Chapter 3. Circulating cell death products predict clinical outcome of colorectal cancer patients
|
|
|
- Virgil Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Circulating cell death products predict clinical outcome of colorectal cancer patients Pim J. Koelink, Daniel W. Hommes, Cornelis B.H.W. Lamers, Hein W. Verspaget Department of Gastroenterology-Hepatology Leiden University Medical Centre, Leiden, The Netherlands. BMC Cancer 29 ;9:88
2 Abstract Tumour cell death generates products that can be measured in the circulation of cancer patients. CK18-Asp396 (M3 antigen) is a caspase-degraded product of cytokeratin 18 (CK18), produced by apoptotic epithelial cells, and is elevated in breast and lung cancer patients. We determined the M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in plasma of 49 colorectal cancer (CRC) patients, before and after surgical resection of the tumor, by ELISA. Correlations with patient and tumour characteristics were determined by Kruskal-Wallis H and Mann Whitney U tests. Disease-free survival was determined using Kaplan-Meier methodology with Log Rank tests, and univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard analysis. Plasma M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in CRC patients were related to disease stage and tumour diameter, and were predictive of disease-free survival, independent of disease-stage, with hazard ratios (HR) of patients with high levels () compared to those with low levels () of 3.58 (95% CI: ) and 3.58 (95% CI: ), respectively. The M3/CK18 ratio, which decreased with tumour progression, was also predictive of disease-free survival, with a low ratio () associated with worse diseasefree survival: HR 2.78 (95% CI: ). Remarkably, the plasma M3 antigen and total CK18 levels after surgical removal of the tumour were also predictive of disease-free survival, with patients with high levels having a HR of 3.78 (95% CI: ) and 4.12 (95% CI: ), respectively, indicating that these parameters also can be used to monitor patients after surgery. M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in the circulation of CRC patients are predictive of tumour progression and prognosis and might be helpful for treatment selection and monitoring of these patients. 48
3 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients Introduction Death of tumour cells generates detectable protein products in the patient s circulation, which may be used for cancer diagnostics and/or monitoring of therapy efficacy 1. Apoptosis is a form of regulated cell death that is characterized by specific structural changes, mediated by proteases of the caspase family 2. Caspase activity itself or the presence of specific degradation products can be used for the detection of tumour cell apoptosis. The M3 antibody detects a caspase-degraded product, CK18-Asp396 (M3 antigen), of the important cytoskeletal protein cytokeratin 18 (CK18) of epithelial cells, which is expressed by most carcinomas, including those of breast, prostate, lung and colon 3. Immunohistochemistry with the M3 antibody has been shown to be as specific as the morphological detection or TdT-mediated dutp-biotin nick end-labelling (TUNEL) technique to establish of apoptosis in tissue 3-5. Importantly, the levels of M3 antigen can also be determined in the circulation by a specific ELISA, allowing the detection of tumour cell apoptosis in the serum/plasma of cancer patients 6, 7. However, M3 antigen detection in the plasma is not tumour specific, healthy controls have background levels, due to apoptosis of normal epithelial cells. Circulating M3 antigen levels were found to be elevated in patients with lung and breast cancer, and were predictive to survival or recurrence outcome 8, 9. In addition, circulating M3 antigen levels increased shortly after chemotherapy in hormone-refractory prostate cancer and lung cancer, implying that this was a result of chemotherapy-induced tumour cell apoptosis During non-programmed cell death, i.e., necrosis, intact CK18 of epithelial tumour cells is released into the circulation, which can be measured by a total CK18 ELISA, that also detects the M3 antigen 11. Cytokeratins and their cleaved forms are secreted in aggregates into the circulation and both M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in human plasma samples have a long-term stability when stored at -8 C 12. The ratio between M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in the circulation depends on the balance between caspase-mediated apoptosis and non-proteolytic necrosis. This balance might be an important factor and denominator to select patient for treatment that induces necrosis vs treatment that increases apoptosis. For instance, docetaxel treatment increased levels of M3 antigen in the serum of breast cancer patients, indicating apoptotic death of tumour cells, while cylcophospamide/ epirubicin/5-fluorouracil treatment increased total CK18 levels, indicating necrotic death of tumour cells 13. The increase of total CK18 serum levels correlated to the clinical therapy response 13. The M3/CK18 ratio was shown to be decreased, i.e., more necrosis over apoptosis, in endometrial cancer stage III/IV when 49
4 compared with stage II, indicating less apoptosis and/or more necrosis during tumour progression 11. In the present study, we determined the M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in plasma of 49 colorectal cancer (CRC) patients and found these levels to predict clinical outcome of these patients. Material&Methods Patients, plasma and tissue collection The study population consisted of 49 CRC patients that did not receive pre-operative treatment and had been admitted to the Leiden University Medical Centre for surgical resection. Citrate plasma samples were collected, with informed consent of the patients, before resection (P1, pre-operative), shortly after surgical resection (P2) and about 4.5 months after the operation (P3, post-operative), when feasible. Citrate plasma samples were collected before 9. a.m. under fasting conditions and stored at -7 C. Fresh tissue was collected from the surgical specimens immediately after resection, and attention was paid to collect material from the non-necrotic part of the tumour. Normal mucosa samples were obtained at a distance of approximately 1 cm from the tumour. Tissue samples were also frozen and stored at -7 C until use. Macroscopic (diameter and localization of the tumor) as well as microscopic data were assessed, including classification according to the WHO. Colonic cancers were classified as being proximal or distal to, and including, the splenic flexure. Follow-up information, including post-operative adjuvant therapy, was available for a period up to 8 years. The study was performed according to the guidelines of the Medical Ethics Committee of the Leiden University Medical Centre in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration. Tissue homogenization and protein determination Frozen tissue specimens were weighed and homogenized on ice for 2 minutes in 1 ml Tris-HCl,.1% Tween 8, ph 7.5 per 6 mg tissue using a Potter device (B Braun, Germany), and centrifuged twice at 8 x g for 2.5 min at 4 C. Protein content was measured according to Lowry et al. and standardized by bovine serum albumin 14. M3 antigen and total CK18 detection For the detection of M3 antigen and total CK18 in the plasma of CRC patients commercially available immunosorbent sandwich ELISAs were used, according to 5
