Akt Phosphorylation Is a Risk Factor for Early Disease Recurrence and Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
|
|
|
- Debra Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 307 Akt Phosphorylation Is a Risk Factor for Early Disease Recurrence and Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Kazuaki Nakanishi, M.D., Ph.D. 1,2 Michiie Sakamoto, M.D., Ph.D. 1,3 Susumu Yamasaki, M.D., Ph.D. 4 Satoru Todo, M.D., Ph.D. 2 Setsuo Hirohashi, M.D., Ph.D. 1 1 Division of Pathology, National Cancer Center Research Institute, Tokyo, Japan. 2 Department of General Surgery, Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan. 3 Department of Pathology, Keio University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. 4 Division of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, National Cancer Center Hospital, Tokyo, Japan. BACKGROUND. Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who showed early massive disease recurrence due to hematogenous intrahepatic metastasis after curative resection had a poor prognosis. The authors previously reported that Akt phosphorylation was correlated with hematogenous intrahepatic metastasis, using HCC cell lines. METHODS. The authors analyzed clinicopathologic features and the status of selected biologic markers, including phosphorylated Akt, to identify risk factors for early disease recurrence and poor prognosis in HCC. In the current series, 49 postoperative patients developed intrahepatic disease recurrence within 6 months () and 86 patients remained disease recurrence free 3 years after resection (). was further divided into 2 subgroups: 19 patients who died of disease recurrence within a year after resection (A) and 27 patients who survived 1 year (B). RESULTS. Using univariate analysis, the risk factors for early disease recurrence were tumor size, macroscopic classification, tumor differentiation, microscopic capsule infiltration, microscopic portal vein (MPV) invasion, microscopic intrahepatic metastasis (MIM), and positive immunostaining for phosphorylated Akt, Ki-67, and p53 (P 0.05). The risk factors for poor prognosis were the number of intrahepatic metastases, tumor differentiation, and positive immunostaining for phosphorylated Akt and Ki-67 (P 0.05). Multivariate analysis revealed that the risk factors for early disease recurrence were MPV invasion, MIM, and positive immunostaining for phosphorylated Akt, and that the risk factors for poor prognosis were positive immunostaining for phosphorylated Akt and Ki-67 (P 0.05). CONCLUSIONS. The current clinical study showed the critical involvement of Akt phosphorylation in the aggressiveness of HCC. The potential benefits of surgery should be assessed carefully in patients with any of these risk factors. Cancer 2005; 103: American Cancer Society. Supported by a Grant-in-Aid for the Second Term Comprehensive 10-Year Strategy for Cancer Control from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of Japan. Dr. Nakanishi is the recipient of a Research Resident Fellowship from the Foundation for Promotion of Cancer Research in Japan. Address for reprints: Setsuo Hirohashi, M.D., Ph.D., National Cancer Center Research Institute, Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo , Japan; Fax: (011) ; shirohas@ncc.go.jp Received April 27, 2004; revision received September 21, 2004; accepted September 28, KEYWORDS: hepatocellular carcinoma, early disease recurrence, poor prognosis, immunostaining, phosphorylated Akt. Hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has become a safe surgical procedure with a very low operative mortality rate as a result of progress in evaluation of hepatic function reserve, surgical technique, and perioperative management. However, prognosis after hepatectomy is still unsatisfactory because of a high incidence of disease recurrence. 1,2 Pathologic and genetic studies have identified two types of recurrence of HCC, i.e., intrahepatic metastasis of the primary HCC and multicentric development of new tumors, although the two types cannot always be distinguished. It is generally believed that disease 2004 American Cancer Society DOI /cncr Published online 8 December 2004 in Wiley InterScience (
2 308 CANCER January 15, 2005 / Volume 103 / Number 2 recurrence due to intrahepatic metastasis is likely to appear soon after surgical resection and that its risk decreases with prolongation of the postoperative period. Conversely, disease recurrence due to multicentric liver carcinogenesis occurs throughout the observation period at a constant rate that varies with the severity of liver disease and the type of hepatitis virus infection. 3 Recent studies also have shown that early disease recurrence is associated with a worse prognosis compared with late disease recurrence. 4 8 A considerable number of patients develop early postoperative massive intrahepatic disease recurrence with poor prognosis, even after curative resection of relatively small HCC tumors. The generation of intrahepatic metastases requires spreading of tumor cells from the primary HCC tumor into the circulation and the survival of the circulating cells without cell-substratum interaction, which is called anchorage-independent growth. Our previous report showed that anchorage-independent growth correlates with phosphorylated (activated) Akt (p-akt) and plays a critical role in hematogenous intrahepatic metastasis in an orthotopic implantation model of HCC. 9 Therefore, it is possible that p-akt status is correlated with early disease recurrence and poor prognosis. In the current study, we retrospectively analyzed clinicopathologic features and the status of p-akt and other biologic markers in patients with clinical HCC to identify the risk factors for early disease recurrence and poor prognosis. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients and Follow-Up From January 1990 to December 2000, 394 patients underwent curative resection of solitary HCC at the National Cancer Center Hospital (Tokyo, Japan). Patients who had intrahepatic metastasis within the whole liver and/or extrahepatic metastasis were excluded from the study. Of these 394 patients, 49 developed intrahepatic disease recurrence within 6 months after resection (). Of these 49 patients, 19 died due to disease recurrence within a year after resection (A) and 27 survived 1 year ( 1B). Eighty-six patients remained disease recurrence free 3 years after surgical resection (). These 135 patients (1 [n 49] and [n 86]) were included in the current study. Disease recurrence after surgical resection was diagnosed by serial measurement of tumor markers, ultrasonography, and computed tomography scans every 3 6 months. Clinical Parameters and Tumor Characteristics We compared the backgrounds of the patients, including age, gender, hepatitis virus infection status, and history of preoperative treatment. We also compared the macroscopic features of the resected specimens with regard to tumor size and macroscopic classification using criteria described previously. 10 Evaluation of microscopic features included portal vein invasion, tumor capsule formation, capsule infiltration, intrahepatic metastasis, and the histology of the noncancerous liver tissue specimens. We also evaluated the histologic grade of the tumor specimens using the World Health Organization classification. Immunohistochemistry of Biologic Markers Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was performed to evaluate three biologic markers: Ki-67, p53, and p-akt. The antibodies used were MIB-1 anti Ki-67 antibody (1: 200 dilution), DO-7 anti-p53 antibody (1:50 dilution), and phospho-akt (Ser 473, IHC-specific) anti p-akt antibody (1: 20 dilution). Both the MIB-1 anti Ki-67 antibody and the DO-7 anti-p53 antibody were purchased from Dako (Glostrup, Denmark) and phospho- Akt (Ser 473, IHC-specific) anti p-akt antibody was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA). Sections (5 m thick) of formalin-fixed, paraffinembedded tissue were deparaffinized with xylene, treated with 0.3% hydrogen peroxide in methanol, immersed in 10 mm citrate buffer (ph 6.0), heated at 121 C in an autoclave for 10 minutes, and allowed to cool at room temperature for 30 minutes. The sections were preincubated in 2% normal swine serum in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and then incubated with each antibody at 4 C overnight, followed by washing 3 times with PBS. The sections with MIB-1 and DO-7 were incubated for 30 minutes with biotinylated secondary antibody at room temperature. For detection, a Vectastain ABC kit (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) was used. A PolyMICA detection kit (The Binding Site Ltd., Birmingham, UK) 11 was used according to the manufacturer s instructions for detection of the anti p-akt antibody. Staining of Ki-67, p53, and p-akt was estimated by counting the percentage of positive nuclei per 1000 tumor cells in the region of the tumor specimen with the greatest density of staining. The percentage of cells expressing nuclear staining of Ki-67, p53, and p-akt was categorized as follows: cells with positive staining in 50% (Ki-67), 10% (p53), and 10%(p-Akt) of tumor cells were graded as negative and those with 50%, 10%, and 10%, respectively, were graded as positive.
