Methodological Issues Naohito Yamaguchi,1 Yoshiyasu Tamura,2 Tomotaka Sobue,3
|
|
|
- August Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluation of Cancer Prevention Strategies by Computeried Simulation Model: Methodological Issues Naohito Yamaguchi,1 Yoshiyasu Tamura,2 Tomotaka Sobue,3 Suminori Akiba,4 Megu Ohtaki,5 Yasumasa Baba,2 Shoichi Miuno,1 and Sha Watanabel 1Division of Epidemiology, National Cancer Center Research Institute, Tokyo, Japan; 2Institute of Statistical Mathematics; 3Radiation Effect Research Foundation; 5Research Institute for Nuclear Medicine and Biology, Hiroshima University A computeried simulation model developed to evaluate the potential impact of primary and secondary prevention is discussed from methodologic perspectives. In the simulation model, named CANSAVE (Cancer Strategy Analysis and Validation of Effect), the natural history of cancer as modeled as a Markovian stochastic process from cancer-free state to death. The lung cancer death rate among Japanese males as projected for 5 years to the year 241. The simulation shoed that the age-adjusted death rate ould increase and reach a peak of 166 per 1, in 1989 and then decrease to 148 in 23. It then shos a tendency to increase again, up to 255 in 228. This change may be attributed to a loer smoking initiation rate among those born in the 1 93s. Promotion of mass screening programs exhibits a more prompt effect than antismoking efforts, but the reduction in annual deaths is expected to be only 1 1 %, even if a 1% participation is realied by the year 2. The reduction in smoking initiation rate, on the other hand, begins to sho a visible effect very sloly. It as predicted that a 1 % annual reduction in smoking initiation rate ould result in a 2% decrease in the number of deaths in 241. The smoking cessation program is in the middle ith regard to promptness. The predicted reductions in lung cancer deaths in 241 ere 13, 47, and 66%, respectively, hen the annual smoking cessation rate as increased from.46% (present status) to 1, 3, and 5%. The combined application of all three preventive measures seems essential to realie the most effective reduction in lung cancer deaths. - Environ Health Perspect 12(Suppl 8):67-71 (1994) Key ords: cancer, lung, smoking, screening, simulation, prevention, evaluation, epidemiology Introduction The incidence and mortality rates of cancer have been changing dynamically, reflecting changes in the prevalence of risk factors, promotion of effective screening programs, or improvement of survival rate by ne treatment technologies. Therefore, to make the medical and public health services more effective, the forecasting of future trends in cancer incidence and mortality is of particular importance in planning and policy making for health resource allocation. In this article, e discuss a simulation model, CANSAVE (Cancer Strategy Analysis and Validation of Effect) (1,2), hich e developed for lung cancer among Japanese males. This model as developed to simulate This paper as presented at the 4th Japan-US Biostatistics Conference on the Study of Human Caner held 9-11 November 1992 in Tokyo, Japan. This study as supported in part by a grant-in-aid for cancer research (#2-3) from the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan. Address correspondence to Naohito Yamaguchi, Cancer, Information and Biometry Epidemiology Division, National Cancer Center Research Institute, Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo 14, Japan. Telephone , ext Fax potential impacts of both primary and secondary preventive measures on the future incidence and mortality rates. An increase in the lung cancer death rate has been noted among Japanese males in recent decades (3,4). It has been argued that cigarette smoking plays a substantial role in this epidemic and emphasis has been placed on the importance of antismoking efforts (5). On the other hand, the Japanese government recommends a community-based mass screening program as a preventive measure of primary choice. Therefore, evaluation of the potential impacts of smoking cessation programs and mass screening for lung cancer is of crucial importance to plan a comprehensive prevention strategy on a nationide basis. Model Description The simulation model CANSAVE is based on a set of formulas that describe the natural history of cancer as a Markovian stochastic process from cancer-free to preclinical, clinical, and finally to terminal state (Figure 1). We adopted the Markovian stochastic process as the basic structure for several reasons. First, e decided to incorporate the preclinical asymptomatic stage into our model, so that the effect of screening can be evaluated in terms of the increase in the number of cases detected and treated successfully during the preclinical stage. Second, e noticed that only limited information is available to evaluate the parameters in the simulation model and that most information for cancer incidence, mortality, and survival is given as yearly Figure 1. Markovian stochastic model of the natural history of lung cancer. Environmental Health Perspectives 67
2 YAMAGUCHI ETAL. aggregate data. Therefore, e decided to make our model as simple as possible, including parameters that are estimable from epidemiologic and clinical data. One of the key issues in modeling the natural history of lung cancer is ho to formulate the effect of smoking on the pathogenesis of cancer. We assumed that the lung cancer death rate increases in proportion to the 4th poer of age among nonsmokers and by a poer of 4.5 of the effective year of smoking among current smokers as follos (6,7): Rate = rn (age)4 for nonsmokers, Rate = r5 (effective year of smoking)45 for current smokers. The effective year of smoking is the duration of smoking minus the period of cancer groth that as assumed to be independent of cigarette smoking and as given on a birth cohort basis; 22.4 years for the cohorts born after 1933, up to 31. years for the cohort born in 192 (7). The parameters r, and rs ere set at.15 x 1-5 and 1.7 x 1-5 per 1,, respectively, based on estimates reported by Miuno et al. (7). The reduction in the relative risk among exsmokers as assumed to be 3% per year, hich as estimated recently by a case-control study in Japan (8). The annual smoking cessation rate among smokers as estimated to be.46% by regression analysis of the increase in exsmokers among eversmokers by age (1). The age-specific smoking rates for this analysis ere obtained from the National Health Survey ofjapan conducted in 198 (9). The transition probabilities from preclinical to clinical, clinical to recovery, and clinical to death ere estimated simultaneously by the least squares method (1), minimiing the departure of survival functions in the model from the observed survival curves in cases detected by screening and through symptoms (1). The estimated transition probabilities ere.64 per year,.13 per year and.69 per year for preclinical to clinical, clinical to recovery, and clinical to death, respectively. The transition probability from preclinical to recovery as estimated to be.16/year for participants of annual screening and as assumed to be ero for nonparticipants. The sensitivity of the screening test for lung cancer as assumed to be.62 (11). The screening participation rate among Japanese males aged 55 to 79 as assumed to be 1% during the period 1973 to 1989 (12). The probability of death from other causes as estimated separately for smokers, exsmokers, and nonsmokers, based on the age-specific death rates among Japanese males during 1973 to The death rates thereafter ere assumed to be constant and the rates in 1989 ere applied. In estimating the death rates for different smoking status, the relative risk of death from all causes as assumed to be proportional to the exponential of the duration of smoking (13). Simulation Procedure Simulation as conducted separately for smokers, exsmokers and nonsmokers, then results ere added to obtain the numbers of deaths from lung cancer for each age and calendar year. In projecting the lung cancer death rate of each birth cohort, the proportion of individuals ho started smoking in that birth cohort as determined so that the simulated lung cancer death rates during 1981 to 1987 became the closest to the observed death rates in the same period. An iterative method as used for this procedure. The mortality data used as the reference ere the death rates observed among Japanese males over 36 years of age during 1981 to For those aged 36 to 39, Poisson regression equations ere fitted to the increases in age-specific death rates to smooth the random fluctuations due to small numbers of deaths. The simulation period as from 1981 to 241; 1981 to 1987 as included for the iterative fitting procedure described above. The smoking initiation rates thus estimated in the process of simulation ere then compared ith observed rates in Nagano Prefecture (4,324 male partici- 6 5 Ir I 2 a 1 l 1 97 pants of a mass screening program in 1988) and in Fukuoka Prefecture (969 male participants of a mass-screening program in 1986) to check the validity of this procedure. The potential impact of prevention programs on future lung cancer deaths as evaluated ith regard to changes in the smoking initiation rate, the smoking cessation rate, and the annual screening rate. Death rates adjusted to the 1985 model population (14) ere used as the index of impact. To scenarios ere provided for the smoking initiation rate among the younger cohorts: the same smoking initiation rate as the cohort born in 1951, and a decrease in the smoking initiation rate at a rate of 1%/year. The smoking cessation rate that originally as set at.46%/year as modified to 1, 3, and 5%/year to evaluate the effects of smoking cessation programs on the future deaths. To see the impact of increased participation in screening program, the annual screening rate, originally set at 1%, as modified to 1% in the year 2 by increasing 1%/year from 1992 to 2. Results Observed and simulated death rates are illustrated in Figure 2 in 5-year age groups from 55 to 59 through 75 to 79. The simulation results displayed in Figure 2 ere for those born before 1952, hose smoking initiation rates ere available. The observed death rates shoed increasing YEAR Figure 2. Observed (circles) and projected (lines) lung cancer death rates among Japanese males by 5-year age groups. 68 Environmental Health Perspectives
