RECEPTORS: RELEVANCE TO ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUGS
|
|
|
- Wesley Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Indian Journal of Pharmacology 2000; 32: EDUCATIONAL FORUM AND 5HT 2 RECEPTORS: RELEVANCE TO ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUGS Department of Pharmacology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh Manuscript Received: Revised: Accepted: SUMMARY The dopamine antagonism of antipsychotic drugs and their ability to upregulate striatal sites are the corner-stones of the dopaminergic hypothesis of schizophrenia. The question of the role of in schizophrenia, however, has been reopened by the development of clozapine, which, while being the best known antipsychotic medication has low affinity for most subtypes of class. To explain this atypical action of clozapine, involvement of many other subtypes namely 5-HT 2,, D 5 and D 4 has been postulated. However, most studies hitherto, have not been able to demonstrate any direct involvement of these other subtypes in the action of atypical antipsychotics. The most popular theory to explain the atypical nature of the newer antipsychotics is, their selectivity for the dopamine in limbic area, as compared to the nigrostriatal area of the CNS. Thus, measurements still provide the best predictor of antipsychotic response, extrapyramidal side effects and elevation of prolactin levels. KEY WORDS, 5-HT 2, atypical antipsychotics Introduction Modern pharmacological treatment for schizophrenia began in 1950s with the identification of chlorpromazine's specific antipsychotic action. The hypothesis that the mechanism of antipsychotic action in schizophrenia is mediated by dopamine blockade, has been consistently supported by subsequent research 1,2. Every known antipsychotic blocks dopamine 3. While this does not prove a causal relationship between blockade and antipsychotic response, the association between the two is undeniable 3. The serotonergic hypothesis of schizophrenia preceded the better-known dopaminergic hypothesis. Following Gaddum s demonstration in 1953 that LSD, a hallucinogenic drug, had affinity for serotonin, several lines of evidence suggested a role for serotonin in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia 4-6. However, the development of effective antipsychotic drugs that were antagonists at dopamine led to a greater focus on and investigation of the dopamine system 7. With the success of clozapine, an atypical antipsychotic, interest in the role of serotonin in schizophrenia has been renewed. The serotonergic hypothesis is best viewed as complementary to the dopaminergic hypothesis, rather than an alternative to it, since these systems are anatomically connected and functionally interactive 8,9. Several authors have proposed that the atypical antipsychotics derive their unique efficacy at least partly from their dual serotonin and dopamine antagonism, exploiting the neurochemical interaction between these two systems 8,10. Atypical antipsychotic agents confer many advantages like: a lack of extrapyramidal side effects, better treatment of negative symptoms of schizophrenia and treatment of resistant cases. Therefore, differentiation of the mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotics from that of classical neuroleptics may provide guidelines for the development of new antipsychotic drugs and for clarification of the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Regulation of by antipsychotic drugs Farde and colleagues 11 proposed that one needs a Correspondence: P. Pandhi
2 , 5HT 2 RECEPTORS AND ANTIPSYCHOTICS 188 threshold of to induce antipsychotic response. Prospective studies have largely confirmed this notion, although it is unclear whether this threshold is 60% or 70% and whether the threshold for inducing response is the same as for maintaining it 12,13. Nonetheless, there is a mechanism of antipsychotic response that relies on alone 14. Further more, it has been noted that as increases, especially as it rises above 80%, the incidence of extrapyramidal side effects increases 11. Elevation of prolactin levels may also show a threshold relationship with respect to 15,16. While may be necessary for response, it is not always sufficient, as there are patients who do not respond despite adequate 17. However, it would be fair to claim that provides a reliable (and perhaps the best) pharmacological predictor of response to antipsychotic medication, extrapyramidal side effects, and elevation of prolactin levels. There are now several antipsychotics that have a lower propensity than typical antipsychotics to cause extrapyramidal side effects and prolactin elevation: clozapine, risperidone, olanzapine, sertindole and quetiapine 9,10,18,19. Given the relevance of for response to antipsychotics, extrapyramidal side effects and prolactin elevation, it is of obvious interest how these antipsychotics compare on this index. Various groups have reported that 6mg/day of risperidone led to 75% to 80%, 10 mg/ day of olanzapine showed an of 66% to 75% while clozapine in therapeutic doses showed an of 30-60% 3,20,21,22. The threshold for antipsychotic response lies in the range of 65%- 70% 14,23. It is interesting, then, that both risperidone and olanzapine become effective antipsychotics only at doses which cross these levels of. Doses of risperidone and olanzapine that do not reach these levels (i.e. <2 mg/day of risperidone and <10mg/day of olanzapine) are not reliably antipsychotic in most clinical situations 3. Clozapine, on the other hand, is able to obtain, an antipsychotic response with levels of (usually 30-60%) that would be insufficient to cause antipsychotic response by themselves 14. Thus, clozapine does not call on the typical mechanism for inducing antipsychotic response; risperidone and olanzapine do. This raises the possibility that despite some similarities in their profile in vitro, the fundamental mechanism of response of clozapine may be different from that of olanzapine and risperidone in patients. While this question can ultimately be resolved in a clinical arena in crossover studies, the data on provides a rationale for why patients who do not respond to risperidone/olanzapine may respond to clozapine and the other way round. Mechanism of lack of extra-pyramidal side effects The most popular hypothesis to explain the lack of extrapyramidal side effects by atypical antipsychotics, is the selective brain action of these agents 19. It is believed that atypical agents (clozapine, sertindole etc.,) demonstrate not only antagonism but also a selective ability to act on cortical dopamine neurons in comparison to nigrostriatal neurons 24. This idea stems from the fact that atypical agents like clozapine and olanzapine uniquely up-regulate dopamine mrnas in the prefrontal and temporal regions of the cerebral cortex but not in the nigrostriatal pathways 24. Typical neuroleptic agents uniformly upregulate dopamine mrna in both the regions 24. These findings lead to the hypothesis that interaction with cortical may be a common site of therapeutic activity of drugs effective in the treatment of schizophrenia 25. This is further supported by the fact that treatment with antagonist but non neuroleptic tiapride 26, produces much less impact on the dopamine mrna s in the cerebral cortex than in the striatum 24. An alternative hypothesis to explain the lack of extrapyramidal side effects of atypical agents was put forward by Deutch et al 27, according to which, interaction with distinct isoforms of the may differentiate atypical from typical antipsychotic drugs. Further research however clearly demonstrate that chronic treatment with all the antipsychotic agents including clozapine, produce similar regulatory effects on both -long isoform -short isoform dopamine 24. Regulation of the D 4 dopamine by antipsychotic drugs Particular attention has recently been paid to the D 4 subtype of the class as a possible candidate for the major dopaminergic site affected in schizophrenia 28,29. This assumption is, in part, based