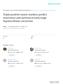
3 Risk Factors for Early HCC Recurrence/Nakanishi et al. 309 FIGURE 1. Immunostaining of phosphorylated Akt. (A) Inhibition of Akt activation by LY Immunoblot analysis of total (Akt) and activated (p-akt) Akt protein in Li7 cells after incubation with various concentrations of LY for 12 hours. (B) Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded Li7 cell pellets treated with (right panel) and without (left panel) LY were immunostained with phospho-akt antibody. Cells treated without LY were stained more strongly in the nucleus compared with those treated with LY (C) Positive staining of poorly differentiated HCC (left panel) and negative staining of moderately differentiated HCC (right panel). Original magnification 200 (C); 400 (B). Statistical Analysis For univariate analysis, the chi-square test and/or the Fisher exact test was used to compare categorized variables and the t test was used to compare continuous variables. Continuous variables were expressed as the mean the standard deviation. Logistic regression analysis was used for multivariate analysis. All statistical analyses were performed with Stat View (Version 5.0) software (Abacus Concepts, Berkeley, CA). P 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS Immunostaining of Phosphorylated Akt As previously reported, 9 Western blotting analysis showed that the Akt protein was constitutively phosphorylated in the human HCC cell line, Li7 (Fig. 1A). Moreover, a specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), LY294002, dose dependently suppressed phosphorylation of Akt. Phosphorylation of Akt in Li7 cells was suppressed completely by 50 M LY294002, and the effect was sustained for 24 hours. IHC of p-akt was evaluated with formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded Li7 cell pellets that had been pretreated with or without 20 M LY In parallel with phosphorylation status by Western blotting analysis, Li7 cells treated without LY stained more strongly in the nucleus than did those treated with LY (Fig. 1B). Thus, the nuclear staining was specific to the phosphorylation status of Akt, and could be evaluated as positive in surgical tissue specimens (Fig. 1C). Staining of p-akt was observed in cancer cells and in some lymphocytes of surgical tissue specimens. In positive cases, p-akt staining was distributed diffusely, although the staining was stronger in the periphery than in the center of the lesions. Risk Factors for Early Disease Recurrence Table 1 shows the univariate analysis of clinical parameters comparing the early () and no () disease recurrence groups. None of the clinical parameters were significantly different. Tables 2 and 3 show the univariate analyses of macroscopic and microscopic characteristics, respectively. Two macroscopic and four microscopic factors were associated with early disease recurrence: tumor size, macroscopic classification, tumor differentiation, microscopic capsule infiltration, microscopic portal vein
4 310 CANCER January 15, 2005 / Volume 103 / Number 2 TABLE 1 Clinical Parameters Associated with Early Disease Recurrence and Poor Prognosis a Clinical parameters A B (n 86) Gender Male 38 (77.6) 15 (78.9) 21 (77.8) 65 (75.6) Female 11 (22.4) 4 (21.1) 6 (22.2) 21 (24.4) Age (yrs) Virus infection HBsAg( ) HCVAb( ) 6 (12.2) 4 (21.1) 2 (7.4) 17 (19.8) HBsAg( ) HCVAb( ) 32 (65.4) 12 (63.1) 18 (66.7) 43 (50.0) HBsAg( ) HCVAb( ) 3 (6.1) 0 3 (11.1) 4 (4.7) HBsAg( ) HCVAb( ) 6 (12.2) 2 (10.5) 3 (11.1) 15 (17.4) Unknown 2 (4.1) 1 (5.3) 1 (3.7) 7 (8.1) History of preoperative treatment Presence 33 (67.3) 14 (73.7) 17 (63.0) 49 (57.0) Absence 16 (32.7) 5 (26.3) 10 (37.0) 37 (43.0) Disease recurrence-free interval (days) HBsAg ( ): hepatitis B surface antigen positive; HBsAg ( ): hepatitis B surface antigen negative; HCVAb ( ): hepatitis C virus antibody positive; HCVAb ( ): hepatitis C virus antibody negative. a Continuous data are expressed as mean standard deviation. TABLE 2 Macroscopic Characteristics Associated with Early Disease Recurrence and Poor Prognosis a Macroscopic characteristics 1A 1B (n 86) Tumor size (cm) b Macroscopic classification b Early (12.8) Type 1 10 (20.4) 1 (5.3) 8 (29.6) 31 (36.0) Type 2 25 (51.0) 13 (68.4) 11 (40.7) 27 (31.4) Type 3 14 (28.6) 5 (26.3) 8 (29.6) 17 (19.8) No. of intrahepatic metastases c 3 37 (75.5) 18 (94.7) 18 (66.7) 0 1 or 2 12 (24.5) 1 (5.3) 9 (33.3) (100) a Continuous data are expressed as mean standard deviation. b Significant difference (P 0.05) between s 1 and 2. c Significant difference (P 0.05) between s 1A and 1B. (MPV) invasion, and microscopic intrahepatic metastasis (MIM; P 0.05). All 3 biologic markers studied by IHC (i.e., Ki-67, p53, and p-akt) were significantly different (P 0.05; Table 4). Of the clinical parameters and tumor characteristics evaluated by univariate analysis, MPV invasion and MIM were associated significantly with early disease recurrence as demonstrated by multivariate analysis. Positive immunostaining for p-akt was an independent risk factor for early disease recurrence as revealed by multivariate analysis of all three biologic markers (Table 5). TABLE 3 Microscopic Characteristics Associated with Early Disease Recurrence and Poor Prognosis Microscopic characteristics 1A 1B (n 86) Tumor differentiation a,b Well (27.9) Moderately 24 (49.0) 5 (26.3) 17 (63.0) 43 (50.0) Poorly 23 (46.9) 12 (63.1) 10 (37.0) 16 (18.6) Unknown 2 (4.1) 2 (10.5) 0 3 (3.5) Tumor capsule formation Negative 3 (6.1) 1 (5.3) 1 (3.7) 16 (18.6) Positive 46 (93.9) 18 (94.7) 26 (96.3) 70 (81.4) Capsule infiltration a Negative 16 (34.8) 5 (27.8) 10 (38.5) 40 (57.1) Positive 30 (65.2) 13 (72.2) 16 (61.5) 30 (42.9) Portal vein invasion a Negative 9 (18.4) 3 (15.8) 6 (22.2) 65 (75.6) Positive 40 (81.6) 16 (84.2) 21 (77.8) 21 (24.4) Intrahepatic metastasis a Negative 12 (24.5) 3 (15.8) 8 (29.6) 81 (94.2) Positive 37 (75.5) 16 (84.2) 19 (70.4) 5 (5.8) Noncancerous liver tissue specimen No cirrhosis 36 (73.5) 13 (72.2) 19 (70.4) 67 (77.9) Nomal 4 (8.2) 2 (11.1) 2 (7.4) 7 (8.1) CH 32 (65.3) 11 (61.1) 14 (63.0) 53 (69.8) Cirrhosis 13 (26.5) 5 (27.8) 8 (29.6) 19 (22.1) CH: chronic hepatitis; PC: precirrhosis. a Significant difference (P 0.05) between s 1 and 2. b Significant difference (P 0.05) between s 1A and 1B.