3 EVALUATION OF CANCER PREVENTION STRATEGIES BY SIMULATION CD Nagano (1988)... Fukuoka(1986) ESTIMATED BIRTH YEAR Figure 3. Smoking initiation rates among Japanese males estimated by the simulation as compared to those observed in Nagano and Fukuoka prefectures Figure 4. Lung cancer death rates observed among Japanese males aged 28 to 39 during 1973 to tendencies in all age groups, ith steeper increases in older age groups. The simulated death rate in the 75 to 79 age group shoed the largest changes ith three phases. It reaches a peak of 457 per 1, in 1994, then decreases to the loest level of 276 per 1, in 214. It shos a tendency to increase again and reaches 616 per 1, in 235. The peak and bottom of the 7 to 74 age group are 296 per 1, in 1989 and 19 per 1, in 29, respectively. The shift of the peak and bottom toard the earlier years indicates that they reflect higher and loer death rates in specific birth cohorts. The peaks correspond to the 1915 to 1919 birth cohort and the bottom to the 1935 to 1939 cohort. The projected death rates for the other age groups shoed similar but smaller changes. The smoking initiation rates estimated by simulation are illustrated in Figure 3. The estimated smoking initiation rate decreased from around 85% among the Table 1. Poisson regression equations fitted to the increase in lung cancer death rates per million by year 1973 to Age Slope S.E. t pvalue b c b a c p<.5. p<.1. Cp<.1. cohorts born prior to 192 to around 65% among the cohorts born in the 193s. The rate then shoed another rising trend, returning to the level of 8% in the cohort born around 195. The loer smoking initiation rates among the cohorts born in the 193s ere confirmed by observed rates in Nagano and Fukuoka prefectures (Figure 3). In fact, the observed death rates among those aged 36 to 39 shoed an increase during the period from 1983 to 1987 (Figure 4). This age group corresponds to the cohort born beteen 1944 and 1951, ho shoed an increase in smoking initiation rate (Figure 3). This as also confirmed by Poisson regression equations fitted to observed death rates as statistically significant increases among those aged 34 and 36 to 39 (Table 1). The simulation results for six scenarios on the smoking initiation rate, smoking cessation rate, and screening rate are illustrated ith the age-adjusted death rate as the index in Figure 5. In the present-status simulation noted in the first scenario, in hich the smoking initiation rate of 8%, smoking cessation rate of.46% per year, and annual screening rate of 1% persist in the future, the age-adjusted lung cancer death rate is predicted to change ith four phases. It reaches the first peak of 166 per 1, in It then decreases to 148 per 1, in 23, shos an increase to 255 per 1, in 228, and stays at that level thereafter. In this scenario, the overall smoking rate among those aged 55 to 79 as predicted to decrease from 64% in 1981 to 51% in 21. It then shoed an increase and reached a plateau of 61% in 229. Among the five prevention strategies labeled 2 through 6 in Figure 5, the increase in screening rate exhibits the most prompt effect on lung cancer deaths. The number of lung cancer deaths decreases to 89% of that of present-status simulation in 23 and stays at that level thereafter. On Volume 12, Supplement 8, November
4 YAMAGUCHI ETAL. Markovian stochastic model is flexible in (1) smoking initiation = constant model building. Modeling can be started (2) smoking initiation = decreasing from the simplest model ith only a causal - 3 (3) smoking cessation = 1 %/o/yr factor and an outcome such as death, and 6 (4) smoking cessation = 3%/o/yr (1) then can be improved by incorporating (5) smoking cessation = 5%/o/yr additional compartments. Second, it is easy (6) to evaluate the (6) screening rate = 1% parameters in the model, (3) based on existing epidemiologic and clinical - 4e 2 (2) data, since the transition rates connecting to compartments in the model are the 1-- same as annual rates reported in epidemiol- 4c (4) ogy literature and in government statistics. The present method might have 1 sacrificed reliability of results by pursuing a (5) simplicity in model building and parameter setting. To assess the sensitivity of simulation results for a subtle change in parameter values, the value of each parameter as 4 modified to 9 and 11%, and the change to in the number of lung cancer deaths in YEAR 21 as compared (1). Of six parameters examined, the transition rate from clinical to Figure 5. Lung cancer death rates projected according to the six scenarios for the future smoking anid recovery caused the largest change screening (solid and broken lines), as compared to the observed death rates (circles). The death rates aestatustad are adjusted (1.4%), folloed by the transition rate to the 1985 model population of Japan. from clinical to lung cancer death (Table 2). The influences ere less marked for other parameters. One interesting finding in the present Discussion analysis of observed lung cancer death rates The projection of future cancer trends can is an increasing trend of age-specific death be done by various methods. 1rhe most rates in the 36 to 39 age group (Table 1, the other hand, of the five prevention strategies, the modification of smoking initiation rate is the sloest to begin to sho a visible effect. The number of lung cancer deaths stays as high as 98% of the presentstatus simulation until 219. It then shos a tendency to decrease to 8% in 241. It as predicted that the overall smoking rate among those aged 55 to 79 ould decrease to 41% in 241 in this scenario. The predicted smoking initiation rate as 3% among the cohort born in 2. The effect of increase in smoking cessation rate becomes visible earlier than the reduction in smoking initiation rate but later than the increase in screening rate. When the three levels of increase in annual smoking cessation rate (1, 3, and 5%) ere compared ith regard to the relative decreases in the number of lung cancer deaths, the differences beteen the three scenarios ere ithin 5% until 25. These differences become more marked thereafter and the numbers of lung cancer deaths in the 3 and 5% annual cessation scenarios become 61 and 4%, respectively, of the 1% annual cessation scenario in 241. The overall smoking rate among those aged 55 to 79 as predicted to decrease to 46, 17, and 6% resulting from 1, 3, and 5% annual cessation, respectively. idely used is fitting of linear or nonlinear Figure 4). This age group corresponds to models to incidence or mortality data and the 1934 to 1937 birth cohort in 1973 and projection using the estimated regression the 1948 to 1951 birth cohort in equations. This method gives us a relatively The smoking initiation rate estimated from reliable estimate for short-term trcend but it these mortality data as 66% for the 1934 does not ork ell for a long-ternn trend of birth cohort versus 8% for the 195 birth more than a fe decades, hich depends cohort. The ever-smokers' rates (= current on risk transitions and changes irn medical + exsmokers) observed in Nagano and public health practices. An allternative Prefecture (1988) ere 69% for the 1934 method used by many epidemiolc )gists is to cohort and 82% for the 1953 cohort calculate the incidence or mort-ality rate (Figure 3). A similar trend in ever-smoker's expected for a hypothetical population rate as observed in Fukuoka Prefecture ith a certain prevalence rate of riisk factor, (1986); 72% in the 1932 to 1936 cohort based on the relative risk and t] he preva- versus 81% in the 1952 to 1956 cohort. lence rate of the risk factor measured in the The 1935 to 1939 birth cohort became 2 real population. This method is useful to make an insight into a limiting state that might be achieved in the long rlan, but it Table 2. Relative changes in the number of lung cancer deaths in 21 hen the parameter values are cannot be used to predict a dynamic change in cancer occurrence becauise it does not take time into account. The present method base( d on the Markovian stochastic process is a hybrid of the to methods mentioned abo ve, in the sense that the effects of smolking and screening ere incorporated as tinne-depen- edure as dent factors and that fitting proc adopted by leaving the birth cohort specific smoking initiation rate as a variatble to be fitted. Several features should be mentioned for the present method. First, the modified to 9% and 1 1%. Modified parameter value, % Parameter 9% 11% Pr (clinical to recoveryla Pr (clinical to lung cancer death) Annual risk reduction in ex-smokers Screening sensitivity Pr (preclinical to recovery) Pr (preclinical to clinical) apr (A to B) indicates the transition probability from state A to state B. 7 Environmental Health Perspectives
