Therapy of Radiation Injury
|
|
|
- Randell Strickland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMMENTARY Therapy of Radiation Injury THOMAS J. MACVITTIE Key Words: Radiation accident. Therapy. Cjrtokines Transplantarion University of Maryland Cancer Center, Baltimore, Maryland, USA INTRODUCTION The International Conference on the Biological Effects of Radiation Injury held March 22-25, 1996, in Minsk focused oral presentations and discussion on the Therapy of Acute Radiation Injuries. The papers contained in this section serve to underscore the omnipresent dilemmas facing the triage and/or treatment physician as well as the limitations of current treatments. Recent history continues to document the acute and chronic health effects of radiation accidents, not only on those working with the radiation source or employed in its clean-up, but also on unsuspecting participants. For instance, the recent 1994 radiation exposure in Kiisa, Estonia, exemplifies the complexity and severity of the radiation accident scenario. An intense radiation source, stolen from a disposal site and kept at a villager s home, resulted in one death and varying degrees of radiation exposure of four other persons. A prevailing theme throughout accident scenarios is that the radiation environment is likely to be uncontrolled and ill-defmed. The radiation may vary in quality, energy, and dose rate. The exposure may be nonuniform and partial-body, depending on the location and movement of the subject in relation to the source and available shielding. The subject may also have been traumatized by thermal bums and/or wounds as well as radiation bums. This underscores a second prevailing theme of the radiation accident, i.e., the difficulty in early and accurate determination of absorbed dose, which is the basis for effective triage and medical treatment. Definition of an effective treatment strategy will depend upon the presence of associated injuries to other organ systems, development of the cutaneous radiation syndrome (CRS), and the degree of radiation-induced marrow aplasia (or, rather, the number of surviving hematopoietic stem cells capable of spontaneous regeneration). N. Duiniuk and S. Sorbu present a cogent review of the acute radiation syndrome (ARS), the hematopoietic response to radiation exposure and stem cell transplantation. The authors focus on several key points to be emphasized with regard to treatment strategy and the potential revelation of additional nonhematopoietic health consequences subsequent to successful treatment of the hematopoietic syndrome. An important consideration in treatment strategy in addition to early, reliable biodosimetry is the potential for surviving hematopoietic stem cells due to a population with enhanced radioresistance and/or the heterogeneity of the radiation exposure. If any good news is to be found in the high-dose radiation accident scenario, it is the fact that its uncontrolled nature would predict the survival of a fraction of stem cells. It is probable that surviving hematopoietic stem cells would require a therapeutic cocktail of cytokinedgrowth factors to stimulate self-renewal instead of differentiation. The authors present a potential realization associated with effective treatment and survival through the hematopoietic syndrome, e.g., the appearance of other organ effects such as the CRS or pneumonia which predominate during the subsequent intermediate and late phases after recovery from the ARS and associated myelosuppression. Duiniuk and Sorbu further suggest that the combination of severe marrow aplasia due to exposure in the high-dose range (5-12 Gy), the potential for hematopoietic stem cell survival with requisite prolonged time to engraftment, the availability of suitable growth factors, and the lack of associated injuries quahfy this group of victims for hematopoietic rescue with stem cell transplantation. Radiation Znjury and the Chernobyl Catastrophe. STEM CELLS 1997;15(suppl2): AlphaMed Press. All rights reserved.
2 264 Commenky: Therapy of Radiation Injury Further analysis of the question regarding stem cell transplantation in the accident scenario is provided by D. Densow et al. In an interesting analysis of 58 of the most severely affected patients selected from the International Computer Database for Radiation Exposure Case Histories, the authors report that of three bone marrow transplant survivors, all benefited from temporary stem cell engraftment and that subsequent to highdose exposure, stem cell transplant is an appropriate therapy option. Considering the role of associated injuries in these patients, it was noted that radiation-induced cutaneous burns and damage to gastrointestinal and lung tissue were the strongest contraindications for stem cell transplantation. It was surprising that physical trauma and thermal bums did not play a decisive role in the outcome of the transplant. The question of bone marrow transplant in the radiation accident scenario has been redefined to a certain extent in light of the relative engraftment efficacy of cytokine-mobilized peripheral blood stem cells. Both M. Bishop and A. Uss et al. report on the relative merits and limitations of stem cell transplantation for radiation accident victims. While Uss et al. show clinical results that confm the therapeutic efficacy of bone marrow compared to peripheral blood transplants, Bishop emphasizes the omnipresent problems of obtaining suitably matched, allogeneic donors regardless of stem cell source, early and accurate estimation of expe sure dose, and the narrow window of radiation exposure for therapeutic benefit of stem cell transplantation relative to optimal therapeutic enhancement due to administration of growth factors after irradiation. POTENTIAL STRATEGIES FOR TREATMENT OF ACUTE RADIATION INJURY Treatment strategies for personnel severely irradiated in accidents have been the subject of several recent conferences in addition to the ones in Houston and Minsk [I-31. Clearly, the results of biomedical research over the last decade will present physicians with a new generation of treatment modalities in addition to a continuous movement of new agents into the therapeutic pipeline in hopes of making the successful transition from bench to bedside. A dynamic area of research and a number of clinical trials have focused on defining therapeutic approaches to enhance hematopoietic recovery from radiation- or chemotherapyinduced myelosuppression, in addition to evaluating alternative sources of stem cells for short-term cellular therapy and/or long-term hematopoietic and immune reconstitution in the host with an ablated bone marrow [4]. Recent therapeutic approaches for enhancing hematopoietic recovery and reducing the obligate periods of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia associated with high-dose radiation and/or chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression have focused on evaluation of lineage-specific cytokines for thrombopoiesis, combination cytokine protocols, and/or new synthetic cytokine receptor agonists. NEW-GENERATION GROWTH FACTORS Two new-generation growth factors, the Mpl ligand (megakaryocyte growth and development factor, Amgen; Thrombopoietin, Genentech), and the synthetic interleukin 3 (IL-3) receptor agonist, Synthokine (G.D. Searle Co.), have progressed through pivotal preclinical evaluations and have recently entered clinical trials. The thrombopoietic potential of the Mpl ligand was suggested early by the magnitude of platelet production and stimulation of marrow-derived megakaryocyte-colony-forming cells in normal nonhuman primates relative to that observed for the other thrombogenic cytokines IL-3, IL-6, leukemia inhibitory factor, and IL-I1 [5]. Evaluation of the Mpl ligand in animal models of radiation- or chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression showed that it lessened or abolished the degree and duration of thrombocytopenia, and that it may have direct or indirect effects on stimulating granulopoiesis and erythropoiesis [6-81. Farese et al. [7] first reported the efficacy of recombinant human polyethylene glycol-megakaryocyte growth and development factor (PEG-rHuMGDF) alone and in combination with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in a rhesus monkey model of radiation-induced myelosuppression. It is important to note that PEG-rHuMGDF coadministered with G-CSF significantly improved all platelet recovery variables to the same degree as PEGrHuMGDF monotherapy. In addition, rhumgdf/g-csf significantly enhanced neutrophil recovery relative to G-CSF monotherapy. The rhumgdf/g-csf combination therapy showed no evidence of lineage competition, while significantly enhancing dual lineage recovery in myelosuppressed nonhuman primates.
