Molecular in vitro diagnostic test for the quantitative detection of the mrna expression of ERBB2, ESR1, PGR and MKI67 in breast cancer tissue.
|
|
|
- Gervais James
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Innovation for your breast cancer diagnostics PGR G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C G AT C G A A A G A A G T TA G ATA G C G A C ERBB2 ESR1 MKI67 Molecular in vitro diagnostic test for the quantitative detection of the mrna expression of ERBB2, ESR1, PGR and MKI67 in breast cancer tissue. BT_MammaTyper_Broschuere_RZ.indd :01
2 Medical Need European Guidelines 1 recommend that all breast cancer tumors be routinely subtyped by using a combination of four molecular markers ERBB2 (HER2), ESR1 (ER), PGR (PR) and MKI67 (marker of proliferation Ki-67) It has become evident that different molecular subtypes of breast cancer tumors require a different treatment approach. Thus a precise separation of the different subtypes is one key parameter to define a successful treatment strategy Innovative RT- qpcr technologies open up new dimensions in breast cancer diagnostics RT-qPCR has a series of widely acknowledged methodological advantages, it is - quantitative by nature with a wide dynamic range (Noske, Loibl, Darb-Esfahani et al. 2011) - precise - highly sensitive - objective - reproducible and reliable 1) 13th St Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference Expert Panel 2
3 Fixing today s obstacles in breast cancer biomarker assessments and subtyping Key Characteristics: 1. High performing test Molecular in vitro diagnostic test for four essential breast cancer biomarkers ERBB2 (HER2), ESR1 (ER), PGR (PR) and MKI67 (marker of proliferation Ki-67) Reproducible, quantitative determination of mrna expression of each marker via RT-qPCR 2. Promising clinical utility Results enable precise and accurate molecular subtyping of tumor tissue acc. to St Gallen into Luminal A-like, (HER2 negative), (HER2 positive), HER2 positive (non-luminal) and Triple negative (validated in retrospective clinical performance evaluation studies analyzing more than 700 patient samples) Extended information for a patient s prognosis and treatment selection based on subtyping 3. Easy to use Stable, reliable and reproducible process for any molecular pathology laboratory From biopsy FFPE sample to result in 1 day Accurate molecular subtyping as a basis for clinical decision making Benefit Precise quantitative measurement of biomarker expression is a prerequisite for future refinement of breast cancer diagnostics and treatment 3
4 MammaTyper delivers precise quantitative results for each biomarker 1. MammaTyper result: Quantitative values (- Cq) per marker 2. Each marker is classified as positive or negative according to validated cut-off values: ERBB2 Negative < Cut-off Positive < >46 Negative < Cut-off Positive ESR1 < >46 Negative <.50 Cut-off.50 Positive.50 PGR < >46 Negative <.50 Cut-off.50 Positive.50 MKI67 < >46 Values in the ranges coloured in light blue/orange have been observed in a cohort of 765 breast cancer samples. Values in the ranges coloured in dark blue/orange have not yet been observed (clinical thresholds shown for Roche LightCycler 480 instrument II; Cut-offs validated in the FinHer trial with 765 breast cancer samples, for study details see page 9). 3. The ΔCq value provides a quantitative measure for the degree of overexpression of each marker (vs. the cut-off) - Cq values with corresponding linear fold changes relative to cutoff Observed expression value with standard deviation Linear fold change relative to cut-off MKI67 < > - Cq Example: -Δ Cq value positive 11.3x above cut-off Cut-off Upper/lower border of range of typically observed - Cq values The logarithmic - Cq scale is particularly well suited to depict the high resolution and wide range of values for marker expression that can be observed. Standard deviations depicted here were determined in a three site technical validation study. For detailed information please refer to the instructions for use. MammaTyper delivers precise and reproducible - Cq values, which are the basis for further differentiation of subtypes beyond today s routine results an important factor for more treatment individualization in the future. 4
5 Quantitative biomarker assessments lead to accurate subtyping The combination of marker results reveal the St Gallen subtypes: Luminal A-like, (HER2 negative), (HER2 positive), HER2 positive (non-luminal) and Triple negative tumors Prognosis and therapy decision is based on the subtype and other clinico-pathological factors ERBB2 ESR1 PGR MKI67 St Gallen Subtype 1 ERBB2 ESR1 PGR MKI67 St Gallen Subtype 1 pos pos pos pos pos pos pos neg pos pos neg pos pos pos neg neg (HER2 positive) (HER2 positive) (HER2 positive) (HER2 positive) neg pos pos pos (HER2 negative) neg pos pos neg Luminal A-like neg pos neg pos neg pos neg neg (HER2 negative) (HER2 negative) pos neg pos pos Not defined 1 neg neg pos pos Not defined 1 pos neg pos neg Not defined 1 neg neg pos neg Not defined 1 pos neg neg pos HER2 positive (non-luminal) neg neg neg pos Triple negative (ductal) pos neg neg neg HER2 positive (non-luminal) neg neg neg neg Triple negative (ductal) The not defined subtypes according to St Gallen (2013) are based on the assumption that a combination showing an ER negative but a PR positive result is not possible. In an epidemiological inquiry 2.4% ER negative/pr positive tumors have been found in an American breast cancer cohort (Ries et al. 2007). These subtypes were also found in two MammaTyper clinical performance evaluation studies in some cases (3.5%). 1) Subtype definition according to 13th St Gallen guidelines (Goldhirsch et al. 2013). 5
