Long term effects of Gamma knife Radiosurgery for treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations
|
|
|
- Sabrina McGee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Research Medical Journal of Islamic Republic of Iran, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov. 2011, pp Long term effects of Gamma knife Radiosurgery for treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations Maziar Azar 1, Farid Kazemi Gazik 2, Mahdi Nikoobakht 3, Mohamad-Reza Yousefi 4, Yaser Ghavami 5 Department of Neurosurgery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services, Tehran, Iran. Received: 19 Feb 2011 Revised: 8 May 2011 Accepted: 11 May 2011 Abstract Background: The Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKR) is an established management option for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMS). Therapeutic benefits of radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations are complete obliteration of nidus with minimal neurological deficit. Methods: Radiosurgery was performed between February 2003 and April 2010 at Kamraniye day clinic, Tehran, Iran, using the Leksell gamma knife model B (Elektra Instruments AB, Stockholm, Sweden) on 82 consecutive patients with AVMs. The male-to-female ratio was 1.4:1(48M, 34F). The age of the patients ranged from 9 to 70 years (mean, 28.5±12 years). The marginal dose to the AVM nidus was 45 to 85% (median, 60%) isodose and ranged from 14 to 30 Gy (mean, 20.57±13Gy).The maximum dose ranged between 20 to 60 Gy (mean, 37.5 Gy ± 10.17Gy ). Follow up of patients for complete AVM obliteration and in the case of complications MRI were performed. Results: Complete obliteration of AVM was achieved in 56 cases (68.29%). It was marked in average 3.62 [SD=3.19] years (from 1 to 5 years) after GKR. Partial obliteration ( 50% reduction of the nidus volume) was marked in 24 cases(31%), and less than 50% reduction of the nidus volume was marked in 2 cases(2.4%) with a follow-up of 5 years. Complete obliteration of AVM had statistically significant associations with smaller score of Spetzler-Martin arteriovenous malformation grading system for AVMs. (p< 0.05) Conclusion: The Gamma Knife Radiosurgery can offer total and partial obliteration to acceptable percent of treated AVM with a low risk of morbidity. Higher success observed in patients with Spetzler-Martin Grade I and II AVMs, which was attributed to smaller volume of AVMs in this group. Keywords: Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKR), Arteriovenous malformations, Obliteration rate Introduction The Cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are vascular anomalies that cause abnormal pathway between arterial system and venous system [1]. Despite the low prevalence (0.06% up to 0.11%) in the general population, AVMs are one of the main cause of intracranial hemorrhage in people younger than 35 years old, and therefore the main goal of treatment is to prevent the bleeding caused by rupture of the pathological vessel pathways [2-5]. Available treatments for AVMs include 1. MD. Associated Professor of Neurosurgery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. maziarazar@yahoo.com 2. MD, Associated Professor of neurosurgery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. faridkazemi@lide.com 3. (Corresponding author), MD. Chief resident of neurosurgery department, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Address: 4 th floor,# 9, Snd Golbarg St., Kharazmi St., Mollasadra Ave.,Tehran, Iran, Tel: , mnikobakht@gmail.com 4. MD. Resident of Neurosurgery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. dr_yousefi1980@yahoo.com 5. MD. ghavami.y@gmail.com
2 Long term Effects of Gamma microsurgery, embolization, Stereotactic radiosurgery or a combination of these methods [6]. The Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKR) is an established management option for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. It can be used as an alternative method to microsurgery in low-grade lesions as a modality of choice for Intermediate grade AVMs and as a part of a combined treatment of high-grade AVMs. In up to 90% of cases, the treatment results in complete obliteration of the AVM within several years after treatment [7-14]. Therapeutic benefits of radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations are the complete obliteration of nidus with minimal neurological deficit. Early complications are associated with hemorrhage from the nidus during latency period [10,15]. When complete obliteration is achieved within several years, the risk of hemorrhage becomes very low; but the possibility of several other complications exists on the long-term follow up [10,15]. The incidence of delayed radiation induced complications range from 3.2 to 12.5%, which have been experienced by all investigators performing radiosurgery for the AVMs using a gamma knife [16,17]. One of the most frequent and important of delayed radiation induced complications is cyst formation in the vicinity of the target area [10, 18-20]. We conducted this study to evaluate long term effects of gamma knife radiosurgery for treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Methods Radiosurgery was performed between February 2003 and April 2010 at Kamraniye day clinic, Tehran, Iran, using the Leksell gamma knife model B (Elektra Instruments AB, Stockholm, Sweden) on 82 consecutive patients with AVMs. The stereotactic frame was fixed to the patient s head under local anesthesia (general anesthesia was generally used for children younger than 10 years of age) and the position of frame was adjusted on the head of patients according to the location of the AVM in the brain to bring the nidus of the AVM closer to the center of the stereotactic system. Table 1. Distribution of symptoms for patients with AVM. Presenting symptoms Percent Headache 68%(56) Hemorrhage 54%(45) Seizures 30%(24) Transient neurologic deficits 40%(32) Decreased mental status 10%(8) Visual deficits 7%(5) Others 10%(8) Data are presented as frequency percentage (NO.). Table 2. Arteriovenous malformation localization. Site percent Parietal 20.75%(17) Occipital 15.9%(13) Temporal 14.6%(12) Frontal 9.8%(8) Thalamus 7.3%(6) Cerebellum 4.9%(4) Corpus Callosum 9.8%(8) Basal Ganglia 2.4%(2) Brain Stem 3.7%(3) Intraventricular 11%(9) Data are presented as frequency percentage (NO.). 120 MJIRI, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov 2011, pp
3 M. Azar, et. al. Table 3. Spetzler Martin arteriovenous malformation classification Grade Percent I 14.6%(12 II 34.1%(28) III 35.4%(29) IV 14.6%(12) V 1.2%(1) Data are presented as frequency percentage (NO.). Table 4. The AVM obliteration after the gamma knife radiosurgery treatment in 82patients Years after GKS Total obliterated Not total obliterated Cumulative Obliteration Rate (%) % % % % % MJIRI, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov 2011, pp Stereotactic localization of the AVMs was done with angiography alone (28 patients) angiography plus computed tomography (9 patients), angiography with magnetic resonance imaging (30 patients) and MRI alone (15 patients). The male-to-female ratio was 1.40: 1 (48M, 34F). The age of the patients ranged from 9 to 70 years (mean, 28.5 ±12 years). Previous microsurgical resection was performed on 5 (6.09% patients), embolization performed on 9 (10.97% patients), stereotactic radiotherapy performed on 1 (1.21% patients), and 3(3.63%patients) had history of CVA and ICH. 7 of these patients (8.53%) had undergone a combination of surgery plus embolization before the gamma knife treatment. Gamma knife radiosurgery was the primary treatment for 60 (73.17%) patients. Various symptoms, localization of the AVM and the Spetzler grade are summarized in Tables 1, 2, 3. The diameter of the AVM nidus ranged between 0.9 and 5.9 cm (mean, 2.7±0.5 cm). The marginal dose to the AVM nidus was 45 to 85% (median, 60%) isodose and ranged from 14 to 30 Gy (mean, 20.57± 3.13Gy). The maximum dose ranged between 20 to 60 Gy (mean, 37.5 Gy±10.17 Gy). In one case in which obliteration was not achieved 3.5 years after radiosurgery in another center, gamma knife was repeated in our center. Follow up patients for complete AVM obliteration and in the case of complications (for example, post irradiation edema or rebleeding) MRI were performed. The MRI scans were performed after the complete obliteration only in cases in which the clinical status was suspicious. Statistical Analysis Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS v.13 software. Data were presented as number, percent, mean and standard deviation (SD). The statistical analysis was conducted using the T test and the p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results Complete obliteration of AVM was achieved in 56 cases (68.29%). It was marked in average 3.62 [SD=3.19] years (from 1 to 5 years) after GKR. Partial obliteration ( 50% reduction of the nidus volume) was marked in 24 cases (31%), and less than 50% reduction of the nidus volume was marked in 2 cases (2.4%) with a follow-up of 5 years (Table 4). Complete obliteration of AVM had statistically significant associations with smaller score of Spetzler-Martin arteriovenous malformation grading system for AVMs [Fig. 1] (p< 0.05).
