Quantitative Analysis of Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Angiogenesis in Retinoblastoma and Their Association with the Clinicopathologic Parameters
|
|
|
- Marilyn Booth
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quantitative Analysis of Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Angiogenesis in Retinoblastoma and Their Association with the Clinicopathologic Parameters * * * Hürkan Kerimoğglu, Hayyam Kıratlı, Ayşse Ayhan Dinçtürk, Figen Söylemezoğlu and Sevgül Bilgiç *Ocular Oncology Service, Department of Ophthalmology; Department of Pathology, Hacettepe Faculty of Medicine, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey Purpose: Quantitative analyses of proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis, which may be important for the prognosis of retinoblastoma, were performed and possible associations with some well-known clinicopathologic parameters were investigated. Methods: Fifty-three pathology specimens (43 enucleations, 10 exenterations) were evaluated by immunohistochemical methods. The proliferative index was detected by Ki67 antibody staining. The apoptotic index was calculated by the in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dutp nick end labeling (TUNEL) method, and angiogenesis was detected by CD34 antibody staining. Results: The mean proliferative index was , the mean apoptotic index was , and the microvessel density and mean vascular area were determined as and , respectively. Statistical analysis showed that the proliferative index was directly proportional to the tumor dimensions (P.001). In addition, the tumor dimensions were larger in cases where the apoptotic index was below 2.4% (P.011). In cases where the apoptotic index was over 2.4%, no metastasis was observed and also a lower proliferative index was found (P.014). Conclusions: Proliferation appears to be more important than apoptosis and angiogenesis in determining the tumor dimensions. The apoptotic index may be an important predictor of metastasis, and may be useful in the follow-up of bilateral cases with 1 eye enucleated. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2003;47: Japanese Ophthalmological Society Key Words: Angiogenesis, apoptosis, in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dutp nick end labeling, proliferative index, retinoblastoma. Introduction Any genetic event acting on the two alleles of the retinoblastoma gene (RB1) and leading to the functional loss of its product, the retinoblastoma protein (prb), ultimately results in the formation of retinoblastoma. 1 The nuclear phosphoprotein prb not only suppresses proliferation through transcription factors, but also modulates apoptosis and cellular differentiation. 2,3 The key aspect of malignancy is uncontrolled tumor growth. Tumor growth is a result of the imbalance between cell proliferation and cell death, either because of suppressed cell death or increased cellular proliferation. These two variables of the equilibrium play important roles as prognostic factors in many human malignancies. 4,5 Received: February 17, 2003 Correspondence and reprint requests to: Hayyam KIRATLI, MD, Associate Professor of Ophthalmology, Hacettepe Hastanesi Göz ABD, Sihhiye TR-06100, Ankara, Turkey. Jpn J Ophthalmol 47, (2003) 2003 Japanese Ophthalmological Society Published by Elsevier Science Inc. The proliferation rate is one of the most important indicators of the biologic behavior of malignancies. Although it can be observed under a light microscope, low reproducibility and high interobserver differences necessitated new and accurate indicators of the proliferation rate. Ki67 is a nuclear protein that is expressed at the beginning of the G 1 phase, increases through the cell cycle, and disappears just after mitosis in a short period of time. 6,7 Thus, proliferating cell fraction can be determined immunohistochemically by using antibodies against Ki67 protein. 7 Apoptosis and necrosis are the two major mechanisms of cell loss in any neoplastic tissue. 8 Apoptosis is a precisely regulated and energy-dependent type of programmed cell death, and has characteristic morphological criteria, including condensation of the nuclear chromatin and cytoplasm and the formation of protuberances on the surface of individual cells. These membrane-bound, well-preserved cell remnants (apoptotic /03/$ see front matter doi: /j.jjo
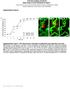
2 566 Jpn J Ophthalmol Vol 47: , 2003 bodies) are subsequently taken up by neighboring cells. 9 Internucleosomal DNA breaks, producing fragments that are multiples of 180 bp, are the major biochemical features of apoptosis and make it possible to identify apoptotic cells by immunohistochemical methods or DNA gel electrophoresis. 10 Angiogenesis is another prognostic parameter. In solid tumors, tumoral angiogenesis is required for tumor growth and metastasis. 11 Angiogenesis is a complex, multi-step process involving extracellular matrix remodelling, endothelial cell migration and proliferation, capillary differentiation, and anastomosis. 12 CD34, a well-known myeloid progenitor cell antigen, can be detected immunohistochemically on the artery, vein, and capillary walls for assessment of microvessel density (MVD), for quantitative analysis of angiogenesis. 13 This immunohistochemical study presents a quantitative analysis of proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis, and their relationship with tumor diameters, differentiation type, necrosis rate, calcification, choroidal, scleral, and optic nerve invasion, presence of metastasis, and surgery type. Materials and Methods A total of 53 enucleation and exenteration specimens obtained from patients with retinoblastoma treated between 1995 and 2001 at the Ocular Oncology Service of the Ophthalmology Department of Hacettepe University Hospital, formed the study group. Clinical data were obtained from the medical records, including age, sex, laterality, presence of metastasis, and operation type. For histopathological and immunohistochemical evaluation, serial 5-µm thick sections were obtained from representative paraffin blocks. Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded sections from all specimens were stained by hematoxylin eosin. The sections were evaluated under a light microscope and neoplasms were grouped as differentiated and undifferentiated. Differentiated tumors were characterised by the presence of Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes and fleurettes, and undifferentiated tumors were composed of small cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and scanty cytoplasms. The extent of necrosis and calcification in tumor tissue was noted and the area of the tissue section occupied by necrosis was recorded as a percentage (%). The presence of invasion of choroid, sclera, and optic nerve surgical borders was noted. For immunohistochemical evaluation of Ki67 and CD34, two series of sections were deparaffinized and rehydrated through xylene and graded alcohol. Endogenous peroxidase was quenched with 3.0% hydrogen peroxidase in methanol for 10 minutes. Following phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) rinses, sections were immersed in citrate buffer (10 mm citric acid monohydrate, adjusted to ph 6.0) and heated in a microwave at boiling point for 20 minutes. Then the microwave-irradiated sections were cooled to room temperature and washed with PBS. They were then incubated in protein blockage solution (Zymed Laboratories, San Francisco, CA, USA) for 10 minutes. Sections were incubated with primary antibodies; mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody (Neomarkers, Fremont, CA, USA) diluted 1:100 in PBS for Ki67 immunostaining and mouse anti-human monoclonal antibody (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) diluted 1:25 in PBS for CD34 immunostaining. No primary antibody was added on sections used as negative controls. After PBS rinse, sections were treated with biotinylated second antibody (Zymed) for 10 minutes and enzyme conjugate (HRP-streptavidin, Zymed) for 10 minutes at room temperature. The reaction was developed with diaminobenzidine (DAKO, Carpinteria, CA, USA) and slides were counterstained in hematoxylin for 5 seconds. For evaluation of the proliferative index (PI) in each section, a minimum of 2000 cells were counted at 40 magnification on the monitor using a video system. The fraction (%) of the cells that showed positive nuclear staining for Ki67 antigen was considered to be the PI (Figure 1A). For assessment of microvessel density (MVD) and mean vascular area (MVA), the entire area of the immunostained tumor at 10 magnification was scanned and the five separate, most highly vascularized areas (hot spots) were identified. Vessels were counted at 40 magnification on the monitor (Sony PVM-1371QM) using a video system (Sony DXC-101P). Any immunolabeled vessel, clearly separate from an adjacent one either totally inside the monitor or touching the borders, was counted as a microvessel. The mean of five counts was used for the analysis of MVD. For analysis of MVA the mean of the endothelial cell count of these five areas was used (Figures 1C and 1D). For evaluation of apoptosis, a commercially available kit (ApopTag-In situ Apoptosis Detection Kit/Peroxidase; Oncor, Gaithersburg, MD, USA) was used. The technique was performed as described elsewhere. 10 Briefly, formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded 5-µm tissue sections were deparaffinized. Nuclear proteins were stripped from DNA by incubating in proteinase K for 30 minutes, and endogenous peroxidase was blocked with 2% H 2 O 2. Sections were incubated in a buffer containing terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) and digoxigenin-labeled dutp, followed by anti-digoxigenin conjugated peroxidase treatment. Diaminobenzidine was used as chromogen, and background staining was done with methyl green. For negative controls TdT reaction solution was replaced by distilled water.