6 MammaTyper vs. current standard methods MammaTyper results show a high degree of agreement with IHC results for ERBB2/HER2, ESR1/ER and PGR/PR pos IHC neg Agreement varies by marker as expected: High overall agreement for ERBB2/HER2, ESR1/ER, PGR/PR pos PCR neg 18% 4% ERBB2/HER2 4% 75% K 0,79 p> OPA 93% PPA 83% NPA 95% 70% 5% ESR1/ER 3% 22% K 0,80 p> OPA 92% PPA 96% NPA 81% Lowest overall agreement for MKI67/Ki-67 OPA = Overall percent agreement NPA = Negative percent agreement PPA = Positive percent agreement 54% 13% PGR/PR K 0,64 p> OPA 83% 55% 19% MKI67/Ki-67 K 0, p> OPA 75% Agreement of mrna expression values determined by MammaTyper with protein expression determined by IHC (IHC/CISH for HER2) in the FinHer samples. 4% 29% PPA 93% NPA 69% 5% 21% PPA 91% NPA 51% MKI67 MammaTyper results are more accurate in discordant cases compared to IHC results according to clinical outcome Analysis of discordant cases shows: Better distant disease-free survival could be shown as a trend, if MKI67 determined by MammaTyper was negative and worse if MKI67 determined by MammaTyper was positive in discordant cases (i.e. in agreement with the concordant cases in this study). Fractions of patients surviving 1,0 0,9 0,8 neg pos Survival curves by MKI67 (MammaTyper ) Kaplan-Meier analysis for the MammaTyper results of MKI67 discrepant cases by RT-qPCR and IHC method. 5-year distant disease-free survival rate is shown for IHC ER positive patients (n=143). MammaTyper MKI67 negative 97% DDFS (blue) vs MammaTyper MKI67 positive 86% DDFS (red); p=0.123; HR 0.205; 95% CI= (based on the FinHer trial. For more trial information please see page 9). 0, Time to distant recurrence [years] 6
7 MammaTyper reproducibility and stability MammaTyper is a highly reproducible test, which avoids disadvantages of intra-/inter-laboratory variation ERBB2 ESR1 Performance characterization: - Cq Ref. 8RNA PGR Ref. 8RNA MKI67 Samples: RNA extracted from FFPE tumor samples of 7 patients and 1 reference RNA Tests: Total of 24 measurements per sample: Each patient RNA was measured 2 times on 3 days, on 4 different LightCycler 480 instruments II On display: - Cq values for the four markers - Cq Ref. 8RNA Ref. 8RNA A marker is evaluated as positive (pos) at or above the cut-off value and negative (neg) below the cut-off value (black dashed line) Test performance is not affected by fluctuations in tumor cell content (TCC). This leads to an agreement of results between enriched and non-enriched samples ERBB2 ESR1 Performance characterization: - Cq Sample pair number PGR Sample pair number MKI67 Paired samples with high (80%) and low (5-50%) tumor cell content have been measured Comparison of results of enriched samples and non enriched samples - Cq Sample pair number Sample pair number Non enriched Cut-off Enriched -Δ Cq values of paired tumor samples with high (80%, gray) and low (5 50%, green) tumor cell content and varying DCIS (10 70%) content adjacent to the tumor. 7
8 MammaTyper is an easy to handle test which allows same day results Step1: RNXtract sample preparation Step2: MammaTyper test preparation and execution Cut 10µm section FFPE biopsy FFPE curl RNXtract Total RNA template MammaTyper A P1 P1 P1 P1 P1 P1 P1 P1 P1 PC PC PC B P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 P2 PC PC PC C P3 P3 P3 P3 P3 P3 P3 P3 P3 PC PC PC D P4 P4 P4 P4 P4 P4 P4 P4 P Run RT-qPCR E P5 P5 P5 P5 P5 P5 P5 P5 P F P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 P6 NC NC NC G P7 P7 P7 P7 P7 P7 P7 P7 P7 NC NC NC H P8 P8 P8 P8 P8 P8 P8 P8 P8 NC NC NC Data analysis Real Time PCR Instrument Versant kpcr or Roche LightCycler 480 II Distribute master mixes, 8 RNA templates, PC and NC in 96 well plate Set up 3 RT-qPCR master mixes RT-qPCR less time-consuming compared to IHC FISH. RNXtract Manual steps (hands-on time) Walk away time MammaTyper Conducted for all 4 markers simultaniously Pathologist time 8:00 9:00 10:00 11:00 12:00 13:00 14:00 MammaTyper result for four markers, including result for ERBB2, in 1 day. Sample processing from section to result in only 5: h for up to 8 patients. MammaTyper reduces hands-on time of technician as well as pathologist time 8
9 Results from clinical performance evaluation studies / hypothesis generating data MammaTyper provides prognostic value through reliable subtyping: MammaTyper results separated low risk Luminal A-like patients accurately from the group of patients with other subtypes with regard to clinical outcome in the FinHer trial Survival curves by Luminal-A-like subgroup (MammaTyper ) Survival curves by Luminal-A-like subgroup (MammaTyper ) Fractions of patients surviving 1,0 0,9 0,8 0,7 Luminal-A-like Combined subgroup Fractions of patients surviving 1,0 0,9 0,8 0,7 Luminal-A-like Combined subgroup Time to distant recurrence [years] Time to death [years] Kaplan Meier analysis of DDFS for patients with up to three positive nodes (n=536). 5-year distant disease-free survival of 97% for Luminal A-like patients versus 88% for other subtypes (p=0.0062; HR 0.241; 95% CI= ) (Combined subgroup = all other subtypes combined). Kaplan Meier analysis of overall survival for patients with up to three positive nodes (n=536). 5-year overall survival of 99% of the Luminal A-like patients versus 94% for other subtypes (p=0.0289; HR 0.108; 95%-CI= ) (Combined subgroup = all other subtypes combined). MammaTyper provides predictive value by identifying subtypes with Taxane benefit by accurate MKI67 determination: Patients classified as (HER2 negative) by MammaTyper showed a significant benefit from Taxane addition in the FinHer trial A significant benefit of docetaxel addition was observed only for the Luminal B like (HER2 negative) subtype, as already published previously for other studies (Nitz et al. 2014). Survival curves by Chemotherapy agent Survival curves by Chemotherapy agent Fractions of patients surviving 1,0 0,9 0,8 0,7 Docetaxel Vinorelbine Fractions of patients surviving 1,0 0,9 0,8 0,7 Docetaxel Vinorelbine Time to distant recurrence [years] Time to death [years] Kaplan Meier analysis of distant disease-free survival of (HER2 negative) patients (n=315) treated either with docetaxel (blue) or vinorelbine (red) in addition to FEC. 5-year distant disease-free survival rate was 88% after docetaxel and 78% after vinorelbine treatment (p=0.0196; HR 0.514; 95%-CI= ). Kaplan Meier analysis of overall survival for (HER2 negative) patients (n=315) treated either with docetaxel (blue) or vinorelbine (red) in addition to FEC. 5-year overall survival was 97% after docetaxel and 89% after vinorelbine treatment (p=0.0115; HR 0.6; 95%-CI= ). FinHer Study: Clinical performance of the MammaTyper kit were validated based on a retrospective analysis of samples which have been collected prospectively during the FinHer-trial (International Controlled Trial: ISRCTN ). The aims of the study were to determine the prognostic and predictive validity of MammaTyper results for node negative and node positive breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant systemic chemotherapy as well as to compare MammaTyper with IHC results. The study cohort comprised 801 FFPE blocks which could be collected retrospectively from patients of the FinHer-study cohort, recruited between Oct 2000 and Sept 2003 (Joensuu et al. 2006, Joensuu et al 2009). 9
