Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) Warunsuda Sripakdee, BCOP,BCP Prince of Songkla University
|
|
|
- Allison Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) 1 Warunsuda Sripakdee, BCOP,BCP Prince of Songkla University
2 Hematologic malignancies CML ALL AML 2
3 CML CD34+ results from an acquired mutation that affects hematopoietic stem cells excessive mature neutrophil production median age at diagnosis is 67 years old more common in males 3
4 Pathogenesis of CML 95% of CML patients have the BCR-ABL fusion gene ₒ TK region 4
5 Molecular abnormality in CML 5
6 Molecular abnormality in CML promoting instability of the leukemic clone marrow progenitor cells - increasing ly likely to undergo proliferation less capacity for selfrenewal! Additional cytogenetic abnormalities such as trisomy 8, isochromosome 17, trisomy 21 and deletion 7 End-stage disease 6
7 CML Risk Factors : ionizing radiation! Signs and symptoms Clinical - abdominal pain - early satiety due to splenomegaly - anorexia - bone pain purport - unexplained weight loss ±fatigue Laboratory - leukocytosis(usua lly >25,000 cells/ mm - increased LDH - other CBC: megakaryocytosis, basophilia, eosinophilia Bone marrow - hypercellular (75-90%) - increased erythropoiesis & megakaryocytic - Blasts <10% 7
8 Natural history of disease Chronic phase Accelerated phase Blast phase World Health Organization (WHO) Criteria Accelerated Phase Blast Crisis Blasts 10-19% of WBCs in peripheral and/or bone marrow Persistent thrombocytopenia (< 100,000 cells/mm 3 ) unrelated to therapy or persistent thrombocytosis (>1,000,000 cells/mm 3 ) unresponsive to therapy Increasing spleen size and increasing WBC unresponsive to therapy blood cells or of bone marrow cells Extramedullary blast proliferation Large foci or clusters of blasts in the bone marrow biopsy Cytogenetic evidence of clonal evolution additional cytogenetic abnormalities (extra Ph, trisomy 8, trisomy 19 and/or isochromosome 17) 8
9 Risk stratifications Study Calculation Sokal et al, Exp x (age in years ) + (spleen ) x 700) 2 Low <0.8 Intermediate High >1.2 Hasford et al, when age 50 years + (0.042 x spleen) when platelet count > 1500 x 10 9 /L + ( x blast cells) when basophils > 3% + ( x eosinophils) x 100 Low 780 Intermediate High >1480 clinical trial & initial treatment selection 9
10 Treatment of CML tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs): 10 yrs OS 80-90% dasatinib, nilotinib, bosutinib, and ponatinib others agent : omacetaxine goals of treatment CP-CML: prevent progression to AP or BP AP-CML : induce second chronic phase BP-CML : induce second chronic phase!! 10
11 Response criteria in CML Type of Response Hematologic Cytogenetic Molecular Criteria Complete (CHR): Normal peripheral blood count WBC < 10,000 cells/ mm 3 Platelets < 450,000 cells/mm 3 No immature cells in the peripheral blood No signs or symptoms of disease Complete (CCyR): 0% Ph+ metaphases Partial (PCyR): 1-35% Ph+ metaphases Major (MCyR): 0-35% Ph+ metaphases (complete + partial responses) Minor: >35% Ph+ metaphases Complete (CMR): no detectable BCR-ABL mrna by QPCR (IS) Major (MMR): Cytogenetic remission with 3 log or greater reduction in BCR- ABL transcripts by QPCR (IS) goal standard - CCyR at 12 month; improved survival now- MMR is early goal for CML 4.5 log reduction of BCR-ABL - outcome predictor 11
12 Response criteria in CML Time Optimal response Warning Failure Baseline 3 mos. BCR-ABL IS 10%* Ph+ 35% (PCyR) 6 mos. BCR-ABL IS <1%* Ph+ 0% (CCyR) High risk Major route CCA/Ph+ BCR-ABL IS >10%* Ph % BCR-ABL IS 1-10%* Ph+ 1-35% 12 No CHR* Ph+ >95% BCR-ABL IS >10%* Ph+ >35% 12 mos. BCR-ABL IS 0.1%* (MMR) BCR-ABL IS 0.1-1%* BCR-ABL IS >1%* Ph+ >0% Then, and at any time UPDATE 2013 European LeukemiaNet Recommendations for the Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) Response definitions for any TKI first line, and 2nd line in case of intolerance, all patients (CP, AP, and BC) MMR or better CCA/Ph- (-7, or 7q-) Loss of CHR Loss of CCyR Loss of MMR, confirmed** Mutations CCA/Ph+ *and/or **in 2 consecutive tests, of which one 1% IS: BCR-ABL on International Scale Treatment recommendations
13 Response criteria in CML RESPONSE MILESTONES c,e BCR-ABL1 (IS) 3 months 6 months 12 months >12 months >10% f YELLOW RED >1% 10% GREEN YELLOW RED >0.1% 1% GREEN YELLOW 0.1% GREEN RED YELLOW CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS Evaluate patient compliance and drug interactions Mutational analysis Evaluate patient compliance and drug interactions Mutational analysis SECOND-LINE AND SUBSEQUENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Switch to alternate TKI (CML-5) and Evaluate for HCT (CML-6) Switch to alternate TKI (CML-5) or Continue same TKI (CML-F) g or Dose escalation of imatinib (to a max of 800 mg) and Evaluate for HCT (CML-6) GREEN Monitor response (CML-F Continue same TKI (CML-F) h 13
14 First line therapy for chronic phase CML 14
15 First line therapy Imatinib: irreversible TKI,bind to the inactive / closed conformation of ABL enzyme, c-kit, PDGFR Results of the IRIS trial Selected Results of the IRIS Trial and Follow-up Studies Endpoint Imatinib IFN + Cytarabine P value FFP at 18 months 96.7% 91.5% < MCyR at 18 months 87.1% 34.7% < CCyR at 18 months 76.2% 14.5% < CCyR at 5 years 87% --- NR OS at 5 years 89% --- NR EFS at 8 years 81% --- NR FFP at 8 years 92% --- NR 15
16 Trial Cortes et al. (2010) ( TOPS ) Hehlmann et al. (2011) ( German CML IV ) Selected Trials of High-Dose Imatinib in Newly Diagnosed CP-CML Population Imatinib Imatinib Endpoint 800 mg/day 400 mg/day 476 patients with newly diagnosed CP-CML 1551 patients with newly diagnosed CP- CML First line therapy Imatinib: TOPS and German CML IV trials: high-dose versus low dose imatinib P value CCyR at 12 months 70% 66% 0.35 High-dose imatinib (>400 mg/day) MMR at 12 months is not currently 46% recommended 40% 0.20 as initial therapy for patients with newly diagnosed CP-CML. MMR at 42 months 50.2% 51.6% NS MMR at 12 months 59% 44% < PFS at 3 years 94% 94% NS OS at 3 years 95% 95% NS PFS at 60 months 87.5% 87.5% NS OS at 60 months 90% 90% NS higher rates of dose interruption, reduction and discontinuation due to grade 3 or 4 adverse events 16
17 First line therapy Dasatinib: inhibit active/inactive ABL and Src family of kinases, c-kit, PDGFR 325 times more potent than imatinib activity against nearly all BCR-ABL mutations resistant to imatinib (except T315I)! Results of the DASISION trial Selected Results from the DASISION Trial and Follow-Up Studies Endpoint Dasatinib Imatinib P value (n = 259) (n = 260) Median time to CCyR 3.1 months 5.8 months NR CCyR at 12 months 83% 72% MMR by 12 months 46% 28% < Median time to MMR 15 months 36 months NR MMR at any time 52% 34% < Disease progression during study treatment 3% 5% NR CCyR at 60 months 83% 78% MMR at 60 months 76% 64% PFS at 60 months 85% 86% NR OS at 60 months 91% 17 90% NR
18 First line therapy Nilotinib inhibit inactive/closed ABL, c-kit, PDGFR better topographic fit to the ATP binding site than imatinib 30 times more potent than imatinib Endpoint CCyR by 12 months MMR by 12 months CCyR by 24 months MMR by 24 months Disease progression by 24 months Treatment failure at 12 months PFS at 48 months OS at 48 months MMR at 60 months Still on initial treatment at 60 months Results of the ENESTnd trial Selected Results from the ENESTnd Trial Nilotinib Nilotinib 300 mg BID 400 mg BID (n = 282) (n = 281) 80% 78% (p < 0.001) (p < 0.001) 44% 43% (p < 0.001) (p < 0.001) 87% 85% (p = ) (p = 0.016) 71% 67% (p < ) (p < ) < 0.7% < 1.9% (p = ) (p = ) 3% 2% (p = NR) (p = NR) 96.7% 97.8% (p = NR) (p = NR) 92.7% 96.7% (p = NR) 77% (p < 0.001) 60% (p = NR) 18 (p = NR) 77% (p < 0.001) 62% (p = NR) Imatinib 400 mg daily (n = 283) 65% 22% 77% 44% 4.8% 8% 93.1% 93.3% 60% 50%
19 Initial selection of TKI low-risk disease: imatinib, nilotinib, dasainib (category 1) high-risk disease : nilotinib, dasatinib (categoy 1) dasatinib and nilotinib -superior CCyR and MMR at lower rates of PD when compared to imatinib Neither dasatinib nor nilotinib - improved OS or PFS compared to imatinib. the DASISION and ENESTnd - intermediate- and high- risk patients may preferentially benefit from dasatinib or nilotinib 19