3 H. KERIMOĞLU ET AL. RETINOBLASTOMA IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY 567 Figure 1. Photomicrographs illustrating the immunohistochemical staining of Ki67 expression (A), in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dutp nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining (B), and CD34 expression (C,D). (A) Positive nuclear Ki67 staining of tumor cells. Bar 25 µm. (B) Two apoptotic neoplastic cells showing TUNEL-positive staining. Bar 10 µm. (C,D) Vascular endothelial staining with CD34. Bars 25 µm). In non-necrotic viable tumor tissue, at least 1000 cells were counted from the same slide for each specimen using an 100 objective. Apoptotic cells were defined by the presence of perinuclear chromatin condensation and apoptotic bodies, while cells showing more diffuse cytoplasmic staining were considered as necrotic and were not counted (Figure 1B). The fraction (%) of the apoptotic cells was considered to be the apoptotic index (AI). SPSS for Windows version 10.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analysis. The relationship between clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical parameters was analysed by χ 2 test, Fisher s Exact Test, independent samples t-test, and Mann Whitney U-test. P.05 was considered as statistically significant. Results Clinical characteristics of patients and histopathological features of retinoblastoma specimens are presented in Table 1. The relationships between clinical, histopathological, and immunohistochemical data were statistically analyzed (Table 2). According to the data reviewed, undifferentiated tumors predominated in exenteration specimens (P.034) and in those tumors with basal diameters 15 mm (P.001). A necrosis rate 50% was detected in cases showing choroidal invasion (P.047) and in cases showing metastasis (P.044). Tumor diameters 15 mm were more frequently associated with choroidal invasion (P.036), had a higher necrosis rate (P.002) and calcification (P.001). Metastasis was more frequent in undifferentiated cases and in cases whose tumor diameters were 15 mm, but the difference was not statistically significant. The mean ( SD) proliferative index of 41 cases was found to be (range, %). The proliferative index was directly proportional to tumor dimensions and was higher in tumors with diameters 15
4 568 Jpn J Ophthalmol Vol 47: , 2003 Table 1. Clinical Characteristics of Retinoblastoma Patients and Histopathological Features of Specimens Analyzed in the Study Characteristics No. of Cases (%) Sex Male 26 (49) Female 27 (51) Age Mean (range) 2.4 years (1 8 years) Laterality Bilateral 23 (43.3) Unilateral 30 (56.7) Metastasis Orbital 9 (17) Central nervous system 1 (1.9) Bone marrow 2 (3.8) Invasion Choroidal 12 (22.6) Scleral 7 (13.2) Optic nerve resection border 8 (15.1) Operation type Enucleation 43 (81.8) Exenteration 10 (18.2) Differentiation Differentiated 28 (52.8) Undifferentiated 25 (47.2) Tumor diameter 15 mm 35 (66) 15 mm 18 (34) Necrosis 50% 14 (26.5) 50% 39 (73.5) Calcification 37 (69.8) 16 (30.2) mm (P.001). The apoptotic index was determined to be lower in cases whose PI was over 35% (P.014). The mean ( SD) apoptotic index was calculated as (range, %). The apoptotic index was definitely lower in cases showing metastasis (P.005). AI was also lower in tumors with basal diameters 15 mm and in exenteration specimens, but the difference was not statistically significant. In cases whose AI was under 2.4%, metastasis was more frequent (P.024) and tumor diameters were larger (P.011). There was no metastasis in cases whose AI was 2.4%. PI was also higher in cases whose AI was 2.4% (P.014). Microvessel density and mean vascular area of 48 cases were determined as (range, 1 11) and (range, ), respectively. MVD was found to be lower in tumors with diameters 15 mm (P.043) and MVA was found to be higher in undifferentiated tumors (P.039). Table 2. Statistical Associations Between Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical parameters No. of Statistical Relationship Examined Specimens Association Undifferentiated RB and 53 P.001* tumor diameter ( 15 mm) Undifferentiated RB and 53 P.034* operation type (exenteration) Undifferentiated RB and 53 P.067* metastasis Undifferentiated RB and 53 P.055* choroidal invasion Necrosis rate ( 50%) and 53 P.047* choroidal invasion Necrosis rate ( 50%) and 53 P.044* metastasis Tumor diameter ( 15 mm) 53 P.036* and choroidal invasion Tumor diameter ( 15 mm) 53 P.002* and necrosis rate Tumor diameter ( 15 mm) 53 P.001* and calcification Higher PI and tumor diameter 41 P.001, t PI ( 35%) and AI 32 P.014, U 28.0 Lower A1 and tumor 36 P.195, t diameter ( 15 mm) Lower A1 and operation 36 P.072, U 56.0 type (exenteration) Lower A1 and metastasis 36 P.005, U 27.0 A1 ( 2.4%) and metastasis 36 P.024* A1 ( 2.4%) and tumor 36 P.011* diameter ( 15 mm) AI ( 2.4%) and PI 32 P.014, t Lower MVD and tumor 48 P.043, t diameter ( 15 mm) Higher MVA and 48 P.039, t undifferentiated RB RB: retinoblastoma, PI: proliferative index, AI: apoptotic index, MVD: microvessel density, MVA: mean vascular area. *Fisher s Exact Test. Independent samples t test. Mann-Whitney U-test. Discussion Histopathological findings including involvement of the optic nerve, choroid, sclera, ciliary body, iris, and anterior chamber were used to determine the biological behavior and prognosis of retinoblastoma for many years. 14,15 In the absence of prb, the cell cycle cannot be stopped at the G 1 restriction point and cells go through the S phase and proliferate continuously. Ki67 immunostaining has the advantage of detecting precisely the proliferating cell population during the cell cycle, except for the G 0 phase. 6