4 Long term Effects of Gamma Table 5- Results after Radiosurgery of arteriovenous malformations Series (ref.no ) No. of patients Obliteration (%) Complications (%) Fatal rebleeding (%) Bollet et al., 2004 (8) Pollock et al., 2003 (13) Friedman, 2002 (15) Inoue and Ohye, 2002 (36) Chang et al., 2000 (37) Touboul et al., 1998 (38) Sasaki et al., 1998 (39) Karlsson et al., 1997 (40) Colombo et al., 1994 (41) Kondziolka et al.,199 (28) Table 6. Number of patients undergone GKRS separated according to years (9.5%) 13(16%) 11(13.5%) 12(15%) 5(6%) 14(17%) 11(13.5%) 8(9.5%) There was not any statistical significant relationship between age, clinical symptoms, sex and complete obliteration rate. In 3 patients, the microsurgical removal of the incompletely obliterated AVM was done 5 years after GKR. Treatment was performed within less than 3 years only in cases in which a new nidus had developed which was not observed in our patients. Before radiosurgery, hemorrhage from AVMs occurred in 45patients (54%). The number of bleedings in a single patient ranged between one and three times, with a mean of one bleeding episode. Rebleeding was seen in the latent period before AVM obliteration in 9 patients (11%) within 3.5 to 37 months (mean, 11.5 months) after the GKS. The neurodeficit after rebleeding impaired in 2 patients (2.4%), and 1 patient (1.2%) died as the consequence of the rebleeding. (only patient who died in our study). The neurological symptoms induced by the AVM was detected prior to gamma knife treatment in 65 patients (79.26%). In 42 patients (51.2%), these neurological symptoms improved significantly after GKS within 6 to 35 months (mean, 12 month). Radiosurgery induced cerebral edema and rebleeding caused worsening of clinical symptoms in 11 cases (13.4%). The cause of morbidity was cerebral edema induced by radiosurgery in 2 patients and rebleeding in 9 patients. Finally, morbidity was observed in 8 patients which represented a cumulative risk of 10% in the group of 82 patients available for evaluation. Epilepsy was detected in 24 patients (30%) before radiosurgery. Termination of the seizures or improvement in seizure frequency was observed in 18 patients 4.2 to 48 months (mean, 16 month) after radiosurgery. A worsening of epilepsy after radiosurgery was detected in 2 patients after radiosurgery because of cerebral edema, and 4 patients (4.8%) had persistent seizure attacks before surgery. Edema was detected by MRI in 15 patients (18.20%) within 3 to 30 months (mean, 11months) after the procedure. Edema was symptomatic only in 2 patients representing a 2.43% morbidity rate. The corticosteroid therapy was given in all 15 patients for a period of 12 months. Edema later resolved in 13 of these 15 patients. The Gamma knife radiosurgery was repeated only in 1 patient (1.2%) because complete obliteration was not achieved within 3.5 years of the first treatment in another center. Number of patients undergone GKRS is separated according to years (from 2003 t0 2010) and is shown in table 6. Discussion The annual rate of bleeding from an un- 122 MJIRI, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov 2011, pp
5 M. Azar, et. al. Table 7. Spetzler-Martin AVM grading system Spetzler-Martin AVM grading system. The Spetzler-Martin AVM grading system allocates points for various features of intracranial AVM's to give a score between 1 and 5 in order to estimate the risk of surgery for that patient. Size of nidus small (<3 cm) = 1 medium (3-6 cm) = 2 large (>6 cm) = 3 Eloquence of adjacent brain non-eloquent = 0 eloquent = 1 Venous drainage superficial only = 0 deep = 1 ruptured Arteriovenous malformation is reported up to 4% and may significantly increases by coexistent factors (for example, deep venous drainage, venous stenosis, aneurysm, high mean arterial pressure, diffuse morphology, periventricular location, and larger size of the nidus)[5,6,11,14,21-23]. Approximately 18% of the first hemorrhages are fatal [21], in addition mortality and morbidity associated with hemorrhages varying between 6 29% and 50 70% in various reported series [11,27,28]. The AVMs can also cause seizures, transient neurologic deficit, headache and decreased mental status [1,5,24]. The AVMs are typically found in young individuals (20-40 years) so life-long probability for various complications is considered to be high enough to give active treatment [15,25,26]. The AVMs with small-to-intermediate size can be effectively treated either by surgery or gamma knife radiosurgery but management of large lesions represents a significant challenge [25, 26, 29-34]. The microsurgical resection for AVMs in the eloquent area can be associated with a high morbidity and mortality. Embolization of cerebral AVMs has been performed for nearly 40 years to reduce the risk of bleeding. Despite advances in the technique, reformation of AVMs after complete endovascular treatment is a wellknown problem. Thus GKS is accepted as an alternative to microsurgery and embolization for the treatment of AVMs, particularly for those in eloquent area. Radiosurgery could be beneficial in the complete obliteration of the AVMs, with a 1 to 4 year latency period in most cases. The purpose of this study was to assess the benefit of radiosurgery in patients with AVM. Unlike microsurgery or embolization, the AVM obliteration after radiosurgery cannot be evaluated immediately after the procedure, so it is impossible to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment in all patients, but delay in the AVM obliteration despite the risk of rebleeding, can have some advantages (for example, gradual restoration of the circulation in the collateral vessels) [35]. Complete obliteration of AVM was achieved in 56 cases (68.29%) in our study that is similar to other studies (Table 5). The maximum obliteration rate was reported by Sasaki et al., 1998 [39] that was 85.7%,and minimum obliteration rates was 51% that reported by Touboul et al., 1998 [38]. It was marked in average 3.62 years (from 1 to 5 years) after GKR that other articles also emphasize on this latent period. Complete obliteration of AVM had statistically significant associations with smaller score of Spetzler-Martin arteriovenous malformation grading system for AVMs (table7) (p<0.05). Higher success was observed in patients with Spetzler-Martin Grade I and II AVMs, which is attributed to smaller volume of AVMs in this group. Since the Spetzler-Martin AVM grading system, considered the diameter of the AVM nidus, its localization in the eloquent areas, and the type of venous drainage [42], it proved to be useful for the prognosis and result of the microsurgical resection [43]. There was not any statistical significant MJIRI, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov 2011, pp
6 relationship between age, clinical symptoms, sex and complete obliteration rate in our study, however some authors emphasized on effect of these factors for determining positive treatment outcomes [12,13,40]. Complications after radiosurgery are classified as acute, subacute, and delayed. Acute complications associated with the performance of the treatment itself, are part of the treatment procedure. However, these complications were not seen in our study and are mentioned infrequently in other articles. Subacute complications are caused by postirradiation edema, which can be observed after a delay of several months, usually within 6 to 24 months, but most frequently within 1 year after radiosurgery. The radiosurgery induced cerebral edema caused worsening of clinical symptoms in 2 cases (2.4%) in our study. Edema observed after radiosurgery occurs at a time when the AVM vessels show continual flow void and obliteration is not accomplished; thus, the reasons are not hemodynamic changes caused by obliteration but rather a toxic effect on the surrounding tissue or the AVM itself [44]. Rebleeding caused worsening of clinical symptoms in 9 cases (10.9%) and 1 patients (1.2%) died as the consequence (the only patient died in our study). The risk of rebleeding during the latency period of the healing process after radiosurgery can be evaluated only in terms of the potential cure rate of alternative treatment methods that cannot calculated in present study. Although the percentage of patients with rebleeding after radiosurgery varies between 3.4 to 10%, the number of fatal hemorrhages is reported between 0 to 3.5%. These percentages are alike our findings. Conclusion Gamma knife radiosurgery can offer total and partial obliteration to acceptable percent of treated AVM with a low risk of morbidity. Higher success was observed in patients with Spetzler-Martin Grade I and II AVMs, which