3 MacVittie 265 Synthokine is a high-affinity IL-3 receptor agonist that was developed in response to the relatively narrow therapeutic index of endogenous or native IL-3 [9]. Synthokine, evaluated for therapeutic efficacy in a nonhuman primate model of radiation-induced myelosuppression significantly reduced the duration of thrombocytopenia, although the duration of neutropenia was unchanged [lo]. The combination of S ynthokine and G-CSF in the same model of radiation-induced myelosuppression further improved the recovery from thrombocytopenia and neutropenia relative to monotherapy with each agent [ 111. These preclinical data on the therapeutic efficacy of Mpl ligand and Synthokine suggest that each may be useful in the treatment of radiation-induced myelosuppression, and if used in combination with G-CSF, may provide the desired dual-lineage stimulus for recovery of both platelets and neutrophils. Two other thrombopoietic cytokines, IL-6 and IL-11, are progressing through clinical trials. IL-6 is in the midst of clinical evaluation as a monotherapy and in combination with G-CSF or IL-3. Phase I and I1 clinical studies of IL-11 have demonstrated thrombopoietic activity and decreased requirements for platelet transfusions. As with the Mpl ligand and Synthokine, the combination of IL-11 with G-CSF may continue to decrease platelet transfusions and accelerate recovery of neutrophils and platelets. IL-3 monotherapy, however, has proven equivocal in both preclinical and clinical studies evaluating therapeutic efficacy in producing platelets and/or neutrophils subsequent to radiation- or chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression. NOVEL CYTOKINES Synthokine, a synthetic IL-3 receptor agonist, has been combined with G-CSF or Mpl ligand to form dual functional receptor agonists called myelopoietin and promegapoietin, respectively. Myelopoietin stimulated recovery of both neutrophils and platelets in myelosuppressed nonhuman primates in a manner comparable to that noted for combined Mpl ligand and G-CSF [12]. The Promegapoietin molecule is a potent stimulus for platelet production and significantly enhanced recovery of platelets in irradiated, myelosuppressed nonhuman primates. All parameters of platelet recovery were substantially improved (J. G. Giri, personal communication). The ability to form multifunctional receptor agonists may allow for manipulation of relative cytokine/receptor binding and signal transduction in hematopoietic target cells, thereby improving their therapeutic index. STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION Current directions in the treatment of severe radiation-induced myelosuppression or myeloablation include a renewed focus on transplantation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Transplantation of cytokine-mobilized peripheral blood stem cells (PBSCT) has resulted in rapid and durable autologous hematopoietic engraftment [ 13, 141. The noted heterogeneity and large number of hematopoietic cells mobilized by cytokine provides a marked advantage for this treatment modality in that the graft may be engineered to provide a high dose of committed progenitor cells for acceleration of short-term engraftment, while the stem cells can provide long-term reconstitution. In what may be more relevant for accidents, recent clinical studies have emphasized the successful use of allogeneic PBSCT. Cautious use of allogeneic PBSCT was based on the unknown long-term toxicity of administration of cytokines to the donors and the increased risk of acute and/or chronic graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) from the large number of T cells infused with the graft. However, early results indicated that unmanipulated allogeneic PBSCT can be performed with cytokine-mobilized cells and provide engraftment without an appreciable increase in the incidence of acute GvHD over that noted with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation [ In this regard, manipulation of the graft by CD34' immunoadsorption can concentrate the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells while also depleting the graft of alloreactive T cells [ 181. This approach underscores the feasibility of "engineered" temporary PBSCT allografts used to bridge the period of cytopenia prior to the regeneration of surviving endogenous stem cells.
4 266 Commentary: Therapy of Radiation Injury Additional advances in stem cell transplantation will undoubtedly be derived from alternative sources such as cord blood, as well as new methodologies to enhance ex vivo expansion of stem and/or progenitor cells harvested from bone marrow, mobilized peripheral blood or cord blood. At this writing, over 200 cord blood transplants have been performed with encouraging results in related and unrelated allogeneic settings [19, 201. There are a number of advantages of cord blood as a source of stem cells. It is abundant and easy to procure without risk to mother or infant, and it can be banked for future use; it should possess fewer infectious agents than adult sources; the stem cells are of better quality than those in peripheral blood or bone marrow; and the immaturity of immunoreactive T cells may reduce the risk of GvHD. On the other hand, the number of cord blood stem cells from a single donor is limited, second access if the graft fails is not an option, and the rate of engraftment is relatively slow. The establishment of cord blood banks will increase the use of cord blood from unrelated donors. Further research into the capability of ex vivo expansion and differences in stem cell biology relative to engraftment in the adult marrow microenvironment will answer questions regarding the full engraftment potential of cord blood stem cells and the severity of GvHD relative to allogeneic marrow or peripheral blood [21]. Ex VIVO EXPANSION Selected cytokine cocktails are capable of enhancing the ex vivo expansion of stem and progenitor cells, regardless of their source. A better understanding of the growth factors involved in expanding pluripotent stem cells compared to committed progenitor cells will allow graft engineering and selec - tive emphasis on short-term recovery of platelets and neutrophils or long-term hematopoietic reconstitution. Brugger et al. [22] recently demonstrated the feasibility of hematopoietic reconstitution using autologous cytokine-mobilized peripheral-blood-derived progenitor cells generated ex vivo in cancer patients after high-dose chemotherapy. The pattern of reconstitution was identical to that in historical controls treated with unseparated mononuclear cells or with selected CD34+ cells. The new generation Mpl and flt-3 ligands, as well as myelopoietin and promegapoietin, are promising additions to the list of cytokines that may allow optimal ex vivo expansion of selected cell populations. Further research is required to define the content and quality of starting cell populations, the proper mix of cytokines to drive renewal, expansion, and/or differentiation, and the precise in vitro culture conditions for specific target cells. SUMMARY It is apparent from preclinical and clinical research to date that continued evaluation of new and alternative treatment strategies is required to eliminate the obligate periods of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia after acute high-dose irradiation. Future treatment strategies may involve new combinations of cytokines to affect hematopoietic stem cell proliferation and engineered cellular grafts to provide short-term in vivo expansion of neutrophils and platelets in an effort to bridge the cytopenic gap until endogenous or transplanted stem cells regenerate the hematopoietic and immune systems. Cytokine-mobilized peripheral blood and cord blood will provide alternative sources of allogeneic stem and progenitor cells in support of primary engraftment, delayed engraftment or secondary failure of the initial graft, as well as starting populations for various ex vivo expansion protocols. Further insights into the relative quality of stem cell populations and the factors that regulate their survival and self renewal, and the identification and roles of adhesion molecules in stem cell mobilization, engraftment, and interaction with the adult marrow microenvironment will provide the basis for future treatment strategies for the radiation-induced hematopoietic syndrome. As our ability to treat the hematopoietic syndrome improves, damage to other organ systems such as the skin, lung, and/or gastrointestinal tissue will emerge as dose-limiting. At the same time, the characterization of receptors for inflammatory cytokines, cytokine receptor antagonists, and