5 H. KERIMOĞLU ET AL. RETINOBLASTOMA IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY 569 The proliferative index and the apoptotic index may have prognostic significance along with other clinicopathologic parameters. Although the proliferative index has been correlated with the clinical course in many human malignancies, there are only a few quantitative studies performed on retinoblastoma. Kim et al 22 investigated the prognostic importance of PI and AI in retinoblastoma patients. PI was found to be 21% for the whole group, ranging from 0.93% to 70.16%. No correlation between differentiation type and PI could be established, but PI was found to be higher in patients with recurrence. Disease-free survival of patients whose PI was 40% was found to be shorter. PI was also directly correlated with the tumor grade, although AI did not correlate with either the tumor grade or the clinical results. 22 In a recent study, Orjuela et al 23 reported a highly significant correlation between advanced clinical stage and a higher Ki67 proliferative index. Among children with unilateral disease, the mean PI was higher in children with advanced clinical disease (stage 3 4) than in those with earlier stage disease (stage 1 2). However, among children with bilateral disease, the mean PI was not significantly higher for children at an advanced clinical stage. It has been suggested that unregulated cell growth contributes to a more aggressive disease phenotype of tumors without a germinal loss of prb. 23 In our study, PI was higher in patients with tumor diameters 15 mm. Although AI was lower in the same group of patients, this result was not statistically significant. However, there was an inversely proportional correlation between AI and PI 35%. These results suggest that proliferation but not apoptosis may be the determining factor in tumor growth. Apoptosis might have balanced proliferation in tumors with a PI 35%; however, the mechanism triggering proliferation may also suppress apoptosis in cases with PI 35%. Necrosis rate was also higher in tumors with a largest diameter 15 mm, and MVD was lower in tumors with a diameter 15 mm. These results can also explain why the main cellular death mechanism was necrosis in larger tumors because of vascular insufficiency and ensuing hypoxia. Also, tumors with a basal diameter 15 mm had a higher rate of choroidal invasion, and PI was higher in tumors with choroidal invasion, but that was not statistically significant. Although apoptosis is a common feature of all malignant tumors, only a few quantitative studies have been performed regarding retinoblastoma. Based on light microscopic findings, Madigan and Penfold 24 reported an AI of (range, ) in a series of 5 cases with retinoblastoma. In another study, the rate of apoptosis was classified qualitatively as high (5 or more apoptotic counts per field under 250 magnification) or low (fewer than 5 per field) rather than using the quantitative data by Kim et al. 22 The other study involved 13 retinoblastoma specimens, and apoptotic cell death was shown by the TUNEL method. It was reported that differentiated tumors had a low ( 1%), and undifferentiated cases had a higher, ( 8%) rate of apoptosis. 25 Necrosis in tumor tissue mainly results from ischemia, and mild hypoxia is a known factor inducing apoptosis. 5 When we grouped the tumors having necrosis under and over 50%, AI was higher in the group with a necrosis rate under 50%, but the difference was not statistically significant. The apoptotic index was definitely lower in cases with metastasis. No metastasis was observed in patients whose AI was 2.4%. Although AI was low in these cases, the necrosis rate was higher and this relation may indicate rapid tumor growth because of suppressed programmed cell death. Necrosis might have been induced by insufficiency of the vascular supply. Two of the three cases who died during follow-up and all of the cases who had metastasis had an AI 2.4%. Therefore, an AI 2.4% can be an indicator of poor prognosis, and especially for bilateral cases it can be an indicator for close follow-up for metastasis. In exenteration specimens, AI was lower than in enucleation specimens and this finding can indicate an aggressive biological behavior. There was no correlation between metastasis and PI. Aggressive behavior of the tumor may be induced by the diminished effect of programmed cell death. Although metastasis was more prevalent among undifferentiated tumors, AI and PI exhibited no significant difference between differentiated and undifferentiated tumors. Tumor growth, progression, and metastasis can be possible only with adequate vascular supply. 11 Many investigators observed the same association of increasing tumor vascularity with various measures of tumor aggressiveness, such as higher stage at presentation, greater incidence of metastasis, and decreased patient survival. 26 An association with MVD, quantified by microvessel counting, and tumor prognosis or metastasis has been reported in several human tumors In one study, aqueous humor from 30 enucleated eyes of retinoblastoma patients and 9 cell cultures from retinoblastoma patients were tested for angiogenesis activity using capillary endothelial cell migration assays. Aqueous humor from 90% of the retinoblastoma eyes stimulated endothelial cell migration, compared with only 25% of control eyes. 34 Several other studies have shown that certain intraocular tumors, such as retinoblastoma, display angiogenesis capacity before clinically evident neovascular changes. 35