3 189 on the observation that clozapine has a high affinity for this 28,29. Although treatments with several typical and atypical antipsychotic agents up-regulated D 4 mrnas in both the cerebral cortex and the striatum, treatments with other typical and atypical drugs had no significant effect on the D 4 in either cortical and striatal tissue 30,31. Further more, the non neuroleptic tiapride produces a statistically significant up-regulation of cortical and striatal D 4 mrna 24. These observations thus indicate that the interaction with D 4 neither confers the atypical profile nor is necessarily relevant for the antipsychotic effectiveness of the drugs. A critical role for D 4 in normal brain activity has also been challenged by the observation that 1 in 500 Germans and 4 in 100 Afro-caribbeans who completely lack functional D 4 due to gene mutation 32,33 appear to have no detectable psychiatric abnormalities. These various findings suggest that ligands directed exclusively at D 4 sites may not be particularly effective as antipsychotic agents. A recently conducted placebo controlled study to see the effect of D 4 /5HT 2A antagonist fananserin does not support the role of D 4 in schizophrenia 44. The possibililty could not be excluded, however, that action at the D 4 that are embedded in the same integrated cortical circuits as the subtype could achieve comparable clinical results by acting through adjuvant mechanisms. interaction Contrary to their effect on, typical and atypical antipsychotic agents have down-regulatory effect on the and D 5 subtypes of dopamine 24. In addition, a recent positron emission tomography imaging study has shown that the in the prefrontal cortex is down-regulated in never-medicated schizophrenic patients compared with control (normal) subjects and further is correlated with poor performance on the Wisconsin Card Sort Test of prefrontal function 34. In light of these several findings, it appears that the therapeutic effects of antipsychotics may be related to the upregulation of in the cortex, whereas, the obligatory -downregulation produced by prolonged treatment with the same drugs may be hindering in alleviation of negative and cognitive symptomatology because they may exacerbate an endogenous insufficiency. Regulation of 5HT 2 by antipsychotic agents It has been suggested that drugs may demonstrate atypical clinical features (i.e. less extrapyramidal side effects and prolactin elevation) if they have at least a 10 times higher affinity for serotonin 5HT 2 than in vitro 35,36. In patients this translates into a preferential of 5HT 2 as opposed to 37. Risperidone has better efficacy than conventional antipsychotics against the negative symptoms and cognitive deficits of schizophrenia; these effects have been attributed to high 5HT 2A 12. Clozapine, risperidone and olanzapine all show a higher affinity for 5HT 2 than in vitro but the amount by which 5HT 2 exceeds is unclear. In animal tissues or cloned human, clozapine shows a much higher 5HT 2 / ratio (20 times higher affinity for 5-HT 2 than for ) compared to either risperidone (11 times) or olanzapine (12 times) 38. On the other hand, measurements in rats following subcutaneous injection showed that risperidone had the highest 5HT 2 / affinity ratio (19 times) as compared with clozapine (5.1 times) and olanzapine (7.5 times) 38. Dose of a drug is a central determinant of its, and any systemic comparison across drugs must compare not just the but also the dose- relationships over the clinically relevant dose range 39. Comparing the doses at which clozapine, risperidone and olanzapine saturate the 5HT 2, it was shown by Kapur et al 3., that all the three drugs saturate the 5HT 2 at subtherapeutic doses, suggesting that 5HT 2 alone is an unlikely explanation for their antipsychotic effects. Moreover, the fact that one continues to see an increasing response to clozapine in doses upto mg/day 40, even after saturating the 5HT 2, makes it unlikely that 5HT 2 is the primary source of the antipsychotic effect of clozapine. A similar conclusion was reached by Trichard et al 41 in the study of chlorpromazine and clozapine. It does not rule out the possibility however, that high levels of 5HT 2 blockade may modulate or enhance the ability of blockade to induce or to delay the related side effects 36,37. However, any benefit provided by a mixed 5-HT 2 / model must express itself in a narrow range. Patients
4 , 5HT 2 RECEPTORS AND ANTIPSYCHOTICS 190 taking risperidone and olanzapine, who have high occupancies, experience extrapyramidal side effects and prolactin elevation despite a concomitantly high 5-HT 2 42,43. Conclusion The dopamine antagonism of antipsychotic drugs and their ability to upregulate striatal sites are the cornerstones of the dopaminergic hypothesis of schizophrenia 1,2. It is widely accepted that provides a reliable pharmacological predictor of response to antipsychotic medication, extrapyramidal side effects and elevation of prolactin levels. Lack of extrapyramidal side effects by atypical antipsychotic agents is believed to be due to selective brain action. It has been demonstrated that in contrast to typical agents, these drugs act selectively on the limbic dopaminergic neurons and not on nigrostriatal neurons 19,24. Other implicated in the response to antipsychotic drugs include the 5HT 2, and D 4. Most recent observations, however, have failed to show any direct role for these in the pharmacological response 24,31,32,40,41. They probably have a modulatory and an indirect role, if any. REFERENCES 1. Snyder SH. The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: Focus on dopamine. Am J Psych 1976;133: Meltzer HY, Stahi SM. The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia : A review. Schizophr Bull 1976;2: Kapur S, Zipursky RB, Remington G. Clinical and theoretical implications of 5-5HT 2 of clozapine, risperidone and olanzapine in schizophrenia. Am J Psych 1999;156: Breier A. Serotonin, schizophrenia and antipsychotic drug action. Schizophr Res 1995;14: Iqbal N, Van Praag HM. The role of serotonin in schizophrenia. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1995;5: Lewis R, Kapur S, Jones C, Dasilva J, Gregory MB, et al. Serotonin 5HT 2 in schizophrenia. A PET study using [ 18 F] setoperone in neuroleptic-naïve patients and normal subjects. Am J Psych 1999;156: Seeman P, Lee T, Chau-Wong M, Wong K. Antipsychotic drug doses and neuroleptic/dopamine. Nature 976;261: Kapur S, Remington G. Serotonin-dopamine interaction and its relevance to schizophrenia. Am J Psych 1996; 153: Ohuoha DC, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE. The role of serotonin in schizophrenia : an overview of the nomenclature, distribution and alterations of serotonin in the central nervous system. Psychopharmacol 1993;112:S5-S Meltzer HY. The role of serotonin in schizophrenia and the place of serotonin-dopamine antagonist antipsychotics. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1995;15:2S-3S. 11. Farde L. Nordstrom AL, Wiesel FA, Pauli S, Halidin C, Sedvall G. Positron emission tomographic analysis of central dopamine in patients treated with classical neuroleptics and clozapine:relation to extrapyramidal side effects. Arch Gen Psych 1992;49: Marder SR, Meibach RC. Risperidone in the treatment of schizophrenia. Am J Psych 1984;151: Tollefson GD, Beasky CM, Tran PV, Street JS, Krueger JA, et al. Olanzapine versus haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective and schizophreniform disorders: results of an international collaborative trial. Am J Psych 1997;154: Nordstrom AL, Farde L, Wiesel FA, Forslund K, Pauli S, Halldin C et al. Central -dopamine in relation to antipsychotic drug effects-a double-blind PET study of schizophrenic patients. Biol Psych 1993;33: Baron JC, Martinot JL, Cambon H, Boulenger JP, Poirier MF, et al. Striatal dopamine during and following withdrawal from neuroleptic treatment: correlative evaluation by positron emission tomography and plasma prolactin levels. Psychopharmacol 1989;99: Schlegel S, Schlosser R, Hiemke C, Nickel O, Bockisch A, Hahn K. Prolactin plasma levels -dopamine measured with IBZM-SPECT. Psychopharmacol 1996;124: Wolkin A, Barouche F, Wolf AP, Rotrosen J, Fowler JS, et al. Dopamine blockade and clinical response: evidence for two biological subgroups of schizophrenia. Am J Psych 1989;146: Kane JM, Freeman HL. Towards more effective antipsychotic treatment. Br J Psych 1994;165: Zimbroff DL, Kane JM, Tamminga CA, Daniel DG, Mack RJ, et al. Sertindole study group: Controlled, dose-response study of sertindole and haloperidol in the treatment of schizophrenia. Am J Psych 1997;154: Nordstrom AL, Farde L, Nyberg S, Karlsson P, Halldin C, Sedvall G., and 5-HT 2 in
