 3. Data Limitations.... Definitions used... 3 5. Overview of STBBI epidemiology
New Brunswick Report on Sexually Transmitted and Blood Borne Infections, 6 Table of Contents. Introduction.... Methodology... 3. Data Limitations.... Definitions used... 3 5. Overview of STBBI epidemiology
Sexually Transmitted Infection surveillance in Northern Ireland An analysis of data for the calendar year 2011
 Sexually Transmitted Infection surveillance in Northern Ireland 2012 An analysis of data for the calendar year 2011 Contents Page Summary points. 3 Surveillance arrangements and sources of data.. 4 1:
Sexually Transmitted Infection surveillance in Northern Ireland 2012 An analysis of data for the calendar year 2011 Contents Page Summary points. 3 Surveillance arrangements and sources of data.. 4 1:
Scottish Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections Reference Laboratory (SBSTIRL) User Report for the period January - December 2011
 Scottish Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections Reference Laboratory (SBSTIRL) User Report for the period January - ember 211 Kirstine Eastick PhD FRCPath (Director) SBSTIRL, Microbiology Edinburgh
Scottish Bacterial Sexually Transmitted Infections Reference Laboratory (SBSTIRL) User Report for the period January - ember 211 Kirstine Eastick PhD FRCPath (Director) SBSTIRL, Microbiology Edinburgh
STI SURVEILLANCE. October December Quarterly Report. Prepared as part of the Ministry of Health contract for scientific services
 STI SURVEILLANCE October December 2003 Quarterly Report Prepared as part of the Ministry of Health contract for scientific services by STI Surveillance Team March 2004 Client Report FW 0414 DISCLAIMER
STI SURVEILLANCE October December 2003 Quarterly Report Prepared as part of the Ministry of Health contract for scientific services by STI Surveillance Team March 2004 Client Report FW 0414 DISCLAIMER
Sexually Transmitted Infection surveillance in Northern Ireland An analysis of data for the calendar year 2016
 Sexually Transmitted Infection surveillance in Northern Ireland 2017 An analysis of data for the calendar year 2016 Contents Page Summary points. 3 Surveillance arrangements and sources of data.. 4 1:
Sexually Transmitted Infection surveillance in Northern Ireland 2017 An analysis of data for the calendar year 2016 Contents Page Summary points. 3 Surveillance arrangements and sources of data.. 4 1:
Summary of the Dental Results from the GP Patient Survey January to March 2018
 Summary of the Dental Results from the GP Patient Survey January to March 2018 Published 9 August 2018 (Annual) About this release Dental questions were originally added to the GP Patient Survey in January
Summary of the Dental Results from the GP Patient Survey January to March 2018 Published 9 August 2018 (Annual) About this release Dental questions were originally added to the GP Patient Survey in January
Notifiable Sexually Transmitted Infections 2009 Annual Report
 Notifiable Sexually Transmitted Infections 29 Annual Report 21 Government of Alberta Alberta Health and Wellness, Surveillance and Assessment Send inquiries to: Health.Surveillance@gov.ab.ca Notifiable
Notifiable Sexually Transmitted Infections 29 Annual Report 21 Government of Alberta Alberta Health and Wellness, Surveillance and Assessment Send inquiries to: Health.Surveillance@gov.ab.ca Notifiable
Sickness absence after inguinal herniorrhaphy
 Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1979, 33, 121-126 Sickness absence after inguinal herniorrhaphy M. GRIFFITHS, W. E. WATERS, AND E. D. ACHESON From the Department of Community Medicine, University
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1979, 33, 121-126 Sickness absence after inguinal herniorrhaphy M. GRIFFITHS, W. E. WATERS, AND E. D. ACHESON From the Department of Community Medicine, University
FAILURES. THEIR CAUSE AND
 VI THE CHEMOTHERAPY OF GONORRHWEA FAILURES. THEIR CAUSE AND PREVENTION * By MORNA RAWLINS, M.B., B.S.(Lond.) I AM going to put before you a few facts an d figures to indicate that we have at last a drug
VI THE CHEMOTHERAPY OF GONORRHWEA FAILURES. THEIR CAUSE AND PREVENTION * By MORNA RAWLINS, M.B., B.S.(Lond.) I AM going to put before you a few facts an d figures to indicate that we have at last a drug
HPSC SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS IN IRELAND, 2010
 HPSC SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS IN IRELAND, 21 Health Protection Surveillance Centre, www.hpsc.ie Version 1. May 212 Table of Contents Acknowledgements... 5 Key Points... 5 Introduction... 7 Methods...
HPSC SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS IN IRELAND, 21 Health Protection Surveillance Centre, www.hpsc.ie Version 1. May 212 Table of Contents Acknowledgements... 5 Key Points... 5 Introduction... 7 Methods...