5 EVALUATION OF CANCER PREVENTION STRATEGIES BY SIMULATION years old from 1955 to 1959, coinciding ith the rapid increase in the sale of filtered cigarettes beginning in the late 195s. In fact, the annual sale of cigarettes increased from 1 billion in the 195s to 3 billion in 1975, more than 95% of hich ere filtered cigarettes. The smoking initiation rate as higher than 8% before 1945, possibly due to artime rationing of cigarettes to soldiers. It then decreased, probably due in some part to economic difficulties. The increase in smoking initiation rate afterard might ell be explained by the sale of filtered cigarettes as mentioned, together ith nationide economic restoration. The present study predicted that the lung cancer death rates, those in 7 to 79 age group in particular, ould begin to decrease ithin 1 years. The results of the present study suggest that this future decrease is due to the loer smoking initiation rates in specific birth cohorts and that the death rate ill increase again, reflecting the increase in smoking initiation rate among those born after 194. Therefore, it is crucially important to implement effective preventive measures as soon as possible. Three kinds of preventive measures, i.e., loering smoking initiation rate, promotion of smoking cessation, and increased screening participation, seem to have both advantages and disadvantages. Loering the smoking initiation rate at an annual rate of 1% ill result in a 2% decrease in the number of lung cancer deaths as ell as the adjusted death rate in 241 hen compared ith the present persistent initiation rate of 8% among those born after 195. Achievement of a 1% annual reduction in smoking initiation rate does not seem to be difficult, as shon in the observed smoking initiation rate in Nagano Prefecture. Hoever, it should also be noted that the effect of reducing the smoking initiation rate ill be realied most sloly compared ith the other measures. The effect of smoking cessation is realied earlier than the effect of reducing the smoking initiation (Figure 5). Moreover, it is the only measure by hich the predicted increase in the number of lung cancer deaths in the coming 5 years can be prevented effectively. The number of lung cancer deaths in 241 can be reduced to 17,, the 1987 level by achieving a 5% annual smoking cessation rate. Hoever, raising the smoking cessation rate is difficult because of nicotine addiction (15). The promotion of screening participation seems the most promising in realiing a rapid decrease in lung cancer deaths. Hoever, the fact that lung cancer deaths can be loered by only 1% by achieving 1% screening participation indicates that primary prevention is more important in the long run. In conclusion, all three preventive measures should be implemented simultaneously so that the disadvantages of one measure can be offset by the others. REFERENCES 1. Yamaguchi N, Tamura Y, Sobue T, Akiba S, Ohtaki M, Baba Y, Miuno S, Watanabe S. Evaluation of cancer prevention strategies by computeried simulation model: an approach to lung cancer. Cancer Causes Control 2: (1991). 2. Yamaguchi N, Miuno S, Akiba S, Sobue T, Watanabe S. A 5-year projection of lung cancer deaths among Japanese males and potential impact evaltuation of anti-smoking measures and screening using a computeried simulation model. Jpn J Cancer Res 83: (1992). 3. Statistics and Information Department. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Vital Statistics 1988 Japan. Tokyo:Health and Welfare Statistics Association, 199; Bureau of Vital Statistics, Ministry of Health and Welfare. Long term trends in cancer mortality rates from 1955 to 1987 in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2: (199). 5. Tominaga S. Smoking and cancer patterns and trends in Japan. In: Tobacco: A Major International Health Haard (Zaride DG, Peto R, eds). Lyon:International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1986; Doll R, Peto R. Cigarette smoking and bronchial carcinoma: dose and time relationships among regular smokers and lifelong non-smokers. J Epidemiol Comm Health 32: (1978). 7. Miuno S, Akiba S, Hirayama T. Lung cancer risk comparison among male smokers beteen the "Six Prefecture Cohort" in Japan and the British Physicians' Cohort. Jpn J Cancer Res 8: (1989). 8. Sobue T, Suuki T, Fujimoto I. Lung cancer risk among exsmokers. Jpn J Cancer Res 82: (199). 9. Ministry of Health and Welfare. National Health Survey 198 Japan. Tokyo:Kosei Tokei Kyoukai, 198;24-25 Japanese). 1. Lung Cancer Task Force, Japanese Joint Committee on TNM Classification and National Cancer Center. 1,334 cases in 1981, 1982, Lung Cancer Task Force, Tokyo:Japanese Joint Committee on TNM Classification and National Cancer Center, 1988; Suuki T, Sobue T, Nakayama N. Sensitivity and specificity of lung cancer screening in Osaka. 28:653 (1988) (apanese). 12. Watanabe S. Cancer morbodity and related problems. In: Fifth National Cancer Morbidity Survey in Japan 199 (Suemasu K, ed). Tokyo:Sougou Igaku Sha, 199;9-16 (apanese). 13. Ohtaki M. A model for age-dependence of lung cancer mortality. Bull Biom Soc Jpn 11: (199). 14. Abe Y, Onodera M, Kamiya K, Saito H, Matsunaga T. On the revision of age-adjusted death rate. Kosei No Shihyo. 38:12-16 (1991) (apanese). 15. Matsushita K, Nakamura M, Miyamoto M, Endo S, Oshima A. 'First Osaka Quit Contest.' Results from one year follo-up. Jpn J Public Health 36:88 (1989) Uapanese). Volume 12, Supplement 8, November
Statistical Analysis of Geographical Features of Lung Cancer Mortality in Japan
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 000;30(1)557 561 Statistical Analysis of Geographical Features of Lung Cancer Mortality in Japan Hiromi Kawasaki 1, Kenichi Satoh, Teruyuki Nakayama 3, Naohito Yamaguchi 4 and Megu Ohtaki
Jpn J Clin Oncol 000;30(1)557 561 Statistical Analysis of Geographical Features of Lung Cancer Mortality in Japan Hiromi Kawasaki 1, Kenichi Satoh, Teruyuki Nakayama 3, Naohito Yamaguchi 4 and Megu Ohtaki
Introduction, Summary, and Conclusions
 Chapter 1 Introduction, Summary, and Conclusions David M. Burns, Lawrence Garfinkel, and Jonathan M. Samet Cigarette smoking is the largest preventable cause of death and disability in developed countries
Chapter 1 Introduction, Summary, and Conclusions David M. Burns, Lawrence Garfinkel, and Jonathan M. Samet Cigarette smoking is the largest preventable cause of death and disability in developed countries
Journal of Epidemiology Vol. 17, No. 2 March 2007
 Journal of Epidemiology Vol. 7, No. March 7 The harm of smoking has been known for many years and evidences from a cohort study shows that smoking is a prominent risk factor for total mortality,, lung
Journal of Epidemiology Vol. 7, No. March 7 The harm of smoking has been known for many years and evidences from a cohort study shows that smoking is a prominent risk factor for total mortality,, lung
LOG- LINEAR ANALYSIS OF FERTILITY USING CENSUS AND SURVEY DATA WITH AN EXAMPLE
 LOG- LIEAR AALYSIS OF FERTILITY USIG CESUS AD SURVEY DATA WITH A EXAMPLE I. Elaine Allen and Roger C. Avery, Cornell University The use of log -linear models is relatively ne to the field of demography,
LOG- LIEAR AALYSIS OF FERTILITY USIG CESUS AD SURVEY DATA WITH A EXAMPLE I. Elaine Allen and Roger C. Avery, Cornell University The use of log -linear models is relatively ne to the field of demography,
Trends in Lung Cancer Incidence by Histological Type in Osaka, Japan
 Original Article Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology Advance Access published August 9, 2008 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2008 doi:10.1093/jjco/hyn072 Trends in Lung Cancer Incidence by Histological Type in Osaka,
Original Article Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology Advance Access published August 9, 2008 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2008 doi:10.1093/jjco/hyn072 Trends in Lung Cancer Incidence by Histological Type in Osaka,
Relationship between Cigarette Smoking and Histologic Type of Lung Cancer, with Special Reference to Sex Difference
 Relationship between Cigarette Smoking and Histologic Type of Lung Cancer, with Special Reference to Sex Difference Tomotaka Sobue, M.D.* 1, Takaichiro Suzuki, M.D. 1, Takeshi Horai, M.D. 2, Minoru Matsuda,
Relationship between Cigarette Smoking and Histologic Type of Lung Cancer, with Special Reference to Sex Difference Tomotaka Sobue, M.D.* 1, Takaichiro Suzuki, M.D. 1, Takeshi Horai, M.D. 2, Minoru Matsuda,
pain" counted as "two," and so forth. The sum of point, the hour point, and so forth. These data are
 FURTHER STUDIES ON THE "PHARMACOLOGY" OF PLACEBO ADMINISTRATION 1 BY LOUIS LASAGNA, VICTOR G. LATIES, AND J. LAWRENCE DOHAN (From the Department of Medicine (Division of Clinical Pharmacology), and the
FURTHER STUDIES ON THE "PHARMACOLOGY" OF PLACEBO ADMINISTRATION 1 BY LOUIS LASAGNA, VICTOR G. LATIES, AND J. LAWRENCE DOHAN (From the Department of Medicine (Division of Clinical Pharmacology), and the
Cohort analysis of cigarette smoking and lung cancer incidence among Norwegian women
 International Epidemiological Association 1999 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 1999;28:1032 1036 Cohort analysis of cigarette smoking and lung cancer incidence among Norwegian