10 Results from clinical performance evaluation studies / hypothesis generating data MammaTyper helps to identify those patients who are likely to benefit from neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on accurate determination of MKI67: Based on the results of the first MammaTyper neoadjuvant study the diagnostic accuracy of MammaTyper compared to IHC has been seven-times better in predicting the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy ROC curves for Path. compl. Response Sensitivity 1,0 0,8 0,6 Ki-67 vihc [% positive nuclei] ,4 0 0,2 no-pcr pcr pcr vihc MammaTyper 0,0 0,0 0,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1, Specificity ROC analysis for pathological complete response using vihc Ki-67 measurements (blue) and continuous MKI67 values measured with MammaTyper (green). ROC curves show a better identification of responders versus non-responders by mrna determination. MKI67 MammaTyper [-Δ Cq] no-pcr pcr pcr Box plots showing the distribution of vihc results (above) and continuous RT-qPCR mrna results (below) in relation to the group of non-responders (no-pcr) and responders (pcr) (n=53). The differences were investigated using Mann-Whitney test. Prof. Sinn at al Comparative analysis of IHC (with automated or visual scoring) versus quantitative real time PCR (on FFPE or fresh-frozen tissue) for the assessment of Ki-67 labeling index and the prediction of pathological complete response in breast cancer. 10
11 The benefit of RT-qPCR approach for improved subtyping of breast cancer is supported by many publications Selected Literature References / Quotes RT-qPCR versus IHC RT-qPCR has a series of widely acknowledged methodological advantages over IHC, which appear particularly beneficial in the context of reducing the bias of routine Ki-67 assessment; it is quantitative by nature with much wider dynamic range, it does not require an experienced eye and results are not affected by subjective interpretations (Noske, Loibl, Darb-Esfahani et al., Comparison of different approaches for assessment of HER2 expression on protein and mrna level: prediction of chemotherapy response in the neoadjuvant GeparTrio trial. Breast Cancer Res. Treat (2011): ). Ki-67 prognostic value Ki-67 is an excellent surrogate for proliferation and broadly accepted. With respect to clinical application, we revealed connections and equivalence between traditional prognostic factors, expression-based subtyping, and prognostic signatures and provided evidence that these signatures should be tested for their ability to spare adjuvant chemotherapy mainly in the low-proliferation subgroup of patients with ER tumors. (Wirapati, Sotiriou et al., Meta-analysis of gene expression profiles in breast cancer: toward a unified understanding of breast cancer subtyping and prognosis signatures. Breast Cancer Res. (2008).). Ki-67 prognostic value Ki-67 has predictive and prognostic value and is a feasible marker for clinical practice. It independently improved the prediction of treatment response and prognosis in a group of breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant treatment. As mean Ki-67 values in patients with a pcr were very high, cut-off values in a high range above which the prognosis may be better than in patients with lower Ki-67 values may be hypothesized. (Fasching et al., Ki-67, chemotherapy response, and prognosis in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant treatment. BMC Cancer (2011): 486.). Ki-67 prognostic value In patients with a low-proliferation primary tumor, a high level of PR expression would indicate an extraordinarily good prognosis (HR 0.39; 95 % CI, ). In patients with higher-proliferation primary tumors, PR status was not capable of differentiating prognostic groups. Ki-67 is useful in addition to known prognostic factors for breast cancer. It is able to indicate a group of women with a poorer prognosis, specifically in the group of patients with PR-positive breast cancer. (Loehberg et al., Prognostic relevance of Ki-67 in the primary tumor for survival after a diagnosis of distant metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. (2013): ). Ki-67 neoadjuvant therapy Despite methodological concerns, overall a strong correlation of Ki-67 with breast cancer outcome is sufficiently supported, particularly by data originating from randomized clinical trials with central review of biomarkers (Luporsi, Andre, Spyratos et al., Ki-67: level of evidence and methodological considerations for its role in the clinical management of breast cancer: analytical and critical review. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. (2012): ). This has also been shown in the neoadjuvant setting, whereby higher Ki-67 values are consistently associated with higher rates of pathological complete response (pcr) (Yerushalmi, Woods, Ravdin et al., Ki-67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol. (2010): ), a finding which reflects the fundamental link between tumor replication fraction and activity of cytotoxic agents. 11
12 Innovation for your breast cancer diagnostics Summary: MammaTyper delivers precise quantitative results for each of the biomarkers: ERBB2 (HER2), ESR1 (ER), PGR (PR) and MKI67 MammaTyper is a highly reproducible test, which avoids disadvantages of intra-/inter-laboratory variation MammaTyper is a precise and reliable test to discriminate the molecular subtypes according to St Gallen Discordant results for MKI67 / Ki-67 were more accurate for RT-qPCR (MammaTyper ) than for IHC according to clinical outcome in the ER positive HER2 negative group MammaTyper is an easy to handle test which allows same day results RT-qPCR is less time-consuming compared to IHC FISH EN Rev. 1.0 MammaTyper and RNXtract are registered trademarks of BioNTech Diagnostics GmbH and STRATIFYER Molecular Pathology GmbH. BioNTech Diagnostics GmbH An der Goldgrube Mainz, Germany Tel: Fax: service@sales.biontech.de Visit us online: biontech.de mammatyper.com
Molecular in vitro diagnostic test for the quantitative detection of the mrna expression of ERBB2, ESR1, PGR and MKI67 in breast cancer tissue.
 Innovation for your breast cancer diagnostics Now valid ated on: -Roche cob as z 480 A nalyzer -Roche L ightcycle r 480 II - ABI 750 0 Fast -Versant kpcr Cyc ler PGR ESR1 MKI67 Molecular in vitro diagnostic
Innovation for your breast cancer diagnostics Now valid ated on: -Roche cob as z 480 A nalyzer -Roche L ightcycle r 480 II - ABI 750 0 Fast -Versant kpcr Cyc ler PGR ESR1 MKI67 Molecular in vitro diagnostic
The intended place in therapy would be to replace IHC testing in people with early-stage breast cancer.