Of those with dementia have a formal diagnosis or are in contact with specialist services. Dementia prevalence for those aged 80+
 Dementia Ref HSCW 18 Why is it important? Dementia presents a significant and urgent challenge to health and social care in County Durham, in terms of both numbers of people affected and the costs associated
Dementia Ref HSCW 18 Why is it important? Dementia presents a significant and urgent challenge to health and social care in County Durham, in terms of both numbers of people affected and the costs associated
Social and psychological factors in the distribution of STD in male clinic attenders III Sexual activity
 Br J VenerDis 1983;59:386-93 Social and psychological factors in the distribution of STD in male clinic attenders III Sexual activity K W M FULFORD,* R D CATTERALL,t E HOINVILLE,* K S LIM, AND G D WILSON*
Br J VenerDis 1983;59:386-93 Social and psychological factors in the distribution of STD in male clinic attenders III Sexual activity K W M FULFORD,* R D CATTERALL,t E HOINVILLE,* K S LIM, AND G D WILSON*
STD. Are sexually transmitted infections (STIs) different from sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)?
 What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? STD Sexually transmitted diseases are diseases that can be passed from person to person through sexual contact. Depending on the STD, sexual contact that
What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? STD Sexually transmitted diseases are diseases that can be passed from person to person through sexual contact. Depending on the STD, sexual contact that
CORONARY HIEART DISEASE IN TRANSPORT WORKERS A PROGRESS REPORT* BY J. N. MORRIS and P. A. B. RAFFLE
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1954, 11, 260. CORONARY HIEART DISEASE IN TRANSPORT WORKERS A PROGRESS REPORT* BY J. N. MORRIS and P. A. B. RAFFLE From the Social Medicine Research Unit, Medical Research Council,
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1954, 11, 260. CORONARY HIEART DISEASE IN TRANSPORT WORKERS A PROGRESS REPORT* BY J. N. MORRIS and P. A. B. RAFFLE From the Social Medicine Research Unit, Medical Research Council,
STD County for St. Charles County
 217 STD Report St. Charles County Department of Public Health STD Cases include Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis There was a total of 1,488 laboratory confirmed reportable STD cases in 217 among St.
217 STD Report St. Charles County Department of Public Health STD Cases include Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis There was a total of 1,488 laboratory confirmed reportable STD cases in 217 among St.
NEWBORN HEARING SCREENING
 NEWBORN HEARING SCREENING UPDATED GUIDELINES FOR SURVEILLANCE AND AUDIOLOGY REFERRAL OF INFANTS AND CHILDREN FOLLOWING NEWBORN HEARING SCREENING (JULY 2012) 1 Document Control Document Control Version
NEWBORN HEARING SCREENING UPDATED GUIDELINES FOR SURVEILLANCE AND AUDIOLOGY REFERRAL OF INFANTS AND CHILDREN FOLLOWING NEWBORN HEARING SCREENING (JULY 2012) 1 Document Control Document Control Version
Sexual relationships, risk behaviour, and condom
 368 Original article Department of Genitourinary Medicine, Charing Cross Hospital, Fulham Palace Road, London W6 8RF B A Evans Charing Cross and Westminster Medical School, Charing Cross Hospital, London
368 Original article Department of Genitourinary Medicine, Charing Cross Hospital, Fulham Palace Road, London W6 8RF B A Evans Charing Cross and Westminster Medical School, Charing Cross Hospital, London
One-off assessments within a community mental health team
 Primary Care Mental Health 2007;4:00 00 # 2007 Radcliffe Publishing International research One-off assessments within a community mental health team Linda Heaney Consultant Psychiatrist, Avon and Wiltshire
Primary Care Mental Health 2007;4:00 00 # 2007 Radcliffe Publishing International research One-off assessments within a community mental health team Linda Heaney Consultant Psychiatrist, Avon and Wiltshire
Summary of the Dental Results from the GP Patient Survey; July to September 2014
 Introduction Summary of the Dental Results from the GP Patient Survey; July to September 2014 1. Dental questions were originally added to the GP Patient Survey in January to March 2010, as the Department
Introduction Summary of the Dental Results from the GP Patient Survey; July to September 2014 1. Dental questions were originally added to the GP Patient Survey in January to March 2010, as the Department
Annex A: Estimating the number of people in problem debt while being treated for a mental health crisis
 Annex A: Estimating the number of people in problem debt while being treated for a mental health crisis A.1 Estimating the number of referrals to NHS crisis response teams in England per year Unfortunately
Annex A: Estimating the number of people in problem debt while being treated for a mental health crisis A.1 Estimating the number of referrals to NHS crisis response teams in England per year Unfortunately
Understanding your child s heart. Pulmonary stenosis
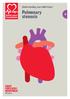 Understanding your child s heart Pulmonary stenosis 4 About this book If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have lots of questions running through your mind.
Understanding your child s heart Pulmonary stenosis 4 About this book If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have lots of questions running through your mind.