5 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients manufacturer s instructions (M3-apoptosense ELISA and M65 ELISA, Peviva, Sweden). For the determination of M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in tissues 1 µg/µl protein homogenates were diluted up to 1 times, dependent on antigen levels. The antigen levels in the plasma were expressed as U/L and antigen levels in tumour tissue or normal mucosa were expressed as U/mg protein. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed with Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) statistical software (version 12. for Windows, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL). For relations between M3 antigen or total CK18 antigen levels in P1, P2 and P3 Wilcoxon signed-rank tests were used. For the relation with patient characteristics non-parametric Mann Whitney U tests were used, because the study parameters did not follow a normal distribution. Disease-free survival was estimated using Kaplan-Meier methodology with cancer-related death and local or distant recurrence as events, dichotomized for M3 antigen, total CK18 or M3/CK18 ratio levels, and Log Rank tests. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard models were used to explore the association of markers with disease-free survival. Kaplan Meier graphs were made with Graphpad Prism (version 4., Graphpad Prism Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) software. Results M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in plasma of CRC patients Overall the plasma M3 antigen and total CK18 levels correlated very well with each other, in plasma before, as well as shortly and longer after tumour resection (overall Spearman correlation coefficient Rho=.64, P<.1). The M3 antigen and total CK18 plasma values increased shortly after surgical resection of the tumour and dropped to about pre-operative values longer after surgery (Table 1). 51
6 Table 1: M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in plasma of CRC patients. P1 (n=49) P2 (n=2) P3 (n=28) Mean time to operation (days, range) -13 (-5-) +2 (7-6) +137 (82-364) M3 antigen level (U/l) Median (IQR) 59.1 ( ) 74.8 ( ) 55.6 ( ) P-value.2 vs P1.11 vs P2 Total CK18 level (U/l) Median (IQR) 26.5 ( ) 38.1 ( ) ( ) P-value.8 vs P1.5 vs P2 P1=pre-operative plasma, P2=post-operative plasma shortly after operation, and P3=post-operative plasma longer after operation. Wilxocon signed-rank tests were used to compare paired observations. P-values.5 were considered significant, shown in bold. Correlation pre-operative plasma M3 antigen and CK18 levels with clinico-pathological patient parameters The clinico-pathological parameters of the 49 CRC patients are shown in Table 2. M3 antigen and total CK18 plasma levels did not correlate with localization of the tumour, also not within the patients with only colonic tumours (not shown). Male and female CRC patients had similar plasma M3 antigen and total CK18 levels, and these were not correlated with patients age. The M3 antigen and total CK18 plasma values were higher in patients with more advanced tumour stages (Figure 1A and B, P=.1 and P=.5, respectively). M3 antigen levels correlated with the diameter of the tumour (Spearman correlation coefficient Rho=.35, P=.2). M3 antigen and total CK18 levels were significantly higher in the eight patients with a Dukes D tumour in which the tumour was not (or not curatively) resected. 52
7 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients Table 2: Clinico-pathological characteristics and pre-operative plasma M3 and total CK18 levels. Patient and tumour No of patients (%) Total n=49 Plasma M3 antigen (U/l) Median (IQR) P-value Total CK18 plasma level (U/l) Median (IQR) P-value characteristics Gender Male Female 31 (63) 18 (37) 61.1 ( ) 5.5 ( ) 26.5 ( ) ( ) Age # (51) 24 (49) 59.1 ( ) 55.6 ( ) ( ) ( ) Location Colon Rectum 38 (78) 11 (22) 59.4 ( ) 56.4 ( ) ( ) 28.4 ( ) Dukes stage.1.5 A/B C/D 27 (55) 22 (45) 49.3 ( ) 69.2 ( ) 235. ( ) ( ) WHO classification Adenocarcinoom Mucinous carcinoom 45 (92) 4 (8) 59.1 ( ) 77.8 ( ) ( ) ( ) Tumour diameter * (55) 2 (45) 49.1 ( ) 64.7 ( ) ( ) ( ) Surgery.1 <.1 Yes, curative resection No, or palliative 41 (84) 8 (16) 51.1 ( ) ( ) 235. ( ) ( ) # Median 68 years, range * Median 4.5 cm, range (some values missing). P-values were calculated with Mann Whitney and Kruskall-Wallis tests and were considered significant when.5, shown in bold. Pre-operative plasma M3 antigen and CK18 levels and disease-free survival The disease-free survival of the patients with low M3 antigen plasma levels before resection () was significantly better compared with patients with high M3 antigen plasma levels (Figure 1C). This was also the case for total CK18 plasma levels (Figure 1D). When the patients were subdivided in early and advanced tumours, Dukes A/B stage carcinoma (n=27) and C/D stage carcinoma (n=22), the plasma M3 antigen level was also prognostic within these subgroups (Figure 1E and F). Calculation of hazard ratios as estimates of relative risk of death or disease recurrence is shown in Table 3. Tumour progression, M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in plasma before surgery were predictive of recurrence or death. 53
8 Pre-operative plasma M3 antigen (U/L) C A Pre-operative plasma total C K 18 (U/L) P=.1 P= A/B C/D A/B C/D n=27 n=22 n=27 n=22 Dukes' stage Dukes' stage D B 4 D isease-free su rvival % E D isease-free survival % M3 antigen M3 antigen 4 2 All patients Pre-operative plasma Log Rank 1.84 P= M3 antigen M3 antigen 4 Dukes A/B Pre-operative plasma 2 Log Rank 4.4 P= D isease-free su rvival % F D isease-free survival % 1 8 Total CK18 6 Total CK18 4 All patients Pre-operative plasma 2 Log Rank 5.91 P= Dukes C/D Pre-oprative plasma Log Rank 5.89 P= Figure 1: Pre-operative plasma M3 antigen and total CK18 levels, and survival. M3 antigen M3 antigen M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in pre-operative plasma of all CRC patients with a Dukes A/B vs Dukes C/D stage carcinoma (P1, A and B). Box plots with line indicating median value, box indicating IQR and bars indicating the range. Kaplan Meier disease-free survival curves of all CRC patients, groups divided upon median values of M3 antigen (C) and total CK18 levels (D) in pre-operative plasma (P1). Patients were also subdivided in Dukes A/B (E, n=22) and Dukes C/D (F, n=27) stage carcinoma. 54
9 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients Table 3: Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis of disease-free survival. Univariate Multivariate Patient and tumour characteristics Hazard Ratio (95% Hazard Ratio (95% confidence interval) P-value confidence interval) P-value Gender.27 Female Male 1.79 ( ) Age (median 68, range 31-84) ( ) Location.32 Colon Rectum.54 ( ) Dukes stage <.1 < A/B 1(ref) C/D 8.21 ( ) ( ) Tumour diameter ( ) WHO classification.82 Adenocarcinoom Mucinous carcinoom.79 ( ) M3 antigen plasma level P ( ) 3.58 ( ) Total CK18 plasma level P ( ) 3.58 ( ) M3/CK18 ratio P ( ) 2.78 ( ) M3 antigen plasma level P ( ) 3.78 ( ) Total CK18 plasma level P ( ) 4.12 ( ) M3/CK18 ratio P ( ) 3.96 ( ) Multivariate Cox hazards analysis of pre-operative or post-operative M3 antigen, total CK18 antigen level or M3/CK18 ratios combined with Dukes stage. P-values.5 were considered significant, shown in bold. The M3/CK18 ratio indicates the balance between caspase-mediated apoptosis and non-proteolytic necrosis. M3/CK18 ratios of pre-operative plasmas of CRC patients were calculated and a large variety was observed in different patients with a median ratio of.2 55