 pat hways MammaTyper in vitro diagnostic test for determining breast cancer subtypes Medtech innovation briefing Published: 18 January 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib135 Summary The technology described
pat hways MammaTyper in vitro diagnostic test for determining breast cancer subtypes Medtech innovation briefing Published: 18 January 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib135 Summary The technology described
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer
 Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Contemporary Classification of Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Vice Chair of Anatomic Pathology Professor of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Outline
Biological subtyping of early breast cancer: a study comparing RT-qPCR with immunohistochemistry
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2016) 157:437 446 DOI 10.1007/s10549-016-3835-7 PRECLINICAL STUDY Biological subtyping of early breast cancer: a study comparing RT-qPCR with immunohistochemistry Ralph M. Wirtz
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2016) 157:437 446 DOI 10.1007/s10549-016-3835-7 PRECLINICAL STUDY Biological subtyping of early breast cancer: a study comparing RT-qPCR with immunohistochemistry Ralph M. Wirtz
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Earlier Disease. Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital
 Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital stefan.aebi@onkologie.ch Switzerland Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis Local Therapy Surgery Radiation therapy Adjuvant
Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Stefan Aebi Luzerner Kantonsspital stefan.aebi@onkologie.ch Switzerland Breast Cancer Earlier Disease Diagnosis and Prognosis Local Therapy Surgery Radiation therapy Adjuvant
OVERVIEW OF GENE EXPRESSION-BASED TESTS IN EARLY BREAST CANCER
 OVERVIEW OF GENE EXPRESSION-BASED TESTS IN EARLY BREAST CANCER Aleix Prat, MD PhD Medical Oncology Department Hospital Clínic of Barcelona University of Barcelona esmo.org Disclosures Advisory role for
OVERVIEW OF GENE EXPRESSION-BASED TESTS IN EARLY BREAST CANCER Aleix Prat, MD PhD Medical Oncology Department Hospital Clínic of Barcelona University of Barcelona esmo.org Disclosures Advisory role for
MammaPrint, the story of the 70-gene profile
 MammaPrint, the story of the 70-gene profile René Bernards Professor of Molecular Carcinogenesis The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam Chief Scientific Officer Agendia Amsterdam The breast cancer
MammaPrint, the story of the 70-gene profile René Bernards Professor of Molecular Carcinogenesis The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam Chief Scientific Officer Agendia Amsterdam The breast cancer
Breast cancer classification: beyond the intrinsic molecular subtypes
 Breast cancer classification: beyond the intrinsic molecular subtypes Britta Weigelt, PhD Signal Transduction Laboratory CRUK London Research Institute Summary Breast cancer heterogeneity Molecular classification
Breast cancer classification: beyond the intrinsic molecular subtypes Britta Weigelt, PhD Signal Transduction Laboratory CRUK London Research Institute Summary Breast cancer heterogeneity Molecular classification
Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing. Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine)
 Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine) Breast Cancer Theory: Halsted Operative breast cancer is a local-regional disease The positive
Breast cancer: Molecular STAGING classification and testing Korourian A : AP,CP ; MD,PHD(Molecular medicine) Breast Cancer Theory: Halsted Operative breast cancer is a local-regional disease The positive
Profili di espressione genica
 Profili di espressione genica Giampaolo Bianchini MD Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan - Italy Gene expression profiles Transcriptomics Gene DNA mrna mirnas Protein metilation Metabolite Genomics Transcriptomics
Profili di espressione genica Giampaolo Bianchini MD Ospedale San Raffaele, Milan - Italy Gene expression profiles Transcriptomics Gene DNA mrna mirnas Protein metilation Metabolite Genomics Transcriptomics
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY Methodology The test is based on the reported 50-gene classifier algorithm originally named PAM50 and is performed on the ncounter Dx Analysis System
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY
 Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Prosigna BREAST CANCER PROGNOSTIC GENE SIGNATURE ASSAY GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING WITH PROSIGNA What is Prosigna? Prosigna Breast Cancer Prognostic Gene Signature Assay is an FDA-approved assay which provides
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours
 Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
* * * * Supplementary Figure 1. DS Lv CK HSA CK HSA. CK Col-3. CK Col-3. See overleaf for figure legend. Cancer cells
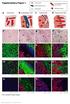 Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Supplementary Figure 1 Cancer cells Desmoplastic stroma Hepatocytes Pre-existing sinusoidal blood vessel New blood vessel a Normal liver b Desmoplastic HGP c Pushing HGP d Replacement HGP e f g h i DS
Adjuvant endocrine therapy (essentials in ER positive early breast cancer)
 Adjuvant endocrine therapy (essentials in ER positive early breast cancer) Giuseppe Curigliano MD, PhD Breast Cancer Program Division of Experimental Therapeutics Outline Picking optimal adjuvant endocrine
Adjuvant endocrine therapy (essentials in ER positive early breast cancer) Giuseppe Curigliano MD, PhD Breast Cancer Program Division of Experimental Therapeutics Outline Picking optimal adjuvant endocrine
Gene Signatures in Breast Cancer: Moving Beyond ER, PR, and HER2? Lisa A. Carey, M.D. University of North Carolina USA
 Gene Signatures in Breast Cancer: Moving Beyond ER, PR, and HER2? Lisa A. Carey, M.D. University of North Carolina USA When Are Biomarkers Ready To Use? Same Rules for Gene Expression Panels Key elements
Gene Signatures in Breast Cancer: Moving Beyond ER, PR, and HER2? Lisa A. Carey, M.D. University of North Carolina USA When Are Biomarkers Ready To Use? Same Rules for Gene Expression Panels Key elements
30 years of progress in cancer research
 Breast Cancer Molecular Knowledge Integrated in Clinical Practice Personalized Medicine Laura J. Esserman UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Retreat Breast Cancer Management Advances 80-90s 1) Screening
Breast Cancer Molecular Knowledge Integrated in Clinical Practice Personalized Medicine Laura J. Esserman UCSF Comprehensive Cancer Center Retreat Breast Cancer Management Advances 80-90s 1) Screening
A new way of looking at breast cancer tumour biology
 A new way of looking at breast cancer tumour biology Contents Intrinsic subtypes of breast cancer 3 Gene expression assays 3 Basis of the Prosigna test 4 Information provided by Prosigna 5 The accuracy
A new way of looking at breast cancer tumour biology Contents Intrinsic subtypes of breast cancer 3 Gene expression assays 3 Basis of the Prosigna test 4 Information provided by Prosigna 5 The accuracy
Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011
 Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011 Robert W. Carlson, M.D. Professor of Medicine Stanford University Chair, NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines Panel Selection of
Multigene Testing in NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines, v1.2011 Robert W. Carlson, M.D. Professor of Medicine Stanford University Chair, NCCN Breast Cancer Treatment Guidelines Panel Selection of
Adjuvan Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
 Adjuvan Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Prof Dr Adnan Aydıner Istanbul University, Oncology Institute aa1 Slide 1 aa1 adnan aydiner; 17.02.2008 15-Year Reductions in Recurrence and Disease-Specific Mortality
Adjuvan Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Prof Dr Adnan Aydıner Istanbul University, Oncology Institute aa1 Slide 1 aa1 adnan aydiner; 17.02.2008 15-Year Reductions in Recurrence and Disease-Specific Mortality
Janet E. Dancey NCIC CTG NEW INVESTIGATOR CLINICAL TRIALS COURSE. August 9-12, 2011 Donald Gordon Centre, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario
 Janet E. Dancey NCIC CTG NEW INVESTIGATOR CLINICAL TRIALS COURSE August 9-12, 2011 Donald Gordon Centre, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario Session: Correlative Studies in Phase III Trials Title: Design
Janet E. Dancey NCIC CTG NEW INVESTIGATOR CLINICAL TRIALS COURSE August 9-12, 2011 Donald Gordon Centre, Queen s University, Kingston, Ontario Session: Correlative Studies in Phase III Trials Title: Design
Review of adjuvant and neo-adjuvant abstracts from SABCS 2011 January 7 th 2012
 Review of adjuvant and neo-adjuvant abstracts from SABCS 2011 January 7 th 2012 Ruth M. O Regan, MD Professor and Vice-Chair for Educational Affairs, Department of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Emory
Review of adjuvant and neo-adjuvant abstracts from SABCS 2011 January 7 th 2012 Ruth M. O Regan, MD Professor and Vice-Chair for Educational Affairs, Department of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Emory
FAQs for UK Pathology Departments
 FAQs for UK Pathology Departments This is an educational piece written for Healthcare Professionals FAQs for UK Pathology Departments If you would like to discuss any of the listed FAQs further, or have
FAQs for UK Pathology Departments This is an educational piece written for Healthcare Professionals FAQs for UK Pathology Departments If you would like to discuss any of the listed FAQs further, or have
She counts on your breast cancer expertise at the most vulnerable time of her life.
 HOME She counts on your breast cancer expertise at the most vulnerable time of her life. Empowering the right treatment choice for better patient outcomes. The comprehensive genomic assay experts trust.