International Epidemiological Association 1999 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 1999;28:1032 1036 Cohort analysis of cigarette smoking and lung cancer incidence among Norwegian
Risk in Japanese Men and Women- Results from Reanalysis of the Six-
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 87, pp. 9-26, 990 Cigarette Smoking and Cancer Mortality Risk in Japanese Men and Women- Results from Reanalysis of the Six- Prefecture Cohort Study Data by Suminori
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 87, pp. 9-26, 990 Cigarette Smoking and Cancer Mortality Risk in Japanese Men and Women- Results from Reanalysis of the Six- Prefecture Cohort Study Data by Suminori
Performance Testing of a Semi-Hermetic Compressor with HFC-236ea and CFC-114 at Chiller Conditions
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Performance Testing of a Semi-Hermetic Compressor ith HFC-236ea and CFC-114
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1994 Performance Testing of a Semi-Hermetic Compressor ith HFC-236ea and CFC-114
Population Attributable Fraction of Mortality Associated with Tobacco Smoking in Japan: A Pooled Analysis of Three Large-scale Cohort Studies
 doi:10.2188/jea.je2007429 Original Article Population Attributable Fraction of Mortality Associated with Tobacco Smoking in Japan: A Pooled Analysis of Three Large-scale Cohort Studies Kota Katanoda, 1
doi:10.2188/jea.je2007429 Original Article Population Attributable Fraction of Mortality Associated with Tobacco Smoking in Japan: A Pooled Analysis of Three Large-scale Cohort Studies Kota Katanoda, 1
Current state and need for improvement of system for antibody testing and counseling for HIV infection at public health centers in Japan
 J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 177 182 Original Article Current state and need for improvement of system for antibody testing and counseling for HIV infection at public health centers in Japan Chika Miyazaki
J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 177 182 Original Article Current state and need for improvement of system for antibody testing and counseling for HIV infection at public health centers in Japan Chika Miyazaki
Changes in Number of Cigarettes Smoked per Day: Cross-Sectional and Birth Cohort Analyses Using NHIS
 Changes in Number of Cigarettes Smoked per Day: Cross-Sectional and Birth Cohort Analyses Using NHIS David M. Burns, Jacqueline M. Major, Thomas G. Shanks INTRODUCTION Smoking norms and behaviors have
Changes in Number of Cigarettes Smoked per Day: Cross-Sectional and Birth Cohort Analyses Using NHIS David M. Burns, Jacqueline M. Major, Thomas G. Shanks INTRODUCTION Smoking norms and behaviors have
Smoking and Mortality in the Japan Collaborative Cohort Study for Evaluation of Cancer (JACC)
 Smoking and Mortality SECTION 6 Smoking and Mortality in the Japan Collaborative Cohort Study for Evaluation of Cancer (JACC) Kotaro Ozasa Abstract In the JACC study, risk of death with all cancers and
Smoking and Mortality SECTION 6 Smoking and Mortality in the Japan Collaborative Cohort Study for Evaluation of Cancer (JACC) Kotaro Ozasa Abstract In the JACC study, risk of death with all cancers and
Trends in mortality from lung cancer in Spain,
 Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1987, 41, 74-78 Trends in mortality from lung cancer in Spain, 1951-80 JESUS VIOQUE AND FRANCISCO BOLUMAR From the Departamento de Salud Comunitaria, Facultad
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1987, 41, 74-78 Trends in mortality from lung cancer in Spain, 1951-80 JESUS VIOQUE AND FRANCISCO BOLUMAR From the Departamento de Salud Comunitaria, Facultad
Future smoking-attributable and all-cause mortality: its sensitivity to indirect estimation techniques
 Short abstract Future attributable and all-cause mortality: its sensitivity to indirect estimation techniques Lenny Stoeldraijer a and Fanny Janssen b,c a Statistics Netherlands, The Hague, the Netherlands
Short abstract Future attributable and all-cause mortality: its sensitivity to indirect estimation techniques Lenny Stoeldraijer a and Fanny Janssen b,c a Statistics Netherlands, The Hague, the Netherlands
Patterns of adolescent smoking initiation rates by ethnicity and sex
 ii Tobacco Control Policies Project, UCSD School of Medicine, San Diego, California, USA C Anderson D M Burns Correspondence to: Dr DM Burns, Tobacco Control Policies Project, UCSD School of Medicine,
ii Tobacco Control Policies Project, UCSD School of Medicine, San Diego, California, USA C Anderson D M Burns Correspondence to: Dr DM Burns, Tobacco Control Policies Project, UCSD School of Medicine,
Today Retrospective analysis of binomial response across two levels of a single factor.
 Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Chapter 18.3 Single Factor. Retrospective Analysis ReCap. Part I (Chapters 1,2,3,4), Part II (Ch 5, 6, 7) ReCap Part III (Ch 9,
Model Based Statistics in Biology. Part V. The Generalized Linear Model. Chapter 18.3 Single Factor. Retrospective Analysis ReCap. Part I (Chapters 1,2,3,4), Part II (Ch 5, 6, 7) ReCap Part III (Ch 9,
Estimating Adolescent Cigarette Consumption in Japan. Yoneatsu Osaki, Katsuhiko Kawaminami, and Masumi Minowa MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Journal of Eoidemiologv Vol. 9, No. 2 Apr Estimating Adolescent Cigarette Consumption in Japan Yoneatsu Osaki, Katsuhiko Kawaminami, and Masumi Minowa We estimated the cigarette consumption among Japanese
Journal of Eoidemiologv Vol. 9, No. 2 Apr Estimating Adolescent Cigarette Consumption in Japan Yoneatsu Osaki, Katsuhiko Kawaminami, and Masumi Minowa We estimated the cigarette consumption among Japanese
Mortality from cancer of the lung in Serbia
 JBUON 2013; 18(3): 723-727 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mortality from cancer of the lung in Serbia M. Ilic 1, H. Vlajinac 2,
JBUON 2013; 18(3): 723-727 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mortality from cancer of the lung in Serbia M. Ilic 1, H. Vlajinac 2,
Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta. Breast Cancer
 Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta Breast Cancer November 2009 Surveillance - Cancer Bureau Health Promotion, Disease and Injury Prevention Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta - 2 Purpose of the
Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta Breast Cancer November 2009 Surveillance - Cancer Bureau Health Promotion, Disease and Injury Prevention Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta - 2 Purpose of the
Trends in electronic cigarette use in England
 Trends in electronic cigarette use in England Robert West Jamie Brown Emma Beard University College London Updated 14 th April 215 Background Electronic cigarette use has become prevalent in many countries
Trends in electronic cigarette use in England Robert West Jamie Brown Emma Beard University College London Updated 14 th April 215 Background Electronic cigarette use has become prevalent in many countries
Cigarette Smoking and Lung Cancer
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Epidemiology Program Office Case Studies in Applied Epidemiology No. 731-703 Cigarette Smoking and Lung Cancer Learning Objectives After completing this case
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Epidemiology Program Office Case Studies in Applied Epidemiology No. 731-703 Cigarette Smoking and Lung Cancer Learning Objectives After completing this case
Genetic Variations. F1 Generation. Mechanisms of Genetics W W. STAAR Biology: Assessment Activities
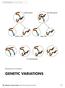 male parent female parent sperm cells egg cells F1 Generation Mechanisms of Genetics 181 182 Mechanisms of Genetics Teacher Pages Purpose The purpose of this activity is to reinforce students understanding
male parent female parent sperm cells egg cells F1 Generation Mechanisms of Genetics 181 182 Mechanisms of Genetics Teacher Pages Purpose The purpose of this activity is to reinforce students understanding
Radiation Biology and Medicine, Hiroshima University
 Title: A mathematical estimation of cancer incidence using data from population-based cancer registries Authors: Ken-ichi Kamo 1,2, Satoshi Kaneko 1, Kenichi Satoh 3, Hirokazu Yanagihara 4, Shoichi Mizuno
Title: A mathematical estimation of cancer incidence using data from population-based cancer registries Authors: Ken-ichi Kamo 1,2, Satoshi Kaneko 1, Kenichi Satoh 3, Hirokazu Yanagihara 4, Shoichi Mizuno
Predicting the population health effects of changing tobacco exposures: Statistical models for regulatory compliance
 Predicting the population health effects of changing tobacco exposures: Statistical models for regulatory compliance NASEM ENDS Workshop February 2017 Annette M. Bachand, Ph.D. Goal of Statistical Models:
Predicting the population health effects of changing tobacco exposures: Statistical models for regulatory compliance NASEM ENDS Workshop February 2017 Annette M. Bachand, Ph.D. Goal of Statistical Models:
Discover Activity. Think It Over Inferring Do you think height in humans is controlled by a single gene, as it is in peas? Explain your answer.
 Section Human Inheritance Reading Previe Key Concepts What are some patterns of inheritance in humans? What are the functions of the sex chromosomes? What is the relationship beteen genes and the environment?
Section Human Inheritance Reading Previe Key Concepts What are some patterns of inheritance in humans? What are the functions of the sex chromosomes? What is the relationship beteen genes and the environment?