20 Initial selection of TKI NCCN Guidelines Version Chronic Myeloid Leukemia NCCN Guidelines Index Table of Contents Discussion CLINICAL PRESENTATION PRIMARY TREATMENT Chronic phase CML Treatment Considerations: Patient comorbidities and drug toxicities Monitor response c Evaluate patient compliance and drug interactions Early toxicity monitoring Low-risk score (See Risk Calculation Table CML-A) Intermediate- or highrisk score (See Risk Calculation Table CML-A) First generation TKI (Imatinib or generic imatinib 400 mg QD) (category 1) or Second generation TKI (Bosutinib or Dasatinib or Nilotinib or Clinical trial First generation TKI (Imatinib or generic imatinib 400 mg QD) or Second generation TKI (Bosutinib d or Dasatinib 100 mg QD d or Nilotinib 300 mg BID d ) or Clinical trial See Response Milestones and Treatment Options (CML-3) c See Response Milestones and Treatment Options (CML-3) c 20
21 Initial selection of TKI Choice of first-line therapy should be individualized. a. Potential toxicity profiles b. Patient s age and ability to tolerate therapy c. Presence of comorbid conditions d. Patient s risk score e. Physician experience 21
22 ! Responding patients should continue therapy indefinitely. STIM & TWISTER trials STIM TWISTER EURO-SKI 100 patients with CP- CML who had CMR for > 2 yrs. 61% of patients relapsed after stop imatinib 95% of relapses occurring within 7 months of stopping imatinib low-risk Sokol score and duration of imatinib therapy >54 months -continued response after imatinib cessation Discontinuation of TKI!! 40 patients with CP- CML who had been in CMR for 2 or more years TFR at 2 years was 45% High Sokal score and shorter duration of interferon treatment - increased risk of relapse patients with CP-CML who had been in long term MR 70% TFR
23 Discontinuation of TKI ALL of the following criteria are met: 1) Consultation with a CML Specialty Center 2) Age 18 years 3) no history of accelerated phase or blast crisis 4) On TKI therapy 3 years 5) Prior evidence of detectable disease via BCR-ABL1 transcript 6) Stable molecular response (MR4) for 2 years (at least 4 tests performed at least 3 months apart) 7) No history of resistance to any TKI 8) Access to reliable response monitoring 9) Monthly molecular monitoring for the first 6 months following discontinuation, bimonthly during months 7-24, and quarterly thereafter if still in MMR 10) Prompt resumption of TKI in patients with loss of MMR 23
24 Second line therapy 24
25 Second line therapy the selection of an alternative TKI is based on prior therapy concurrent disease states mutational testing 25
26 Second line therapy 2nd lind Tx: dasatinib, nilotinib or bosutinib 1st line imatinib yes no other TKIs other TKIs except imatinib 26
27 Second line therapy TREATMENT OPTIONS BASED ON BCR-ABL1 MUTATION PROFILE Mutation Y253H, E255K/V, or F359V/C/I F317L/V/I/C, T315A, or V299L E255K/V, F317L/V/I/C, F359V/C/I, T315A, or Y253H T315I Treatment Recommendation j Dasatinib Nilotinib Bosutinib Ponatinib, k Omacetaxine, l allogeneic HCT (CML-6), or clinical trial 27
28 Predictive factors for achievement of a cytogenetic response to second-line TKI therapy 1. Low Sokal score at diagnosis 2. Best cytogenetic response on imatinib 3. Neutropenia at any time during imatinib therapy requiring dose reduction despite growth factor support 4. Time from detection of imatinib failure to start of second-line TKI 28
29 Second line therapy Bosutinib : inhibit dual ABL/SRC family of kinases! minimal inhibit: c-kit, PDGFR, Src, Lyn and Hck kinases against many BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations that are resistant to imatinib, dasatinib and nilotinib (except T315I and V299)! 200 times more potent than imatinib 29
30 Second line therapy: Bosutinib Bosutinib Versus Imatinib in Newly Diagnosed Chronic- Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Results From the BELA Trial A Complete Cytogenetic Response (%) Bosutinib Imatinib * B Major Molecular Response (%) Bosutinib Imatinib 3 27 * * * 27 Time Since Treatment Initiation (months) Time Since Treatment Initiation (months) The trial did not meet its primary endpoint of improved CCyR at 12 months. 30
31 not currently recommended in the first-line setting (prep course 2017) The ASCO Post Results from the randomized BFORE trial. J Clin Oncol. November 1, 2017 Second line therapy: Bosutinib FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Bosutinib for Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Philadelphia Chromosome " Positive CML # $ By The ASCO Post December 25, 2017 Tweet this page On December 19, 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted accelerated approval to bosutinib (Bosulif) for treatment of patients with newly diagnosed chronic-phase Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). Approval was based on data from an open-label, randomized, multicenter BFORE trial in 487 patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive newly diagnosed chronic phase CML who were randomized to receive either bosutinib at 400 mg once daily or imatinib (Gleevec) at 400 mg once daily. The major e!cacy outcome measure was major molecular response (MMR) at 12 months, defined as 0.1% BCR-ABL ratio on international scale (corresponding to 3 log reduction from standardized baseline) with a minimum of 3,000 ABL transcripts as assessed by the central laboratory. MMR at 12 months was 47.2% (95% confidence interval [CI] = ) in the bosutinib arm and 36.9% (95% CI = ) in the imatinib arm (P =.0200). The most common adverse reactions in patients with newly diagnosed CML (incidence 20%) are diarrhea, nausea, thrombocytopenia, rash, increased alanine aminotransferase, abdominal pain, and increased aspartate aminotransferase. 31 1
32 Second line therapy: Bosutinib Selected Trials of Bosutinib in the Second-Line Setting Citation Population MCyR CCyR PFS OS Cortes et al. (2011) 288 pts with imatinib-resistant or intolerant CP-CML 53% 41% 79% at 24 mo 92% at 24 mo 32
33 Second line therapy: Dasatinib Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic-phase, chronic myeloid leukemia patients: 7-year follow-up of study CA Am. J. Hematol. 91: , VC 2016
34 Second line therapy: Dasatinib Drug-Related Adverse Events of Interest Over Time Treated patients, n/at risk (%) 100 mg QD (n 5 165) Other dose groups (n 5 497) 2-year 5-year 7-year 2-year 5-year 7-year Pleural effusion 23/121 (14) 40/55 (24) 46/42 (28) 118/309 (24) 158/127 (32) 174/91 (35) Pulmonary hypertension 0 (0) 0 (0) 3 (2) 5 (1) 8 (2) 13 (3) Pulmonary arterial hypertension 0 (0) 1 (<1) 0 (0) 0 (0) 34
35 Second line therapy: Nilotinib nilotinib in the second-line setting Selected Trials of Nilotinib in the Second-Line Setting Citation Population MCyR CCyR PFS OS Kantarjian et al. (2011) Giles et al. 321 pts with imatinib-resistant or intolerant CP-CML 321 pts with imatinib-resistant or intolerant CP-CML 59% 44% 64% at 24 mo 87% at 24 mo 59% 45% 57% at 48 mo 78% at 48 mo 35
36 Second line therapy: Milestone for second line drug Time Optimal response Warnings Failure Baseline 3 mos. BCR-ABL IS 10%* Ph+ <65% 6 mos. BCR-ABL IS 10%* Ph+ <35% (PCyR) 12 mos. BCR-ABL IS <1%* Ph+ 0 (CCyR) Then, and at any time MMR or better No CHR Loss of CHR on imatinib Lack of CyR to 1 st line TKI High risk BCR-ABL IS >10%* Ph % BCR-ABL IS 10%* Ph % BCR-ABL IS 1-10%* Ph+ 1-35% CCA/Ph- (-7 or 7q-) or BCR-ABL IS >0.1% No CHR, or Ph+ >95%, or New mutations BCR-ABL IS >10%* Ph+ >65%* New mutations BCR-ABL IS >10%* Ph+ >35%* New mutations Loss of CHR, or Loss of CCyR or PCyR New mutations Loss of MMR** CCA/Ph+ *and/or **in 2 consecutive tests, of which one 1% IS: BCR-ABL on International Scale NCE EUROPEAN LEUKEMIANET - PUBLISHER: 36
37 Third line therapy and beyond 37
38 Third line therapy and beyond No TKI is specifically indicated for treatment failure of both first- and second-generation TKIs. current literature restricted to observational studies or studies with small patient populations Allogeneic stem cell transplantation may be considered! 38