HOME She counts on your breast cancer expertise at the most vulnerable time of her life. Empowering the right treatment choice for better patient outcomes. The comprehensive genomic assay experts trust.
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples
 Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer
 Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer Kathy S. Albain, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Dean s Scholar Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Cardinal Bernardin
Role of Genomic Profiling in (Minimally) Node Positive Breast Cancer Kathy S. Albain, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Dean s Scholar Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Cardinal Bernardin
Luminal A and B Where are we? (or lost in translation?)
 Luminal A and B Where are we? (or lost in translation?) Emiel J. Rutgers The Netherlands Cancer Institute Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek Hospital Amsterdam How to determine adjuvant or neoadjuvant treatment for
Luminal A and B Where are we? (or lost in translation?) Emiel J. Rutgers The Netherlands Cancer Institute Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek Hospital Amsterdam How to determine adjuvant or neoadjuvant treatment for
A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast
 Original Research Article A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast E. Rajesh Goud 1, M. Muralidhar 2*, M. Srinivasulu 3 1Senior
Original Research Article A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Hormonal and Her-2 Receptor Status in Carcinoma Breast E. Rajesh Goud 1, M. Muralidhar 2*, M. Srinivasulu 3 1Senior
Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors)
 Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors) Kael Mikesell, DO McKay-Dee Hospital May 14, 2015 Outline Update to DNA Testing
Current Status of Biomarkers (including DNA Tumor Markers and Immunohistochemistry in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Tumors) Kael Mikesell, DO McKay-Dee Hospital May 14, 2015 Outline Update to DNA Testing
Nadia Harbeck Breast Center University of Cologne, Germany
 Evidence in Favor of Taxane Based Combinations and No Anthracycline in Adjuvant and Metastatic Settings Nadia Harbeck Breast Center University of Cologne, Germany Evidence in Favor of Taxane Based Combinations
Evidence in Favor of Taxane Based Combinations and No Anthracycline in Adjuvant and Metastatic Settings Nadia Harbeck Breast Center University of Cologne, Germany Evidence in Favor of Taxane Based Combinations
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva
 Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Breast Cancer: ASCO Poster Review
 Breast Cancer: ASCO Poster Review Carmen Criscitiello, MD, PhD Istituto Europeo di Oncologia Milano HER2+ SUBTYPE Research questions in early HER2+ BC De-escalation of toxicity without compromising efficacy
Breast Cancer: ASCO Poster Review Carmen Criscitiello, MD, PhD Istituto Europeo di Oncologia Milano HER2+ SUBTYPE Research questions in early HER2+ BC De-escalation of toxicity without compromising efficacy
EARLY STAGE BREAST CANCER ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY. Dr. Carlos Garbino
 EARLY STAGE BREAST CANCER ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY Dr. Carlos Garbino EARLY BREAST CANCER ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY SUSTANTIVE DIFFICULTIES FOR A WORLDWIDE APPLICABILITY DUE TO IMPORTANT INEQUALITIES + IN DIFFERENT
EARLY STAGE BREAST CANCER ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY Dr. Carlos Garbino EARLY BREAST CANCER ADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY SUSTANTIVE DIFFICULTIES FOR A WORLDWIDE APPLICABILITY DUE TO IMPORTANT INEQUALITIES + IN DIFFERENT
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Impact of BMI on pathologic complete response (pcr) following neo adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for locally advanced breast cancer
 Impact of BMI on pathologic complete response (pcr) following neo adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for locally advanced breast cancer Rachna Raman, MD, MS Fellow physician University of Iowa hospitals and clinics
Impact of BMI on pathologic complete response (pcr) following neo adjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for locally advanced breast cancer Rachna Raman, MD, MS Fellow physician University of Iowa hospitals and clinics
Point of View on Early Triple Negative
 Point of View on Early Triple Negative Valentina Rossi, MD UOSD Oncologia dei Tumori della Mammella Azienda Ospedaliera S.Camillo-Forlanini VRossi@scamilloforlanini.rm.it Outline Neoadjuvant Setting IPSY-2
Point of View on Early Triple Negative Valentina Rossi, MD UOSD Oncologia dei Tumori della Mammella Azienda Ospedaliera S.Camillo-Forlanini VRossi@scamilloforlanini.rm.it Outline Neoadjuvant Setting IPSY-2
Breast cancer pathology
 Breast cancer pathology Giancarlo Pruneri, M.D. National Cancer Institute (INT) Milan University of Milan, School of Medicine Giancarlo.Pruneri@unimi.it Currently accepted prognostic/predictive parameters
Breast cancer pathology Giancarlo Pruneri, M.D. National Cancer Institute (INT) Milan University of Milan, School of Medicine Giancarlo.Pruneri@unimi.it Currently accepted prognostic/predictive parameters
Comparison of immunohistochemistry with PCR for assessment of ER, PR, and Ki-67 and prediction of pathological complete response in breast cancer
 Sinn et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:124 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3111-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of immunohistochemistry with PCR for assessment of ER, PR, and Ki-67 and prediction of pathological
Sinn et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:124 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3111-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of immunohistochemistry with PCR for assessment of ER, PR, and Ki-67 and prediction of pathological
Giuseppe Viale for the BIG 1 98 Collaborative and International Breast Cancer Study Groups
 Central Review of ER, PgR and HER2 in BIG 1 98 Evaluating Letrozole vs. Letrozole Tamoxifen vs. Tamoxifen Letrozole as Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy for Postmenopausal Women with Hormone Receptor Positive
Central Review of ER, PgR and HER2 in BIG 1 98 Evaluating Letrozole vs. Letrozole Tamoxifen vs. Tamoxifen Letrozole as Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy for Postmenopausal Women with Hormone Receptor Positive
Biomarkers for HER2-directed Therapies : Past Failures and Future Perspectives
 Biomarkers for HER2-directed Therapies : Past Failures and Future Perspectives Ian Krop Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Inchon 2018 Adjuvant Trastuzumab Improves Outcomes in HER2+ Breast
Biomarkers for HER2-directed Therapies : Past Failures and Future Perspectives Ian Krop Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Inchon 2018 Adjuvant Trastuzumab Improves Outcomes in HER2+ Breast
The Role of Pathologic Complete Response (pcr) as a Surrogate Marker for Outcomes in Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now?