5 Risk Factors for Early HCC Recurrence/Nakanishi et al. 311 TABLE 4 Biologic Markers Associated with Early Disease Recurrence and Poor Prognosis Biologic markers A B (n 81) p-akt a,b Negative 36 (73.5) 10 (52.6) 23 (85.2) 79 (97.5) Positive 13 (26.5) 9 (47.4) 4 (14.8) 2 (2.5) Ki-67 a,b Low 34 (69.4) 10 (52.6) 23 (85.2) 72 (88.9) High 15 (30.6) 9 (47.4) 4 (14.8) 9 (11.1) p53 a Negative 33 (67.3) 12 (63.2) 20 (74.1) 73 (90.1) Positive 16 (32.7) 7 (36.8) 7 (25.9) 8 (9.9) p-akt: phosphorylated Akt. a Significant difference (P 0.05) between s 1 and 2. b Significant difference (P 0.05) between s 1A and 1B. TABLE 5 Multivariate Analysis of the Risk Factors Associated with Early Disease Recurrence Variables Risk ratio 95% CI P value Macroscopic and microscopic characteristics Portal vein invasion (positive) Intrahepatic metastasis (positive) Biologic markers p-akt (positive) CI: confidence interval; p-akt: phosphorylated Akt. Risk Factors for Poor Prognosis in Patients with Early Disease Recurrence To investigate the clinical impact of early disease recurrence, we subdivided into A (which included patients who died within 1 year) and B (which included patients who survived 1 year). In general, prognosis after disease recurrence is believed to depend on the treatment received, the effectiveness of the treatment, and the length of the disease recurrence-free interval after surgical resection. In the current study, the use of transarterial chemoembolization after disease recurrence (data not shown) and the disease recurrence-free interval after surgical resection (Table 1) were similar between s 1A and 1B. The number of intrahepatic metastases was associated significantly with a poor prognosis (Table 2). Moreover, in the univariate analysis, one pathologic characteristic and two biologic markers showed significant differences between s 1A 1B: tumor differentiation and positive immunostaining for Ki-67 and p-akt (P 0.05; Tables 3 and 4). Clinical parameters were not significantly different TABLE 6 Multivariate Analysis of the Risk Factors Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Early Disease Recurrence Variables Risk ratio 95% CI P value p-akt (positive) Ki-67 (positive) CI: confidence interval; p-akt: phosphorylated Akt. (Table 1). When the multivariate analysis was conducted, including the significant variables obtained on univariate analysis, positive immunostaining for Ki-67 and p-akt was an independent risk factor associated with poor prognosis (Table 6). DISCUSSION The disease recurrence rate after curative resection for HCC is still high. Surgery might be of little benefit in patients with early massive disease recurrence and very poor prognosis. Therefore, it is necessary to identify this high-risk group of patients with early disease recurrence and poor prognosis. In the current study, p-akt was recognized as a risk factor for early disease recurrence and poor prognosis. The serine/threonine kinase Akt was identified originally as an oncogene in mouse thymoma. 12 Akt is activated fully by phosphorylation after activation of PI3K. 13 p-akt regulates multiple processes, such as apoptosis, cell proliferation, and glucose utilization. 14 Overexpression of wild-type Akt may cause oncogenesis, as Akt has been found to be amplified with high frequency in gastric, pancreatic, breast, and ovarian tumors Moreover, we previously showed that p- Akt plays a critical role in hematogenous intrahepatic metastasis in an orthotopic implantation model of HCC. We also demonstrated a significant correlation between Akt activation and early disease recurrence, in the form of intrahepatic metastasis, in clinical patients. Currently, the molecular mechanism of early disease recurrence remains unclear. Intrahepatic metastasis is a more likely mechanism for the generation of early disease recurrence than multicentric development of new tumors. The first step of intrahepatic metastasis is dissemination of cancer cells into the circulation. Indeed, dissemination of cancer cells from primary HCC into the portal vein during surgical resection has been observed. 20 Nevertheless, disseminated cells do not always survive in the circulation and form metastatic sites, although anchorage-independent growth and rapid growth of cancer cells after surgical resection may be important factors for early
6 312 CANCER January 15, 2005 / Volume 103 / Number 2 disease recurrence. The current findings suggest that Akt phosphorylation is involved in such malignant behavior. Previous reports have suggested risk factors for early disease recurrence, such as tumor volume, histopathologic dedifferentiation, microscopic invasiveness, high cellular proliferation, and p53 mutation. A high serum concentration of -fetoprotein, which reflects tumor volume, was reported to be a predictor of early disease recurrence, and a previous report showed that p53 mutation was associated with the progression of HCC as a late event in hepatocarcinogenesis. 27 These observations are compatible with our current results. In conclusion, our clinical study has demonstrated the critical involvement of Akt phosphorylation in the aggressiveness of HCC and has identified Akt phosphorylation as a significant risk factor for early disease recurrence and poor prognosis. In patients with this risk factor, surgery may be of little benefit. Therefore, careful assessment of the indications for surgery is necessary in these patients. REFERENCES 1. Nagao T, Inoue S, Goto S, et al. Hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clinical features and long-term prognosis. Ann Surg. 1987;205: Nagao T, Inoue S, Yoshimi F, et al. Postoperative recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 1990;211: Sakon M, Umeshita K, Nagano H, et al. Clinical significance of hepatic resection in hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis by disease-free survival curves. Arch Surg. 2000;135: Ikeda Y, Kajiyama K, Adachi E, Yamagata M, Shimada M, Yanaga K. Early recurrence after surgery of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 1995;42: Matsumata T, Kanematsu T, Takenaka K, Yoshida Y, Nishizaki T, Sugimachi K. Patterns of intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1989;9: Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Different risk factors and prognosis for early and late intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2000;89: Shirabe K, Kanematsu T, Matsumata T, Adachi E, Akazawa K, Sugimachi K. Factors linked to early recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: univariate and multivariate analyses. Hepatology. 1991;14: Yamanaka J, Yamanaka N, Nakasho K, et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of stage II-III hepatocellular carcinoma showing early massive recurrence after liver resection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2000;15: Nakanishi K, Sakamoto M, Yasuda J, et al. Critical involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway in anchorage-independent growth and hematogeneous intrahepatic metastasis of liver cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62: Kanai T, Hirohashi S, Upton MP, et al. Pathology of small hepatocellular carcinoma. A proposal for a new gross classification. Cancer. 