5 MacVittie 267 anti-endotoxin antibodies has allowed significant insights into the mechanisms and pathogenesis of sepsis. However, translation of this knowledge into a treatment modality for septic patients is precluded by the lack of any clear-cut beneficial effect from the many clinical trials. The research and clinical results presented in this volume and recent conferences reflect the body of knowledge that will lead to further developments in assessment, prophylaxis, and treatment of radiation injuries in the areas of infectious disease and the hematopoietic, gastrointestinal, and cutaneous syndromes. REFERENCES 1 The Medical Basis for Radiation Accident Preparedness II: Clinical Experience and Follow-up Since Oct., 1988, Oak Ridge, Tennessee. In: Ricks RC, Fry SA, eds. The Medical Basis for Radiation Accident Preparedness. New York: Elsevier Science Inc., First Consensus Development Conference on the Treatment of Radiation Injuries May, 1989, Washington, DC. In: Browne D, Weiss JF, MacVittie TJ et al., eds. Proceedings in Treatment of Radiation Injuries. New York: Plenum Press, Second Consensus Development Conference on the Treatment of Radiation Injuries April, 1993, Bethesda, Maryland. In: MacVittie TJ, Weiss JF, Browne D, eds. Proceedings in Advances in the Treatment of Radiation Injuries. Tarrytown, NY: Pergamon, Elsevier Science Inc., MacVittie TJ, Farese AM. Experimental approaches for therapeutic treatment of radiation-induced hematopoietic injury. In: Hendry JH, Lord BI, eds. Radiation Toxicology: Bone Marrow and Leukemia. London: Taylor and Francis, 1996: Farese AM, Hunt P, Boone TC et al. Recombinant human megakaqocyte growth and development factor (r-humgdf) stimulates megakaqocytopoiesis in normal primates. Blood 1995;86: Hokom MM, Lacey D, Kinst 0 et al. Megakaryocyte growth and development factor abrogates the lethal thrombocytopenia associated with carboplatin and irradiation in mice. Blood 1995 $ Farese AM, Hunt P, Grab LB et al. Combined administration of recombinant human megakaryocyte growth and development factor and granulocyte colony stimulating factor enhances multi-lineage hematopoietic reconstitution in nonhuman primates following radiation-induced marrow aplasia. J Clin Invest 1996;97: Kaushansky K, Lin NL, Grossmann A et al. Thrombopoietin expands erythroid, granulocytemacrophage, and megakaryocytic progenitor cells in normal and myelosuppressed mice. Exp Hematol 1996;24: Thomas JW, Baum CM, Hood WF et al. Potent interleukin 3 receptor agonist with selectively enhanced hematopoietic activity relative to recombinant human interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995;92: Farese AM, Herodin F, McKeam JP et al. Acceleration of hematopoietic reconstitution with a synthetic cytokine (SC-55494) after radiation-induced bone marrow aplasia. Blood 1996;87: MacVittie TJ, Farese AM, Herodin F et al. Combination therapy for radiation-induced bone marrow aplasia in nonhuman primates using Synthokine SC and recombinant human granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Blood 1996;87: MacVittie TJ, Farese AM, Grab LB et al. Stimulation of multilineage hematopoietic recovery in a nonhuman primate, bone marrow aplasia model by a multifunctional agonist of human IL-3 and G-CSF receptors. Blood 1995;86 (suppl 1) 499a. 13 Weaver CH, Bucknmer CD, Longin K et al. Syngeneic transplantation with peripheral blood mononuclear cells collected after the administration of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood 1993;82: Brugger W, Henschler R, Heimfeld S et al. Positively selected autologous blood CD34' cells and unseparated peripheral blood progenitor cells mediate identical hematopoietic engraftment after high dose VP16, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and epirubicin. Blood 1994;84: Korbling M, Prezepiozka D, Huh YO et al. Allogeneic blood stem cell transplantation for refractory leukemia and lymphoma: potential advantage of blood over marrow allografts. Blood 199Si85: s.
6 268 Commentary: Therapy of Radiation Injury 16 Schmitz N, Dreger P, Suttorp M et al. Primary transplantation of allogeneic peripheral blood progenitor cells mobilized by Filgrastim (granulocyte colony stimulating factor). Blood 1995;85: Russell JA, Brown C, Bowen T. Allogeneic blood cell transplants for haematological malignancy: preliminary comparison of outcomes with bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1996; 17: Cottler-Fox M, Cipolone K, Yu M et al. Positive selection of CD34+ hematopoietic cells using an immunoaffinity column results in T- cell depletion equivalent to elutriation. Exp Hematol 1995;23: Wagner JE, Kernan NA, Steinbuch M et al. Allogeneic sibling umbilical cord blood transplantation in forty-four children with malignant and nonmalignant disease. Lancet 1995;346: Kurtzberg J, Laughlin M, Graham ML et al. Placental blood as a source of hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation into unrelated recipients. N Engl J Med 1996;335: Broxmeyer HE. Questions to be answered regarding umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and their use in transplantation. Transplantation 1995;35: Brugger W, Heimfeld S, Berenson RJ et al. Reconstitution of hematopoiesis after high-dose chemotherapy by autologous progenitor cells generated ex vivo. N Engl J Med 1995;333:
Cord Blood Stem Cell Banking and Transplantation
 Cord Blood Stem Cell Banking and Transplantation JOHN W. ADAMSON New York Blood Center, New York, New York, USA Key Words. Cord blood Stem cells Cord blood banking Cord blood transplantation. Cord blood.stern
Cord Blood Stem Cell Banking and Transplantation JOHN W. ADAMSON New York Blood Center, New York, New York, USA Key Words. Cord blood Stem cells Cord blood banking Cord blood transplantation. Cord blood.stern
Leukine. Leukine (sargramostim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Leukine Description Leukine (sargramostim)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Leukine Description Leukine (sargramostim)
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology. Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases
 One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
Leukine. Leukine (sargramostim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.85.08 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Leukine Description Leukine
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.85.08 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Leukine Description Leukine
AETNA BETTER HEALTH Non-Formulary Prior Authorization guideline for Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF)
 AETNA BETTER HEALTH Non-Formulary Prior Authorization guideline for Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF) Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF) Neupogen (filgrastim; G-CSF), Neulasta (peg-filgrastim; G-CSF); Neulasa
AETNA BETTER HEALTH Non-Formulary Prior Authorization guideline for Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF) Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF) Neupogen (filgrastim; G-CSF), Neulasta (peg-filgrastim; G-CSF); Neulasa
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT
 UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute
UMBILICAL CORD BLOOD STEM CELLS EXPANDED IN THE PRESENCE OF NICOTINAMIDE (NICORD) PROVIDE LONG TERM MULITI-LINEAGE ENGRAFTMENT Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute
Hematopoietic Growth Factors Colony Stimulating Factors. Erythropoietin (Epoetin alfa). Granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating factor (G-CSF).
