Does the proliferation fraction help identify mature B cell lymphomas with double- and triple-hit translocations?
|
|
|
- Cory Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Histopathology 2012, 61, DOI: /j x SHORT REPORT Does the proliferation fraction help identify mature B cell lymphomas with double- and triple-hit translocations? Emarene Mationg-Kalaw, 1 Leonard H C Tan, 2 Kevin Tay, 3 Soon Thye Lim, 3 Tiffany Tang, 3 Yvonne Y L Lee 3 & Soo Yong Tan 2 1 NCCS-VARI Translational Research Laboratory, Singapore, 2 Department of Pathology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore, and 3 Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Centre, Singapore, Singapore Date of submission 1 March 2012 Accepted for publication 13 June 2012 Mationg-Kalaw E, Tan L H C, Tay K, Lim S T, Tang T, Lee Y Y L & Tan S Y (2012) Histopathology 61, Does the proliferation fraction help identify mature B cell lymphomas with double- and triplehit translocations? Aims: The entity B cell lymphoma, unclassifiable, with features intermediate between diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and Burkitt lymphoma (BL) refers to B cell neoplasms that share overlapping characteristics of BL and DLBCL. A subset of these grey-zone lymphomas possesses C-MYC and IGH translocations but, in addition, contains additional rearrangements of BCL2 and or BCL6 genes. The aim of this study was to investigate if the proliferation fraction by Ki67 immunostaining can be used to identify such double- triple-hit lymphomas. Methods and results: We studied 492 cases of mature aggressive B cell neoplasms by histology, immunohistochemistry and interphase fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) using break-apart probes against C-MYC, BCL2, BCL6, IGH, MALT1, PAX5 and CCND1. Forty Burkitt lymphomas and 28 cases of MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas were identified. Of the latter, 77% and 54% displayed proliferation fractions exceeding 75% and 90%, respectively. With a cut-off of >75% by Ki67 immunostaining, the sensitivity and specificity for detection of MYC + double triple translocations was 0.77 and Raising the proliferation fraction criterion to >90% improved the specificity to 0.62 at the expense of a low sensitivity of Conclusions: Immunostaining for Ki67 is not a useful approach to prescreen B cell lymphomas for MYC + double triple translocations. Keywords: chromosomal translocation, diffuse, Ki-67 antigen, large B cell, lymphoma Abbreviations: BL, Burkitt lymphoma; DLBCL, diffuse large B cell lymphoma; FISH, fluorescence in-situ hybridization Introduction The accurate classification of aggressive mature B cell neoplasms is important, because the prognosis and chemotherapeutic regimens used are quite different. Burkitt lymphoma has an aggressive clinical behaviour, Address for correspondence: S Y Tan, Department of Pathology, Singapore General Hospital, Outram Road, Singapore , Singapore. drtansy@gmail.com but responds well to intensive chemotherapy such as HyperCVAD or CODOX-M IVAC. In contrast, diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) has a poorer overall survival compared to Burkitt lymphoma, and is usually treated with R-CHOP chemotherapy. Demonstration of the characteristic t(8;14), t(2;8) and t(8;22) translocations involving C-MYC and an immunoglobulin gene is characteristic of BL. As a surrogate marker, a high proliferation fraction of almost 100% by Ki67 immunostaining had been suggested, 1 but a subset of DLBCL with morphological Ó 2012 Blackwell Publishing Limited.
2 Ki67 in double- triple-hit lymphomas 1215 and phenotypic overlap with BL also possesses a high proliferation fraction. Currently, demonstration of the C-MYC IGH translocation is almost mandatory in the diagnosis of BL, usually by karyotyping or interphase fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH). However, C-MYC translocation is not limited to BL. It is known that DLBCL can also possess C-MYC translocations, but often in such instances the translocation partner may be a nonimmunoglobulin gene 2 or there is an additional second or third translocation, usually involving BCL2 or BCL Such cases of MYC + double- or triple-hit lymphomas usually show higher proliferation fractions 7 and a poorer prognosis when treated with either BL- or DLBCL-type therapies. In contrast, true BL cases possess C-MYC translocations to an immunoglobulin gene only, without additional alterations in BCL2 and BCL6 as seen in MYC + DLBCL. This is also confirmed by comparative genomic hybridization data, which have demonstrated that BL is genetically stable while DLBCL with C-MYC translocations tend to have more alterations at the genomic level. 4,8 It may now become necessary for the pathologist to interrogate for translocations of not only C-MYC and IGH, but also BCL2 and BCL6 when confronted with the differential diagnosis of BL versus DLBCL. In addition, if no IGH rearrangement is noted in a lymphoma with C-MYC translocation, rearrangement of IGK and IGL genes has to be ascertained. Even when the diagnosis is clearly that of DLBCL, there may be a need to separate out cases of MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas that do not respond well to standard R-CHOP therapy. This poses a significant burden on the resources of the pathology laboratory, and the question has been raised as to whether Ki67 immunostaining can help to predict the presence of MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas. Would it be feasible to prescreen DLBCL for cases with high proliferation fraction for further analysis by interphase FISH to diagnose double- triple-hit lymphomas? Methods A total of 492 cases of DLBCL, grey-zone lymphomas and BL from 2004 to 2011 in the archives of the Department of Pathology, Singapore General Hospital were characterized by review of histology, an extended panel of immunostains (including those for BCL2, BCL6, CD10, MUM1, FoxP1, LMO2 and Ki67) and classified according to Hans criteria. 9 Where phenotyping by Hans criteria remained indeterminate (e.g. CD10 ) BCL6 ) MUM1 ) ), expression of germinal centre marker LMO2 versus post-germinal centre marker FoxP1 was used to make the final arbitration. Assessment of Ki67 immunostaining was performed by a single observer and divided into four categories (<50%, >50 75%, >75 90%, >90%), based on the percentage of cells stained. To assess the degree of inter- and intraobserver error, Ki67 staining in 121 cases was graded independently by two pathologists (K.E. and T.S.Y.). To assess the degree of intraobserver agreement, the same cases were reassessed by the study pathologist (K.E.) more than 3 months apart, blinded to results of the previous assessment. Statistical analysis for inter- and intraobserver agreement was performed and the weighted kappa statistics calculated using spss software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). All cases were also investigated by interphase FISH using break-apart probes to BCL2, BCL6, IGH, C-MYC, CCND1, MALT1 and PAX5. In the event of a C-MYC translocation but intact IGH gene, FISH for IGK and IGL was performed. Results Forty cases of Burkitt lymphoma were identified, of which sufficient material was available in 28 cases for both immunohistochemistry and complete FISH analysis. All cases tested displayed a high proliferation fraction of >95% and possessed C-MYC translocation to an immunoglobulin gene. Of all cases of DLBCL, 46 showed double or triple translocations in addition to IGH (Table 1; Figure 1). Of these, 28 showed C-MYC translocations (14 cases involving C-MYC and BCL2; nine involving C-MYC and BCL6; and five triple-hit cases). The remaining 18 double-hit lymphomas lack C-MYC translocations and were not considered further in this study, which focussed only on MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas. MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas showed male predominance, comprising 19 males and nine females (M:F = 2:1) with a median age of 57.8 years (range 31 84). Nodal disease was seen in 43% and, of the majority that presented in extranodal sites, the head and neck region (14%) and gastrointestinal tract (11%) were most commonly involved. Assessment of a starry-sky architecture and prominence of nucleoli in neoplastic cells did not distinguish double- triple-hit lymphomas from DLBCL without these alterations. In terms of phenotype, using Hans criteria there were slightly more MYC + double- triplehit lymphomas in the germinal centre B cell-like (GCB) subgroup (61%) than in the activated B cell-like (ABC) subgroup (39%). However, with additional markers LMO2 and FoxP1, they were divided more evenly between GCB (52%) and ABC (48%) phenotypes.