10 (IQR: ). The M3/CK18 ratio tended to decrease with increasing Dukes stage (Figure 2A), indicating more necrosis over apoptosis, during tumour progression. The disease-free survival of patients with high ratios tended to be better when compared with those with lower ratios (Figure 2B). This relation was particularly present in patients with Dukes C/D stage carcinomas (Figure 2C), in contrast to patients with Dukes A/B stage carcinomas where no such relation was found (Figure 2D). Pre-operative plasma M3/CK18 ratio C Disease-free survival % A A B C D n=5 n=22 n=14 n=8 D ukes' stage Dukes C/D Pre-operative plasma Log Rank 6.63 P=.1 M3/CK18 ratio M3/CK18 ratio median D isease-free su rvival % Disease-free survival % B 4 All patients Pre-operative plasma 2 Log Rank 3.8 P= D M3/CK18 ratio M3/CK18 ratio median M3/CK18 ratio median M3/CK18 ratio Dukes A/B Pre-operative plasma Log Rank 1.5 P= Figure 2: Pre-operative plasma M3/CK18 ratios and survival. Pre-operative plasma M3/CK18 ratios decrease with increasing Dukes stage (P1, A). Box plots with line indicating median value, box indicating IQR and bars indicating the range. Kaplan Meier disease-free survival curves of all CRC patients, groups divided upon median pre-operative plasma M3/CK18 ratios (B). Patients were also subdivided in Dukes C/D (C, n=22) and Dukes A/B stage carcinoma (D, n=27) 56
11 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients M3 antigen, CK18 levels and M3 antigen/ck18 ratios in post-operative plasma Post-operative plasma M3 antigen levels of patients about 4.5 months after resection of Dukes C/D stage carcinomas were also somewhat, but not significantly, higher compared with patients with Dukes A/B stage carcinomas (Figure 3A). The total CK18 plasma levels, however, were significantly higher in Dukes C/D tumour patients compared with Dukes A/B tumour patients (Figure 3B). High M3 antigen levels as well as total CK18 plasma levels after tumour resection were associated with worse disease-free survival (Figure 3C and D), also found in the univariate Cox hazard analysis (Table 3). M3/CK18 ratios in postoperative patients plasma were in a similar range as in the patients plasma before surgery, and also tended to decrease with increasing Dukes stage, i.e., significantly higher in Dukes A/B compared with Dukes C/D patients (Figure 3E). The disease-free survival was again better in patients with high post-operative plasma M3/CK18 ratios (Figure 3F). In 8 of the 28 patients post-operative treatment with radiotherapy and in only one patient treatment with combined radio-chemotherapy was started before collection of the 4.5 months plasma samples. There were no significant differences in post-operative plasma M3 antigen and total CK18 levels, and in M3/CK18 ratios in patients receiving post-operative adjuvant therapy compared to the patients without adjuvant therapy (Figure 4). Multivariate Cox regression analysis A multivariate Cox proportional hazards model of disease-free survival was used to evaluate whether the plasma M3 antigen and total CK18 levels showed independent prognostic significance from tumour staging. These analyses showed that patients with high pre-operative M3 antigen plasma levels have a 3.6 times increased relative risk of CRCrelated-death or disease recurrence (Table 3), independent of Dukes staging. For total CK18 levels, this was quite similar although just not significant. Patients with low pre-operative plasma M3/CK18 ratios had a 2.8 times increased risk to develop recurrence or death. Postoperative M3 antigen, total CK18 and M3/CK18 ratio levels all had similar prognostic significance, although not significant (Table 3). 57
12 Post-operative plasm a M 3 antigen (U/L) C D isease-free su rvival % E A P=.11 M3 antigen M3 antigen 4 All patients 2 Post-operative plasma Log Rank 4.48 P= Post-operative plasm a M 3/CK18 ratio P=.46 Post-operative plasm a total CK18 (U/L) D isease-free su rvival % Disease-free survival % P=.3 A/B C/D A/B C/D n=17 n=11 n=17 n=11 Dukes' stage Dukes' stage A/B C/D n=17 n=11 Dukes' stage D B 5 Total CK18 Total CK18 4 All patients 2 Post-operative plasma Log Rank 4.44 P= M3/CK18 ratio M3/CK18 ratio median 4 All patients Post-operative plasma 2 Log Rank 5.24 P= Figure 3: Post-operative M3 antigen, total CK18 and M3/CK18 ratios, and survival. Post-operative (P3) M3 antigen and total CK18 levels of CRC patients with a Dukes A/B vs Dukes C/D stage carcinoma (A and B). Box plots with line indicating median value, box indicating IQR and bars indicating the range. Kaplan Meier disease-free survival curves of all CRC patients, groups divided upon median postoperative M3 antigen (C, n=28) and total CK18 levels (D, n=28). Plasma M3/CK18 ratios were decreased in patients Dukes C/D vs Dukes A/B (E). Kaplan Meier disease-free survival curves of CRC patients, groups divided upon median post-operative plasma M3/CK18 ratios (F, n=28). F 58
13 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients Correlation tumour and plasma M3 antigen Corresponding CRC tissue was obtained in 4 cases. M3 antigen levels were significantly (P=.5) higher in tumor tissue when compared with normal adjacent tissue with a median value of 2.1 (IQR:.3-7.7, n=4) vs 1.8 (IQR:.1-4.2, n=36) U/mg, respectively. Tumour M3 antigen, total CK18 levels and M3/CK18 ratios were only found to correlate with tumour location, with rectal tumours having higher levels (Table 4). Surprisingly, M3 antigen plasma levels showed a tendency to inversely correlate with the M3 antigen level of the tumour (Rho=-.37, P=.54). Tumour M3 antigen, total CK18 levels and M3/CK18 ratios were found to be not prognostic for disease-free survival (Figure 5). Table 4: Clinico-pathological characteristics and tumour M3, total CK18 and M3/CK18 ratios. Patient and tumour characteristics No of patients (%) Total n=4 M3 antigen level (U/mg) Median (IQR) P- value Total CK18 level (U/mg) Median (IQR) P- value M3 /CK18 x 1 Median (IQR) P- value Gender Male Female (.2-7.7) 1.3 (.2-1.3) 23. ( ) 159. ( ) 1.9 (.3-3.7) 1.7 (.2-3.6) Age# (.3-6.1) 2.2 (.2-9.7) 165. ( ) ( ) 1.8 (.5-3.4) 2.2 (.2-3.8) Location Colon Rectum (.2-5.7) 12.7 ( ) 147. ( ) ( ) 1.4 (.2-2.4) 3.7 ( ) Dukes stage A/B C/D (.3-9.7) 1.3 (.1-5.9) ( ) ( ) 1.8 (.2-3.4) 2. (.4-3.8) WHO classification Adenocarcinoom Mucinous carcinoom (.3-7.7) ( ) (.3-3.4) 1.7 Tumour diameter* (.3-1.3) 1.3 (.1-5.7) 23. ( ) 154. ( ) 2.3 (.3-3.9) 1.6 (.2-2.3) Clinico-pathological characteristics and tumour M3 antigen, total CK18 and M3/CK18 ratios. P-values were calculated with Mann Whitney and Kruskall-Wallis tests and were considered significant when.5, shown in bold. # median 68, range 31-84), * median 4.5, range (some values missing). 59
14 A 4 B 25 Post-operativ e plasma M3 antigen (U/L) P=.49 Post-operative plasma total CK18 (U/L) P=.81 C Post-operativ e plasma M3/CK18 ratio non-treated treated non-treated treated n=19 n=9 n=19 n=9 P=.49. non-treated treated n=19 n=9 Figure 4: Post-operative therapy and post-operative plasma M3, total CK18 and M3/CK18 ratios. Post-operative plasma M3 antigen (A), total CK18 (B) and M3/CK18 ratios (C) in plasma of the CRC patients treated with adjuvant therapy (n=9) vs non-treated patients (n=19). Box plots with line indicating median value, box indicating IQR and bars indicating the range. 6