5 191 relation to clozapine serum concentration : a PET study of schizophrenic patients. Am J Psych 1995;152: Farde L, Nyberg S, Oxenstierna G, Nakashima Y, Halldin C, Ericsson B. Positron emission tomography studies on and 5HT 2 binding in risperidone-treated schizophrenic patients. J Clin Psychopharmacol 1995;15: Nyberg S, Farde L, Halldin C. A PET study of 5-HT 2 dopamine induced by olanzapine in healthy subjects. Neuropsychopharmacol 1997;1: Kapur S, Remington G, Jones C, Wilson A, Dasilva J, et al. High levels of dopamine with low-dose haloperidol treatment: a PET study. Am J Psych 1996;153: Lidow MS, Goldman-Rakic PS. Differential regulation of dopamine mrnas in the primate cerebral cortex vs neostriatum: Effects of chronic treatment with typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1997;283: Lidow MS, Goldman-Rakic PS. A common action of clozapine, haloperidol and remoxipride on dopamine in the primate cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1994;91: Eggers C, Rothenberger A, Berghans U. Clinical and neurobiological findings in children suffering from disease following treatment with tiapride. Eur Arch Psychiar Neurol Sci 1988;237: Deutch AY, Maghaddam B, Innis RB, Krystal JH, Aghajanian GK, et al. Mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotic drugs: implications for novel therapeutic strategies for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 1991;4: Brunello N, Masotto C, Steardo L, Markstein R, Racagni G. New insights into the biology of schizophrenia through the mechanism of action of clozapine. Neuropsychopharmacol 1995;13: Seeman P. Dopamine sequences: Therapeutic levels of neuroleptic occupy, clozapine occupies D 4. Neuropsychopharmacol 1992;7: Kusumi I, Ishikane T, Matsubara S, Koyama T. Long term treatment with haloperidol or clozapine does not affect dopamine D 4 in rat frontal cortex. J Neurol Transm 1995;101: Seeman P, Guan HC, VanTol HH. Dopamine D 4 elevated in schizophrenia. Nature 1993a;365: Northsen M, Cichon S, Hemmer S, Hebebrand J, Remschmidt H, et al. Human dopamine D 4 gene: Frequent occurrence of a null allele and observations of the homozygosity. Human Mol Genetics 1994;3: Seeman P, Ulpian C, Chouinard G, VanTol HHM, Dwosh H, et al. Dopamine D 4 variant, D 4 glicine 194 in Africans, but not in Caucasians: No association with schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet 1994;54: Okubo Y, Suhara T, Suzuki K, Kobayashi K, Inoue O, et al. Decreased prefrontal in schizophrenia revealed by PET. Nature 1997;385: Meltzer HY, Masubara S, Lee JC. The ratios of serotonin- 2 and dopamine-2 affinities differentiate atypical and typical antipsychotic drugs. Psychopharmacol Bull 1989; 25: Meltzer HY, Matsubara S, Lee JC. Classification of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on the basis of dopamine, and serotonin-2 pk1 values. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1989;251: Kapur S. A new frame work for investigating antipsychotic action in humans: lessons from PET imaging. Mol Psychiatry 1998;3: Schotte A, Janssen PEM, Gommeren W, Luyten WHML, VanGompel P, et al. Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo binding. Psychopharmacol 1996;124: Pilowsky LS, Busatto GF, Taylor M, Costa DC, Sharma T, et al. Dopamine D- 2 in vivo by the novel atypical antipsychotic olanzapine-a I-123 IBZM single photon emission tomography (SPET) study. Psychopharmacol 1996;124: VanderZwaag C, McGee M, McEvoy JP, Freudenreich O, Wilson WH, Cooper TB. Response of patients with treatment-refractory schizophrenia to clozapine within three serum level ranges. Am J Psych 1996;153: Trichard C, Paillere-Martinot ML, Attar-Levy D, Recassens C, Monnet F, Martinot JL. Binding of antipsychotic drugs to cortical 5HT 2A : a PET study of chlorpromazine, clozapine, and amisulpride in schizophrenic patients. Am J Psych 1998;155: Kapur S, Zipursky RB, Remington G, Jones C, DaSilva J, et al. 5-HT 2 of olanzapine in schizophrenia: a PET investigation. Am J Psych 1998; 155: Truffinet P, Tamminga CA, Fabre LF, Meltzer HY, Riviere ME, Downey CP. Placebo-controlled study of the D 4 /5- HT 2A antagonist Fananserin in the treatment of schizophrenia. Am J Psych 1999;156: Nyberg S, Eriksson B, Oxenstierna G, Halldin C, Farde L. Suggested minimal effective dose of risperidone based on PET-measured and 5-HT 2A in schizophrenic patients. Am J Psych 1999;156:
Probing cortical sites of antipsychotic drug action with in vivo receptor imaging
 3 Probing cortical sites of antipsychotic drug action with in vivo receptor imaging P. Shaw a and L.S. Pilowsky b, a Department of Psychiatry, South London and Maudsley N.H.S. Trust, Denmark Hill, London
3 Probing cortical sites of antipsychotic drug action with in vivo receptor imaging P. Shaw a and L.S. Pilowsky b, a Department of Psychiatry, South London and Maudsley N.H.S. Trust, Denmark Hill, London
Suggested Minimal Effective Dose of Risperidone Based on PET-Measured D 2 and 5-HT 2A Receptor Occupancy in Schizophrenic Patients
 Suggested Minimal Effective Dose of Risperidone Based on PET-Measured D 2 and 5-HT 2A Receptor Occupancy in Schizophrenic Patients Svante Nyberg, M.D., Ph.D., Bo Eriksson, B.Sc., Gabriella Oxenstierna,
Suggested Minimal Effective Dose of Risperidone Based on PET-Measured D 2 and 5-HT 2A Receptor Occupancy in Schizophrenic Patients Svante Nyberg, M.D., Ph.D., Bo Eriksson, B.Sc., Gabriella Oxenstierna,
5-HT 2 and D 2 Receptor Occupancy of Olanzapine in Schizophrenia: A PET Investigation
 KAPUR, ZIPURSKY, REMINGTON, ET AL. Am J Psychiatry AND 155:7, July RECEPTOR 1998 OCCUPANCY 5-HT2 D2 5-HT 2 and D 2 Receptor Occupancy of Olanzapine in Schizophrenia: A PET Investigation Shitij Kapur, M.D.,
KAPUR, ZIPURSKY, REMINGTON, ET AL. Am J Psychiatry AND 155:7, July RECEPTOR 1998 OCCUPANCY 5-HT2 D2 5-HT 2 and D 2 Receptor Occupancy of Olanzapine in Schizophrenia: A PET Investigation Shitij Kapur, M.D.,
Schizophrenia is a chronic, severe, and disabling brain
 D 2 Receptor Occupancy During High- and Low- Dose Therapy with the Atypical Antipsychotic Amisulpride: A 123 I-Iodobenzamide SPECT Study Christian la Fougère, MD 1 ; Eva Meisenzahl, MD 2 ; Gisela Schmitt,
D 2 Receptor Occupancy During High- and Low- Dose Therapy with the Atypical Antipsychotic Amisulpride: A 123 I-Iodobenzamide SPECT Study Christian la Fougère, MD 1 ; Eva Meisenzahl, MD 2 ; Gisela Schmitt,
Clinically effective antipsychotic drugs share dopamine
 Article Is Regionally Selective D 2 /D 3 Dopamine Occupancy Sufficient for Atypical Antipsychotic Effect? An In Vivo Quantitative [ 123 I]Epidepride SPET Study of Amisulpride-Treated Patients Rodrigo A.
Article Is Regionally Selective D 2 /D 3 Dopamine Occupancy Sufficient for Atypical Antipsychotic Effect? An In Vivo Quantitative [ 123 I]Epidepride SPET Study of Amisulpride-Treated Patients Rodrigo A.
Switching antipsychotics: Basing practice on pharmacology & pharmacokinetics
 Switching antipsychotics: Basing practice on pharmacology & pharmacokinetics John Donoghue Liverpool L imagination est plus important que le savoir Albert Einstein Switching Antipsychotics: Objectives
Switching antipsychotics: Basing practice on pharmacology & pharmacokinetics John Donoghue Liverpool L imagination est plus important que le savoir Albert Einstein Switching Antipsychotics: Objectives
APRIL 2008 DELHI PSYCHIATRY JOURNAL Vol. 11 No.1. Harish Arora, Rajdeep Kaur Department of Psychiatry, G.G.S. Medical College, Faridkot, Punjab
 APRIL 2008 DELHI PSYCHIATRY JOURNAL Vol. 11 No.1 Original Article An Open Label Study on Amisulpride in Augmentation with Atypical Antipsychotics in Treatment Resistant Patients of Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective
APRIL 2008 DELHI PSYCHIATRY JOURNAL Vol. 11 No.1 Original Article An Open Label Study on Amisulpride in Augmentation with Atypical Antipsychotics in Treatment Resistant Patients of Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective
Since the 1970s, excessive dopaminergic PROCEEDINGS
 BIOLOGIC MECHANISMS OF PSYCHOSIS AND ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG ACTIONS: FROM DOPAMINE EXCESS TO DOPAMINE STABILIZATION * Bryan L. Roth, MD, PhD ABSTRACT *Based on a presentation given by Dr Roth at a symposium
BIOLOGIC MECHANISMS OF PSYCHOSIS AND ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG ACTIONS: FROM DOPAMINE EXCESS TO DOPAMINE STABILIZATION * Bryan L. Roth, MD, PhD ABSTRACT *Based on a presentation given by Dr Roth at a symposium
Theoretical insights into the mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotics
 Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 30 (2006) 541 548 Review article Theoretical insights into the mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotics Adriano B.L. Tort a,b, *, Diogo
Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 30 (2006) 541 548 Review article Theoretical insights into the mechanism of action of atypical antipsychotics Adriano B.L. Tort a,b, *, Diogo
SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Atypical (2
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu SP.236 / ESG.SP236 Exploring Pharmacology Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Atypical (2
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
Treatment Response to Olanzapine and Haloperidol and its Association With Dopamine D 2. Receptor Occupancy in First-Episode Psychosis
 Original Research Treatment Response to Olanzapine and Haloperidol and its Association With Dopamine D 2 Receptor Occupancy in First-Episode Psychosis Robert B Zipursky, MD, FRCPC 1, Bruce K Christensen,
Original Research Treatment Response to Olanzapine and Haloperidol and its Association With Dopamine D 2 Receptor Occupancy in First-Episode Psychosis Robert B Zipursky, MD, FRCPC 1, Bruce K Christensen,
Current evidence indicates that some level of dopamine
 Article A PET Study of Dopamine D 2 and Serotonin 5-HT 2 Receptor Occupancy in Patients With Schizophrenia Treated With Therapeutic Doses of Ziprasidone David Mamo, M.D., M.Sc., F.R.C.P.(C) Shitij Kapur,
Article A PET Study of Dopamine D 2 and Serotonin 5-HT 2 Receptor Occupancy in Patients With Schizophrenia Treated With Therapeutic Doses of Ziprasidone David Mamo, M.D., M.Sc., F.R.C.P.(C) Shitij Kapur,
Recent Advances in the Antipsychotic Treatment of People with schizophrenia. Robert W. Buchanan, M.D.