is attributed to smaller volume AVMs Long term Effects of Gamma in this group. Radiosurgery induced cerebral edema and rebleeding caused worsening of clinical symptoms in 11 cases (13.4%).The cause of morbidity was cerebral edema induced by radiosurgery in 2 patients and rebleeding in 9 patients. Finally, morbidity was observed in 8 patients which represented a cumulative risk of 10% in the group of 82 patients available for evaluation. References 1. Brown RD, Wiebers DO, Torner JC, et al. Frequency of intracranial hemorrhages as a presenting symptom and subtype analysis: a population-based study of intracranial vascular malformations in Olmsted County, Minnesota. J Neurosurg 1996; 85: Fleetwood IG, Steinberg GK. Arteriovenous malformations. Lancet 2002; 359: Karhunen PJ, Penttila A, Erkinjuntti T. Arteriovenous malformation of the brain: imaging by postmortem angiography. Forensic Sci Int 1990; 48: Ondra SL, Troupp H, George ED, Schwab K. The natural history of symptomatic arteriovenous malformations of the brain: a 24-year follow-up assessment. J Neurosurg 1990; 73: Soderman M, Andersson T, Karlsson B, Wallace MC, Edner G. Management of patients with brain arteriovenous malformations. Eur J Radiol 2003; 46: Maesawa S, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD: Repeated radiosurgery for incompletely obliterated arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 92: , Andrade-Souza YM, Zadeh G, Scora D, et al. Radiosurgery for basal ganglia, internal capsule, and thalamus ateriovenous malformation: clinical outcome. Neurosurgery 2005; 56: Bollet MA, Anxionnat R, Buchheit I, et al. Efficacy and morbidity of arc-therapy radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a comparison with the natural history. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004; 58: Friedman WA, Bova FJ, Bollampally S, et al. Analysis of factors predictive of success or complications in arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 2003; 52: Izawa M, Hayashi M, Chernov M, et al. Longterm complications after Gamma Knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 2005; 102(Suppl): Liscak R, Vladyka V, Simonova G, et al. Arteriovenous malformations after Leksell Gamma Knife 124 MJIRI, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov 2011, pp
7 M. Azar, et. al. radiosurgery: rate of obliteration and complications. Neurosurgery 2007; 60: Pollock BE, Flickinger JC. A proposed radiosurgery-based grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 2002; 96: Pollock BE, Gorman DA, Coffey RJ. Patient outcomes after arteriovenous malformation radiosurgical management: results based on a 5- to 14-year follow-up study. Neurosurgery 2003;52: Zabel-du Bois A, Milker-Zabel S, Huber P, et al. Risk of hemorrhage and obliteration rates of LIN- AC-based radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations treated after prior partial embolization. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007; 68: Friedman WA. Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: the University of Florida experience. In: Kondziolka D, editor. Radiosurgery 2002; 4. Basel7 Karger, pp Steiner L, Lindquist C, Steiner M. Radiosurgery. In:Symon L, ed. Advances and technical standards in neurosurgery. Wien: Springer-Verlag, 1992; Yamamoto M, Ban S, Ide M, Jimbo M. A diffuse white matter ischemic lesion appearing 7 years after stereotactic radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformation: case report. Neurosurgery 1997; 41: Pan HC, Sheehan J, Stroila M, et al. Late cyst formation following gamma knife surgery of arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 2005;102(Suppl 1): Pollock BE, Brown RD. Management of cysts arising after radiosurgery to treat intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 2001; 49: Yonekawa Y, Imhof HG, Bjeljac M, et al. Three cases of AVM at eloquent areas finally treated with conventional microsurgical method. Acta Neurochir Suppl 2005; 94: Al-Shahi R, Warlow C.A systematic review of the frequency and prognosis of arteriovenous malformations of the brain in adults. Brain 2001; 124: Alexander MJ, Tolbert ME. Targeting cerebral arteriovenous malformations for minimally invasive therapy. Neurosurgery 2006; 59 (Suppl 3):S Jayaraman MV, Marcellus ML, Do HM, et al. Hemorrhage rate in patients with Spetzler-Martin grades IV and V arteriovenous malformations: is treatment justified? Stroke 2007; 38: Hoh BL, Chapman PH, Loeffler JS, et al. Results of multimodality treatment for 141 patients with brain arteriovenous malformations and seizures: factors associated with seizure incidence and seizure outcomes. Neurosurgery 2002; 51: Chang SD, Marcellus ML, Marks MP, et al. Multimodality treatment of giant intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 2003; 53: Henkes H, Nahser HC, Berg-Dammer E, et al. MJIRI, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov 2011, pp Endovascular therapy of brain AVMs prior to radiosurgery. Neurol Res 1998; 20: FriedmanWA, Blatt DL, Bova FJ, Buatti JM, Mendenhall WM,Kubilis PS. The risk of hemorrhage after radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations.j Neurosurg 1996; 84: Kondziolka D, McLaughin MR, Kestle JRW. Simple risk predictions for arte-riovenous malformation hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 1995; 37: Deruty R, Pelissou-Guyotat I, Morel C, et al. Reflections on the management of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Surg Neurol 1998; 50: Han PP, Ponce FA, Spetzler RF. Intention-totreat analysis of Spetzler-Martin grades IV and V arteriovenous malformations: natural history and treatment paradigm. J Neurosurg 2003;98: Karlsson B, Lindqvist M, Blomgren H, et al. Long-term results after fractionated radiation therapy for large brain arterioveous malformations. Neurosurgery 2005; 57: Raza SM, Jabbour S, Thai QA, et al. Repeat stereotactic radiosurgery for high-grade and large intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Surg Neurol 2007; 68: Raymond J, Iancu D, Weill A, et al. Embolization as one modality in a combined strategy for the management of cerebral riovenous malformations. Interv Neuroradiol 2005; 11(Suppl 1): Richling B, Killer M, Al-Schameri AR, et al. Therapy of brain arteriovenous malformations: multimodality treatment from a balanced standpoint. Neurosurgery 2006; 59(Suppl 3):S Miyasaka Y, Yada K, Ohwada T, Kitahara T, Endoh M, Saito M, Kurata A,Ohtaka H: Retrograde thrombosis of feeding arteries after removal of arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 1990;72: Inoue HK, Ohye C: Hemorrhage risks and obliteration rates of arteriovenous malformations after gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg ; [Suppl 5]: Chang JH, Chang JW, Park YG, Chung SS: Factors related to complete occlusionof arteriovenous malformations after gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 2000; 93 [Suppl 3]: Touboul E, Al Halabi A, Buffat L, Merienne L, Huart J, Schlienger M, Lefkopoulos D, Mammar H, Missir O, Meder JF, Laurent A, Housset M: Singlefraction stereotactic radiotherapy: A dose-response analysis of arteriovenous malformation obliteration. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1998; 41: Sasaki T, Kurita H, Saito I, Kawamoto S, Nemoto S, Terahara A, Kirino T,Takakura K: Arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia and thalamus: Management and results in 101 cases. J Neurosurg 1998; 88: Karlsson B, Lindquist C, Steiner L: Prediction of obliteration after gamma knife surgery for cerebral arteriovneous malformations. Neurosurgery 1997; 40:
8 Long term Effects of Gamma 41. Colombo F, Pozza F, Chierego G, Casentini L, De Luca G, Francescon P:Linear accelerator radiosurgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: An update. Neurosurgery 1994; 34: Spetzler RF, Martin NA: A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 1986; 65: Morgan MK, Sekhon LH, Finfer S, Grinnell V: Delayed neurological deteriotion following resection of arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg 1999; 90: Rothbart D, Awad IA, Lee J, Kim J, Harbaugh R, Criscuolo GR. Expression of angiogenic factors and structural proteins in central nervous system vascular malformations. Neurosurgery 1996; 38: MJIRI, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov 2011, pp
ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Dr. Maitri P Gandhi 1, Dr. Chandni P Shah 2 1 Junior resident, Gujarat Cancer & Research
ANALYSIS OF TREATMENT OUTCOMES WITH LINAC BASED STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY IN INTRACRANIAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Dr. Maitri P Gandhi 1, Dr. Chandni P Shah 2 1 Junior resident, Gujarat Cancer & Research