39 Third line therapy and beyond Omacetaxine mepesuccinate (Synribo ) MOA antileukemic effect of omacetaxine is independent of BCR-ABL binding option for patients with resistance and/or intolerance to two or more TKIs 39
40 Third line therapy and beyond Omacetaxine mepesuccinate (Synribo ) 2 phase II studies have been conducted in CP-CML: patients with a T315I mutation or who had failed treatment with one or more TKIs patients that had failed treatment with two or more TKIs allowed enrollment of patients who were in AP-CML CCyR of 4-16% ; median PFS months major adverse effects - myelosuppression subcutaneous, twice-daily dosing schedule - limit compliance 40
41 Primary Resistance Resistance to TKIs A. Primary hematologic resistance failure to achieve a hematologic remission 3-6 months after initiation of therapy B. Primary cytogenetic resistance! failure to achieve any cytogenetic response at 6 months, MCyR at 12 months, or CCyR at 18 months! 41
42 Resistance to TKIs Primary Resistance Dose escalation of imatinib : 800 mg/day Pt with cytogenetic relapse who achieved a complete cytogenetic response with standarddose imatinib suboptimal cytogenetic response to standard dose imatinib! 42
43 Resistance to TKIs Secondary Resistance T315I mutation gatekeeper resistance to all currently available TKIs except ponatinib 43
44 BCR-ABL1 mutation analysis results may predict response to TKIs BCR-ABL1 mutation T315I V299L Predicts resistance to Imatinib Dasatinib Nilotinib Bosutinib Dasatinib Bosutinib Consider preferential use of Ponatinib Nilotinib F317L/V/I/C Dasatinib Bosutinib Y253F/H Nilotinib Bosutinib E255K/V Nilotinib No preference F359V/I/C Nilotinib Bosutinib 44
45 Treatment of T315I mutated CML Ponatinib or Omacetaxine Ponatinib : 3rd generation TKIs PACE study : patients with resistance or intolerance to prior TKI therapy or with the T315I mutation A Chronic-Phase CML Total Resistance or side effects (N=267) (N=203) Patients (%) Complete Hematologic Response Major Cytogenetic Response Complete Cytogenetic Response Major T315I (N=64) Molecular Response Total (N=149) Probability of Susatained Major Cytogenetic Response Resistance or side effects (N=104) Months after First Major Cytogenetic Response T315I (N=45) Probability of Overall Survival Total (N=267) Resistance or side effects (N=203) Months T315I (N=64) 4-year MMR rate - 61%, 4-year PFS- 56%, 4- year OS -77%
46 Treatment of T315I mutated CML Ponatinib : Epic trial was terminated after the observation of arterial thrombotic events.! pan-vegf inhibition Black Box Warning Current guidelines recommend consideration of ponatinib only for patients with a T315I mutation and for patients who have failed 2 or more prior TKIs 46
47 TKI Toxicities 47
48 TKI Toxicities strong negative association between comorbidities at diagnosis and OS in patients with CP-CML no negative effect of comorbidities on remission rates or progression to advanced stages of disease 48
49 TKI toxicities Suggestions for management of common TKI toxicities Toxicity Neutropenia Anemia Thrombocytopenia Rash Management Strategy Hold until recovery, potential dose reduction Myeloid growth factors may be considered ESAs not supported in patients with myeloid malignancies. Hold until recovery, potential dose reduction Topical or systemic steroids Dose reduction, interruption or discontinuation 49
50 Unique TKI toxicities related to the agent s off-target kinase profile Imatinib Dasatinib Fluid retention (pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, edema, ascites) Muscle cramps Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) Fluid retention (pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, edema, ascites) Platelet inhibition Loop diuretics Decrease sodium intake Supportive care Consider checking left ventricular ejection fraction Dose reduction, interruption or discontinuation Calcium supplementation Tonic water Discontinue therapy Diuretics Supportive care, including oxygen and thoracentesis Consider short course of corticosteroids Dose reduction, interruption or discontinuation Use caution with other anti-platelet agents (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel) 50
51 Unique TKI toxicities Nilotinib Bosutinib Ponatinib QT prolongation Elevated serum lipase or amylase Hepatic toxicity Peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD) Metabolic syndrome (hyperglycemia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia) Hepatic toxicity Diarrhea Hepatic toxicity Ischemic reactions, hypertension, vascular occlusion, heart failure Elevated serum lipase or amylase Symptomatic pancreatitis ECG to measure QTc at baseline, 7 days after initiation and periodically thereafter Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia Consider dose reduction or discontinuation 51 Hold until recovery, then dose reduction Hold until recovery, then dose reduction or discontinuation Eliminate all risk factors (smoking, obesity, hypertension, etc) Consider prophylactic aspirin therapy Discontinue therapy Maximize glycemic, cholesterol and triglyceride control Hold until recovery, then dose reduction or discontinuation Antidiarrheal medication and fluid replacement Hold until recovery Hold until recovery, then dose reduction or discontinuation Control risk factors for hypertension and atherosclerosis Referral to cardiologist Discontinue therapy Hold until recovery, then dose reduction
52 Pharmacologic considerations of TKI therapy Table 12. Pharmacologic considerations of TKI therapy. Imatinib Dasatinib Nilotinib Bosutinib Ponatinib Chronic phase dosing Dose reductions required Food-drug interactions 400 mg PO daily Hematologic Renal impairment Hepatic impairment Improved tolerability with food Take with a large glass of water 100 mg PO daily Hematologic Improved tolerability with food 300 mg PO twice daily Hematologic Hepatic impairment Take on an empty stomach (1 hour before or 2 hours after eating) 500 mg PO daily Hematologic Hepatic impairment Improved tolerability with food Take with a large glass of water 45 mg PO daily Hematologic Hepatic impairment Can be taken with or without food Metabolism CYP3A4 substrate and inhibitor Weak inhibitor of CYP2D6 and 2C9 CYP3A4 substrate CYP3A4 substrate and inhibitor *Also 2C8, 2C9 and 2D6 CYP3A4 substrate CYP3A4 substrate Potential drug interactions Use warfarin with caution Requires acidic gastric environment - avoid acid reducers (H2 antagonists and PPIs) and separate antacids by 2 hours Black box warning for QT-prolonging drugs PPIs may decrease bosutinib concentrations consider using H2 antagonists or short-acting antacids Elevated gastric ph may reduce bioavailability avoid PPIs, H2 antagonists and antacids if possible Assistance 52
53 Accelerated phase / blast crisis Goal - return patient to chronic phase Bone marrow cytogenetics and mutational analysis prior to the initiation of treatment use TKIs to reduce the disease burden prior to allo HSCT Achieving MCyR or CCyR to TKI therapy prior to allo HSCT - better transplant outcome! 53
54 Accelerated phase Treatment : accelerated phase - imatinib 600 mg OD, dasatinib 140 mg OD, nilotinib 400 mg bid or bosutinib 500 mg OD - Omacetaxine - not an option for patients who present with AP-CML. 54
55 Blast crisis blast crisis - TKI+chemotherapy - RR 25-60% (AML or ALL) + HCST - TKI + steroids! 55
56 TKIs for the treatment of relapse after allo HSCT! 1.TKI ± DLI- imatinib, dasatinib, nilotinib, bosutinib 2. Omacetaxine! 56
57 57
The BCR-ABL1 fusion. Epidemiology. At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine
 At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Robert E. Richard MD PhD rrichard@uw.edu robert.richard@va.gov Philadelphia chromosome
At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Robert E. Richard MD PhD rrichard@uw.edu robert.richard@va.gov Philadelphia chromosome
The speaker has no financial relationships with a commercial interest to disclose and no conflicts of interest to resolve.