3 1216 E Mationg-Kalaw et al. Table 1. Summary of genetic alterations and proliferation fraction by Ki67 immunostaining Lymphoma Alteration Type Subtotal Total MYC + double- and triple-hit lymphomas Double-hit MYC BCL MYC BCL6 9 Triple-hit MYC BCL2 BCL6 4 MYC BCL2 PAX5 1 MYC double- and triple-hit lymphomas Double-hit BCL2 BCL PAX5 BCL2 1 PAX5 BCL6 3 Burkitt lymphoma 40 DLBCL without double- or triple-hit translocations 406 Total 492 Proliferation fraction using Ki67 > 75% as cut-off Lymphoma Ki67 < 75% Ki67 > 75% Total DLBCL with MYC + double- triple-hit translocations DLBCL without MYC + double- triple-hit translocations Total Proliferation fraction using Ki67 > 90% as cut-off Lymphoma Ki67 < 90% Ki67 > 90% Total DLBCL with MYC + double- triple-hit translocations DLBCL without MYC + double- triple-hit translocations Total DLBCL: diffuse large B cell lymphoma. DLBCLs with BCL2 and C-MYC translocations tended to show the GCB phenotype (71%), while cases with BCL6 and C-MYC translocations tended to show the ABC phenotype (89%). The proliferation fraction in MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas ranged from 30 to 100% and was generally high, exceeding 75% in 20 of 26 cases (77%). In fact, 14 of 26 cases (54%) displayed a very high proliferation fraction of >90%. Conversely, proliferation fractions of >75% and >90% were seen in 64% and 38% of DLBCL without double triple translocations, respectively (range 20 95%). The lowest proliferation fraction of 30% was seen in three (12%) of 26 MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas, while cases without MYC + double- triple-hit translocations displayed the lowest proliferation fraction of 20% focally. In other words, it is not possible to define a proliferation fraction below which all cases of double- triple-hit translocations are excluded. Interobserver agreement was 90.5% with a weighted kappa value of 0.677, indicating good agreement. The percentage of intraobserver agreement was 83.26%, with a weighted kappa statistic of Using a proliferation fraction cut-off of >75% to predict MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas, a sensitivity of 0.77 was achieved, with a low specificity of Raising the proliferation fraction cut-off to >90% had the effect of increasing the specificity to 0.62, but dropping the sensitivity to Conclusion Diffuse large B cell lymphomas with MYC + double- triple-hit translocations present commonly in older
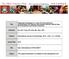
4 Ki67 in double- triple-hit lymphomas 1217 A B C D Figure 1. A, Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with proliferation fractions of 80% and 95% by immunostaining for Ki67. B, Interphase fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) using break-apart probes in DLBCL with double-hit translocations involving C-MYC, BCL2 and IGH. C, DLBCL with double-hit translocations showing rearrangements of C-MYC, BCL6 and IGH. D. FISH using break-apart probes in this case shows translocations of BCL2, BCL6, C-MYC and IGH, in keeping with a triple-hit lymphoma.
5 1218 E Mationg-Kalaw et al. males. Nodal disease was seen in 43% and the most common extranodal sites were the head and neck region and gastrointestinal tract. Neither immunophenotype by Hans criteria, a starry-sky appearance nor the presence of prominent nucleoli predicted DLBCL with multiple translocations. The most common alterations in MYC + double-hit lymphomas contained C-MYC, BCL2 and IGH translocations, followed by C-MYC, BCL6, IGH translocations, while the most common triple-hit translocation involved BCL2, BCL6, C-MYC and IGH genes. Assessment of the proliferation fraction by Ki67 immunostaining may be hampered by differing fixation conditions, large numbers of tumour-associated inflammatory cells, prolonged storage and storage conditions. It has also been shown that Ki67 staining suffers from high interlaboratory variability, 10 although the interobserver agreement achieved in this study was good. However, to be useful as an assay to prescreen DLBCLs for detection of MYC + double- triple-hit translocations, the test must be sufficiently sensitive to identify most cases for confirmation by FISH. Using a cut-off criterion of >75% by Ki67 immunostaining, the sensitivity of 0.77 is fair, although as many as a quarter of cases will be missed. However, the specificity of only 0.36 means that a large number of translocation-negative cases will be interrogated unnecessarily by FISH. This will not result in very significant savings. Conversely, raising the bar to >90% by Ki67 immunostaining improves the specificity somewhat to 0.62 at the cost of a reduced sensitivity of Given the poor sensitivity and specificity data, we conclude that Ki67 immunostaining is not suitable as a means to prescreen DLBCL for MYC + double- triple-hit lymphomas. Acknowledgements This study of the Singapore Lymphoma Study Group was funded by the Program Project Grant and the CISSP Program of the National Medical Research Council of Singapore, the Singhealth Foundation Project Grant and HSBC Trustee (Singapore) Limited as trustees of the Major John Long Trust Fund and the Chew Woon Poh Trust Fund. References 1. Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H et al. A revised European American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994; 84; Bertrand P, Bastard C, Maingonnat C et al. Mapping of MYC breakpoints in 8q24 rearrangements involving non-immunoglobulin partners in B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2007; 21; Haralambieva E, Boerma E-J, van Imhoff GW et al. Clinical, immunophenotypic, and genetic analysis of adult lymphomas with morphologic features of Burkitt lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005; 29; Hummel M, Bentink S, Berger H et al. A biologic definition of Burkitt s lymphoma from transcriptional and genomic profiling. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006; 354; Liu D, Shimonov J, Primanneni S, Lai Y, Ahmed T, Seiter K. t(8;14;18): a 3-way chromosome translocation in two patients with Burkitt s lymphoma leukemia. Mol. Cancer 2007; 6; Ueda C, Nishikori M, Kitawaki T, Uchiyama T, Ohno H. Coexistent rearrangements of c-myc, BCL2, and BCL6 genes in a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int. J. Hematol. 2004; 79; Stein HWR, Chan WC, Jaffe ES, CHan JKC, Gatter KC, Campo E. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified. In Swerdlow SHCE, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Vardiman JW eds. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon: IARC, 2008; Salaverria I, Zettl A, Beà S et al. Chromosomal alterations detected by comparative genomic hybridization in subgroups of gene expression-defined Burkitt s lymphoma. Haematologica 2008; 93; Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004; 103; Mengel M, von Wasielewski R, Wiese B, Rudiger T, Muller- Hermelink HK, Kreipe H. Inter-laboratory and inter-observer reproducibility of immunohistochemical assessment of the Ki-67 labelling index in a large multi-centre trial. J. Pathol. 2002; 198;
Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification
 Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno Bellinzona, January 29-31, 2016 Evolution of lymphoma classification Rappaport Lukes
Defined lymphoma entities in the current WHO classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno Bellinzona, January 29-31, 2016 Evolution of lymphoma classification Rappaport Lukes
Use of MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 FISH for investigations of high grade B cell lymphoma
 Use of MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 FISH for investigations of high grade B cell lymphoma Dr Anthony Bench Haematopathology and Oncology Diagnostic Service Cambrıdge Unıversıty Hospitals NHS Foundatıon Trust Cambridge
Use of MYC, BCL2 and BCL6 FISH for investigations of high grade B cell lymphoma Dr Anthony Bench Haematopathology and Oncology Diagnostic Service Cambrıdge Unıversıty Hospitals NHS Foundatıon Trust Cambridge
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells. Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital
 Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Differential diagnosis of hematolymphoid tumors composed of medium-sized cells Brian Skinnider B.C. Cancer Agency, Vancouver General Hospital Lymphoma classification Lymphoma diagnosis starts with morphologic
Aggressive B-cell lymphomas and gene expression profiling towards individualized therapy?