6 570 Jpn J Ophthalmol Vol 47: , 2003 In our study, MVD was higher in tumors with diameters 15 mm. Although it was expected that larger tumors need more vascular supply and would have higher MVD, it is possible that the rate of proliferation exceeds the rate of angiogenesis in these tumors. This theory is also supported by the higher rate of necrosis in larger tumors, which is induced by hypoxia. Mean vascular area was higher in undifferentiated retinoblastomas. When we consider that choroidal invasion and metastasis were seen more frequently in undifferentiated cases, higher mean vascular area may support the fact that cases with undifferentiated retinoblastoma have a well-developed vascular supply. Conclusion This study provides quantitative data about the rate of proliferation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis, and their association with the well-known clinicopathologic parameters concerning retinoblastoma. It revealed that tumor dimensions were larger and choroidal invasion was more frequent in undifferentiated cases. Proliferation is more important than apoptosis and angiogenesis in determining the tumor growth. For bilateral cases, the apoptotic index may be an important indicator of metastasis after enucleation of 1 eye. Presented in part at the European Association for Vision and Eye Research meeting 2002, Alicante, Spain. References 1. Harbour JW. Molecular basis of low penetrance retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol 2001;119: Herwig S, Strauss M. The retinoblastoma protein: a master regulator of cell cycle, differentiation and apoptosis. Eur J Biochem 1997; 246: Hu QJ, Lees JA, Buchkovich KJ, Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein physically associates with the human cdc2 kinase. Mol Cell Biol 1992;12: Giuliano M, Lauricella M, Vassallo E, Carabillo M, Vento R, Tesoriere G. Induction of apoptosis in human retinoblastoma cells by topoisomerase inhibitors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998;39: Kerr JF, Winterford CM, Harmon BV. Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 1994;73: Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH, Schwab U, Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation: associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol 1984;133: Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H, Stein H. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer 1983;31: Wyllie AH. The biology of cell death in tumours. Anticancer Res 1985;5: Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 1972;26: Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 1992;119: Folkman J. Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 1995;333: Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other diseases. Nat Med 1995;1: Weidner N. Intratumor microvessel density as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol 1995;147: Redler LD, Ellsworth RM. Prognostic importance of choroidal invasion in retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol 1973;90: Stannard C, Lipper S, Sealy R, Sevel D. Retinoblastoma: correlation of invasion of the optic nerve and choroid with prognosis and metastases. Br J Ophthalmol 1979;63: Gerdes J. Ki-67 and other proliferation markers useful for immunohistological diagnostic and prognostic evaluations in human malignancies. Semin Cancer Biol 1990;1: Matsumoto M, Komiyama K, Okaue M, et al. Predicting tumor metastasis in patients with oral cancer by means of the proliferation marker Ki67. J Oral Sci 1999;41: Sökmensüer C, Gedikoglu G, Uzunalimoglu B. Importance of proliferation markers in gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors: a clinicopathologic study. Hepatogastroenterology 2001;48: Watanabe T, Oda Y, Tamiya S, Kinukawa N, Masuda K, Tsuneyoshi M. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: high Ki67 labelling index is the significant prognostic indicator. Histopathology 2001; 39: Wu TT, Chen JH, Lee YH, Huang JK. The role of bcl-2, p53, and ki-67 index in predicting tumor recurrence for low grade superficial transitional cell bladder carcinoma. J Urol 2000;163: Losa M, Barzaghi RL, Mortini P, et al. Determination of the proliferation and apoptotic index in adrenocorticotropin-secreting pituitary tumors: comparison between micro- and macroadenomas. Am J Pathol 2000;156: Kim JC, Chi JG, Choi HS, et al. Proliferation not apoptosis as a prognostic indicator in retinoblastoma. Virchows Arch 1999;434: Orjuela M, Orlow I, Dudas M, et al. Alterations of cell cycle regulators affecting the RB pathway in nonfamilial retinoblastoma. Hum Pathol 2001;32: Madigan MC, Penfold PL. Human retinoblastoma: a morphological study of apoptotic, leukocytic and vascular elements. Ultrastruct Pathol 1997;21: Cha SC, Suh KS, Song KS, Lim K. Cell death in retinoblastoma; electron microscopic, immunohistochemical and DNA fragmentation studies. Ultrastruct Pathol 2000;24: Weidner N. Intratumoral microvessel density as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol 1995;147: Weidner N, Carroll PR, Flax J, Blumenfeld W, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol 1993;143: Guidi AJ, Schnitt SJ, Fischer L, et al. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) expression and angiogenesis in patients with ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer 1997;80: Wakisaka N, Wen QH, Yoshizaki T, et al. Association of vascular endothelial growth factor expression with angiogenesis and lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope 1999; 109:
7 H. KERIMOĞLU ET AL. RETINOBLASTOMA IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY Nativ O, Sabo E, Reiss A, Wald M, Madjar S, Moskovitz B. Clinical significance of tumor angiogenesis in patients with localized renal cell carcinoma. Urology 1998;51: Schoell WM, Pieber D, Reich O, et al. Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic factor in ovarian carcinoma: quantification of endothelial immunoreactivity by image analysis. Cancer 1997;80: Simpson JF, Ahn C, Battifora H, Esteban JM. Endothelial area as a prognostic indicator for invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer 1996;77: Mäkitie T, Summanen P, Tarkkanen A, Kivelä T. Microvascular density in predicting survival of patients with choroidal and ciliary body melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999;40: Albert DM, Tapper D, Robinson NL, Felman R. Retinoblastoma and angiogenesis activity. Retina 1984;4: Tapper D, Langer R, Bellows AR, Folkman J. Angiogenesis capacity as a diagnostic marker for human eye tumors. Surgery 1979; 86:36 40.
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Retinoblastoma. Protocol applies to retinoblastoma only.