 Hana Safah MD Professor of Medicine Tulane University School of Medicine Director of the SCT program, Tulane Medical Center The speaker has no financial relationships with a commercial interest to disclose
Hana Safah MD Professor of Medicine Tulane University School of Medicine Director of the SCT program, Tulane Medical Center The speaker has no financial relationships with a commercial interest to disclose
A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable.
 1 Case 1 A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable. CBC and bone marrow aspiration and biopsy were done. Chromosome study showed she had t(9;22)
1 Case 1 A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable. CBC and bone marrow aspiration and biopsy were done. Chromosome study showed she had t(9;22)
CML: Living with a Chronic Disease
 CML: Living with a Chronic Disease Jorge Cortes, MD Chief, CML and AML Sections Department of Leukemia M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas Survival in Early Chronic Phase CML TKI Interferon Chemotherapy
CML: Living with a Chronic Disease Jorge Cortes, MD Chief, CML and AML Sections Department of Leukemia M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas Survival in Early Chronic Phase CML TKI Interferon Chemotherapy
2nd generation TKIs to first line therapy
 New Horizons 2011 Newly diagnosed CML moving 2nd generation TKIs to first line therapy Gianantonio Rosti Dept. Of Hematology and Oncology St. Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital Bologna (Italy) GIMEMA
New Horizons 2011 Newly diagnosed CML moving 2nd generation TKIs to first line therapy Gianantonio Rosti Dept. Of Hematology and Oncology St. Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital Bologna (Italy) GIMEMA
HOW I TREAT CML. 4. KONGRES HEMATOLOGOV IN TRANSFUZIOLOGOV SLOVENIJE Z MEDNARODNO UDELEŽBO Terme Olimia, Podčetrtek,
 HOW I TREAT CML 4. KONGRES HEMATOLOGOV IN TRANSFUZIOLOGOV SLOVENIJE Z MEDNARODNO UDELEŽBO Terme Olimia, Podčetrtek, 12. - 14. april, 2012 Gianantonio Rosti Dpt of Hematology and Oncological Sciences S.
HOW I TREAT CML 4. KONGRES HEMATOLOGOV IN TRANSFUZIOLOGOV SLOVENIJE Z MEDNARODNO UDELEŽBO Terme Olimia, Podčetrtek, 12. - 14. april, 2012 Gianantonio Rosti Dpt of Hematology and Oncological Sciences S.
Contemporary and Future Approaches in CML. Emory Meeting; Sea Island August 2014 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D.
 Contemporary and Future Approaches in CML Emory Meeting; Sea Island August 2014 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. 1 CML. Historical vs. Modern Perspective Parameter Historical Modern Course Fatal Indolent Prognosis
Contemporary and Future Approaches in CML Emory Meeting; Sea Island August 2014 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. 1 CML. Historical vs. Modern Perspective Parameter Historical Modern Course Fatal Indolent Prognosis
CML TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 CML TREATMENT GUIDELINES INITIAL INVESTIGATION Propose enrolment in the CML Registry of the CML-MPN Quebec Research Group. Medical history : Question for cardio-respiratory disorders, diabetes, pancreatitis,
CML TREATMENT GUIDELINES INITIAL INVESTIGATION Propose enrolment in the CML Registry of the CML-MPN Quebec Research Group. Medical history : Question for cardio-respiratory disorders, diabetes, pancreatitis,
Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute
 Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute Natural History of CML Accumulation of immature myeloid cells New cytogenetic changes Chronic Phase Accelerated Phase
Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute Natural History of CML Accumulation of immature myeloid cells New cytogenetic changes Chronic Phase Accelerated Phase
Welcome and Introductions
 Living with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Welcome and Introductions Living with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Living with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) Neil P. Shah, MD, PhD Edward S. Ageno Distinguished Professor
Living with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Welcome and Introductions Living with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Living with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) Neil P. Shah, MD, PhD Edward S. Ageno Distinguished Professor
What is the optimal management strategy for younger CP-CML patients with matched, related donors who fail to achieve CCyR
 What is the optimal management strategy for younger CP-CML patients with matched, related donors who fail to achieve CCyR after 18 months of imatinib? Second generation TKIs as a bridge to allogeneic SCT
What is the optimal management strategy for younger CP-CML patients with matched, related donors who fail to achieve CCyR after 18 months of imatinib? Second generation TKIs as a bridge to allogeneic SCT
2 nd Generation TKI Frontline Therapy in CML
 2 nd Generation TKI Frontline Therapy in CML Elias Jabbour, M.D. April 212 New York Frontline Therapy of CML in 212 - imatinib 4 mg daily - nilotinib 3 mg BID - dasatinib 1 mg daily Second / third line
2 nd Generation TKI Frontline Therapy in CML Elias Jabbour, M.D. April 212 New York Frontline Therapy of CML in 212 - imatinib 4 mg daily - nilotinib 3 mg BID - dasatinib 1 mg daily Second / third line
CML Clinical Case Scenario
 CML Clinical Case Scenario Neil Shah, MD, PhD Edward S. Ageno Distinguished Professor in Hematology/Oncology Leader, Hematopoietic Malignancies Program Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center at
CML Clinical Case Scenario Neil Shah, MD, PhD Edward S. Ageno Distinguished Professor in Hematology/Oncology Leader, Hematopoietic Malignancies Program Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center at
Discontinuation of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What s Stopping us from Stopping?
 Discontinuation of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What s Stopping us from Stopping? David Pham, PharmD PGY2 Hematology/Oncology Pharmacy Resident South Texas VA Health Care System
Discontinuation of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What s Stopping us from Stopping? David Pham, PharmD PGY2 Hematology/Oncology Pharmacy Resident South Texas VA Health Care System
ELN Recommendations on treatment choice and response. Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy
 ELN Recommendations on treatment choice and response Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy ELN 2013 Response to Front-line Treatment Baseline 3 months 6 months OPTIMAL
ELN Recommendations on treatment choice and response Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy ELN 2013 Response to Front-line Treatment Baseline 3 months 6 months OPTIMAL
IRIS 8-Year Update. Management of TKI Resistance Will KD mutations matter? Sustained CCyR on study. 37% Unacceptable Outcome 17% 53% 15%
 Management of TKI Resistance Will KD mutations matter? IRIS 8-Year Update 17% 53% 5% 15% 37% Unacceptable Outcome No CCyR Lost CCyR CCyR Other 3% 7% Safety Lost-regained CCyR Sustained CCyR on study Deininger
Management of TKI Resistance Will KD mutations matter? IRIS 8-Year Update 17% 53% 5% 15% 37% Unacceptable Outcome No CCyR Lost CCyR CCyR Other 3% 7% Safety Lost-regained CCyR Sustained CCyR on study Deininger
Contemporary and Future Approaches in Management of CML. Disclosures
 Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Contemporary and Future Approaches in Management of CML Hagop Kantarjian, MD Chairman and Professor, Department of Leukemia University of Texas M. D. Anderson
Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University Contemporary and Future Approaches in Management of CML Hagop Kantarjian, MD Chairman and Professor, Department of Leukemia University of Texas M. D. Anderson
CML: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow. Jorge Cortes, MD Chief CML Section Department of Leukemia The University of Texas, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center
 CML: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Jorge Cortes, MD Chief CML Section Department of Leukemia The University of Texas, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Five Years of Signal Transduction Inhibition The Beginning
CML: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow Jorge Cortes, MD Chief CML Section Department of Leukemia The University of Texas, M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Five Years of Signal Transduction Inhibition The Beginning
Guidelines and real World: Management of CML in chronic and advanced phases. Carolina Pavlovsky. FUNDALEU May 2017 Frankfurt
 Guidelines and real World: Management of CML in chronic and advanced phases Carolina Pavlovsky. FUNDALEU 26-28 May 217 Frankfurt Some Issues in CML 217 First Line treatment: Imatinib vs 2nd generation
Guidelines and real World: Management of CML in chronic and advanced phases Carolina Pavlovsky. FUNDALEU 26-28 May 217 Frankfurt Some Issues in CML 217 First Line treatment: Imatinib vs 2nd generation
Role of Second Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Newly Diagnosed CML. GIUSEPPE SAGLIO, MD University of Torino, Italy
 Role of Second Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Newly Diagnosed CML GIUSEPPE SAGLIO, MD University of Torino, Italy Outcome in 282 Patients Treated with Imatinib First Line in Hammersmith Hospital
Role of Second Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Newly Diagnosed CML GIUSEPPE SAGLIO, MD University of Torino, Italy Outcome in 282 Patients Treated with Imatinib First Line in Hammersmith Hospital
CML David L Porter, MD University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Abramson Cancer Center CML Current treatment options for CML
 1 CML 2012 LLS Jan 26, 2012 David L Porter, MD University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Abramson Cancer Center CML 2012 Current treatment options for CML patients Emerging therapies for CML treatment
1 CML 2012 LLS Jan 26, 2012 David L Porter, MD University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Abramson Cancer Center CML 2012 Current treatment options for CML patients Emerging therapies for CML treatment
TKIs ( Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors ) Mechanism of action and toxicity in CML Patients. Moustafa Sameer Hematology Medical Advsior,Novartis oncology
 TKIs ( Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors ) Mechanism of action and toxicity in CML Patients Moustafa Sameer Hematology Medical Advsior,Novartis oncology Introduction In people with chronic myeloid leukemia, A
TKIs ( Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors ) Mechanism of action and toxicity in CML Patients Moustafa Sameer Hematology Medical Advsior,Novartis oncology Introduction In people with chronic myeloid leukemia, A
SESSION III: Chronic myeloid leukemia PONATINIB. Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy
 SESSION III: Chronic myeloid leukemia PONATINIB Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy Ponatinib A Pan-BCR-ABL Inhibitor Rationally designed inhibitor of BCR- ABL
SESSION III: Chronic myeloid leukemia PONATINIB Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy Ponatinib A Pan-BCR-ABL Inhibitor Rationally designed inhibitor of BCR- ABL
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Version 1.2015 NCCN.org Continue Version 1.2015, 08/28/14 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2014,
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Version 1.2015 NCCN.org Continue Version 1.2015, 08/28/14 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2014,
New drugs in first-line therapy
 New drugs in first-line therapy Gianantonio Rosti Dept of Hematology and Oncology Seràgnoli, Bologna University (Italy) GIMEMA (Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche dell Adulto) CML WORKING PARTY IRIS
New drugs in first-line therapy Gianantonio Rosti Dept of Hematology and Oncology Seràgnoli, Bologna University (Italy) GIMEMA (Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche dell Adulto) CML WORKING PARTY IRIS
BOSULIF (bosutinib) oral tablet
 BOSULIF (bosutinib) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
BOSULIF (bosutinib) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
Accepted Manuscript. Improving Outcomes in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Over Time in the Era of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Pradnya Chopade, Luke P.