 Aggressive B-cell lymphomas and gene expression profiling towards individualized therapy? Andreas Rosenwald Institute of Pathology, University of Würzburg, Germany Barcelona, June 18, 2010 NEW WHO CLASSIFICATION
Aggressive B-cell lymphomas and gene expression profiling towards individualized therapy? Andreas Rosenwald Institute of Pathology, University of Würzburg, Germany Barcelona, June 18, 2010 NEW WHO CLASSIFICATION
Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Updated WHO classification Elias Campo
 Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Updated WHO classification Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma A Heterogeneous Category Subtypes with differing: Histology and
Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Updated WHO classification Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma A Heterogeneous Category Subtypes with differing: Histology and
The next lymphoma classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno
 Evolution of classification The next classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno The Lymphoma Forum of Excellence, Bellinzona, January 2011 Rappaport Lukes and Collins (immunophenotype)
Evolution of classification The next classification Luca Mazzucchelli Istituto cantonale di patologia, Locarno The Lymphoma Forum of Excellence, Bellinzona, January 2011 Rappaport Lukes and Collins (immunophenotype)
Citation International Journal of Hematology, 2013, v. 98 n. 4, p The original publication is available at
 Title Diagnostic challenges in a case of B cell lymphoma unclassifiable with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma Author(s) So, JCC; Yung, KH; Chu, ML; Wan,
Title Diagnostic challenges in a case of B cell lymphoma unclassifiable with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma Author(s) So, JCC; Yung, KH; Chu, ML; Wan,
Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Tres
 Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco
Gray Zones and Double Hits Distinguishing True Burkitt Lymphoma from Other High-Grade B-NHLs Burkitt Lymphoma Burkitt-Like Lymphoma DLBCL Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco
IX. Is it only about MYC? How to approach the diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas
 Hematological Oncology Hematol Oncol 2015; 33: 50 55 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2217 Supplement Article IX. Is it only about MYC? How to approach the diagnosis of
Hematological Oncology Hematol Oncol 2015; 33: 50 55 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2217 Supplement Article IX. Is it only about MYC? How to approach the diagnosis of
Clinical Impact of t(14;18) in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
 160 Original Article Clinical Impact of t(14;18) in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Hong-wei Zhang 1,#, Niu-liang Cheng 1*, Zhen-wen Chen 2, Jin-fen Wang 3, Su-hong Li 3, Wei Bai 3 1 Department of Biochemistry
160 Original Article Clinical Impact of t(14;18) in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Hong-wei Zhang 1,#, Niu-liang Cheng 1*, Zhen-wen Chen 2, Jin-fen Wang 3, Su-hong Li 3, Wei Bai 3 1 Department of Biochemistry
DOUBLE-HIT AND TRIPLE-HIT LYMPHOMAS: NEW PERSPECTIVES FOR THEIR CLASSIFICATION
 DOUBLE-HIT AND TRIPLE-HIT LYMPHOMAS: NEW PERSPECTIVES FOR THEIR CLASSIFICATION *Cristiano Claudino Oliveira, Maria Aparecida Custódio Domingues Department of Pathology, Botucatu School of Medicine, São
DOUBLE-HIT AND TRIPLE-HIT LYMPHOMAS: NEW PERSPECTIVES FOR THEIR CLASSIFICATION *Cristiano Claudino Oliveira, Maria Aparecida Custódio Domingues Department of Pathology, Botucatu School of Medicine, São
HIGH GRADE B-CELL LYMPHOMA DAVID NOLTE, MD (PGY-2) HUSSAM AL-KATEB, PHD, FACMG DEBORAH FUCHS, MD
 HIGH GRADE B-CELL LYMPHOMA DAVID NOLTE, MD (PGY-2) HUSSAM AL-KATEB, PHD, FACMG DEBORAH FUCHS, MD OUTLINE High grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements Patient presentation 2008/2016
HIGH GRADE B-CELL LYMPHOMA DAVID NOLTE, MD (PGY-2) HUSSAM AL-KATEB, PHD, FACMG DEBORAH FUCHS, MD OUTLINE High grade B-cell lymphoma with MYC and BCL2 and/or BCL6 rearrangements Patient presentation 2008/2016
PhenoPath. Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA
 PhenoPath Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA C urrent diagnosis of B cell non-hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) is based on the 2008 WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid
PhenoPath Diagnoses you can count on B CELL NON-HODGKIN LYMPHOMA C urrent diagnosis of B cell non-hodgkin lymphoma (B-NHL) is based on the 2008 WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid
Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas
 Neoplastic Hematopathology Update 2018 Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Raju K. Pillai City of Hope National Medical Center I do not have any disclosures Disclosures Outline New entities and changes in WHO
Neoplastic Hematopathology Update 2018 Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Raju K. Pillai City of Hope National Medical Center I do not have any disclosures Disclosures Outline New entities and changes in WHO
EQA SCHEME CIRCULATION 33 EDUCATIONAL SLIDES DR GRAEME SMITH MONKLANDS DGH
 EQA SCHEME CIRCULATION 33 EDUCATIONAL SLIDES DR GRAEME SMITH MONKLANDS DGH CASE E1 M: 68 yrs Left destructive sinonasal lesion.?lymphoma?adenocarcinoma CD20 CD10 BCL6 MIB1 Answers Diffuse large B cell
EQA SCHEME CIRCULATION 33 EDUCATIONAL SLIDES DR GRAEME SMITH MONKLANDS DGH CASE E1 M: 68 yrs Left destructive sinonasal lesion.?lymphoma?adenocarcinoma CD20 CD10 BCL6 MIB1 Answers Diffuse large B cell
Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas
 Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas Stephen Hamilton Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus Kommunehospital B-lymphoblastic lymphoma Diffuse large cell lymphoma, NOS T-cell / histiocyte-rich;
Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas Stephen Hamilton Dutoit Institute of Pathology Aarhus Kommunehospital B-lymphoblastic lymphoma Diffuse large cell lymphoma, NOS T-cell / histiocyte-rich;
Learn more about diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common aggressive form of B-cell non-hodgkin s lymphoma 1
 Learn more about diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common aggressive form of B-cell non-hodgkin s lymphoma 1 Expression of B-cell surface antigens drives several non-hodgkin s lymphomas (NHLs)
Learn more about diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common aggressive form of B-cell non-hodgkin s lymphoma 1 Expression of B-cell surface antigens drives several non-hodgkin s lymphomas (NHLs)
Significance of MYC/BCL2 Double Expression in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphomas: A Single-center Observational Preliminary Study of 88 Cases
 Original Article Significance of MYC/BCL Double Expression in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphomas: A Single-center Observational Preliminary Study of 88 Cases Chutima Pinnark 1 ; Jerasit Surintrspanont ; Thiamjit
Original Article Significance of MYC/BCL Double Expression in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphomas: A Single-center Observational Preliminary Study of 88 Cases Chutima Pinnark 1 ; Jerasit Surintrspanont ; Thiamjit
Immunopathology of Lymphoma
 Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
Immunopathology of Lymphoma Noraidah Masir MBBCh, M.Med (Pathology), D.Phil. Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Lymphoma classification has been challenging to pathologists.