 1 The Role of Pathologic Complete Response (pcr) as a Surrogate Marker for Outcomes in Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now? Terry Mamounas, M.D., M.P.H., F.A.C.S. Medical Director, Comprehensive Breast Program
1 The Role of Pathologic Complete Response (pcr) as a Surrogate Marker for Outcomes in Breast Cancer: Where Are We Now? Terry Mamounas, M.D., M.P.H., F.A.C.S. Medical Director, Comprehensive Breast Program
Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer
 Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer Hee Jung Kwon, Nuri Jang, Min Hui Park, Young Kyung Bae Department of Pathology, Yeungnam
Prognostic significance of stroma tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer Hee Jung Kwon, Nuri Jang, Min Hui Park, Young Kyung Bae Department of Pathology, Yeungnam
Profili Genici e Personalizzazione del trattamento adiuvante nel carcinoma mammario G. RICCIARDI
 Profili Genici e Personalizzazione del trattamento adiuvante nel carcinoma mammario G. RICCIARDI UOC Oncologia Medica, A.O. Papardo, Messina Dir. Prof. V. Adamo BREAST CANCER Brain Adjuvant Medical Therapies
Profili Genici e Personalizzazione del trattamento adiuvante nel carcinoma mammario G. RICCIARDI UOC Oncologia Medica, A.O. Papardo, Messina Dir. Prof. V. Adamo BREAST CANCER Brain Adjuvant Medical Therapies
Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer
 Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological
Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological
Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
 JBUON 2018; 23(4): 877-882 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
JBUON 2018; 23(4): 877-882 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is adjuvant chemotherapy necessary for Luminal A-like breast cancer?
ADAPT. Adjuvant Dynamic marker- Adjusted Personalized Therapy trial optimizing risk assessment and therapy response prediction in early breast cancer
 ADAPT Adjuvant Dynamic marker- Adjusted Personalized Therapy trial optimizing risk assessment and therapy response prediction in early breast cancer Therapieindikation gesteuert durch prognostische Information
ADAPT Adjuvant Dynamic marker- Adjusted Personalized Therapy trial optimizing risk assessment and therapy response prediction in early breast cancer Therapieindikation gesteuert durch prognostische Information
Current Status and Future Development of Tools for Prognosis and Prediction - USA
 Current Status and Future Development of Tools for Prognosis and Prediction - USA John H. Ward, MD Professor of Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine Huntsman Cancer Institute October18, 2009
Current Status and Future Development of Tools for Prognosis and Prediction - USA John H. Ward, MD Professor of Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine Huntsman Cancer Institute October18, 2009
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Fumagalli D, Venet D, Ignatiadis M, et al. RNA Sequencing to predict response to neoadjuvant anti-her2 therapy: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO randomized clinical trial.
Supplementary Online Content Fumagalli D, Venet D, Ignatiadis M, et al. RNA Sequencing to predict response to neoadjuvant anti-her2 therapy: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO randomized clinical trial.
NeoadjuvantTreatment In BC When, How, Who?
 NeoadjuvantTreatment In BC When, How, Who? Clifford Hudis, M.D. Chief, Breast Cancer Medicine Service, MSKCC Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College President, ASCO 15 Potential Benefits Of
NeoadjuvantTreatment In BC When, How, Who? Clifford Hudis, M.D. Chief, Breast Cancer Medicine Service, MSKCC Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College President, ASCO 15 Potential Benefits Of
Kathy Albain, MD. Chemotherapy in Luminal Breast Cancer: Who Benefits? Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine
 Chemotherapy in Luminal Breast Cancer: Who Benefits? Kathy Albain, MD Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine, Director, Breast Clinical Research Program, Cardinal Bernardin Cancer Center,
Chemotherapy in Luminal Breast Cancer: Who Benefits? Kathy Albain, MD Loyola University Chicago Stritch School of Medicine, Director, Breast Clinical Research Program, Cardinal Bernardin Cancer Center,
Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer
 Original Articles Jpn J Clin Oncol 2012;42(6)471 476 doi:10.1093/jjco/hys046 Advance Access Publication 3 April 2012 Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer Junnan Li,
Original Articles Jpn J Clin Oncol 2012;42(6)471 476 doi:10.1093/jjco/hys046 Advance Access Publication 3 April 2012 Clinical Features and Survival Analysis of T1mic, a, bn0m0 Breast Cancer Junnan Li,
Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts
 Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts 7 th SGH Annual Breast Pathology Course Professor Michael Bilous Conjoint Professor Western Sydney University Consultant Pathologist, Australian Clinical Labs,
Reporting of Breast Cancer Do s and Don ts 7 th SGH Annual Breast Pathology Course Professor Michael Bilous Conjoint Professor Western Sydney University Consultant Pathologist, Australian Clinical Labs,
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 335 340 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4435-y Risk factors of recurrence in small-sized, node negative breast cancer in young women: a retrospective
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences RESEARCH PAPER April 2013 Vol.56 No.4: 335 340 doi: 10.1007/s11427-013-4435-y Risk factors of recurrence in small-sized, node negative breast cancer in young women: a retrospective
Radiation Therapy for the Oncologist in Breast Cancer
 REVIEW ARTICLE Chonnam National University Medical School Sung-Ja Ahn, M.D. Adjuvant Tamoxifen with or without in Patients 70 Years of Age with Stage I ER-Positive Breast Cancer: Efficacy Outcomes (10
REVIEW ARTICLE Chonnam National University Medical School Sung-Ja Ahn, M.D. Adjuvant Tamoxifen with or without in Patients 70 Years of Age with Stage I ER-Positive Breast Cancer: Efficacy Outcomes (10
Sustained benefits for women with HER2-positive early breast cancer JORGE MADRID BIG GOCCHI PROTOCOLO HERA
 Sustained benefits for women with HER2-positive early breast cancer JORGE MADRID BIG GOCCHI PROTOCOLO HERA The fascinating history of Herceptin 1981 1985 1987 1990 1992 1998 2000 2005 2006 2008 2011 Murine
Sustained benefits for women with HER2-positive early breast cancer JORGE MADRID BIG GOCCHI PROTOCOLO HERA The fascinating history of Herceptin 1981 1985 1987 1990 1992 1998 2000 2005 2006 2008 2011 Murine
Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
 Implementing a National Cancer Clinical Trials System for the 21 st Century, Workshop #2 Session #5: Accelerating Innovation Through Effective Partnerships Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
Implementing a National Cancer Clinical Trials System for the 21 st Century, Workshop #2 Session #5: Accelerating Innovation Through Effective Partnerships Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
The Oncotype DX Assay A Genomic Approach to Breast Cancer
 The Oncotype DX Assay A Genomic Approach to Breast Cancer Pathology: 20 th and 21 st Century Size Age Phenotype Nodal status Protein/Gene Genomic Profiling Prognostic & Predictive Markers Used in Breast
The Oncotype DX Assay A Genomic Approach to Breast Cancer Pathology: 20 th and 21 st Century Size Age Phenotype Nodal status Protein/Gene Genomic Profiling Prognostic & Predictive Markers Used in Breast
Principles of breast radiation therapy
 ANZ 1601/BIG 16-02 EXPERT ESMO Preceptorship Program 2017 Principles of breast radiation therapy Boon H Chua Professor Director of Cancer and Haematology Services UNSW Sydney and Prince of Wales Hospital