 Accepted Manuscript Improving Outcomes in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Over Time in the Era of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Pradnya Chopade, Luke P. Akard PII: S2152-2650(18)30343-4 DOI: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.029
Accepted Manuscript Improving Outcomes in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Over Time in the Era of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Pradnya Chopade, Luke P. Akard PII: S2152-2650(18)30343-4 DOI: 10.1016/j.clml.2018.06.029
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Version 3.2014 NCCN.org Continue Version 3.2014, 01/15/14 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2014,
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Version 3.2014 NCCN.org Continue Version 3.2014, 01/15/14 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2014,
What is New in CML in Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. February 2011
 What is New in CML in 2011 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. February 2011 1 CML. Historical vs. Modern Perspective Parameter Historical Modern Course Fatal Indolent Prognosis Poor Excellent 10-yr survival 10% 84-90%
What is New in CML in 2011 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. February 2011 1 CML. Historical vs. Modern Perspective Parameter Historical Modern Course Fatal Indolent Prognosis Poor Excellent 10-yr survival 10% 84-90%
BMS Satellite Symposium
 ICKSH 2018 BMS Satellite Symposium Emerging Trends in CML Management CHAIRMAN The Head of Catholic Hematology Hospital The Director of the Catholic Leukemia Research Institute at the Catholic University
ICKSH 2018 BMS Satellite Symposium Emerging Trends in CML Management CHAIRMAN The Head of Catholic Hematology Hospital The Director of the Catholic Leukemia Research Institute at the Catholic University
Bosulif. Bosulif (bosutinib) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.22 Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1,2018 Subject: Bosulif Page: 1 of 5 Last Review
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.22 Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1,2018 Subject: Bosulif Page: 1 of 5 Last Review
CML and Future Perspective. Hani Al-Hashmi, MD
 CML and Future Perspective Hani Al-Hashmi, MD Objectives Learning from CML history Outcome of interest to clinician Patient and community interest!! Learning from CML history Survival Probability (All
CML and Future Perspective Hani Al-Hashmi, MD Objectives Learning from CML history Outcome of interest to clinician Patient and community interest!! Learning from CML history Survival Probability (All
How I treat high risck CML
 Torino, September 14, 2018 How I treat high risck CML Patrizia Pregno Hematology Dept. Citta della Salute e della Scienza Torino Disclosures Advisory Board: Novartis, Pfizer, Incyte Speaker Honoraria:
Torino, September 14, 2018 How I treat high risck CML Patrizia Pregno Hematology Dept. Citta della Salute e della Scienza Torino Disclosures Advisory Board: Novartis, Pfizer, Incyte Speaker Honoraria:
DAVID S. SNYDER, M.D.
 CML UPDATE 2019 DAVID S. SNYDER, M.D. MARCH 21,2019 Click to edit Master Presentation Date Disclosures I do not have anything to disclose 2001 2016 Loss in expectation of life of patients with chronic
CML UPDATE 2019 DAVID S. SNYDER, M.D. MARCH 21,2019 Click to edit Master Presentation Date Disclosures I do not have anything to disclose 2001 2016 Loss in expectation of life of patients with chronic
A COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS OF PATIENTS NEWLY INITIATING TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA.
 A COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS OF PATIENTS NEWLY INITIATING TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Melea Ward A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of
A COMPARATIVE EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS OF PATIENTS NEWLY INITIATING TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Melea Ward A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of
New drugs and trials. Andreas Hochhaus
 New drugs and trials. Andreas Hochhaus Hadera I Oct 2018 Introduction ABL001 is a potent, specific inhibitor of BCR-ABL1 with a distinct allosteric mechanism of action BCR-ABL1 Protein Binds a distinct
New drugs and trials. Andreas Hochhaus Hadera I Oct 2018 Introduction ABL001 is a potent, specific inhibitor of BCR-ABL1 with a distinct allosteric mechanism of action BCR-ABL1 Protein Binds a distinct
Subject: Dasatinib (Sprycel ) Tablets
 09-J1000-43 Original Effective Date: 01/01/12 Reviewed: 01/10/18 Revised: 02/15/18 Subject: Dasatinib (Sprycel ) Tablets THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION, EXPLANATION
09-J1000-43 Original Effective Date: 01/01/12 Reviewed: 01/10/18 Revised: 02/15/18 Subject: Dasatinib (Sprycel ) Tablets THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION, CERTIFICATION, EXPLANATION
Approval based on the successful BFORE Phase 3 study conducted by Avillion under a collaborative development agreement with Pfizer
 Avillion Announces US Approval of Pfizer s BOSULIF (bosutinib) for the Treatment of Patients with Newly-Diagnosed Ph+ Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Approval based on the successful BFORE Phase 3 study
Avillion Announces US Approval of Pfizer s BOSULIF (bosutinib) for the Treatment of Patients with Newly-Diagnosed Ph+ Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Approval based on the successful BFORE Phase 3 study
C Longer follow up on IRIS data
 hronic Myeloid Leukemia Drs. Rena Buckstein, Mervat Mahrous & Eugenia Piliotis with input from Dr. J. Lipton (PMH) Updated August 2008* Updates: C Longer follow up on IRIS data Guidelines for monitoring
hronic Myeloid Leukemia Drs. Rena Buckstein, Mervat Mahrous & Eugenia Piliotis with input from Dr. J. Lipton (PMH) Updated August 2008* Updates: C Longer follow up on IRIS data Guidelines for monitoring
Tasigna. Tasigna (nilotinib) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.77 Subject: Tasigna Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Tasigna Description Tasigna (nilotinib)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.77 Subject: Tasigna Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Tasigna Description Tasigna (nilotinib)
Taiwan Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Taiwan Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Taiwan CML Study Group Coordinator: Lee-Yung Shih 2013/11/30 1 Contents Initial work-up at diagnosis and define baseline prognostic factors
Taiwan Guidelines for the Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Taiwan CML Study Group Coordinator: Lee-Yung Shih 2013/11/30 1 Contents Initial work-up at diagnosis and define baseline prognostic factors
CML UPDATE 2018 DAVID S. SNYDER, M.D. MARCH
 CML UPDATE 2018 DAVID S. SNYDER, M.D. MARCH 15, 2018 Click to edit Master Presentation Date DISCLOSURES I have nothing to disclose 2001 2016 Loss in expectation of life of patients with chronic myeloid
CML UPDATE 2018 DAVID S. SNYDER, M.D. MARCH 15, 2018 Click to edit Master Presentation Date DISCLOSURES I have nothing to disclose 2001 2016 Loss in expectation of life of patients with chronic myeloid
What is New in CML Jorge Cortes, MD Chief, CML and AML Sections Department of Leukemia MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas
 What is New in CML 2018 Jorge Cortes, MD Chief, CML and AML Sections Department of Leukemia MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas Final Results CML-IV Molecular Response with Imatinib 1538 pts newly
What is New in CML 2018 Jorge Cortes, MD Chief, CML and AML Sections Department of Leukemia MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, Texas Final Results CML-IV Molecular Response with Imatinib 1538 pts newly
NCCP Chemotherapy Protocol. Bosutinib Monotherapy
 Bosutinib Monotherapy INDICATIONS FOR USE: INDICATION Treatment of adult patients with chronic phase (CP), accelerated phase (AP), and blast phase (BP) Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelogenous
Bosutinib Monotherapy INDICATIONS FOR USE: INDICATION Treatment of adult patients with chronic phase (CP), accelerated phase (AP), and blast phase (BP) Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myelogenous