J. E. R. STADDON DUKE UNIVERSITY. The relative inability of the usual differential. to ask whether performance under DRL schedules
 JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR 1969, 12, 27-38 NUMBER I (JANUARY) THE EFFECT OF INFORMATIVE FEEDBACK ON TEMPORAL TRACKING IN THE PIGEON' J. E. R. STADDON DUKE UNIVERSITY Pigeons emitted
JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR 1969, 12, 27-38 NUMBER I (JANUARY) THE EFFECT OF INFORMATIVE FEEDBACK ON TEMPORAL TRACKING IN THE PIGEON' J. E. R. STADDON DUKE UNIVERSITY Pigeons emitted
powder and liquid and several laboratory prepared mixes were used in this investigation. The materials used to prepare various
 Thermal Analysis During Setting of Zinc Oxide-Eugenol Cements H. M. EL-TAHAWI and R. G. CRAIG School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 4814, USA Characteristic thermal transitions
Thermal Analysis During Setting of Zinc Oxide-Eugenol Cements H. M. EL-TAHAWI and R. G. CRAIG School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 4814, USA Characteristic thermal transitions
Smoking in Iranian Physicians: Preliminary Report
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Tanaffos (2005) 4(16), 63-67 2005 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran Smoking in Iranian Physicians: Preliminary Report Gholam Reza Heydari
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Tanaffos (2005) 4(16), 63-67 2005 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran Smoking in Iranian Physicians: Preliminary Report Gholam Reza Heydari
MATCHING LAYER DESIGN OF AN ULTRASONIC TRANS- DUCER FOR WIRELESS POWER TRANSFER SYSTEM
 MATCHIN LAYE DESIN OF AN ULTASONIC TANS- DUCE FO WIELESS POWE TANSFE SYSTEM unn Hang Electronics and Telecommunications esearch Institute, Multidisciplinary Sensor esearch roup, Daejeon, South Korea email:
MATCHIN LAYE DESIN OF AN ULTASONIC TANS- DUCE FO WIELESS POWE TANSFE SYSTEM unn Hang Electronics and Telecommunications esearch Institute, Multidisciplinary Sensor esearch roup, Daejeon, South Korea email:
tied at 8 a.m. No cigarettes or solid food were allowed during the following 12-hour experimental period. Two
 CLINICAL USES OF 2,3-DIMERCAPTOPROPANOL (BAL). II. THE EFFECT OF BAL ON THE EXCRETION OF ARSENIC IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND AFTER MINIMAL EX- POSURE TO ARSENICAL SMOKE By J. WEXLER,1 H. EAGLE, H. J. TATUM,2
CLINICAL USES OF 2,3-DIMERCAPTOPROPANOL (BAL). II. THE EFFECT OF BAL ON THE EXCRETION OF ARSENIC IN NORMAL SUBJECTS AND AFTER MINIMAL EX- POSURE TO ARSENICAL SMOKE By J. WEXLER,1 H. EAGLE, H. J. TATUM,2
Setting The setting was a hospital and the community. The economic analysis was carried out in the USA.
 Economic model of sustained-release bupropion hydrochloride in health plan and work site smoking-cessation programs Halpern M T, Khan Z M, Young T L, Battista C Record Status This is a critical abstract
Economic model of sustained-release bupropion hydrochloride in health plan and work site smoking-cessation programs Halpern M T, Khan Z M, Young T L, Battista C Record Status This is a critical abstract
Tellado, J: Quasi-Minimum-BER Linear Combiner Equalizers 2 The Wiener or Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE) solution is the most often used, but it is e
 Quasi-Minimum-BER Linear Combiner Equalizers Jose Tellado and John M. Cio Information Systems Laboratory, Durand 112, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-9510 Phone: (415) 723-2525 Fax: (415) 723-8473
Quasi-Minimum-BER Linear Combiner Equalizers Jose Tellado and John M. Cio Information Systems Laboratory, Durand 112, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305-9510 Phone: (415) 723-2525 Fax: (415) 723-8473
Tobacco and Cigarette Taxes
 Idaho Center for Fiscal Policy Primer Tobacco and Cigarette Taxes Idaho s Tobacco and Cigarette Taxes Generate Revenue Used to Help Communities Thrive In order for Idaho communities to thrive, they need
Idaho Center for Fiscal Policy Primer Tobacco and Cigarette Taxes Idaho s Tobacco and Cigarette Taxes Generate Revenue Used to Help Communities Thrive In order for Idaho communities to thrive, they need
Appendix. Background Information: New Zealand s Tobacco Control Programme. Report from the Ministry of Health
 Appendix Background Information: New Zealand s Tobacco Control Programme Report from the Ministry of Health April 2016 1 Contents The cost of smoking to individuals and society... 3 What impact is New
Appendix Background Information: New Zealand s Tobacco Control Programme Report from the Ministry of Health April 2016 1 Contents The cost of smoking to individuals and society... 3 What impact is New
Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta. Kidney Cancer
 Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta Kidney Cancer November 29 Surveillance - Cancer Bureau Health Promotion, Disease and Injury Prevention Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta - 2 Purpose of the Report
Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta Kidney Cancer November 29 Surveillance - Cancer Bureau Health Promotion, Disease and Injury Prevention Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta - 2 Purpose of the Report
Projections of future numbers of dementia cases in Australia with and without prevention
 Projections of future numbers of dementia cases in Australia with and without prevention Anthony F. Jorm, Keith B.G. Dear, Nicole M. Burgess Objective: To produce projections of the number of dementia
Projections of future numbers of dementia cases in Australia with and without prevention Anthony F. Jorm, Keith B.G. Dear, Nicole M. Burgess Objective: To produce projections of the number of dementia
Exploratory Approach for Modeling Human Category Learning
 Exploratory Approach for Modeling Human Category Learning Toshihiko Matsuka (matsuka@psychology.rutgers.edu RUMBA, Rutgers University Neark Abstract One problem in evaluating recent computational models
Exploratory Approach for Modeling Human Category Learning Toshihiko Matsuka (matsuka@psychology.rutgers.edu RUMBA, Rutgers University Neark Abstract One problem in evaluating recent computational models
Sperm motility index: a new parameter for human sperm evaluation
 r FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1991 The American Fertility Society Yol. 56, No.1, July 1991 Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. Sperm motility index: a ne parameter for human sperm evaluation Benjamin
r FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1991 The American Fertility Society Yol. 56, No.1, July 1991 Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. Sperm motility index: a ne parameter for human sperm evaluation Benjamin
Scale-free tests ofan additive model for the size-weight illusion*
 Perception &Psychophysics 1974, Vol. 16 (2), 276-282 Scale-free tests ofan additive model for the size-eight illusion* MICHAEL H. BIRNBAUMt Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas 66506 and CLAIRICET.
Perception &Psychophysics 1974, Vol. 16 (2), 276-282 Scale-free tests ofan additive model for the size-eight illusion* MICHAEL H. BIRNBAUMt Kansas State University, Manhattan, Kansas 66506 and CLAIRICET.
Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta. Melanoma of the Skin
 Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta Melanoma of the Skin November 29 Surveillance - Cancer Bureau Health Promotion, Disease and Injury Prevention Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta - 2 Purpose of
Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta Melanoma of the Skin November 29 Surveillance - Cancer Bureau Health Promotion, Disease and Injury Prevention Report on Cancer Statistics in Alberta - 2 Purpose of
Fast Facts. Morbidity and Mortality (Related to Tobacco Use)
 Fast Facts Morbidity and Mortality (Related to Tobacco Use) Tobacco and Disease Tobacco use causes o Cancer o Heart disease o Lung diseases (including emphysema, bronchitis, and chronic airway obstruction)
Fast Facts Morbidity and Mortality (Related to Tobacco Use) Tobacco and Disease Tobacco use causes o Cancer o Heart disease o Lung diseases (including emphysema, bronchitis, and chronic airway obstruction)
RADM Patrick O Carroll, MD, MPH Senior Advisor, Assistant Secretary for Health, US DHSS
 Ending the Tobacco Epidemic RADM Patrick O Carroll, MD, MPH Senior Advisor, Assistant Secretary for Health, US DHSS Tim McAfee, MD, MPH Senior Medical Officer, Office on Smoking and Health, CDC www.nwcphp.org/hot-topics
Ending the Tobacco Epidemic RADM Patrick O Carroll, MD, MPH Senior Advisor, Assistant Secretary for Health, US DHSS Tim McAfee, MD, MPH Senior Medical Officer, Office on Smoking and Health, CDC www.nwcphp.org/hot-topics
ing the fixed-interval schedule-were observed during the interval of delay. Similarly, Ferster
 JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAIOR 1969, 12, 375-383 NUMBER 3 (MAY) DELA YED REINFORCEMENT ERSUS REINFORCEMENT AFTER A FIXED INTERAL' ALLEN J. NEURINGER FOUNDATION FOR RESEARCH ON THE NEROUS
JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAIOR 1969, 12, 375-383 NUMBER 3 (MAY) DELA YED REINFORCEMENT ERSUS REINFORCEMENT AFTER A FIXED INTERAL' ALLEN J. NEURINGER FOUNDATION FOR RESEARCH ON THE NEROUS
FETP Introductory Course 2015 Agenda ver. 21 April 2015
 FETP Introductory Course 2015 Agenda ver. 21 April 2015 Note: This agenda is provisional version. This may be changed without notice. Some lectures will be given in English with no interpreter. 1-Apr Welcome
FETP Introductory Course 2015 Agenda ver. 21 April 2015 Note: This agenda is provisional version. This may be changed without notice. Some lectures will be given in English with no interpreter. 1-Apr Welcome
Modeling the Population Health Effects of Camel Snus with Reduced Risk Information
 Modeling the Population Health Effects of Camel Snus with Reduced Risk Information Geoffrey Curtin, Ph.D. - RAI Services Company Annette Bachand, Ph.D., Sandra Sulsky, Ph.D. - Ramboll Environ; Saul Shiffman,
Modeling the Population Health Effects of Camel Snus with Reduced Risk Information Geoffrey Curtin, Ph.D. - RAI Services Company Annette Bachand, Ph.D., Sandra Sulsky, Ph.D. - Ramboll Environ; Saul Shiffman,
Community response to Shinkansen noise and vibration: a survey in areas along the Sanyo Shinkansen Line
 Community response to noise and vibration: a survey in areas along the Sanyo Line Takashi Yano Kumamoto University, Kurokami, 2-39-1, Kumamoto 860-8555, Japan, yano@gpo.kumamoto-u.ac.jp, Takashi Morihara
Community response to noise and vibration: a survey in areas along the Sanyo Line Takashi Yano Kumamoto University, Kurokami, 2-39-1, Kumamoto 860-8555, Japan, yano@gpo.kumamoto-u.ac.jp, Takashi Morihara
Comfort, the Intelligent Home System. Comfort Scene Control Switch
 Comfort, the Intelligent Home System Comfort Scene Control Sitch Introduction...1 Specifications...3 Equipment...3 Part Numbers...3 Identifying the SCS Version...4 Contents...4 Assembly...4 Settings...5
Comfort, the Intelligent Home System Comfort Scene Control Sitch Introduction...1 Specifications...3 Equipment...3 Part Numbers...3 Identifying the SCS Version...4 Contents...4 Assembly...4 Settings...5
Cost-effectiveness of a mass media campaign and a point of sale intervention to prevent the uptake of smoking in children and young people:
 Cost-effectiveness of a mass media campaign and a point of sale intervention to prevent the uptake of smoking in children and young people: Economic modelling report M. Raikou, A. McGuire LSE Health, London
Cost-effectiveness of a mass media campaign and a point of sale intervention to prevent the uptake of smoking in children and young people: Economic modelling report M. Raikou, A. McGuire LSE Health, London
Cigarette Consumption in China ( ) Cigarette Consumption in Poland ( )
 Section C Global Burden Global Smoking Prevalence Source: adapted by CTLT from The Tobacco Atlas. (2006). 2 1 Cigarette Consumption in China (1952 1996) Average Number of Manufactured Cigarettes Smoked
Section C Global Burden Global Smoking Prevalence Source: adapted by CTLT from The Tobacco Atlas. (2006). 2 1 Cigarette Consumption in China (1952 1996) Average Number of Manufactured Cigarettes Smoked
Key words: Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome, Incidence Rate, Geographical Distribution, Temporal Distribution, Japan. METHODS
 doi:10.2188/jea.je2008030 Original Article Monthly Observation of the Number of Patients with Kawasaki Disease and its Incidence Rates in Japan: Chronological and Geographical Observation from Nationwide
doi:10.2188/jea.je2008030 Original Article Monthly Observation of the Number of Patients with Kawasaki Disease and its Incidence Rates in Japan: Chronological and Geographical Observation from Nationwide
Save Our Sievert! Ches Mason BHP Billiton Uranium, 55 Grenfell Street, Adelaide, SA5000, Australia
 Save Our Sievert! Ches Mason BHP Billiton Uranium, 55 Grenfell Street, Adelaide, SA5000, Australia Abstract The protection quantity effective dose was devised by the International Commission on Radiological
Save Our Sievert! Ches Mason BHP Billiton Uranium, 55 Grenfell Street, Adelaide, SA5000, Australia Abstract The protection quantity effective dose was devised by the International Commission on Radiological
Building Capacity for Tobacco Dependence Treatment in Japan. Request for Proposals (RFP) - Background and Rationale
 Building Capacity for Tobacco Dependence Treatment in Japan Request for Proposals (RFP) - Background and Rationale Geographic Scope Japan Application process This application process has two steps: Letters
Building Capacity for Tobacco Dependence Treatment in Japan Request for Proposals (RFP) - Background and Rationale Geographic Scope Japan Application process This application process has two steps: Letters
Changes in Cardiac Output and Stroke Volume
 Brit. Heart J., 1967, 29, 859. Changes in Cardiac Output and Stroke Volume During First Four Months After Cardiac Infarction FRANK NAGER*, MICHAEL THOMAS, AND JOHN SHILLINGFORD From the Medical Research
Brit. Heart J., 1967, 29, 859. Changes in Cardiac Output and Stroke Volume During First Four Months After Cardiac Infarction FRANK NAGER*, MICHAEL THOMAS, AND JOHN SHILLINGFORD From the Medical Research
SYNOPSIS An investigation into the noise levels in a clinical chemistry laboratory has been. 'newer' extension laboratory, are separated by a
 J. clin Path., 1970, 23, 445-449 P. D. GRIFFITHS, R. L. KELL, AND W. TAYLOR From the Departments of Clinical Chemistry and Social and Occupational Medicine, University of Dundee SYNOPSIS An investigation
J. clin Path., 1970, 23, 445-449 P. D. GRIFFITHS, R. L. KELL, AND W. TAYLOR From the Departments of Clinical Chemistry and Social and Occupational Medicine, University of Dundee SYNOPSIS An investigation
Fatigued? Or fit for work? How to tell if your workers are tired enough to make mistakes and how to prevent this happening
 Fatigued? Or fit for ork? Ho to tell if your orkers are tired enough to make mistakes and ho to prevent this happening Safetree Fatigued? Or fit for ork? u 1 Tired orkers are more likely to have accidents
Fatigued? Or fit for ork? Ho to tell if your orkers are tired enough to make mistakes and ho to prevent this happening Safetree Fatigued? Or fit for ork? u 1 Tired orkers are more likely to have accidents
Impact of smoking habit on medical care use and its costs: a prospective observation of National Health Insurance beneficiaries in Japan
 International Epidemiological Association 2001 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 2001;30:616 621 Impact of smoking habit on medical care use and its costs: a prospective observation
International Epidemiological Association 2001 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 2001;30:616 621 Impact of smoking habit on medical care use and its costs: a prospective observation
REINFORCEMENT OF DRINKING BY RUNNING:
 JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR VOLUME 7, NUMBER I JANUARY, 1 964 REINFORCEMENT OF DRINKING BY RUNNING: EFFECT OF FIXED RATIO AND REINFORCEMENT TIME' DAVID PREMACK, ROBERT W. SCHAEFFER2,
JOURNAL OF THE EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF BEHAVIOR VOLUME 7, NUMBER I JANUARY, 1 964 REINFORCEMENT OF DRINKING BY RUNNING: EFFECT OF FIXED RATIO AND REINFORCEMENT TIME' DAVID PREMACK, ROBERT W. SCHAEFFER2,