1987;60: Mangham DC, Isaacson PG. A novel immunohistochemical detection system using mirror image complementary antibodies (MICA). Histopathology. 1999;35: Bellacosa A, Testa JR, Staal SP, Tsichlis PN. A retroviral oncogene, akt, encoding a serine-threonine kinase containing an SH2-like region. Science. 1991;254: Kandel ES, Hay N. The regulation and activities of the multifunctional serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB. Exp Cell Res. 1999;253: Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME. Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 1999;13: Aoki M, Batista O, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis P, Vogt PK. The akt kinase: molecular determinants of oncogenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95: Staal SP. Molecular cloning of the akt oncogene and its human homologues AKT1 and AKT2: amplification of AKT1 in a primary human gastric adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987;84: Bellacosa A, de Feo D, Godwin AK, et al. Molecular alterations of the AKT2 oncogene in ovarian and breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 1995;64: Cheng JQ, Ruggeri B, Klein WM, et al. Amplification of AKT2 in human pancreatic cells and inhibition of AKT2 expression and tumorigenicity by antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93: Ruggeri BA, Huang L, Wood M, Cheng JQ, Testa JR. Amplification and overexpression of the AKT2 oncogene in a subset of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Mol Carcinog. 1998;21: Yamanaka N, Okamoto E, Fujihara S, et al. Do the tumor cells of hepatocellular carcinomas dislodge into the portal venous stream during hepatic resection? Cancer. 1992;70: Yamanaka N, Okamoto E, Toyosaka A, et al. Prognostic factors after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinomas. A univariate and multivariate analysis. Cancer. 1990;65: Hanazaki K, Wakabayashi M, Sodeyama H, Kajikawa S, Amano J. Hepatic function immediately after hepatectomy as a significant risk factor for early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999;46: Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results of treatment and prognostic factors. Ann Surg. 1999;229: Shimada M, Takenaka K, Gion T, et al. Prognosis of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma: a 10-year surgical experience in Japan. Gastroenterology. 1996;111: Takata M, Yamanaka N, Tanaka T, et al. What patients can survive disease free after complete resection for hepatocellular carcinoma? A multivariate analysis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2000;30: Hayashi H, Sugio K, Matsumata T, Adachi E, Takenaka K, Sugimachi K. The clinical significance of p53 gene mutation in hepatocellular carcinomas from Japan. Hepatology. 1995; 22: Oda T, Tsuda H, Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S. Different mutations of the p53 gene in nodule-in-nodule hepatocellular carcinoma as a evidence [sic] for multistage progression. Cancer Lett. 1994;83:
Pancreatic intraglandular metastasis predicts poorer outcome in postoperative patients with pancreatic
 Pancreatic intraglandular metastasis predicts poorer outcome in postoperative patients with pancreatic ductal carcinoma Seiji Oguro, MD * +, Kazuaki Shimada, MD, PhD, Yoshinori Ino, PhD *, Minoru Esaki,
Pancreatic intraglandular metastasis predicts poorer outcome in postoperative patients with pancreatic ductal carcinoma Seiji Oguro, MD * +, Kazuaki Shimada, MD, PhD, Yoshinori Ino, PhD *, Minoru Esaki,
Celsion Symposium New Paradigms in HCC Staging: HKLC vs. BCLC Staging
 Celsion Symposium New Paradigms in HCC Staging: HKLC vs. BCLC Staging Ronnie T.P. Poon, MBBS, MS, PhD Chair Professor of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery Chief of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery
Celsion Symposium New Paradigms in HCC Staging: HKLC vs. BCLC Staging Ronnie T.P. Poon, MBBS, MS, PhD Chair Professor of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery Chief of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Management of hepatocellular carcinoma should consider both tumor factors and background liver factors
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Column: Editorial Management of hepatocellular carcinoma should consider both tumor factors and background liver factors Shuji Nomoto, Mitsuhiro Hishida, Yoshikuni Inokawa, Hiroyuki
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Column: Editorial Management of hepatocellular carcinoma should consider both tumor factors and background liver factors Shuji Nomoto, Mitsuhiro Hishida, Yoshikuni Inokawa, Hiroyuki
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Diabetes Mellitus After Hepatic Resection
 Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Diabetes Mellitus After Hepatic Resection YASUHARU IKEDA, MITSUO SHIMADA, HIROFUMI HASEGAWA, TOMONOBU GION, KIYOSHI KAJIYAMA, KEN SHIRABE, KATSUHIKO YANAGA, KENJI
Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Diabetes Mellitus After Hepatic Resection YASUHARU IKEDA, MITSUO SHIMADA, HIROFUMI HASEGAWA, TOMONOBU GION, KIYOSHI KAJIYAMA, KEN SHIRABE, KATSUHIKO YANAGA, KENJI
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Takahito Nakagawa, MD, Toshiya Kamiyama, MD, Kazuaki Nakanishi, MD, Hideki Yokoo, MD, Hirofumi Kamachi, MD, Michiaki Matsushita, MD, Satoru Todo, MD
 Pulmonary for metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma: Factors influencing prognosis Takahito Nakagawa, MD, Toshiya Kamiyama, MD, Kazuaki Nakanishi, MD, Hideki Yokoo, MD, Hirofumi Kamachi, MD, Michiaki
Pulmonary for metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma: Factors influencing prognosis Takahito Nakagawa, MD, Toshiya Kamiyama, MD, Kazuaki Nakanishi, MD, Hideki Yokoo, MD, Hirofumi Kamachi, MD, Michiaki
Hepatic resection is a well-accepted therapy for hepatocellular
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Early and Late After Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications Nazario Portolani, MD,* Arianna Coniglio, MD,* Sara Ghidoni, MD,* Mara Giovanelli,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Early and Late After Liver Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications Nazario Portolani, MD,* Arianna Coniglio, MD,* Sara Ghidoni, MD,* Mara Giovanelli,
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1
 Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Microsatellite Distribution and Indication for Locoregional Therapy in Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 299 Microsatellite Distribution and Indication for Locoregional Therapy in Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma Atsushi Sasaki, M.D., Ph.D. Seiichiro Kai, M.D. Yukio Iwashita, M.D., Ph.D. Seitaro Hirano, M.D.
299 Microsatellite Distribution and Indication for Locoregional Therapy in Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma Atsushi Sasaki, M.D., Ph.D. Seiichiro Kai, M.D. Yukio Iwashita, M.D., Ph.D. Seitaro Hirano, M.D.
