Treatment Modalities: Radiation Therapy & Bone Marrow Transplant
|
|
|
- Cleopatra Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Treatment Modalities: Radiation Therapy & Bone Marrow Transplant Karen Anderson MN, RN, OCN, BMTCN Immunotherapy Clinical Operations Manager Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Objectives Discuss the role radiation therapy and hematopoietic cell transplant in the treatment of cancer. 1. Principles of radiation therapy 2. Assessment 3. Radiation safety precautions 4. Transplant process basics 5. Patient teaching and preparation for transplant for the community oncology nurse 6. Follow-up care for the community oncology nurse Radiation Sources of Radiation Radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium Ionizing: has enough energy to remove electrons from atoms, creating ions Alpha particles Beta particles Gamma rays X-rays Neutrons Protons 1
2 Types of Radiation Radiation as Cancer Treatment Photon Radiation X-Rays Gamma Rays Particle Radiation Alpha Beta Proton Neutron Electron Carbon Damages DNA directly or creates free radicals which damage DNA May affect normal and tumor cells Goals of Radiation therapy Cancers treated with Radiation Definitive: primary cancer treatment Neoadjuvant: given prior to surgery Adjuvant: after chemo or surgery Prophylaxis: to prevent spread to high risk tissues Control: slow growth and spread of tumor Palliation: decrease symptoms related to disease Breast Lung GI Cervical Lymphoma Prostate Brain Sarcoma Head/Neck Renal Cell Pancreatic Cancers Thyroid 2
3 Radiosensitivity Bergonie and Treibondeau s Law: Radiosensitivity is highest in tissues with the highest mitotic index, and lowest in well-differentiated tissues. RadioSensitivity Well-oxygenated tumors are more radiosensitive Tumor Lymphoid, bone marrow, blood, testes, ovaries, intestines Skin, cornea, oral, esophagus, rectum, bladder, vagina, cervix, ureters Stomach, vasculature, growing bone and cartilage Salivary glands, lungs, kidneys, liver, breast, pancreas, thyroid, adrenals, pituitary Muscle, brain, spinal cord Radiosensitivity High Fairly High Moderate Fairly Low Low Itano, Brant, Conde & Saria. (2015). Core curriculum for oncology nursing (5th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Saunders. Medications effects: Radiosensitizers: 5-Flouracil; cisplatin, metronidazole and analogues Radioprotectors: Amifostine Citrin, D., & Mitchell, J. (2014). Altering the response to radiation: Sensitizers and protectors. Seminars in Oncology, 41(6), Treatment dosing Radiation Therapy Team Measured in Gray (Gy): the absorption of one joule of radiation energy per one kilogram of matter 1/100 th of Gray= Centigray (cgy) =100 rad Example: Typical treatment dose for breast cancer may be Gy. Radiation Tech: delivers daily dose of radiation treatments Radiation Dosimetrist: has an understanding of radiation therapies, physics, and works with the physicist and MD to calculate radiation doses Nurse: symptom management, care coordination, patient and family education Physicist: expert in physics, radiation equipment, radiation dosimetry Radiation Oncologist: Physician specializing in radiation for cancer treatment Yarbro, C., Wujcik, Debra, & Gobel, Barbara Holmes. (2011). Cancer nursing principles and practice (7th ed.). Sudbury, Mass.: Jones and Bartlett. page257. Siglin, J., Champ, C., Vakhnenko, Y., Anne, P., & Simone, N. (2012). Radiation therapy for locally recurrent breast cancer. International Journal of Breast Cancer, 12 (Article ID ). doi: /2012/ Retrieved 8/29/15. 3
4 External Beam Radiation Radiation delivered by a machine X-Ray Therapy or Particle Beams Most common type of radiation therapy Often delivered a linear accelerator External Beam Radiation 3D-Conformal Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT) Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Image-guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy (IMPT) Stereotractic Radiosurgery & Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SRS & SBRT): Gamma Knife, Cyberknife National Cancer Institute. Understanding Radiation therapy. What to Know about External Beam Radiation Therapy. Retrieved fromhttp:// on 8/26/15 External Beam Radiation: Simulation & Treatment Planning Imaging: CT, MRI, or PET to obtain details about tumor and surrounding tissues Simulation of a treatment Tattoos or ink markings to denote treatment area Blocks created Body Molds/Masks may be created Dosimetry calculations External Beam Treatments Treatment are often daily M-F for 2-10 weeks Pt must lie still during treatments Radiation therapist remains in the next room during treatments Treatment may last 15-30mins due to set-up though the radiation is only 1-5 minutes Pt is NOT radioactive 4
5 Fractionation Division of total dose of radiation into smaller doses called fractions Hyperfractionation: Smaller doses given more often: (2x/day) Hypofractionation: Large doses given less often over a shorter period of time Goal to maximize tumor kill while minimizing impacts on surrounding tissues. The 4 R s of Fractionation Repair: Allows time between doses for normal tissues to repair themselves Redistribution: Cell cycle redistribution, increasing tumor radiosensitivity Repopulation: New growth of normal tissues occurs Reoxygenation: Allows oxygenation of tumor, increasing radiosensitivity Yarbro, C., Wujcik, Debra, & Gobel, Barbara Holmes. (2011). Cancer nursing principles and practice (7th ed.). Sudbury, Mass.: Jones and Bartlett. P 257 Brachytherapy: Internal Radiation Delivery of radiation directly to the tumor or in nearby tissues via a sealed source (ie: implant, seed) Interstitial Radiation: ex: Mammosite for breast CA, seed implants for prostate CA Intracavitary Radiation: ex: vaginal cylinder for uterine CA Radioembolization for cancers of the liver General Radiation Safety with Internal Radiation Patients may be radioactive for a short time May be instructed to avoid small children and pregnant women or to keep a distance from others for a short time Body fluids are not usually radioactive (exception: some types of radioembolization) If implant removed, patient is no longer radioactive If permanent implants are placed, radioactivity decays over time until gone. Source: ACR-SIR practice parameter for radioembolization with microsphere brachytherapy device (RMBD) for treatment of liver malignancies. 5
6 Brachytherapy: Balloon Brachytherapy After lumpectomy, a saline filled balloon with attached catheter is inserted into the lumpectomy pocket Radiation is delivered via a seed that is inserted into the catheter during treatments and then removed. Balloon is typically left in place for 5 days Brachytherapy: Prostate Seed Implants Seeds are implanted in the prostate May be removed or left in place Urinary incontinence, rectal discomfort, diarrhea, or erectile dysfunction are potential side effects Avoidance of children on lap and wearing condoms may be recommended What is Mammosite? Retrieved from on 8/26/15 Systemic Radiation Therapy I-131 Radiation Treatments Radioactive antibody infusions: Ibritumomab Tiuxetan (Zevalin) Radiopharmaceutical Infusions: Radium 223, Strontium 89- used for bone metastases Radioactive iodine (I-131) treatments for thyroid cancer Pt is radioactive If hospitalized, rooms are covered with plastic or paper covering to protect from body fluids Cover personal electronics or belongings with plastic Men should sit to use the toilet Flush toilet twice & use separate bathroom Avoid sharing utensils & disposable trays in hospitalized Sleep alone for a period of time Minimize time with pregnant women and children for several days 6