The Standardized Development Method of the Japanese Guidelines for Cancer Screening
 Original Article Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology Advance Access published March 12, 2008 Jpn J Clin Oncol doi:10.1093/jjco/hyn016 The Standardized Development Method of the Japanese Guidelines for
Original Article Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology Advance Access published March 12, 2008 Jpn J Clin Oncol doi:10.1093/jjco/hyn016 The Standardized Development Method of the Japanese Guidelines for
Chapter 14. Lessons. Bellringer
 Tobacco Tobacco Lessons Lesson 1 Tobacco Products: An Overview Lesson 2 Tobacco s Effects Lesson 3 Tobacco, Disease, and Death Lesson 4 Tobacco and Addiction Lesson 5 Quitting Lesson 6 Why People Use Tobacco
Tobacco Tobacco Lessons Lesson 1 Tobacco Products: An Overview Lesson 2 Tobacco s Effects Lesson 3 Tobacco, Disease, and Death Lesson 4 Tobacco and Addiction Lesson 5 Quitting Lesson 6 Why People Use Tobacco
The cost-effectiveness of raising the legal smoking age in California Ahmad S
 The cost-effectiveness of raising the legal smoking age in California Ahmad S Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each
The cost-effectiveness of raising the legal smoking age in California Ahmad S Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each
Perceived relative harm of e cigarettes and attitudes towards their availability, advertising and use: A longitudinal survey
 Perceived relative harm of e cigarettes and attitudes towards their availability, advertising and use: A longitudinal survey Leonie S Brose a,b,c, Sara C Hitchman b,c, Jamie Brown b,d, Ann McNeill b,c
Perceived relative harm of e cigarettes and attitudes towards their availability, advertising and use: A longitudinal survey Leonie S Brose a,b,c, Sara C Hitchman b,c, Jamie Brown b,d, Ann McNeill b,c
Cost-effectiveness of brief intervention and referral for smoking cessation
 Cost-effectiveness of brief intervention and referral for smoking cessation Revised Draft 20 th January 2006. Steve Parrott Christine Godfrey Paul Kind Centre for Health Economics on behalf of PHRC 1 Contents
Cost-effectiveness of brief intervention and referral for smoking cessation Revised Draft 20 th January 2006. Steve Parrott Christine Godfrey Paul Kind Centre for Health Economics on behalf of PHRC 1 Contents
Smoking and Smoking Cessation in England 2011: Findings from the Smoking Toolkit Study
 Smoking and Smoking Cessation in England 211: Findings from the Smoking Toolkit Study Robert West and Jamie Brown Cancer Research UK Health Behaviour Research Centre University College London robert.west@ucl.ac.uk
Smoking and Smoking Cessation in England 211: Findings from the Smoking Toolkit Study Robert West and Jamie Brown Cancer Research UK Health Behaviour Research Centre University College London robert.west@ucl.ac.uk
BASIC SKILLS FOR WORKING WITH SMOKERS
 BASIC SKILLS FOR WORKING WITH SMOKERS Course Description Goals and Learning Objectives 55 Lave Ave No, Worcester, MA 01655 www.umassmed.edu/tobacco 2016 Basic Skills for Working with Smokers 1 Table of
BASIC SKILLS FOR WORKING WITH SMOKERS Course Description Goals and Learning Objectives 55 Lave Ave No, Worcester, MA 01655 www.umassmed.edu/tobacco 2016 Basic Skills for Working with Smokers 1 Table of
There has been a growing interest in lung cancer in neversmokers,
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE,, and Time of Diagnosis Are Important Factors for Prognosis Analysis of 1499 Never-Smokers with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan Tomoya Kawaguchi, MD,* Minoru Takada, MD,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE,, and Time of Diagnosis Are Important Factors for Prognosis Analysis of 1499 Never-Smokers with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Japan Tomoya Kawaguchi, MD,* Minoru Takada, MD,*
Effects of smoking and smoking cessation on productivity in China
 Effects of smoking and smoking cessation on productivity in China Team *Hong Wang; MD, PhD **Heng-Fu Zou; PhD I. Introduction *: Yale University; **: World Bank 1. Aim of Project We will study smoking
Effects of smoking and smoking cessation on productivity in China Team *Hong Wang; MD, PhD **Heng-Fu Zou; PhD I. Introduction *: Yale University; **: World Bank 1. Aim of Project We will study smoking
New Jersey s Comprehensive Tobacco Control Program: Importance of Sustained Funding
 New Jersey s Comprehensive Tobacco Control Program: Importance of Sustained Funding History of Tobacco Control Funding Tobacco use is the leading preventable cause of death in the U.S., killing more than
New Jersey s Comprehensive Tobacco Control Program: Importance of Sustained Funding History of Tobacco Control Funding Tobacco use is the leading preventable cause of death in the U.S., killing more than
Body mass decrease after initial gain following smoking cessation
 International Epidemiological Association 1998 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 1998;27:984 988 Body mass decrease after initial gain following smoking cessation Tetsuya Mizoue,
International Epidemiological Association 1998 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 1998;27:984 988 Body mass decrease after initial gain following smoking cessation Tetsuya Mizoue,
The Sesim-LEV model. Lisa Brouwers Pontus Johansson Karin Mossler Nils Janlöv Anders Ekholm. Ministry of Health and Social Affairs
 The Sesim-LEV model Lisa Brouwers Pontus Johansson Karin Mossler Nils Janlöv Anders Ekholm Ministry of Health and Social Affairs Outline Project aims Model Data Health in SESIM-LEV Results Impact Most
The Sesim-LEV model Lisa Brouwers Pontus Johansson Karin Mossler Nils Janlöv Anders Ekholm Ministry of Health and Social Affairs Outline Project aims Model Data Health in SESIM-LEV Results Impact Most
Decrease in Risk of Lung Cancer Death in Males after Smoking Cessation by Age at Quitting: Findings from the JACC Study
 Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 92, 821 828, August 2001 Decrease in Risk of Lung Cancer Death in Males after Smoking Cessation by Age at Quitting: Findings from the JACC Study Kenji Wakai, 1, 8 Nao Seki, 3 Akiko
Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 92, 821 828, August 2001 Decrease in Risk of Lung Cancer Death in Males after Smoking Cessation by Age at Quitting: Findings from the JACC Study Kenji Wakai, 1, 8 Nao Seki, 3 Akiko
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association Sociodemographic characteristics of New Zealand adult smokers, ex-smokers, and non-smokers: results from the 2006 Census Sharon
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association Sociodemographic characteristics of New Zealand adult smokers, ex-smokers, and non-smokers: results from the 2006 Census Sharon
Psychosocial Correlates of Youth Smoking in Mississippi
 Psychosocial Correlates of Youth Smoking in Mississippi Robert McMillen Nell Baldwin SSRC Social Science Research Center Mississippi State University Background Increasing knowledge about the dangers of
Psychosocial Correlates of Youth Smoking in Mississippi Robert McMillen Nell Baldwin SSRC Social Science Research Center Mississippi State University Background Increasing knowledge about the dangers of
Study of cigarette sales in the United States Ge Cheng1, a,
 2nd International Conference on Economics, Management Engineering and Education Technology (ICEMEET 2016) 1Department Study of cigarette sales in the United States Ge Cheng1, a, of pure mathematics and
2nd International Conference on Economics, Management Engineering and Education Technology (ICEMEET 2016) 1Department Study of cigarette sales in the United States Ge Cheng1, a, of pure mathematics and
Leukemia: Lessons from the Japanese Experience
 Leukemia: Lessons from the Japanese Experience STUART C. FINCH Cooper Hospital, Camden, New Jersey, USA Key Words. Leukemia. Japan Life Span Study Atomic bomb. Radiation ABSTRACT Probably more has been
Leukemia: Lessons from the Japanese Experience STUART C. FINCH Cooper Hospital, Camden, New Jersey, USA Key Words. Leukemia. Japan Life Span Study Atomic bomb. Radiation ABSTRACT Probably more has been
S ocial status and health are strongly related and smoking
 604 RESEARCH REPORT Impact of smoking on the social gradient in health expectancy in Denmark Henrik Brønnum-Hansen, Knud Juel... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Mr H Brønnum-Hansen,
604 RESEARCH REPORT Impact of smoking on the social gradient in health expectancy in Denmark Henrik Brønnum-Hansen, Knud Juel... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Mr H Brønnum-Hansen,
Impact of Sterilization on Fertility in Southern India
 Impact of Sterilization on Fertility in Southern India Background The first two international conferences on population were mainly focused on the need for curtailing rapid population growth by placing
Impact of Sterilization on Fertility in Southern India Background The first two international conferences on population were mainly focused on the need for curtailing rapid population growth by placing
Heat Disorder Information System for Japan in 2012.