Incidence of venereal diseases in the Netherlands
 Brit. J. vener. Dis. (197) 46, 247 Incidence of venereal diseases in the Netherlands H. BIJKERK Geneeskundige Hoofinspectie van de Volksgezondheid, Leidschendam, The Netherlands V.D. CLINICS IN THE NETHERLANDS.1967
Brit. J. vener. Dis. (197) 46, 247 Incidence of venereal diseases in the Netherlands H. BIJKERK Geneeskundige Hoofinspectie van de Volksgezondheid, Leidschendam, The Netherlands V.D. CLINICS IN THE NETHERLANDS.1967
STIs: Practical Aspects of Management
 STIs: Practical Aspects of Management Dr Heather Young FAChSHM DipPH Christchurch Sexual Health heathery@xtra.co.nz 027 343 4963 Sexually Transmitted Infections BACTERIAL STIs: CHLAMYDIA GONORRHOEA SYPHILIS
STIs: Practical Aspects of Management Dr Heather Young FAChSHM DipPH Christchurch Sexual Health heathery@xtra.co.nz 027 343 4963 Sexually Transmitted Infections BACTERIAL STIs: CHLAMYDIA GONORRHOEA SYPHILIS
Sperm Donation - Information for Donors
 Sperm Donation - Information for Donors The donation of sperm to help someone to have a child is one of the most generous gifts anyone can give. Many donors feel a sense of pride, knowing the joy they
Sperm Donation - Information for Donors The donation of sperm to help someone to have a child is one of the most generous gifts anyone can give. Many donors feel a sense of pride, knowing the joy they
6: Service considerations a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 2009
 UK Data Archive Study Number - Adult Dental Health Survey, 009 6: Service considerations a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 009 Copyright 0, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All
UK Data Archive Study Number - Adult Dental Health Survey, 009 6: Service considerations a report from the Adult Dental Health Survey 009 Copyright 0, The Health and Social Care Information Centre. All
HIV Risk Behaviour in Irish Intravenous Drug Users
 Abstract HIV Risk Behaviour in Irish Intravenous Drug Users A. Dorman, E. Keenan, C. Schuttler, J. Merry, J. J. O Connor The Drug Treatment Centre Board, Trinity Court, 30/31 Pearse Street, Dublin 2. The
Abstract HIV Risk Behaviour in Irish Intravenous Drug Users A. Dorman, E. Keenan, C. Schuttler, J. Merry, J. J. O Connor The Drug Treatment Centre Board, Trinity Court, 30/31 Pearse Street, Dublin 2. The
SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF STD
 SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF STD Sexually Transmitted Diseases A Guide for Decision-makers, Health Care Workers, and Communicators WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION REGIONAL OFFICE FOR THE WESTERN PACIFIC MANILA
SYNDROMIC CASE MANAGEMENT OF STD Sexually Transmitted Diseases A Guide for Decision-makers, Health Care Workers, and Communicators WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION REGIONAL OFFICE FOR THE WESTERN PACIFIC MANILA
Background. Yet, as a nation, we find it hard to talk about and harder still to help people dealing with a bereavement.
 A better grief 2 A better grief Background We all experience bereavement and grief at some stage in our lives. Seventy-two per cent of us have been bereaved at least once in the last five years, according
A better grief 2 A better grief Background We all experience bereavement and grief at some stage in our lives. Seventy-two per cent of us have been bereaved at least once in the last five years, according
Deciding whether a person has the capacity to make a decision the Mental Capacity Act 2005
 Deciding whether a person has the capacity to make a decision the Mental Capacity Act 2005 April 2015 Deciding whether a person has the capacity to make a decision the Mental Capacity Act 2005 The RMBI,
Deciding whether a person has the capacity to make a decision the Mental Capacity Act 2005 April 2015 Deciding whether a person has the capacity to make a decision the Mental Capacity Act 2005 The RMBI,
NEW GENERAL MEDICAL SERVICES CONTRACT SPECIFICATION FOR THE PROVISION OF AN ENHANCED SERVICE SERVICE SPECIFICATION CHLAMYDIA SCREENING
 NEW GENERAL MEDICAL SERVICES CONTRACT SPECIFICATION FOR THE PROVISION OF AN ENHANCED SERVICE SERVICE SPECIFICATION CHLAMYDIA SCREENING April 1, 2013 March 31, 2014 SERVICE CHLAMYDIA SCREENING REFERENCE
NEW GENERAL MEDICAL SERVICES CONTRACT SPECIFICATION FOR THE PROVISION OF AN ENHANCED SERVICE SERVICE SPECIFICATION CHLAMYDIA SCREENING April 1, 2013 March 31, 2014 SERVICE CHLAMYDIA SCREENING REFERENCE
RECORDS OF DEA1" MUTISM IN NORTHERN IRELAND
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1955), 9, 196-200 RECORDS OF DEA1" MUTISM IN NORTHERN IRELAND BY Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, The Queen's University of Belfast INTRODUCTION A recent survey of
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1955), 9, 196-200 RECORDS OF DEA1" MUTISM IN NORTHERN IRELAND BY Department of Social and Preventive Medicine, The Queen's University of Belfast INTRODUCTION A recent survey of
Statistics on Drug Misuse: England, 2008
 Statistics on Drug Misuse: England, 2008 Summary This annual statistical report presents information on drug misuse among both adults and children. It includes a focus on young adults. The topics covered
Statistics on Drug Misuse: England, 2008 Summary This annual statistical report presents information on drug misuse among both adults and children. It includes a focus on young adults. The topics covered
Reviewing Sexual Health and HIV NM2715
 Reviewing Sexual Health and HIV NM2715 Learning objectives To observe and learn from a case study. What happens to a couple who attend a GUM clinic, for screening and subsequent treatment? Revision of