7 Assessment for Acute Radiation Toxicities Acute Toxicities: Think Site Fatigue Pain Esophagitis/Mucositis Diarrhea Skin erythema Wet Desquamation N/V Pneumonitis Myelosuppression Reproductive changes Sexual dysfunction Alopecia Increased cerebral edema Cystitis General: Fatigue, Skin Care Head/Neck XRT: Mucositis Brain: Neuro cognitive changes Breast: Skin care Pelvic cancer: Sexual impacts, infertility GI: Diarrhea, dehydration Management of Skin Toxicities Management of Mucositis Erythema & pigmentation. May progress to dry and wet desquamation. Wash with mild soap and water Wear loose fitting clothes over the area Avoid razors Avoid sun Moisturize, but not before treatments If moist desquamation- hydrocolloid or silicone dressings may be applied. Basic oral care Saline or baking soda rinses Keep tissues moist Topical lidocaine mouth rinses Pain control Swallowing exercises Secretion management Consult nutrition for support Salvo, N., Barnes, E., van Draanen, J., Stacey, E., Mitera, G., Breen, D., De Angelis, C. (2010). Prophylaxis and management of acute radiation-induced skin reactions: a systematic review of the literature. Current Oncology, 17(4),
8 Patient Teaching Emphasize Treatment Adherence: Missing treatments can negatively impact disease control Missing even one treatment in head/neck cancer treatment may decrease local control of tumor by 1.4% Radiation Safety for Staff ALARA: As low as reasonably achievable Dosimetry monitoring for staff Fetal dosimeter monitor for pregnant staff. Dosimetry monitoring required for those that might get 10% of annual limit (0.5 rem/year) or staff that enter high radiation areas. Geiger counters Bese, N. S., Hendry, J., & Jeremic, B. (2007). Effects of prolongation of overall treatment time due to unplanned interruptions during radiotherapy of different tumor sites and practical methods for compensation. International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics, 68(3), doi : metryrequirements. Radiation Safety Principles Time Distance Shielding Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Containment 8
9 Why a Transplant? High risk disease features at diagnosis Relapsed or refractory disease with standard treatments Correction of malfunctioning component of the immune or hematopoietic system Curative potential HSCT Process 1. Planning phase 2. Preparing for transplant 3. Conditioning 4. Transplant 5. Awaiting Engraftment 6. Post-engraftment recovery 7. Long-term follow-up Indications for HSCT Approaches to Transplant Non-malignant diseases: Hematologic Disorders (ex: Aplastic Anemia, Sickle Cell Anemia) Congenital Immunodeficiencies (ex: SCID, Wiskott Aldrich Syndrome, HLH) Inborn Errors of Metabolism (ex: Hurler s Syndrome) Autoimmune Diseases (ex: Systemic Sclerosis, Multiple Sclerosis) Malignant diseases: Acute and Chronic Leukemia Hodgkin's lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma Myelodysplastic Syndromes Multiple myeloma Selected solid tumors Autologous Allogeneic Related or Unrelated Myeloablative Non-myeloablative 9
10 Autologous vs Allogeneic Stem Cell Sources Autologous High dose chemo and/or radiation Stem cells rescue the ablated marrow Risk for tumor in stem cell product Avoid graft-vs-host disease Allogeneic Standard: High Dose Chemo and/or radiation. Stem cells rescue the marrow. Non-myeloblative: Lower dose chemo and/or radiation. Graft versus malignancy effect Risk for graft versus host disease Bone Marrow Peripheral Blood Umbilical Cord Blood Advantages Good source of stem cells Less risk of cgvhd Most abundant source of stem cells Faster Engraftment Readily available HLA mismatch more acceptable Lack of donor risks Less risk of GVHD Disadvantages Anesthesia & surgical risks for donor Longer time to engraftment than PBSC Increased risk of graft failure Growth factors given to healthy donors Higher risk of cgvhd Delayed engraftment Smaller dose of stem cells Autologous HSCT: Mobilization and Apheresis Mobilization: A technique used to increase the number of circulating hematopoietic stem cells from the bone marrow into the bloodstream High Dose Chemotherapy + G-CSF ± plerixafor G-CSF Apheresis: The method for stem cell collection using a dialysis-type machine with cell separators that are programmed to collect stem cells. Allogenic Stem Cell Collection Donor apheresis procedure after receiving several days of filgrastim injections Stem cells collected over 1-2 days Donor bone marrow harvest Surgical procedure under anesthesia Multiple aspirations of marrow are taken Volume collected is based on recipient weight but may be between cc Bone marrow regenerates in about 4-6 weeks ; 10
11 Transplant Planning in the Community Patient & Donor Planning Oncologist reviews transplant with patient & family Transplant center consultation Address fertility now, if needed HLA type patient & siblings if needed Search the donor registries Transplant Planning in the Community Other Preparations Assess finances (insurance coverage or pay cash) Select transplant center (statistics on NMDP website) Select a caregiver Make plans for relocation if necessary HLA Typing Preparative Phase Degree of compatibility between donor and patient Important HLA markers for HSCT are A, B, C, & DRB1 Matched or mismatched donor options 25% chance that each sibling will be an HLA-match 70% of people do not have suitable family donors Medical and psycho-social evaluations. Evaluation of disease status and ability to tolerate transplant procedure. Family Conference & Informed Consent Process Preparation of the Family and Caregiver Orientation to center; Caregiver classes & support groups Central Line Placement 11
12 Conditioning Chemotherapy Myeloablative Myelosuppressive Common Drugs: Melphalan, Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide, Etoposide, Busulfan Radiation Total Body Irradiation Mini TBI Chemotherapy drugs listed w/ exception of busulfan are used off-label for transplant conditioning Transplant Stem cell infusion administered like an RBC transfusion Cryopreserved Preserved with DMSO Can cause hemolysis Causes garlic breath Transfusion reactions Fresh Awaiting Engraftment Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea Mucositis May effect the entire length of GI tract May need PCA & TPN Infections Transfusion support Rare: Graft Failure Allogeneic HSCT: Post Engraftment Recovery Patients are closely followed at the transplant center for several months Acute GVHD and infection are major concerns Seen daily to once/week for medical evaluation and blood tests Management of symptoms Infusion therapy At approximately day +80, patients are completely evaluated for disease state and complications and prepared for discharge home 12