 Recent Advances in the Antipsychotic Treatment of People with schizophrenia Robert W. Buchanan, M.D. Antipsychotic medications are the primary class of drugs used in the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia.
Recent Advances in the Antipsychotic Treatment of People with schizophrenia Robert W. Buchanan, M.D. Antipsychotic medications are the primary class of drugs used in the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia.
Schizophrenic twin. Normal twin
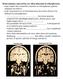 Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Citation for published version (APA): Knegtering, H. (2003). Antipsychotic treatment and sexual functioning: rol of prolactin Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Antipsychotic treatment and sexual functioning Knegtering, Henderikus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Antipsychotic treatment and sexual functioning Knegtering, Henderikus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI
 Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
Schizophrenia FAHAD ALOSAIMI MBBS, SSC - PSYCH C ONSULTATION LIAISON PSYCHIATRIST K ING SAUD UNIVERSITY Schizophrenia - It is not a single disease but a group of disorders with heterogeneous etiologies.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
Drugs for psychosis and mood: unique actions at D3, D2, and D1 dopamine receptor subtypes
 CNS Spectrums (2017), 22, 375 384. Cambridge University Press 2017 doi:10.1017/s1092852917000608 Drugs for psychosis and mood: unique actions at,, and dopamine receptor subtypes Stephen M. Stahl ISSUE:
CNS Spectrums (2017), 22, 375 384. Cambridge University Press 2017 doi:10.1017/s1092852917000608 Drugs for psychosis and mood: unique actions at,, and dopamine receptor subtypes Stephen M. Stahl ISSUE:
Alternative Thresholds for Negative and Positive Symptoms in the CATIE Trial: Implications for Negative Symptom Clinical Trials
 Alternative Thresholds for Negative and Positive Symptoms in the CATIE Trial: Implications for Negative Symptom Clinical Trials Eduardo Dunayevich, Chao-Yin Chen, Stephen Marder and Jonathan Rabinowitz
Alternative Thresholds for Negative and Positive Symptoms in the CATIE Trial: Implications for Negative Symptom Clinical Trials Eduardo Dunayevich, Chao-Yin Chen, Stephen Marder and Jonathan Rabinowitz
Quetiapine is a dibenzothiapine derivative that interacts
 0271-0749/02/2204-0347/0 Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology Vol. 22, No. 4 Copyright 2002 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Therapeutic Tolerance and Rebound Psychosis During
0271-0749/02/2204-0347/0 Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology Vol. 22, No. 4 Copyright 2002 by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Therapeutic Tolerance and Rebound Psychosis During
ANTIPSYCHOTIC POLYPHARMACY
 Psychiatry and Addictions Case Conference UW Medicine Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences ANTIPSYCHOTIC POLYPHARMACY RYAN KIMMEL, MD MEDICAL DIRECTOR HOSPITAL PSYCHIATRY UWMC GENERAL DISCLOSURES The University
Psychiatry and Addictions Case Conference UW Medicine Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences ANTIPSYCHOTIC POLYPHARMACY RYAN KIMMEL, MD MEDICAL DIRECTOR HOSPITAL PSYCHIATRY UWMC GENERAL DISCLOSURES The University
The Scourge of EPS: Have Atypical Antipsychotics Solved the Problem? Copyright 2001 Physicians Postgraduate Press, Inc.
 The Scourge of EPS: Have Atypical Antipsychotics Solved the Problem? T his ACADEMIC HIGHLIGHTS section of The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry summarizes the highlights of a symposium entitled Clear Vision
The Scourge of EPS: Have Atypical Antipsychotics Solved the Problem? T his ACADEMIC HIGHLIGHTS section of The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry summarizes the highlights of a symposium entitled Clear Vision
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal
 ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
ESSENTIAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY, 2011 Neurobiology of Schizophrenia Carl Salzman MD Montreal EVOLVING CONCEPTS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA Psychotic illness with delusions, hallucinations, thought disorder and deterioration;
Treatments for schizophrenia: a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs
 FEATURE REVIEW : a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs S Miyamoto 1, GE Duncan 2, CE Marx 3 and JA Lieberman 2 (2005) 10, 79 104 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group
FEATURE REVIEW : a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs S Miyamoto 1, GE Duncan 2, CE Marx 3 and JA Lieberman 2 (2005) 10, 79 104 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group
What is the mechanism for aripiprazole's effect on reducing olanzapine-associated obesity?
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2010 What is the mechanism for aripiprazole's effect on reducing olanzapine-associated
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2010 What is the mechanism for aripiprazole's effect on reducing olanzapine-associated
APPLYING ANTIPSYCHOTIC PHARMACOKINETICS TO BEST DOSING PRACTICES: DEPOT MEDICATIONS
 APPLYING ANTIPSYCHOTIC PHARMACOKINETICS TO BEST DOSING PRACTICES: DEPOT MEDICATIONS Objectives Review the kinetic parameters of depot antipsychotics Review loading strategies for those depot medications
APPLYING ANTIPSYCHOTIC PHARMACOKINETICS TO BEST DOSING PRACTICES: DEPOT MEDICATIONS Objectives Review the kinetic parameters of depot antipsychotics Review loading strategies for those depot medications
Olanzapine: Preclinical and Clinical Profiles of a Novel Antipsychotic Agent
 CNS Drug Reviews Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 303 363 2000 Neva Press, Branford, Connecticut Olanzapine: Preclinical and Clinical Profiles of a Novel Antipsychotic Agent Gary D. Tollefson and Cindy C. Taylor Lilly
CNS Drug Reviews Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 303 363 2000 Neva Press, Branford, Connecticut Olanzapine: Preclinical and Clinical Profiles of a Novel Antipsychotic Agent Gary D. Tollefson and Cindy C. Taylor Lilly
Potential control of risperidone-related cognitive deficits by adjunctive aripiprazole treatment
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2011 Potential control of risperidone-related cognitive deficits by adjunctive
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2011 Potential control of risperidone-related cognitive deficits by adjunctive
Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
 International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (24), 7 (Supplement 1), S1 S5. Copyright f 24 CINP DOI : 1.117/S146114574411 Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (24), 7 (Supplement 1), S1 S5. Copyright f 24 CINP DOI : 1.117/S146114574411 Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
Method. NeuRA Paliperidone August 2016
 Introduction Second generation antipsychotics (sometimes referred to as atypical antipsychotics) are a newer class of antipsychotic medication than first generation typical antipsychotics. Second generation
Introduction Second generation antipsychotics (sometimes referred to as atypical antipsychotics) are a newer class of antipsychotic medication than first generation typical antipsychotics. Second generation
Recent Findings on Dopamine in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia. Cristy A. Ku Whittier College
 40 Recent Findings on Dopamine in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia Cristy A. Ku Whittier College The original dopamine hypothesis (Carlsson & Lindqvist, 1963 as cited in Laruelle, Abi-Dargham, Gil,
40 Recent Findings on Dopamine in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia Cristy A. Ku Whittier College The original dopamine hypothesis (Carlsson & Lindqvist, 1963 as cited in Laruelle, Abi-Dargham, Gil,
Functional neuroimaging in schizophrenia: diagnosis and drug discovery
 Review Functional neuroimaging in schizophrenia: diagnosis and drug discovery Philip McGuire 1, Oliver D Howes 1, James Stone 2 and Paolo Fusar-Poli 1 1 Sections of Neuroimaging, Division of Psychological
Review Functional neuroimaging in schizophrenia: diagnosis and drug discovery Philip McGuire 1, Oliver D Howes 1, James Stone 2 and Paolo Fusar-Poli 1 1 Sections of Neuroimaging, Division of Psychological