Reviewing Sexual Health and HIV NM2715 Learning objectives To observe and learn from a case study. What happens to a couple who attend a GUM clinic, for screening and subsequent treatment? Revision of
Help us prioritise research into alcohol-related liver disease
 Help us prioritise research into alcohol-related liver disease In June 2015 we launched a survey to collect questions about the diagnosis, prevention, care and treatment of alcohol-related liver disease
Help us prioritise research into alcohol-related liver disease In June 2015 we launched a survey to collect questions about the diagnosis, prevention, care and treatment of alcohol-related liver disease
Characteristics of Patients Referred for HIV Pre~ lumpur TestCounselling at Universe ty Hospital Kuala
 Characteristics of Patients Referred for HIV Pre~ TestCounselling at Universe ty Hospital Kuala lumpur 1991.. 1994 B Yen, Dip Soc Work*, C L Teng, MMed**, M Y M Shajahan, MCGP** *Medical Social Work Unit,
Characteristics of Patients Referred for HIV Pre~ TestCounselling at Universe ty Hospital Kuala lumpur 1991.. 1994 B Yen, Dip Soc Work*, C L Teng, MMed**, M Y M Shajahan, MCGP** *Medical Social Work Unit,
Abnormal Smear (Cytology) Results What do they mean?
 Abnormal Smear (Cytology) Results What do they mean? Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Services This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure,
Abnormal Smear (Cytology) Results What do they mean? Obstetrics & Gynaecology Women & Children s Services This leaflet has been designed to give you important information about your condition / procedure,
Understanding your child s heart. Pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect
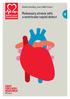 Understanding your child s heart Pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect 13 About this book Contents If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have
Understanding your child s heart Pulmonary atresia with a ventricular septal defect 13 About this book Contents If you re reading this book, you ve probably just had some very upsetting news, and have
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children
 Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children March 2019 Version 3.0 Document information Document purpose Document name Author Policy Circumcision for Children Welsh Health
Specialised Services Commissioning Policy: CP34 Circumcision for children March 2019 Version 3.0 Document information Document purpose Document name Author Policy Circumcision for Children Welsh Health
PROCEDURE Mental Capacity Act. Number: E 0503 Date Published: 20 January 2016
 1.0 Summary of Changes This document has been redrafted and should be read in full by all officers and staff engaged in providing any response to the public concerning all aspects of Mental Health. This
1.0 Summary of Changes This document has been redrafted and should be read in full by all officers and staff engaged in providing any response to the public concerning all aspects of Mental Health. This
Trends in Reportable Sexually Transmitted Diseases in the United States, 2007
 Trends in Reportable Sexually Transmitted Diseases in the United States, 2007 National Surveillance Data for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) remain a major public
Trends in Reportable Sexually Transmitted Diseases in the United States, 2007 National Surveillance Data for Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, and Syphilis Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) remain a major public
Transplant Activity in the UK
 Transplant Activity in the UK 2006-2007 This document has been produced by the Statistics and Audit Directorate. UK Transplant August 2007 Cover pictures: Members of Glamorgan County cricket team help
Transplant Activity in the UK 2006-2007 This document has been produced by the Statistics and Audit Directorate. UK Transplant August 2007 Cover pictures: Members of Glamorgan County cricket team help
Vocabulary. Bias. Blinding. Block. Cluster sample
 Bias Blinding Block Census Cluster sample Confounding Control group Convenience sample Designs Experiment Experimental units Factor Level Any systematic failure of a sampling method to represent its population
Bias Blinding Block Census Cluster sample Confounding Control group Convenience sample Designs Experiment Experimental units Factor Level Any systematic failure of a sampling method to represent its population
PUBLIC HEALTH GUIDANCE FINAL SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE PUBLIC HEALTH GUIDANCE FINAL SCOPE 1 Guidance title How to stop smoking in pregnancy and following childbirth. 1.1 Short title Quitting smoking in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE PUBLIC HEALTH GUIDANCE FINAL SCOPE 1 Guidance title How to stop smoking in pregnancy and following childbirth. 1.1 Short title Quitting smoking in
Women s Sexual Health: STI and HIV Screening. Barbara E. Wilgus, MSN, CRNP STD/HIV Prevention Training Center at Johns Hopkins
 Women s Sexual Health: STI and HIV Screening Barbara E. Wilgus, MSN, CRNP STD/HIV Prevention Training Center at Johns Hopkins I have no disclosures! Review most recent rates of STIs and HIV across the
Women s Sexual Health: STI and HIV Screening Barbara E. Wilgus, MSN, CRNP STD/HIV Prevention Training Center at Johns Hopkins I have no disclosures! Review most recent rates of STIs and HIV across the
CHLAMYDIA, GONORRHEA & SYPHILIS: STDS ON THE RISE
 CHLAMYDIA, GONORRHEA & SYPHILIS: STDS ON THE RISE What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are passed from person to person through sexual activity. These infections