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Triple positive tumor markers predict recurrence and survival in early stage hepatocellular carcinoma
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/25864747 Triple positive tumor markers predict recurrence and survival in early stage hepatocellular
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/25864747 Triple positive tumor markers predict recurrence and survival in early stage hepatocellular
Management of Rare Liver Tumours
 Gian Luca Grazi Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery National Cancer Institute Regina Elena Rome Fibrolamellar Carcinoma Mixed Hepato Cholangiocellular Carcinoma Hepatoblastoma Carcinosarcoma Primary Hepatic
Gian Luca Grazi Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery National Cancer Institute Regina Elena Rome Fibrolamellar Carcinoma Mixed Hepato Cholangiocellular Carcinoma Hepatoblastoma Carcinosarcoma Primary Hepatic
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Abstract. Introduction
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognoses for Multicentric Occurrence and Intrahepatic Metastasis in Synchronous Multinodular Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Shi-Lai Li 1, Ming
RESEARCH ARTICLE Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognoses for Multicentric Occurrence and Intrahepatic Metastasis in Synchronous Multinodular Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Shi-Lai Li 1, Ming
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth
 Original Article / Liver Risk factors for early recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection Yan-Ming Zhou, Jia-Mei Yang, Bin Li, Zheng-Feng Yin, Feng Xu, Bin Wang, Wen Xu and
Original Article / Liver Risk factors for early recurrence of small hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection Yan-Ming Zhou, Jia-Mei Yang, Bin Li, Zheng-Feng Yin, Feng Xu, Bin Wang, Wen Xu and
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Prognostic Significance of Extranodal Cancer Invasion of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Lung Cancer
 Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 198, 1 (), 7-1 Prognostic Significance of Extranodal Cancer Invasion of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Lung Cancer KEIICHI SUEMASU, M.D. AND TSUGUO NARUKE, M.D. Department of Surgery,
Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 198, 1 (), 7-1 Prognostic Significance of Extranodal Cancer Invasion of Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Lung Cancer KEIICHI SUEMASU, M.D. AND TSUGUO NARUKE, M.D. Department of Surgery,
Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study
 Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 346-352 Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study Subhankar Chakraborty
Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 346-352 Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study Subhankar Chakraborty
Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients
 Yonago Acta medica 2012;55:57 61 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients Hiroaki Saito, Seigo Takaya, Yoji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Shigeru Tatebe and Masahide
Yonago Acta medica 2012;55:57 61 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients Hiroaki Saito, Seigo Takaya, Yoji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Shigeru Tatebe and Masahide
Although hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with lymph node
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of Histologically Confirmed Lymph Node Metastases on Patient Survival After Surgical Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Report of a Japanese Nationwide Survey Kiyoshi Hasegawa,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of Histologically Confirmed Lymph Node Metastases on Patient Survival After Surgical Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Report of a Japanese Nationwide Survey Kiyoshi Hasegawa,
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Evaluation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and Bcl-2 protein in nonsmall cell lung cancer
 166 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 35, No.4, 2005 Evaluation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and cl-2 protein in nonsmall cell lung cancer LEVENT DERTS Z 1, GÜLY ÖZ L M 2, LKNUR KÜKNER 2, REM
166 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 35, No.4, 2005 Evaluation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and cl-2 protein in nonsmall cell lung cancer LEVENT DERTS Z 1, GÜLY ÖZ L M 2, LKNUR KÜKNER 2, REM
Expression of p53, Bcl-2, VEGF, Ki67 and PCNA and Prognostic Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Expression of p53, Bcl-2, VEGF, Ki67 and PCNA and Prognostic Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cezar Stroescu 1, Adrian Dragnea 2, Bogdan Ivanov 1, Catalin Pechianu 3, Vlad Herlea 3, Olivia Sgarbura
Expression of p53, Bcl-2, VEGF, Ki67 and PCNA and Prognostic Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cezar Stroescu 1, Adrian Dragnea 2, Bogdan Ivanov 1, Catalin Pechianu 3, Vlad Herlea 3, Olivia Sgarbura
p53 expression in invasive pancreatic adenocarcinoma and precursor lesions
 Malaysian J Pathol 2011; 33(2) : 89 94 ORIGINAL ARTICLE p53 expression in invasive pancreatic adenocarcinoma and precursor lesions NORFADZILAH MY MBBCH,* Jayalakshmi PAILOOR MPath, FRCPath,* RETNESWARI
Malaysian J Pathol 2011; 33(2) : 89 94 ORIGINAL ARTICLE p53 expression in invasive pancreatic adenocarcinoma and precursor lesions NORFADZILAH MY MBBCH,* Jayalakshmi PAILOOR MPath, FRCPath,* RETNESWARI
Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma
 Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma RYOJI KAIZAKI 1, MASAKAZU YASHIRO 1,2, OSAMU SHINTO 1, KOICHI YASUDA 1, TARO MATSUZAKI 1, TETSUJI SAWADA 1 and KOSEI HIRAKAWA 1 1 Department of Surgical
Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma RYOJI KAIZAKI 1, MASAKAZU YASHIRO 1,2, OSAMU SHINTO 1, KOICHI YASUDA 1, TARO MATSUZAKI 1, TETSUJI SAWADA 1 and KOSEI HIRAKAWA 1 1 Department of Surgical
Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer. Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics of intramural metastasis in gastric cancer Tatsuya Hashimoto Kuniyoshi Arai Yuichi Yamashita Yoshiaki Iwasaki Tsunekazu Hishima Author for correspondence: T. Hashimoto
Two Rare Metachronous Metastases of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation
 Int Surg 2013;98:432 436 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00026.1 Case Report Two Rare Metachronous Metastases of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation Satoshi Shinya 1, Tomoaki Noritomi 1, Yasushi
Int Surg 2013;98:432 436 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00026.1 Case Report Two Rare Metachronous Metastases of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Liver Transplantation Satoshi Shinya 1, Tomoaki Noritomi 1, Yasushi
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Qian Liu, Jian-Jun Bi, Yan-Tao Tian, Qiang Feng, Zhao-Xu Zheng, Zheng Wang* Abstract. Introduction. Materials and Methods
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Outcome after Simultaneous Resection of Gastric Primary Tumour and Synchronous Liver Metastases: Survival Analysis of a Single-center Experience in China Qian Liu, Jian-Jun Bi, Yan-Tao
RESEARCH ARTICLE Outcome after Simultaneous Resection of Gastric Primary Tumour and Synchronous Liver Metastases: Survival Analysis of a Single-center Experience in China Qian Liu, Jian-Jun Bi, Yan-Tao
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 30: 91-98, 2013
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 30: 91-98, 2013 Lack of correlation between the antibody to hepatitis B core antigen and survival after surgical resection for hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma HIROKI
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 30: 91-98, 2013 Lack of correlation between the antibody to hepatitis B core antigen and survival after surgical resection for hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma HIROKI