Psychopharmacology. MATTHEW MACALUSO, DO ALEXANDRA FLYNN, MD, PhD SHELDON PRESKORN, MD
 Psychopharmacology Determining Whether a Definitive Causal Relationship Exists Between Aripiprazole and Tardive Dyskinesia and/or Dystonia in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Part 2: Preclinical
Psychopharmacology Determining Whether a Definitive Causal Relationship Exists Between Aripiprazole and Tardive Dyskinesia and/or Dystonia in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder, Part 2: Preclinical
New Hope in Pharmacotherapy for Schizophrenia
 Clinical Review Article New Hope in Pharmacotherapy for Schizophrenia Leonardo Cortese, BSc, MD, FRCP(C) Schizophrenia is a debilitating mental disorder that, in the US, has a lifetime prevalence of approximately
Clinical Review Article New Hope in Pharmacotherapy for Schizophrenia Leonardo Cortese, BSc, MD, FRCP(C) Schizophrenia is a debilitating mental disorder that, in the US, has a lifetime prevalence of approximately
With growing knowledge of disease
 PHARMACOLOGIC STRATEGIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS Terry E. Goldberg, PhD* ABSTRACT Cognitive dysfunction is considered a major determinant and predictor of long-term disability and has,
PHARMACOLOGIC STRATEGIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF COGNITIVE SYMPTOMS Terry E. Goldberg, PhD* ABSTRACT Cognitive dysfunction is considered a major determinant and predictor of long-term disability and has,
Article. Brain and Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Aripiprazole in Patients With Schizophrenia: An [ 18 F]Fallypride PET Study
![Article. Brain and Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Aripiprazole in Patients With Schizophrenia: An [ 18 F]Fallypride PET Study Article. Brain and Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Aripiprazole in Patients With Schizophrenia: An [ 18 F]Fallypride PET Study](/thumbs/88/117549476.jpg) Article Brain and Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Aripiprazole in Patients With Schizophrenia: An [ 18 F]Fallypride PET Study Gerhard Gründer, M.D. Christine Fellows, M.D. Hildegard Janouschek, M.D. Tanja Veselinovic,
Article Brain and Plasma Pharmacokinetics of Aripiprazole in Patients With Schizophrenia: An [ 18 F]Fallypride PET Study Gerhard Gründer, M.D. Christine Fellows, M.D. Hildegard Janouschek, M.D. Tanja Veselinovic,
Lundbeck Medical Education: Request for Independent Medical Education Grant Proposals
 Lundbeck Medical Education: Request for Independent Medical Education Grant Proposals Therapeutic Area Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia The objective of this RFP is to support activities that improve
Lundbeck Medical Education: Request for Independent Medical Education Grant Proposals Therapeutic Area Treatment Resistant Schizophrenia The objective of this RFP is to support activities that improve
Higher occupancy of muscarinic receptors by olanzapine than risperidone in patients with schizophrenia
 Psychopharmacology (2001) 156:53 57 DOI 10.1007/s002130000679 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION J. Lavalaye J. Booij D.H. Linszen L. Reneman E.A. van Royen Higher occupancy of muscarinic receptors by olanzapine than
Psychopharmacology (2001) 156:53 57 DOI 10.1007/s002130000679 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION J. Lavalaye J. Booij D.H. Linszen L. Reneman E.A. van Royen Higher occupancy of muscarinic receptors by olanzapine than
Clinical Advantages of Amisulpride in the Treatment of Acute Schizophrenia
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2001; 29: 451 466 Clinical Advantages of Amisulpride in the Treatment of Acute Schizophrenia T BURNS 1 AND R BALE 2 1 Department of Psychiatry; 2 Department
The Journal of International Medical Research 2001; 29: 451 466 Clinical Advantages of Amisulpride in the Treatment of Acute Schizophrenia T BURNS 1 AND R BALE 2 1 Department of Psychiatry; 2 Department
Serotonin 5-HT 2 Receptors in Schizophrenia: A PET Study Using [ 18 F]Setoperone in Neuroleptic-Naive Patients and Normal Subjects
![Serotonin 5-HT 2 Receptors in Schizophrenia: A PET Study Using [ 18 F]Setoperone in Neuroleptic-Naive Patients and Normal Subjects Serotonin 5-HT 2 Receptors in Schizophrenia: A PET Study Using [ 18 F]Setoperone in Neuroleptic-Naive Patients and Normal Subjects](/thumbs/89/101175393.jpg) Serotonin 5-HT 2 Receptors in Schizophrenia: A PET Study Using [ 18 F]Setoperone in Neuroleptic-Naive Patients and Normal Subjects Ralph Lewis, M.D., F.R.C.P.C., Shitij Kapur, M.D., Ph.D., F.R.C.P.C.,
Serotonin 5-HT 2 Receptors in Schizophrenia: A PET Study Using [ 18 F]Setoperone in Neuroleptic-Naive Patients and Normal Subjects Ralph Lewis, M.D., F.R.C.P.C., Shitij Kapur, M.D., Ph.D., F.R.C.P.C.,
RECEPTOR PROFILES OF THE ATYPICAL AGENTS
 SCHIZOPHRENIA: FROM NEUROSCIENCE TO CLINICAL EXPERIENCE Peter F. Buckley, MD,* and Donald E. N. Addington, MBBS, MRCPsych, FRCPC ABSTRACT Typical first-generation agents work through potent blockade of
SCHIZOPHRENIA: FROM NEUROSCIENCE TO CLINICAL EXPERIENCE Peter F. Buckley, MD,* and Donald E. N. Addington, MBBS, MRCPsych, FRCPC ABSTRACT Typical first-generation agents work through potent blockade of
Amisulpride in Addition to Clozapine: A Retrospective Study Indicates Improved Efficacy and Good Tolerability
 Reprinted from the German Journal of Psychiatry http://www.gjpsy.uni-goettingen.de ISSN 1433-1055 Amisulpride in Addition to Clozapine: A Retrospective Study Indicates Improved Efficacy and Good Tolerability
Reprinted from the German Journal of Psychiatry http://www.gjpsy.uni-goettingen.de ISSN 1433-1055 Amisulpride in Addition to Clozapine: A Retrospective Study Indicates Improved Efficacy and Good Tolerability
CHLORPROMAZINE EQUIVALENTS VERSUS DEFINED DAILY DOSES: HOW TO COMPARE ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG DOSES?
 CHLORPROMAZINE EQUIVALENTS VERSUS DEFINED DAILY DOSES: HOW TO COMPARE ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG DOSES? C.A.W. Rijcken 1, T.B.M. Monster 1, J.R.B.J. Brouwers 1, L.T.W. de Jong van den Berg 1 1 Department of Social
CHLORPROMAZINE EQUIVALENTS VERSUS DEFINED DAILY DOSES: HOW TO COMPARE ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG DOSES? C.A.W. Rijcken 1, T.B.M. Monster 1, J.R.B.J. Brouwers 1, L.T.W. de Jong van den Berg 1 1 Department of Social
) and serotonin Type 2 (5-HT 2A
 Latuda (lurasidone HCl) Fact Sheet Schizophrenia FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What type of patient with schizophrenia is appropriate for LATUDA? LATUDA is an atypical antipsychotic agent indicated for the
Latuda (lurasidone HCl) Fact Sheet Schizophrenia FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What type of patient with schizophrenia is appropriate for LATUDA? LATUDA is an atypical antipsychotic agent indicated for the
Potential control of antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia and obesity in children and adolescents by aripiprazole
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2010 Potential control of antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2010 Potential control of antipsychotic-induced hyperprolactinemia and
Treatment of Schizophrenia
 Treatment of Schizophrenia Conduct comprehensive assessment and use measurement-based care as found in the Principles of Practice (review pages 4-7). Most importantly assess social support system (housing,
Treatment of Schizophrenia Conduct comprehensive assessment and use measurement-based care as found in the Principles of Practice (review pages 4-7). Most importantly assess social support system (housing,
Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter Chapter 8 Chapter
 CONTENTS Preface Chapter 1 Principles of Chemical Neurotransmission Chapter 2 Receptors and Enzymes as the Targets of Drug Action Chapter 3 Special Properties of Receptors Chapter 4 Chemical Neurotransmission
CONTENTS Preface Chapter 1 Principles of Chemical Neurotransmission Chapter 2 Receptors and Enzymes as the Targets of Drug Action Chapter 3 Special Properties of Receptors Chapter 4 Chemical Neurotransmission
SAFETY AND TOLERABILITY: HOW DO NEWER GENERATION ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS COMPARE?