CHLAMYDIA, GONORRHEA & SYPHILIS: STDS ON THE RISE What are sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are passed from person to person through sexual activity. These infections
The objectives of this presentation are; to increase awareness of the issue of antimicrobial resistant gonorrhea, and to inform primary care and
 1 Antimicrobial resistant gonorrhea is an emerging public health threat that needs to be addressed. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is able to develop resistance to antimicrobials quickly. Effective antibiotic stewardship
1 Antimicrobial resistant gonorrhea is an emerging public health threat that needs to be addressed. Neisseria gonorrhoeae is able to develop resistance to antimicrobials quickly. Effective antibiotic stewardship
Developed by Marion Wood and Children s Dental Needs Steering Group
 Title Document Type Issue no DNA Policy Policy Clinical Governance Support Team Use Issue date 30.05.13 Review date 30.05.15 Distribution Prepared by Dental Staff Marion Wood Developed by Marion Wood and
Title Document Type Issue no DNA Policy Policy Clinical Governance Support Team Use Issue date 30.05.13 Review date 30.05.15 Distribution Prepared by Dental Staff Marion Wood Developed by Marion Wood and
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 Strategy,, policy and commissioning on hepatitis B and C testing NICE Pathways bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. NICE Pathways are interactive and designed to
Strategy,, policy and commissioning on hepatitis B and C testing NICE Pathways bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. NICE Pathways are interactive and designed to
The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical considerations
 British journal of Clinical Psychology (1991), 30, 223-229 Printed in Great Britain 2 2 3 1991 The British Psychological Society The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical
British journal of Clinical Psychology (1991), 30, 223-229 Printed in Great Britain 2 2 3 1991 The British Psychological Society The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical
Principles of publishing
 Principles of publishing Issues of authorship, duplicate publication and plagiarism in scientific journal papers can cause considerable conflict among members of research teams and embarrassment for both
Principles of publishing Issues of authorship, duplicate publication and plagiarism in scientific journal papers can cause considerable conflict among members of research teams and embarrassment for both
Understanding patient experience of diabetes in London: Identifying what s needed to support those living and coping with diabetes
 Understanding patient experience of diabetes in London: Identifying what s needed to support those living and coping with diabetes Author: Paul Trevatt, Lead London Diabetes Strategic Clinical Network
Understanding patient experience of diabetes in London: Identifying what s needed to support those living and coping with diabetes Author: Paul Trevatt, Lead London Diabetes Strategic Clinical Network
- The development of a training, qualifications and registration system for BSL / English Interpreters.
 SUBJECT: INTERPRETING CONFERENCE SUPPORTING DEAF PEOPLE AN INTERNATIONAL ONLINE CONFERENCE FOR INTERPRETING PROFESSIONALS. THEMES: TRAINING, ETHICS AND PROFESSIONALISM AND EDUCATIONAL INTERPRETING. CACDP
SUBJECT: INTERPRETING CONFERENCE SUPPORTING DEAF PEOPLE AN INTERNATIONAL ONLINE CONFERENCE FOR INTERPRETING PROFESSIONALS. THEMES: TRAINING, ETHICS AND PROFESSIONALISM AND EDUCATIONAL INTERPRETING. CACDP
AQA (A) Research methods. Model exam answers
 AQA (A) Research methods Model exam answers These answers are not for you to copy or learn by heart, they are for you to see how to develop you answers to get the marks. They have been written according
AQA (A) Research methods Model exam answers These answers are not for you to copy or learn by heart, they are for you to see how to develop you answers to get the marks. They have been written according
Cervical screening: your results explained. Updated guidance
 Cervical screening: your results explained Updated guidance This leaflet will explain the results of your cervical screening test which is designed to pick up any changes in cells on the cervix (lower
Cervical screening: your results explained Updated guidance This leaflet will explain the results of your cervical screening test which is designed to pick up any changes in cells on the cervix (lower
National Drug and Alcohol Treatment Waiting Times
 National Drug and Alcohol Treatment Waiting Times 1 April 30 June 2018 Publication date 25 September 2018 A National Statistics publication for Scotland This is a National Statistics Publication National
National Drug and Alcohol Treatment Waiting Times 1 April 30 June 2018 Publication date 25 September 2018 A National Statistics publication for Scotland This is a National Statistics Publication National
STATISTICAL PRESS NOTICE NHS REFERRAL TO TREATMENT (RTT) WAITING TIMES DATA JANUARY 2013
 STATISTICAL PRESS NOTICE NHS REFERRAL TO TREATMENT (RTT) WAITING TIMES DATA JANUARY 2013 Data are published on consultant-led Referral to Treatment (RTT) waiting times for patients who were treated during
STATISTICAL PRESS NOTICE NHS REFERRAL TO TREATMENT (RTT) WAITING TIMES DATA JANUARY 2013 Data are published on consultant-led Referral to Treatment (RTT) waiting times for patients who were treated during
Beyond the Diagnosis. Young Onset Dementia and the Patient Experience
 Beyond the Diagnosis Young Onset Dementia and the Patient Experience November 2017 1 Contents Executive Summary... 4 Recommendations... 4 1. Introduction... 6 2. Background & Rationale... 6 3. Methodology...