ANZ 1601/BIG 16-02 EXPERT ESMO Preceptorship Program 2017 Principles of breast radiation therapy Boon H Chua Professor Director of Cancer and Haematology Services UNSW Sydney and Prince of Wales Hospital
SFSPM Novembre Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante
 SFSPM Novembre 217 Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante Dr Fabien REYAL Service de Chirurgie INSERM U932 Immunity
SFSPM Novembre 217 Valeur prédictive et pronostique de l infiltrat immunitaire dans les cancers du sein traités par chimiothérapie néoadjuvante Dr Fabien REYAL Service de Chirurgie INSERM U932 Immunity
Prognostic and predictive biomarkers. Marc Buyse International Drug Development Institute (IDDI) Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium
 Prognostic and predictive biomarkers Marc Buyse International Drug Development Institute (IDDI) Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium marc.buyse@iddi.com 1 Prognostic biomarkers (example: gene signature) 2 PROGNOSTIC
Prognostic and predictive biomarkers Marc Buyse International Drug Development Institute (IDDI) Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium marc.buyse@iddi.com 1 Prognostic biomarkers (example: gene signature) 2 PROGNOSTIC
Lecture 5. Primary systemic therapy: clinical and biological endpoints
 Lecture 5 Primary systemic therapy: clinical and biological endpoints Valentina Guarneri, M.D., Ph.D. Primary systemic therapy in breast cancer Firstly introduced d into clinical i l practice in 70s for
Lecture 5 Primary systemic therapy: clinical and biological endpoints Valentina Guarneri, M.D., Ph.D. Primary systemic therapy in breast cancer Firstly introduced d into clinical i l practice in 70s for
FISH mcgh Karyotyping ISH RT-PCR. Expression arrays RNA. Tissue microarrays Protein arrays MS. Protein IHC
 Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
ORMONOTERAPIA ADIUVANTE: QUALE LA DURATA OTTIMALE? MARIANTONIETTA COLOZZA
 ORMONOTERAPIA ADIUVANTE: QUALE LA DURATA OTTIMALE? MARIANTONIETTA COLOZZA THE NATURAL HISTORY OF HORMONE RECEPTOR- POSITIVE BREAST CANCER IS VERY LONG Recurrence hazard rate 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 ER+ (n=2,257)
ORMONOTERAPIA ADIUVANTE: QUALE LA DURATA OTTIMALE? MARIANTONIETTA COLOZZA THE NATURAL HISTORY OF HORMONE RECEPTOR- POSITIVE BREAST CANCER IS VERY LONG Recurrence hazard rate 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 ER+ (n=2,257)
Development and verification of the PAM50-based Prosigna breast cancer gene signature assay
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2015 Development and verification of the PAM50-based Prosigna breast cancer gene signature assay Jacqueline Snider
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2015 Development and verification of the PAM50-based Prosigna breast cancer gene signature assay Jacqueline Snider
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, et al. Pathological
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, et al. Pathological
Ki-67 is a biological tumor marker that reflects tumor
 Evaluation of Ki-67 Index in Core Needle Biopsies and Matched Breast Cancer Surgical Specimens Soomin Ahn, MD; Junghye Lee, MD; Min-Sun Cho, MD, PhD; Sanghui Park, MD, PhD; Sun Hee Sung, MD, PhD Context.
Evaluation of Ki-67 Index in Core Needle Biopsies and Matched Breast Cancer Surgical Specimens Soomin Ahn, MD; Junghye Lee, MD; Min-Sun Cho, MD, PhD; Sanghui Park, MD, PhD; Sun Hee Sung, MD, PhD Context.
8/8/2011. PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant Chemotherapy in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer. Overview
 Overview PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer Jennifer K. Litton, M.D. Assistant Professor The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Using multigene assay
Overview PONDERing the Need to TAILOR Adjuvant in ER+ Node Positive Breast Cancer Jennifer K. Litton, M.D. Assistant Professor The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Using multigene assay
Neo-adjuvant and adjuvant treatment for HER-2+ breast cancer
 Neo-adjuvant and adjuvant treatment for HER-2+ breast cancer Angelo Di Leo «Sandro Pitigliani» Medical Oncology Unit Hospital of Prato Istituto Toscano Tumori Prato, Italy NOAH: Phase III, Open-Label Trial
Neo-adjuvant and adjuvant treatment for HER-2+ breast cancer Angelo Di Leo «Sandro Pitigliani» Medical Oncology Unit Hospital of Prato Istituto Toscano Tumori Prato, Italy NOAH: Phase III, Open-Label Trial
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience
 Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease
 GBCC 2018, April 6, Songdo ConvensiA, Incheon, Korea Panel Discussion 4, How Can We Better Treat Patients with Metastatic Disease? Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease Tadahiko
GBCC 2018, April 6, Songdo ConvensiA, Incheon, Korea Panel Discussion 4, How Can We Better Treat Patients with Metastatic Disease? Role of Primary Resection for Patients with Oligometastatic Disease Tadahiko
Sesiones interhospitalarias de cáncer de mama. Revisión bibliográfica 4º trimestre 2015
 Sesiones interhospitalarias de cáncer de mama Revisión bibliográfica 4º trimestre 2015 Selected papers Prospective Validation of a 21-Gene Expression Assay in Breast Cancer TAILORx. NEJM 2015 OS for fulvestrant
Sesiones interhospitalarias de cáncer de mama Revisión bibliográfica 4º trimestre 2015 Selected papers Prospective Validation of a 21-Gene Expression Assay in Breast Cancer TAILORx. NEJM 2015 OS for fulvestrant
The Oncotype DX Assay in the Contemporary Management of Invasive Early-stage Breast Cancer
 The Oncotype DX Assay in the Contemporary Management of Invasive Early-stage Breast Cancer Cancer The Biology Century Understanding and treating the underlying tumor biology Cancer genetic studies demonstrate
The Oncotype DX Assay in the Contemporary Management of Invasive Early-stage Breast Cancer Cancer The Biology Century Understanding and treating the underlying tumor biology Cancer genetic studies demonstrate
Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the. Subtypes. Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy
 Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the Classification of Molecular Subtypes Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy We know it is many diseases Breast cancer is
Present Role of Immunohistochemistry in the Classification of Molecular Subtypes Beppe Viale European Institute of Oncology University of Milan Milan-Italy We know it is many diseases Breast cancer is
Rationale For & Design of TAILORx. Joseph A. Sparano, MD Albert Einstein College of Medicine Montefiore-Einstein Cancer Center Bronx, New York
 Rationale For & Design of TAILORx Joseph A. Sparano, MD Albert Einstein College of Medicine Montefiore-Einstein Cancer Center Bronx, New York Declining Breast Cancer Mortality & Event Rates in Adjuvant
Rationale For & Design of TAILORx Joseph A. Sparano, MD Albert Einstein College of Medicine Montefiore-Einstein Cancer Center Bronx, New York Declining Breast Cancer Mortality & Event Rates in Adjuvant
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
National Medical Policy
 National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: MammaPrint, Prosigna and Other Gene Expression Tests for Breast Cancer NMP520 Effective Date*: May 2013 Updated: June 2017 This National Medical Policy is
National Medical Policy Subject: Policy Number: MammaPrint, Prosigna and Other Gene Expression Tests for Breast Cancer NMP520 Effective Date*: May 2013 Updated: June 2017 This National Medical Policy is
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium. Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin
 UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
UK Interdisciplinary Breast Cancer Symposium Should lobular phenotype be considered when deciding treatment? Michael J Kerin Professor of Surgery National University of Ireland, Galway and Galway University
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Adjuvant Chemotherapy + Trastuzumab