DECISION MAKING IN AVM TREATMENT STRATEGY TREATMENT BOARD SYSTEM AT TOHOKU UNIVERSITY
 Kitakanto Med. J. (S1) : 79-84, 1998 79 DECISION MAKING IN AVM TREATMENT STRATEGY TREATMENT BOARD SYSTEM AT TOHOKU UNIVERSITY Takashi Yoshimoto, Hidefumi Jokura Department of Neurosurgery, Tohoku University
Kitakanto Med. J. (S1) : 79-84, 1998 79 DECISION MAKING IN AVM TREATMENT STRATEGY TREATMENT BOARD SYSTEM AT TOHOKU UNIVERSITY Takashi Yoshimoto, Hidefumi Jokura Department of Neurosurgery, Tohoku University
KEY WORDS: Arteriovenous malformation, Complications, Outcome, Radiosurgery
 CLINICAL STUDIES ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS AFTER LEKSELL GAMMA KNIFE RADIOSURGERY: RATE OF OBLITERATION AND COMPLICATIONS Roman Liščák, M.D. Department of Stereotactic and Radiation Neurosurgery, Vilibald
CLINICAL STUDIES ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS AFTER LEKSELL GAMMA KNIFE RADIOSURGERY: RATE OF OBLITERATION AND COMPLICATIONS Roman Liščák, M.D. Department of Stereotactic and Radiation Neurosurgery, Vilibald
Estimating the Risks of Adverse Radiation Effects After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations
 Estimating the Risks of Adverse Radiation Effects After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations Hideyuki Kano, MD, PhD; John C. Flickinger, MD; Daniel Tonetti, MD; Alan Hsu, MD; Huai-che
Estimating the Risks of Adverse Radiation Effects After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Arteriovenous Malformations Hideyuki Kano, MD, PhD; John C. Flickinger, MD; Daniel Tonetti, MD; Alan Hsu, MD; Huai-che
The Risk of Hemorrhage after Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations
 The new england journal of medicine original article The Risk of Hemorrhage after Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Keisuke Maruyama, M.D., Nobutaka Kawahara, M.D., Ph.D., Masahiro
The new england journal of medicine original article The Risk of Hemorrhage after Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Keisuke Maruyama, M.D., Nobutaka Kawahara, M.D., Ph.D., Masahiro
Despite recent progress in microsurgical techniques, endovascular
 Application of Single-Stage Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations >10 cm 3 Shunya Hanakita, MD; Tomoyuki Koga, MD, PhD; Masahiro Shin, MD, PhD; Hiroshi Igaki, MD, PhD; Nobuhito
Application of Single-Stage Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations >10 cm 3 Shunya Hanakita, MD; Tomoyuki Koga, MD, PhD; Masahiro Shin, MD, PhD; Hiroshi Igaki, MD, PhD; Nobuhito
Influenced by the high morbidity and mortality associated
 Hemorrhage Risk of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Before and During the Latency Period After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Chun-Po Yen, MD; Jason P. Sheehan, MD, PhD; Lucia Schwyzer, MD; David Schlesinger,
Hemorrhage Risk of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Before and During the Latency Period After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Chun-Po Yen, MD; Jason P. Sheehan, MD, PhD; Lucia Schwyzer, MD; David Schlesinger,
Long-term control of large pontine arteriovenous malformation using gamma knife therapy: a review with illustrative case
 Long-term control of large pontine arteriovenous malformation using gamma knife therapy: a review with illustrative case Martin M. Mortazavi 1, Daxa Patel 1, Christoph J. Griessenauer 1, R. Shane Tubbs
Long-term control of large pontine arteriovenous malformation using gamma knife therapy: a review with illustrative case Martin M. Mortazavi 1, Daxa Patel 1, Christoph J. Griessenauer 1, R. Shane Tubbs
Microsurgical Resection of Incompletely Obliterated Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformations Following Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 II-2. Selection of Treatment Microsurgical Resection of Incompletely Obliterated Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformations Following Stereotactic Radiosurgery Steven D. CHANG*, Gary K. STEINBERG*, Richard
II-2. Selection of Treatment Microsurgical Resection of Incompletely Obliterated Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformations Following Stereotactic Radiosurgery Steven D. CHANG*, Gary K. STEINBERG*, Richard
Methods. Treatment options for intracranial arteriovenous malformations
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1139 1143, August 2004 Complete Obliteration of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation with Endovascular Cyanoacrylate Embolization: Initial Success and Rate of Permanent Cure
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1139 1143, August 2004 Complete Obliteration of Intracranial Arteriovenous Malformation with Endovascular Cyanoacrylate Embolization: Initial Success and Rate of Permanent Cure
EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Intracranial arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:945 953, 2015 A quantitative analysis of adverse radiation effects following Gamma Knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations Or Cohen-Inbar, MD, PhD, 1 Cheng-Chia
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:945 953, 2015 A quantitative analysis of adverse radiation effects following Gamma Knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations Or Cohen-Inbar, MD, PhD, 1 Cheng-Chia
Xiaochuan Huo, PhD, Yuhua Jiang, PhD, Xianli Lv, PhD, Hongchao Yang, MD, Yang Zhao, MD, and
 clinical article J Neurosurg 124:767 776, 2016 Gamma Knife surgical treatment for partially embolized cerebral arteriovenous malformations Xiaochuan Huo, PhD, Yuhua Jiang, PhD, Xianli Lv, PhD, Hongchao
clinical article J Neurosurg 124:767 776, 2016 Gamma Knife surgical treatment for partially embolized cerebral arteriovenous malformations Xiaochuan Huo, PhD, Yuhua Jiang, PhD, Xianli Lv, PhD, Hongchao
Spetzler-Martin Grade III arteriovenous malformations. Radiosurgery for Spetzler-Martin Grade III arteriovenous malformations.
 See the corresponding editorial in this issue, pp 955 958. J Neurosurg 120:959 969, 2014 AANS, 2014 Radiosurgery for Spetzler-Martin Grade III arteriovenous malformations Clinical article Dale Ding, M.D.,
See the corresponding editorial in this issue, pp 955 958. J Neurosurg 120:959 969, 2014 AANS, 2014 Radiosurgery for Spetzler-Martin Grade III arteriovenous malformations Clinical article Dale Ding, M.D.,
Life after ARUBA: Management of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
 Life after ARUBA: Management of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) Eric L. Zager, MD University of Pennsylvania Department of Neurosurgery No Disclosures Brain AVMs Incidence ~1 in 100,000
Life after ARUBA: Management of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) Eric L. Zager, MD University of Pennsylvania Department of Neurosurgery No Disclosures Brain AVMs Incidence ~1 in 100,000
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh
 Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Endovascular Treatment of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations Bs. Nguyễn Ngọc Pi Doanh- Bs Đặng Ngọc Dũng Khoa Ngoại Thần Kinh Stroke Vascular Malformations of the Brain Epidemiology: - Incidence: 0.1%,
Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis
 Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Original article: Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous malformations : a clinical analysis Dr. Rajneesh Gour 1, Dr. S. N. Ghosh 2, Dr. Sumit Deb 3 1Dept.Of Surgery,Chirayu Medical College & Research Centre,
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations. December Reference : NHSCB/D5/4
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D5/4 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations First published: December
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations December 2012 Reference : NHSCB/D5/4 NHS Commissioning Board Clinical Commissioning Policy: Arteriovenous Malformations First published: December
Arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia and thalamus: management and results in 101 cases
 J Neurosurg 88:285 292, 1998 Arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia and thalamus: management and results in 101 cases TOMIO SASAKI, M.D., PH.D., HIROKI KURITA, M.D., ISAMU SAITO, M.D., PH.D.,
J Neurosurg 88:285 292, 1998 Arteriovenous malformations in the basal ganglia and thalamus: management and results in 101 cases TOMIO SASAKI, M.D., PH.D., HIROKI KURITA, M.D., ISAMU SAITO, M.D., PH.D.,
Long term neuroimaging and clinical outcome of brain Arteriovenous Malformations (bavm) treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS).