Beyond the Diagnosis Young Onset Dementia and the Patient Experience November 2017 1 Contents Executive Summary... 4 Recommendations... 4 1. Introduction... 6 2. Background & Rationale... 6 3. Methodology...
HIV, STDs, and TB: An Overview of Testing Results (1997)
 HIV, STDs, and TB: An Overview of Testing Results (1997) prepared for Delaware Department of Health and Social Services Division of Public Health by Edward C. Ratledge and Anne M. Gurchik Center for Applied
HIV, STDs, and TB: An Overview of Testing Results (1997) prepared for Delaware Department of Health and Social Services Division of Public Health by Edward C. Ratledge and Anne M. Gurchik Center for Applied
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE QUALITY AND OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK (QOF) INDICATOR DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME QOF indicator area: Epilepsy Briefing paper Potential output: Recommendations
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE QUALITY AND OUTCOMES FRAMEWORK (QOF) INDICATOR DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME QOF indicator area: Epilepsy Briefing paper Potential output: Recommendations
TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS
 TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS What s New: There are no changes to this guideline. Introduction Trichomonas vaginalis (TV) is a flagellated protozoan that is a parasite of the genital tract. Due to site specificity,
TRICHOMONAS VAGINALIS What s New: There are no changes to this guideline. Introduction Trichomonas vaginalis (TV) is a flagellated protozoan that is a parasite of the genital tract. Due to site specificity,
Not either/or but both/and: Why we need Rape Crisis Centres and Sexual Assault Referral Centres
 Not either/or but both/and: Why we need Rape Crisis Centres and Sexual Assault Referral Centres The development of provision for victims-survivors of sexual assault has historically been piecemeal and
Not either/or but both/and: Why we need Rape Crisis Centres and Sexual Assault Referral Centres The development of provision for victims-survivors of sexual assault has historically been piecemeal and
Report on the data collected by Healthwatch Oldham at our Low Mood, Anxiety and Depression Forum held in January 2017
 Report on the data collected by Healthwatch Oldham at our Low Mood, Anxiety and Depression Forum held in January 17 Healthwatch Oldham 1 Manchester Chambers, West Street, Oldham, Lancashire, OL1 1LF. Tel:
Report on the data collected by Healthwatch Oldham at our Low Mood, Anxiety and Depression Forum held in January 17 Healthwatch Oldham 1 Manchester Chambers, West Street, Oldham, Lancashire, OL1 1LF. Tel:
The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns
 International Journal of Epidemiology Oxford University Press 82 Vol. 11, No. 1 Printed in Great Britain The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns M J GARDNER*. C POWER". D J P BARKER* and R PADDAY*
International Journal of Epidemiology Oxford University Press 82 Vol. 11, No. 1 Printed in Great Britain The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns M J GARDNER*. C POWER". D J P BARKER* and R PADDAY*
Directed Enhanced Service (DES) for H1N1 Vaccination Programme JCVI priority groups
 Directed Enhanced Service (DES) for H1N1 Vaccination Programme JCVI priority groups October 2009 Introduction NHS Employers and the General Practitioners Committee (GPC) of the BMA have agreed arrangements
Directed Enhanced Service (DES) for H1N1 Vaccination Programme JCVI priority groups October 2009 Introduction NHS Employers and the General Practitioners Committee (GPC) of the BMA have agreed arrangements
Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Summary of CDC Treatment Guidelines
 DC 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Summary of CDC Treatment Guidelines These summary guidelines reflect the June 2015 update to the 2010 CDC Guidelines for Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
DC 2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Summary of CDC Treatment Guidelines These summary guidelines reflect the June 2015 update to the 2010 CDC Guidelines for Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
Special Education Fact Sheet. Special Education Impartial Hearings in New York City
 New York Lawyers For The Public Interest, Inc. 151 West 30 th Street, 11 th Floor New York, NY 10001-4017 Tel 212-244-4664 Fax 212-244-4570 TTD 212-244-3692 www.nylpi.org Special Education Fact Sheet Special
New York Lawyers For The Public Interest, Inc. 151 West 30 th Street, 11 th Floor New York, NY 10001-4017 Tel 212-244-4664 Fax 212-244-4570 TTD 212-244-3692 www.nylpi.org Special Education Fact Sheet Special
2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL)
 E10d 2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No.