 Hematopoietic Growth Factors Colony Stimulating Factors. Erythropoietin (Epoetin alfa). Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor(g-csf). Granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating factor (G-CSF). Interleukin-11
Hematopoietic Growth Factors Colony Stimulating Factors. Erythropoietin (Epoetin alfa). Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor(g-csf). Granulocyte-macrophage colonystimulating factor (G-CSF). Interleukin-11
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B
 Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow
 White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Leukine. Leukine (sargramostim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.10.08 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 13, 2014 Leukine Description Leukine (sargramostim)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.10.08 Subject: Leukine Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 13, 2014 Leukine Description Leukine (sargramostim)
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014
 Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
NiCord Single Unit Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Results of Phase I/II Trials
 NiCord Single Unit Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Results of Phase I/II Trials Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute Adult Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
NiCord Single Unit Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Results of Phase I/II Trials Mitchell E. Horwitz, MD Duke University Medical Center Duke Cancer Institute Adult Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
What s a Transplant? What s not?
 What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
Haematopoietic stem cells
 Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate
 3rd Annual ASBMT Regional Conference for NPs, PAs and Fellows Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate Claudio G. Brunstein Associate Professor University of Minnesota Medical School Take home message Finding a donor
3rd Annual ASBMT Regional Conference for NPs, PAs and Fellows Haplo vs Cord vs URD Debate Claudio G. Brunstein Associate Professor University of Minnesota Medical School Take home message Finding a donor
Stem cells. -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA. Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT
 Stem cells -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, Flow of presentation Update on stem cell uses Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Stem cells -Dr Dinesh Bhurani, MD, DM, FRCPA -Director, Department of Haematology and BMT Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute, Delhi, Flow of presentation Update on stem cell uses Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
of Thrombopoietic Growth Factors
 Opportunities for the Use of Thrombopoietic Growth Factors CHARLES A. SCHIFFER Wayne State University School of Medicine, Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute, Detroit, Michigan, USA Key Words. Thrornbopoietin
Opportunities for the Use of Thrombopoietic Growth Factors CHARLES A. SCHIFFER Wayne State University School of Medicine, Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute, Detroit, Michigan, USA Key Words. Thrornbopoietin
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation. David Rice, PhD, RN, NP
 BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation March 16, 2017 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice and Education No disclosures Objectives Describe basic concepts
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation March 16, 2017 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice and Education No disclosures Objectives Describe basic concepts
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EHA/ICML Bendamustine in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EHA/ICML 2011 Bendamustine in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders Report on EHA/ICML 2011 presentations Efficacy and safety of bendamustine plus
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EHA/ICML 2011 Bendamustine in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders Report on EHA/ICML 2011 presentations Efficacy and safety of bendamustine plus
Physiologic Role of TPO in Thrombopoiesis
 Physiologic Role of TPO in Thrombopoiesis Hiroshi Miyazaki Pharmaceutical Research Laboratory, Kirin Brewery Co., Ltd., Gunma, Japan Key Words. Thrombopoietin Megakaryocyte Megakaryocyte progenitor cell
Physiologic Role of TPO in Thrombopoiesis Hiroshi Miyazaki Pharmaceutical Research Laboratory, Kirin Brewery Co., Ltd., Gunma, Japan Key Words. Thrombopoietin Megakaryocyte Megakaryocyte progenitor cell
T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes
 T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes J.H. Frederik Falkenburg Department of Hematology L M U C Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) for non-malignant disorders: no need for anti-tumor
T cell manipulation of the graft: Yes J.H. Frederik Falkenburg Department of Hematology L M U C Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (SCT) for non-malignant disorders: no need for anti-tumor
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy
 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy Grace Totoe, MBChB, SBB CME August 2012 Accra-Ghana Hematopoietic Stem Cells Cells capable of self renewal and differentiation into all blood cell lineages Objectives Historical
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy Grace Totoe, MBChB, SBB CME August 2012 Accra-Ghana Hematopoietic Stem Cells Cells capable of self renewal and differentiation into all blood cell lineages Objectives Historical
Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO
 Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Dedicated to Gordon. Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey
 Dedicated to Gordon Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey 1949 Jacobson et al: Radioprotection by lead shielding of the spleen of a lethally irradiated animal 1951 Lorenz et al: Radiation protection
Dedicated to Gordon Stem Cell Transplantation: The Journey 1949 Jacobson et al: Radioprotection by lead shielding of the spleen of a lethally irradiated animal 1951 Lorenz et al: Radiation protection
Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives
 Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota February, 2013 No matched sib: where to look? URD donor requires close HLA matching and 3-12 weeks
Haploidentical Transplantation today: and the alternatives Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota February, 2013 No matched sib: where to look? URD donor requires close HLA matching and 3-12 weeks
Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion
 Prevention of graftversus-host disease (GVHD) Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion Information for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and their families 2 This
Prevention of graftversus-host disease (GVHD) Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion Information for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and their families 2 This
The National Marrow Donor Program. Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Simon Bostic, URD Transplant Recipient
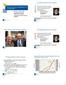 1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
Radiation Injury Treatment Network: Planning for the worst, using experience from hematology & transplantation
 Radiation Injury Treatment Network: Planning for the worst, using experience from hematology & transplantation Daniel Weisdorf, MD University of Minnesota Radiation Injury Treatment Network weisd001@umn.edu
Radiation Injury Treatment Network: Planning for the worst, using experience from hematology & transplantation Daniel Weisdorf, MD University of Minnesota Radiation Injury Treatment Network weisd001@umn.edu
Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018
 Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Transplantation
 Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
AETNA BETTER HEALTH Non-Formulary Prior Authorization guideline for Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF)
 AETNA BETTER HEALTH Non-Formulary Prior Authorization guideline for Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF) Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF) Neupogen (filgrastim; G-CSF), Neulasta (peg-filgrastim; G-CSF); Neulasa
AETNA BETTER HEALTH Non-Formulary Prior Authorization guideline for Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF) Colony Stimulating Factor (CSF) Neupogen (filgrastim; G-CSF), Neulasta (peg-filgrastim; G-CSF); Neulasa
Donatore HLA identico di anni o MUD giovane?