 Long term neuroimaging and clinical outcome of brain Arteriovenous Malformations (bavm) treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). Poster No.: C-2489 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Long term neuroimaging and clinical outcome of brain Arteriovenous Malformations (bavm) treated with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). Poster No.: C-2489 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
DOWNLOAD PDF RADIOSURGERY FOR CAVERNOUS MALFORMATIONS IN BASAL GANGLIA, THALAMUS AND BRAINSTEM KIDA, Y
 Chapter 1 : Stereotactic radiosurgery for cavernous malformations â Mayo Clinic Most of the lesions were located in the brainstem, followed by the lobar region, cerebellum, thalamus, and basal ganglia
Chapter 1 : Stereotactic radiosurgery for cavernous malformations â Mayo Clinic Most of the lesions were located in the brainstem, followed by the lobar region, cerebellum, thalamus, and basal ganglia
Seizure control of Gamma Knife radiosurgery for non-hemorrhagic arteriovenous malformations
 Acta Neurochir Suppl (2006) 99: 97 101 # Springer-Verlag 2006 Printed in Austria Seizure control of Gamma Knife radiosurgery for non-hemorrhagic arteriovenous malformations Y. J. Lim, C. Y. Lee, J. S.
Acta Neurochir Suppl (2006) 99: 97 101 # Springer-Verlag 2006 Printed in Austria Seizure control of Gamma Knife radiosurgery for non-hemorrhagic arteriovenous malformations Y. J. Lim, C. Y. Lee, J. S.
Surgical Neurology International
 Surgical Neurology International OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: James I. Ausman, MD, PhD University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA Original
Surgical Neurology International OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: James I. Ausman, MD, PhD University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA Original
Brain Edema after Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Large Arteriovenous Malformation: A Case Report
 Posted online 2016 Jul. 19 Exp Neurobiol. 2016 Aug;25(4) pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Case Report Brain Edema after Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Large Arteriovenous Malformation: A Case Report
Posted online 2016 Jul. 19 Exp Neurobiol. 2016 Aug;25(4) pissn 1226-2560 eissn 2093-8144 Case Report Brain Edema after Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Large Arteriovenous Malformation: A Case Report
Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos
 Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Endovascular Therapy and Associated Therapeutic Protocols Jorge Guedes Cabral de Campos Neuroradiology Department Hospital de Santa Maria University of Lisbon CEREBRAL AVM CLINICAL / EPIDEMIOLOGY Brain
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
7 TI - Radiosurgery of angiographically occult vascular malformations. AU - Kida Y, et al.
 1 TI - Cerebral arteriovenous malformation in pregnancy: presentation and neurologic, obstetric, and ethical significance. AU - Finnerty JJ, et al. SO - Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Aug;181(2):296-303. Review.
1 TI - Cerebral arteriovenous malformation in pregnancy: presentation and neurologic, obstetric, and ethical significance. AU - Finnerty JJ, et al. SO - Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Aug;181(2):296-303. Review.
The treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurologic Complications of Arteriovenous Malformation Embolization Using Liquid Embolic Agents
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.V. Jayaraman M.L. Marcellus S. Hamilton H.M. Do D. Campbell S.D. Chang G.K. Steinberg M.P. Marks Neurologic Complications of Arteriovenous Malformation Embolization Using Liquid Embolic
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.V. Jayaraman M.L. Marcellus S. Hamilton H.M. Do D. Campbell S.D. Chang G.K. Steinberg M.P. Marks Neurologic Complications of Arteriovenous Malformation Embolization Using Liquid Embolic
Stereotactic radiosurgery with neoadjuvant embolization of larger arteriovenous malformations: An institutional experience
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurosurgery Faculty Papers Department of Neurosurgery 1-22-2014 Stereotactic radiosurgery with neoadjuvant embolization of larger arteriovenous
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurosurgery Faculty Papers Department of Neurosurgery 1-22-2014 Stereotactic radiosurgery with neoadjuvant embolization of larger arteriovenous
VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS. Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University
 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University Introduction Brain and spinal cord vascular malformations can be separated into five main categories: 1) Arteriovenous malformation,
VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Owen Samuels, MD Adam Webb, MD Emory University Introduction Brain and spinal cord vascular malformations can be separated into five main categories: 1) Arteriovenous malformation,
Cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126:852 858, 2017 Comparative analysis of arteriovenous malformation grading scales in predicting outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery Bruce E. Pollock, MD, 1,2 Curtis
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126:852 858, 2017 Comparative analysis of arteriovenous malformation grading scales in predicting outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery Bruce E. Pollock, MD, 1,2 Curtis
Forward treatment planning techniques to reduce the normalization effect in Gamma Knife radiosurgery
 Received: 7 November 2016 Revised: 9 August 2017 Accepted: 21 August 2017 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12193 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Forward treatment planning techniques to reduce the normalization effect in
Received: 7 November 2016 Revised: 9 August 2017 Accepted: 21 August 2017 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12193 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Forward treatment planning techniques to reduce the normalization effect in
Arteriovenous Malformations in the Pediatric Population: Review of the Existing Literature
 Published online: September 1, 2016 1664 9737/16/0054 0218$39.50/0 Review Arteriovenous Malformations in the Pediatric Population: Review of the Existing Literature Mohammad El-Ghanem a Tareq Kass-Hout
Published online: September 1, 2016 1664 9737/16/0054 0218$39.50/0 Review Arteriovenous Malformations in the Pediatric Population: Review of the Existing Literature Mohammad El-Ghanem a Tareq Kass-Hout
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (2):
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (2): 957-962 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis on the effect and prognostic factors of cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVM) after endovascular embolization combined
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (2): 957-962 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis on the effect and prognostic factors of cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVM) after endovascular embolization combined
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke. Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery)
 Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Case Report Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery in a Large Bilateral Thalamic and Basal Ganglia Arteriovenous Malformation
 Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 631028, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/631028 Case Report Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery in a Large Bilateral Thalamic
Case Reports in Neurological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 631028, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/631028 Case Report Hypofractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery in a Large Bilateral Thalamic
The outcome of treatment for arteriovenous malformations of the brain: A five-year retrospective series from the Philippines
 Neurology Asia 2006; 11 : 91 96 ORIGINAL ARTICLES The outcome of treatment for arteriovenous malformations of the brain: A five-year retrospective series from the Philippines Roland Mark M GIGATARAS MD,
Neurology Asia 2006; 11 : 91 96 ORIGINAL ARTICLES The outcome of treatment for arteriovenous malformations of the brain: A five-year retrospective series from the Philippines Roland Mark M GIGATARAS MD,
Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations.
 Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. E. Rodriguez 1, A. Lopez Moreno 1, D. Sánchez Paré
Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. E. Rodriguez 1, A. Lopez Moreno 1, D. Sánchez Paré
The management of large (> 10 cm3) arteriovenous
 Neurosurg Focus 37 (3):E18, 2014 AANS, 2014 Volume-staged versus dose-staged radiosurgery outcomes for large intracranial arteriovenous malformations Shayan Moosa, B.A., 1 Ching-Jen Chen, M.D., 1 Dale
Neurosurg Focus 37 (3):E18, 2014 AANS, 2014 Volume-staged versus dose-staged radiosurgery outcomes for large intracranial arteriovenous malformations Shayan Moosa, B.A., 1 Ching-Jen Chen, M.D., 1 Dale
Cerebral haemorrhage from a remote varix in the venous outflow of an arteriovenous malformation treated successfully by embolisation
 The British Journal of Radiology, 83 (2010), e129 e134 CASE REPORT Cerebral haemorrhage from a remote varix in the venous outflow of an arteriovenous malformation treated successfully by embolisation 1
The British Journal of Radiology, 83 (2010), e129 e134 CASE REPORT Cerebral haemorrhage from a remote varix in the venous outflow of an arteriovenous malformation treated successfully by embolisation 1
Over the last 25 years the management options for. Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the cerebellum.