E10d 2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No.
caspa Comparison and Analysis of Special Pupil Attainment
 caspa Comparison and Analysis of Special Pupil Attainment Analysis and bench-marking in CASPA This document describes of the analysis and bench-marking features in CASPA and an explanation of the analysis
caspa Comparison and Analysis of Special Pupil Attainment Analysis and bench-marking in CASPA This document describes of the analysis and bench-marking features in CASPA and an explanation of the analysis
abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
 Chief Medical Officer Directorate Chief Medical Officer and Secretariat Division abcdefghijklmnopqrstu T: 0131-244 2399 F: 0131-244 2989 E: sandra.falconer@scotland.gsi.gov.uk NHS Board Medical and Nursing
Chief Medical Officer Directorate Chief Medical Officer and Secretariat Division abcdefghijklmnopqrstu T: 0131-244 2399 F: 0131-244 2989 E: sandra.falconer@scotland.gsi.gov.uk NHS Board Medical and Nursing
Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1990, 7, 155-162 Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department GARY BELL, NICK HINDLEY, GITENDRA RAJIYAH & RACHEL ROSSER Department of Psychiatry,
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1990, 7, 155-162 Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department GARY BELL, NICK HINDLEY, GITENDRA RAJIYAH & RACHEL ROSSER Department of Psychiatry,
Waiting Times for Suspected and Diagnosed Cancer Patients
 Waiting Times for Suspected and Diagnosed Cancer Patients 2015-16 Annual Report Waiting Times for Suspected and Diagnosed Cancer Patients 1 Waiting Times for Suspected and Diagnosed Cancer Patients Prepared
Waiting Times for Suspected and Diagnosed Cancer Patients 2015-16 Annual Report Waiting Times for Suspected and Diagnosed Cancer Patients 1 Waiting Times for Suspected and Diagnosed Cancer Patients Prepared
2010 National Survey. University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
 National Cancer Patient Experience Programme 2010 National Survey University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Published January 2011 The National Cancer Patient Experience Survey Programme
National Cancer Patient Experience Programme 2010 National Survey University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Published January 2011 The National Cancer Patient Experience Survey Programme
NHS public health functions agreement
 NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis and Hib programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION
NHS public health functions agreement 2016-17 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis and Hib programme Classification: official NHS England INFORMATION
Sexual health in adolescents in the UK: What do the data show? Dr Gwenda Hughes and Dr Anthony Nardone Health Protection Services Colindale
 Sexual health in adolescents in the UK: What do the data show? Dr Gwenda Hughes and Dr Anthony Nardone Health Protection Services Colindale 30 November 2011 Overview Present data on sexual health in adolescents
Sexual health in adolescents in the UK: What do the data show? Dr Gwenda Hughes and Dr Anthony Nardone Health Protection Services Colindale 30 November 2011 Overview Present data on sexual health in adolescents
Domestic Abuse Matters: Police responders and Champions training
 Domestic Abuse Matters: Police responders and Champions training safelives.org.uk info@safelives.org.uk 0117 403 3220 1 77% 75% of First Responders felt training would help them respond to victims in a
Domestic Abuse Matters: Police responders and Champions training safelives.org.uk info@safelives.org.uk 0117 403 3220 1 77% 75% of First Responders felt training would help them respond to victims in a
APPENDIX 26: RESULTS OF SURVEY OF ANTENATAL AND POSTNATAL MENTAL HEALTH PRIMARY CARE SERVICES IN ENGLAND AND WALES
 APPENDIX 26: RESULTS OF SURVEY OF ANTENATAL AND POSTNATAL MENTAL HEALTH PRIMARY CARE SERVICES IN ENGLAND AND WALES Background In order to inform the guideline development process, the guideline development
APPENDIX 26: RESULTS OF SURVEY OF ANTENATAL AND POSTNATAL MENTAL HEALTH PRIMARY CARE SERVICES IN ENGLAND AND WALES Background In order to inform the guideline development process, the guideline development
Classification: official 1
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis, Hib and HepB programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis, Hib and HepB programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement
Sexual Health, HIV, and STDs
 Sexual Health, HIV, and STDs Richard J. Wolitski, PhD Deputy Director, Behavioral and Social Science Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention Centers for Disease Control & Prevention Fenway Institute, Boston, MA
Sexual Health, HIV, and STDs Richard J. Wolitski, PhD Deputy Director, Behavioral and Social Science Division of HIV/AIDS Prevention Centers for Disease Control & Prevention Fenway Institute, Boston, MA
Make connections, get support