 Psychiatric Quarterly, Vol. 73, No. 4, Winter 2002 ( C 2002) SAFETY AND TOLERABILITY: HOW DO NEWER GENERATION ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS COMPARE? Rajiv Tandon, M.D. Previously, clinicians worked with antipsychotic
Psychiatric Quarterly, Vol. 73, No. 4, Winter 2002 ( C 2002) SAFETY AND TOLERABILITY: HOW DO NEWER GENERATION ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS COMPARE? Rajiv Tandon, M.D. Previously, clinicians worked with antipsychotic
EFFECT OF TYPICAL AND ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS ON PLASMA PROLACTIN LEVELS IN SCHIZOPHRENIA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EFFECT OF TYPICAL AND ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS ON PLASMA PROLACTIN LEVELS IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Muhammad Sami Bilal 1, Mowadat Hussain Rana 2 1 Department of Psychiatry, Combined Military Hospital,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EFFECT OF TYPICAL AND ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS ON PLASMA PROLACTIN LEVELS IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Muhammad Sami Bilal 1, Mowadat Hussain Rana 2 1 Department of Psychiatry, Combined Military Hospital,
Risperidone as a Janus in Mood Disorder
 KISEP Review Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 2003; 1: 7-21 Risperidone as a Janus in Mood Disorder Doh Joon Yoon - Key points KEY WORDS: INTRODUCTION Address for correspondence: - - - - Risperidone
KISEP Review Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 2003; 1: 7-21 Risperidone as a Janus in Mood Disorder Doh Joon Yoon - Key points KEY WORDS: INTRODUCTION Address for correspondence: - - - - Risperidone
ARTICLES. nature publishing group
 nature publishing group Modeling of Brain D 2 Receptor Occupancy- Plasma Concentration Relationships with a Novel Antipsychotic, YKP1358, Using Serial PET Scans in Healthy Volunteers KS Lim 1, JS Kwon
nature publishing group Modeling of Brain D 2 Receptor Occupancy- Plasma Concentration Relationships with a Novel Antipsychotic, YKP1358, Using Serial PET Scans in Healthy Volunteers KS Lim 1, JS Kwon
Effectiveness of paliperidone long-acting injection in clinical practice.
 Ther Adv Psychopharmacol (2018) 1 7 doi: 10.1177/ 2045125317753332 Effectiveness of paliperidone long-acting injection in clinical practice. Paul Nicholas Deslandes 1,2, Elan Haf Ward 3, Kathryn Norris
Ther Adv Psychopharmacol (2018) 1 7 doi: 10.1177/ 2045125317753332 Effectiveness of paliperidone long-acting injection in clinical practice. Paul Nicholas Deslandes 1,2, Elan Haf Ward 3, Kathryn Norris
A Case of Hyper Sexuality Probably Associated with Clozapine
 Complicated Case Histories Key Words: atypical antipsychotic, adverse drug reaction, hypersexuality A Case of Hyper Sexuality Probably Associated with Clozapine By Sereen Rose Thomson, Navin Patil, Balaji
Complicated Case Histories Key Words: atypical antipsychotic, adverse drug reaction, hypersexuality A Case of Hyper Sexuality Probably Associated with Clozapine By Sereen Rose Thomson, Navin Patil, Balaji
NEUROPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY 2001 VOL. 25, NO American College of Neuropsychopharmacology
 Dopamine D 2 Receptor Occupancy Is a Common Mechanism Underlying Animal Models of Antipsychotics and Their Clinical Effects Marie-Louise G. Wadenberg, Ph.D., Alexandra Soliman, H.B.Sc., Susan C. VanderSpek,
Dopamine D 2 Receptor Occupancy Is a Common Mechanism Underlying Animal Models of Antipsychotics and Their Clinical Effects Marie-Louise G. Wadenberg, Ph.D., Alexandra Soliman, H.B.Sc., Susan C. VanderSpek,
Volinanserin (MDL-100,907 / M100907)
 Volinanserin (MDL-100,907 / M100907) Volinanserin (MDL-100,907) is a highly selective 5-HT 2A receptor antagonist. It is widely used in scientific research to investigate the function of the 5-HT 2A receptor.
Volinanserin (MDL-100,907 / M100907) Volinanserin (MDL-100,907) is a highly selective 5-HT 2A receptor antagonist. It is widely used in scientific research to investigate the function of the 5-HT 2A receptor.
AMISULPRIDE VERSUS RISPERIDONE IN THE TREATMENT
 AMISULPRIDE VERSUS RISPERIDONE IN THE TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIC PATIENTS: A DOUBLE-BLIND PILOT STUDY IN TAIWAN Tzung J. Hwang, 1 Shin-Min Lee, 2 Hsiao-Ju Sun, 3 Hsin-Nan Lin, 1 Shih-Jen Tsai, 4 Ying-Chiao
AMISULPRIDE VERSUS RISPERIDONE IN THE TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIC PATIENTS: A DOUBLE-BLIND PILOT STUDY IN TAIWAN Tzung J. Hwang, 1 Shin-Min Lee, 2 Hsiao-Ju Sun, 3 Hsin-Nan Lin, 1 Shih-Jen Tsai, 4 Ying-Chiao
혈장 Homovanillic Acid 농도의주간및 Insulin 유도성변동 *
 KISEP Original Articles 생물정신의학 Vol. 5, No. 2, December 1998 혈장 Homovanillic Acid 농도의주간및 Insulin 유도성변동 * 정경천 ** 김병효 ** 한규희 ** Diurnal and Insulin-Induced Variations of Plasma Homovanillic Acid Concentrations*
KISEP Original Articles 생물정신의학 Vol. 5, No. 2, December 1998 혈장 Homovanillic Acid 농도의주간및 Insulin 유도성변동 * 정경천 ** 김병효 ** 한규희 ** Diurnal and Insulin-Induced Variations of Plasma Homovanillic Acid Concentrations*
What Have We Learned from Molecular Imaging Studies of Dopamine Neurotransmission in Schizophrenia and in Mediating Reward Behaviors
 What Have We Learned from Molecular Imaging Studies of Dopamine Neurotransmission in Schizophrenia and in Mediating Reward Behaviors Robert M Kessler, MD Professor of Radiology University of Alabama at
What Have We Learned from Molecular Imaging Studies of Dopamine Neurotransmission in Schizophrenia and in Mediating Reward Behaviors Robert M Kessler, MD Professor of Radiology University of Alabama at
Schizophrenia. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Overview. Characterized by. Disorganized Thoughts Hallucinations Delusions Bizarre behaviors
 Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Overview Schizophrenia Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Probably consists of more than one disorder Is the most devastating
Effects of Antipsychotic Drugs on Extracellular Dopamine Levels in Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Nucleus Accumbens 1
 0022-3565/99/2882-0774$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 288, No. 2 Copyright 1999 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/99/2882-0774$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 288, No. 2 Copyright 1999 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
Pharmacotherapy of psychosis and schizophrenia in youth
 Pharmacotherapy of psychosis and schizophrenia in youth Benedetto Vitiello Pavia, 2 December 2017 Disclosure Benedetto Vitiello, M.D. Professor of Child and Adolescent Neuropsychiatry University of Turin,
Pharmacotherapy of psychosis and schizophrenia in youth Benedetto Vitiello Pavia, 2 December 2017 Disclosure Benedetto Vitiello, M.D. Professor of Child and Adolescent Neuropsychiatry University of Turin,
What's New in the World of Antipsychotics?