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Adjuvant Chemotherapy + Trastuzumab (Optimal Drugs / Dosage / Trastuzumab) Adjuvant Chemotherapy (Optimal Drugs / Optimal Dosage
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Adjuvant Chemotherapy + Trastuzumab (Optimal Drugs / Dosage / Trastuzumab) Adjuvant Chemotherapy (Optimal Drugs / Optimal Dosage
Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:
 Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:7332-7341 Presented by Deming Mi 7/25/2006 Major reasons for few prognostic factors to
Roadmap for Developing and Validating Therapeutically Relevant Genomic Classifiers. Richard Simon, J Clin Oncol 23:7332-7341 Presented by Deming Mi 7/25/2006 Major reasons for few prognostic factors to
Summary BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3
 ESMO 2016 Congress 7-11 October, 2016 Copenhagen, Denmark Table of Contents Summary... 2 BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3 Large data analysis reveals similar survival outcomes with sequential
ESMO 2016 Congress 7-11 October, 2016 Copenhagen, Denmark Table of Contents Summary... 2 BREAST CANCER - Early Stage Breast Cancer... 3 Large data analysis reveals similar survival outcomes with sequential
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer
 Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer Rob Baxter Laboratory for Cellular and Diagnostic Proteomics Kolling Institute, University of Sydney, Royal North Shore Hospital robert.baxter@sydney.edu.au
Proteomic Biomarker Discovery in Breast Cancer Rob Baxter Laboratory for Cellular and Diagnostic Proteomics Kolling Institute, University of Sydney, Royal North Shore Hospital robert.baxter@sydney.edu.au
Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease
 Should gene array assays be routinely used in node positive disease? Yes Christy A. Russell, MD University of Southern California Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease 1 Validity of the Oncotype
Should gene array assays be routinely used in node positive disease? Yes Christy A. Russell, MD University of Southern California Oncotype DX testing in node-positive disease 1 Validity of the Oncotype
Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers q
 European Journal of Cancer 40 (2004) 1837 1841 European Journal of Cancer www.ejconline.com Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers
European Journal of Cancer 40 (2004) 1837 1841 European Journal of Cancer www.ejconline.com Good Old clinical markers have similar power in breast cancer prognosis as microarray gene expression profilers
How to Use MRI Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
 Global Breast Cancer Conference 2016 & 5 th International Breast Cancer Symposium April 29 th 2016, 09:40-10:50 How to Use MRI Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
Global Breast Cancer Conference 2016 & 5 th International Breast Cancer Symposium April 29 th 2016, 09:40-10:50 How to Use MRI Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (NAC) in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
Quantitative Assay for Measurement of HER2 Total Protein Expression and HER2 Dimers
 Quantitative Assay for Measurement of HER2 Total Protein Expression and HER2 Dimers Policy Number: 2.04.76 Last Review: 12/2017 Origination: 12/2015 Next Review: 12/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield
Quantitative Assay for Measurement of HER2 Total Protein Expression and HER2 Dimers Policy Number: 2.04.76 Last Review: 12/2017 Origination: 12/2015 Next Review: 12/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield
The Current Status and the Future Prospects of Multigene testing in Europe
 The Current Status and the Future Prospects of Multigene testing in Europe Emiel J. Rutgers The Netherlands Cancer Institute Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek Hospital Amsterdam St. Gallen Recommendations 2009 =
The Current Status and the Future Prospects of Multigene testing in Europe Emiel J. Rutgers The Netherlands Cancer Institute Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek Hospital Amsterdam St. Gallen Recommendations 2009 =
Quantitative Assay for Measurement of HER2 Total Protein Expression and HER2 Dimers
 Quantitative Assay for Measurement of HER2 Total Protein Expression and HER2 Dimers Policy Number: 2.04.76 Last Review: 12/2018 Origination: 12/2015 Next Review: 12/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield
Quantitative Assay for Measurement of HER2 Total Protein Expression and HER2 Dimers Policy Number: 2.04.76 Last Review: 12/2018 Origination: 12/2015 Next Review: 12/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield
The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative
 Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Original Article The effect of delayed adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse of triplenegative breast cancer Shuang Li 1#, Ding Ma 2#, Hao-Hong Shi 3#, Ke-Da Yu 2, Qiang Zhang 1 1 Department of Breast Surgery,
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer. Pathology. AGO e. V. in der DGGG e.v. sowie in der DKG e.v.
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Diagnosis and Treatment of Patients with Primary and Metastatic Breast Cancer Pathology Pathology Versions 2004 2017: Blohmer / Costa / Fehm / Friedrichs / Huober / Kreipe / Lück / Schneeweis / Sinn /
Layered-IHC (L-IHC): A novel and robust approach to multiplexed immunohistochemistry So many markers and so little tissue
 Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to
Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to
10/15/2012. Biologic Subtypes of TNBC. Topics. Topics. Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical relevance
 Biologic Subtypes of TNBC Andrea L. Richardson M.D. Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Topics Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical
Biologic Subtypes of TNBC Andrea L. Richardson M.D. Ph.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Topics Histopathology Molecular pathology Clinical
Modern classification of breast cancer-should we stick with morphology or convert to molecular profiles?
 Modern classification of breast cancer-should we stick with morphology or convert to molecular profiles? Ian Ellis Professor of Cancer Pathology Molecular Medical Sciences University of Nottingham Dept
Modern classification of breast cancer-should we stick with morphology or convert to molecular profiles? Ian Ellis Professor of Cancer Pathology Molecular Medical Sciences University of Nottingham Dept
Triple negative breast cancer Biology and targeted therapy
 Triple negative breast cancer Biology and targeted therapy MR SCI MED DR I BOŽOVIĆ -SPASOJEVIĆ INSTITUT ZA ONKOLOGIJU I RADIOLOGIJU SRBIJE I VA N A B O Z O V I C @ O U T L O O K. C O M Current challanges
Triple negative breast cancer Biology and targeted therapy MR SCI MED DR I BOŽOVIĆ -SPASOJEVIĆ INSTITUT ZA ONKOLOGIJU I RADIOLOGIJU SRBIJE I VA N A B O Z O V I C @ O U T L O O K. C O M Current challanges
CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS
 CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS S. Chahbouni¹, A. Amarti 2, N. Hammas 3, L. Chbani 3, H. El fatemi 3 1 Department
CLINICOPATHOLOGIC FEATURES AND MOLECULAR SUBTYPES OF BREAST CANCER IN FEZ-MEKNES REGION (MOROCCO): A STUDY OF 390 PATIENTS S. Chahbouni¹, A. Amarti 2, N. Hammas 3, L. Chbani 3, H. El fatemi 3 1 Department
Editorial Process: Submission:05/09/2017 Acceptance:08/23/2018
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:05/09/2017 Acceptance:08/23/2018 Predictors of Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Iranian Breast Cancer Patients Pegah Sasanpour
RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:05/09/2017 Acceptance:08/23/2018 Predictors of Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Iranian Breast Cancer Patients Pegah Sasanpour