13 Infections and HSCT Pre-engraftment : HSV, gram negative bacilli, staphylococcus epidermidis, GI-tract streptococci, candida, aspergillus Early Engraftment: candida, staphylococcus epidermidis, aspergillus, CMV, pneumocystis jiroveci Late Phase: CMV, VZV, encapsulated bacteria, aspergillus, pneumocysitis jiroveci Immune reconstitution after HSCT Innate immunity usually returns by day 100 Adaptive Immunity: CD4+ helper T-cells numbers may take months to return to normal levels Serum immunoglobulins may take months to years normalize and gain full functionality Immunosuppressants and chronic GVHD further impair immune reconstitution Acute Graft vs. Host Disease (agvhd) Predictive Factors for agvhd Donor T lymphocytes (the graft) recognize the antigens and cells in the transplant recipient (the host) as foreign and mount an immunologic attack. Estimated incidence between 35-80%. Donor/Host Factors HLA disparity Parity of female donor Age of donor and recipient HSC Source PBSC > BM > UCB Immunomodulation Omission of adequate agvhd prophylaxis TBI recipients 13
14 Clinical Features of agvhd Skin Maculopapular rash, often beginning with palmar/planter surfaces and extending to the face, abdomen and trunk Sunburned appearance to desquamation and loss of skin integrity Gut Anorexia, nausea and vomiting, early satiety Diarrhea, intestinal bleeding and abdominal pain to ileus Liver Elevated alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin RUQ pain, hepatomegaly and jaundice to ascites and encephalopathy Prevention of agvhd Highest degree of histocompatibility from donor (when multiple donors are available.) Prophylactic immunosuppression methotrexate, cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, sirolimus Selective T-cell depletion Immunosuppressive drugs listed are used off-label Treatment & Prognosis for agvhd Steroids: Prednisone 1-2mg/kg/day usual starting dose Secondary therapies may include other immunosuppressive agents that impact T-cell function such as biologic agents and ATG. Prognosis depends upon grade of GVHD and response to initial therapy Patients that do not respond to treatment for agvhd have a high risk for non-relapse mortality Allogeneic HSCT: Long-term Follow-Up (LTFU) Late complications Chronic GVHD Late infectious complications Pulmonary complications Bronchiolitis obliterans, pulmonary fibrosis Neurological complications Psychological complications Cataracts Sexual disorders (ex: dry vaginal mucosa) and impaired fertility Orthopedic complications Fragile joints due to steroids Secondary malignancy 14
15 Nursing Care for the LTFU Patient in the Community Refer to treatment plan from the discharging transplant center Follow guidelines from transplant center about safe living with impaired immune function Support psychosocial needs as patient returns to community after intense treatment at transplant center Monitor infection & immunosuppression Monitor for s/sx of chronic GVHD Immunizations Care coordination with transplant center and primary oncologist Chronic GVHD Pathophysiology is poorly understood Immune dysfunction T-cells B-cells Fibrotic changes Resembles autoimmune or collagen vascular disorder Estimated incidence between 30-70% Predictive factors & prognosis for cgvhd Previous agvhd PBSC Older donor or recipient HLA disparity Clinical Manifestations of Chronic GVHD Oral Symptoms GI Tract Skin Liver Nails Lung Mortality in cgvhd is largely attributed to infection. Major morbidity is often present with extensive chronic GVHD and requires long-term therapy. Scalp & Body Hair Eyes Genitalia Muscles/Fascia/Joints Hematopoietic/Immune 15
16 Treatment of cgvhd Primary Prednisone 1mg/kg/day or less, with a slow taper after improvement usually in combination with cyclosporine or tacrolimus Salvage: Various other immunosuppressive agents Supportive Care in cgvhd Infection prophylaxis Symptom palliation Manage dry skin and protect from sun Artificial tears Oral care Gynecology consult Nutritional intervention PT and OT Massage Psychosocial support Donor-Host Tolerance Donor-host tolerance can develop If no GVHD evident, patients can be tapered off immunosuppression slowly under medical supervision while watching to see of GVHD occurs Patients are educated to notify physician between visits if GVHD sx occur Transplant Survivorship Concerns Fatigue Fertility & Sexuality Growth and development for children Secondary Cancers Finances & employment Caregiver burnout Intimacy Learning and memory problems Late organ damage 16
17 Factors influencing HSCT outcomes Diagnosis Disease status at time of transplant Co-morbidities Severity of GVHD Web resources for outcome statistics: Resources: National Marrow Donor Program Understanding Cancer topics Seattle Cancer Care Alliance American Society for Radiation Oncology Oncology Nursing Society Questions? Karen Anderson, MN, RN, OCN, BMTCN 17
Objectives. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Approaches to Transplant. Indications for HSCT. Define HSCT. Provide overview of HSCT process
 Objectives Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Karen Anderson, MN, RN, OCN University of Washington Medical Center Define HSCT Provide overview of HSCT process Discuss acute complications of HSCT Discuss
Objectives Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Karen Anderson, MN, RN, OCN University of Washington Medical Center Define HSCT Provide overview of HSCT process Discuss acute complications of HSCT Discuss
Objectives. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Indications for HSCT. Approaches to Transplant. Define HSCT. Provide overview of HSCT process
 Objectives Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Karen Anderson, MN, RN, OCN, BMTCN Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Define HSCT Provide overview of HSCT process Discuss acute complications of HSCT Discuss chronic/late
Objectives Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Karen Anderson, MN, RN, OCN, BMTCN Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Define HSCT Provide overview of HSCT process Discuss acute complications of HSCT Discuss chronic/late
5/9/2018. Bone marrow failure diseases (aplastic anemia) can be cured by providing a source of new marrow
 5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
5/9/2018 or Stem Cell Harvest Where we are now, and What s Coming AA MDS International Foundation Indianapolis IN Luke Akard MD May 19, 2018 Infusion Transplant Conditioning Treatment 2-7 days STEM CELL
Radiotherapy physics & Equipments
 Radiotherapy physics & Equipments RAD 481 Lecture s Title: An Overview of Radiation Therapy for Health Care Professionals Dr. Mohammed Emam Vision :IMC aspires to be a leader in applied medical sciences,
Radiotherapy physics & Equipments RAD 481 Lecture s Title: An Overview of Radiation Therapy for Health Care Professionals Dr. Mohammed Emam Vision :IMC aspires to be a leader in applied medical sciences,
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT POLICY
 PAGE: 1 of 8 This medical policy is not a guarantee of benefits or coverage, nor should it be deemed as medical advice. In the event of any conflict concerning benefit coverage, the employer/member summary
PAGE: 1 of 8 This medical policy is not a guarantee of benefits or coverage, nor should it be deemed as medical advice. In the event of any conflict concerning benefit coverage, the employer/member summary
First, how does radiation work?