10 YEARS EXPERIENCE OF TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CML IN OXFORD
 10 YEARS EXPERIENCE OF TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CML IN OXFORD Dalia Khan 1, Noemi Roy 1, Vasha Bari 1, Grant Vallance 1, Helene Dreau 1, Timothy Littlewood 1, Andrew Peniket 1, Paresh Vyas
10 YEARS EXPERIENCE OF TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CML IN OXFORD Dalia Khan 1, Noemi Roy 1, Vasha Bari 1, Grant Vallance 1, Helene Dreau 1, Timothy Littlewood 1, Andrew Peniket 1, Paresh Vyas
Tasigna. Tasigna (nilotinib) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.77 Subject: Tasigna Page: 1of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Tasigna Description Tasigna (nilotinib)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.77 Subject: Tasigna Page: 1of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Tasigna Description Tasigna (nilotinib)
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia
 Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Molecular Response: What is really important? Jeff Szer The Royal Melbourne Hospital PROBABILITY, % PROBABILITY OF SURVIVAL AFTER MYELOABLATIVE TRANSPLANTS FOR CML IN CHRONIC
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Molecular Response: What is really important? Jeff Szer The Royal Melbourne Hospital PROBABILITY, % PROBABILITY OF SURVIVAL AFTER MYELOABLATIVE TRANSPLANTS FOR CML IN CHRONIC
Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring
 Received: 13 December 2017 Accepted: 17 December 2017 DOI: 10.1002/ajh.25011 ANNUAL CLINICAL UPDATES IN HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring
Received: 13 December 2017 Accepted: 17 December 2017 DOI: 10.1002/ajh.25011 ANNUAL CLINICAL UPDATES IN HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring
Does Generic Imatinib Change the Treatment Approach in CML?
 Does Generic Imatinib Change the Treatment Approach in CML? Jerald P. Radich, MD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center/ Seattle Cancer Care Alliance NCCN.org For Clinicians NCCN.org/patients For Patients
Does Generic Imatinib Change the Treatment Approach in CML? Jerald P. Radich, MD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center/ Seattle Cancer Care Alliance NCCN.org For Clinicians NCCN.org/patients For Patients
CML: definition. CML epidemiology. CML diagnosis. CML: peripheralbloodsmear. Cytogenetic abnormality of CML
 MolecularDiagnostic.be Third Scientific Meeting Molecular Diagnostics.be t(9;22) CML: definition Management of CML patients treated with TKI: the place of molecular monitoring Antwerp, December 13 th 11
MolecularDiagnostic.be Third Scientific Meeting Molecular Diagnostics.be t(9;22) CML: definition Management of CML patients treated with TKI: the place of molecular monitoring Antwerp, December 13 th 11
BCCA Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using PONAtinib
 BCCA Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using PONAtinib Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician ULKCMLP Leukemia Dr. Donna Forrest ELIGIBILITY:
BCCA Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using PONAtinib Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician ULKCMLP Leukemia Dr. Donna Forrest ELIGIBILITY:
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Bosutinib (Bosulif) for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia April 21, 2015
 pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Bosutinib (Bosulif) for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia April 21, 2015 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report is primarily
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Bosutinib (Bosulif) for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia April 21, 2015 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional Advice This report is primarily
The Future of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: New Treatments on the Horizon
 The Future of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: New Treatments on the Horizon Imatinib revolutionized the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), improving the prognosis to such an extent that the
The Future of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: New Treatments on the Horizon Imatinib revolutionized the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), improving the prognosis to such an extent that the
Imatinib & Ponatinib. Two ends of the spectrum in 2016s reality
 Imatinib & Ponatinib Two ends of the spectrum in 2016s reality CML 2016 Benefits & risks Steve O Brien CML Horizons, May 2016 Disclosures Research funding, participation in company trial, speaker, consultant,
Imatinib & Ponatinib Two ends of the spectrum in 2016s reality CML 2016 Benefits & risks Steve O Brien CML Horizons, May 2016 Disclosures Research funding, participation in company trial, speaker, consultant,
EUROPEAN LEUKEMIANET RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
 EUROPEAN LEUKEMIANET RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA SAN DIEGO, 11 DECEMBER 2011 AMSTERDAM, 14 JUNE 2012 BALTIMORE, 20 SEPTEMBER 2012 ATLANTA, 6 DECEMBER 2012 ELN, CML Panel Jane Apperley
EUROPEAN LEUKEMIANET RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA SAN DIEGO, 11 DECEMBER 2011 AMSTERDAM, 14 JUNE 2012 BALTIMORE, 20 SEPTEMBER 2012 ATLANTA, 6 DECEMBER 2012 ELN, CML Panel Jane Apperley
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Version 1.2019 August 1, 2018 NCCN.org Continue Version 1.2019, 08/01/18 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2018, All rights reserved.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Version 1.2019 August 1, 2018 NCCN.org Continue Version 1.2019, 08/01/18 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2018, All rights reserved.
MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1)
 MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1) Moleculaire Biologie en Cytometrie cursus Barbara Denys LAbo Hematologie UZ Gent 6 mei 2011 2008 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms o WHO classification 2008:
MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1) Moleculaire Biologie en Cytometrie cursus Barbara Denys LAbo Hematologie UZ Gent 6 mei 2011 2008 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms o WHO classification 2008:
NEW DRUGS IN HEMATOLOGY Bologna, 9-11 May 2016 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA STATUS OF THE ART OF TREATMENT.
 NEW DRUGS IN HEMATOLOGY Bologna, 9-11 May 2016 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA STATUS OF THE ART OF TREATMENT Michele.baccarani@unibo.it Michele BACCARANI, MD Professor of Hematology at the Universities of Trieste,
NEW DRUGS IN HEMATOLOGY Bologna, 9-11 May 2016 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA STATUS OF THE ART OF TREATMENT Michele.baccarani@unibo.it Michele BACCARANI, MD Professor of Hematology at the Universities of Trieste,
ICLUSIG (ponatinib) oral tablet
 ICLUSIG (ponatinib) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
ICLUSIG (ponatinib) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
Stopping Treatment in CML and dose reduction in clinical practice: Can we do it safely? YES WE CAN!
 Stopping Treatment in CML and dose reduction in clinical practice: Can we do it safely? YES WE CAN! Dragana Milojković The Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK Leukemic burden Current Aim of TKI therapy Molecular
Stopping Treatment in CML and dose reduction in clinical practice: Can we do it safely? YES WE CAN! Dragana Milojković The Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK Leukemic burden Current Aim of TKI therapy Molecular
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Version 1.2018 July 26, 2017 NCCN.org Continue Version 1.2018, 07/26/17 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2017, All rights reserved.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Version 1.2018 July 26, 2017 NCCN.org Continue Version 1.2018, 07/26/17 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. 2017, All rights reserved.
Should nilotinib replace imatinib as first line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP)?