 Retinoblastoma Protocol applies to retinoblastoma only. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying Checklist) Biopsy (No Accompanying
Retinoblastoma Protocol applies to retinoblastoma only. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying Checklist) Biopsy (No Accompanying
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
& IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
CD15 and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 8, No., 8 CD and CEA expression in thymic epithelial neoplasms AYTEKİN AKYOL, AYŞEGÜL ÜNER Hacettepe University, Department of Pathology, Ankara-Turkey ABSTRACT The aim
Deregulation of Cell Growth and Caspase-3 Expression in Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Salivary Glands
 J Med Sci 00;():0-00 http://jms.ndmctsgh.edu.tw/00.pdf Copyright 00 JMS Kuo-Chou Chou, et al. Deregulation of Cell Growth and Caspase- Expression in Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Salivary Glands Kuo-Chou
J Med Sci 00;():0-00 http://jms.ndmctsgh.edu.tw/00.pdf Copyright 00 JMS Kuo-Chou Chou, et al. Deregulation of Cell Growth and Caspase- Expression in Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma of the Salivary Glands Kuo-Chou
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization with Colorectal Carcinoma: A Pilot Study
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Journal of Adenocarcinoma Vol. 1 No. 1:5 DOI: 10.21767/2572-309X.10005 Correlation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Neovascularization
Expression of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 (TTF-1) in Lung Carcinomas and Its Correlations with Apoptosis and Angiogenesis
 16 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2009) 6: 16~20 DOI 10.1007/s11805-009-0016-z Expression of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 (TTF-1) in Lung Carcinomas and Its Correlations with Apoptosis and Angiogenesis Xiaoyan
16 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2009) 6: 16~20 DOI 10.1007/s11805-009-0016-z Expression of Thyroid Transcription Factor-1 (TTF-1) in Lung Carcinomas and Its Correlations with Apoptosis and Angiogenesis Xiaoyan
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma
 Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas
 Anatomic Pathology / EVALUATION OF NECROTIC MALIGNANT MELANOMAS Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas Daisuke Nonaka, MD, Jordan Laser, MD, Rachel Tucker, HTL(ASCP), and Jonathan
Anatomic Pathology / EVALUATION OF NECROTIC MALIGNANT MELANOMAS Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Necrotic Malignant Melanomas Daisuke Nonaka, MD, Jordan Laser, MD, Rachel Tucker, HTL(ASCP), and Jonathan
Evaluation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and Bcl-2 protein in nonsmall cell lung cancer
 166 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 35, No.4, 2005 Evaluation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and cl-2 protein in nonsmall cell lung cancer LEVENT DERTS Z 1, GÜLY ÖZ L M 2, LKNUR KÜKNER 2, REM
166 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 35, No.4, 2005 Evaluation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and cl-2 protein in nonsmall cell lung cancer LEVENT DERTS Z 1, GÜLY ÖZ L M 2, LKNUR KÜKNER 2, REM
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
Apoptosis in Retinal Ganglion Cell Decrease in Human Glaucomatous Eyes
 ELSEVIER Apoptosis in Retinal Ganglion Cell Decrease in Human Glaucomatous Eyes Shigekuni Okisaka, Akira Murakami, Atsushi Mizukawa and Junji Ito Department of Ophthalmology, National Defense Medical College,
ELSEVIER Apoptosis in Retinal Ganglion Cell Decrease in Human Glaucomatous Eyes Shigekuni Okisaka, Akira Murakami, Atsushi Mizukawa and Junji Ito Department of Ophthalmology, National Defense Medical College,
Assessment of Microvessel Density (Angiogenesis) And Its Correlation with Tumor Grade
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. XI (March. 2017), PP 15-19 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Microvessel Density (Angiogenesis)
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 3 Ver. XI (March. 2017), PP 15-19 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Microvessel Density (Angiogenesis)
Uveal Melanoma. Protocol applies to malignant melanoma of the uvea.
 Uveal Melanoma Protocol applies to malignant melanoma of the uvea. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying Checklist) Biopsy (No Accompanying
Uveal Melanoma Protocol applies to malignant melanoma of the uvea. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying Checklist) Biopsy (No Accompanying
Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67 and p53 Expressions to Histopathology Grading of Breast Cancer in Makassar, Indonesia
 Cancer Research Journal 2016; 4(3): 43-47 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20160403.11 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67
Cancer Research Journal 2016; 4(3): 43-47 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20160403.11 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Correlation Between GATA-3, Ki67
Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs
 151 Technical note Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs Lukas Günther a, and Peter Hufnagl b a Department of Surgery, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg,
151 Technical note Technique and feasibility of a dual staining method for estrogen receptors and AgNORs Lukas Günther a, and Peter Hufnagl b a Department of Surgery, University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
 Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Original Article Middle East Journal of Cancer; April 2018; 9(2): 85-90 A Comparison of Endothelial Cell-Selective Adhesion Molecule and von Willebrand Factor Expression in Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor survival in breast cancer patients
 Journal of BUON 17: 663-668, 2012 2012 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor
Journal of BUON 17: 663-668, 2012 2012 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor
Potential Value of Hormone Receptor Assay in Carcinoma In Situ of Breast
 Potential Value of Hormone Receptor Assay in Carcinoma In Situ of Breast ROBERT BARNES, M.D. AND SHAHLA MASOOD, M.D. The estrogen receptor (ER) expression of invasive breast cancer has been extensively
Potential Value of Hormone Receptor Assay in Carcinoma In Situ of Breast ROBERT BARNES, M.D. AND SHAHLA MASOOD, M.D. The estrogen receptor (ER) expression of invasive breast cancer has been extensively
Research Article Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Expression in Indonesian Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
 Oncology Volume 2016, Article ID 3215463, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3215463 Research Article Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Expression in Indonesian Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
Oncology Volume 2016, Article ID 3215463, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3215463 Research Article Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Expression in Indonesian Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
Tumor Angiogenesis in Stage II Colorectal Carcinoma Association With Survival
 ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY Original Article Tumor Angiogenesis in Stage II Carcinoma Association With Survival BARBARA F. BANNER, MD, ROB WHITEHOUSE, STEPHEN P. BAKER, MSPH, AND RICHARD S. SWANSON, MD We studied
ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY Original Article Tumor Angiogenesis in Stage II Carcinoma Association With Survival BARBARA F. BANNER, MD, ROB WHITEHOUSE, STEPHEN P. BAKER, MSPH, AND RICHARD S. SWANSON, MD We studied
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Method of data collection: Clinical details were obtained for 50 IDC-NOS cases
 Assessment of Microvessel Density (Angiogenesis) and its Correlation with Hormonal Status of Carcinoma Breast Dr. P. Vijaya Baskar 1, Dr. M. Gunasundari 2 1, 2 Institute of Pathology, Madras Medical College,
Assessment of Microvessel Density (Angiogenesis) and its Correlation with Hormonal Status of Carcinoma Breast Dr. P. Vijaya Baskar 1, Dr. M. Gunasundari 2 1, 2 Institute of Pathology, Madras Medical College,
Pathologic characteristics of prostatic adenocarcinomas: a mapping analysis of Korean patients
 Pathologic characteristics of prostatic adenocarcinomas: a mapping analysis of Korean patients SY Song 1 *, SR Kim 1, G Ahn 1 & HY Choi 2 1 Department of Pathology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine,
Pathologic characteristics of prostatic adenocarcinomas: a mapping analysis of Korean patients SY Song 1 *, SR Kim 1, G Ahn 1 & HY Choi 2 1 Department of Pathology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine,
Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma
 Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 19/May 12, 2014 Page 5307
 PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY (KI67 EXPRESSION) IN OSTEOSARCOMA IN CHILDREN Moumita Paul 1, Arnab Karmakar 2, Uttara Chatterjee 3, Uttam Kumar Saha 4, Koushik Saha 5, Nanda Dulal Chatterjee
PROGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY (KI67 EXPRESSION) IN OSTEOSARCOMA IN CHILDREN Moumita Paul 1, Arnab Karmakar 2, Uttara Chatterjee 3, Uttam Kumar Saha 4, Koushik Saha 5, Nanda Dulal Chatterjee
3/22/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Ki-67 in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms According to WHO 2017.