 Hello, I am Prajnan Das, Faculty Member in the Department of Radiation Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. We are going to talk today about some of the basic principles regarding
Hello, I am Prajnan Das, Faculty Member in the Department of Radiation Oncology at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. We are going to talk today about some of the basic principles regarding
An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation
 An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation October 24, 2009 Stephen Couban Department of Medicine Dalhousie University Objectives What are the types of blood and marrow transplantation? Who may benefit
An Overview of Blood and Marrow Transplantation October 24, 2009 Stephen Couban Department of Medicine Dalhousie University Objectives What are the types of blood and marrow transplantation? Who may benefit
Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University
 Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD) Background GVHD is an immunologic reaction of the donor immune cells (Graft) against
Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease (agvhd) Udomsak Bunworasate Chulalongkorn University Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD) Background GVHD is an immunologic reaction of the donor immune cells (Graft) against
What s a Transplant? What s not?
 What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
What s a Transplant? What s not? How to report the difference? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Anti-cancer effects of BMT or PBSCT [HSCT] Kill the cancer Save the patient Restore immunocompetence
Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia
 Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Number of Transplants 10/24/2011 Stem Cell Transplantation for Severe Aplastic Anemia Claudio Anasetti, MD Professor of Oncology and Medicine Chair, Blood and Marrow Transplant Dpt Moffitt Cancer Center
Stem cell transplantation. Dr Mohammed Karodia NHLS & UP
 Stem cell transplantation Dr Mohammed Karodia NHLS & UP The use of haemopoeitic stem cells from a donor harvested from peripheral blood or bone marrow, to repopulate recipient bone marrow. Allogeneic From
Stem cell transplantation Dr Mohammed Karodia NHLS & UP The use of haemopoeitic stem cells from a donor harvested from peripheral blood or bone marrow, to repopulate recipient bone marrow. Allogeneic From
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014
 Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Trends in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation AAMAC Patient Education Day Oct 2014 Objectives Review the principles behind allogeneic stem cell transplantation Outline the process of transplant, some of
Radiation Therapy for Cancer: Questions and Answers
 Radiation Therapy for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors (see Question 1). About half of all people with cancer are
Radiation Therapy for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors (see Question 1). About half of all people with cancer are
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018
 Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Introduction to Clinical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (HCT) George Chen, MD Thursday, May 03, 2018 The transfer of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cells for therapeutic purposes Hematopoietic Cell
Understanding Radiation Therapy. For Patients and the Public
 Understanding Radiation Therapy For Patients and the Public Introduction to Radiation Oncology Radiation has been an effective tool for treating cancer for more than 100 years. Radiation oncologists are
Understanding Radiation Therapy For Patients and the Public Introduction to Radiation Oncology Radiation has been an effective tool for treating cancer for more than 100 years. Radiation oncologists are
A Handbook for Families. Radiation. Therapy ONCOLOGY SERIES
 A Handbook for Families Radiation Therapy ONCOLOGY SERIES A Handbook for Families Radiation Therapy ONCOLOGY SERIES RADIATION THERAPY A HANDBOOK FOR FAMILIES Author Hilda Haynes-Lewis, MS ANP BC AOCNP
A Handbook for Families Radiation Therapy ONCOLOGY SERIES A Handbook for Families Radiation Therapy ONCOLOGY SERIES RADIATION THERAPY A HANDBOOK FOR FAMILIES Author Hilda Haynes-Lewis, MS ANP BC AOCNP
BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE
 BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE Jennifer Shamai MS, RN, AOCNS, BMTCN Professional Practice Leader Department of Clinical Practice And Professional Education Click How to edit the Master Experts
BMTCN REVIEW COURSE PRE-TRANSPLANT CARE Jennifer Shamai MS, RN, AOCNS, BMTCN Professional Practice Leader Department of Clinical Practice And Professional Education Click How to edit the Master Experts
Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation.
 Radiation Therapy Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation. One person in three will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime.
Radiation Therapy Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation. One person in three will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime.