 Should nilotinib replace imatinib as first line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP)? http://test.metromomsblog.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/tortoise-and-the-hare.jpg D. Van
Should nilotinib replace imatinib as first line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP)? http://test.metromomsblog.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/tortoise-and-the-hare.jpg D. Van
Management of CML in blast crisis. Lymphoma Tumor Board November 27, 2015
 Management of CML in blast crisis Lymphoma Tumor Board November 27, 2015 Chronic Phase CML - 2. Peter Maslak, ASH Image Bank 2011; 2011-2455 Copyright 2011 American Society of Hematology. Copyright restrictions
Management of CML in blast crisis Lymphoma Tumor Board November 27, 2015 Chronic Phase CML - 2. Peter Maslak, ASH Image Bank 2011; 2011-2455 Copyright 2011 American Society of Hematology. Copyright restrictions
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 Small Cell NCCN Lung Table Guidelines of Contents Index Staging,, CML Table of References Contents NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Version
Small Cell NCCN Lung Table Guidelines of Contents Index Staging,, CML Table of References Contents NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines ) Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Version
Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019
 Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019 Disclosures Richard A. Larson, MD Research funding to the University
Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019 Disclosures Richard A. Larson, MD Research funding to the University
9/26/2018. Learning Objectives
 ADVANCES IN CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Alison Wakoff Loren, MD, MSCE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Blood & Marrow Transplantation Vice Chair, Faculty Development Department of Medicine Perelman
ADVANCES IN CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Alison Wakoff Loren, MD, MSCE Associate Professor of Medicine Director, Blood & Marrow Transplantation Vice Chair, Faculty Development Department of Medicine Perelman
What Can We Expect from Imatinib? CML Case Presentation. Presenter Disclosure Information. CML Case Presentation (cont)? Session 2: 8:15 AM - 9:00 AM
 Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 2: 8:15 AM - 9: AM Miami, FL December 18, 29 Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia: Imatinib and Beyond Speaker: Daniel J. DeAngelo, MD, PhD Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Welcome to Master Class for Oncologists Session 2: 8:15 AM - 9: AM Miami, FL December 18, 29 Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia: Imatinib and Beyond Speaker: Daniel J. DeAngelo, MD, PhD Dana-Farber Cancer Institute
Allogeneic SCT for. 1st TKI. Vienna Austria. Dr. Eduardo Olavarría Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra
 The International Congress on Controversies in Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies (COSTEM) Berlin, Germany September 8-11, 2011 Vienna Austria Allogeneic SCT for CML Allogeneic after failure
The International Congress on Controversies in Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapies (COSTEM) Berlin, Germany September 8-11, 2011 Vienna Austria Allogeneic SCT for CML Allogeneic after failure
The concept of TFR (Treatment Free Remission) in CML
 The concept of TFR (Treatment Free Remission) in CML Giuseppe Saglio University of Turin, Italy What can we expect today on long-term therapy with TKIs in CML? German CML study IV Relative and overall
The concept of TFR (Treatment Free Remission) in CML Giuseppe Saglio University of Turin, Italy What can we expect today on long-term therapy with TKIs in CML? German CML study IV Relative and overall
Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Benjamin Powers, MD; and Suman Kambhampati, MD The dramatic improvement in survival with tyrosine kinase inhibitors has not been demonstrated in the advanced blast
Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Benjamin Powers, MD; and Suman Kambhampati, MD The dramatic improvement in survival with tyrosine kinase inhibitors has not been demonstrated in the advanced blast
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, Version
 1108 NCCN Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, Version 1.2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology Jerald P. Radich, MD; Michael Deininger, MD, PhD; Camille N. Abboud, MD; Jessica K. Altman, MD; Ellin Berman,
1108 NCCN Chronic Myeloid Leukemia, Version 1.2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology Jerald P. Radich, MD; Michael Deininger, MD, PhD; Camille N. Abboud, MD; Jessica K. Altman, MD; Ellin Berman,
Dose reduction. What do we know and how we do it in clinical practice. Andreas Hochhaus
 Dose reduction. What do we know and how we do it in clinical practice. Andreas Hochhaus Hadera I Oct 2018 Front-line Randomized Trials in CML-CP Trial Drugs References IRIS IM 400 vs IFN/AraC TOPS IM
Dose reduction. What do we know and how we do it in clinical practice. Andreas Hochhaus Hadera I Oct 2018 Front-line Randomized Trials in CML-CP Trial Drugs References IRIS IM 400 vs IFN/AraC TOPS IM
La terapia della LMC: è possibile guarire senza trapianto? Fabrizio Pane
 La terapia della LMC: è possibile guarire senza trapianto? Fabrizio Pane What could be the concept of Cure in CML? Sustained DMR with or without TKI therapy And 100% CML-related survival And QoL comparable
La terapia della LMC: è possibile guarire senza trapianto? Fabrizio Pane What could be the concept of Cure in CML? Sustained DMR with or without TKI therapy And 100% CML-related survival And QoL comparable
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body
 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body Jeffrey H Lipton, PhD MD FRCPC Staff Physician, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Professor of Medicine University of Toronto POGO November,
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body Jeffrey H Lipton, PhD MD FRCPC Staff Physician, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Professor of Medicine University of Toronto POGO November,
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia
 Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Dr Simon Watt Dr Katherine O Neill Dr Fiona Dignan Written July 2017 Prof Tim Somervaille Review July 2019 1 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction 3 2.0
Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Dr Simon Watt Dr Katherine O Neill Dr Fiona Dignan Written July 2017 Prof Tim Somervaille Review July 2019 1 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction 3 2.0
Form 2012 R3.0: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (CML) Pre-Infusion Data
 Form 2012 R3.0: Chronic Myelogeus Leukemia (CML) Pre-Infusion Data Key Fields Sequence Number: Date Received: - - CIBMTR Center Number: CIBMTR Research ID: Event date: - - HCT type: (check all that apply)
Form 2012 R3.0: Chronic Myelogeus Leukemia (CML) Pre-Infusion Data Key Fields Sequence Number: Date Received: - - CIBMTR Center Number: CIBMTR Research ID: Event date: - - HCT type: (check all that apply)
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Guidelines
 Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Guidelines Approved by Pathway Board for Haematological Malignancies Coordinating author: Heather Oakervee, Bart s Health NHST Date of issue: 12.03.2015 Version number:v1.0 These
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Guidelines Approved by Pathway Board for Haematological Malignancies Coordinating author: Heather Oakervee, Bart s Health NHST Date of issue: 12.03.2015 Version number:v1.0 These
Low doses of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in CML
 CML Horizons Conference Warsaw 4-6 May 2018 Low doses of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in CML Delphine Rea, MD, PhD Pôle Hématologie Oncologie Radiothérapie INSERM UMR-1160 Centre Hospitalo-Universitaire
CML Horizons Conference Warsaw 4-6 May 2018 Low doses of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in CML Delphine Rea, MD, PhD Pôle Hématologie Oncologie Radiothérapie INSERM UMR-1160 Centre Hospitalo-Universitaire
State of the Art Therapy and Monitoring of CML Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. Grand Rounds Hackensack, New Jersey. September 22, 2010
 State of the Art Therapy and Monitoring of CML - 2010 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. Grand Rounds Hackensack, ew Jersey September 22, 2010 1 CML. Historical vs. Modern Perspective Parameter Historical Modern Course
State of the Art Therapy and Monitoring of CML - 2010 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. Grand Rounds Hackensack, ew Jersey September 22, 2010 1 CML. Historical vs. Modern Perspective Parameter Historical Modern Course
History of CML Treatment
 History of CML Treatment Eduardo Olavarria No conflict of interest Lisbon, 20th March 2018 #EBMT18 www.ebmt.or What is CML? The mystery of chronic myeloid leukaemia Chronic myeloid leukaemia Often diagnosed
History of CML Treatment Eduardo Olavarria No conflict of interest Lisbon, 20th March 2018 #EBMT18 www.ebmt.or What is CML? The mystery of chronic myeloid leukaemia Chronic myeloid leukaemia Often diagnosed
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Introduction. Methods Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
 BCR/ABL level at 6 months identifies good risk CML subgroup after failing early molecular response at 3 months following imatinib therapy for CML in chronic phase AJH Dennis (Dong Hwan) Kim, 1 * Nada Hamad,