 Donatore HLA identico di 60-70 anni o MUD giovane? Stella Santarone Dipartimento di Ematologia, Medicina Trasfusionale e Biotecnologie Pescara AGENDA 1. Stem Cell Donation: fatalities and severe events
Donatore HLA identico di 60-70 anni o MUD giovane? Stella Santarone Dipartimento di Ematologia, Medicina Trasfusionale e Biotecnologie Pescara AGENDA 1. Stem Cell Donation: fatalities and severe events
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES. Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr.
 BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
Idelalisib treatment is associated with improved cytopenias in patients with relapsed/refractory inhl and CLL
 Idelalisib treatment is associated with improved cytopenias in patients with relapsed/refractory inhl and CLL Susan M O Brien, Andrew J Davies, Ian W Flinn, Ajay K Gopal, Thomas J Kipps, Gilles A Salles,
Idelalisib treatment is associated with improved cytopenias in patients with relapsed/refractory inhl and CLL Susan M O Brien, Andrew J Davies, Ian W Flinn, Ajay K Gopal, Thomas J Kipps, Gilles A Salles,
University of Maryland Greenebaum Cancer Center, Baltimore, Maryland, USA; Amgen, Inc., Thousand Oaks, California, USA
 Stem Cells Original Article Hematopoietic Recovery Following Autologous Bone Marrow Transplantation in a Nonhuman Primate: Effect of Variation in Treatment Schedule with PEG-rHuMGDF ANN M. FARESE, a THOMAS
Stem Cells Original Article Hematopoietic Recovery Following Autologous Bone Marrow Transplantation in a Nonhuman Primate: Effect of Variation in Treatment Schedule with PEG-rHuMGDF ANN M. FARESE, a THOMAS
XIV. HLA AND TRANSPLANTATION MEDICINE
 XIV. HLA AND TRANSPLANTATION MEDICINE A. Introduction 1. The HLA system includes a complex array of genes and their molecular products that are involved in immune regulation and cellular differentiation.
XIV. HLA AND TRANSPLANTATION MEDICINE A. Introduction 1. The HLA system includes a complex array of genes and their molecular products that are involved in immune regulation and cellular differentiation.
Abstract 861. Stein AS, Topp MS, Kantarjian H, Gökbuget N, Bargou R, Litzow M, Rambaldi A, Ribera J-M, Zhang A, Zimmerman Z, Forman SJ
 Treatment with Anti-CD19 BiTE Blinatumomab in Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (R/R ALL) Post-Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Abstract
Treatment with Anti-CD19 BiTE Blinatumomab in Adult Patients With Relapsed/Refractory B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (R/R ALL) Post-Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Abstract
The future of HSCT. John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD
 The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
The future of HSCT John Barrett, MD, NHBLI, NIH Bethesda MD Transplants today Current approaches to improve SCT outcome Optimize stem cell dose and source BMT? PBSCT? Adjusting post transplant I/S to minimize
Overview of Use of G-CSF in the Treatment of Acute Radiation Injury
 Overview of Use of G-CSF in the Treatment of Acute Radiation Injury Applied Research Associates, Inc. Glen Reeves Distribution Statement A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. This
Overview of Use of G-CSF in the Treatment of Acute Radiation Injury Applied Research Associates, Inc. Glen Reeves Distribution Statement A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. This
Transplantation - Challenges for the future. Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust
 Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Transplantation - Challenges for the future Dr Gordon Cook S t James s Institute of Oncology, Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust Bone Marrow Transplantation Timeline, 1957-2006 Appelbaum F. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1472-1475
Corporate Medical Policy
 White Blood Cell Growth Factors Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: white_blood_cell_growth_factors 9/2016 4/2017 4/2018 6/2017 Description of
White Blood Cell Growth Factors Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: white_blood_cell_growth_factors 9/2016 4/2017 4/2018 6/2017 Description of
International Journal of Cell Cloning (1991)
 Concise Review International Journal of Cell Cloning 9542-547 (1991) Hybrid Cytokines as Hematopoietic Growth Factors Douglas E. Williamsa, Linda S. Park", Hal E. Broxmeyerb, Li Lub 'Immunex Research and
Concise Review International Journal of Cell Cloning 9542-547 (1991) Hybrid Cytokines as Hematopoietic Growth Factors Douglas E. Williamsa, Linda S. Park", Hal E. Broxmeyerb, Li Lub 'Immunex Research and
Granix. Granix (tbo-filgrastim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.10.16 Subject: Granix 1 of 7 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Granix Description Granix (tbo-filgrastim)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.10.16 Subject: Granix 1 of 7 Last Review Date: September 18, 2015 Granix Description Granix (tbo-filgrastim)
Overview of Aplastic Anemia. Overview of Aplastic Anemia. Epidemiology of aplastic anemia. Normal hematopoiesis 10/6/2017
 Overview of Aplastic Anemia Overview of Aplastic Anemia Peter Westervelt, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chief, BMT/Leukemia Section Washington University School of Medicine Epidemiology Normal hematopoiesis
Overview of Aplastic Anemia Overview of Aplastic Anemia Peter Westervelt, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chief, BMT/Leukemia Section Washington University School of Medicine Epidemiology Normal hematopoiesis
Na#onal Neutropenia Network Family Conference July 12, 2014
 Na#onal Neutropenia Network Family Conference July 12, 2014 Jim Connelly, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics and Communicable Diseases Blood and Marrow Transplant Program University of Michigan Transplant
Na#onal Neutropenia Network Family Conference July 12, 2014 Jim Connelly, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics and Communicable Diseases Blood and Marrow Transplant Program University of Michigan Transplant
Pharmacy Prior Authorization
 Pharmacy Prior Authorization MERC CARE (MEDICAID) Colony Stimulating Factors (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign
Pharmacy Prior Authorization MERC CARE (MEDICAID) Colony Stimulating Factors (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review information, sign
12 Dynamic Interactions between Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells and the Bone Marrow: Current Biology of Stem Cell Homing and Mobilization
 Table of Contents: PART I: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Hematology 1 Anatomy and Pathophysiology of the Gene 2 Genomic Approaches to Hematology 3 Regulation of Gene Expression, Transcription, Splicing,
Table of Contents: PART I: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Hematology 1 Anatomy and Pathophysiology of the Gene 2 Genomic Approaches to Hematology 3 Regulation of Gene Expression, Transcription, Splicing,
Granix. Granix (tbo-filgrastim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.85.16 Subject: Granix 1 of 7 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Granix Description Granix (tbo-filgrastim)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.85.16 Subject: Granix 1 of 7 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Granix Description Granix (tbo-filgrastim)
Induction Therapy & Stem Cell Transplantation for Myeloma
 Induction Therapy & Stem Cell Transplantation for Myeloma William Bensinger, MD Professor of Medicine, Division of Oncology University of Washington School of Medicine Director, Autologous Stem Cell Transplant
Induction Therapy & Stem Cell Transplantation for Myeloma William Bensinger, MD Professor of Medicine, Division of Oncology University of Washington School of Medicine Director, Autologous Stem Cell Transplant
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
 Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility E-mail: js2745@columbia.edu Hematopoietic Stem Cells Sustain hematopoiesis
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility E-mail: js2745@columbia.edu Hematopoietic Stem Cells Sustain hematopoiesis
