Downloaded by Guangxi University for Nationalities from online.liebertpub.com at 02/19/18. For personal use only. ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Berniece Hood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF CHILD AND ADOLESCENT PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY Volume 12, Number 1, 2002 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 3 9 Phenomenology of Prepubertal and Early Adolescent Bipolar Disorder: Examples of Elated Mood, Grandiose Behaviors, Decreased Need for Sleep, Racing Thoughts and Hypersexuality BARBARA GELLER, M.D., 1 BETSY ZIMERMAN, M.A., 1 MARLENE WILLIAMS, R.N., 1 MELISSA P. DELBELLO, M.D., 2 JEANNE FRAZIER, B.S.N., 1 and LINDA BERINGER, R.N. 1 ABSTRACT Objective: Children are developmentally incapable of many manifestations of bipolar symptoms described in adults (e.g., children do not max out credit cards or have four marriages). To address this issue, our group investigated prepubertal and early adolescent age equivalents of adult mania behaviors. Methods: Details of the methods appear in the companion article in this issue (Geller et al. 2002a). Subjects had a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype (PEA- BP) that was validated by reliable assessment (Geller et al. 2001b), 6-month stability (Geller et al. 2000c), and 1- and 2-year longitudinal diagnostic outcome (Geller et al. 2001a, 2002b). Results: Examples of elation, grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, racing thoughts, and hypersexuality in PEA-BP subjects were compared to examples in prepubertal normal controls and to examples in late teenage/adult-onset mania. Because it is not intuitive that children can be pathologically happy or expansive, sections on guidelines for differentiating normal versus impairing elation and grandiosity are provided. Conclusion: Due to the high comorbidity of PEA-BP and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), recognition of mania symptoms that do not overlap with those for ADHD may aid in avoiding both under- and overdiagnosis of child bipolar disorder. A discussion of how nonoverlapping with ADHD Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (4th ed.) mania symptoms can be useful in the differential diagnosis of irritability is also provided. 1Department of Psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, Missouri. 2Department of Psychiatry, University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, Ohio. This study was supported by National Institute of Mental Health Grant R01 MH to Dr. Geller. 3
2 GELLER ET AL. INTRODUCTION BOTH CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS AND INVESTIGATIONS of child bipolar disorders have been beset by substantial controversy over the differentiation of mania from attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) (Fristad et al. 1992; Geller et al. 1995, 1998a, 1998b, 2000b, 2002a). Unlike late-teenage and adult-onset bipolar disorders, in which schizophrenia was one of the main differential diagnoses (Goodwin and Jamison 1990), ADHD has been the major differential problem in prepubertal and early adolescent subjects. This child-age specific differential diagnostic problem stems from the very high prevalence of comorbid ADHD among child-onset bipolar disorder subjects and from the overlap of certain Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. (DSM-IV; American Psychiatric Association 1994) criteria for mania and ADHD (e.g., hyperactivity, distractibility) (Fristad et al. 1992; Geller et al. 1995, 1998a, 1998b, 2000c, 2002a, 2002b). Our group has addressed the issue of differentiating child-onset mania from ADHD through the use of the following definition (Geller et al. 2000a, 2000b, 2000c, 2001a, 2001b, 2002a). A prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype (PEA-BP) was defined by a current episode of DSM-IV mania/hypomania with grandiosity and/or elation as one inclusion criterion. The latter criterion was selected to ensure that subjects were not diagnosed just by criteria that overlapped with those for ADHD and that they had at least one of the two cardinal features of mania (i.e., elation and/or grandiosity). The PEA- BP has been validated by reliable assessment (Geller et al. 2001b), 6-month stability (Geller et al. 2000c) and 1- and 2-year longitudinal diagnostic outcome (Geller et al. 2001a, 2002b). An important research question in investigating PEA-BP was what were pediatric age equivalents of adult symptoms of mania (Geller et al. 1995; Geller and Luby 1997; Geller et al. 2001a). Manifestations of DSM-IV mania criteria in adults have been widely accepted for decades (Goodwin and Jamison 1990), but include behaviors that do not occur during the prepubertal and early adolescent years. For example, children will not have had four marriages and will not have maxed out credit cards. To investigate pediatric manifestations of bipolar disorders, Geller et al. (1996, 1998b, 2001b) developed an instrument specifically for research interview assessment of PEA-BP symptoms. This tool, the Washington University in St. Louis Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia (WASH-U-KSADS; Geller et al. 1996), which has been described in detail elsewhere (Geller et al. 2001b), has excellent reliability (Geller et al. 2001b) and has been validated against parent and teacher reports (Geller et al. 1998a). It is a semistructured interview given to mothers about their children and separately to children about themselves by experienced research nurses who have established interrater reliability. As noted in the recent National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) Research Roundtable on Prepubertal Bipolar Disorder (2001), the WASH-U-KSADS is used in the large majority of NIMH-funded studies of child bipolar disorders. This widespread use of the WASH-U-KSADS supports the increasing consensus on the existence of child mania and the usefulness of the WASH-U-KSADS in the assessment of child mania. To our knowledge, this is the first report of examples of DSM-IV mania symptoms in PEA-BP and of their comparison to manifestations in adults with bipolar disorder. METHODS The methodology of ascertaining and assessing the 268 participants (93 PEA-BP, 81 ADHD, and 94 normal community controls) in the ongoing Phenomenology and Course of Pediatric Bipolar Disorders study has been detailed in the companion article in this issue and elsewhere (Geller et al. 1998a, 1998b, 2000a, 2000b, 2000c, 2001a, 2001b, 2002a, 2002b). The five DSM-IV mania symptoms presented in this article are euphoric mood, grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, racing thoughts, and hypersexuality. These were selected as examples because they were excellent discriminators between PEA-BP and ADHD subjects as reported by Geller et al. (2002a) in the companion article in this issue. 4
3 PHENOMENOLOGY OF PREPUBERTAL MANIA It can be noted that the examples presented in this article were only a small part of the comprehensive diagnostic process, which included multiple informants, school and medical records, videotaped observations, and consensus conferences. These are described in the companion article and elsewhere (e.g., Geller et al. 2000a, 2000b, 2000c, 2001a, 2001b, 2002a, 2002b). Detailed instructions on how DSM-IV symptoms on the WASH-U-KSADS were rated on a severity scale appear in the WASH-U-KSADS instrument (Geller et al. 1996, 2001b). These instructions take numerous relevant factors into account (e.g., frequency, duration, context, intensity, functional impairment, occurrence in multiple settings, noticed by peers and adults). Representative, typical examples of mania symptoms were taken from WASH-U-KSADS research interviews and from other settings. Although the WASH-U-KSADS was administered to mothers about their children and to children about themselves, the examples discussed in this article are largely from the children s interviews about themselves. Examples for bipolar adults were taken from the clinical experience of the authors. Tables 1 5 were constructed to provide examples of mania symptoms in PEA-BP subjects, normal children, and bipolar adults. Because it is not intuitive that children can be pathologically happy or expansive, sections on guidelines for differentiating normal versus functionally impairing elation and grandiosity are provided. After complete description of the study to parents and children, written informed consent was obtained from parents and written assent was obtained from children. Guidelines for differentiating normal from pathological manic euphoria Normal children were extremely elated when going to Disneyland, when grandparents were visiting, and on Christmas morning. This mood was appropriate to context, expected by the adults, and nonimpairing. This can be compared to a child who was elated and giggling in the classroom, when others were not, and who got sent to the principal and suspended from school for this behavior. In this example, the elated mood was inappropriate to context and impairing and thus was pathological. This example demonstrates that the guideline for pathological elated mood was inappropriateness to context and association with impairment. Guidelines for differentiating normal expansive