 J Neurosurg 120:583 590, 2014 AANS, 2014 Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the cerebellum Clinical article Greg Bowden, M.D., M.Sc., 1,3,5 Hideyuki Kano, M.D., Ph.D., 1,3 Daniel
J Neurosurg 120:583 590, 2014 AANS, 2014 Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the cerebellum Clinical article Greg Bowden, M.D., M.Sc., 1,3,5 Hideyuki Kano, M.D., Ph.D., 1,3 Daniel
Delayed Radiation Necrosis 7 Years After Gamma Knife Surgery for Arteriovenous Malformation
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 50, 62 66, 2010 Delayed Radiation Necrosis 7 Years After Gamma Knife Surgery for Arteriovenous Malformation Two Case Reports Tatsuki OYOSHI, Kazuho HIRAHARA*, KoichiUETSUHARA*,
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 50, 62 66, 2010 Delayed Radiation Necrosis 7 Years After Gamma Knife Surgery for Arteriovenous Malformation Two Case Reports Tatsuki OYOSHI, Kazuho HIRAHARA*, KoichiUETSUHARA*,
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Unruptured Epileptogenic Brain Arteriovenous Malformations
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.9190-13.1 Received: 31.08.2013 / Accepted: 24.09.2013 Published Online: 16.02.2016 Original Investigation Unruptured Epileptogenic Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Yong SUN
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.9190-13.1 Received: 31.08.2013 / Accepted: 24.09.2013 Published Online: 16.02.2016 Original Investigation Unruptured Epileptogenic Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Yong SUN
Diagnosis and Management of AVM in the Pregnant Patient
 Diagnosis and Management of AVM in the Pregnant Patient Wade Cooper, D.O. University of Michigan Assistant Professor Departments of Neurology & Anesthesiology Disclosures Wade Cooper - None Developmental
Diagnosis and Management of AVM in the Pregnant Patient Wade Cooper, D.O. University of Michigan Assistant Professor Departments of Neurology & Anesthesiology Disclosures Wade Cooper - None Developmental
Serial Follow-up MR Imaging after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Vestibular Schwannoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1540 1546, September 2000 Serial Follow-up MR Imaging after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Vestibular Schwannoma Hiroyuki Nakamura, Hidefumi Jokura, Kou Takahashi, Nagatoshi Boku,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1540 1546, September 2000 Serial Follow-up MR Imaging after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Vestibular Schwannoma Hiroyuki Nakamura, Hidefumi Jokura, Kou Takahashi, Nagatoshi Boku,
Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations
 126 Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations Radiocirugia para malformações arteriovenosas cerebrais William A. Friedman 1 Frank J. Bova 1 Abstract Radiosurgery has become a popular alternative to
126 Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations Radiocirugia para malformações arteriovenosas cerebrais William A. Friedman 1 Frank J. Bova 1 Abstract Radiosurgery has become a popular alternative to
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 03/01/2013 Section:
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 03/01/2013 Section:
Staged-Volume Radiosurgery of Large AVMs
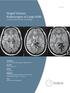 Case Study Staged-Volume Radiosurgery of Large AVMs Using Gamma Knife Technology Institution New York University Langone Medical Center Location New York City, NY Patient 18 patients Diagnosis Each patient
Case Study Staged-Volume Radiosurgery of Large AVMs Using Gamma Knife Technology Institution New York University Langone Medical Center Location New York City, NY Patient 18 patients Diagnosis Each patient
Delayed Radiation Necrosis With Extensive Brain Edema After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Multiple Cerebral Cavernous Malformations
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43, 391 395, 2003 Delayed Radiation Necrosis With Extensive Brain Edema After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Multiple Cerebral Cavernous Malformations Case Report Nobuo TAKENAKA,
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43, 391 395, 2003 Delayed Radiation Necrosis With Extensive Brain Edema After Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Multiple Cerebral Cavernous Malformations Case Report Nobuo TAKENAKA,
Michael K. Morgan, MD, 1 Markus K. Hermann Wiedmann, MD, 1 Marcus A. Stoodley, PhD, 1 and Gillian Z. Heller, PhD 2
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 127:1105 1116, 2017 Microsurgery for Spetzler-Ponce Class A and B arteriovenous malformations utilizing an outcome score adopted from Gamma Knife radiosurgery: a prospective
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 127:1105 1116, 2017 Microsurgery for Spetzler-Ponce Class A and B arteriovenous malformations utilizing an outcome score adopted from Gamma Knife radiosurgery: a prospective
Alt h o u g h infratentorial AVMs comprise only
 Neurosurg Focus 26 (5):E12, 2009 Posterior fossa arteriovenous malformations Om a r M. Arn a o u t, B.A., 1 Br a d l e y A. Gr o s s, M.D., 2 Ch r i s t o p h e r S. Ed d l e m a n, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Be r
Neurosurg Focus 26 (5):E12, 2009 Posterior fossa arteriovenous malformations Om a r M. Arn a o u t, B.A., 1 Br a d l e y A. Gr o s s, M.D., 2 Ch r i s t o p h e r S. Ed d l e m a n, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Be r
Neurological Change after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases Involving the Motor Cortex
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain Tumor Res Treat 2016;4(2):111-115 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 http://dx.doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2016.4.2.111 Neurological Change after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Brain Tumor Res Treat 2016;4(2):111-115 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 http://dx.doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2016.4.2.111 Neurological Change after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases
IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOSURGERY USING THE GAMMA KNIFE
 IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOSURGERY USING THE GAMMA KNIFE L. D. LUNSFORD INTRODUCTION Image guided brain surgery became a reality in the mid-1970s after the introduction of the first methods to obtain axial imaging
IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOSURGERY USING THE GAMMA KNIFE L. D. LUNSFORD INTRODUCTION Image guided brain surgery became a reality in the mid-1970s after the introduction of the first methods to obtain axial imaging
Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations
 J Neurosurg 78: 167-175, 1993 Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations NAYEF R. F. AL-RODHAN, M.D., PH.D., THORALF
J Neurosurg 78: 167-175, 1993 Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations NAYEF R. F. AL-RODHAN, M.D., PH.D., THORALF
Published February 7, 2013 as /ajnr.A3409
 Published February 7, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3409 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Combined Treatment of Brain AVMs with Use of Onyx Embolization Followed by Radiosurgery L. Pierot, K. Kadziolka, F. Litré,
Published February 7, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3409 ORIGINAL RESEARCH INTERVENTIONAL Combined Treatment of Brain AVMs with Use of Onyx Embolization Followed by Radiosurgery L. Pierot, K. Kadziolka, F. Litré,
Leksell Gamma Knife References 1992 December Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
 Leksell Gamma Knife References 1992 December 2011 Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Vascular Malformation Bibliography 2006-2016 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Includes Gamma Knife-focused abstracts posted to PubMed during
Leksell Gamma Knife References 1992 December 2011 Gamma Knife Radiosurgery Vascular Malformation Bibliography 2006-2016 VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS Includes Gamma Knife-focused abstracts posted to PubMed during
The preliminary investigation of application of single-staged hybrid operation in treatment of complex cerebral arteriovenous malformation.