Negative impact of low body mass index on liver cirrhosis patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
 Li et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:294 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0713-4 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Negative impact of low body mass index on liver cirrhosis
Li et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2015) 13:294 DOI 10.1186/s12957-015-0713-4 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Negative impact of low body mass index on liver cirrhosis
Natural History and Treatment Trends in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Subtypes: Insights From a National Cancer Registry
 2015;112:872 876 Natural History and Treatment Trends in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Subtypes: Insights From a National Cancer Registry PETER L. JERNIGAN, MD, KOFFI WIMA, MS, DENNIS J. HANSEMAN, PhD, RICHARD
2015;112:872 876 Natural History and Treatment Trends in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Subtypes: Insights From a National Cancer Registry PETER L. JERNIGAN, MD, KOFFI WIMA, MS, DENNIS J. HANSEMAN, PhD, RICHARD
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
carcinoma at a single Japanese Inst Citation Hepato-Gastroenterology, 56(91-92),
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Treatment of concomitant gastric va carcinoma at a single Japanese Inst Nanashima, Atsushi; Sumida, Yorihis Kenichirou; Tomoshige, Kouichi; Tak Fukuoka,
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Treatment of concomitant gastric va carcinoma at a single Japanese Inst Nanashima, Atsushi; Sumida, Yorihis Kenichirou; Tomoshige, Kouichi; Tak Fukuoka,
SECONDARIES: A PRELIMINARY REPORT
 HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 2, pp. 69-72 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORTS
HPB Surgery, 1990, Vol. 2, pp. 69-72 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Harwood Academic Publishers GmbH Printed in the United Kingdom CASE REPORTS
The most prominent etiological factors associated with hepatocellular
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparison of the Surgical Outcomes Among Patients With -positive, -positive, and Non-B Non-C Hepatocellular Carcinoma A Nationwide Study of 11,95 Patients Tohru Utsunomiya, MD, PhD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparison of the Surgical Outcomes Among Patients With -positive, -positive, and Non-B Non-C Hepatocellular Carcinoma A Nationwide Study of 11,95 Patients Tohru Utsunomiya, MD, PhD,
Concurrent Analysis of Human Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 1 and Ribonucleotide
 1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Concurrent Analysis of Human Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 1 and Ribonucleotide Reductase Subunit 1 Expression Increases Predictive Value for Prognosis in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Concurrent Analysis of Human Equilibrative Nucleoside Transporter 1 and Ribonucleotide Reductase Subunit 1 Expression Increases Predictive Value for Prognosis in Cholangiocarcinoma Patients
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Is the p53 Gene Mutation of Prognostic Value in Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Resection?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is the p53 Gene Mutation of Prognostic Value in Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Resection? Kuo-Shyang Jeng, MD; I-Shyan Sheen, MD; Be-Fong Chen, MD; Ju-Yann Wu Hypothesis: Mutant p53 gene
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is the p53 Gene Mutation of Prognostic Value in Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Resection? Kuo-Shyang Jeng, MD; I-Shyan Sheen, MD; Be-Fong Chen, MD; Ju-Yann Wu Hypothesis: Mutant p53 gene
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 5: , 2013
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 5: 149-154, 2013 Epithelial-mesenchymal transition expression profiles as a prognostic factor for disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical significance of transforming
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 5: 149-154, 2013 Epithelial-mesenchymal transition expression profiles as a prognostic factor for disease-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical significance of transforming
Role of cyclin E and p53 expression in progression of early gastric cancer
 160 Gastric Cancer (1998) 1: 160 165 L. Jiaqing et al.: Cyclin E in early gastric cancer 1998 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Original article Role of cyclin E and p53 expression
160 Gastric Cancer (1998) 1: 160 165 L. Jiaqing et al.: Cyclin E in early gastric cancer 1998 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Original article Role of cyclin E and p53 expression
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
& IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Preoperative Chemolipiodolization of the Whole Liver for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Preoperative Chemolipiodolization of the Whole Liver for Hepatocellular Carcinoma MASAKI KAIBORI 1, NOBORU TANIGAWA 2, YOICHI MATSUI 1, A-HON KWON 1, SATOSHI SAWADA 2 and YASUO KAMIYAMA 1 1 Department
Preoperative Chemolipiodolization of the Whole Liver for Hepatocellular Carcinoma MASAKI KAIBORI 1, NOBORU TANIGAWA 2, YOICHI MATSUI 1, A-HON KWON 1, SATOSHI SAWADA 2 and YASUO KAMIYAMA 1 1 Department
Importance of luminal membrane mesothelin expression in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1583-1589, 2015 Importance of luminal membrane mesothelin expression in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms TAKAHIRO EINAMA 1,2,3, HIROFUMI KAMACHI 1, HIROSHI NISHIHARA 4, SHIGENORI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 1583-1589, 2015 Importance of luminal membrane mesothelin expression in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms TAKAHIRO EINAMA 1,2,3, HIROFUMI KAMACHI 1, HIROSHI NISHIHARA 4, SHIGENORI
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most
 Original Article / Biliary Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor thrombus after R0 resection: a matched study Ding-Ding Wang, Li-Qun
Original Article / Biliary Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with bile duct tumor thrombus after R0 resection: a matched study Ding-Ding Wang, Li-Qun
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Di-Ya Wang 1&, Lei Liu 2&, Xing-Shun Qi 3& *, Chun-Ping Su 4, Xue Chen 3, Xu Liu 3, Jiang Chen 3, Hong-Yu Li 3, Xiao-Zhong Guo 3 *
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.13.5573 Re-Resection versus TACE for Recurrent HCC - a Meta-Analysis RESEARCH ARTICLE Hepatic Re-resection Versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for the Treatment
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.13.5573 Re-Resection versus TACE for Recurrent HCC - a Meta-Analysis RESEARCH ARTICLE Hepatic Re-resection Versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for the Treatment
Clinico-pathological significance of extra-nodal spread in special types of breast cancer
 Cancer Biol Med 2014;11:116-122. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.02.006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinico-pathological significance of extra-nodal spread in special types of breast cancer Ecmel Isik Kaygusuz,
Cancer Biol Med 2014;11:116-122. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.02.006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinico-pathological significance of extra-nodal spread in special types of breast cancer Ecmel Isik Kaygusuz,
How to apply HCC prediction models to practice?
 How to apply HCC prediction models to practice? Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine Woo Jin Chung HCC prediction models 독특하게간세포암환자들의생존은암의진행상태뿐아니라기저간기능의중증정도에영향을받는특성이있다.
How to apply HCC prediction models to practice? Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine Woo Jin Chung HCC prediction models 독특하게간세포암환자들의생존은암의진행상태뿐아니라기저간기능의중증정도에영향을받는특성이있다.