play from manic grandiosity Normal children were expansive and grandiose when playing. For example, a child played at being a fire fighter after school and directed the other fire fighters on what to do. Another child played at being the teacher after school and directed an imaginary group of students. In these examples, the context is appropriate (i.e., play after school hours), and the grandiose idea that they were teachers and fire fighters was developmentally expected. Because it was after school and only in an imaginary play situation, it was nonimpairing. Compare the above to a child who got up during the class and began instructing the teacher on how to educate and began telling the students what they should learn or the child who went to the principal demanding that his teacher be fired. Both of these students received school suspensions. In these examples, the grandiosity was not in play after school but was acted upon in real-life situations. It was impairing in that it disrupted the class and led to punishment. Thus, similar to pathological elated mood, pathological grandiosity is inappropriate to context and functionally impairing. RESULTS Tables 1 5 present examples for each of the five mania symptoms. Flight of ideas was also an excellent discriminator between subjects with PEA-BP and ADHD (Geller et al. 2002a), but manifestations of flight of ideas were similar to those of adults with bipolar disorder, so these were not provided in the tables. 5
4 GELLER ET AL. TABLE 1. EXAMPLES OF ELATED MOOD IN PREPUBERTAL AND EARLY ADOLESCENT BIPOLAR DISORDER SUBJECTS, NORMAL CHILDREN, AND BIPIOLAR ADULTS Child was super happy on days A 7-year-old boy was repeatedly A 40-year-old man giggled family went to Disneyland, on taken to the principal for clowning infectiously while being placed in Christmas morning, and during and giggling in class (when no one restraints in the emergency room. A grandparents visits. Child s joy else was) and was suspended from 50-year-old man in the emergency was appropriate to context. school. He had to leave church with room was infectiously amusing as he Child s behavior was not his family for similar behaviors. described multiple hospitalizations, impairing. A 9-year-old girl continually danced losing jobs, and losing family ties. around at home stating, I m high, over the mountain high after suspension from school. TABLE 2. EXAMPLES OF GRANDIOSE BEHAVIORS IN PREPUBERTAL AND EARLY ADOLESCENT BIPOLAR DISORDER SUBJECTS, NORMAL CHILDREN, AND BIPOLAR ADULTS A 7-year-old boy played at being A 7-year-old boy stole a go-cart An adult man kept his family in a fire fighter, directing other fire because he just wanted to have it, increasing debt due to multiple fighters and rescuing victims. The even though he knew stealing was unrealistic business ventures. A child was not calling the fire station wrong. He did not, however, believe 21-year-old man believed he to tell them what to do. Play was it was wrong for him to steal. When could commit a homicide and during afterschool hours; it was the police arrived, the child thought not be arrested because the age appropriate and not impairing. the officers were there to play with laws would not pertain to him. him. An 8-year-old girl opened a An 18-year-old woman rang the paper flower store in her classroom mayor s home doorbell because and was annoyed and refused to do she knew they were engaged. classwork when asked by the teacher. When asked if she had ever An 8-year-old girl, failing at school, met the mayor, she stated that spent her evenings practicing for did not matter. when she would be the first female president. She was also planning how to train her husband to be the First Gentleman. When asked how she could fail school and still be president, she said she just knew. TABLE 3. EXAMPLES OF DECREASED NEED FOR SLEEP IN PREPUBERTAL AND EARLY ADOLESCENT BIPOLAR DISORDER SUBJECTS, NORMAL CHILDREN, AND BIPOLAR ADULTS Normal children sleep approximately An 8-year-old boy chronically A 25-year-old woman worked both 8 to 10 hours a night and are tired stayed up until 2 a.m. rearranging the day and evening full-time jobs the next day if they sleep fewer furniture or playing games. Then he seemingly without fatigue. A hours than usual. awoke at 6 a.m. for school and was father described his wife as she energetic during the day without parties for days in a row and evident tiredness or fatigue. A 7-year- then sleeps for days in a row. old girl, daily, knocked on a friend s door at 6 a.m. ready to play. 6
5 PHENOMENOLOGY OF PREPUBERTAL MANIA TABLE 4. EXAMPLES OF HYPERSEXUAL BEHAVIORS IN PREPUBERTAL AND EARLY ADOLESCENT BIPOLAR DISORDER SUBJECTS, NORMAL CHILDREN, AND BIPOLAR ADULTS A 7-year-old child played doctor An 8-year-old boy imitated a rock Numerous adults who had four or with a same-aged friend. A star by gyrating his hips and more marriages not due to death of 12-year-old boy looked at his rubbing his crotch during a research spouses or who had multiple father s pornographic interview. A 9-year-old boy drew extramarital affairs. magazines. pictures of naked ladies in public, stating they were drawings of his future wife. A 14-year-old girl passed notes to boys in class asking them to f her. Another girl faxed a similar note to the local police station. A 7-year-old girl touched the teacher s breasts and propositioned boys in class. A 10-year-old boy used explicit sexual act language in restaurants and other public places. Another child called sex lines, which his parents discovered when the phone bill arrived at the end of the month. TABLE 5. EXAMPLES OF RACING THOUGHTS IN PREPUBERTAL AND EARLY ADOLESCENT BIPOLAR DISORDER SUBJECTS, NORMAL CHILDREN, AND BIPOLAR ADULTS Normal subjects did not give Unlike manic adults, children gave Adults conceptually understand affirmative responses to concrete answers to describe their racing thoughts and can describe inquiries about racing racing thoughts. Examples are: A girl them using the word racing. thoughts. pointed to the middle of her forehead and stated, I need a stoplight up there. Other children noted the following: It s like an energizer bunny in my head. Too much stuff is flying around up there. I don t know what to think first. My thoughts broke the speed limit. My thoughts broke the sound barrier of my mind. DISCUSSION Recognition of mania symptoms that do not overlap with those for ADHD may be useful to avoid both under- and overdiagnosis of child bipolar disorder. Over diagnosis may be occurring because of the complex differential diagnosis of irritability in children. The importance of the symptom of irritability was observed by Biederman (2000) and in the very popular book by Papolos and Papolos (1999). These authors noted that, in their work, irritability was the most common symptom of child mania. Some families and practitioners may have misinterpreted most common to mean that irritability was a pathognomonic symptom of mania. A comparison to strep throat may be useful to put irritability in proper perspective. Sore throat is the most common symptom of strep throat, but only 5% or fewer of children who present with a sore throat actually 7
6 GELLER ET AL. have strep throat. By analogy, only a very small percentage of children with irritability will have mania. Irritability is also a very frequent symptom and a very common reason for clinical referral in children with numerous other child psychiatric disorders (e.g., ADHD, oppositional defiant disorder, conduct disorder, autism, Asperger s syndrome). Thus, clinicians need to be watchful for potentially overdiagnosing mania in children with irritable mood but without nonoverlapping with ADHD mania symptoms. It is also useful to be mindful that co-occurring irritability and elation was very frequent in both child and adult bipolar disorder (Geller et al. 2002a; Goodwin and Jamison 1990). Underdiagnosis may occur if mania is not considered in the differential diagnosis of children who have ADHD. Data that support the occurrence of underdiagnosis were reported by Geller et al. (2002b) in a 2- year follow-up of subjects with PEA-BP who were comprehensively assessed in our research unit at 6- month intervals. These subjects received all of their treatment from their own community practitioners. Less than half had received any antimanic medication (defined as lithium, an anticonvulsant, or a neuroleptic) from their community practitioners during the 2 years. These data may reflect that community physicians recognize ADHD but do not yet recognize symptoms of child mania or do not consider mania in their differential diagnosis of ADHD. Knowledge of examples of pediatric equivalents of adult manifestations of mania can help clinicians and investigators with the differential diagnosis of irritability and of ADHD and thus help avoid over- or underdiagnosis of child mania. REFERENCES American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed. (DSM-IV). Washington (DC), American Psychiatric Association, Biederman J: Advances in the psychopharmacology of pediatric bipolar disorder and ADHD. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 10: , Fristad MA, Weller EB, Weller RA: The mania rating scale: Can it be used in children? A preliminary report. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 31: , Geller B, Sun K, Zimerman B, Luby J, Frazier J, Williams M: Complex and rapid-cycling in bipolar children and adolescents: A preliminary study. J Affect Disord 34: , Geller B, Williams M, Zimerman B, Frazier J: Washington University in St. Louis Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia (WASH-U-KSADS). St. Louis, Washington University, Geller B, Luby J: Child and adolescent bipolar disorder: A review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 36: , Geller B, Warner K, Williams M, Zimerman B: Prepubertal and young adolescent bipolarity versus ADHD: Assessment and validity using the WASH-U-KSADS, CBCL and TRF. J Affect Disord 51:93 100, 1998a. Geller B, Williams M, Zimerman B, Frazier J, Beringer L, Warner KL: Prepubertal and early adolescent bipolarity differentiate from ADHD by manic symptoms, grandiose delusions, ultrarapid or ultradian cycling. J Affect Disord 51:81 91, 1998b. Geller B, Bolhofner K, Craney JL, Williams M, DelBello MP, Gundersen K: Psychosocial functioning in a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39: , 2000a. Geller B, Zimerman B, Williams M, Bolhofner K, Craney JL, DelBello MP, Soutullo CA: Diagnostic characteristics of 93 cases of a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype by gender, puberty and comorbid ADHD. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 10: , 2000b. Geller B, Zimerman B, Williams M, Bolhofner K, Craney JL, DelBello MP, Soutullo CA: Six-month stability and outcome of a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 10: , 2000c. Geller B, Craney JL, Bolhofner K, DelBello MP, Williams M, Zimerman B: One-year recovery and relapse rates of children with a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype. Am J Psychiatry 158: , 2001a. 8
7 PHENOMENOLOGY OF PREPUBERTAL MANIA Geller B, Zimerman B, Williams M, Bolhofner K, Craney JL, DelBello M, Soutullo C: Reliability of the Washington University in St. Louis Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia (WASH-U-KSADS) mania and rapid cycling sections. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40: , 2001b. Geller B, Zimerman B, Williams M, DelBello MP, Bolhofner K, Craney JL, Frazier J, Beringer L, Nickelsburg MJ: DSM-IV mania symptoms in a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype compared to attentiondeficit hyperactive and normal controls. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 12:11 26, 2002a. Geller B, Craney JL, Bolhofner K, Nickelsburg MJ, Williams M, Zimerman B: Two year prospective follow-up of children with a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype. Am J Psychiatry 2002b (in press). Goodwin FK, Jamison KR (eds): Manic-Depressive Illness. New York, Oxford University Press, National Institute of Mental Health research roundtable on prepubertal bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40: , Papolos DF, Papolos J: The Bipolar Child: The Definitive and Reassuring Guide to Childhood s Most Misunderstood Disorder. New York, Broadway Books, Address reprint requests to: Barbara Geller, M.D. Washington University School of Medicine 660 South Euclid Avenue, Box 8134 St. Louis, MO gellerb@medicine.wustl.edu 9
CONTROVERSIES AND NEW DIRECTIONS
 BIPOLAR Introduction DISORDER IN CHILDHOOD AND EARLY ADOLESCENCE Introduction MELISSA P. D ELBELLO, DAVID AXELSON, and BARBARA GELLER CONTROVERSIES AND NEW DIRECTIONS Although the existence and diagnostic
BIPOLAR Introduction DISORDER IN CHILDHOOD AND EARLY ADOLESCENCE Introduction MELISSA P. D ELBELLO, DAVID AXELSON, and BARBARA GELLER CONTROVERSIES AND NEW DIRECTIONS Although the existence and diagnostic
Article. Two-Year Prospective Follow-Up of Children. with a prepubertal and early adolescent. Bipolar Disorder Phenotype
 Article Two-Year Prospective Follow-Up of Children With a Prepubertal and Early Adolescent Bipolar Disorder Phenotype Barbara Geller, M.D. James L. Craney, M.S., M.P.H. Kristine Bolhofner, B.S. Michael
Article Two-Year Prospective Follow-Up of Children With a Prepubertal and Early Adolescent Bipolar Disorder Phenotype Barbara Geller, M.D. James L. Craney, M.S., M.P.H. Kristine Bolhofner, B.S. Michael
APPENDIX 11: CASE IDENTIFICATION STUDY CHARACTERISTICS AND RISK OF BIAS TABLES
 APPENDIX 11: CASE IDENTIFICATION STUDY CHARACTERISTICS AND RISK OF BIAS TABLES 1 Study characteristics table... 3 2 Methodology checklist: the QUADAS-2 tool for studies of diagnostic test accuracy... 4
APPENDIX 11: CASE IDENTIFICATION STUDY CHARACTERISTICS AND RISK OF BIAS TABLES 1 Study characteristics table... 3 2 Methodology checklist: the QUADAS-2 tool for studies of diagnostic test accuracy... 4
BIPOLAR DISORDER AND ADHD IN CHILDREN
 BIPOLAR DISORDER AND ADHD IN CHILDREN BIPOLAR I DISORDER IS BEING DIAGNOSED WITH INCREASING FREQUENCY (INTENSITY) IN PRE-PUBERTAL CHIDREN WITH THE CAVEAT (WARNING / STIPULATION) THAT CLASSIC MANIC EPISODES
BIPOLAR DISORDER AND ADHD IN CHILDREN BIPOLAR I DISORDER IS BEING DIAGNOSED WITH INCREASING FREQUENCY (INTENSITY) IN PRE-PUBERTAL CHIDREN WITH THE CAVEAT (WARNING / STIPULATION) THAT CLASSIC MANIC EPISODES
Forty-Eighth Annual Teaching Conference Pediatrics for the Practitioner -UT Health Science Center San Antonio School of Medicine June 10-12, 2011
 Adelaide Robb, MD Associate Professor Psychiatry and Pediatrics Source Advisory Board Disclosure Speaker s Bureau Bristol Myers Squibb Yes Yes Yes Epocrates Research Contract Royalties Yes Stock Janssen
Adelaide Robb, MD Associate Professor Psychiatry and Pediatrics Source Advisory Board Disclosure Speaker s Bureau Bristol Myers Squibb Yes Yes Yes Epocrates Research Contract Royalties Yes Stock Janssen
CASE 5 - Toy & Klamen CASE FILES: Psychiatry
 CASE 5 - Toy & Klamen CASE FILES: Psychiatry A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being found in the basement of his home by his parents during the middle of a school day. The
CASE 5 - Toy & Klamen CASE FILES: Psychiatry A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being found in the basement of his home by his parents during the middle of a school day. The
Practice Parameter for the Assessment and Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Bipolar Disorder,
 Practice Parameter for the Assessment and Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Bipolar Disorder, Journal of the Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 1997 Primary Authors: Jon McClellan MD
Practice Parameter for the Assessment and Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Bipolar Disorder, Journal of the Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 1997 Primary Authors: Jon McClellan MD
Comprehensive Quick Reference Handout on Pediatric Bipolar Disorder By Jessica Tomasula
 Comprehensive Quick Reference Handout on Pediatric Bipolar Disorder By Jessica Tomasula Official Name Bipolar Disorder; also referred to as Manic Depression Definitions (DSM-IV-TR, 2000) Bipolar I Disorder
Comprehensive Quick Reference Handout on Pediatric Bipolar Disorder By Jessica Tomasula Official Name Bipolar Disorder; also referred to as Manic Depression Definitions (DSM-IV-TR, 2000) Bipolar I Disorder
J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2012; 8(1):1-5. Editorial
 1 J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2012; 8(1):1-5 Editorial Controversies in Paediatric Bipolar Disorder Vivek Agarwal 1, Sivakumar T 2 1.Editor JIACAM & Associate Professor, Department of
1 J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2012; 8(1):1-5 Editorial Controversies in Paediatric Bipolar Disorder Vivek Agarwal 1, Sivakumar T 2 1.Editor JIACAM & Associate Professor, Department of
Differentiating Unipolar vs Bipolar Depression in Children
 Differentiating Unipolar vs Bipolar Depression in Children Mai Uchida, M.D. Director, Center for Early Identification and Prevention of Pediatric Depression Massachusetts General Hospital Assistant Professor
Differentiating Unipolar vs Bipolar Depression in Children Mai Uchida, M.D. Director, Center for Early Identification and Prevention of Pediatric Depression Massachusetts General Hospital Assistant Professor
Mood swings in young people
 Mood swings in young people Bipolar I & II Disorders are uncommon before puberty; Mood Dysregulation (MD) is very common before puberty Are they the same problem? What are the beginnings of bipolar? What
Mood swings in young people Bipolar I & II Disorders are uncommon before puberty; Mood Dysregulation (MD) is very common before puberty Are they the same problem? What are the beginnings of bipolar? What
DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help
 DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help Introduction: The DSM5 is a foreign language! Three Questions: I. The first was, What the key assumptions made to determine the organization of the DSM5? A. Mental
DSM5: How to Understand It and How to Help Introduction: The DSM5 is a foreign language! Three Questions: I. The first was, What the key assumptions made to determine the organization of the DSM5? A. Mental
Typical or Troubled? Teen Mental Health
 Typical or Troubled? Teen Mental Health Adolescence is a difficult time for many teens, but how does one know the difference between typical teen issues and behavior that might signal a more serious problem?