15 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients D isease-free survival (%) D isease-free survival (%) Tumour M3 antigen Log Rank:.2 P= Tumour M3/CK18 ratio Log Rank:.3 P= D isease-free survival (%) Tumour total CK18 Log Rank:.4 P= <m edian >m edian Figure 5: Tumour M3 antigen, total CK18 levels or M3/CK18 ratios and disease-free survival. Kaplan Meier disease-free survival curves of CRC patients, groups divided upon median tumour M3 antigen, total CK18 levels or M3/CK18 ratios. All n=4. Discussion In the present study we found M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in plasma from CRC patients to be related to patient and tumour characteristics, to change in relation to tumour resection, and to be a predictor for disease-free survival. The observation that the death of tumour cells generates detectable products in the circulation of cancer patients is interesting for diagnostics purposes and monitoring therapy that induces tumour cell death. Cytokeratins are abundantly present in epithelial cells and their expression is usually retained or even increased after oncogenic transformation 15. CK18 is cleaved by caspase-3 during apoptosis, resulting in the release of the degraded CK18-Asp396 product, i.e., the M3 antigen, into the circulation. It has previously been shown that circulating M3 antigen levels are elevated in patients with various epithelial cancer types and to be increased during chemotherapy 8, 9, 13. The M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in the plasma of CRC patients, before and after surgical resection of the tumour, correlated very well with each other, as expected, 61
16 because the CK18 ELISA recognizes the soluble fragments of CK18 that are detected in the M3 ELISA, as well as other soluble non-caspase cleaved CK18 fragments. Both M3 antigen and total CK18 plasma values increased shortly after surgical resection of the tumour, likely due to the surgical procedure. Because the apoptotic cells are randomly distributed throughout colorectal carcinomas 16, it is evident that products of apoptotic tumour cells do not all enter the circulation of these patients but are released into the lumen and leave the body via stool, especially in tumours that have not invaded and spread to adjacent lymph nodes. Our results showed a correlation between M3 antigen and total CK18 plasma levels and CRC stage, confirming that patients with advanced disease have higher M3 antigen and total CK18 levels. The positive correlation of M3 antigen plasma levels with tumour diameter further supports that the plasma levels are indeed elevated due to the presence of the tumour, with larger tumors responsible for more antigen secretion. Because we found no correlation between tumour diameter or Dukes stage with M3 antigen level within the tumour, these parameters might be the cause of the inverse correlation between M3 antigen plasma levels and M3 antigen tumour levels. Taken together these results strongly indicate that M3 antigen and total CK18 levels are reflected in the plasma of CRC patients due through the presence of the tumour. M3 antigen plasma levels were related to patient s outcome, independent from Dukes stage, with patients with higher levels having worse disease-free survival. These observations are comparable to the reports about M3 antigen levels in sera of patients with breast and lung cancer 8, 9. Patients with recurrent breast cancer also had highest M3 antigen levels in their circulation and there was a correlation with the number of organs affected, suggesting increased M3 antigen levels in the circulation associated with cancer progression 8, which concurs with our observation of a relation with Dukes stage. Patients with lung cancer also had increased serum levels of M3 antigen, and patients with the lowest basal M3 antigen levels showed the best survival 9. Moreover, M3 antigen and/or total CK18 levels were found to be increased due to chemotherapy in lung, prostate and breast cancer patients, showing the induction of tumour cell death 9-11, 13. In addition, the increase in total CK18 levels in breast cancer patients correlated with clinical response to therapy and survival. Thus, circulating M3 antigen and total CK18 levels could potentially be used to monitor treatment efficacy in cancer patients. However, we did not find a relation between post-operative plasma M3 antigen and/or total CK18 levels, in the plasmas obtained about 4.5 months after surgical intervention, and the post-operative adjuvant treatment the patients received, that started already within 1 month after surgery. Apparently, plasma M3 antigen 62
17 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients and/or total CK18 levels in CRC patients are intrinsically related to the tumour and less indicative for treatment response. The ratio between plasma M3 antigen and total CK18 levels reflects differences in apoptosis and necrosis, and might reflect tumour-related differences in those two cell death modes. Necrosis is believed to be a major process in hypoxic tumours as it does not need ATP to be executed, in contrast to apoptosis. Furthermore, hypoxia blocks apoptosis and contributes to treatment resistance 17, 18. Therefore, plasma M3/CK18 ratios can potentially be used to predict the response and determine which patients should be treated aggressively. In the present study, the M3/CK18 ratio tended to lower with increasing Dukes stage, indicating that necrosis increases more than apoptosis during tumour progression, similar as reported for endometrial cancer 11. High levels of necrosis in more advanced tumour stages fits with the idea that hypoxia forces the tumour to form new blood-vessels and to invade the muscularis mucosa to reach the circulation for oxygen supply, finally resulting in more advanced tumor stages 19, 2. Decreased plasma M3/CK18 ratios during tumour progression, furthermore, fit with the idea that there is a decrease in apoptotic sensitivity of tumour cells during colorectal tumour progression 16. Interestingly, the patients M3 antigen plasma levels and M3/CK18 ratios after tumour resection are also of prognostic relevance for the patient s disease-free survival. Both post-operative plasma M3 antigen and M3/CK18 ratios were independent of the post-operative treatment the patients received. Thus, determination of plasma M3 antigen and M3/CK18 ratios might also be a powerful independent tool to monitor patients after resection. In order to be conclusive, however, these interesting preliminary observations, due to the limited power of our study with only 49 CRC patients, merit further evaluation in larger patient groups. Conclusions M3 antigen and total CK18 levels in the circulation of colorectal cancer are prognostic for disease-free survival independent of disease-stage, and might be helpful to select patient s treatment and in monitoring the patient after surgery, which should be confirmed in larger prospective studies. Acknowledgements Tramedico BV, The Netherlands and the Gastrostart Foundation (grant 27-14) are appreciated for funding the study and Peter Bjørklund (Peviva AB) for support regarding the M3 and M65 ELISAs. 63