7 Omar Abu Reesh. Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour
 7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
7 Omar Abu Reesh Dr. Ahmad Mansour Dr. Ahmad Mansour -Leukemia: neoplastic leukocytes circulating in the peripheral bloodstream. -Lymphoma: a neoplastic process in the lymph nodes, spleen or other lymphatic
Immunohistochemical differentiation between follicular lymphoma and nodal marginal zone lymphoma combined performance of multiple markers
 Published Ahead of Print on June 11, 2015, as doi:10.3324/haematol.2014.120956. Copyright 2015 Ferrata Storti Foundation. Immunohistochemical differentiation between follicular lymphoma and nodal marginal
Published Ahead of Print on June 11, 2015, as doi:10.3324/haematol.2014.120956. Copyright 2015 Ferrata Storti Foundation. Immunohistochemical differentiation between follicular lymphoma and nodal marginal
Aggressive B cell Lymphomas
 Aggressive B cell Lymphomas I have nothing to disclose. Disclosures Raju K. Pillai City of Hope National Medical Center Outline WHO 2016 Classification Large B cell Lymphomas New entities and changes in
Aggressive B cell Lymphomas I have nothing to disclose. Disclosures Raju K. Pillai City of Hope National Medical Center Outline WHO 2016 Classification Large B cell Lymphomas New entities and changes in
Recent advances in the genetics & biology of lymphoma
 Recent advances in the genetics & biology of lymphoma Chris Bacon Northern Institute for Cancer Research Newcastle University & Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Lymphoma Rate per 100,000
Recent advances in the genetics & biology of lymphoma Chris Bacon Northern Institute for Cancer Research Newcastle University & Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Lymphoma Rate per 100,000
High grade B-cell lymphomas (HGBL): Altered terminology in the 2016 WHO Classification (Update of the 4 th Edition) and practical issues Xiao-Qiu Li,
 High grade B-cell lymphomas (HGBL): Altered terminology in the 2016 WHO Classification (Update of the 4 th Edition) and practical issues Xiao-Qiu Li, M.D., Ph.D. Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center
High grade B-cell lymphomas (HGBL): Altered terminology in the 2016 WHO Classification (Update of the 4 th Edition) and practical issues Xiao-Qiu Li, M.D., Ph.D. Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center
LINFOMA B (INCLASIFICABLE) CON RASGOS INTERMEDIOS ENTRE LINFOMA DE BURKITT Y LINFOMA B DIFUSO DE CÉLULAS GRANDES.
 Congreso Nacional SEAP 2013. LINFOMA B (INCLASIFICABLE) CON RASGOS INTERMEDIOS ENTRE LINFOMA DE BURKITT Y LINFOMA B DIFUSO DE CÉLULAS GRANDES. Santiago Montes Moreno Servicio de Anatomía Patológica, HUMV
Congreso Nacional SEAP 2013. LINFOMA B (INCLASIFICABLE) CON RASGOS INTERMEDIOS ENTRE LINFOMA DE BURKITT Y LINFOMA B DIFUSO DE CÉLULAS GRANDES. Santiago Montes Moreno Servicio de Anatomía Patológica, HUMV
Lymphoma Update: Lymphoma Update: What s Likely to be New in the New WHO. Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco
 Lymphoma Update: What s Likely to be New in the New WHO Blood 127:2375; 2016 Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco Lymphoma Update: What IS New in the New WHO! Patrick Treseler,
Lymphoma Update: What s Likely to be New in the New WHO Blood 127:2375; 2016 Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD University of California San Francisco Lymphoma Update: What IS New in the New WHO! Patrick Treseler,
Aggressive B-cell Lymphoma 2013
 Aggressive B-cell Lymphoma 2013 Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Burkitt Lymphoblastic lymphoma Gray zone Intermediate DLBCL/HL Intermediate BL/DLBCL Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma Common morphology: diffuse
Aggressive B-cell Lymphoma 2013 Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Burkitt Lymphoblastic lymphoma Gray zone Intermediate DLBCL/HL Intermediate BL/DLBCL Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma Common morphology: diffuse
Pathology of aggressive lymphomas
 Institute of Pathology Pathology of aggressive lymphomas Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez Changes in the new 2016 WHO Aggressive B-cell lymphoid neoplasms Major changes that impact how cases should be evaludated
Institute of Pathology Pathology of aggressive lymphomas Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez Changes in the new 2016 WHO Aggressive B-cell lymphoid neoplasms Major changes that impact how cases should be evaludated
Methods used to diagnose lymphomas
 Institut für Pathologie Institut für Pathologie Methods used to diagnose lymphomas Prof. Dr.Med. Leticia Quintanilla-Fend Molecular techniques NGS histology Cytology AS-PCR Sanger seq. MYC Immunohistochemistry
Institut für Pathologie Institut für Pathologie Methods used to diagnose lymphomas Prof. Dr.Med. Leticia Quintanilla-Fend Molecular techniques NGS histology Cytology AS-PCR Sanger seq. MYC Immunohistochemistry
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU
 Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Molecular Pathology of Lymphoma (Part 1) Rex K.H. Au-Yeung Department of Pathology, HKU Lecture outline Time 10:00 11:00 11:15 12:10 12:20 13:15 Content Introduction to lymphoma Review of lymphocyte biology
Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(1):307-311 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1311029 Case Report A case of EBV positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the adolescent Qilin Ao 2, Ying Wang 1, Sanpeng Xu 2,
Clinicopathologic Profile and Outcome of Extranodal Diffuse Large B-Cell NHL: Egyptian National Cancer Institute Experience
 HeSMO 6(3) 2015 8 12 DOI: 10.1515/fco-2015-0013 Forum of Clinical Oncology Clinicopathologic Profile and Outcome of Extranodal Diffuse Large B-Cell NHL: Egyptian National Cancer Institute Experience Ola
HeSMO 6(3) 2015 8 12 DOI: 10.1515/fco-2015-0013 Forum of Clinical Oncology Clinicopathologic Profile and Outcome of Extranodal Diffuse Large B-Cell NHL: Egyptian National Cancer Institute Experience Ola
Pathology of aggressive lymphomas
 Institute of Pathology Pathology of aggressive lymphomas Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez Changes in the new 2016 WHO Aggressive B-cell lymphoid neoplasms Major changes that impact how cases should be evaludated
Institute of Pathology Pathology of aggressive lymphomas Leticia Quintanilla-Martinez Changes in the new 2016 WHO Aggressive B-cell lymphoid neoplasms Major changes that impact how cases should be evaludated