 Handout for the Neuroscience Education Institute (NEI) online activity: What's New in the World of Antipsychotics? (page 7 in syllabus) Stephen M. Stahl, MD, PhD Adjunct Professor, Department of Psychiatry
Handout for the Neuroscience Education Institute (NEI) online activity: What's New in the World of Antipsychotics? (page 7 in syllabus) Stephen M. Stahl, MD, PhD Adjunct Professor, Department of Psychiatry
Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity
 Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity : What is Schizophrenia? Literally split mind A mental disorder comprising most major psychotic disorders; characterized
Schizophrenia: Uncovering a molecular origin so humanity may better deal with insanity : What is Schizophrenia? Literally split mind A mental disorder comprising most major psychotic disorders; characterized
The Efficacy and Safety of Lower Doses of Aripiprazole for the Treatment of Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Schizophrenia
 The Efficacy and Safety of Lower Doses of for the Treatment of Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Schizophrenia By Andrew J. Cutler, MD, Ronald N. Marcus, MD, Sterling A. Hardy, MS, Amy O Donnell, MD,
The Efficacy and Safety of Lower Doses of for the Treatment of Patients with Acute Exacerbation of Schizophrenia By Andrew J. Cutler, MD, Ronald N. Marcus, MD, Sterling A. Hardy, MS, Amy O Donnell, MD,
University of Groningen. Pharmacy data as a tool for assessing antipsychotic drug use Rijcken, Claudia
 University of Groningen Pharmacy data as a tool for assessing antipsychotic drug use Rijcken, Claudia IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
University of Groningen Pharmacy data as a tool for assessing antipsychotic drug use Rijcken, Claudia IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
Schizophrenia and comorbid cannabis use disorders: Brain structure, function and the effect of antipsychotic medications Machielsen, Marise
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Schizophrenia and comorbid cannabis use disorders: Brain structure, function and the effect of antipsychotic medications Machielsen, Marise Link to publication Citation
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Schizophrenia and comorbid cannabis use disorders: Brain structure, function and the effect of antipsychotic medications Machielsen, Marise Link to publication Citation
WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM GROUP PSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATIONS
 WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM GROUP PSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATIONS DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS Excessive limbic dopamine is hypothesised to cause psychosis Many antipsychotics inhibit dopamine 2 receptors in mesolimbic and
WESTMEAD PRIMARY EXAM GROUP PSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATIONS DOPAMINE HYPOTHESIS Excessive limbic dopamine is hypothesised to cause psychosis Many antipsychotics inhibit dopamine 2 receptors in mesolimbic and
Method. NeuRA First versus second generation antipsychotics August 2016
 Introduction First generation typical are an older class of antipsychotic than second generation atypical. First generation are used primarily to treat positive symptoms including the experiences of perceptual
Introduction First generation typical are an older class of antipsychotic than second generation atypical. First generation are used primarily to treat positive symptoms including the experiences of perceptual
The Impact of Mental Illness on Sexual Dysfunction
 Balon R (ed): Sexual Dysfunction. The Brain-Body Connection. Adv Psychosom Med. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 29, pp 89 106 The Impact of Mental Illness on Sexual Dysfunction Zvi Zemishlany Abraham Weizman
Balon R (ed): Sexual Dysfunction. The Brain-Body Connection. Adv Psychosom Med. Basel, Karger, 2008, vol 29, pp 89 106 The Impact of Mental Illness on Sexual Dysfunction Zvi Zemishlany Abraham Weizman
Serum concentrations of paliperidone versus risperidone and clinical effects
 Serum concentrations of paliperidone versus risperidone and clinical effects Yasmin Nazirizadeh, Friederike Vogel, Wolfgang Bader, Ekkehard Haen, Bruno Pfuhlmann, Gerhard Gründer, Michael Paulzen, Markus
Serum concentrations of paliperidone versus risperidone and clinical effects Yasmin Nazirizadeh, Friederike Vogel, Wolfgang Bader, Ekkehard Haen, Bruno Pfuhlmann, Gerhard Gründer, Michael Paulzen, Markus
Schizophrenia Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE -NURSING PROGRAM
 Schizophrenia Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE -NURSING PROGRAM NURS 203 GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY DANITA NARCISO PHARM D Learning Objectives Understand the result of dopamine binding to D2 receptors
Schizophrenia Pharmacology UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I HILO PRE -NURSING PROGRAM NURS 203 GENERAL PHARMACOLOGY DANITA NARCISO PHARM D Learning Objectives Understand the result of dopamine binding to D2 receptors
ISCTM Autumn Meeting Philadelphia, PA. 2 October, 2013 Presenter Disclosure Information for Bruce J. Kinon, M.D.
 ISCTM Autumn Meeting Philadelphia, PA. 2 October, 213 Presenter Disclosure Information for Bruce J. Kinon, M.D. I will discuss investigational use in my presentation. I have financial relationships to
ISCTM Autumn Meeting Philadelphia, PA. 2 October, 213 Presenter Disclosure Information for Bruce J. Kinon, M.D. I will discuss investigational use in my presentation. I have financial relationships to
A systematic review of atypical antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia. Atypical antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia
 A systematic review of atypical antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia Atypical antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia A-M Bagnall 1 * S Gilbody 3 L Jones 1 L Davies 4 L Ginnelly 2 D Torgerson 2 R Lewis 1
A systematic review of atypical antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia Atypical antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia A-M Bagnall 1 * S Gilbody 3 L Jones 1 L Davies 4 L Ginnelly 2 D Torgerson 2 R Lewis 1
Schizophrenia and Related Psychotic Disorders
 and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
and Related Psychotic Disorders Anand K. Pandurangi, MD Professor & Chair, Div. of Inpatient Psychiatry Director, Program VCU Medical Center 1 Kraeplin 1896 Dementia Praecox. Single, Homogenous Disorder
SiGMA/ MMHSCT GUIDELINES FOR ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA. [compatible with NICE guidance]
![SiGMA/ MMHSCT GUIDELINES FOR ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA. [compatible with NICE guidance] SiGMA/ MMHSCT GUIDELINES FOR ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA. [compatible with NICE guidance]](/thumbs/80/80440271.jpg) SiGMA/ MMHSCT GUIDELINES FOR ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA [compatible with NICE guidance] Medicines Management Committee August 2002 For review August 2003 Rationale The SiGMA algorithm
SiGMA/ MMHSCT GUIDELINES FOR ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUG TREATMENT OF SCHIZOPHRENIA [compatible with NICE guidance] Medicines Management Committee August 2002 For review August 2003 Rationale The SiGMA algorithm
Relationship between Dose, Drug Levels, and D2 Receptor Occupancy for the Atypical Antipsychotics Risperidone and Paliperidone
 1521-0103/12/3411-81 89 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 341, No. 1 U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright 189076/3754801 JPET 341:81 89, 2012 Relationship between
1521-0103/12/3411-81 89 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 341, No. 1 U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright 189076/3754801 JPET 341:81 89, 2012 Relationship between
The Relationship of Clozapine and Haloperidol Treatment Response to Prefrontal, Hippocampal, and Caudate Brain Volumes
 Article The Relationship of Clozapine and Haloperidol Treatment Response to Prefrontal, Hippocampal, and Caudate Brain Volumes Celso Arango, M.D. Alan Breier, M.D. Robert McMahon, Ph.D. William T. Carpenter,
Article The Relationship of Clozapine and Haloperidol Treatment Response to Prefrontal, Hippocampal, and Caudate Brain Volumes Celso Arango, M.D. Alan Breier, M.D. Robert McMahon, Ph.D. William T. Carpenter,
Diagnosis and treatment of acute agitation and aggression in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: evidence for the efficacy of atypical
 Diagnosis and treatment of acute agitation and aggression in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: evidence for the efficacy of atypical antipsychotics 1 Abstract Acute agitation and aggression
Diagnosis and treatment of acute agitation and aggression in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: evidence for the efficacy of atypical antipsychotics 1 Abstract Acute agitation and aggression
Are Two Antipsychotics Better Than One?