18 References 1. Holdenrieder S, Stieber P. Apoptotic markers in cancer. Clin Biochem 24;37: Degterev A, Yuan J. Expansion and evolution of cell death programmes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 28;9: Leers MP, Kolgen W, Bjorklund V, Bergman T, Tribbick G, Persson B, Bjorklund P, Ramaekers FC, Bjorklund B, Nap M, Jornvall H, Schutte B. Immunocytochemical detection and mapping of a cytokeratin 18 neo-epitope exposed during early apoptosis. J Pathol 1999;187: Koornstra JJ, Rijcken FE, De Jong S, Hollema H, De Vries EG, Kleibeuker JH. Assessment of apoptosis by M3 immunoreactivity and the correlation with morphological criteria in normal colorectal mucosa, adenomas and carcinomas. Histopathology 24;44: Chiu PM, Ngan YS, Khoo US, Cheung AN. Apoptotic activity in gestational trophoblastic disease correlates with clinical outcome: assessment by the caspase-related M3 CytoDeath antibody. Histopathology 21;38: Hagg M, Biven K, Ueno T, Rydlander L, Bjorklund P, Wiman KG, Shoshan M, Linder S. A novel high-through-put assay for screening of pro-apoptotic drugs. Invest New Drugs 22;2: Biven K, Erdal H, Hagg M, Ueno T, Zhou R, Lynch M, Rowley B, Wood J, Zhang C, Toi M, Shoshan MC, Linder S. A novel assay for discovery and characterization of pro-apoptotic drugs and for monitoring apoptosis in patient sera. Apoptosis 23;8: Ueno T, Toi M, Biven K, Bando H, Ogawa T, Linder S. Measurement of an apoptotic product in the sera of breast cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 23;39: Ulukaya E, Yilmaztepe A, Akgoz S, Linder S, Karadag M. The levels of caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 are elevated in serum from patients with lung cancer and helpful to predict the survival. Lung Cancer 27;56: Kramer G, Schwarz S, Hagg M, Havelka AM, Linder S. Docetaxel induces apoptosis in hormone refractory prostate carcinomas during multiple treatment cycles. Br J Cancer 26;94: Kramer G, Erdal H, Mertens HJ, Nap M, Mauermann J, Steiner G, Marberger M, Biven K, Shoshan MC, Linder S. Differentiation between cell death modes using measurements of different soluble forms of extracellular cytokeratin 18. Cancer Res 24;64: Cummings J, Ranson M, Butt F, Moore D, Dive C. Qualification of M3 and M65 ELISAs as surrogate biomarkers of cell death: long term antigen stability in cancer patient plasma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 27;6: Olofsson MH, Ueno T, Pan Y, Xu R, Cai F, van der KH, Muerdter TE, Sonnenberg M, Aulitzky WE, Schwarz S, Andersson E, Shoshan MC, Havelka AM, Toi M, Linder S. Cytokeratin-18 is a useful serum biomarker for early determination of response of breast carcinomas to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 27;13: Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 1951;193: Pankov R, Umezawa A, Maki R, Der CJ, Hauser CA, Oshima RG. Oncogene activation of human keratin 18 transcription via the Ras signal transduction pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994;91: Koornstra JJ, De Jong S, Hollema H, De Vries EG, Kleibeuker JH. Changes in apoptosis during the development of colorectal cancer: a systematic review of the literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 23;45:
19 Circulating cell death products in CRC patients 17. Kim M, Park SY, Pai HS, Kim TH, Billiar TR, Seol DW. Hypoxia inhibits tumor necrosis factorrelated apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by blocking Bax translocation. Cancer Res 24;64: Erler JT, Cawthorne CJ, Williams KJ, Koritzinsky M, Wouters BG, Wilson C, Miller C, Demonacos C, Stratford IJ, Dive C. Hypoxia-mediated down-regulation of Bid and Bax in tumors occurs via hypoxiainducible factor 1-dependent and -independent mechanisms and contributes to drug resistance. Mol Cell Biol 24;24: Keith B, Simon MC. Hypoxia-inducible factors, stem cells, and cancer. Cell 27;129: Liao D, Johnson RS. Hypoxia: a key regulator of angiogenesis in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 27;26:
20 66
Oncology Cell Death Products from basic research to disease modelling to clinical trials
 Oncology Cell Death Products from basic research to disease modelling to clinical trials US Customer Service: US Technical Service: Peviva Cell Death Products Monoclonal Antibody Products M5 and M6 Keratin
Oncology Cell Death Products from basic research to disease modelling to clinical trials US Customer Service: US Technical Service: Peviva Cell Death Products Monoclonal Antibody Products M5 and M6 Keratin
Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect Diagnostics.
 M3 CytoDEATH ELISA Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect Diagnostics. Bio-Connect Diagnostics B.V. T NL +31 ()26 326 44 6 T BE +32 ()2 52 12 53 Begonialaan 3a F NL +31 ()26
M3 CytoDEATH ELISA Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect Diagnostics. Bio-Connect Diagnostics B.V. T NL +31 ()26 326 44 6 T BE +32 ()2 52 12 53 Begonialaan 3a F NL +31 ()26
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 fragment (M30) as marker of postoperative residual tumor load in colon cancer patients
 Caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 fragment (M30) as marker of postoperative residual tumor load in colon cancer patients C. Ausch, V. Buxhofer-Ausch, U. Olszewski, W. Hinterberger, E. Ogris, R. Schiessel,
Caspase-cleaved cytokeratin 18 fragment (M30) as marker of postoperative residual tumor load in colon cancer patients C. Ausch, V. Buxhofer-Ausch, U. Olszewski, W. Hinterberger, E. Ogris, R. Schiessel,
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER?
 CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
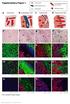 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer. Cheol Min Kang 2018/04/05
 Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
M30 Apoptosense ELISA. A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH
 M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
Treatment of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: Current Concepts
 Treatment of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: Current Concepts James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine, EVMS Case Presentation
Treatment of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: Current Concepts James J. Stark, MD, FACP Medical Director, Cancer Program and Palliative Care Maryview Medical Center Professor of Medicine, EVMS Case Presentation
Mismatch repair status, inflammation and outcome in patients with primary operable colorectal cancer
 Mismatch repair status, inflammation and outcome in patients with primary operable colorectal cancer Park JH, Powell AG, Roxburgh CSD, Richards CH, Horgan PG, McMillan DC, Edwards J James Park Clinical
Mismatch repair status, inflammation and outcome in patients with primary operable colorectal cancer Park JH, Powell AG, Roxburgh CSD, Richards CH, Horgan PG, McMillan DC, Edwards J James Park Clinical
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38705 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Gijn, Willem van Title: Rectal cancer : developments in multidisciplinary treatment,
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38705 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Gijn, Willem van Title: Rectal cancer : developments in multidisciplinary treatment,
Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer
 Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Jai Sule 1, Kah Wai Cheong 2, Stella Bee 2, Bettina Lieske 2,3 1 Dept of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, University Surgical Cluster,
Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Jai Sule 1, Kah Wai Cheong 2, Stella Bee 2, Bettina Lieske 2,3 1 Dept of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery, University Surgical Cluster,
Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)?
 Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)? Department of General Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University, College of Medicine, 126-, Anam-dong
Are there the specific prognostic factors for triplenegative subtype of early breast cancers (pt1-2n0m0)? Department of General Surgery, Anam Hospital, Korea University, College of Medicine, 126-, Anam-dong
Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer
 Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer Emad Sadaka, Alaa Maria and Mohamed El-Shebiney. Clinical Oncology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Egypt alaamaria1@hotmail.com
Lymph node ratio as a prognostic factor in stage III colon cancer Emad Sadaka, Alaa Maria and Mohamed El-Shebiney. Clinical Oncology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta University, Egypt alaamaria1@hotmail.com
Although the international TNM classification system
 Prognostic Significance of Perioperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of 1,000 Consecutive Resections for Clinical Stage I Disease Morihito Okada, MD, PhD, Wataru
Prognostic Significance of Perioperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of 1,000 Consecutive Resections for Clinical Stage I Disease Morihito Okada, MD, PhD, Wataru
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy
 Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2011;15:152-156 Original Article Treatment outcomes and prognostic factors of gallbladder cancer patients after postoperative radiation therapy Suzy Kim 1,#, Kyubo
Xiang Hu*, Liang Cao*, Yi Yu. Introduction
 Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
17 th December 2008 Glasgow eprints Service
 McMillan, D.C. and Hole, D.J. and McArdle, C.S. (2008) The impact of old age on cancer-specific and non-cancer-related survival following elective potentially curative surgery for Dukes A/B colorectal
McMillan, D.C. and Hole, D.J. and McArdle, C.S. (2008) The impact of old age on cancer-specific and non-cancer-related survival following elective potentially curative surgery for Dukes A/B colorectal
Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients
 Yonago Acta medica 2012;55:57 61 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients Hiroaki Saito, Seigo Takaya, Yoji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Shigeru Tatebe and Masahide
Yonago Acta medica 2012;55:57 61 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients Hiroaki Saito, Seigo Takaya, Yoji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Shigeru Tatebe and Masahide
Lower lymph node yield following neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer has no clinical significance
 Original Article Lower lymph node yield following neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer has no clinical significance Dedrick Kok Hong Chan 1,2, Ker-Kan Tan 1,2 1 Division of Colorectal Surgery, University
Original Article Lower lymph node yield following neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer has no clinical significance Dedrick Kok Hong Chan 1,2, Ker-Kan Tan 1,2 1 Division of Colorectal Surgery, University
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva
 Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Deposited on: 4 November 2009
 Roxburgh, C.S.D. and Crozier, J.E.M. and Maxwell, F. and Foulis, A.K. and Brown, J. and McKee, R.F. and Anderson, J.H. and Horgan, P.G. and McMillan, D.C. (2009) Comparison of tumour-based (Petersen Index)
Roxburgh, C.S.D. and Crozier, J.E.M. and Maxwell, F. and Foulis, A.K. and Brown, J. and McKee, R.F. and Anderson, J.H. and Horgan, P.G. and McMillan, D.C. (2009) Comparison of tumour-based (Petersen Index)
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection
 Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Landmarking, immortal time bias and. Dynamic prediction
 Landmarking and immortal time bias Landmarking and dynamic prediction Discussion Landmarking, immortal time bias and dynamic prediction Department of Medical Statistics and Bioinformatics Leiden University
Landmarking and immortal time bias Landmarking and dynamic prediction Discussion Landmarking, immortal time bias and dynamic prediction Department of Medical Statistics and Bioinformatics Leiden University
Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27(5)305 309 Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis -, -, - - 1 Chest Department and 2 Section of Thoracic Surgery,
Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27(5)305 309 Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis -, -, - - 1 Chest Department and 2 Section of Thoracic Surgery,
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data
 Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Follow up The way ahead. John Griffith
 Follow up The way ahead John Griffith Key Emerging Principles Risk stratified pathways of care Personalised care plan and treatment summary with a hand held record Information and education Remote monitoring
Follow up The way ahead John Griffith Key Emerging Principles Risk stratified pathways of care Personalised care plan and treatment summary with a hand held record Information and education Remote monitoring
Analysis of the outcome of young age tongue squamous cell carcinoma
 Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy
 Original Article Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy Shupeng Zhang 1, Liangliang Wu 2, Xiaona Wang 2, Xuewei Ding 2, Han Liang 2 1 Department of General
Original Article Satisfactory surgical outcome of T2 gastric cancer after modified D2 lymphadenectomy Shupeng Zhang 1, Liangliang Wu 2, Xiaona Wang 2, Xuewei Ding 2, Han Liang 2 1 Department of General
COLORECTAL CARCINOMA
 QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS MANAGEMENT OF COLORECTAL CARCINOMA Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Colorectal Surgeons Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Malaysian
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS MANAGEMENT OF COLORECTAL CARCINOMA Ministry of Health Malaysia Malaysian Society of Colorectal Surgeons Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Malaysian
After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
 ESTS METASTASECTOMY SUPPLEMENT Alberto Oliaro, MD, Pier L. Filosso, MD, Maria C. Bruna, MD, Claudio Mossetti, MD, and Enrico Ruffini, MD Abstract: After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
ESTS METASTASECTOMY SUPPLEMENT Alberto Oliaro, MD, Pier L. Filosso, MD, Maria C. Bruna, MD, Claudio Mossetti, MD, and Enrico Ruffini, MD Abstract: After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
Prognostic Impact of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Receiving Definite Radiotherapy
 Prognostic Impact of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Receiving Definite Radiotherapy 2016.04.08 KCCH 김문홍 DM and prediabetes in cancer Negative impact on
Prognostic Impact of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Locally Advanced Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Receiving Definite Radiotherapy 2016.04.08 KCCH 김문홍 DM and prediabetes in cancer Negative impact on
following radiotherapy
 British Journal of Cancer (1995) 72, 1536-154 r) 1995 Stockton Press All rights reserved 7-92/95 $12. Serum tumour markers in carcinoma of the uterine cervix and outcome following radiotherapy ARM Sproston',
British Journal of Cancer (1995) 72, 1536-154 r) 1995 Stockton Press All rights reserved 7-92/95 $12. Serum tumour markers in carcinoma of the uterine cervix and outcome following radiotherapy ARM Sproston',
The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative
 Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study
 Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 346-352 Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study Subhankar Chakraborty
Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 346-352 Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study Subhankar Chakraborty
ABSTRACT. Shuisheng Zhang 1, Xiaozhun Huang 2, Yuan Tian 3, Saderbieke Aimaiti 1, Jianwei Zhang 1, Jiuda Zhao 4, Yingtai Chen 1 and Chengfeng Wang 1
 Clinicopathologic characteristics, laboratory parameters, treatment protocols, and outcomes of pancreatic cancer: a retrospective cohort study of 1433 patients in China Shuisheng Zhang 1, Xiaozhun Huang
Clinicopathologic characteristics, laboratory parameters, treatment protocols, and outcomes of pancreatic cancer: a retrospective cohort study of 1433 patients in China Shuisheng Zhang 1, Xiaozhun Huang
Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease
 GBCC 2018, April 6, Songdo ConvensiA, Incheon, Korea Panel Discussion 4, How Can We Better Treat Patients with Metastatic Disease? Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease Tadahiko
GBCC 2018, April 6, Songdo ConvensiA, Incheon, Korea Panel Discussion 4, How Can We Better Treat Patients with Metastatic Disease? Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease Tadahiko
CHAPTER 7 Concluding remarks and implications for further research
 CONCLUDING REMARKS AND IMPLICATIONS FOR FURTHER RESEARCH CHAPTER 7 Concluding remarks and implications for further research 111 CHAPTER 7 Molecular staging of large sessile rectal tumors In this thesis,
CONCLUDING REMARKS AND IMPLICATIONS FOR FURTHER RESEARCH CHAPTER 7 Concluding remarks and implications for further research 111 CHAPTER 7 Molecular staging of large sessile rectal tumors In this thesis,
Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
Prognostic significance of K-Ras mutation rate in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Bruno Vincenzi Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma
 Prognostic significance of K-Ras mutation rate in metastatic colorectal cancer patients Bruno Vincenzi Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma Colorectal cancer 3 rd most common cancer worldwide Approximately
Prognostic significance of K-Ras mutation rate in metastatic colorectal cancer patients Bruno Vincenzi Università Campus Bio-Medico di Roma Colorectal cancer 3 rd most common cancer worldwide Approximately
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Molecular in vitro diagnostic test for the quantitative detection of the mrna expression of ERBB2, ESR1, PGR and MKI67 in breast cancer tissue.