2. Is therapy prescribed by, or in consultation with, a hematologist and/or oncologist?
 Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH EW JERSE (MEDICAID) Colony Stimulating Factors (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review
Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH EW JERSE (MEDICAID) Colony Stimulating Factors (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review
Neutrophil Recovery: The. Posttransplant Recovery. Bus11_1.ppt
 Neutrophil Recovery: The First Step in Posttransplant Recovery No conflicts of interest to disclose Bus11_1.ppt Blood is Made in the Bone Marrow Blood Stem Cell Pre-B White cells B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte
Neutrophil Recovery: The First Step in Posttransplant Recovery No conflicts of interest to disclose Bus11_1.ppt Blood is Made in the Bone Marrow Blood Stem Cell Pre-B White cells B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte
Hematopoiesis. - Process of generation of mature blood cells. - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human)
 Hematopoiesis - Process of generation of mature blood cells - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human) 1,000,000,000,000 total cells 200,000,000,000 red blood cells 70,000,000,000 neutrophils Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis - Process of generation of mature blood cells - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human) 1,000,000,000,000 total cells 200,000,000,000 red blood cells 70,000,000,000 neutrophils Hematopoiesis
Granix. Granix (tbo-filgrastim) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.10.16 Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1, 2014 Subject: Granix 1 of 7 Last Review Date:
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.10.16 Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1, 2014 Subject: Granix 1 of 7 Last Review Date:
BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE
 BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE Jennifer Shamai MS, RN, AOCNS, BMTCN Professional Practice Leader Department of Clinical Practice And Professional Education Click How to edit the Master Experts
BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE Jennifer Shamai MS, RN, AOCNS, BMTCN Professional Practice Leader Department of Clinical Practice And Professional Education Click How to edit the Master Experts
Sickle Cell Diseasechronic. curable disease? Objectives. Why would a family ask about cure for SCD?
 Sickle Cell Diseasechronic illness or curable disease? Gregory M.T. Guilcher MD, FRCPC, FAAP Objectives To review the general principles of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), including risks
Sickle Cell Diseasechronic illness or curable disease? Gregory M.T. Guilcher MD, FRCPC, FAAP Objectives To review the general principles of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), including risks
HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia Shang-Ju Wu, Ming Yao,* Jih-Luh Tang, Bo-Sheng Ko, Hwei-Fang
BRIEF COMMUNICATION HLA-DR-matched Parental Donors for Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with High-risk Acute Leukemia Shang-Ju Wu, Ming Yao,* Jih-Luh Tang, Bo-Sheng Ko, Hwei-Fang
Clinical Policy: Donor Lymphocyte Infusion
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.101 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 11/16 Coding Implications Revision Log This policy describes the medical necessity requirements for a donor lymphocyte
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.101 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 11/16 Coding Implications Revision Log This policy describes the medical necessity requirements for a donor lymphocyte
5/9/2018. Bone marrow failure diseases (aplastic anemia) can be cured by providing a source of new marrow
 5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS
 DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC February 19, 2015 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
DISCOVERING ATCC IMMUNOLOGICAL CELLS - MODEL SYSTEMS TO STUDY THE IMMUNE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMS James Clinton, Ph.D. Scientist, ATCC February 19, 2015 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration. Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research.
 Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
Stem cells: units of development and regeneration Fernando D. Camargo Ph.D. Whitehead Fellow Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Concepts 1. Embryonic vs. adult stem cells 2. Hematopoietic stem
LCD for Sargramostim (GM-CSF, Leukine ) (L29275)
 LCD for Sargramostim (GM-CSF, Leukine ) (L29275) Contractor Information Contractor Name First Coast Service Options, Inc. Contractor Number 09102 Contractor Type MAC - Part B LCD ID Number L29275 LCD Information
LCD for Sargramostim (GM-CSF, Leukine ) (L29275) Contractor Information Contractor Name First Coast Service Options, Inc. Contractor Number 09102 Contractor Type MAC - Part B LCD ID Number L29275 LCD Information
Is in vitro T-cell depletion necessary for Haploidentical TransplantationTitle of Presentation. Disclosure of Interest: Nothing to Disclose
 Rupert Handgretinger Children s University Hospital, Tübingen, Germany Is in vitro T-cell depletion necessary for Haploidentical TransplantationTitle of Presentation Disclosure of Interest: Nothing to
Rupert Handgretinger Children s University Hospital, Tübingen, Germany Is in vitro T-cell depletion necessary for Haploidentical TransplantationTitle of Presentation Disclosure of Interest: Nothing to
ASH 2011 aktualijos: MSC TPŠL gydyme. Mindaugas Stoškus VULSK HOTC MRMS
 ASH 2011 aktualijos: MSC TPŠL gydyme Mindaugas Stoškus VULSK HOTC MRMS #3042. Yukiyasu Ozawa et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells As a Treatment for Steroid-Resistant Acute Graft Versus Host Disease (agvhd);
ASH 2011 aktualijos: MSC TPŠL gydyme Mindaugas Stoškus VULSK HOTC MRMS #3042. Yukiyasu Ozawa et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells As a Treatment for Steroid-Resistant Acute Graft Versus Host Disease (agvhd);
WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME. An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency
 WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency WHAT IS WISKOTT ALDRICH SYNDROME? Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (WAS) is a serious medical condition that causes problems both with the immune system
WISKOTT-ALDRICH SYNDROME An X-linked Primary Immunodeficiency WHAT IS WISKOTT ALDRICH SYNDROME? Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (WAS) is a serious medical condition that causes problems both with the immune system
Neupogen (Filgrastim)/Neulasta (Pegfilgrastim)
 Policy Number Reimbursement Policy NEU12182013RP Approved By UnitedHealthcare Medicare Reimbursement Policy Committee Current Approval Date 12/18/2013 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY This
Policy Number Reimbursement Policy NEU12182013RP Approved By UnitedHealthcare Medicare Reimbursement Policy Committee Current Approval Date 12/18/2013 IMPORTANT NOTE ABOUT THIS REIMBURSEMENT POLICY This
Back to the Future: The Resurgence of Bone Marrow??