Prevalent lymphomas in Africa
 Prevalent lymphomas in Africa Dr Zainab Mohamed Clinical Oncologist GSH/UCT Groote Schuur Hospital Disclaimer I declare that I have no conflict of interest Groote Schuur Hospital Denis Burkitt 1911-1993
Prevalent lymphomas in Africa Dr Zainab Mohamed Clinical Oncologist GSH/UCT Groote Schuur Hospital Disclaimer I declare that I have no conflict of interest Groote Schuur Hospital Denis Burkitt 1911-1993
Clinicopathologic features of 112 cases with mantle cell lymphoma
 Cancer Biol Med 2015;12:46-52. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2015.0007 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinicopathologic features of 112 cases with mantle cell lymphoma Dong-Mei Zhou, Gang Chen, Xiong-Wei Zheng, Wei-Feng
Cancer Biol Med 2015;12:46-52. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2015.0007 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinicopathologic features of 112 cases with mantle cell lymphoma Dong-Mei Zhou, Gang Chen, Xiong-Wei Zheng, Wei-Feng
5003 Immunohistochemistry in hematopathology, what's in, what's out, what's useful
 www.ascp.org/ascp2014 5003 Immunohistochemistry in hematopathology, what's in, what's out, what's useful Kathryn Rizzo, DO, PhD VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIVERSITY Department of Pathology School of Medicine
www.ascp.org/ascp2014 5003 Immunohistochemistry in hematopathology, what's in, what's out, what's useful Kathryn Rizzo, DO, PhD VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIVERSITY Department of Pathology School of Medicine
Chapter 4. F.H. Heyning 1, P.C.W. Hogendoorn 2, M.H.H. Kramer 3, C.T.Q. Holland 2, E. Dreef 2, P.M. Jansen 2
 Primary Lymphoma of Bone: Extranodal Lymphoma with Favourable Survival Independent of Germinal Centre, Post Germinal Centre, or Indeterminate Phenotype F.H. Heyning 1, P.C.W. Hogendoorn 2, M.H.H. Kramer
Primary Lymphoma of Bone: Extranodal Lymphoma with Favourable Survival Independent of Germinal Centre, Post Germinal Centre, or Indeterminate Phenotype F.H. Heyning 1, P.C.W. Hogendoorn 2, M.H.H. Kramer
Case Report Synchronous Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Mantle Cell Lymphoma of the Lymph Node
 Case Reports in Genetics Volume 2011, Article ID 945181, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/945181 Case Report Synchronous Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Mantle Cell Lymphoma of the Lymph Node Yu Sun, 1 Yun-Fei
Case Reports in Genetics Volume 2011, Article ID 945181, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/945181 Case Report Synchronous Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Mantle Cell Lymphoma of the Lymph Node Yu Sun, 1 Yun-Fei
VENTANA hematopathology solutions Comprehensive aids for detecting and subtyping
 VENTANA hematopathology solutions Comprehensive aids for detecting and subtyping 1 12/4/2015 9:47:24 AM 2 Hematopathology diagnostic solutions Contents VENTANA hematopathology assays 3 Detecting and subtyping
VENTANA hematopathology solutions Comprehensive aids for detecting and subtyping 1 12/4/2015 9:47:24 AM 2 Hematopathology diagnostic solutions Contents VENTANA hematopathology assays 3 Detecting and subtyping
VENTANA hematopathology solutions. Deliver diagnostic confidence
 VENTANA hematopathology solutions Deliver diagnostic confidence 2 Hematopathology diagnostic solutions Contents VENTANA hematopathology assays 3 Detecting and subtyping hematological cancers 4 The importance
VENTANA hematopathology solutions Deliver diagnostic confidence 2 Hematopathology diagnostic solutions Contents VENTANA hematopathology assays 3 Detecting and subtyping hematological cancers 4 The importance
OSCO/OU ASH-SABC Review. Lymphoma Update. Mohamad Cherry, MD
 OSCO/OU ASH-SABC Review Lymphoma Update Mohamad Cherry, MD Outline Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Double Hit Lymphoma Follicular and Indolent B Cell Lymphomas Mantle Cell Lymphoma T Cell Lymphoma Hodgkin
OSCO/OU ASH-SABC Review Lymphoma Update Mohamad Cherry, MD Outline Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Double Hit Lymphoma Follicular and Indolent B Cell Lymphomas Mantle Cell Lymphoma T Cell Lymphoma Hodgkin
Abstract. Hematopathology / HIGH KI-67 INDEX AND STARRY-SKY PATTERN IN BL AND DLBCL
 Hematopathology / HIGH KI-67 INDEX AND STARRY-SKY PATTERN IN BL AND DLBCL Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry in Distinguishing Burkitt Lymphoma From Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma With Very High Proliferation
Hematopathology / HIGH KI-67 INDEX AND STARRY-SKY PATTERN IN BL AND DLBCL Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry in Distinguishing Burkitt Lymphoma From Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma With Very High Proliferation
ESMO DOUBLE-HIT LYMPHOMAS
 ESMO DOUBLE-HIT LYMPHOMAS Professor Dr. med. Georg Lenz Director Department of Hematology and Oncology Universitätsklinikum Münster, Germany OVERVIEW Definition of double-hit lymphomas Introduction in
ESMO DOUBLE-HIT LYMPHOMAS Professor Dr. med. Georg Lenz Director Department of Hematology and Oncology Universitätsklinikum Münster, Germany OVERVIEW Definition of double-hit lymphomas Introduction in
CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1364 CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting Sakthi Sankari S 1 *, Arjunan A 2, Bhuvaneswari M.G. 2, Sindhuja
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1364 CD5 Positive Follicular Lymphomas- A Diagnostic Dilemma in a Resource Restricted Laboratory Setting Sakthi Sankari S 1 *, Arjunan A 2, Bhuvaneswari M.G. 2, Sindhuja
Update on the Classification of Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas and Hodgkin Lymphoma
 Update on the Classification of Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas and Hodgkin Lymphoma Nancy Lee Harris, M. D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas WHO 4 th Edition
Update on the Classification of Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas and Hodgkin Lymphoma Nancy Lee Harris, M. D. Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Aggressive B-cell Lymphomas WHO 4 th Edition
Primary Cutaneous Follicle Center Lymphoma Associated With an Extracutaneous Dissemination
 AJCP / Case Report Primary Cutaneous Follicle Center Lymphoma Associated With an Extracutaneous Dissemination A Cytogenetic Finding of Potential Prognostic Value Shivakumar Subramaniyam, PhD, Cynthia M.