Inverse relationship between cirrhosis and massive tumours in hepatocellular carcinoma
 DOI:10.1111/j.1477-2574.2012.00507.x HPB ORIGINAL ARTICLE Inverse relationship between cirrhosis and massive tumours in hepatocellular carcinoma Umut Sarpel 1, Diego Ayo 2, Iryna Lobach 3, Ruliang Xu 4
DOI:10.1111/j.1477-2574.2012.00507.x HPB ORIGINAL ARTICLE Inverse relationship between cirrhosis and massive tumours in hepatocellular carcinoma Umut Sarpel 1, Diego Ayo 2, Iryna Lobach 3, Ruliang Xu 4
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the AJCC/UICC 8 th edition updates
 Review Article Page 1 of 5 Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the AJCC/UICC 8 th edition updates Andrew J. Lee, Yun Shin Chun Department of Surgical Oncology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center,
Review Article Page 1 of 5 Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the AJCC/UICC 8 th edition updates Andrew J. Lee, Yun Shin Chun Department of Surgical Oncology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center,
Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer
 He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
Key words: gastric cancer, lymphovascular invasion, recurrence
 Key words: gastric cancer, lymphovascular invasion, recurrence 139 (2177) Table I Relationship between clinicopathologic factors and lymphatic invasion in 2146 patients with gastric cancer Factors P-value
Key words: gastric cancer, lymphovascular invasion, recurrence 139 (2177) Table I Relationship between clinicopathologic factors and lymphatic invasion in 2146 patients with gastric cancer Factors P-value
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Prognostic factors after hepatic resection for the single hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 5 cm
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 2288-6575 eissn 2288-6796 http://dx.doi.org/1174/astr.216.91.3.14 Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research Prognostic factors after hepatic resection for the single hepatocellular
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 2288-6575 eissn 2288-6796 http://dx.doi.org/1174/astr.216.91.3.14 Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research Prognostic factors after hepatic resection for the single hepatocellular
Embolotherapy for Cholangiocarcinoma: 2016 Update
 Embolotherapy for Cholangiocarcinoma: 2016 Update Igor Lobko,MD Chief, Division Vascular and Interventional Radiology Long Island Jewish Medical Center GEST 2016 Igor Lobko, M.D. No relevant financial
Embolotherapy for Cholangiocarcinoma: 2016 Update Igor Lobko,MD Chief, Division Vascular and Interventional Radiology Long Island Jewish Medical Center GEST 2016 Igor Lobko, M.D. No relevant financial
Decoding multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma: an opportune pursuit
 Editorial Decoding multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma: an opportune pursuit György Baffy Department of Medicine, VA Boston Healthcare System and Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Editorial Decoding multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma: an opportune pursuit György Baffy Department of Medicine, VA Boston Healthcare System and Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Multiple Primary Quiz
 Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
A Rare Case of Recurrent Alphafetoprotein-producing. without Re-elevation of Serum AFP
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2006; 34: 109 114 A Rare Case of Recurrent Alphafetoprotein-producing Gastric Cancer without Re-elevation of Serum AFP K TOMIYAMA 1, M TAKAHASHI 2, T FUJII
The Journal of International Medical Research 2006; 34: 109 114 A Rare Case of Recurrent Alphafetoprotein-producing Gastric Cancer without Re-elevation of Serum AFP K TOMIYAMA 1, M TAKAHASHI 2, T FUJII
P16 GENE EXPRESSION IN OVARIAN EPITHELIAL CYSTADENOCARCINOMA
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 9(1):61-65,1997. P16 GENE EXPRESSION IN OVARIAN EPITHELIAL CYSTADENOCARCINOMA Ni Xinghao ~,~ Zhang Gu ~-~ Xu Shenhua i~_~ Qian Lijuan ~l~fl~ Wu Xiongwei ~://~ Gao Yongliang
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research 9(1):61-65,1997. P16 GENE EXPRESSION IN OVARIAN EPITHELIAL CYSTADENOCARCINOMA Ni Xinghao ~,~ Zhang Gu ~-~ Xu Shenhua i~_~ Qian Lijuan ~l~fl~ Wu Xiongwei ~://~ Gao Yongliang
Alpha-Fetoprotein-L3 for Detection of Hepatocellular (Liver) Cancer. Original Policy Date
 MP 2.04.35 Alpha-Fetoprotein-L3 for Detection of Hepatocellular (Liver) Cancer Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature
MP 2.04.35 Alpha-Fetoprotein-L3 for Detection of Hepatocellular (Liver) Cancer Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature
Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules
 Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules YASUHIRO ITO, TAKUYA HIGASHIYAMA, YUUKI TAKAMURA, AKIHIRO MIYA, KAORU KOBAYASHI, FUMIO MATSUZUKA, KANJI KUMA
Long-term Follow-up for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Treated as Benign Nodules YASUHIRO ITO, TAKUYA HIGASHIYAMA, YUUKI TAKAMURA, AKIHIRO MIYA, KAORU KOBAYASHI, FUMIO MATSUZUKA, KANJI KUMA
Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver
 Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver Noboru Terayama, Tadashi Terada and Yasuni Nakanuma Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa One
Histologic Growth Patterns of Metastatic Carcinomas of the Liver Noboru Terayama, Tadashi Terada and Yasuni Nakanuma Second Department of Pathology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa One
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Original Article. Spontaneous Healing of Breast Cancer
 Breast Cancer Vol. 12 No. 2 April 2005 Original Article Rie Horii 1, 3, Futoshi Akiyama 1, Fujio Kasumi 2, Morio Koike 3, and Goi Sakamoto 1 1 Department of Breast Pathology, the Cancer Institute of the
Breast Cancer Vol. 12 No. 2 April 2005 Original Article Rie Horii 1, 3, Futoshi Akiyama 1, Fujio Kasumi 2, Morio Koike 3, and Goi Sakamoto 1 1 Department of Breast Pathology, the Cancer Institute of the
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Title Author(s) Citation Kobe University Repository : Kernel Issue date 1997-01-24 Resource Type Resource Version DOI URL Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer Regions (AgNOR) in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Title Author(s) Citation Kobe University Repository : Kernel Issue date 1997-01-24 Resource Type Resource Version DOI URL Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer Regions (AgNOR) in Colorectal Cancer Patients
Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation: Comparative Analysis with Partial Hepatectomy
 Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2017; 51: 79-86 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation: Comparative Analysis with Partial Hepatectomy Kyuho Lee
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2017; 51: 79-86 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Liver Transplantation: Comparative Analysis with Partial Hepatectomy Kyuho Lee
Key words: advanced gastric cancer, prognostic factor, Cox proportional hazards model. univariate analysis, multivariate analysis, Variable
 Key words: advanced gastric cancer, prognostic factor, Cox proportional hazards model univariate analysis, multivariate analysis, Age Sex Variable Gross pattern Tumor size Serosal invasion Peritoneal dissemination
Key words: advanced gastric cancer, prognostic factor, Cox proportional hazards model univariate analysis, multivariate analysis, Age Sex Variable Gross pattern Tumor size Serosal invasion Peritoneal dissemination
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Validation of The Hong Kong Liver Cancer Staging System in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Intent Treatment
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.6.1697 RESEARCH ARTICLE Validation of The Hong Kong Liver Cancer Staging System in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Intent Treatment Alan Chuncharunee 1,
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.6.1697 RESEARCH ARTICLE Validation of The Hong Kong Liver Cancer Staging System in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Intent Treatment Alan Chuncharunee 1,
Metastatic mechanism of spermatic cord tumor from stomach cancer
 Int Canc Conf J (2013) 2:191 195 DOI 10.1007/s13691-013-0-9 CANCER BOARD CONFERENCE Metastatic mechanism of spermatic cord tumor from stomach cancer Masahiro Seike Yoshikazu Kanazawa Ryuji Ohashi Tadashi
Int Canc Conf J (2013) 2:191 195 DOI 10.1007/s13691-013-0-9 CANCER BOARD CONFERENCE Metastatic mechanism of spermatic cord tumor from stomach cancer Masahiro Seike Yoshikazu Kanazawa Ryuji Ohashi Tadashi
Endoscopic Ultrasonography Assessment for Ampullary and Bile Duct Malignancy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