Typical or Troubled? Teen Mental Health Adolescence is a difficult time for many teens, but how does one know the difference between typical teen issues and behavior that might signal a more serious problem?
Pediatric Bipolar Disorder and ADHD
 Pediatric Bipolar Disorder and ADHD Janet Wozniak, M.D. Director, Pediatric Bipolar Disorder Research Program Associate Professor Psychiatry Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Disclosures
Pediatric Bipolar Disorder and ADHD Janet Wozniak, M.D. Director, Pediatric Bipolar Disorder Research Program Associate Professor Psychiatry Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Disclosures
Brief Notes on the Mental Health of Children and Adolescents
 Brief Notes on the Mental Health of Children and Adolescents The future of our country depends on the mental health and strength of our young people. However, many children have mental health problems
Brief Notes on the Mental Health of Children and Adolescents The future of our country depends on the mental health and strength of our young people. However, many children have mental health problems
III. Anxiety Disorders Supplement
 K-SADS-PL A. Screen Interview B. Supplements I. Disorders Supplement II. Psychotic Disorders Supplement III. Anxiety Disorders Supplement IV. Disorders Supplement V. Substance Disorders Supplement Advanced
K-SADS-PL A. Screen Interview B. Supplements I. Disorders Supplement II. Psychotic Disorders Supplement III. Anxiety Disorders Supplement IV. Disorders Supplement V. Substance Disorders Supplement Advanced
Bipolar disorder in children and young people on the autism spectrum
 Exclusively sponsored by: Bipolar disorder in children and young people on the autism spectrum We are members of a multidisciplinary tertiary second opinion referral service for youth (under age 18 years)
Exclusively sponsored by: Bipolar disorder in children and young people on the autism spectrum We are members of a multidisciplinary tertiary second opinion referral service for youth (under age 18 years)
Mood disorders. Carolyn R. Fallahi, Ph. D.
 Mood disorders Carolyn R. Fallahi, Ph. D. Childhood bipolar disorder Dramatic mood swings Occur in cycles Exhilaration and agitation = mania Depression Normal mood The typical adult cycle How do children
Mood disorders Carolyn R. Fallahi, Ph. D. Childhood bipolar disorder Dramatic mood swings Occur in cycles Exhilaration and agitation = mania Depression Normal mood The typical adult cycle How do children
Practitioner Review: The assessment of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents
 Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 50:3 (2009), pp 203 215 doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01953.x Practitioner Review: The assessment of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents Argelinda Baroni,
Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 50:3 (2009), pp 203 215 doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2008.01953.x Practitioner Review: The assessment of bipolar disorder in children and adolescents Argelinda Baroni,
Presented by Bevan Gibson Southern IL Professional Development Center -Part of the Illinois Community College Board Service Center Network
 Bipolar Disorder: What It Means to You and Your Classroom Presented by Bevan Gibson Southern IL Professional Development Center -Part of the Illinois Community College Board Service Center Network Introduction
Bipolar Disorder: What It Means to You and Your Classroom Presented by Bevan Gibson Southern IL Professional Development Center -Part of the Illinois Community College Board Service Center Network Introduction
Preferred Practice Guidelines Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents
 BadgerCare Plus Preferred Practice Guidelines Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents These Guidelines are based in part on the following: American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry s Practice
BadgerCare Plus Preferred Practice Guidelines Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents These Guidelines are based in part on the following: American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry s Practice
MCPAP Clinical Conversations:
 MCPAP Clinical Conversations: After the screen: A Practical Approach to Mental Health Assessment in the Pediatric Primary Care Setting Barry Sarvet, MD Professor and Chair of Psychiatry, UMMS-Baystate
MCPAP Clinical Conversations: After the screen: A Practical Approach to Mental Health Assessment in the Pediatric Primary Care Setting Barry Sarvet, MD Professor and Chair of Psychiatry, UMMS-Baystate
Chronic irritability in youth that may be misdiagnosed as bipolar disorder. Ellen Leibenluft, M.D.
 Chronic irritability in youth that may be misdiagnosed as bipolar disorder Ellen Leibenluft, M.D. Chief, Section on Bipolar Spectrum Disorders Emotion and Development Branch National Institute of Mental
Chronic irritability in youth that may be misdiagnosed as bipolar disorder Ellen Leibenluft, M.D. Chief, Section on Bipolar Spectrum Disorders Emotion and Development Branch National Institute of Mental
The shift in nosology from the Diagnostic PROCEEDINGS FROM CHILDHOOD TO ADOLESCENCE: DIAGNOSIS AND COMORBIDITY ISSUES * Thomas J. Spencer, MD ABSTRACT
 FROM CHILDHOOD TO ADOLESCENCE: DIAGNOSIS AND COMORBIDITY ISSUES * Thomas J. Spencer, MD ABSTRACT Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) tends to manifest differently in adolescents than in children,
FROM CHILDHOOD TO ADOLESCENCE: DIAGNOSIS AND COMORBIDITY ISSUES * Thomas J. Spencer, MD ABSTRACT Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) tends to manifest differently in adolescents than in children,
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
 Walden University ScholarWorks School of Counseling Publications College of Social and Behavioral Sciences 2015 Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder Brandy L. Gilea Walden University Rachel M. O Neill
Walden University ScholarWorks School of Counseling Publications College of Social and Behavioral Sciences 2015 Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder Brandy L. Gilea Walden University Rachel M. O Neill
Early-Onset Bipolar Spectrum Disorders: Diagnostic Issues
 Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev Vol. 12(3):271-293 (2009) ISSN: (print 1096-4037)(online 1573-2827) doi: 10.1007/s10567-009-0055-2 This is a peer reviewed pre-print version of the following article: Early-Onset
Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev Vol. 12(3):271-293 (2009) ISSN: (print 1096-4037)(online 1573-2827) doi: 10.1007/s10567-009-0055-2 This is a peer reviewed pre-print version of the following article: Early-Onset
WORKING WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) OPPOSITIONAL DEFIANT DISORDER CONDUCT DISORDER
 COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US WORKING WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) OPPOSITIONAL DEFIANT DISORDER CONDUCT DISORDER WORKING WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD)
COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US WORKING WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) OPPOSITIONAL DEFIANT DISORDER CONDUCT DISORDER WORKING WITH ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD)
Differentiating MDD vs. Bipolar Depression In Youth
 Differentiating MDD vs. Bipolar Depression In Youth Mai Uchida, M.D. Staff Physician Clinical and Research Programs in Pediatric Psychopharmacology Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I
Differentiating MDD vs. Bipolar Depression In Youth Mai Uchida, M.D. Staff Physician Clinical and Research Programs in Pediatric Psychopharmacology Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I
RANZCP 2010 AUCKLAND, NEW ZEALAND
 RANZCP 2010 AUCKLAND, NEW ZEALAND Dr Veronica Stanganelli et al. RANZCP 2010 1 INTRODUCTION Bipolar disorder within young people has been debated for years. It is still controversial in DSM V (1), whether
RANZCP 2010 AUCKLAND, NEW ZEALAND Dr Veronica Stanganelli et al. RANZCP 2010 1 INTRODUCTION Bipolar disorder within young people has been debated for years. It is still controversial in DSM V (1), whether
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY
 Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Advocating for people with mental health needs and developmental disability GLOSSARY Accrued deficits: The delays or lack of development in emotional, social, academic, or behavioral skills that a child