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation
 Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
Reduced-intensity Conditioning Transplantation Current Role and Future Prospect He Huang M.D., Ph.D. Bone Marrow Transplantation Center The First Affiliated Hospital Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
Mobilization & Pre-Transplant Conditioning Regimens
 Transplant Process & Pre-Transplant Conditioning Regimens (auto patients only) 30 days before BMT (allo donors) 5 days before BMT Conditioning (auto AND allo patients) Transplant A technique used to increase
Transplant Process & Pre-Transplant Conditioning Regimens (auto patients only) 30 days before BMT (allo donors) 5 days before BMT Conditioning (auto AND allo patients) Transplant A technique used to increase
THE ROLE OF TBI IN STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION. Dr. Biju George Professor Department of Haematology CMC Vellore
 THE ROLE OF TBI IN STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION Dr. Biju George Professor Department of Haematology CMC Vellore Introduction Radiotherapy is the medical use of ionising radiation. TBI or Total Body Irradiation
THE ROLE OF TBI IN STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION Dr. Biju George Professor Department of Haematology CMC Vellore Introduction Radiotherapy is the medical use of ionising radiation. TBI or Total Body Irradiation
Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Faculty Disclosures Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Nothing to disclose Jeanne McCarthy-Kaiser, PharmD, BCOP Clinical Pharmacist, Autologous Stem Cell Transplant/Long- Term Follow-Up
Faculty Disclosures Introduction to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Nothing to disclose Jeanne McCarthy-Kaiser, PharmD, BCOP Clinical Pharmacist, Autologous Stem Cell Transplant/Long- Term Follow-Up
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016
 BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation How the Experts Treat Hematologic Malignancies Las Vegas, NV, March 10, 2016 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice
PROGRESS IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY. Fox Chase Cancer Center. Jean Holland RN MSN AOCN Department of Radiation Oncology April 2017
 PROGRESS IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY Fox Chase Cancer Center Jean Holland RN MSN AOCN Department of Radiation Oncology April 2017 Radiation Therapy Therapeutic use of electromagnetic energy from a machine or
PROGRESS IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY Fox Chase Cancer Center Jean Holland RN MSN AOCN Department of Radiation Oncology April 2017 Radiation Therapy Therapeutic use of electromagnetic energy from a machine or
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD
 Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: State of the Art in 2018 RICHARD W. CHILDS M.D. BETHESDA MD Overview: Update on allogeneic transplantation for malignant and nonmalignant diseases: state
ACR TXIT TM EXAM OUTLINE
 ACR TXIT TM EXAM OUTLINE Major Domain Sub-Domain 1 Statistics 1.1 Study design 1.2 Definitions of statistical terms 1.3 General interpretation & analysis 1.4 Survival curves 1.5 Specificity/sensitivity
ACR TXIT TM EXAM OUTLINE Major Domain Sub-Domain 1 Statistics 1.1 Study design 1.2 Definitions of statistical terms 1.3 General interpretation & analysis 1.4 Survival curves 1.5 Specificity/sensitivity
DEPARTMENT OF CLINICAL HEMATOLOGY
 DEPARTMENT OF CLINICAL HEMATOLOGY What is blood? Blood is the vital fluid of the body, which performs diverse functions from delivering oxygen to each and every cell of the body to fighting against infections
DEPARTMENT OF CLINICAL HEMATOLOGY What is blood? Blood is the vital fluid of the body, which performs diverse functions from delivering oxygen to each and every cell of the body to fighting against infections
Where in the TED Does HCT Stuff Go?
 Where in the TED Does HCT Stuff Go? Diane J. Knutson TED07_1.ppt Key Concepts What is an HSCT? Why perform one? Who can benefit? Mechanics of transplant Early and Late complications Where on new TED? TED07_2.ppt
Where in the TED Does HCT Stuff Go? Diane J. Knutson TED07_1.ppt Key Concepts What is an HSCT? Why perform one? Who can benefit? Mechanics of transplant Early and Late complications Where on new TED? TED07_2.ppt
Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Symptoms. Types
 Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) usually develops in the lymphatic system, a part of the body's immune system. This system carries disease-fighting white blood cells throughout the body. Lymph tissue
Donor work up, follow up and ethical issues
 Donor work up, follow up and ethical issues Hans Hägglund MD. PhD. Associate Professor Hematology Center, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden Outline The donor has been identified as a match
Donor work up, follow up and ethical issues Hans Hägglund MD. PhD. Associate Professor Hematology Center, Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden Outline The donor has been identified as a match
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B
 Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation and the Potential Role of Iomab-B Hillard M. Lazarus, MD, FACP Professor of Medicine, Director of Novel Cell Therapy Case Western Reserve University 1 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Introduction to clinical Radiotherapy
 Introduction to clinical Radiotherapy Sarah Brothwood Radiotherapy Practice Educator Rosemere Cancer Centre Sarah.brothwood@lthtr.nhs.uk 01772 522694 Radiotherapy We have been able to see and document
Introduction to clinical Radiotherapy Sarah Brothwood Radiotherapy Practice Educator Rosemere Cancer Centre Sarah.brothwood@lthtr.nhs.uk 01772 522694 Radiotherapy We have been able to see and document
Colorectal Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Scan for mobile link. Colorectal Cancer Treatment Colorectal cancer overview Colorectal cancer, also called large bowel cancer, is the term used to describe malignant tumors found in the colon and rectum.
Side effects of radiotherapy.
 Side effects of radiotherapy. Paweł Potocki, MD Jagiellonian University Medical College Kraków University Hospital Departament of Clinical Oncology ppotocki@su.krakow.pl Basics Techniques: Radiation type:
Side effects of radiotherapy. Paweł Potocki, MD Jagiellonian University Medical College Kraków University Hospital Departament of Clinical Oncology ppotocki@su.krakow.pl Basics Techniques: Radiation type:
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology. Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases
 One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
One Day BMT Course by Thai Society of Hematology Management of Graft Failure and Relapsed Diseases Piya Rujkijyanont, MD Division of Hematology-Oncology Department of Pediatrics Phramongkutklao Hospital
Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion
 Prevention of graftversus-host disease (GVHD) Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion Information for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and their families 2 This
Prevention of graftversus-host disease (GVHD) Understanding the role of ex vivo T cell depletion Information for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation in AML and their families 2 This
Cervical Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Cervical Cancer Treatment Cervical cancer overview Cervical cancer occurs in the cervix, the part of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina and uterus. Almost all
Scan for mobile link. Cervical Cancer Treatment Cervical cancer overview Cervical cancer occurs in the cervix, the part of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina and uterus. Almost all
Complications/Adverse Effects of Radiotherapy
 Complications/Adverse Effects of Radiotherapy Dr Omar Din Consultant in Clinical Oncology An Introduction to Acute Oncology Thursday 15 th March 2018 Outline Background History of radiotherapy Classification
Complications/Adverse Effects of Radiotherapy Dr Omar Din Consultant in Clinical Oncology An Introduction to Acute Oncology Thursday 15 th March 2018 Outline Background History of radiotherapy Classification
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Transplantation
 Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
Hematopoietic Stem Cells, Stem Cell Processing, and Joseph (Yossi) Schwartz, M irector, Hemotherapy and Stem Cell Processing Facility Bone Marrow Can Cure: Leukemia Lymphoma Multiple Myeloma Genetic iseases:
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK. HCT in Children
 Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
Rob Wynn RMCH & University of Manchester, UK HCT in Children Summary Indications for HCT in children Donor selection for Paediatric HCT Using cords Achieving engraftment in HCT Conditioning Immune action
Questions may be submitted anytime during the presentation.