BCR/ABL level at 6 months identifies good risk CML subgroup after failing early molecular response at 3 months following imatinib therapy for CML in chronic phase AJH Dennis (Dong Hwan) Kim, 1 * Nada Hamad,
Long-term side effects, comorbidities & their impact on choice of treatment CML management and quality of life. Andreas Hochhaus
 Long-term side effects, comorbidities & their impact on choice of treatment CML management and quality of life Andreas Hochhaus Frankfurt I 27.5.2017 sola dosis facit venenum Paracelsus 1493-1541 Swiss
Long-term side effects, comorbidities & their impact on choice of treatment CML management and quality of life Andreas Hochhaus Frankfurt I 27.5.2017 sola dosis facit venenum Paracelsus 1493-1541 Swiss
Outlook CML 2016: What is being done on the way to cure
 New Horizons 2011 Outlook CML 2016: What is being done on the way to cure Gianantonio Rosti Dept. Of Hematology and Oncology St. Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital Bologna (Italy) GIMEMA CML Working Party
New Horizons 2011 Outlook CML 2016: What is being done on the way to cure Gianantonio Rosti Dept. Of Hematology and Oncology St. Orsola-Malpighi University Hospital Bologna (Italy) GIMEMA CML Working Party
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Ponatinib (Iclusig) for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia / Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
 pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Ponatinib (Iclusig) for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia / Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia October 1, 2015 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional
pan-canadian Oncology Drug Review Final Clinical Guidance Report Ponatinib (Iclusig) for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia / Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia October 1, 2015 DISCLAIMER Not a Substitute for Professional
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML
 Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Practical Guidance for the Management of CML in 2016
 Practical Guidance for the Management of CML in 2016 Neil Shah, MD, PhD Edward S. Ageno Distinguished Professor in Hematology/Oncology Leader, Hematopoietic Malignancies Program Helen Diller Family Comprehensive
Practical Guidance for the Management of CML in 2016 Neil Shah, MD, PhD Edward S. Ageno Distinguished Professor in Hematology/Oncology Leader, Hematopoietic Malignancies Program Helen Diller Family Comprehensive
CML Update 2016 Arthur 2016
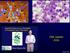 CML Update 2016 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Splenomegaly CML (3 phase disease) Increased white cells Malignant proliferation of myeloid white cells Initially mature cells a) chronic phase of disease Evolution
CML Update 2016 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Splenomegaly CML (3 phase disease) Increased white cells Malignant proliferation of myeloid white cells Initially mature cells a) chronic phase of disease Evolution
New Anti Leukemic treatments deserve a Cardioncology approach. Guido Gini AOU «Ospedali Riuniti» Università Politecnica delle Marche Ancona
 New Anti Leukemic treatments deserve a Cardioncology approach Guido Gini AOU «Ospedali Riuniti» Università Politecnica delle Marche Ancona CML Is Linked to a Single Cytogenetic Abnormality: The Philadelphia
New Anti Leukemic treatments deserve a Cardioncology approach Guido Gini AOU «Ospedali Riuniti» Università Politecnica delle Marche Ancona CML Is Linked to a Single Cytogenetic Abnormality: The Philadelphia
State of the Art Therapy and Monitoring of CML Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. Grand Rounds UT Southwestern. October 28, 2010
 State of the Art Therapy and Monitoring of CML - 2010 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. Grand Rounds UT Southwestern October 28, 2010 1 CML. Historical vs. Modern Perspective Parameter Historical Modern Course Fatal
State of the Art Therapy and Monitoring of CML - 2010 Hagop Kantarjian, M.D. Grand Rounds UT Southwestern October 28, 2010 1 CML. Historical vs. Modern Perspective Parameter Historical Modern Course Fatal
Executive summary Overview
 Executive summary Overview In this appraisal, we have demonstrated that dasatinib is clinically more effective, as well as more cost effective, than imatinib, the current standard of care. In the pivotal
Executive summary Overview In this appraisal, we have demonstrated that dasatinib is clinically more effective, as well as more cost effective, than imatinib, the current standard of care. In the pivotal
Hull and East Yorkshire and North Lincolnshire NHS Trusts Haematology Multidisciplinary Team Guideline and Pathway. Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia
 Hull and East Yorkshire and North Lincolnshire NHS Trusts Haematology Multidisciplinary Team Guideline and Pathway Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia 1 BACKGROUND The Hull and North Lincolnshire Haematology Multidisciplinary
Hull and East Yorkshire and North Lincolnshire NHS Trusts Haematology Multidisciplinary Team Guideline and Pathway Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia 1 BACKGROUND The Hull and North Lincolnshire Haematology Multidisciplinary
TREATMENT INTENT Disease modification- see European LeukemiaNet (ELN) 2013 guidelines for treatment goals.
 BOSUTINIB INDICATION Licensed / NICE TA401 (BLUETEQ required) The treatment of adult patients with chronic, accelerated and blast phase Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukaemia (Ph+ CML)
BOSUTINIB INDICATION Licensed / NICE TA401 (BLUETEQ required) The treatment of adult patients with chronic, accelerated and blast phase Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukaemia (Ph+ CML)
I nuovi guariti? La malattia minima residua nella leucemia mieloide cronica. Fabrizio Pane
 I nuovi guariti? La malattia minima residua nella leucemia mieloide cronica Fabrizio Pane What could be the concept of Cure in CML? Sustained DMR with or without TKI therapy And 100% CML-related survival
I nuovi guariti? La malattia minima residua nella leucemia mieloide cronica Fabrizio Pane What could be the concept of Cure in CML? Sustained DMR with or without TKI therapy And 100% CML-related survival
Juan Luis Steegmann Hospital de la Princesa. Madrid. JL Steegmann
 Juan Luis Steegmann Hospital de la Princesa. Madrid. Juan Luis Steegmann Hospital de la Princesa. Madrid No rush,at least in Chronic Phase Blast Phase*: SCT asap, after restablishing CP with TKI Accelerated
Juan Luis Steegmann Hospital de la Princesa. Madrid. Juan Luis Steegmann Hospital de la Princesa. Madrid No rush,at least in Chronic Phase Blast Phase*: SCT asap, after restablishing CP with TKI Accelerated
Chronic Leukemia Review and Update Todd Kliewer, MD Optim Oncology
 Chronic Leukemia Review and Update 2013 Todd Kliewer, MD Optim Oncology Leukemia A myeloproliferative malignancy arising from the bone marrow. Cells exhibit both rapid clonal division and biologic immortality.
Chronic Leukemia Review and Update 2013 Todd Kliewer, MD Optim Oncology Leukemia A myeloproliferative malignancy arising from the bone marrow. Cells exhibit both rapid clonal division and biologic immortality.
t(9;22)(q34;q11) as part of a single or complex translocation, or BCR-ABL transcripts must be present in every case
 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKAEMIA Diagnostic Criteria Chronic phase CML t(9;22)(q34;q11) as part of a single or complex translocation, or BCR-ABL transcripts must be present in every case Maximally cellular marrow
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKAEMIA Diagnostic Criteria Chronic phase CML t(9;22)(q34;q11) as part of a single or complex translocation, or BCR-ABL transcripts must be present in every case Maximally cellular marrow
BCCA Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using dasatinib
 BCCA Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using dasatinib Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician ULKCMLD Leukemia Dr. Donna Forrest ELIGIBILITY:
BCCA Protocol Summary for Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using dasatinib Protocol Code Tumour Group Contact Physician ULKCMLD Leukemia Dr. Donna Forrest ELIGIBILITY:
Venice Meeting Highlights: Key lessons. Conclusions Michele Baccarani Rüdiger Hehlmann
 Venice Meeting Highlights: Key lessons Conclusions Michele Baccarani Rüdiger Hehlmann CML therapy in the imatinib era CML prognosis has improved dramatically Cellular and molecular biology studies help
Venice Meeting Highlights: Key lessons Conclusions Michele Baccarani Rüdiger Hehlmann CML therapy in the imatinib era CML prognosis has improved dramatically Cellular and molecular biology studies help
Molecular monitoring of CML patients
 EHA, Education Session, CML Stockholm, 14 June 2013 Molecular monitoring of CML patients Martin C. Müller Medical Faculty Mannheim Ruprecht-Karls-University Heidelberg Mannheim, Germany Disclosures Research
EHA, Education Session, CML Stockholm, 14 June 2013 Molecular monitoring of CML patients Martin C. Müller Medical Faculty Mannheim Ruprecht-Karls-University Heidelberg Mannheim, Germany Disclosures Research
Oxford Style Debate on STOPPING Treatment.
 Oxford Style Debate on STOPPING Treatment. This house believes that there are good reasons NOT to stop CML treatment. It should be done within clinical trials, OR only in expert centers where frequent,
Oxford Style Debate on STOPPING Treatment. This house believes that there are good reasons NOT to stop CML treatment. It should be done within clinical trials, OR only in expert centers where frequent,