 Innovation for your breast cancer diagnostics PGR G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C ERBB2
Innovation for your breast cancer diagnostics PGR G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C ERBB2
VUmc. VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy
 MicroRNA-21 (mir-21) in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: correlation with clinical outcome and pharmacological aspects underlying its role in the modulation of gemcitabine activity Elisa Giovannetti, Niccola
MicroRNA-21 (mir-21) in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: correlation with clinical outcome and pharmacological aspects underlying its role in the modulation of gemcitabine activity Elisa Giovannetti, Niccola
Impact of Screening Colonoscopy on Outcomes in Colon Cancer Surgery
 Impact of Screening Colonoscopy on Outcomes in Colon Cancer Surgery The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Impact of Screening Colonoscopy on Outcomes in Colon Cancer Surgery The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Giannakeas V, Sopik V, Narod SA. Association of Radiotherapy With Survival in Women Treated for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ With Lumpectomy or Mastectomy. JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1(4):e181100.
Supplementary Online Content Giannakeas V, Sopik V, Narod SA. Association of Radiotherapy With Survival in Women Treated for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ With Lumpectomy or Mastectomy. JAMA Netw Open. 2018;1(4):e181100.
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Choosing the Correct Statistical Test
 Choosing the Correct Statistical Test T racie O. Afifi, PhD Departments of Community Health Sciences & Psychiatry University of Manitoba Department of Community Health Sciences COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, FACULTY
Choosing the Correct Statistical Test T racie O. Afifi, PhD Departments of Community Health Sciences & Psychiatry University of Manitoba Department of Community Health Sciences COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, FACULTY
B eta catenin was first identified as a protein associated
 347 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nuclear b catenin as a potential prognostic and diagnostic marker in patients with colorectal cancer from Hong Kong S C C Wong, E S F Lo, A K C Chan, K C Lee, W L Hsiao... See end
347 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Nuclear b catenin as a potential prognostic and diagnostic marker in patients with colorectal cancer from Hong Kong S C C Wong, E S F Lo, A K C Chan, K C Lee, W L Hsiao... See end
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION
 Preoperative Serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA 125 as Prognostic Factors for Colorectal Cancer RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Preoperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen, Carbohydrate Antigen19-9 and Carbohydrate Antigen
Preoperative Serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA 125 as Prognostic Factors for Colorectal Cancer RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Preoperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen, Carbohydrate Antigen19-9 and Carbohydrate Antigen
Correlation between serum level of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 and poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Correlation between serum level of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 and poor prognosis in breast cancer J.H. Sun 1, N. Fan 2 and Y. Zhang 1 1 Xianyang Hospital of Yan an University Clinical Laboratory,
Correlation between serum level of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 18 and poor prognosis in breast cancer J.H. Sun 1, N. Fan 2 and Y. Zhang 1 1 Xianyang Hospital of Yan an University Clinical Laboratory,
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Hyponatremia in small cell lung cancer is associated with a poorer prognosis
 Original Article Hyponatremia in small cell lung cancer is associated with a poorer prognosis Wenxian Wang 1, Zhengbo Song 1,2, Yiping Zhang 1,2 1 Department of Chemotherapy, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital,
Original Article Hyponatremia in small cell lung cancer is associated with a poorer prognosis Wenxian Wang 1, Zhengbo Song 1,2, Yiping Zhang 1,2 1 Department of Chemotherapy, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital,
Summary BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3
 ESMO 2016 Congress 7-11 October, 2016 Copenhagen, Denmark Table of Contents Summary... 2 BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3 Large data analysis reveals similar survival outcomes with sequential
ESMO 2016 Congress 7-11 October, 2016 Copenhagen, Denmark Table of Contents Summary... 2 BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3 Large data analysis reveals similar survival outcomes with sequential
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Factors Affecting Survival in Patients with Colorectal Cancer in Shiraz, Iran
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.1.159 RESEARCH ARTICLE Factors Affecting Survival in Patients with Colorectal Cancer in Shiraz, Iran Mohammad Zare-Bandamiri 1, Narges Khanjani 2 *, Yunes Jahani
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.1.159 RESEARCH ARTICLE Factors Affecting Survival in Patients with Colorectal Cancer in Shiraz, Iran Mohammad Zare-Bandamiri 1, Narges Khanjani 2 *, Yunes Jahani
Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer. Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
Apoptosis and colorectal cancer. Studies on pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets Koornstra, Jan
 University of Groningen Apoptosis and colorectal cancer. Studies on pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets Koornstra, Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Apoptosis and colorectal cancer. Studies on pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets Koornstra, Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
Colorectal Cancer Demographics and Survival in a London Cancer Network
 Cancer Research Journal 2017; 5(2): 14-19 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20170502.12 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Colorectal Cancer Demographics and
Cancer Research Journal 2017; 5(2): 14-19 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/crj doi: 10.11648/j.crj.20170502.12 ISSN: 2330-8192 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8214 (Online) Colorectal Cancer Demographics and
Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor survival in breast cancer patients
 Journal of BUON 17: 663-668, 2012 2012 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor
Journal of BUON 17: 663-668, 2012 2012 Zerbinis Medical Publications. Printed in Greece ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha and carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression are associated with poor
Reviews in Clinical Medicine
 Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS) Reviews in Clinical Medicine Clinical Research Development Center Ghaem Hospital Prognostic value of HER2/neu expression in patients with prostate cancer:
Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS) Reviews in Clinical Medicine Clinical Research Development Center Ghaem Hospital Prognostic value of HER2/neu expression in patients with prostate cancer:
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer. Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M. Hoffman, William L. Gerald Table of Contents
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of prostate cancer Gennadi V. Glinsky, Anna B. Glinskii, Andrew J. Stephenson, Robert M. Hoffman, William L. Gerald Table of Contents
Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Podocalyxin-like protein as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer: Functional studies and clinical implication