 Back to the Future: The Resurgence of Bone Marrow?? Thomas Spitzer, MD Director. Bone Marrow Transplant Program Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Bone Marrow
Back to the Future: The Resurgence of Bone Marrow?? Thomas Spitzer, MD Director. Bone Marrow Transplant Program Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Bone Marrow
The number of nucleated cells reflects the hematopoietic content of umbilical cord blood for transplantation
 Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1999) 24, 965 970 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0268 3369/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bmt The number of nucleated cells reflects the hematopoietic
Bone Marrow Transplantation, (1999) 24, 965 970 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0268 3369/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bmt The number of nucleated cells reflects the hematopoietic
Myeloproliferative Disorders - D Savage - 9 Jan 2002
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Hemopoietic Precursors in Human Bone Marrow Transplantation
 International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 11-18 Suppl 1 (1986) Hemopoietic Precursors in Human Bone Marrow Transplantation H.A. Messner Ontario Cancer Institute, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
International Journal of Cell Cloning 4: 11-18 Suppl 1 (1986) Hemopoietic Precursors in Human Bone Marrow Transplantation H.A. Messner Ontario Cancer Institute, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario,
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Policy Specific Section:
 Medical Policy Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Myeloproliferative Type: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section:
Medical Policy Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Myeloproliferative Type: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section:
STEM CELL TRANSPLANT IN PEDIATRICS. Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Medical Director, Apheresis Nationwide Children s Hospital Columbus, OH 5/6/17
 STEM CELL TRANSPLANT IN PEDIATRICS Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Medical Director, Apheresis Nationwide Children s Hospital Columbus, OH 5/6/17 Disclosures Nothing to Disclose Overview Stem Cell Transplant History
STEM CELL TRANSPLANT IN PEDIATRICS Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Medical Director, Apheresis Nationwide Children s Hospital Columbus, OH 5/6/17 Disclosures Nothing to Disclose Overview Stem Cell Transplant History
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016
 BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice
Duchez P, Chevaleyre J, Dazey B, Vlaski M, Ivanovic Z.
 EX-VIVO EXPANSION OF CORD BLOOD HEMATOPOIETIC STEM AND PROGENITOR CELLS FOR TRANSPLANTATION USING AN ANTIOXYDANT-SUPPLIED MEDIUM AND A CYTOKINE COCKTAIL INDUCING HYPOXIC-LIKE CELLULAR RESPONSE Duchez P,
EX-VIVO EXPANSION OF CORD BLOOD HEMATOPOIETIC STEM AND PROGENITOR CELLS FOR TRANSPLANTATION USING AN ANTIOXYDANT-SUPPLIED MEDIUM AND A CYTOKINE COCKTAIL INDUCING HYPOXIC-LIKE CELLULAR RESPONSE Duchez P,
Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Faculty Disclosures Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Nothing to disclose Jeanne McCarthy-Kaiser, PharmD, BCOP Clinical Pharmacist, Autologous Stem Cell Transplant/Long- Term Follow-Up
Faculty Disclosures Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Nothing to disclose Jeanne McCarthy-Kaiser, PharmD, BCOP Clinical Pharmacist, Autologous Stem Cell Transplant/Long- Term Follow-Up
An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant
 Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Use of TPO mimetics for Indications Other Than ITP
 Use of TPO mimetics for Indications Other Than ITP Mazyar Shadman, MD, MPH Discussant: Siobán Keel, MD Hematology Fellows Conference June 28, 2013 Thrombopoietin (TPO) and other c mpl ligands TPO mimetics
Use of TPO mimetics for Indications Other Than ITP Mazyar Shadman, MD, MPH Discussant: Siobán Keel, MD Hematology Fellows Conference June 28, 2013 Thrombopoietin (TPO) and other c mpl ligands TPO mimetics
Placental and Umbilical Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells
 Placental and Umbilical Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells Policy Number: 7.01.50 Last Review: 12/2018 Origination: 12/2001 Next Review: 12/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Placental and Umbilical Cord Blood as a Source of Stem Cells Policy Number: 7.01.50 Last Review: 12/2018 Origination: 12/2001 Next Review: 12/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
For peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) mobilization prior to and during leukapheresis in cancer patients preparing to undergo bone marrow ablation
 Last Review: 4/2010 NON-FORMULARY Clinical Guideline Neupogen (filgrastim; G-CSF), Neulasta (peg-filgrastim; G-CSF), Neumega (oprelvekin; rh-il-11), Leukine (sargramostim; GM-CSF) Indications Neupogen
Last Review: 4/2010 NON-FORMULARY Clinical Guideline Neupogen (filgrastim; G-CSF), Neulasta (peg-filgrastim; G-CSF), Neumega (oprelvekin; rh-il-11), Leukine (sargramostim; GM-CSF) Indications Neupogen
Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease
 Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease Rhiannon is now cured of sickle cell disease after BMT. Blood and marrow transplant (BMT) is a proven cure for sickle cell disease. This handbook
Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease Rhiannon is now cured of sickle cell disease after BMT. Blood and marrow transplant (BMT) is a proven cure for sickle cell disease. This handbook
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll 2/2001
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for CLL and SLL File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_cell_transplantation_for_cll_and_sll 2/2001
Hematopoetic Stem Cell Therapies in TURKIYE
 Hematopoetic Stem Cell Therapies in TURKIYE World Location of transplant centers participating in CIBMTR (2010) Dr. Mustafa ÇETİN Mustafa CETIN, M.D. Erciyes University Medical Faculty Kayseri-TURKIYE
Hematopoetic Stem Cell Therapies in TURKIYE World Location of transplant centers participating in CIBMTR (2010) Dr. Mustafa ÇETİN Mustafa CETIN, M.D. Erciyes University Medical Faculty Kayseri-TURKIYE
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Acute Myeloid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplant_for_acute_myeloid_leukemia
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Acute Myeloid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem-cell_transplant_for_acute_myeloid_leukemia
UICC EML Review 2014
 UICC EML Review 2014 Granulocyte Stimulating Agents (G- CSF) Supplemental Document Many antineoplastic agents are cytotoxic to the bone marrow and prevent the development of granulocytes necessary to fight
UICC EML Review 2014 Granulocyte Stimulating Agents (G- CSF) Supplemental Document Many antineoplastic agents are cytotoxic to the bone marrow and prevent the development of granulocytes necessary to fight
Valencia, 05/04/ #EBMT16