SOMATOSTATIN RECEPTORS IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA. Marie LEQUOY Saint-Antoine Hospital, Department of Hepatology, Paris, France
 SOMATOSTATIN RECEPTORS IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA Marie LEQUOY Saint-Antoine Hospital, Department of Hepatology, Paris, France Somatostatin : SST Somatostatin (SST) protein : 2 active forms (alternative
SOMATOSTATIN RECEPTORS IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA Marie LEQUOY Saint-Antoine Hospital, Department of Hepatology, Paris, France Somatostatin : SST Somatostatin (SST) protein : 2 active forms (alternative
A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma. in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis. of Lymph Node Metastasis
 Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
Kitakanto Med J 2002 ; 52 : 189-193 189 A Proposed Strategy for Treatment of Superficial Carcinoma in the Thoracic Esophagus Based on an Analysis of Lymph Node Metastasis Susumu Kawate,' Susumu Ohwada,'
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
ATAD2 as a Poor Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Resection
 pissn 1598-2998, eissn 25-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 215;47(4):853-861 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1143/crt.214.177 Open Access ATAD2 as a Poor Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative
pissn 1598-2998, eissn 25-9256 Cancer Res Treat. 215;47(4):853-861 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1143/crt.214.177 Open Access ATAD2 as a Poor Prognostic Marker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative
Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor
 Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor Authors Kensuke Yokoyama 1,JunUshio 1,NorikatsuNumao 1, Kiichi Tamada 1, Noriyoshi Fukushima 2, Alan
Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor Authors Kensuke Yokoyama 1,JunUshio 1,NorikatsuNumao 1, Kiichi Tamada 1, Noriyoshi Fukushima 2, Alan
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Original Article Relationship of different surgical margins with recurrence-free survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(3):3404-3409 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0004822 Original Article Relationship of different surgical margins with recurrence-free survival in patients with hepatocellular
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(3):3404-3409 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0004822 Original Article Relationship of different surgical margins with recurrence-free survival in patients with hepatocellular
Clinicopathological and prognostic differences between mucinous gastric carcinoma and signet-ring cell carcinoma
 Original Article Clinicopathological and prognostic differences between mucinous gastric carcinoma and signet-ring cell carcinoma Zhaode Bu, Zhixue Zheng, Ziyu Li, Xiaojiang Wu, Lianhai Zhang, Aiwen Wu,
Original Article Clinicopathological and prognostic differences between mucinous gastric carcinoma and signet-ring cell carcinoma Zhaode Bu, Zhixue Zheng, Ziyu Li, Xiaojiang Wu, Lianhai Zhang, Aiwen Wu,
Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance
 Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance Gi-Ae Kim, Han Chu Lee *, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim,
Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance Gi-Ae Kim, Han Chu Lee *, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim,
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Management of HepatoCellular Carcinoma
 9th Symposium GIC St Louis - 2010 Management of HepatoCellular Carcinoma Overview Pierre A. Clavien, MD, PhD Department of Surgery University Hospital Zurich Zurich, Switzerland Hepatocellular carcinoma
9th Symposium GIC St Louis - 2010 Management of HepatoCellular Carcinoma Overview Pierre A. Clavien, MD, PhD Department of Surgery University Hospital Zurich Zurich, Switzerland Hepatocellular carcinoma
Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories
 Original Article Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories Wu Song, Yulong He, Shaochuan Wang, Weiling
Original Article Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories Wu Song, Yulong He, Shaochuan Wang, Weiling
Actual 10-year survival following hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma
 DOI:10.1111/hpb.12206 HPB ORIGINAL ARTICLE Actual 10-year survival following hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma Bernardo Franssen, Ghalib Jibara, Parissa Tabrizian, Myron E. Schwartz & Sasan Roayaie
DOI:10.1111/hpb.12206 HPB ORIGINAL ARTICLE Actual 10-year survival following hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma Bernardo Franssen, Ghalib Jibara, Parissa Tabrizian, Myron E. Schwartz & Sasan Roayaie
Expression and significance of Bmi-1 and Ki67 in colorectal carcinoma tissues
 [Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:12, 568-573; December Expression 2008]; 2008 and significance Sun Yat-sen of University Bmi-1 and Cancer Ki67 in Center colorectal carcinoma tissues Clinical Research Paper
[Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:12, 568-573; December Expression 2008]; 2008 and significance Sun Yat-sen of University Bmi-1 and Cancer Ki67 in Center colorectal carcinoma tissues Clinical Research Paper
Perigastric lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: comparison of different staging systems
 Gastric Cancer (1999) 2: 201 205 Original article 1999 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Perigastric lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: comparison of different staging systems
Gastric Cancer (1999) 2: 201 205 Original article 1999 by International and Japanese Gastric Cancer Associations Perigastric lymph node metastases in gastric cancer: comparison of different staging systems
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma
 Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Effectiveness of additional resection of the invasive cancer-positive proximal bile duct margin in cases of hilar cholangiocarcinoma
 Original Article Effectiveness of additional resection of the invasive cancer-positive proximal bile duct margin in cases of hilar cholangiocarcinoma Wen-Jie Ma 1#, Zhen-Ru Wu 2#, Anuj Shrestha 1,3, Qin
Original Article Effectiveness of additional resection of the invasive cancer-positive proximal bile duct margin in cases of hilar cholangiocarcinoma Wen-Jie Ma 1#, Zhen-Ru Wu 2#, Anuj Shrestha 1,3, Qin
(Received for Publication: March 24, 2015) Key words portal venous pressure, major hepatectomy, liver
 55 Original Article J. St. Marianna Univ. Vol. 6, pp. 55 61, 2015 Usefulness of Intraoperative Measurement of Portal Venous Pressure for Confirming the Most Appropriate Hepatectomy in Patients with Borderline
55 Original Article J. St. Marianna Univ. Vol. 6, pp. 55 61, 2015 Usefulness of Intraoperative Measurement of Portal Venous Pressure for Confirming the Most Appropriate Hepatectomy in Patients with Borderline
Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S136 S140 Detection and Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Imaging OSAMU MATSUI Department of Imaging Diagnosis and Interventional Radiology,
Gang Huang, MD; Wan Yee Lau, MD, FRCS; Wei-ping Zhou, MD, PhD; Feng Shen, MD, PhD; Ze-ya Pan, MD; Sheng-xian Yuan, MD; Meng-chao Wu, MD
 Research Original Investigation Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence in Patients With Low Hepatitis B Virus DNA Levels and High Preoperative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Gang Huang,
Research Original Investigation Prediction of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence in Patients With Low Hepatitis B Virus DNA Levels and High Preoperative Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Levels Gang Huang,
Focus on Dysplastic Nodules and Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Eastern Point of View. Masamichi Kojiro
 Focus on Dysplastic Nodules and Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Eastern Point of View Masamichi Kojiro Although increasing numbers of equivocal nodular lesions have been detected in patients with liver
Focus on Dysplastic Nodules and Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Eastern Point of View Masamichi Kojiro Although increasing numbers of equivocal nodular lesions have been detected in patients with liver
Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers
 Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers The term cancer applies to a group of diseases in which cells grow abnormally and form a malignant tumor. It is a long term multistage genetic process. The first
Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers The term cancer applies to a group of diseases in which cells grow abnormally and form a malignant tumor. It is a long term multistage genetic process. The first