 Podocalyxin-like protein as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer: Functional studies and clinical implication Karin Jirström Professor, Pathology Lund University, Regional Laboratories Region Skåne
Podocalyxin-like protein as a prognostic marker in colorectal cancer: Functional studies and clinical implication Karin Jirström Professor, Pathology Lund University, Regional Laboratories Region Skåne
Differential lymph node retrieval in rectal cancer: associated factors and effect on survival
 Original Article Differential lymph node retrieval in rectal cancer: associated factors and effect on survival Cedrek McFadden 1, Brian McKinley 1, Brian Greenwell 2, Kaylee Knuckolls 1, Patrick Culumovic
Original Article Differential lymph node retrieval in rectal cancer: associated factors and effect on survival Cedrek McFadden 1, Brian McKinley 1, Brian Greenwell 2, Kaylee Knuckolls 1, Patrick Culumovic
Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008
 Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Special Report Temporal Trends in Demographics and Overall Survival of Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients at Moffitt Cancer Center From 1986 to 2008 Matthew B. Schabath, PhD, Zachary J. Thompson, PhD,
Stage III Colon Cancer Susquehanna Cancer Center Warren L Robinson, MD, FACP May 9, 2007
 Stage III Colon Cancer Susquehanna Cancer Center 1997-21 Warren L Robinson, MD, FACP May 9, 27 Stage III Colon Cancer Susquehanna Cancer Center 1997-21 Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer
Stage III Colon Cancer Susquehanna Cancer Center 1997-21 Warren L Robinson, MD, FACP May 9, 27 Stage III Colon Cancer Susquehanna Cancer Center 1997-21 Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer
A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Association of microrna-7 and its binding partner CDR1-AS with the prognosis and prediction of 1 st -line tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer
 www.nature.com/scientificreports Received: 1 March 2018 Accepted: 12 June 2018 Published: xx xx xxxx OPEN Association of microrna-7 and its binding partner CDR1-AS with the prognosis and prediction of
www.nature.com/scientificreports Received: 1 March 2018 Accepted: 12 June 2018 Published: xx xx xxxx OPEN Association of microrna-7 and its binding partner CDR1-AS with the prognosis and prediction of
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Salvage prostatectomy for post-radiation adenocarcinoma with treatment effect: Pathological and oncological outcomes
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Salvage prostatectomy for post-radiation adenocarcinoma with treatment effect: Pathological and oncological outcomes Michael J. Metcalfe, MD ; Patricia Troncoso, MD 2 ; Charles C. Guo,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Salvage prostatectomy for post-radiation adenocarcinoma with treatment effect: Pathological and oncological outcomes Michael J. Metcalfe, MD ; Patricia Troncoso, MD 2 ; Charles C. Guo,
Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China
 1663 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2016; 7(12): 1663-1667. doi: 10.7150/jca.15216 Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous
1663 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2016; 7(12): 1663-1667. doi: 10.7150/jca.15216 Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells in lung-cancer-associated pleural effusion
 Received: 1 May 2016 Revised: 19 June 2016 Accepted: 10 July 2016 DOI: 10.1111/crj.12527 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells
Received: 1 May 2016 Revised: 19 June 2016 Accepted: 10 July 2016 DOI: 10.1111/crj.12527 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells
The Impact of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (LCNC)
 The Impact of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (LCNC) Disclosure None Background Torino, Italy LCNC Rare tumor (2% to 3% all resected primary lung cancers) Preoperative
The Impact of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (LCNC) Disclosure None Background Torino, Italy LCNC Rare tumor (2% to 3% all resected primary lung cancers) Preoperative
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF COLON AND RECTAL CANCERS IN SENTINEL LYMPH NODE MAPPING
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp 10-14, 2007 Copyright 2007 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 Original Contribution COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF COLON AND
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 5, No. 1, pp 10-14, 2007 Copyright 2007 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 Original Contribution COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF COLON AND
Effect of Tumor Deposits on Overall Survival in Colorectal Cancer Patients with Regional Lymph Node Metastases
 J Rural Med 2014; 9(1): 20 26 Original article Effect of Tumor Deposits on Overall Survival in Colorectal Cancer Patients with Regional Lymph Node Metastases Eiichi Yabata, Masaru Udagawa and Hiroyuki
J Rural Med 2014; 9(1): 20 26 Original article Effect of Tumor Deposits on Overall Survival in Colorectal Cancer Patients with Regional Lymph Node Metastases Eiichi Yabata, Masaru Udagawa and Hiroyuki
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Clinical Outcome of Reconstruction With Tissue Expanders for Patients With Breast Cancer and Mastectomy
 Clinical Outcome of Reconstruction With Tissue Expanders for Patients With Breast Cancer and Mastectomy Mitsui Memorial Hospital Department of Breast and Endocine surgery Daisuke Ota No financial support
Clinical Outcome of Reconstruction With Tissue Expanders for Patients With Breast Cancer and Mastectomy Mitsui Memorial Hospital Department of Breast and Endocine surgery Daisuke Ota No financial support
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Biological predictors of survival in stage II colorectal cancer
 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 1: 643-648, 2013 Biological predictors of survival in stage II colorectal cancer YOSHITAKE UEDA 1, KAZUHIRO YASUDA 1, MASAFUMI INOMATA 1, NORIO SHIRAISHI 1, SHIGEO YOKOYAMA
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 1: 643-648, 2013 Biological predictors of survival in stage II colorectal cancer YOSHITAKE UEDA 1, KAZUHIRO YASUDA 1, MASAFUMI INOMATA 1, NORIO SHIRAISHI 1, SHIGEO YOKOYAMA
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples
 Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Local Excision for early rectal cancer
 Local Excision for early rectal cancer M. Trompetto, E. Ganio, G. Clerico, A. Realis Luc, RJ Nicholls Colorectal Eporediensis Centre Clinica S. Rita Vercelli Gruppo Policlinico di Monza Mortality Morbidity
Local Excision for early rectal cancer M. Trompetto, E. Ganio, G. Clerico, A. Realis Luc, RJ Nicholls Colorectal Eporediensis Centre Clinica S. Rita Vercelli Gruppo Policlinico di Monza Mortality Morbidity
Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for
 INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for more deaths than both cervical and endometrial tumours.
INTRODUCTION Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of mortality from gynecologic malignancies in the industrialized countries and is responsible for more deaths than both cervical and endometrial tumours.
Cellular Immune Parameters Associated with Improved Survival in Breast Cancer Patients after Immunization with a HER2-Specific Vaccine
 Cellular Immune Parameters Associated with Improved Survival in Breast Cancer Patients after Immunization with a HER2-Specific Vaccine Tumor Vaccine Group University of Washington John Strickler November
Cellular Immune Parameters Associated with Improved Survival in Breast Cancer Patients after Immunization with a HER2-Specific Vaccine Tumor Vaccine Group University of Washington John Strickler November