 carersuk.org Make connections, get support Recognising ourselves and others as carers 02 Introduction Introduction 6.5 million people in the UK are providing unpaid care to a family member or friend, that
carersuk.org Make connections, get support Recognising ourselves and others as carers 02 Introduction Introduction 6.5 million people in the UK are providing unpaid care to a family member or friend, that
FGM, FORCED MARRIAGE AND HONOUR-BASED ABUSE THE LEGAL FRAMEWORK
 FGM, FORCED MARRIAGE AND HONOUR-BASED ABUSE THE LEGAL FRAMEWORK W O R K I N G T O G E T H E R T O P R O T E C T A N D S U P P O R T G I R L S N E E L A M S A R K A R I A V I C E - P R E S I D E N T, A
FGM, FORCED MARRIAGE AND HONOUR-BASED ABUSE THE LEGAL FRAMEWORK W O R K I N G T O G E T H E R T O P R O T E C T A N D S U P P O R T G I R L S N E E L A M S A R K A R I A V I C E - P R E S I D E N T, A
The Core Components of a Sports Physical
 Millions of American athletes - many of them teens - undergo sports physicals each year before they get into their game of choice. Also called a pre-participation examination, the sports physical may seem
Millions of American athletes - many of them teens - undergo sports physicals each year before they get into their game of choice. Also called a pre-participation examination, the sports physical may seem
28 May 2012 Reference: ENF/S/12/017
 To: Lead Food Officers Heads of Service Cc: REHIS, CoSLA, SFELC 28 May 2012 Reference: ENF/S/12/017 Dear Colleagues GUIDANCE ON THE MORATORIUM ON THE PRODUCTION AND USE OF DESINEWED MEAT FROM NON RUMINANT
To: Lead Food Officers Heads of Service Cc: REHIS, CoSLA, SFELC 28 May 2012 Reference: ENF/S/12/017 Dear Colleagues GUIDANCE ON THE MORATORIUM ON THE PRODUCTION AND USE OF DESINEWED MEAT FROM NON RUMINANT
1 Define the term stigma. [2 marks] When someone has been labelled as mentally ill, people will judge negatively on that.
![1 Define the term stigma. [2 marks] When someone has been labelled as mentally ill, people will judge negatively on that. 1 Define the term stigma. [2 marks] When someone has been labelled as mentally ill, people will judge negatively on that.](/thumbs/93/111610556.jpg) These answers have not been through the AQA approval process. 5 HEALTH Example answers AS LEVEL 1 Define the term stigma. [2 marks] When someone has been labelled as mentally ill, people will judge negatively
These answers have not been through the AQA approval process. 5 HEALTH Example answers AS LEVEL 1 Define the term stigma. [2 marks] When someone has been labelled as mentally ill, people will judge negatively
Quarterly report on sexually transmitted infections - Quarter 1, 2001
 Quarterly report on sexually transmitted infections - Quarter 1, 2001 Item type Authors Rights Report National Disease Surveillance Centre (NDSC) National Disease Surveillance Centre Downloaded 7-Jul-2018
Quarterly report on sexually transmitted infections - Quarter 1, 2001 Item type Authors Rights Report National Disease Surveillance Centre (NDSC) National Disease Surveillance Centre Downloaded 7-Jul-2018
This report summarizes the stakeholder feedback that was received through the online survey.
 vember 15, 2016 Test Result Management Preliminary Consultation Online Survey Report and Analysis Introduction: The College s current Test Results Management policy is under review. This review is being
vember 15, 2016 Test Result Management Preliminary Consultation Online Survey Report and Analysis Introduction: The College s current Test Results Management policy is under review. This review is being
Norfolk and Suffolk NHS Foundation Trust. Suicide Prevention Strategy,
 Norfolk and Suffolk NHS Foundation Trust Suicide Prevention Strategy, 2017-2022 Foreword It is likely that we will know someone, directly or indirectly, who has died by suicide. It may also be possible
Norfolk and Suffolk NHS Foundation Trust Suicide Prevention Strategy, 2017-2022 Foreword It is likely that we will know someone, directly or indirectly, who has died by suicide. It may also be possible
HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (HIV PrEP) in Scotland. An update for registered practitioners September 2017
 HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (HIV PrEP) in Scotland An update for registered practitioners September 2017 Key Messages HIV is a major public health challenge for Scotland with an annual average of 359
HIV Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (HIV PrEP) in Scotland An update for registered practitioners September 2017 Key Messages HIV is a major public health challenge for Scotland with an annual average of 359
Good Practice in Action 072 Commonly Asked Questions. Unplanned endings within the counselling professions
 Good Practice in Action 072 Commonly Asked Questions Unplanned within the counselling professions 2 Good Practice in Action 072 Commonly Asked Questions Resource Good Practice in Action 072: Commonly Asked
Good Practice in Action 072 Commonly Asked Questions Unplanned within the counselling professions 2 Good Practice in Action 072 Commonly Asked Questions Resource Good Practice in Action 072: Commonly Asked