Current. A bad boy s behavior problems CASES THAT TEST YOUR SKILLS
 Two weeks after changing medications, a hyperactive 11-year-old becomes manic and attempts suicide. Is the new regimen or an undiagnosed mental disorder to blame? A. Kenneth Fuller, MD Chief of psychiatry
Two weeks after changing medications, a hyperactive 11-year-old becomes manic and attempts suicide. Is the new regimen or an undiagnosed mental disorder to blame? A. Kenneth Fuller, MD Chief of psychiatry
For more than 100 years, extremely hyperactive
 8 W H A T W E K N O W AD/HD Predominantly Inattentive Type For more than 100 years, extremely hyperactive children have been recognized as having behavioral problems. In the 1970s, doctors recognized that
8 W H A T W E K N O W AD/HD Predominantly Inattentive Type For more than 100 years, extremely hyperactive children have been recognized as having behavioral problems. In the 1970s, doctors recognized that
Pediatric Bipolar Disorder: Advances in Diagnosis and Research
 Pediatric Bipolar Disorder: Advances in Diagnosis and Research Janet Wozniak, M.D. Associate Professor of Psychiatry Director, Pediatric Bipolar Disorder Research Program Harvard Medical School Massachusetts
Pediatric Bipolar Disorder: Advances in Diagnosis and Research Janet Wozniak, M.D. Associate Professor of Psychiatry Director, Pediatric Bipolar Disorder Research Program Harvard Medical School Massachusetts
CHILD AND ADOLESCENT ISSUES BEHAVIORAL HEALTH. SAP K-12 Bridge Training Module for Standard 4 Section 3: Behavioral Health & Observable Behaviors
 CHILD AND ADOLESCENT BEHAVIORAL HEALTH ISSUES SAP K-12 Bridge Training Module for Standard 4 Section 3: Behavioral Health & Observable Behaviors MODULE 4: SECTION 34: SECTION 3 4.b. Articulate the school
CHILD AND ADOLESCENT BEHAVIORAL HEALTH ISSUES SAP K-12 Bridge Training Module for Standard 4 Section 3: Behavioral Health & Observable Behaviors MODULE 4: SECTION 34: SECTION 3 4.b. Articulate the school
Understanding Disruptive Behaviour in Children and Helping them Cope
 Understanding Disruptive Behaviour in Children and Helping them Cope Presented by: Lauren Snailham Clinical Psychologist laurensnailham@dbnmail.co.za INTRODUCTION Disruptive Behaviour Disorders * Oppositional
Understanding Disruptive Behaviour in Children and Helping them Cope Presented by: Lauren Snailham Clinical Psychologist laurensnailham@dbnmail.co.za INTRODUCTION Disruptive Behaviour Disorders * Oppositional
Mood Disorders for Care Coordinators
 Mood Disorders for Care Coordinators David A Harrison, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Dept of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences University of Washington School of Medicine Introduction 1 of 3 Mood disorders
Mood Disorders for Care Coordinators David A Harrison, MD, PhD Assistant Professor, Dept of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences University of Washington School of Medicine Introduction 1 of 3 Mood disorders
Mental Health and Children with Additional Needs. Amanda Pryde-Jarman Highly Specialist Speech and Language Therapist
 Mental Health and Children with Additional Needs Amanda Pryde-Jarman Highly Specialist Speech and Language Therapist Role of the AHP Primarily to support the child/young person and their family Help parents/carers
Mental Health and Children with Additional Needs Amanda Pryde-Jarman Highly Specialist Speech and Language Therapist Role of the AHP Primarily to support the child/young person and their family Help parents/carers
Perspective Truth on ADHD & Medications. Thomas L. Matthews, M.D. Associate Dean of Student Affairs Professor of Psychiatry
 Perspective Truth on ADHD & Medications Thomas L. Matthews, M.D. Associate Dean of Student Affairs Professor of Psychiatry Disclosures National Institute of Health ADHD and Aggression Study Co- Investigator
Perspective Truth on ADHD & Medications Thomas L. Matthews, M.D. Associate Dean of Student Affairs Professor of Psychiatry Disclosures National Institute of Health ADHD and Aggression Study Co- Investigator
Bipolar Disorder in Child Psychiatric Practice: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Bipolar Disorder in Child Psychiatric Practice: A Case Report 1. 2, 2, * A. Tsarkov *, P. Petlovanyi 1 Chainama Hills College Hospital, Lusaka, Zambia 2 Department of Psychiatry, School of
CASE REPORT Bipolar Disorder in Child Psychiatric Practice: A Case Report 1. 2, 2, * A. Tsarkov *, P. Petlovanyi 1 Chainama Hills College Hospital, Lusaka, Zambia 2 Department of Psychiatry, School of
ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER COMORBIDITIES 23/02/2011. Oppositional Defiant Disorder
 ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER COMORBIDITIES The comorbidity of ADHD with other disorders is between 60% and 80% The most commonly comorbid disorder that occur alongside ADHD are: Oppositional
ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER COMORBIDITIES The comorbidity of ADHD with other disorders is between 60% and 80% The most commonly comorbid disorder that occur alongside ADHD are: Oppositional
Preschool Bipolar Disorder
 Preschool Bipolar Disorder Joan L. Luby, MD*, MiniTandon, DO, Andy Belden, PhD KEYWORDS Preschool Bipolar Mania Despite significant progress over the last decade in the characterization and validation
Preschool Bipolar Disorder Joan L. Luby, MD*, MiniTandon, DO, Andy Belden, PhD KEYWORDS Preschool Bipolar Mania Despite significant progress over the last decade in the characterization and validation
5 COMMON QUESTIONS WHEN TREATING DEPRESSION
 5 COMMON QUESTIONS WHEN TREATING DEPRESSION Do Antidepressants Increase the Possibility of Suicide? Will I Accidentally Induce Mania if I Prescribe an SSRI? Are Depression Medications Safe and Effective
5 COMMON QUESTIONS WHEN TREATING DEPRESSION Do Antidepressants Increase the Possibility of Suicide? Will I Accidentally Induce Mania if I Prescribe an SSRI? Are Depression Medications Safe and Effective
Aging with Bipolar Disorder. Neha Jain, MD, FAPA Assistant Professor of Psychiatry, UConn Health
 Aging with Bipolar Disorder Neha Jain, MD, FAPA Assistant Professor of Psychiatry, UConn Health Objectives Define bipolar disorder in the elderly Review comorbidities How does it differ from bipolar in
Aging with Bipolar Disorder Neha Jain, MD, FAPA Assistant Professor of Psychiatry, UConn Health Objectives Define bipolar disorder in the elderly Review comorbidities How does it differ from bipolar in
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Module 2
 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Module 2 Programmed Learning Forms Handbook The information in this training module was taken from an online article by the National Institute of Mental Health.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Module 2 Programmed Learning Forms Handbook The information in this training module was taken from an online article by the National Institute of Mental Health.
MOOD DISORDERS 101: A primer for recognizing and intervening with children with DMDD JULIE T. STECK, PH.D., HSPP CRG/CHILDREN S RESOURCE GROUP
 MOOD DISORDERS 101: A primer for recognizing and intervening with children with DMDD JULIE T. STECK, PH.D., HSPP CRG/CHILDREN S RESOURCE GROUP OBJECTIVES Participants will develop an understanding of Disruptive
MOOD DISORDERS 101: A primer for recognizing and intervening with children with DMDD JULIE T. STECK, PH.D., HSPP CRG/CHILDREN S RESOURCE GROUP OBJECTIVES Participants will develop an understanding of Disruptive
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Module 2
 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Module 2 Programmed Learning Forms Handbook The information in this training module was taken from an online article by the National Institute of Mental Health.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Module 2 Programmed Learning Forms Handbook The information in this training module was taken from an online article by the National Institute of Mental Health.
ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Date: Full Name: Date of Birth: If applicable, please complete the following: Partner s Name: Partner s Age: Partner s Occupation: IF YOU HAVE CHILDREN PLEASE LIST THEIR NAMES
ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Date: Full Name: Date of Birth: If applicable, please complete the following: Partner s Name: Partner s Age: Partner s Occupation: IF YOU HAVE CHILDREN PLEASE LIST THEIR NAMES
Jonathan Haverkampf BIPOLAR DISORDR BIPOLAR DISORDER. Dr. Jonathan Haverkampf, M.D.