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Ki-67 in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms According to WHO 2017. USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Ki-67 in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms According to WHO 2017. USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to influence or control
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry
 Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Single and Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Steve Westra, BS Reagent Product Specialist Leica Biosystems IHC Theory Polyclonal vs Monoclonal Polyclonal reagents Detect a multitude of epitopes Batch to batch
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
OMPJ Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia 10.5005/jp-journals-10037-1003 and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma ORIGINAL RESEARCH Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression
DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY)
 Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Spontaneous Regression Mechanisms of Lumbar Disc Herniation Role of apoptosis and macrophages during disc tissue resorption
 Spontaneous Regression Mechanisms of Lumbar Disc Herniation Role of apoptosis and macrophages during disc tissue resorption Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD, 1 Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 2, Adam Meir, FRCS, 2 1 Dept.
Spontaneous Regression Mechanisms of Lumbar Disc Herniation Role of apoptosis and macrophages during disc tissue resorption Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD, 1 Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 2, Adam Meir, FRCS, 2 1 Dept.
Immunohistochemical and Immunogenetic Analyses of Ocular Adnexal Lymphoid Proliferation
 Immunohistochemical and Immunogenetic Analyses of Ocular Adnexal Lymphoid Proliferation Toshinobu Kubota, Yasushi Yatabe, Shinobu Awaya, Junpei Asai and Naoyoshi Mori Department of Ophthalmology and Pathology,
Immunohistochemical and Immunogenetic Analyses of Ocular Adnexal Lymphoid Proliferation Toshinobu Kubota, Yasushi Yatabe, Shinobu Awaya, Junpei Asai and Naoyoshi Mori Department of Ophthalmology and Pathology,
Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts
 Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Turk J Med Sci 33 (2003) 243-247 TÜB TAK CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Expression of the Tumour Suppressor Gene p53 in Odontogenic Cysts Ayla ÖZVEREN 1, Can TUSKAN 3, Mehmet YALTIRIK 3, Belir ATALAY 3, Gülçin
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
The Significance Of Angiogenesis in the Biological Behavior of Colorectal Carcinoma and its Metastatic Lymph Nodes Using CD34 Antibody
 The Significance Of Angiogenesis in the Biological Behavior of Colorectal Carcinoma and its Metastatic Lymph Nodes Using CD34 Antibody Professor Dr.Salem R. Hammodi* Dr. Dahlia R. Mohammed** *M.B.Ch B.
The Significance Of Angiogenesis in the Biological Behavior of Colorectal Carcinoma and its Metastatic Lymph Nodes Using CD34 Antibody Professor Dr.Salem R. Hammodi* Dr. Dahlia R. Mohammed** *M.B.Ch B.
Apoptosis in cutaneous melanomas
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(4):343 347 ORIGINAL PAPER Apoptosis in cutaneous melanomas MARIANA COSTACHE 1), OLGA SIMIONESCU 2), MARIA SAJIN 3), ALINA CHEFANI 4), ANA MARIA ENE
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2007, 48(4):343 347 ORIGINAL PAPER Apoptosis in cutaneous melanomas MARIANA COSTACHE 1), OLGA SIMIONESCU 2), MARIA SAJIN 3), ALINA CHEFANI 4), ANA MARIA ENE
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test
 753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
753 Differentiation of Tumors with Specific Red Cell Adherence (SRCA) test Dr. Abhishek A Mangaonkar *, Dr. A G Valand 1 Intern, Grant Medical College and Sir J.J. Group of Hospitals, Mumbai, India 2 Professor,
Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression Determines Neoangiogenesis in Gallbladder Carcinomas
 & Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression Determines Neoangiogenesis in Gallbladder Carcinomas Mateja Legan¹*, Boštjan Luzar², Vera Ferlan-Marolt², Andrej Cör¹ 1. Institute of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of
& Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression Determines Neoangiogenesis in Gallbladder Carcinomas Mateja Legan¹*, Boštjan Luzar², Vera Ferlan-Marolt², Andrej Cör¹ 1. Institute of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis
 Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
Role of cyclin E and p53 expression in progression of early gastric cancer
 160 Gastric Cancer (1998) 1: 160 165 L. Jiaqing et al.: Cyclin E in early gastric cancer 1998 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Original article Role of cyclin E and p53 expression
160 Gastric Cancer (1998) 1: 160 165 L. Jiaqing et al.: Cyclin E in early gastric cancer 1998 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Original article Role of cyclin E and p53 expression
Object Localization Procedure for Intratumoral Microvessel Density Estimation
 Object Localization Procedure for Intratumoral Microvessel Density Estimation OVIDIU GRIGORE ANDRE PUGA Telecommunications and Multimedia Department INESC Porto Praça da Republica 93, 4050-497 Porto PORTUGAL
Object Localization Procedure for Intratumoral Microvessel Density Estimation OVIDIU GRIGORE ANDRE PUGA Telecommunications and Multimedia Department INESC Porto Praça da Republica 93, 4050-497 Porto PORTUGAL
CD10 expression in stromal component of invasive breast carcinoma: A potential prognostic determinant
 Original article CD10 expression in stromal component of invasive breast carcinoma: A potential prognostic determinant Fereshteh Mohammadizadeh 1, Majid Salavati 2, Noushin Afshar Moghaddam 1 1 2 Associate
Original article CD10 expression in stromal component of invasive breast carcinoma: A potential prognostic determinant Fereshteh Mohammadizadeh 1, Majid Salavati 2, Noushin Afshar Moghaddam 1 1 2 Associate
HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer
 P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
P A T H O L O G Y HER2 CISH pharmdx TM Kit Interpretation Guide Breast Cancer FROM CERTAINTY COMES TRUST For in vitro diagnostic use HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit HER2 CISH pharmdx Kit is intended for dual-color
Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):3726-3731 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0077355 Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma Minhua
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(7):3726-3731 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0077355 Original Article CyclinD1 promotes lymph node metastasis by inducing lymphangiogenesis in human ovarian carcinoma Minhua
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
Središnja medicinska knjižnica
 Središnja medicinska knjižnica Ulamec M., Džombeta T., Čupić H., Leniček T., Tomas D., Krušlin B. (2012) Periacinar retraction clefting and d2-40 expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Pathology Oncology
Središnja medicinska knjižnica Ulamec M., Džombeta T., Čupić H., Leniček T., Tomas D., Krušlin B. (2012) Periacinar retraction clefting and d2-40 expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Pathology Oncology
Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