 Heat Disorder Information System for Japan in 1. Michihiko Tonouchi (*1), Masaji Ono (*),Koji Murayama (*1) *1 Japan Meteorological Business Support Center, Japan * National Institute for Environmental
Heat Disorder Information System for Japan in 1. Michihiko Tonouchi (*1), Masaji Ono (*),Koji Murayama (*1) *1 Japan Meteorological Business Support Center, Japan * National Institute for Environmental
Passive smoking by pregnant women and fetal growth
 Division of Epidemiology, Aichi Cancer Centre Research Institute, 1-1 Kanokoden, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya 464, Japan H Ogawa S Tominaga Aichi Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, Nagoya, Japan K Hori
Division of Epidemiology, Aichi Cancer Centre Research Institute, 1-1 Kanokoden, Chikusa-ku, Nagoya 464, Japan H Ogawa S Tominaga Aichi Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, Nagoya, Japan K Hori
Prevent Chronic Diseases Through Tobacco Control
 10 Prevent Chronic Diseases Through Tobacco Control Situation It has been scientifically proven that tobacco smoking increases the risk of many diseases such as cancer (including lung cancer), myocardial
10 Prevent Chronic Diseases Through Tobacco Control Situation It has been scientifically proven that tobacco smoking increases the risk of many diseases such as cancer (including lung cancer), myocardial
IDENTIFICATION OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN FROM GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID IN SYSTEMIC DISEASE
 IDENTIFICATION OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN FROM GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID IN SYSTEMIC DISEASE Amelia S * Department of Periodontology, Faculty of Dental Medicine University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Grigore
IDENTIFICATION OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN FROM GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID IN SYSTEMIC DISEASE Amelia S * Department of Periodontology, Faculty of Dental Medicine University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Grigore
The ability of different strains of rats to acquire a visual nonmatching-to-sample task
 Psychobiology 1996. 24 (1). 44-48 The ability of different strains of rats to acquire a visual nonmatching-to-sample task JOHN P. AGGLETON University of Wales, CoUege of Cardiff, Cardiff, Wales Rats offour
Psychobiology 1996. 24 (1). 44-48 The ability of different strains of rats to acquire a visual nonmatching-to-sample task JOHN P. AGGLETON University of Wales, CoUege of Cardiff, Cardiff, Wales Rats offour
The Role of Herd Immunity in Control of Measles
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 55 (1982), 351-36 The Role of Herd Immunity in Control of Measles FRANCIS L. BLACK, Ph.D. Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, Yale University School of
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 55 (1982), 351-36 The Role of Herd Immunity in Control of Measles FRANCIS L. BLACK, Ph.D. Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, Yale University School of
HAEMOLYTIC DISEASE OF THE NEWBORN
 SERUM ENZYME CTVTY N PREMTURTY ND N HEMOLYTC DSESE OF THE NEWBORN BY M. BREND MORRS and J. KNG From the Paediatric and Pathology Departments, North Lonsdale Hospital, the Barro and Furness Hospital Group
SERUM ENZYME CTVTY N PREMTURTY ND N HEMOLYTC DSESE OF THE NEWBORN BY M. BREND MORRS and J. KNG From the Paediatric and Pathology Departments, North Lonsdale Hospital, the Barro and Furness Hospital Group
BASIC SKILLS FOR WORKING WITH SMOKERS
 BASIC SKILLS FOR WORKING WITH SMOKERS Course Description Goals and Learning Objectives 368 Plantation Street, Worcester, MA 01605 www.umassmed.edu/tobacco 2018 Basic Skills for Working with Smokers 1 Table
BASIC SKILLS FOR WORKING WITH SMOKERS Course Description Goals and Learning Objectives 368 Plantation Street, Worcester, MA 01605 www.umassmed.edu/tobacco 2018 Basic Skills for Working with Smokers 1 Table
Public Health Unit Tobacco Use Cessation Services
 March 2017 Public Health Unit Tobacco Use Cessation Services Under the Ontario Public Health Standards, 1 Public Health Units (PHUs) are required to do a number of activities related to tobacco use cessation
March 2017 Public Health Unit Tobacco Use Cessation Services Under the Ontario Public Health Standards, 1 Public Health Units (PHUs) are required to do a number of activities related to tobacco use cessation
The Economics of Smoking
 The Economics of Smoking One of the potential problems (from an economic perspective) with smoking is that there may be an externality in consumption, so there may be difference between the private and
The Economics of Smoking One of the potential problems (from an economic perspective) with smoking is that there may be an externality in consumption, so there may be difference between the private and
A revision of the number of radon-related lung cancers in Ireland: preliminary results
 A revision of the number of radon-related lung cancers in Ireland: preliminary results Paul M Walsh National Cancer Registry (NCRI) (in collaboration with EPA & others) Background / Rationale Radon is
A revision of the number of radon-related lung cancers in Ireland: preliminary results Paul M Walsh National Cancer Registry (NCRI) (in collaboration with EPA & others) Background / Rationale Radon is
Serial learning, interitem associations, phrasing cues, interference, overshadowing, chunking, memory, and extinction
 Animal Learning & Behavior 1984,12 (1), 7-20 Serial learning, interitem associations, phrasing cues, interference, overshadoing, chunking, memory, and extinction E. J. CAPALDI, DONNA R. VERRY, TIMOTHY
Animal Learning & Behavior 1984,12 (1), 7-20 Serial learning, interitem associations, phrasing cues, interference, overshadoing, chunking, memory, and extinction E. J. CAPALDI, DONNA R. VERRY, TIMOTHY
Query Length Impact on Misuse Detection in Information Retrieval Systems
 uery Length Impact on Misuse Detection in Information Retrieval Systems Nazli Goharian and Ling Ma Information Retrieval Laboratory, Illinois Institute of Technology {goharian}@ir.iit.edu BSTRCT Misuse
uery Length Impact on Misuse Detection in Information Retrieval Systems Nazli Goharian and Ling Ma Information Retrieval Laboratory, Illinois Institute of Technology {goharian}@ir.iit.edu BSTRCT Misuse
TOBACCO CONTROL ECONOMICS TOBACCO FREE INITIATIVE PREVENTION OF NONCOMMUNICABLE DISEASES
 Page 1 1. Smoking prevalence The rate of smoking tends to increase with development reflecting higher prevalence of cigarette use among women as incomes increase. The rate of smoking is relatively high
Page 1 1. Smoking prevalence The rate of smoking tends to increase with development reflecting higher prevalence of cigarette use among women as incomes increase. The rate of smoking is relatively high
Alveograph Algorithms to Predict Functional Properties of Wheat in Bread and Cookie Baking'
 Alveograph Algorithms to Predict Functional Properties of Wheat in Bread and Cookie Baking' A. BETTGE, 2 G. L. RUBENTHALER, 2 and Y. POMERANZ 2 ABSTRACT Cereal Chem. 66(2):81-86 A total of 73 heat samples
Alveograph Algorithms to Predict Functional Properties of Wheat in Bread and Cookie Baking' A. BETTGE, 2 G. L. RUBENTHALER, 2 and Y. POMERANZ 2 ABSTRACT Cereal Chem. 66(2):81-86 A total of 73 heat samples
Minnesota Postsecondary Institutions Tobacco-use Policies and Changes in Student Tobacco-use Rates ( )
 Minnesota Postsecondary Institutions Tobacco-use Policies and Changes in Student Tobacco-use Rates (2007 2013) Boynton Health Service Minnesota Postsecondary Institutions Tobacco-use Policies and Changes
Minnesota Postsecondary Institutions Tobacco-use Policies and Changes in Student Tobacco-use Rates (2007 2013) Boynton Health Service Minnesota Postsecondary Institutions Tobacco-use Policies and Changes
Joint Impact of Smoking and Hypertension on Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in Japan: NIPPON DATA80, a 19-Year Follow-Up
 1169 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.12 p.1169-1175 Joint Impact of Smoking and Hypertension on Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in Japan: NIPPON DATA80, a 19-Year Follow-Up
1169 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.12 p.1169-1175 Joint Impact of Smoking and Hypertension on Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in Japan: NIPPON DATA80, a 19-Year Follow-Up
Executive Summary. Context. Guideline Origins
 Executive Summary Context In America today, tobacco stands out as the agent most responsible for avoidable illness and death. Millions of Americans consume this toxin on a daily basis. Its use brings premature
Executive Summary Context In America today, tobacco stands out as the agent most responsible for avoidable illness and death. Millions of Americans consume this toxin on a daily basis. Its use brings premature
Use of e-cigarettes (vapourisers) among adults in Great Britain
 May 2017 Use of e-cigarettes (vapourisers) among adults in Great Britain Summary of findings Level of use (page 3) An estimated 2.9 million adults in Great Britain currently use e-cigarettes (vape) up
May 2017 Use of e-cigarettes (vapourisers) among adults in Great Britain Summary of findings Level of use (page 3) An estimated 2.9 million adults in Great Britain currently use e-cigarettes (vape) up
D. Hilton. Keywords Epidemiological methods, aging, prevalence.
 Computational Methods in Official Statistics with an Example on Calculating and Predicting Diabetes Mellitus [DM] Prevalence in Different Age Groups within Australia in Future Years, in Light of the Aging
Computational Methods in Official Statistics with an Example on Calculating and Predicting Diabetes Mellitus [DM] Prevalence in Different Age Groups within Australia in Future Years, in Light of the Aging
Human taste response as a function of locus of stimulation on the tongue and soft palate*
 Perception & Psychophysics 1974, Vol. 16,No.1, 169-174 Human taste response as a function of locus of stimulation on the tongue and soft palate* VIRGINIA B. COLLINGSt University ofpittsburgh, Pittsburgh,
Perception & Psychophysics 1974, Vol. 16,No.1, 169-174 Human taste response as a function of locus of stimulation on the tongue and soft palate* VIRGINIA B. COLLINGSt University ofpittsburgh, Pittsburgh,
Economic Analysis of Interventions for Smoking Cessation Aimed at Pregnant Women
 Y O R K Health Economics C O N S O R T I U M NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Economic Analysis of Interventions for Smoking Cessation Aimed at Pregnant Women Supplementary Report
Y O R K Health Economics C O N S O R T I U M NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Economic Analysis of Interventions for Smoking Cessation Aimed at Pregnant Women Supplementary Report