 Are Two Antipsychotics Better Than One? Lauren Hanna, M.D and Delbert Robinson, M.D. Northwell Health National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office
Are Two Antipsychotics Better Than One? Lauren Hanna, M.D and Delbert Robinson, M.D. Northwell Health National Council for Behavioral Health Montefiore Medical Center Northwell Health New York State Office
Antipsychotics. Something Old, Something New, Something Used to Treat the Blues
 Antipsychotics Something Old, Something New, Something Used to Treat the Blues Objectives To provide an overview of the key differences between first and second generation agents To an overview the newer
Antipsychotics Something Old, Something New, Something Used to Treat the Blues Objectives To provide an overview of the key differences between first and second generation agents To an overview the newer
Is Lurasidone more safe and effective in the treatment ofschizoaffective disorder and schizophrenia than other commonanti-psychotic medications?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Lurasidone more safe and effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2015 Is Lurasidone more safe and effective
Anti-psychotic Polypharmacy in the Treatment of Patients with Resistant Schizophrenia: A Descriptive Study
 Research Reviews: Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences e-issn: 2320-1215 www.rroij.com Anti-psychotic Polypharmacy in the Treatment of Patients with Resistant Schizophrenia: A Descriptive Study Etwal Bou
Research Reviews: Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences e-issn: 2320-1215 www.rroij.com Anti-psychotic Polypharmacy in the Treatment of Patients with Resistant Schizophrenia: A Descriptive Study Etwal Bou
An update of the preclinical profile of lurasidone
 review An update of the preclinical profile of lurasidone Marco A. Riva Department of Pharmacological and Biomolecular Sciences, University of Milan Abstract Lurasidone is a novel antipsychotic drug approved
review An update of the preclinical profile of lurasidone Marco A. Riva Department of Pharmacological and Biomolecular Sciences, University of Milan Abstract Lurasidone is a novel antipsychotic drug approved
Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development. John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University
 Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University Four problems We don t know the disorders sufficiently The biology is complex and heterogeneous We have animal
Experimental Medicine and Psychiatry Drug Development John H. Krystal, M.D. Yale University Four problems We don t know the disorders sufficiently The biology is complex and heterogeneous We have animal
Minimising the Impact of Medication on Physical Health in Schizophrenia
 Minimising the Impact of Medication on Physical Health in Schizophrenia John Donoghue Liverpool Imagination is more important than knowledge Albert Einstein LIFESTYLE Making choices TREATMENT Worse Psychopathology,
Minimising the Impact of Medication on Physical Health in Schizophrenia John Donoghue Liverpool Imagination is more important than knowledge Albert Einstein LIFESTYLE Making choices TREATMENT Worse Psychopathology,
M ost studies that have examined the pattern of cerebral
 106 PAPER Immediate and delayed effects of risperidone on cerebral metabolism in neuroleptic naïve schizophrenic patients: correlations with symptom change E T C Ngan, C J Lane, T J Ruth, P F Liddle...
106 PAPER Immediate and delayed effects of risperidone on cerebral metabolism in neuroleptic naïve schizophrenic patients: correlations with symptom change E T C Ngan, C J Lane, T J Ruth, P F Liddle...
Pharmacotherapy of treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a clinical perspective
 Pharmacotherapy of treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a clinical perspective Markus Dold, 1 Stefan Leucht 1,2 1 Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Technical University Munich, Klinikum rechts
Pharmacotherapy of treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a clinical perspective Markus Dold, 1 Stefan Leucht 1,2 1 Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Technical University Munich, Klinikum rechts
Chapter 161 Antipsychotics
 Chapter 161 Antipsychotics Episode Overview Extrapyramidal syndromes are a common complication of antipsychotic medications. First line treatment is benztropine or diphenhydramine. Lorazepam is used in
Chapter 161 Antipsychotics Episode Overview Extrapyramidal syndromes are a common complication of antipsychotic medications. First line treatment is benztropine or diphenhydramine. Lorazepam is used in
ECNP consensus meeting. Negative, depressive and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Nice, March 2004 B
 European Neuropsychopharmacology (2007) 17, 70 77 www.elsevier.com/locate/euroneuro ECNP consensus meeting. Negative, depressive and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Nice, March 2004 B S.A. Montgomery
European Neuropsychopharmacology (2007) 17, 70 77 www.elsevier.com/locate/euroneuro ECNP consensus meeting. Negative, depressive and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. Nice, March 2004 B S.A. Montgomery
a Flügelman s (Mazra) Mental Health Medical Center, Acre, b Rappaport Faculty *Michael Segal and Avi Avital have contributed equally.
 192 Original article Prolactin serum levels in paranoid versus nonparanoid male schizophrenia patients treated with risperidone Michael Segal a,b,*, Avi Avital c,d,*, Andrei Derevenski a, Severina Berstein
192 Original article Prolactin serum levels in paranoid versus nonparanoid male schizophrenia patients treated with risperidone Michael Segal a,b,*, Avi Avital c,d,*, Andrei Derevenski a, Severina Berstein
Aripiprazole: an appraisal of the translation of complex receptor effects into clinical outcomes
 DRUG PROFILE Aripiprazole: an appraisal of the translation of complex receptor effects into clinical outcomes Peter F Buckley & Simon Sebastian Author for correspondence Department of Psychiatry and Health
DRUG PROFILE Aripiprazole: an appraisal of the translation of complex receptor effects into clinical outcomes Peter F Buckley & Simon Sebastian Author for correspondence Department of Psychiatry and Health
CHAPTER 3. Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment
 CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
CHAPTER 3 Schizophrenia and Antipsychotic Treatment What is it? It is a severe, chronic, disabling brain disease Considered to have biological origins but exact unknown 1% of population affected Schizophrenia
Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders
 Psychiatric Disorder Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders JMAJ 45(12): 538 544, 2002 Yoshio HIRAYASU Associate Professor, Department of Neuropsychiatry Kyorin University School of Medicine
Psychiatric Disorder Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders JMAJ 45(12): 538 544, 2002 Yoshio HIRAYASU Associate Professor, Department of Neuropsychiatry Kyorin University School of Medicine
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs
 Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
Mechanism of action of clozapine in the context of dopamine D 1 -D 2 receptor hetero-dimerization a working hypothesis
 Pharmacological Reports 2008, 60, 581 587 ISSN 1734-1140 Copyright 2008 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Review Mechanism of action of clozapine in the context of dopamine D 1 -D
Pharmacological Reports 2008, 60, 581 587 ISSN 1734-1140 Copyright 2008 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Review Mechanism of action of clozapine in the context of dopamine D 1 -D
NEUROPSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY 2002 VOL. 27, NO American College of Neuropsychopharmacology
 SR46349-B, a 5-HT 2A/2C Receptor Antagonist, Potentiates Haloperidol-induced Dopamine Release in Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Nucleus Accumbens Stefania Bonaccorso, M.D., Herbert Y. Meltzer, M.D.,
SR46349-B, a 5-HT 2A/2C Receptor Antagonist, Potentiates Haloperidol-induced Dopamine Release in Rat Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Nucleus Accumbens Stefania Bonaccorso, M.D., Herbert Y. Meltzer, M.D.,
Lurasidone: A New Antipsychotic For Schizophrenia. Objectives. Introduction. Pharmacology/Pharmacokinetics. Mechanism of Action. Mechanism of Action
 Lurasidone: A New Antipsychotic For Schizophrenia Theodore Pikoulas, PharmD PGY2 Psychiatric Pharmacy Resident Louis Stokes Cleveland VAMC Objectives Review the pharmacology and the pharmacokinetics Identify
Lurasidone: A New Antipsychotic For Schizophrenia Theodore Pikoulas, PharmD PGY2 Psychiatric Pharmacy Resident Louis Stokes Cleveland VAMC Objectives Review the pharmacology and the pharmacokinetics Identify
Disruption and Potentiation of Latent Inhibition by Risperidone: The Latent Inhibition Model of Atypical Antipsychotic Action
 (2003) 28, 499 509 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0893-133X/03 $25.00 www.neuropsychopharmacology.org Disruption and Potentiation of Latent Inhibition by Risperidone: The Latent Inhibition
(2003) 28, 499 509 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0893-133X/03 $25.00 www.neuropsychopharmacology.org Disruption and Potentiation of Latent Inhibition by Risperidone: The Latent Inhibition
Metaanalytische Evaluierung atypischer Antipsychotika
 Metaanalytische Evaluierung atypischer Antipsychotika Cochrane Schizophrenia Group OA PD Dr. Stefan Leucht Klinik für Psychiatrie und Psychotherapie der TU-München Pfizer Study: Ziprasidone as Effective
Metaanalytische Evaluierung atypischer Antipsychotika Cochrane Schizophrenia Group OA PD Dr. Stefan Leucht Klinik für Psychiatrie und Psychotherapie der TU-München Pfizer Study: Ziprasidone as Effective