 Understanding Radiation Therapy and its Role in Treating Patients with Pancreatic Cancer Presented by Pancreatic Cancer Action Network www.pancan.org August 18, 2014 If you experience technical difficulty
Understanding Radiation Therapy and its Role in Treating Patients with Pancreatic Cancer Presented by Pancreatic Cancer Action Network www.pancan.org August 18, 2014 If you experience technical difficulty
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017
 Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Haploidentical Transplantation: The Answer to our Donor Problems? Mary M. Horowitz, MD, MS CIBMTR, Medical College of Wisconsin January 2017 Allogeneic Transplant Recipients in the US, by Donor Type 9000
Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy. Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington
 Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington Objective: Helping you make informed decisions Introduction Process Radiation
Sarcoma and Radiation Therapy Gabrielle M Kane MB BCh EdD FRCPC Muir Professorship in Radiation Oncology University of Washington Objective: Helping you make informed decisions Introduction Process Radiation
Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO
 Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Peripheral blood stem cell transplantation (Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation) Dr.PSRK.Sastry MD, ECMO Consultant, Medical Oncology Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital Normal hematopoiesis Historical
Transplant Booklet D Page 1
 Booklet D Pretest Correct Answers 4. (A) is correct. Technically, performing a hematopoietic stem cell transplant is one of the simplest transplantation procedures. The hematopoietic stem cells are infused
Booklet D Pretest Correct Answers 4. (A) is correct. Technically, performing a hematopoietic stem cell transplant is one of the simplest transplantation procedures. The hematopoietic stem cells are infused
Cancer Treatment: Radiation. Combination of treatments: ü
 Combination of treatments: ü Cancer Treatment: External radiation: The radiation comes from a large machine outside the body. Radiation ü Internal radiation (implant radiation or brachytherapy): The radiation
Combination of treatments: ü Cancer Treatment: External radiation: The radiation comes from a large machine outside the body. Radiation ü Internal radiation (implant radiation or brachytherapy): The radiation
Brain Tumor Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Overview A brain tumor is a group of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. Tumors can directly destroy healthy brain cells. They can
The National Marrow Donor Program. Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Simon Bostic, URD Transplant Recipient
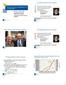 1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
1988 199 1992 1994 1996 1998 2 22 24 26 28 21 212 214 216 218 Adult Donors Cord Blood Units The National Donor Program Graft Sources for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Dennis L. Confer, MD Chief Medical
Therapeutic ratio - An Overview. Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga
 Therapeutic ratio - An Overview Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga Radiation Oncology Discipline of human medicine concerned with the generation, conservation and dissemination of knowledge concerning
Therapeutic ratio - An Overview Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga Radiation Oncology Discipline of human medicine concerned with the generation, conservation and dissemination of knowledge concerning
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation. David Rice, PhD, RN, NP
 BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation March 16, 2017 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice and Education No disclosures Objectives Describe basic concepts
BMTCN Review Course Basic Concepts and Indications for Transplantation March 16, 2017 David Rice, PhD, RN, NP Director, Professional Practice and Education No disclosures Objectives Describe basic concepts
Brachytherapy. What is brachytherapy and how is it used?
 Scan for mobile link. Brachytherapy Brachytherapy places radioactive sources inside the patient on a temporary or permanent basis to damage cancer cells DNA and destroy their ability to divide and grow.
Scan for mobile link. Brachytherapy Brachytherapy places radioactive sources inside the patient on a temporary or permanent basis to damage cancer cells DNA and destroy their ability to divide and grow.
Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer overview Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer in American men, most prevalent in men over age 65 and fairly common in men 50-64
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Treatment Prostate cancer overview Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer in American men, most prevalent in men over age 65 and fairly common in men 50-64
Indolent Lymphomas. Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital
 Indolent Lymphomas Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital What does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with
Indolent Lymphomas Dr. Melissa Toupin The Ottawa Hospital What does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with
Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Linear accelerators. Basic technique. Indications of SRS
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
Sickle Cell Diseasechronic. curable disease? Objectives. Why would a family ask about cure for SCD?
 Sickle Cell Diseasechronic illness or curable disease? Gregory M.T. Guilcher MD, FRCPC, FAAP Objectives To review the general principles of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), including risks
Sickle Cell Diseasechronic illness or curable disease? Gregory M.T. Guilcher MD, FRCPC, FAAP Objectives To review the general principles of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), including risks
Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells (lymphocytes) of the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system.
 Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Scan for mobile link. Lymphoma Lymphoma is a cancer that develops in the white blood cells of the lymphatic system. Symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, night sweats
Neutrophil Recovery: The. Posttransplant Recovery. Bus11_1.ppt
 Neutrophil Recovery: The First Step in Posttransplant Recovery No conflicts of interest to disclose Bus11_1.ppt Blood is Made in the Bone Marrow Blood Stem Cell Pre-B White cells B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte
Neutrophil Recovery: The First Step in Posttransplant Recovery No conflicts of interest to disclose Bus11_1.ppt Blood is Made in the Bone Marrow Blood Stem Cell Pre-B White cells B Lymphocyte T Lymphocyte
An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant
 Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
Introduction to Blood Cancers An Introduction to Bone Marrow Transplant Rushang Patel, MD, PhD, FACP Florida Hospital Medical Group S My RBC Plt Gran Polycythemia Vera Essential Thrombocythemia AML, CML,
11/20/2015. Post Transplant. Problems and limitations of SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant for SAA: Managing Post BMT Health and Support.