 BIPOLAR DISORDER Dr., M.D. Abstract - Bipolar disorder is a condition affecting an individual s affective states (mood). The different flavors of bipolar disorder have in common that there are alterations
BIPOLAR DISORDER Dr., M.D. Abstract - Bipolar disorder is a condition affecting an individual s affective states (mood). The different flavors of bipolar disorder have in common that there are alterations
Depressive, Bipolar and Related Disorders
 Depressive, Bipolar and Related Disorders Robert Kelly, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Weill Cornell Medical College White Plains, New York Lecture available at www.robertkelly.us Financial Conflicts
Depressive, Bipolar and Related Disorders Robert Kelly, MD Assistant Professor of Psychiatry Weill Cornell Medical College White Plains, New York Lecture available at www.robertkelly.us Financial Conflicts
It's Cycling, Not Polarity Understanding and Diagnosing the Bipolar Spectrum
 It's Cycling, Not Polarity Understanding and Diagnosing the Bipolar Spectrum Session 4022: American Psychiatric Nurses Association National Conference, Louisville, KY Andrew Penn, RN, MS, NP, CNS Psychiatric
It's Cycling, Not Polarity Understanding and Diagnosing the Bipolar Spectrum Session 4022: American Psychiatric Nurses Association National Conference, Louisville, KY Andrew Penn, RN, MS, NP, CNS Psychiatric
A META-ANALYTICAL STUDY OF PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER: SYMPTOMATOLOGY AND COMORBIDITY. A Dissertation. Presented to the Faculty of
 A META-ANALYTICAL STUDY OF PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER: SYMPTOMATOLOGY AND COMORBIDITY A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of Antioch University Seattle Seattle, WA. In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
A META-ANALYTICAL STUDY OF PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER: SYMPTOMATOLOGY AND COMORBIDITY A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of Antioch University Seattle Seattle, WA. In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
Bipolar disorder and severe irritability in youth: Diagnosis and treatment. Ellen Leibenluft, M.D.
 Bipolar disorder and severe irritability in youth: Diagnosis and treatment Ellen Leibenluft, M.D. Chief, Section on Bipolar Spectrum Disorders Emotion and Development Branch National Institute of Mental
Bipolar disorder and severe irritability in youth: Diagnosis and treatment Ellen Leibenluft, M.D. Chief, Section on Bipolar Spectrum Disorders Emotion and Development Branch National Institute of Mental
ADULT INTAKE/PSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT. Name: Date: Referred by:
 ADULT INTAKE/PSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT Name: Date: Referred by: Date of Birth: SSN: Identifying Information (age, marital status, ethnicity, and sex) 1. Reason for Referral: (Why are you here? Describe problems,
ADULT INTAKE/PSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT Name: Date: Referred by: Date of Birth: SSN: Identifying Information (age, marital status, ethnicity, and sex) 1. Reason for Referral: (Why are you here? Describe problems,
Misunderstood Girls: A look at gender differences in Autism
 Misunderstood Girls: A look at gender differences in Autism By Lauren Lowry Hanen Certified SLP and Clinical Staff Writer Several years ago I worked on a diagnostic assessment team. I remember the first
Misunderstood Girls: A look at gender differences in Autism By Lauren Lowry Hanen Certified SLP and Clinical Staff Writer Several years ago I worked on a diagnostic assessment team. I remember the first
A. The Broad Continuum of Attention Problems
 A. The Broad Continuum of Attention Problems 3 Facts Sheets: (1) Developmental Variations (2) Problems (3) Disorders The American Academy of Pediatrics has produced a manual for primary care providers
A. The Broad Continuum of Attention Problems 3 Facts Sheets: (1) Developmental Variations (2) Problems (3) Disorders The American Academy of Pediatrics has produced a manual for primary care providers
Your journal: how can it help you?
 Journal Your journal: how can it help you? By monitoring your mood along with other symptoms like sleep, you and your treatment team will be better able to follow the evolution of your symptoms and therefore
Journal Your journal: how can it help you? By monitoring your mood along with other symptoms like sleep, you and your treatment team will be better able to follow the evolution of your symptoms and therefore
Severe Mood Dysregulation in Children and Adolescents Research Findings Support Diagnostic Validity of Pediatric Bipolar Disorder
 Severe Mood Dysregulation in Children and Adolescents Research Findings Support Diagnostic Validity of Pediatric Bipolar Disorder Janet Wozniak, M.D. Associate Professor of Psychiatry Director, Pediatric
Severe Mood Dysregulation in Children and Adolescents Research Findings Support Diagnostic Validity of Pediatric Bipolar Disorder Janet Wozniak, M.D. Associate Professor of Psychiatry Director, Pediatric
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 April 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014 April ; 53(4): 408 416. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2013.12.026. Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014 April ; 53(4): 408 416. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2013.12.026. Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
#CHAIR2016. September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL. Sponsored by
 #CHAIR2016 September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL Sponsored by Pediatric Bipolar Disorder: Diagnosis and Management Karen Dineen Wagner, MD, PhD University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston,
#CHAIR2016 September 15 17, 2016 The Biltmore Hotel Miami, FL Sponsored by Pediatric Bipolar Disorder: Diagnosis and Management Karen Dineen Wagner, MD, PhD University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston,
Class Objectives 10/19/2009. Chapter 5 Mood Disorders. Depressive Disorders. What are Unipolar Mood Disorders?
 Chapter 5 Mood Disorders Class Objectives Depressive Disorders What are Mood Disorders? What is Major Depressive Disorder? What is Post Partum Disorder? What are Unipolar Mood Disorders? What is Mania?
Chapter 5 Mood Disorders Class Objectives Depressive Disorders What are Mood Disorders? What is Major Depressive Disorder? What is Post Partum Disorder? What are Unipolar Mood Disorders? What is Mania?
BIPOLAR DISORDER IN CHILDREN: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE KRISTY BAYNTON. A Final Project Submitted to the
 BIPOLAR DISORDER IN CHILDREN: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE BY KRISTY BAYNTON A Final Project Submitted to the Campus Alberta Applied Psychology: Counselling Initiative In partial fulfillment of the requirements
BIPOLAR DISORDER IN CHILDREN: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE BY KRISTY BAYNTON A Final Project Submitted to the Campus Alberta Applied Psychology: Counselling Initiative In partial fulfillment of the requirements
SECTION 1. Children and Adolescents with Depressive Disorder: Summary of Findings. from the Literature and Clinical Consultation in Ontario
 SECTION 1 Children and Adolescents with Depressive Disorder: Summary of Findings from the Literature and Clinical Consultation in Ontario Children's Mental Health Ontario Children and Adolescents with
SECTION 1 Children and Adolescents with Depressive Disorder: Summary of Findings from the Literature and Clinical Consultation in Ontario Children's Mental Health Ontario Children and Adolescents with
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder How to manage these disorganized and inattentive children.