 Biomedical Research 217; 28 (21): 9558-9563 ISSN 97-938X www.biomedres.info The preliminary investigation of application of single-staged hybrid operation in treatment of complex cerebral arteriovenous
Biomedical Research 217; 28 (21): 9558-9563 ISSN 97-938X www.biomedres.info The preliminary investigation of application of single-staged hybrid operation in treatment of complex cerebral arteriovenous
Gamma Knife Radiosurgeryin Medium-sized Arteriovenous Malformations: Preliminary Report
 Original Article Gamma Knife Radiosurgeryin Medium-sized Arteriovenous Malmations: Preliminary Rept Masaaki YAMAMOTO, M.D.,1 Mitsunobu IDE, M.D.,1 Minu JIMBO, M.D.,1 Kintomo TAKAKURA, M.D.,2 Tatsuo HIRAI,
Original Article Gamma Knife Radiosurgeryin Medium-sized Arteriovenous Malmations: Preliminary Rept Masaaki YAMAMOTO, M.D.,1 Mitsunobu IDE, M.D.,1 Minu JIMBO, M.D.,1 Kintomo TAKAKURA, M.D.,2 Tatsuo HIRAI,
I ntracranial haemorrhage is the main cause of morbidity and
 294 PAPER Concurrent arterial aneurysms in brain arteriovenous malformations with haemorrhagic presentation C Stapf, J P Mohr, J Pile-Spellman, R R Sciacca, A Hartmann, H C Schumacher, H Mast... See end
294 PAPER Concurrent arterial aneurysms in brain arteriovenous malformations with haemorrhagic presentation C Stapf, J P Mohr, J Pile-Spellman, R R Sciacca, A Hartmann, H C Schumacher, H Mast... See end
Diagnosis and evaluation of intracranial arteriovenous malformations
 Surg Neurol Int. 2015; 6: 76. Published online 2015 May 12. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.156866 PMCID: PMC4429335 Diagnosis and evaluation of intracranial arteriovenous malformations Andrew Conger, Charles Kulwin,
Surg Neurol Int. 2015; 6: 76. Published online 2015 May 12. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.156866 PMCID: PMC4429335 Diagnosis and evaluation of intracranial arteriovenous malformations Andrew Conger, Charles Kulwin,
Pediatric arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are rare,
 CHAPTER 17 Gamma Knife Surgery for Pediatric Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review Stephen James Monteith, MD, Chun-Po Yen, MD, and Jason P. Sheehan, MD, PhD Pediatric arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
CHAPTER 17 Gamma Knife Surgery for Pediatric Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review Stephen James Monteith, MD, Chun-Po Yen, MD, and Jason P. Sheehan, MD, PhD Pediatric arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS IN THE TEMPORAL LOBE: MICROSURGICAL TREATMENT AND RESULTS IN 89 CASES
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE MEDICINE OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Research article ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS IN THE TEMPORAL LOBE: MICROSURGICAL TREATMENT AND RESULTS IN 89 CASES LEON DĂNĂILĂ 1 National Institute
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE MEDICINE OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Research article ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS IN THE TEMPORAL LOBE: MICROSURGICAL TREATMENT AND RESULTS IN 89 CASES LEON DĂNĂILĂ 1 National Institute
Patterns of Brain Arteriovenous Malformation Treatment Prospective, Population-Based Study
 Patterns of Brain Arteriovenous Malformation Treatment Prospective, Population-Based Study Janneke van Beijnum, MD; Jo J. Bhattacharya, MSc, FRCR; Carl E. Counsell, MD, MRCP; Vakis Papanastassiou, MD,
Patterns of Brain Arteriovenous Malformation Treatment Prospective, Population-Based Study Janneke van Beijnum, MD; Jo J. Bhattacharya, MSc, FRCR; Carl E. Counsell, MD, MRCP; Vakis Papanastassiou, MD,
Factors Predictive of Obliteration After Arteriovenous Malformation Radiosurgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors Predictive of Obliteration After Arteriovenous Malformation Radiosurgery C. Herbert, V. Moiseenko, M. McKenzie, G. Redekop, F. Hsu, E. Gete, B. Gill, R. Lee, K. Luchka, A. Lee,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors Predictive of Obliteration After Arteriovenous Malformation Radiosurgery C. Herbert, V. Moiseenko, M. McKenzie, G. Redekop, F. Hsu, E. Gete, B. Gill, R. Lee, K. Luchka, A. Lee,
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 04/01/2014 Section:
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.008 05/12/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 04/01/2014 Section:
Gamma Knife Surgery Vascular Malformations Bibliography _Omslag_LGKS.indd
 Gamma Knife Surgery Vascular Malformations Bibliography 2006-2012 1 Neurology.2012;Epub 2012/03/31 Radiosurgery for unruptured cerebral arteriovenous malformations: Long-term seizure outcome Yang, S. Y.,
Gamma Knife Surgery Vascular Malformations Bibliography 2006-2012 1 Neurology.2012;Epub 2012/03/31 Radiosurgery for unruptured cerebral arteriovenous malformations: Long-term seizure outcome Yang, S. Y.,
SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF METASTATIC BRAIN TUMOR BY CYBERKNIFE: A CASE REPORT
 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF METASTATIC BRAIN TUMOR BY CYBERKNIFE: A CASE REPORT Cheng-Ta Hsieh, 1 Cheng-Fu Chang, 1 Ming-Ying Liu, 1 Li-Ping Chang, 2 Dueng-Yuan Hueng, 3 Steven D. Chang, 4 and Da-Tong Ju 1
SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF METASTATIC BRAIN TUMOR BY CYBERKNIFE: A CASE REPORT Cheng-Ta Hsieh, 1 Cheng-Fu Chang, 1 Ming-Ying Liu, 1 Li-Ping Chang, 2 Dueng-Yuan Hueng, 3 Steven D. Chang, 4 and Da-Tong Ju 1
Modern treatment of brain arteriovenous malformation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Brain AVM Embolization with Onyx BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: To report the initial experience by using a new liquid embolic agent (Onyx) for embolization
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Brain AVM Embolization with Onyx BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: To report the initial experience by using a new liquid embolic agent (Onyx) for embolization
Treatment decisions for patients with brain arteriovenous
 Risk of Endovascular Treatment of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations A. Hartmann, MD; J. Pile-Spellman, MD; C. Stapf, MD; R.R. Sciacca, EngScD; A. Faulstich, MS; J.P. Mohr, MD; H.C. Schumacher, MD; H. Mast,
Risk of Endovascular Treatment of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations A. Hartmann, MD; J. Pile-Spellman, MD; C. Stapf, MD; R.R. Sciacca, EngScD; A. Faulstich, MS; J.P. Mohr, MD; H.C. Schumacher, MD; H. Mast,
A lthough more than 90% of intracranial meningiomas are
 226 PAPER Complications after gamma knife radiosurgery for benign meningiomas J H Chang, J W Chang, J Y Choi, Y G Park, S S Chung... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Professor
226 PAPER Complications after gamma knife radiosurgery for benign meningiomas J H Chang, J W Chang, J Y Choi, Y G Park, S S Chung... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Professor
Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation
 206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
Results of acoustic neuroma radiosurgery: an analysis of 5 years experience using current methods
 See the Letter to the Editor and the Response in this issue in Neurosurgical Forum, pp 141 142. J Neurosurg 94:1 6, 2001 Results of acoustic neuroma radiosurgery: an analysis of 5 years experience using
See the Letter to the Editor and the Response in this issue in Neurosurgical Forum, pp 141 142. J Neurosurg 94:1 6, 2001 Results of acoustic neuroma radiosurgery: an analysis of 5 years experience using
Transarterial Embolization of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations: Improvement of Results with Experience
 Transarterial Embolization of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations: Improvement of Results with Experience Gunnar Wikholm, Christer Lundqvist, and Paul Svendsen PURPOSE: To present the treatment outcome
Transarterial Embolization of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations: Improvement of Results with Experience Gunnar Wikholm, Christer Lundqvist, and Paul Svendsen PURPOSE: To present the treatment outcome
Seizure, second only to hemorrhage, is a common
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126:845 851, 2017 Seizure outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations Benjamin J. Ditty, MD, Nidal B. Omar, MD, Paul
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg 126:845 851, 2017 Seizure outcomes after stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of cerebral arteriovenous malformations Benjamin J. Ditty, MD, Nidal B. Omar, MD, Paul
Radiosurgery for unruptured cerebral arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients
 Acta Neurochir (2015) 157:281 291 DOI 10.1007/s00701-014-2305-4 CLINICAL ARTICLE - VASCULAR Radiosurgery for unruptured cerebral arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients Dale Ding & Zhiyuan Xu
Acta Neurochir (2015) 157:281 291 DOI 10.1007/s00701-014-2305-4 CLINICAL ARTICLE - VASCULAR Radiosurgery for unruptured cerebral arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients Dale Ding & Zhiyuan Xu
LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF ACOUSTIC SCHWANNOMA RADIOSURGERY WITH MARGINAL TUMOR DOSES OF 12 TO 13 Gy
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.01.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 3, pp. 845 851, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.01.001 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 3, pp. 845 851, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
Vascular malformations: Venous malformations anomalous veins drain normal brain tissue for 65% of all cases 2.5%. was 0, 3% per year