 Transplant 11/20/2015 Bone Marrow Transplant for SAA: Managing Post BMT Health and Support Richard W. Childs, M.D. Clinical Director NHLBI Chief, Laboratory of Transplantation Immunotherapy Senior Investigator,
Transplant 11/20/2015 Bone Marrow Transplant for SAA: Managing Post BMT Health and Support Richard W. Childs, M.D. Clinical Director NHLBI Chief, Laboratory of Transplantation Immunotherapy Senior Investigator,
Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers
 Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Biological therapies use the body s immune system to fight cancer or to lessen the side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments
Biological Therapies for Cancer: Questions and Answers Key Points Biological therapies use the body s immune system to fight cancer or to lessen the side effects that may be caused by some cancer treatments
Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and collection. Koen Theunissen Hematologie Jessa Ziekenhuis Hasselt Limburgs Oncologisch Centrum
 Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and collection Koen Theunissen Hematologie Jessa Ziekenhuis Hasselt Limburgs Oncologisch Centrum Transplants Transplant Activity in the U.S. 1980-2010 14,000 12,000
Hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and collection Koen Theunissen Hematologie Jessa Ziekenhuis Hasselt Limburgs Oncologisch Centrum Transplants Transplant Activity in the U.S. 1980-2010 14,000 12,000
Indolent Lymphomas: Current. Dr. Laurie Sehn
 Indolent Lymphomas: Current Dr. Laurie Sehn Why does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with current standard
Indolent Lymphomas: Current Dr. Laurie Sehn Why does indolent mean? Slow growth Often asymptomatic Chronic disease with periods of relapse (long natural history possible) Incurable with current standard
RADIATION THERAPY IN 2018 AND BEYOND. Rex Hoffman, MD Providence Saint Josephs Medical Center Disney Family Cancer Center Burbank, CA
 RADIATION THERAPY IN 2018 AND BEYOND Rex Hoffman, MD Providence Saint Josephs Medical Center Disney Family Cancer Center Burbank, CA RADIATION THERAPY IN 2018 AND BEYOND I. Introduction II. III. IV. History
RADIATION THERAPY IN 2018 AND BEYOND Rex Hoffman, MD Providence Saint Josephs Medical Center Disney Family Cancer Center Burbank, CA RADIATION THERAPY IN 2018 AND BEYOND I. Introduction II. III. IV. History
Bone Marrow Transplantation
 Bone Marrow Transplantation Introduction Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside all of your bones, including your hip and thigh bones. The bone marrow is like a factory that makes different types of blood
Bone Marrow Transplantation Introduction Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside all of your bones, including your hip and thigh bones. The bone marrow is like a factory that makes different types of blood
Oncology 101. Cancer Basics
 Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Oncology 101 Cancer Basics What Will You Learn? What is Cancer and How Does It Develop? Cancer Diagnosis and Staging Cancer Treatment What is Cancer? Cancer is a group of more than 100 different diseases
Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components
 AUSTRALIAN & NEW ZEALAND SOCIETY OF BLOOD TRANSFUSION INC. AUSTRALIAN RED CROSS BLOOD SERVICE NEW ZEALAND BLOOD SERVICE Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components Revised 2003 AN ZS B T Australian
AUSTRALIAN & NEW ZEALAND SOCIETY OF BLOOD TRANSFUSION INC. AUSTRALIAN RED CROSS BLOOD SERVICE NEW ZEALAND BLOOD SERVICE Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components Revised 2003 AN ZS B T Australian
Cervical Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Cervical Cancer Treatment Cervical cancer overview Cervical cancer is the term used to describe malignant tumors that start in the lining of the cervix the lower part of the uterus
Scan for mobile link. Cervical Cancer Treatment Cervical cancer overview Cervical cancer is the term used to describe malignant tumors that start in the lining of the cervix the lower part of the uterus
Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease
 Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease Rhiannon is now cured of sickle cell disease after BMT. Blood and marrow transplant (BMT) is a proven cure for sickle cell disease. This handbook
Blood and Marrow Transplant (BMT) for Sickle Cell Disease Rhiannon is now cured of sickle cell disease after BMT. Blood and marrow transplant (BMT) is a proven cure for sickle cell disease. This handbook
Disclosures 5/13/2013. Principles and Practice of Radiation Oncology First Annual Cancer Rehabilitation Symposium May 31, 2013
 Principles and Practice of Radiation Oncology First Annual Cancer Rehabilitation Symposium May 31, 2013 Josh Yamada MD FRCPC Department of Radiation Oncology Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Disclosures
Principles and Practice of Radiation Oncology First Annual Cancer Rehabilitation Symposium May 31, 2013 Josh Yamada MD FRCPC Department of Radiation Oncology Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Disclosures
NEWS FROM. Roswell Park s BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANT PROGRAM
 NEWS FROM Roswell Park s BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANT PROGRAM THE BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANT TEAM Philip McCarthy, MD Medical Director, BMT Program Hong Liu, MD, PhD Attending Physician Our multidisciplinary
NEWS FROM Roswell Park s BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANT PROGRAM THE BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANT TEAM Philip McCarthy, MD Medical Director, BMT Program Hong Liu, MD, PhD Attending Physician Our multidisciplinary
Acknowledgements. Department of Hematological Malignancy and Cellular Therapy, University of Kansas Medical Center
 The Addition of Extracorporeal Photopheresis (ECP) to Tacrolimus and Methotrexate to Prevent Acute and Chronic Graft- Versus Host Disease in Myeloablative Hematopoietic Cell Transplant (HCT) Anthony Accurso,
The Addition of Extracorporeal Photopheresis (ECP) to Tacrolimus and Methotrexate to Prevent Acute and Chronic Graft- Versus Host Disease in Myeloablative Hematopoietic Cell Transplant (HCT) Anthony Accurso,
ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment
 ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment Badria Al Hatali, MD Medical Toxicologist Department of Environmental and Occupational Health MOH - Oman Objectives Provide a review of radiation basics
ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment Badria Al Hatali, MD Medical Toxicologist Department of Environmental and Occupational Health MOH - Oman Objectives Provide a review of radiation basics
Principle of Radiation Therapy
 Principle of Radiation Therapy Janjira Petsuksiri, M.D. Division of Radiation Therapy Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Basic sciences for residents Aug 11, 2010 Outlines Basic Radiation physics Basic
Principle of Radiation Therapy Janjira Petsuksiri, M.D. Division of Radiation Therapy Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Basic sciences for residents Aug 11, 2010 Outlines Basic Radiation physics Basic
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum, below the bladder and above the base of the penis. Your doctor may perform
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum, below the bladder and above the base of the penis. Your doctor may perform
Nothing to disclose. Title of the presentation - Author
 Nothing to disclose Title of the presentation - Author 1 www.ebmt.org Complications after HSCT Alicia Rovó MD London 9/04/2013 Introduction Risk factors for transplant complication Type of complications
Nothing to disclose Title of the presentation - Author 1 www.ebmt.org Complications after HSCT Alicia Rovó MD London 9/04/2013 Introduction Risk factors for transplant complication Type of complications
OneMatch Stem Cell and Marrow Network. Training Guide
 OneMatch Stem Cell and Marrow Network Training Guide What is OneMatch all about? OneMatch is a Canadian Program that matches and coordinates the collection of stem cells from potential donors to help save
OneMatch Stem Cell and Marrow Network Training Guide What is OneMatch all about? OneMatch is a Canadian Program that matches and coordinates the collection of stem cells from potential donors to help save
Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program IU Graduate School & The Department of Radiation Oncology IU Simon Cancer Center
 Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program IU Graduate School & The Department of Radiation Oncology IU Simon Cancer Center All students accepted into the Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program
Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program IU Graduate School & The Department of Radiation Oncology IU Simon Cancer Center All students accepted into the Medical Dosimetry Graduate Certificate Program
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation
 Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation Current Results John E. Wagner, M.D. Blood and Marrow Transplant Program and Stem Cell Institute University of Minnesota Donor Choices Unrelated Marrow/PBSC Results
HALF. Who gets radiotherapy? Who gets radiotherapy? Half of all cancer patients get radiotherapy. By 1899 X rays were being used for cancer therapy
 The Physical and Biological Basis of By 1899 X rays were being used for cancer therapy David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Department of Radiation Oncology Columbia University Medical
The Physical and Biological Basis of By 1899 X rays were being used for cancer therapy David J. Brenner, PhD, DSc Center for Radiological Research Department of Radiation Oncology Columbia University Medical
The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness.