 Transplantation of Ex vivo Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood (NiCord ) Results in Decreased Infection Burden and Hospital Length of Stay in the First 100 Days Sarah Anand, Samantha Thomas, Terry Hyslop, Kelly
Transplantation of Ex vivo Expanded Umbilical Cord Blood (NiCord ) Results in Decreased Infection Burden and Hospital Length of Stay in the First 100 Days Sarah Anand, Samantha Thomas, Terry Hyslop, Kelly
The question is not whether or not to deplete T-cells, but how to deplete which T-cells
 The question is not whether or not to deplete T-cells, but how to deplete which T-cells CD34+ positive selection Negative Depletion of: CD3/CD19 TcRαβ/CD19 T-cell depletion: positive selection versus negative
The question is not whether or not to deplete T-cells, but how to deplete which T-cells CD34+ positive selection Negative Depletion of: CD3/CD19 TcRαβ/CD19 T-cell depletion: positive selection versus negative
Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components
 AUSTRALIAN & NEW ZEALAND SOCIETY OF BLOOD TRANSFUSION INC. AUSTRALIAN RED CROSS BLOOD SERVICE NEW ZEALAND BLOOD SERVICE Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components Revised 2003 AN ZS B T Australian
AUSTRALIAN & NEW ZEALAND SOCIETY OF BLOOD TRANSFUSION INC. AUSTRALIAN RED CROSS BLOOD SERVICE NEW ZEALAND BLOOD SERVICE Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components Revised 2003 AN ZS B T Australian
Federica Galaverna, 1 Daria Pagliara, 1 Deepa Manwani, 2 Rajni Agarwal-Hashmi, 3 Melissa Aldinger, 4 Franco Locatelli 1
 Administration of Rivogenlecleucel (Rivo-cel, BPX-501) Following αβ T- and B-Cell Depleted Haplo-HSCT in Children With Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Federica Galaverna, 1 Daria Pagliara, 1 Deepa Manwani,
Administration of Rivogenlecleucel (Rivo-cel, BPX-501) Following αβ T- and B-Cell Depleted Haplo-HSCT in Children With Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Federica Galaverna, 1 Daria Pagliara, 1 Deepa Manwani,
REVIEW ARTICLE. Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Where Do We Stand? ASBMT BB&MT. Raymond C. Wadlow, David L. Porter
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 8:637-647 (2002) 2002 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation ASBMT REVIEW ARTICLE Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Where Do We Stand? Raymond
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 8:637-647 (2002) 2002 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation ASBMT REVIEW ARTICLE Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation: Where Do We Stand? Raymond
Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT
 Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Assistant Medical Director of Blood, Tissue, and Apheresis Services Children s Healthcare
Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Assistant Medical Director of Blood, Tissue, and Apheresis Services Children s Healthcare
Status of umbilical cord blood transplantation in the year 2001
 428 J Clin Pathol 2001;54:428 434 Status of umbilical cord blood transplantation in the year 2001 JMHows Abstract Umbilical cord blood (UCB) transplantation is limited to small recipients because of the
428 J Clin Pathol 2001;54:428 434 Status of umbilical cord blood transplantation in the year 2001 JMHows Abstract Umbilical cord blood (UCB) transplantation is limited to small recipients because of the
Dr Claire Burney, Lymphoma Clinical Fellow, Bristol Haematology and Oncology Centre, UK
 EMBT LWP 2017-R-05 Research Protocol: Outcomes of patients treated with Ibrutinib post autologous stem cell transplant for mantle cell lymphoma. A retrospective analysis of the LWP-EBMT registry. Principle
EMBT LWP 2017-R-05 Research Protocol: Outcomes of patients treated with Ibrutinib post autologous stem cell transplant for mantle cell lymphoma. A retrospective analysis of the LWP-EBMT registry. Principle
Jeanne Palmer, MD Mayo Clinic, Arizona
 Setting the stage for Transplant in MPN Jeanne Palmer, MD Mayo Clinic, Arizona What will be covered What is a bone marrow transplant? When to start thinking about bone marrow transplant Timing of transplant
Setting the stage for Transplant in MPN Jeanne Palmer, MD Mayo Clinic, Arizona What will be covered What is a bone marrow transplant? When to start thinking about bone marrow transplant Timing of transplant
TRANSPLANTATION OF PERIPHERAL-BLOOD CELLS IN PATIENTS WITH HEMATOLOGIC CANCERS
 TRANSPLANTATION OF BLOOD CELLS IN PATIENTS WITH HEMATOLOGIC CANCERS TRANSPLANTATION OF AS COMPARED WITH BLOOD CELLS FROM HLA-IDENTICAL RELATIVES IN PATIENTS WITH HEMATOLOGIC CANCERS WILLIAM I. BENSINGER,
TRANSPLANTATION OF BLOOD CELLS IN PATIENTS WITH HEMATOLOGIC CANCERS TRANSPLANTATION OF AS COMPARED WITH BLOOD CELLS FROM HLA-IDENTICAL RELATIVES IN PATIENTS WITH HEMATOLOGIC CANCERS WILLIAM I. BENSINGER,
Transplant Booklet D Page 1
 Booklet D Pretest Correct Answers 4. (A) is correct. Technically, performing a hematopoietic stem cell transplant is one of the simplest transplantation procedures. The hematopoietic stem cells are infused
Booklet D Pretest Correct Answers 4. (A) is correct. Technically, performing a hematopoietic stem cell transplant is one of the simplest transplantation procedures. The hematopoietic stem cells are infused
Non-Myeloablative Transplantation
 Non-Myeloablative Transplantation David G. Maloney, Brenda M. Sandmaier, Stephen Mackinnon, and Judith A. Shizuru The concept of utilizing enhanced immunosuppression rather than myeloablative cytotoxic
Non-Myeloablative Transplantation David G. Maloney, Brenda M. Sandmaier, Stephen Mackinnon, and Judith A. Shizuru The concept of utilizing enhanced immunosuppression rather than myeloablative cytotoxic
Michael Grimley 1, Vinod Prasad 2, Joanne Kurtzberg 2, Roy Chemaly 3, Thomas Brundage 4, Chad Wilson 4, Herve Mommeja-Marin 4
 Twice-weekly Brincidofovir (BCV, CMX1) Shows Promising Antiviral Activity in Immunocompromised Transplant Patients with Asymptomatic Adenovirus Viremia Michael Grimley 1, Vinod Prasad, Joanne Kurtzberg,
Twice-weekly Brincidofovir (BCV, CMX1) Shows Promising Antiviral Activity in Immunocompromised Transplant Patients with Asymptomatic Adenovirus Viremia Michael Grimley 1, Vinod Prasad, Joanne Kurtzberg,
Analysis of the Viability of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells. Sachdeva N
 Jsrm/Vol5No.11, 2009 Original Article Analysis of the of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells Sachdeva N Dr. Neelam Sachdeva Reader, Department of Zoology, Gargi College, University of Delhi, Siri Fort Road,
Jsrm/Vol5No.11, 2009 Original Article Analysis of the of Umbilical Cord blood Stem Cells Sachdeva N Dr. Neelam Sachdeva Reader, Department of Zoology, Gargi College, University of Delhi, Siri Fort Road,
What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016
 What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016 Division of Hematology-Oncology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine 1 Who should be transplanted and how? Updates
What s new in Blood and Marrow Transplant? Saar Gill, MD PhD Jan 22, 2016 Division of Hematology-Oncology University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine 1 Who should be transplanted and how? Updates