 Vascular malformations: 1. Venous malformations: congenital venous anomalies pathologically characterised by anomalous veins (thickened and hyalinised walls) separated by normal brain. These anatomically
Vascular malformations: 1. Venous malformations: congenital venous anomalies pathologically characterised by anomalous veins (thickened and hyalinised walls) separated by normal brain. These anatomically
PREDICTION OF COMPLICATIONS IN GAMMA KNIFE RADIOSURGERY OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Acta Oncologica Vol. 35, No. I, pp. 49-55, 1996 PREDICTION OF COMPLICATIONS IN GAMMA KNIFE RADIOSURGERY OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS INGMAR LAX and BENGT KARLSSON The incidence of complications following
Acta Oncologica Vol. 35, No. I, pp. 49-55, 1996 PREDICTION OF COMPLICATIONS IN GAMMA KNIFE RADIOSURGERY OF ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS INGMAR LAX and BENGT KARLSSON The incidence of complications following
OBLITERATION DYNAMICS IN CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS AFTER CYBERKNIFE RADIOSURGERY: QUANTIFICATION WITH SEQUENTIAL NIDUS VOLUMETRY
 TECHNICAL STUDIES OBLITERATION DYNAMICS IN CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS AFTER CYBERKNIFE RADIOSURGERY: QUANTIFICATION WITH SEQUENTIAL NIDUS VOLUMETRY AND 3-TESLA 3-DIMENSIONAL TIME-OF-FLIGHT MAGNETIC
TECHNICAL STUDIES OBLITERATION DYNAMICS IN CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS AFTER CYBERKNIFE RADIOSURGERY: QUANTIFICATION WITH SEQUENTIAL NIDUS VOLUMETRY AND 3-TESLA 3-DIMENSIONAL TIME-OF-FLIGHT MAGNETIC
Intensity-modulated stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: guidance for treatment planning
 Sonier et al. Radiation Oncology 2014, 9:73 RESEARCH Open Access Intensity-modulated stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: guidance for treatment planning Marcus Sonier 1,3*, Ermias
Sonier et al. Radiation Oncology 2014, 9:73 RESEARCH Open Access Intensity-modulated stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: guidance for treatment planning Marcus Sonier 1,3*, Ermias
Transarterial Embolisation of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations
 Transarterial Embolisation of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations How Few Can You Do? G. WIKHOLM, C. LUNDQVIST*, P. SVENDSEN Section of Interventional Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology, * Department
Transarterial Embolisation of Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations How Few Can You Do? G. WIKHOLM, C. LUNDQVIST*, P. SVENDSEN Section of Interventional Neuroradiology, Department of Radiology, * Department
Angioarchitecture of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations and the Risk of Bleeding: An Analysis of Patients in Northeastern Malaysia
 Brief Communication Angioarchitecture of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations and the Risk of Bleeding: An Analysis of Patients in Northeastern Malaysia Shibani KanDai 1, Mohd Shafie abdullah 1, Nyi Nyi naing
Brief Communication Angioarchitecture of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations and the Risk of Bleeding: An Analysis of Patients in Northeastern Malaysia Shibani KanDai 1, Mohd Shafie abdullah 1, Nyi Nyi naing
Surgical interventions in intracranial arteriovenous malformations: Indications and outcome analysis in a changing scenario
 Original Article Surgical interventions in intracranial arteriovenous malformations: Indications and outcome analysis in a changing scenario Amit Thapa, P. Sarat Chandra, Sumit Sinha, Aditya Gupta, Manmohan
Original Article Surgical interventions in intracranial arteriovenous malformations: Indications and outcome analysis in a changing scenario Amit Thapa, P. Sarat Chandra, Sumit Sinha, Aditya Gupta, Manmohan
Gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: general principles and preliminary results in a Swiss cohort
 Published 03 April 2018 doi:10.4414/smw.2018.14602 Cite this as: Gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: general principles and preliminary results in a Swiss cohort Raboud Matthieu a,
Published 03 April 2018 doi:10.4414/smw.2018.14602 Cite this as: Gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: general principles and preliminary results in a Swiss cohort Raboud Matthieu a,
Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of 27 Cases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :, March 00 Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of ases Maneesh. Patel, Timothy J. Hodgson, Andras A. Kemeny, and David M. Forster BAKGROUND AND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :, March 00 Spontaneous Obliteration of Pial Arteriovenous Malformations: A Review of ases Maneesh. Patel, Timothy J. Hodgson, Andras A. Kemeny, and David M. Forster BAKGROUND AND
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center. Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh
 UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
UPSTATE Comprehensive Stroke Center Neurosurgical Interventions Satish Krishnamurthy MD, MCh Regional cerebral blood flow is important Some essential facts Neurons are obligatory glucose users Under anerobic
Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Moyamoya Syndrome with contra lateral DACA aneurysm: First Case report with review of literature Ashish Kumar Dwivedi, Pradeep Kumar,
Radiosurgery for temporal lobe arteriovenous malformations: effect of temporal location on seizure outcomes
 clinical article J Neurosurg 123:924 934, 2015 Radiosurgery for temporal lobe arteriovenous malformations: effect of temporal location on seizure outcomes Dale Ding, MD, 1 Mark Quigg, MD, MSc, 2 Robert
clinical article J Neurosurg 123:924 934, 2015 Radiosurgery for temporal lobe arteriovenous malformations: effect of temporal location on seizure outcomes Dale Ding, MD, 1 Mark Quigg, MD, MSc, 2 Robert
England. Clinical Commissioning Policy: Radiosurgery/Radiotherapy for Cavernous Venous Malformations (Cavernomas)
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Radiosurgery/Radiotherapy for Cavernous Venous Malformations (Cavernomas) September 2013 Reference: NHS ENGLAND D05/P/g England 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Radiosurgery/Radiotherapy for Cavernous Venous Malformations (Cavernomas) September 2013 Reference: NHS ENGLAND D05/P/g England 1 NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate
Dural arteriovenous shunts (DAVSs), also called dural
 Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Gamma Knife Surgery for Brain Metastasis from Renal Cell Carcinoma : Relationship Between Radiological Characteristics and Initial Tumor Response
 online ML Comm www.jkns.or.kr Clinical Article Jin Wook Kim, M.D. Jung Ho Han, M.D. Chul-Kee Park, M.D. Hyun-Tai Chung, Ph.D. Sun Ha Paek, M.D. Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery Seoul National
online ML Comm www.jkns.or.kr Clinical Article Jin Wook Kim, M.D. Jung Ho Han, M.D. Chul-Kee Park, M.D. Hyun-Tai Chung, Ph.D. Sun Ha Paek, M.D. Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery Seoul National
Editorial. Radiosurgery in cavernous malformations: anatomy of a controversy
 See the corresponding article in this issue, pp 23 29. J Neurosurg 113:16 22, 2010 Editorial Radiosurgery in cavernous malformations: anatomy of a controversy La d i s l a u St e i n e r, M.D., Ph.D.,
See the corresponding article in this issue, pp 23 29. J Neurosurg 113:16 22, 2010 Editorial Radiosurgery in cavernous malformations: anatomy of a controversy La d i s l a u St e i n e r, M.D., Ph.D.,
Johnny Wong, PhD; Alana Slomovic, BSc; George Ibrahim, PhD; Ivan Radovanovic, PhD; Michael Tymianski, MD, PhD
 Microsurgery for ARUBA Trial (A Randomized Trial of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformation) Eligible Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Johnny Wong, PhD; Alana Slomovic, BSc; George Ibrahim,
Microsurgery for ARUBA Trial (A Randomized Trial of Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformation) Eligible Unruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformations Johnny Wong, PhD; Alana Slomovic, BSc; George Ibrahim,
Summary of some of the landmark articles:
 Summary of some of the landmark articles: The significance of unruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms: Weibers et al Mayo clinic. 1987 1. 131 patients with 161 aneurysms were followed up at until death,
Summary of some of the landmark articles: The significance of unruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms: Weibers et al Mayo clinic. 1987 1. 131 patients with 161 aneurysms were followed up at until death,
Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations S.-F. GONG 1,2, X.-B. WANG 1,3, Y.-Q. LIAO 1,2, T.-P. JIANG 1,2, J.-B. HE 1,2,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Microsurgery for ruptured cerebellar arteriovenous malformations S.-F. GONG 1,2, X.-B. WANG 1,3, Y.-Q. LIAO 1,2, T.-P. JIANG 1,2, J.-B. HE 1,2,
Proposal of Classification of Aneurysms Coexisting with Avm and Possible Treatment Strategies
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.8600-13.1 Received: 23.05.2013 / Accepted: 18.07.2013 Original Investigation Proposal of Classification of Aneurysms Coexisting with Avm and Possible Treatment Strategies Xianli
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.8600-13.1 Received: 23.05.2013 / Accepted: 18.07.2013 Original Investigation Proposal of Classification of Aneurysms Coexisting with Avm and Possible Treatment Strategies Xianli