 The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness. Robert Liwski, MD, PhD, FRCPC Medical Director HLA Typing Laboratory Department of Pathology Dalhousie
The role of HLA in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Platelet Refractoriness. Robert Liwski, MD, PhD, FRCPC Medical Director HLA Typing Laboratory Department of Pathology Dalhousie
Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT
 Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Assistant Medical Director of Blood, Tissue, and Apheresis Services Children s Healthcare
Case-Control Study: ABO-Incompatible Plasma Causing Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease in HSCT Erin Meyer, DO, MPH Assistant Medical Director of Blood, Tissue, and Apheresis Services Children s Healthcare
Blood Product Modifications: Leukofiltration, Irradiation and Washing
 1. Leukocyte Reduction Definitions and Standards: o Process also known as leukoreduction, or leukofiltration o Applicable AABB Standards, 25th ed. Leukocyte-reduced RBCs At least 85% of original RBCs
1. Leukocyte Reduction Definitions and Standards: o Process also known as leukoreduction, or leukofiltration o Applicable AABB Standards, 25th ed. Leukocyte-reduced RBCs At least 85% of original RBCs
What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine
 What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine What is Cancer? Layman s terms: cancer starts when cells grow out of control (in any place in the body) and crowd out normal cells
What is Cancer? Petra Ketterl, MD Medical Oncology and Functional Medicine What is Cancer? Layman s terms: cancer starts when cells grow out of control (in any place in the body) and crowd out normal cells
MUD SCT. Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University
 MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
MUD SCT Pimjai Niparuck Division of Hematology, Department of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University Outlines Optimal match criteria for unrelated adult donors Role of ATG in MUD-SCT Post-transplant
Leukemia. There are different types of leukemia and several treatment options for each type.
 Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Leukemia Introduction Leukemia is the name of a group of cancers of the blood cells. Hundreds of thousands of people worldwide are diagnosed with leukemia each year. There are different types of leukemia
Survivorship After Stem Cell Transplantation and Long-term Followup
 Survivorship After Stem Cell Transplantation and Long-term Followup Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Director, Blood & Marrow Transplant Program, Cleveland Clinic Professor, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Survivorship After Stem Cell Transplantation and Long-term Followup Navneet Majhail, MD, MS Director, Blood & Marrow Transplant Program, Cleveland Clinic Professor, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem_cell_transplantation_for_waldenstrom_macroglobulinemia
Corporate Medical Policy Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: hematopoietic_stem_cell_transplantation_for_waldenstrom_macroglobulinemia
Hospice Skills Checklist
 _ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
_ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy
 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy Grace Totoe, MBChB, SBB CME August 2012 Accra-Ghana Hematopoietic Stem Cells Cells capable of self renewal and differentiation into all blood cell lineages Objectives Historical
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Therapy Grace Totoe, MBChB, SBB CME August 2012 Accra-Ghana Hematopoietic Stem Cells Cells capable of self renewal and differentiation into all blood cell lineages Objectives Historical
Oncology Skills Checklist
 _ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
_ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Treatments for Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD) following Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Treatments for Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD) following Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Reference: NHS England F01X08/01 1 Information Reader Box (IRB)
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Treatments for Graft versus Host Disease (GvHD) following Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Reference: NHS England F01X08/01 1 Information Reader Box (IRB)
Radiotherapy Physics and Equipment
 Radiological Sciences Department Radiotherapy Physics and Equipment RAD 481 Lecture s Title: Introduction Dr. Mohammed EMAM Ph.D., Paris-Sud 11 University Vision :IMC aspires to be a leader in applied
Radiological Sciences Department Radiotherapy Physics and Equipment RAD 481 Lecture s Title: Introduction Dr. Mohammed EMAM Ph.D., Paris-Sud 11 University Vision :IMC aspires to be a leader in applied
Your Guide to Prostate Cancer
 Your Guide to Prostate Cancer If you face a diagnosis of prostate cancer, what s next? We can help. A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. The good news is that while prostate cancer can be serious,
Your Guide to Prostate Cancer If you face a diagnosis of prostate cancer, what s next? We can help. A prostate cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. The good news is that while prostate cancer can be serious,
Prostate Cancer. What is prostate cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
Scan for mobile link. Prostate Cancer Prostate cancer is a tumor of the prostate gland, which is located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. Your doctor may perform a physical exam, prostate-specific
An introduction to different types of radiotherapy
 An introduction to different types of radiotherapy Radiotherapy can cure cancer. It is delivered to around half of cancer patients and is a vital part of curative treatment in around 40% of patients 1.
An introduction to different types of radiotherapy Radiotherapy can cure cancer. It is delivered to around half of cancer patients and is a vital part of curative treatment in around 40% of patients 1.
Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Meng Yao Lu/ Kai Hsin Lin Department of Pediatrics National Taiwan University Hospital
 Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Meng Yao Lu/ Kai Hsin Lin Department of Pediatrics National Taiwan University Hospital Outline Overview Indication Stem cell source New revolution Cord
Pediatric Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Meng Yao Lu/ Kai Hsin Lin Department of Pediatrics National Taiwan University Hospital Outline Overview Indication Stem cell source New revolution Cord
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) BONE (Version , 03/28/18)
 BONE (Version 2.2018, 03/28/18) NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) Radiation Therapy Specialized techniques such as intensity-modulated RT (IMRT); particle beam RT with protons, carbon ions,
BONE (Version 2.2018, 03/28/18) NCCN GUIDELINES ON PROTON THERAPY (AS OF 4/23/18) Radiation Therapy Specialized techniques such as intensity-modulated RT (IMRT); particle beam RT with protons, carbon ions,
Lung Cancer Treatment
 Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
Scan for mobile link. Lung Cancer Treatment Lung cancer overview More than one in four of all diagnosed cancers involve the lung, and lung cancer remains the most common cancer-related cause of death among