Table of Contents. 1. Overview. 2. Interpretation Guide. 3. Staining Gallery Cases Negative for CINtec PLUS
 Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
P16 INK4A EXPRESSION AS A POTENTIAL PROGNOSTIC MARKER IN CERVICAL PRECANCEROUS AND CANCEROUS LESIONS IN MOROCCO
 P16 INK4A EXPRESSION AS A POTENTIAL PROGNOSTIC MARKER IN CERVICAL PRECANCEROUS AND CANCEROUS LESIONS IN MOROCCO Yassine Zouheir Laboratory of histo-cytopathology of Institut Pasteur of Morocco, Casablanca,
P16 INK4A EXPRESSION AS A POTENTIAL PROGNOSTIC MARKER IN CERVICAL PRECANCEROUS AND CANCEROUS LESIONS IN MOROCCO Yassine Zouheir Laboratory of histo-cytopathology of Institut Pasteur of Morocco, Casablanca,
Clinico-pathological significance of extra-nodal spread in special types of breast cancer
 Cancer Biol Med 2014;11:116-122. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.02.006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinico-pathological significance of extra-nodal spread in special types of breast cancer Ecmel Isik Kaygusuz,
Cancer Biol Med 2014;11:116-122. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.02.006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinico-pathological significance of extra-nodal spread in special types of breast cancer Ecmel Isik Kaygusuz,
Cytokeratin 5/6 expression in bladder cancer: association with clinicopathologic parameters and prognosis
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3319-4 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH NOTE Open Access Cytokeratin 5/6 expression in bladder cancer: association with clinicopathologic parameters and prognosis Atif Ali
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3319-4 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH NOTE Open Access Cytokeratin 5/6 expression in bladder cancer: association with clinicopathologic parameters and prognosis Atif Ali
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma
 Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma T.J. Zhou 1, X.H. Huang 1, L. Gong 1 and L. Xiang 2 1 Department of Pathology, the Affiliated Hospital
Vasculogenic mimicry and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cervical squamous cell carcinoma T.J. Zhou 1, X.H. Huang 1, L. Gong 1 and L. Xiang 2 1 Department of Pathology, the Affiliated Hospital
Cyclin-D1 protooncogen expression in prostate cancer
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.30 / No. 1/2000 Cyclin-D1 protooncogen expression in prostate cancer EMİN ÖZBEK 1, BÜLENT MIZRAK 2, MUSTAFA ÖZBEK 3, SÜLEYMAN BÜYÜKBERBER 4, MÜRSEL DAVARCI 1 Departments of
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.30 / No. 1/2000 Cyclin-D1 protooncogen expression in prostate cancer EMİN ÖZBEK 1, BÜLENT MIZRAK 2, MUSTAFA ÖZBEK 3, SÜLEYMAN BÜYÜKBERBER 4, MÜRSEL DAVARCI 1 Departments of
Immunohistochemical determinations in evaluating the prognostic in patient with urinary bladder tumors
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(2):175 179 ORIGINAL PAPER Immunohistochemical determinations in evaluating the prognostic in patient with urinary bladder tumors E. TRAŞCĂ 1), R.
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(2):175 179 ORIGINAL PAPER Immunohistochemical determinations in evaluating the prognostic in patient with urinary bladder tumors E. TRAŞCĂ 1), R.
S ince the introduction of the UK National Breast
 919 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thymidine phosphorylase expression and stromal vascularity in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast N B Teo, B S Shoker, C Jarvis, J P Sloane, C Holcombe... See end of article for
919 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thymidine phosphorylase expression and stromal vascularity in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast N B Teo, B S Shoker, C Jarvis, J P Sloane, C Holcombe... See end of article for
Comparison of CD10 expression in stroma of epithelial and mesenchymal tumors of the breast
 Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science (ISSN: 2315-5159) Vol. 4(1) pp. 051-056, January, 2015 Available online http://garj.org/garjmms/index.htm Copyright 2015 Global Advanced
Global Advanced Research Journal of Medicine and Medical Science (ISSN: 2315-5159) Vol. 4(1) pp. 051-056, January, 2015 Available online http://garj.org/garjmms/index.htm Copyright 2015 Global Advanced
Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland
 Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
Asadi-Amoli et al Adenocarcinoma of RPE Iranian Journal of Ophthalmology - Volume 19, Number 4, 2007
 Adenocarcinoma of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Clinically Diagnosed as Malignant Melanoma; A Case Report with Unsystematic Review of Literature Fahimeh Asadi-Amoli, MD, 1 Hedyeh Moradi, MD 2 Mohammad-Taher
Adenocarcinoma of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Clinically Diagnosed as Malignant Melanoma; A Case Report with Unsystematic Review of Literature Fahimeh Asadi-Amoli, MD, 1 Hedyeh Moradi, MD 2 Mohammad-Taher
S100 protein expression in pituitary adenomas
 S100 protein expression in pituitary adenomas Eugen MELnIc Department of Morphopathology, Nicolae Testemitsanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy Chisinau, the Republic of Moldova Corresponding
S100 protein expression in pituitary adenomas Eugen MELnIc Department of Morphopathology, Nicolae Testemitsanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy Chisinau, the Republic of Moldova Corresponding
Senior of Histopathology Department at Khartoum, Radiation and Isotopes Center
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Immune Histochemical Evaluation of AMACR (P504S) in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Immune Histochemical Evaluation of AMACR (P504S) in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
Bilateral retinoblastoma in early infancy
 Saiju R et al Case report Bilateral retinoblastoma in early infancy Saiju R, Duwal S Tilganga Institute of Ophthalmology, Kathmandu, Nepal Abstract Introduction: Retinoblastoma is the most common primary
Saiju R et al Case report Bilateral retinoblastoma in early infancy Saiju R, Duwal S Tilganga Institute of Ophthalmology, Kathmandu, Nepal Abstract Introduction: Retinoblastoma is the most common primary
3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS
 3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS 3.1 Histopathology 3.1.1 Normal Squamous Epithelium The squamous epithelium that covers the ectocervix of the uterus is composed of different layers starting at the basement membrane
3 CHAPTER 3: RESULTS 3.1 Histopathology 3.1.1 Normal Squamous Epithelium The squamous epithelium that covers the ectocervix of the uterus is composed of different layers starting at the basement membrane
Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K)
 Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Prognostic Importance of the Mitotic Marker Phosphohistone H3 in Cutaneous Nodular Melanoma
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Importance of the Mitotic Marker Phosphohistone H3 in Cutaneous Nodular Melanoma Rita G. Ladstein 1, Ingeborg M. Bachmann 1,2, Oddbjørn Straume 1 and Lars A. Akslen 1,3 Mitotic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Importance of the Mitotic Marker Phosphohistone H3 in Cutaneous Nodular Melanoma Rita G. Ladstein 1, Ingeborg M. Bachmann 1,2, Oddbjørn Straume 1 and Lars A. Akslen 1,3 Mitotic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Figure S1 Treatment with both Sema6D and Plexin-A1 sirnas induces the phenotype essentially identical to that induced by treatment with Sema6D sirna alone or Plexin-A1 sirna alone. (a,b) The cardiac tube