AJCP / Case Report Primary Cutaneous Follicle Center Lymphoma Associated With an Extracutaneous Dissemination A Cytogenetic Finding of Potential Prognostic Value Shivakumar Subramaniyam, PhD, Cynthia M.
Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation
 Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case Report Primary central nervous system B cell lymphoma with features intermediate between diffuse large B cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2012;5(1):72-76 www.ijcep.com /ISSN: 1936-2625/IJCEP1111004 Case Report Primary central nervous system B cell lymphoma with features intermediate between diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2012;5(1):72-76 www.ijcep.com /ISSN: 1936-2625/IJCEP1111004 Case Report Primary central nervous system B cell lymphoma with features intermediate between diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Aggressive B cell Lymphomas
 Aggressive B cell Lymphomas Raju K. Pillai City of Hope National Medical Center I have no disclosures Outline What is new in the WHO 2016 classification Insights from genomic studies Double Hit Lymphoma
Aggressive B cell Lymphomas Raju K. Pillai City of Hope National Medical Center I have no disclosures Outline What is new in the WHO 2016 classification Insights from genomic studies Double Hit Lymphoma
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is one of the
 Practical Applications in Immunohistochemistry Evaluation of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Related Large B-Cell Lymphomas Dennis P. O Malley, MD; Aaron Auerbach, MD; Lawrence M. Weiss, MD Context.
Practical Applications in Immunohistochemistry Evaluation of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Related Large B-Cell Lymphomas Dennis P. O Malley, MD; Aaron Auerbach, MD; Lawrence M. Weiss, MD Context.
3.1 Introduction. It is emphasised that not all tests are necessarily required in every case. 3.2 Taxonomic structure
 CHAPTER 3 CLASSIFICATION 3.1 Introduction Accurate diagnosis underpins lymphoma management. Historically, competing lymphoma classifications have been a source of frustration to pathologists, clinicians
CHAPTER 3 CLASSIFICATION 3.1 Introduction Accurate diagnosis underpins lymphoma management. Historically, competing lymphoma classifications have been a source of frustration to pathologists, clinicians
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Mantle Cell Lymphoma Elias Campo
 Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Mantle Cell Lymphoma Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY CELL CLL MCL FL MZL Small cell size Low proliferation
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Mantle Cell Lymphoma Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY CELL CLL MCL FL MZL Small cell size Low proliferation
Initial Diagnosis and Treatment 81 Male
 Case SH2017-0359 Shiraz Fidai 1, Sandeep Gurbuxani 1, Girish Venkataraman 1, Gordana Raca 2, Madina Sukhanova 3, Michelle M Le Beau 3, Y. Lynn Wang 4, Mir Alikhan 4, Megan M.McNerney 4, Yuri Kobzev 4,
Case SH2017-0359 Shiraz Fidai 1, Sandeep Gurbuxani 1, Girish Venkataraman 1, Gordana Raca 2, Madina Sukhanova 3, Michelle M Le Beau 3, Y. Lynn Wang 4, Mir Alikhan 4, Megan M.McNerney 4, Yuri Kobzev 4,
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. Mixed follicular and paracortical hyperplasia. Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Burkitt lymphoma. Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8
 Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Heme 8 Burkitt lymphoma Sporadic Endemic in Africa associated with EBV Translocations involving MYC gene on chromosome 8 Most common is t(8;14) Believed to be the fastest growing tumor in humans!!!! Morphology
Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Lymphoid Neoplasms
 Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Lymphoid Neoplasms (Part II) Rational use of molecular testing in lymphomas Beirut, Lebanon Friday December 2, 2011: Hematopathology Session Adam Bagg University of Pennsylvania
Diagnostic Molecular Pathology of Lymphoid Neoplasms (Part II) Rational use of molecular testing in lymphomas Beirut, Lebanon Friday December 2, 2011: Hematopathology Session Adam Bagg University of Pennsylvania
Leukaemia Section Short Communication
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Short Communication Classification of Hodgkin lymphoma over years Antonino Carbone, Annunziata
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL INIST-CNRS Leukaemia Section Short Communication Classification of Hodgkin lymphoma over years Antonino Carbone, Annunziata
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this talk.
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Ó Journal of Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences University 104
 ISSN 2231-4261 CASE REPORT Unusual Alveolar Pattern in Node Based Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma 1* 1 1 1 Archana C. Buch, Jay Y. Sheth, Sunita A Bamanikar, Aditi A. Pandey 1 Department of Pathology, Padmashri
ISSN 2231-4261 CASE REPORT Unusual Alveolar Pattern in Node Based Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma 1* 1 1 1 Archana C. Buch, Jay Y. Sheth, Sunita A Bamanikar, Aditi A. Pandey 1 Department of Pathology, Padmashri
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies. Patricia Aoun MD MPH
 Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Classification of Hematologic Malignancies Patricia Aoun MD MPH Objectives Know the basic principles of the current classification system for hematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies Understand the differences
Low-grade B-cell lymphoma
 Low-grade B-cell lymphoma Patho-Basic 11. September 2018 Stephan Dirnhofer Pathology Outline Definition LPL, MBL/CLL/SLL, MCL FL Subtypes & variants Diagnosis including Grading Transformation Summary Be
Low-grade B-cell lymphoma Patho-Basic 11. September 2018 Stephan Dirnhofer Pathology Outline Definition LPL, MBL/CLL/SLL, MCL FL Subtypes & variants Diagnosis including Grading Transformation Summary Be
Methotrexate-associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 Methotrexate-associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A lymphoid proliferation or lymphoma in a patient immunosuppressed with methotrexate, typically for treatment of autoimmune disease (rheumatoid
Methotrexate-associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders Definition A lymphoid proliferation or lymphoma in a patient immunosuppressed with methotrexate, typically for treatment of autoimmune disease (rheumatoid
Machine learning and big data for prognosis and prediction in aggressive lymphomas
 School of something School of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF OTHER BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Machine learning and big data for prognosis and prediction in aggressive lymphomas David R. Westhead With
School of something School of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF OTHER BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Machine learning and big data for prognosis and prediction in aggressive lymphomas David R. Westhead With
WHO UPDATE ON LYMPHOMAS. Dr Priya Mary Jacob Asst Professor, Pathology.
 WHO UPDATE ON LYMPHOMAS Dr Priya Mary Jacob Asst Professor, Pathology 3 rd 4 th 4 th revised 2001 2008 2017 The Change The Significance of the Change- Diagnostic, Prognostic The Rationale behind the change.
WHO UPDATE ON LYMPHOMAS Dr Priya Mary Jacob Asst Professor, Pathology 3 rd 4 th 4 th revised 2001 2008 2017 The Change The Significance of the Change- Diagnostic, Prognostic The Rationale behind the change.
ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43
 ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43 IN A PATIENT WITH THERAPY-RELATED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AND A HISTORY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Yen-Chuan Hsieh, 1 Chien-Liang Lin, 2 Chao-Jung Tsao, 2 Pin-Pen Hsieh,
ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43 IN A PATIENT WITH THERAPY-RELATED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AND A HISTORY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Yen-Chuan Hsieh, 1 Chien-Liang Lin, 2 Chao-Jung Tsao, 2 Pin-Pen Hsieh,
Large cell immunoblastic Diffuse histiocytic (DHL) Lymphoblastic lymphoma Diffuse lymphoblastic Small non cleaved cell Burkitt s Non- Burkitt s
 Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma Introduction 6th most common cause of cancer death in United States. Increasing in incidence and mortality. Since 1970, the incidence of has almost doubled. Overview The types of
Non Hodgkin s Lymphoma Introduction 6th most common cause of cancer death in United States. Increasing in incidence and mortality. Since 1970, the incidence of has almost doubled. Overview The types of
Management of high-risk diffuse large B cell lymphoma: case presentation
 Management of high-risk diffuse large B cell lymphoma: case presentation Daniel J. Landsburg, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania January
Management of high-risk diffuse large B cell lymphoma: case presentation Daniel J. Landsburg, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania January
JMSCR Vol. 03 Issue 06 Page June 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x An Indolent Natural Killer Cell Leukemia Presenting with Bilateral Ankle Arthritis and Low Grade Fever Abstract Author Subhash Chandra
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x An Indolent Natural Killer Cell Leukemia Presenting with Bilateral Ankle Arthritis and Low Grade Fever Abstract Author Subhash Chandra
Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies
 Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies Megan S. Lim MD PhD University of Pennsylvania October 8, 2018 Objectives To understand how the trend toward less invasive lymph
Pearls and pitfalls in interpretation of lymphoid lesions in needle biopsies Megan S. Lim MD PhD University of Pennsylvania October 8, 2018 Objectives To understand how the trend toward less invasive lymph
Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):7100-7104 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001717 Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case Jenny
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):7100-7104 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001717 Case Report Parotid gland follicular lymphoma lacking both cytoplasmic and surface light chains: a rare case Jenny
9/28/2017. Follicular Lymphoma and Nodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma. Follicular Lymphoma Definition. Low-Grade B-Cell Lymphomas in WHO Classification
 and L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD DISCLOSURES I do not have anything to disclose Low-Grade B-Cell Lymphomas in WHO Classification Lymphoma Type Frequency Follicular lymphoma 22.1 % Extranodal MALT-lymphoma 7.6
and L. Jeffrey Medeiros, MD DISCLOSURES I do not have anything to disclose Low-Grade B-Cell Lymphomas in WHO Classification Lymphoma Type Frequency Follicular lymphoma 22.1 % Extranodal MALT-lymphoma 7.6
Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo
 Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas Antigen selection NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY B-CELL MCL FL LPL MZL CLL Small cell
Pathology of the indolent B-cell lymphomas Elias Campo Hospital Clinic, University of Barcelona Small B-cell lymphomas Antigen selection NAIVE -B LYMPHOCYTE MEMORY B-CELL MCL FL LPL MZL CLL Small cell
Case Report Follicular lymphoma mimicking marginal zone lymphoma in lymph node: a case report
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):7076-7081 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001940 Case Report Follicular lymphoma mimicking marginal zone lymphoma in lymph node: a case report Ikuo Matsuda 1, Yoshifumi
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(10):7076-7081 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001940 Case Report Follicular lymphoma mimicking marginal zone lymphoma in lymph node: a case report Ikuo Matsuda 1, Yoshifumi
Pulmonary biopsy specimens demonstrate
 A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO THE EVALUATION OF LYMPHOID AND PLASMA CELL INFILTRATES IN THE LUNG Fiona E. Craig, MD KEYWORDS Lymphoma Pulmonary Immunophenotyping Genotyping ABSTRACT Pulmonary biopsy specimens
A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO THE EVALUATION OF LYMPHOID AND PLASMA CELL INFILTRATES IN THE LUNG Fiona E. Craig, MD KEYWORDS Lymphoma Pulmonary Immunophenotyping Genotyping ABSTRACT Pulmonary biopsy specimens
3/23/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Pitfalls in Immunohistochemistry in Hematopathology: CD20 and CD3 Can Let Me Down?!
 Pitfalls in Immunohistochemistry in Hematopathology: CD20 and CD3 Can Let Me Down?! Judith A. Ferry Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all
Pitfalls in Immunohistochemistry in Hematopathology: CD20 and CD3 Can Let Me Down?! Judith A. Ferry Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all
Policy for Central Nervous System [CNS] Prophylaxis in Lymphoid Malignancies
![Policy for Central Nervous System [CNS] Prophylaxis in Lymphoid Malignancies Policy for Central Nervous System [CNS] Prophylaxis in Lymphoid Malignancies](/thumbs/90/104309591.jpg) Policy for Central Nervous System [CNS] Prophylaxis in Lymphoid Malignancies UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED Note: NOSCAN Haematology MCN has approved the information contained within this document to guide
Policy for Central Nervous System [CNS] Prophylaxis in Lymphoid Malignancies UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED Note: NOSCAN Haematology MCN has approved the information contained within this document to guide
CME/SAM. B-Cell Lymphoma With Hyaline Vascular Castleman Disease Like Features A Clinicopathologic Study
 Hematopathology / B-Cell Lymphomas With Castleman Disease Features B-Cell Lymphoma With Hyaline Vascular Castleman Disease Like Features A Clinicopathologic Study Imran N. Siddiqi, MD, PhD, 1 Russell K.
Hematopathology / B-Cell Lymphomas With Castleman Disease Features B-Cell Lymphoma With Hyaline Vascular Castleman Disease Like Features A Clinicopathologic Study Imran N. Siddiqi, MD, PhD, 1 Russell K.