 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder How to manage these disorganized and inattentive children. One of the leading authorities on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Russell Barkley, PhD., defines
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder How to manage these disorganized and inattentive children. One of the leading authorities on Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Russell Barkley, PhD., defines
COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US
 COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US Individual Planning: A Treatment Plan Overview for with Individuals Hypomania and Mania in Bipolar Disorder Control Problems. Individual Planning: A Treatment Plan Overview
COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US Individual Planning: A Treatment Plan Overview for with Individuals Hypomania and Mania in Bipolar Disorder Control Problems. Individual Planning: A Treatment Plan Overview
A Closer Examination of Bipolar Disorder in School Age Children
 University of Lethbridge Research Repository OPUS Faculty Research and Publications http://opus.uleth.ca Bernes, Kerry 2005 A Closer Examination of Bipolar Disorder in School Age Children Bernes, Kerry
University of Lethbridge Research Repository OPUS Faculty Research and Publications http://opus.uleth.ca Bernes, Kerry 2005 A Closer Examination of Bipolar Disorder in School Age Children Bernes, Kerry
PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER
 PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER Swapna Deshpande, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Associate Training Director, Child/Adolescent Fellowship Program Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences University of
PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER Swapna Deshpande, MD Clinical Assistant Professor Associate Training Director, Child/Adolescent Fellowship Program Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences University of
The CBCL predicts DSM bipolar disorder in children: a receiver operating characteristic curve analysis
 Bipolar Disorders 2005: 7: 518 524 Copyright ª Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 BIPOLAR DISORDERS Original Article The CBCL predicts DSM bipolar disorder in children: a receiver operating characteristic curve
Bipolar Disorders 2005: 7: 518 524 Copyright ª Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 BIPOLAR DISORDERS Original Article The CBCL predicts DSM bipolar disorder in children: a receiver operating characteristic curve
2. Conduct Disorder encompasses a less serious disregard for societal norms than Oppositional Defiant Disorder.
 COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US Print Test 1. Conduct Disorder is a psychiatric disorder of childhood and adolescence that is characterized by a persistent disregard for societal norms and rules, as
COURSES ARTICLE - THERAPYTOOLS.US Print Test 1. Conduct Disorder is a psychiatric disorder of childhood and adolescence that is characterized by a persistent disregard for societal norms and rules, as
Screening for Depression and Suicide
 Screening for Depression and Suicide Christa Smith, PsyD Western Interstate Commission for Higher Education Boulder, Colorado 10/2/2008 Background My background A word about language Today stopics Why
Screening for Depression and Suicide Christa Smith, PsyD Western Interstate Commission for Higher Education Boulder, Colorado 10/2/2008 Background My background A word about language Today stopics Why
Differentiating the irritable, oppositional child with attentiondeficit/hyperactivity
 Audio at CurrentPsychiatry.com Dr. Baum: What to do when parents don t agree with your diagnosis Clinical characteristics, rating scales, nomograms help guide diagnosis Rebecca Baum, MD Clinical Assistant
Audio at CurrentPsychiatry.com Dr. Baum: What to do when parents don t agree with your diagnosis Clinical characteristics, rating scales, nomograms help guide diagnosis Rebecca Baum, MD Clinical Assistant
DIAN KUANG 馬 萬. Giovanni Maciocia
 DIAN KUANG 癫狂 馬 萬 Giovanni Maciocia 里 BIPOLAR DISORDER (MANIC-DEPRESSION) DIAN Qi and Phlegm stagnating Heart and Spleen deficiency with Phlegm Qi deficiency with Phlegm KUANG Phlegm-Fire harassing upwards
DIAN KUANG 癫狂 馬 萬 Giovanni Maciocia 里 BIPOLAR DISORDER (MANIC-DEPRESSION) DIAN Qi and Phlegm stagnating Heart and Spleen deficiency with Phlegm Qi deficiency with Phlegm KUANG Phlegm-Fire harassing upwards
Increasing rates of depression
 Increasing rates of depression Rates of depression have increased 10-20 times compared to 50 years ago. The average age of a person experiencing depression has gone down. Seligman identifies three causes
Increasing rates of depression Rates of depression have increased 10-20 times compared to 50 years ago. The average age of a person experiencing depression has gone down. Seligman identifies three causes
Mood Disorders. Moderate depression that will go away without therapy. Restlessness, inability to concentrate, and rapid speech. Dysthymic Disorder
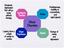 Moderate depression that will go away without therapy Dysthymic Disorder Mania Restlessness, inability to concentrate, and rapid speech Mood Disorders Lasting from a couple of weeks to months Major Depression
Moderate depression that will go away without therapy Dysthymic Disorder Mania Restlessness, inability to concentrate, and rapid speech Mood Disorders Lasting from a couple of weeks to months Major Depression
5/16/2018. Pediatric Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Do you get it?
 Pediatric Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Do you get it? Mashelle Jansen, DNP, FNP BC Clinical Assistant Professor SUNY Upstate Medical University ADHD is a Commonly diagnosed Childhood Neurodevelopmental
Pediatric Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: Do you get it? Mashelle Jansen, DNP, FNP BC Clinical Assistant Professor SUNY Upstate Medical University ADHD is a Commonly diagnosed Childhood Neurodevelopmental
READY. Book. CURRICULUM ASSOCIATES, Inc. A Quick-Study Program TEST
 A Quick-Study Program TEST Book 6 READY LONGER READING PASSAGES READY Reviews Key Concepts in Reading Comprehension Provides Practice Answering a Variety of Comprehension Questions Develops Test-Taking
A Quick-Study Program TEST Book 6 READY LONGER READING PASSAGES READY Reviews Key Concepts in Reading Comprehension Provides Practice Answering a Variety of Comprehension Questions Develops Test-Taking
Overview. Classification, Assessment, and Treatment of Childhood Disorders. Criteria for a Good Classification System
 Classification, Assessment, and Treatment of Childhood Disorders Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Overview Classification: Identifying major categories or dimensions of behavioral disorders Diagnosis:
Classification, Assessment, and Treatment of Childhood Disorders Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos Overview Classification: Identifying major categories or dimensions of behavioral disorders Diagnosis:
2018 Texas Focus: On the Move! Let s Talk: Starting the Mental Health Conversation with Your Teen Saturday, March 3, :45-11:15 AM
 Texas School for the Blind & Visually Impaired Outreach Programs www.tsbvi.edu 512-454-8631 1100 W. 45 th St. Austin, TX 78756 2018 Texas Focus: On the Move! Let s Talk: Starting the Mental Health Conversation
Texas School for the Blind & Visually Impaired Outreach Programs www.tsbvi.edu 512-454-8631 1100 W. 45 th St. Austin, TX 78756 2018 Texas Focus: On the Move! Let s Talk: Starting the Mental Health Conversation
ADHD and Behavioural Paediatrics. Dr Tsui Kwing Wan Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine Alice Ho Miu Ling Nethersole Hospital
 ADHD and Behavioural Paediatrics Dr Tsui Kwing Wan Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine Alice Ho Miu Ling Nethersole Hospital DSM V Diagnostic Criteria Inattention and/or Hyperactivity impulsivity
ADHD and Behavioural Paediatrics Dr Tsui Kwing Wan Department of Paediatrics and Adolescent Medicine Alice Ho Miu Ling Nethersole Hospital DSM V Diagnostic Criteria Inattention and/or Hyperactivity impulsivity
Paediatric Bipolar Disorder & Transitions to adult services. Adi Sharma on behalf of ABS
 Paediatric Bipolar Disorder & Transitions to adult services Adi Sharma on behalf of ABS Talk Paediatric Bipolar Disorder [PBD]: Why bother DMDD Comorbidity and/or Differential Diagnoses: EUPD, ADHD & ASD
Paediatric Bipolar Disorder & Transitions to adult services Adi Sharma on behalf of ABS Talk Paediatric Bipolar Disorder [PBD]: Why bother DMDD Comorbidity and/or Differential Diagnoses: EUPD, ADHD & ASD
23/06/2015. Absolutely none!!
 Absolutely none!! Child and adolescent Mental Health can we help? Dr Tina Nicholson CCFP Family Practitioner and Medical Lead, Cochrane Clinical Lecturer Dept Family Med. U of C. Member of CanReach Faculty
Absolutely none!! Child and adolescent Mental Health can we help? Dr Tina Nicholson CCFP Family Practitioner and Medical Lead, Cochrane Clinical Lecturer Dept Family Med. U of C. Member of CanReach Faculty
Running head: LARS AND THE REAL GIRL: AN ASSESSEMENT 1
 Running head: LARS AND THE REAL GIRL: AN ASSESSEMENT 1 Lars and the Real Girl: An Assessment Kayla Jackson University of Missouri LARS AND THE REAL GIRL: AN ASSESSMENT 2 Lars and the Real Girl: An Assessment
Running head: LARS AND THE REAL GIRL: AN ASSESSEMENT 1 Lars and the Real Girl: An Assessment Kayla Jackson University of Missouri LARS AND THE REAL GIRL: AN ASSESSMENT 2 Lars and the Real Girl: An Assessment
Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders
 Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders Introduction Attention deficit and disruptive behavior disorders are commonly known as child behavior disorders. A child behavior disorder is when a
Attention Deficit and Disruptive Behavior Disorders Introduction Attention deficit and disruptive behavior disorders are commonly known as child behavior disorders. A child behavior disorder is when a
Introduction. PMDC Team
 Best Practices for Outpatient Program in Bipolar Disorder: Pediatric Mood Disorders Program at the University of Illinois at Chicago Julie A. Carbray PhD, PMHN-CNS Introduction five fold increase in diagnosis
Best Practices for Outpatient Program in Bipolar Disorder: Pediatric Mood Disorders Program at the University of Illinois at Chicago Julie A. Carbray PhD, PMHN-CNS Introduction five fold increase in diagnosis
SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION
 Risk factors for the development and outcome of childhood psychopathology SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION Chapter 147 In this chapter I present a summary of the results of the studies described in this thesis followed
Risk factors for the development and outcome of childhood psychopathology SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION Chapter 147 In this chapter I present a summary of the results of the studies described in this thesis followed
Mood lability and psychopathology in youth
 Psychological Medicine (2009), 39, 1237 1245. f 2008 Cambridge University Press ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:10.1017/s0033291708004662 Printed in the United Kingdom Mood lability and psychopathology in youth A.