Pathological and clinical characteristics of large prostate cancers predominantly located in the transition zone
 Pathological and clinical characteristics of large prostate cancers predominantly located in the transition zone (2002) 5, 279 284 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1365 7852/02 $25.00
Pathological and clinical characteristics of large prostate cancers predominantly located in the transition zone (2002) 5, 279 284 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1365 7852/02 $25.00
Tumor Angiogenesis: Determined By VEGF Expression, MAGS Scoring, Doppler Study, As Prognostic Indicator In Carcinoma Breast
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 Tumor Angiogenesis: Determined By VEGF Expression, MAGS Scoring, Doppler Study, As Prognostic Indicator In Carcinoma Breast R Shankar, S Tiwary,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 8 Number 1 Tumor Angiogenesis: Determined By VEGF Expression, MAGS Scoring, Doppler Study, As Prognostic Indicator In Carcinoma Breast R Shankar, S Tiwary,
Higher expression of deoxyuridine triphosphatase (dutpase) may predict the metastasis potential of colorectal cancer
 1 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kurume University Hospital, Kurume, Japan; 2 Department of Surgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan; 3 Biostatistics Center, Kurume University,
1 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kurume University Hospital, Kurume, Japan; 2 Department of Surgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan; 3 Biostatistics Center, Kurume University,
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Prognostic Significance of Microvessel Density in Breast Cancer of Indian Population
 Prognostic Significance of Microvessel Density in Breast Cancer of Indian Population Kamlesh Verma MS, Sandeep Kumar MS,FRCS,PhD, A N Srivastava MD. ABSTRACT: INTRODUCTION : Angiogenesis is of key importance
Prognostic Significance of Microvessel Density in Breast Cancer of Indian Population Kamlesh Verma MS, Sandeep Kumar MS,FRCS,PhD, A N Srivastava MD. ABSTRACT: INTRODUCTION : Angiogenesis is of key importance
Title Receptor, and Laminin/Collagen Rece. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1993, 38
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Investigation o Keratin, EMA, Laminin, Fibronectin, Receptor, and Laminin/Collagen Rece Senba, Masachika; Zhong, Xue-Yun; I Citation
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Investigation o Keratin, EMA, Laminin, Fibronectin, Receptor, and Laminin/Collagen Rece Senba, Masachika; Zhong, Xue-Yun; I Citation
Breast Carcinoma in Pakistani Females: A. Morphological Study of 572 Breast Specimens
 Breast Carcinoma in Pakistani Females: A. Morphological Study of 572 Breast Specimens M. Shahid Siddiqui,Naila Kayani,Sara Sulaiman,Akbar S. Hussainy,Sajid H. Shah,Suhail Muzaffar ( Faculty of Health Sciences,
Breast Carcinoma in Pakistani Females: A. Morphological Study of 572 Breast Specimens M. Shahid Siddiqui,Naila Kayani,Sara Sulaiman,Akbar S. Hussainy,Sajid H. Shah,Suhail Muzaffar ( Faculty of Health Sciences,
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Afrah A. Khalil, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Seta A. Sarkis, B.D.S., M.Sc., Ph.D. (2) ABSTRACT Background: Understanding the
Immunohistochemical Expressions of AKT, ATM and Cyclin E in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Afrah A. Khalil, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Seta A. Sarkis, B.D.S., M.Sc., Ph.D. (2) ABSTRACT Background: Understanding the
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 3 Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma. B Rattan, A Baghla, M Manjari, P Kakkar, S Kahlon, S Paul Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 3 Immunohistochemical Expression Of Cytokeratin 8 And 18 In Breast Carcinoma. B Rattan, A Baghla, M Manjari, P Kakkar, S Kahlon, S Paul Citation
Brief Formalin Fixation and Rapid Tissue Processing Do Not Affect the Sensitivity of ER Immunohistochemistry of Breast Core Biopsies
 Brief Formalin Fixation and Rapid Tissue Processing Do Not Affect the Sensitivity of ER Immunohistochemistry of Breast Core Biopsies Victoria Sujoy, MD, Mehrdad Nadji, MD, and Azorides R. Morales, MD From
Brief Formalin Fixation and Rapid Tissue Processing Do Not Affect the Sensitivity of ER Immunohistochemistry of Breast Core Biopsies Victoria Sujoy, MD, Mehrdad Nadji, MD, and Azorides R. Morales, MD From
An Official Periodical of The International Academy of Cytology and the Italian Society of Urologic Pathology
 ANALYTICAL AND QUANTITATIVE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY ARTICLES An Official Periodical of The International Academy of Cytology and the Italian Society of Urologic Pathology Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis
ANALYTICAL AND QUANTITATIVE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY ARTICLES An Official Periodical of The International Academy of Cytology and the Italian Society of Urologic Pathology Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis
WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic Adenocarcinoma to Body Fluids
 Anatomic Pathology / WT1, ESTROGEN RECEPTOR, AND PROGESTERONE RECEPTOR IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic
Anatomic Pathology / WT1, ESTROGEN RECEPTOR, AND PROGESTERONE RECEPTOR IN CYTOLOGY OF BODY FLUIDS WT1, Estrogen Receptor, and Progesterone Receptor as Markers for Breast or Ovarian Primary Sites in Metastatic
Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF- a) Expression in Mice Infected with Aspergillus Fumigatus Using Immunohistochemichal Technique
 International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 (Print & Online) http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
International Journal of Sciences: Basic and Applied Research (IJSBAR) ISSN 2307-4531 (Print & Online) http://gssrr.org/index.php?journal=journalofbasicandapplied ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Cell Death and Cancer. SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou
 Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
Cell Death and Cancer SNC 2D Ms. Papaiconomou How do cells die? Necrosis Death due to unexpected and accidental cell damage. This is an unregulated cell death. Causes: toxins, radiation, trauma, lack of
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r
 Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
Tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis in conjunctival malignant melanoma
 BJO Online First, published on July 23, 2009 as 10.1136/bjo.2008.147355 Tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis in conjunctival malignant melanoma Paul Zimmermann* 1, Tina Dietrich* 1,2, Felix Bock 1, Folkert
BJO Online First, published on July 23, 2009 as 10.1136/bjo.2008.147355 Tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis in conjunctival malignant melanoma Paul Zimmermann* 1, Tina Dietrich* 1,2, Felix Bock 1, Folkert
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis. Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval
 Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