DOWNLOAD OR READ : WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF SOFT TISSUE AND BONE MEDICINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF SOFT TISSUE AND BONE MEDICINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 who classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone medicine who classification of
DOWNLOAD OR READ : WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF SOFT TISSUE AND BONE MEDICINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 who classification of tumours of soft tissue and bone medicine who classification of
High-Grade B-cell Lymphoma Double Hit or Double Expressing
 High-Grade B-cell Lymphoma Double Hit or Double Expressing Professeur Alexandra Traverse-Glehen Hematopathology Hospices Civils de Lyon Université Lyon 1 France MYC-R confer inferior pronostic DOUBLE/TRIPLE
High-Grade B-cell Lymphoma Double Hit or Double Expressing Professeur Alexandra Traverse-Glehen Hematopathology Hospices Civils de Lyon Université Lyon 1 France MYC-R confer inferior pronostic DOUBLE/TRIPLE
Double hit lymphoma Clinical perspectives
 Double hit lymphoma Clinical perspectives Peter Johnson Some definitions, for clarity Double-hit lymphoma (5% of DLBL) Rearranged MYC (8q24) by FISH Plus either rearranged BCL2 (18q21) or BCL6 (3q27) Double-expression
Double hit lymphoma Clinical perspectives Peter Johnson Some definitions, for clarity Double-hit lymphoma (5% of DLBL) Rearranged MYC (8q24) by FISH Plus either rearranged BCL2 (18q21) or BCL6 (3q27) Double-expression
Introduction: The Revised (4 th Edition) World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues
 Society for Hematopathology Scientific Symposium USCAP Companion Meeting, Boston, MA March 8, 2009 Boston, MA Steven H. Swerdlow and James Vardiman, Moderators Introduction: The Revised (4 th Edition)
Society for Hematopathology Scientific Symposium USCAP Companion Meeting, Boston, MA March 8, 2009 Boston, MA Steven H. Swerdlow and James Vardiman, Moderators Introduction: The Revised (4 th Edition)
Primary Mediastinal (Thymic) Large B-Cell Lymphoma
 Resident Short Review Primary Mediastinal (Thymic) Large B-Cell Lymphoma A Short Review With Brief Discussion of Mediastinal Gray Zone Lymphoma N (PMBCL) is a subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Resident Short Review Primary Mediastinal (Thymic) Large B-Cell Lymphoma A Short Review With Brief Discussion of Mediastinal Gray Zone Lymphoma N (PMBCL) is a subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA
 FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Hodgkin Lymphoma*
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Hodgkin Lymphoma* Version: Hodgkin 3.1.0.1 Protocol Posting Date: October 2013 This protocol is NOT required for accreditation purposes *This
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Hodgkin Lymphoma* Version: Hodgkin 3.1.0.1 Protocol Posting Date: October 2013 This protocol is NOT required for accreditation purposes *This
BCR-ABL1 positive Myeloid Sarcoma Nicola Austin
 BCR-ABL1 positive Myeloid Sarcoma Nicola Austin Cytocell UK & Ireland User Group Meeting Jesus College, Cambridge 4 th - 5 th April 2017 Myeloid Sarcoma WHO Classification Tumours of Haematopoietic and
BCR-ABL1 positive Myeloid Sarcoma Nicola Austin Cytocell UK & Ireland User Group Meeting Jesus College, Cambridge 4 th - 5 th April 2017 Myeloid Sarcoma WHO Classification Tumours of Haematopoietic and
GENETIC MARKERS IN LYMPHOMA a practical overview. P. Heimann Dpt of Medical Genetics Erasme Hospital - Bordet Institute
 GENETIC MARKERS IN LYMPHOMA a practical overview P. Heimann Dpt of Medical Genetics Erasme Hospital - Bordet Institute B and T cell monoclonalities Rearrangement of immunoglobin and TCR genes may help
GENETIC MARKERS IN LYMPHOMA a practical overview P. Heimann Dpt of Medical Genetics Erasme Hospital - Bordet Institute B and T cell monoclonalities Rearrangement of immunoglobin and TCR genes may help
How I treat High-risk follicular lymphoma
 How I treat High-risk follicular lymphoma Michele Ghielmini Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland Bellinzona 1) median OS raised from 10 to 18 y 2) advanced FL remains uncurable Stanford, n = 1334
How I treat High-risk follicular lymphoma Michele Ghielmini Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland Bellinzona 1) median OS raised from 10 to 18 y 2) advanced FL remains uncurable Stanford, n = 1334
Primary Burkitt's lymphoma of the thyroid without Epstein Barr virus infection: A case report and literature review
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 7: 1519-1524, 2014 Primary Burkitt's lymphoma of the thyroid without Epstein Barr virus infection: A case report and literature review LIYING ZHANG 1, LANXIANG GAO 1, GUANG LIU 1, LUPING
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 7: 1519-1524, 2014 Primary Burkitt's lymphoma of the thyroid without Epstein Barr virus infection: A case report and literature review LIYING ZHANG 1, LANXIANG GAO 1, GUANG LIU 1, LUPING
New Concepts and Clinical Implications of the 2008 WHO Classification of Lymphomas Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D.
 New Concepts and Clinical Implications of the 2008 WHO Classification of Lymphomas Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D. The first step in wisdom is to know the things themselves; this notion consists in having a true
New Concepts and Clinical Implications of the 2008 WHO Classification of Lymphomas Elaine S. Jaffe, M.D. The first step in wisdom is to know the things themselves; this notion consists in having a true
Mediastinal B-cell Lymphomas
 Mediastinal B-cell Lymphomas A Spectrum of Diseases Wyndham H. Wilson, MD, PhD Mediastinal B-cell Lymphomas Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin Lymphoma Mediastinal grey zone lymphoma Primary mediastinal B-cell
Mediastinal B-cell Lymphomas A Spectrum of Diseases Wyndham H. Wilson, MD, PhD Mediastinal B-cell Lymphomas Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin Lymphoma Mediastinal grey zone lymphoma Primary mediastinal B-cell
Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell lung Cancer (NSCLC) By CISH Technique
 Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell
Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach
 Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
Hepatic Lymphoma Diagnosis An Algorithmic Approach Ryan M. Gill, M.D., Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco PLEASE TURN OFF YOUR CELL PHONES Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL THESIS SUMMARY DIAGNOSTIC, HYSTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL ASPECTS IN DIFFUSE LARGE B CELL LYMPHOMA Scientific coordinator: Prof.
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL THESIS SUMMARY DIAGNOSTIC, HYSTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL ASPECTS IN DIFFUSE LARGE B CELL LYMPHOMA Scientific coordinator: Prof.
Lymphoid Neoplasms Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Study of 382 Patients
 Hematopathology / LYMPHOMAS WITH IGM PARAPROTEIN Lymphoid Neoplasms Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Study of 382 Patients Pei Lin, MD, 1 Suyang Hao, MD, 1* Beverly C. Handy, MD, 2 Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos,
Hematopathology / LYMPHOMAS WITH IGM PARAPROTEIN Lymphoid Neoplasms Associated With IgM Paraprotein A Study of 382 Patients Pei Lin, MD, 1 Suyang Hao, MD, 1* Beverly C. Handy, MD, 2 Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos,
Exploring the Borderlands between Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma and Classical Hodgkin s Lymphoma
 Exploring the Borderlands between Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma and Classical Hodgkin s Lymphoma Elaine S. Jaffe National Cancer Institute Bethesda, MD, USA On the Pathological Changes In Hodgkin s Disease
Exploring the Borderlands between Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma and Classical Hodgkin s Lymphoma Elaine S. Jaffe National Cancer Institute Bethesda, MD, USA On the Pathological Changes In Hodgkin s Disease
Department of Pathology, University of California San Diego Health Sciences, 3855 Health Sciences Drive, San Diego, CA 92093, USA.
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2011;4(2):190-196 www.ijcep.com /IJCEP1012012 Case Report Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting as an isolated nasopharyngeal mass: a case report
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2011;4(2):190-196 www.ijcep.com /IJCEP1012012 Case Report Anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting as an isolated nasopharyngeal mass: a case report
NEW ENTITIES IN AGGRESSIVE B CELL LYMPHOMA. Joon Seong Park, M.D. Dept. of Hematology-Oncology Ajou University School of Medicine
 NEW ENTITIES IN AGGRESSIVE B CELL LYMPHOMA Joon Seong Park, M.D. Dept. of Hematology-Oncology Ajou University School of Medicine Historical background of Lymphoma classification Rappaport classification
NEW ENTITIES IN AGGRESSIVE B CELL LYMPHOMA Joon Seong Park, M.D. Dept. of Hematology-Oncology Ajou University School of Medicine Historical background of Lymphoma classification Rappaport classification