Psychological Medicine (2009), 39, 1237 1245. f 2008 Cambridge University Press ORIGINAL ARTICLE doi:10.1017/s0033291708004662 Printed in the United Kingdom Mood lability and psychopathology in youth A.
Current concepts in the validity, diagnosis and treatment of paediatric bipolar disorder
 International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (2003), 6, 293 300. Copyright f 2003 CINP DOI: 10.1017/S1461145703003547 Current concepts in the validity, diagnosis and treatment of paediatric bipolar
International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (2003), 6, 293 300. Copyright f 2003 CINP DOI: 10.1017/S1461145703003547 Current concepts in the validity, diagnosis and treatment of paediatric bipolar
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Introduction. Introduction 9/10/ % of US suffers from Mood Disorders
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 17 Mood Disorders Introduction 12% of US suffers from Mood Disorders MD are a group of psychiatric DO characterized by physical, emotional
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 17 Mood Disorders Introduction 12% of US suffers from Mood Disorders MD are a group of psychiatric DO characterized by physical, emotional
With additional support from Florida International University and The Children s Trust.
 The Society for Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology (SCCAP): Initiative for Dissemination of Evidence-based Treatments for Childhood and Adolescent Mental Health Problems With additional support from
The Society for Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology (SCCAP): Initiative for Dissemination of Evidence-based Treatments for Childhood and Adolescent Mental Health Problems With additional support from
Mental Health Strategy. Easy Read
 Mental Health Strategy Easy Read Mental Health Strategy Easy Read The Scottish Government, Edinburgh 2012 Crown copyright 2012 You may re-use this information (excluding logos and images) free of charge
Mental Health Strategy Easy Read Mental Health Strategy Easy Read The Scottish Government, Edinburgh 2012 Crown copyright 2012 You may re-use this information (excluding logos and images) free of charge
CHILD / ADOLESCENT HISTORY
 CHILD / ADOLESCENT HISTORY PERSON FILLING OUT THIS FORM DATE PATIENT NAME: DATE OF BIRTH AGE APPOINTMENT DATE: HOME TELEPHONE: MOTHER NAME: _ OCCUPATION WK TEL FATHER NAME: OCCUPATION _ WK TEL YOU ARE
CHILD / ADOLESCENT HISTORY PERSON FILLING OUT THIS FORM DATE PATIENT NAME: DATE OF BIRTH AGE APPOINTMENT DATE: HOME TELEPHONE: MOTHER NAME: _ OCCUPATION WK TEL FATHER NAME: OCCUPATION _ WK TEL YOU ARE
Childhood Anxiety Disorders
 Childhood Anxiety Disorders Check-Lists and Descriptions for 5 Anxiety Disorders: Separation Anxiety Disorder Social Phobia Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Specific Phobia Generalized Anxiety Disorder Gregory
Childhood Anxiety Disorders Check-Lists and Descriptions for 5 Anxiety Disorders: Separation Anxiety Disorder Social Phobia Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Specific Phobia Generalized Anxiety Disorder Gregory
Bipolar Disorder in Children and Teens
 Bipolar Disorder in Children and Teens Does your child go through intense mood changes? Does your child have extreme behavior changes? Does your child get much more excited and active than other kids his
Bipolar Disorder in Children and Teens Does your child go through intense mood changes? Does your child have extreme behavior changes? Does your child get much more excited and active than other kids his
The Practitioner Scholar: Journal of Counseling and Professional Psychology 84 Volume 2, 2013
 The Practitioner Scholar: Journal of Counseling and Professional Psychology 84 Volume 2, 2013 The Addition of Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder to DSM-5: Differential Diagnosis and Case Examples Robert
The Practitioner Scholar: Journal of Counseling and Professional Psychology 84 Volume 2, 2013 The Addition of Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder to DSM-5: Differential Diagnosis and Case Examples Robert
Substance Abusing Man with Bipolar Disorder & ADHD. Dr. Abdel-Moneim Abdel-Hakam Senior Consultant Psychiatry Department HMC
 Substance Abusing Man with Bipolar Disorder & ADHD Dr. Abdel-Moneim Abdel-Hakam Senior Consultant Psychiatry Department HMC Introduction Adam is a 25 year old, single, white, man who is referred after
Substance Abusing Man with Bipolar Disorder & ADHD Dr. Abdel-Moneim Abdel-Hakam Senior Consultant Psychiatry Department HMC Introduction Adam is a 25 year old, single, white, man who is referred after
AMPS : A Quick, Effective Approach To The Primary Care Psychiatric Interview
 AMPS : A Quick, Effective Approach To The Primary Care Psychiatric Interview February 7, 2012 Robert McCarron, D.O. Assosicate Clinical Professor Internal Medicine / Psychiatry / Pain Medicine UC Davis,
AMPS : A Quick, Effective Approach To The Primary Care Psychiatric Interview February 7, 2012 Robert McCarron, D.O. Assosicate Clinical Professor Internal Medicine / Psychiatry / Pain Medicine UC Davis,
Analysis of Angelhead
 Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2011 Analysis of Angelhead Jennifer Ivy Parkland College Recommended Citation Ivy, Jennifer, "Analysis of Angelhead" (2011). A with Honors Projects.
Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2011 Analysis of Angelhead Jennifer Ivy Parkland College Recommended Citation Ivy, Jennifer, "Analysis of Angelhead" (2011). A with Honors Projects.
The Increase of Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents
 Providence College DigitalCommons@Providence Social Work Theses Social Work 5-6-2008 The Increase of Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents Kristen Wroblewski Providence College, wroblenski.kristen@gmail.com
Providence College DigitalCommons@Providence Social Work Theses Social Work 5-6-2008 The Increase of Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents Kristen Wroblewski Providence College, wroblenski.kristen@gmail.com
BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW Ken Tellerman M.D.
 BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW Ken Tellerman M.D. Name: Age: Birthdate: Date of Evaluation: School: Grade: Number of classmates Informant(s): Counseling Time: What are your major concerns? BEHAVIORAL INVENTORY:
BEHAVIORAL INTERVIEW Ken Tellerman M.D. Name: Age: Birthdate: Date of Evaluation: School: Grade: Number of classmates Informant(s): Counseling Time: What are your major concerns? BEHAVIORAL INVENTORY:
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER IN A COMMERCIALLY INSURED POPULATION. Stacie B. Dusetzina
 DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER IN A COMMERCIALLY INSURED POPULATION Stacie B. Dusetzina A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF PEDIATRIC BIPOLAR DISORDER IN A COMMERCIALLY INSURED POPULATION Stacie B. Dusetzina A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Autism Spectrum. Mental Health Issues. A guidebook for mental health professionals
 Autism Spectrum & Disorder Mental Health Issues A guidebook for mental health professionals Introduction to Autism & Mental Health This guide has been developed to provide mental health professionals with
Autism Spectrum & Disorder Mental Health Issues A guidebook for mental health professionals Introduction to Autism & Mental Health This guide has been developed to provide mental health professionals with
